motion picture camera on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A movie camera (also known as a film camera and cine-camera) is a type of photographic camera that rapidly takes a sequence of photographs, either onto
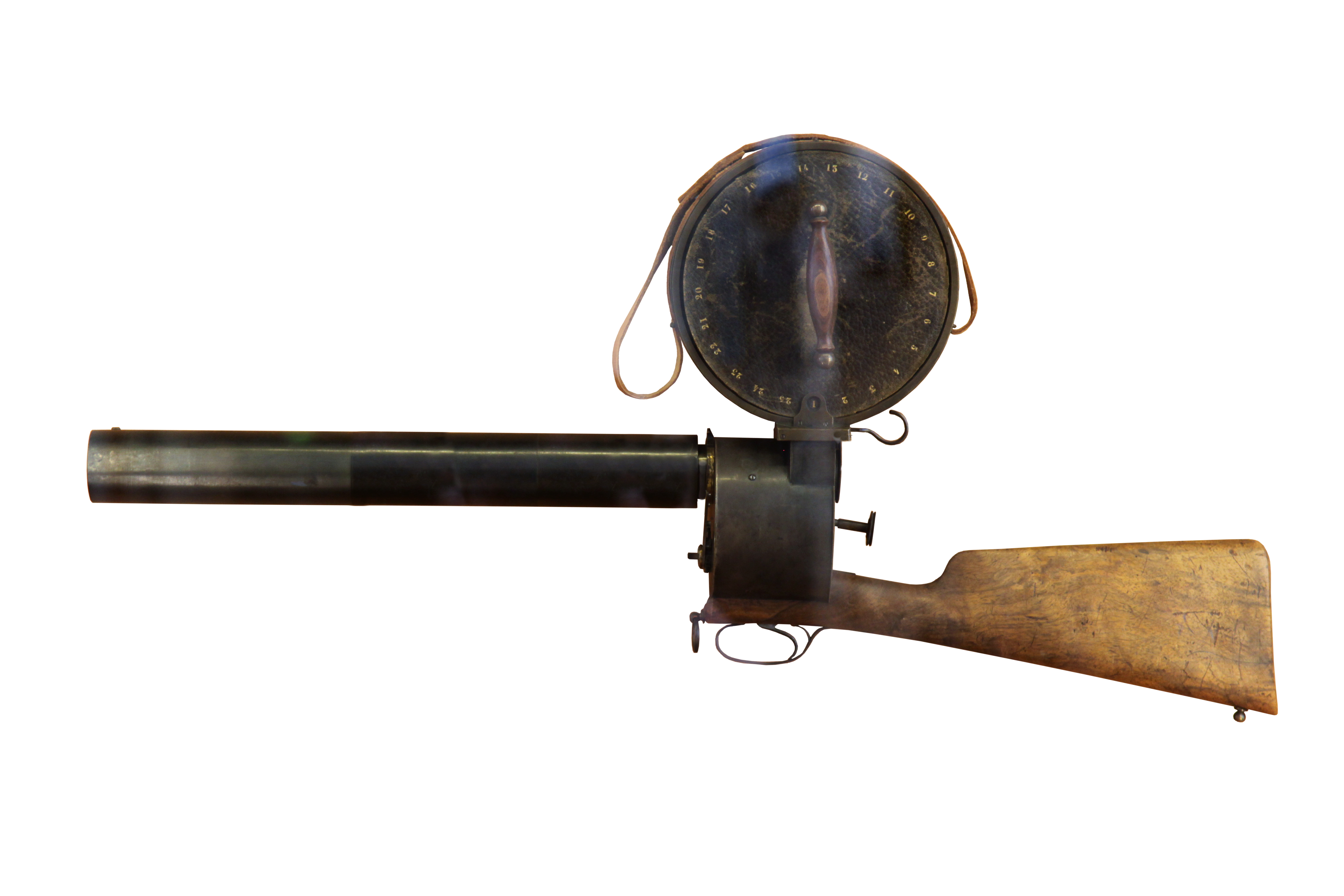 The chronophotographic gun was invented in 1882 by Étienne-Jules Marey, a French scientist and chronophotographer. It could shoot 12 images per second and was the first invention to capture moving images on the same chronomatographic plate using a metal shutter.
The chronophotographic gun was invented in 1882 by Étienne-Jules Marey, a French scientist and chronophotographer. It could shoot 12 images per second and was the first invention to capture moving images on the same chronomatographic plate using a metal shutter.
 In 1876,
In 1876,
 Due to the work of Le Prince, Friese-Greene, Edison, and the Lumière brothers, the movie camera had become a practical reality by the mid-1890s. The first firms were soon established for the manufacture of movie camera, including
Due to the work of Le Prince, Friese-Greene, Edison, and the Lumière brothers, the movie camera had become a practical reality by the mid-1890s. The first firms were soon established for the manufacture of movie camera, including
 Digital movie cameras do not use analog
Digital movie cameras do not use analog
 Most of the optical and mechanical elements of a movie camera are also present in the
Most of the optical and mechanical elements of a movie camera are also present in the  The standardized frame rate for commercial sound film is 24 frames per second. The standard commercial (i.e., movie-theater film) width is 35 millimeters, while many other
The standardized frame rate for commercial sound film is 24 frames per second. The standard commercial (i.e., movie-theater film) width is 35 millimeters, while many other
 Multiple cameras may be placed side-by-side to record a single angle of a scene and repeated throughout the runtime. The film is then later projected simultaneously, either on a single three-image screen ( Cinerama) or upon multiple screens forming a complete circle, with gaps between screens through which the projectors illuminate an opposite screen. (See Circle-Vision 360°) Convex and concave mirrors are used in cameras as well as mirrors.
Multiple cameras may be placed side-by-side to record a single angle of a scene and repeated throughout the runtime. The film is then later projected simultaneously, either on a single three-image screen ( Cinerama) or upon multiple screens forming a complete circle, with gaps between screens through which the projectors illuminate an opposite screen. (See Circle-Vision 360°) Convex and concave mirrors are used in cameras as well as mirrors.
 Movie cameras were available before
Movie cameras were available before
film stock
Film stock is an analog medium that is used for recording motion pictures or animation. It is recorded on by a movie camera, developed,
edited, and projected onto a screen using a movie projector. It is a strip or sheet of transparent pl ...
or an image sensor An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into s ...
, in order to produce a moving image to display on a screen. In contrast to the still camera
A camera is an instrument used to capture and store images and videos, either digitally via an electronic image sensor, or chemically via a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. As a pivotal technology in the fields of photograp ...
, which captures a single image at a time, the movie camera takes a series of images by way of an intermittent mechanism or by electronic means; each image is a ''frame'' of film or video. The frames are projected through a movie projector
A movie projector (or film projector) is an optics, opto-mechanics, mechanical device for displaying Film, motion picture film by projecting it onto a movie screen, screen. Most of the optical and mechanical elements, except for the illuminat ...
or a video projector
A video projector is an image projector that receives a video signal and projects the corresponding image onto a projection screen using a lens system. Video projectors use a very bright ultra-high-performance lamp (a special mercury arc l ...
at a specific frame rate
Frame rate, most commonly expressed in frame/s, or FPS, is typically the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images (Film frame, frames) are captured or displayed. This definition applies to film and video cameras, computer animation, and moti ...
(number of frames per second) to show the moving picture. When projected at a high enough frame rate (24 frames per second or more), the persistence of vision
Persistence of vision is the optical illusion that occurs when the visual perception of an object does not cease for some time after the Light ray, rays of light proceeding from it have ceased to enter the eye.
The illusion has also been descr ...
allows the eyes and brain of the viewer to merge the separate frames into a continuous moving picture.
History
A forerunner to the movie camera was the machine invented byFrancis Ronalds
Sir Francis Ronalds Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (21 February 17888 August 1873) was an English scientist and inventor, and arguably the first History of electrical engineering, electrical engineer. He was knighted for creating the first wo ...
at the Kew Observatory
The King's Observatory (called for many years the Kew Observatory) is a Grade I listed building in Richmond, London. Now a private dwelling, it formerly housed an astronomical observatory, astronomical and Terrestrial magnetism, terrestrial mag ...
in 1845. A photosensitive surface was drawn slowly past the aperture diaphragm of the camera by a clockwork mechanism to enable continuous recording over a 12- or 24-hour period. Ronalds applied his cameras to trace the ongoing variations of scientific instruments and they were used in observatories around the world for over a century.
 The chronophotographic gun was invented in 1882 by Étienne-Jules Marey, a French scientist and chronophotographer. It could shoot 12 images per second and was the first invention to capture moving images on the same chronomatographic plate using a metal shutter.
The chronophotographic gun was invented in 1882 by Étienne-Jules Marey, a French scientist and chronophotographer. It could shoot 12 images per second and was the first invention to capture moving images on the same chronomatographic plate using a metal shutter.
 In 1876,
In 1876, Wordsworth Donisthorpe
__NOTOC__Wordsworth Donisthorpe (24 March 1847 – 30 January 1914) was an English barrister, individualist anarchist and inventor, pioneer of cinematography and chess enthusiast.
Life and work
Donisthorpe was born in Leeds, on 24 March 1847 ...
proposed a camera to take a series of pictures on glass plates, to be printed on a roll of paper film. In 1889, he would patent a moving picture camera in which the film moved continuously. Another film camera was designed in England by Frenchman Louis Le Prince
Louis Aimé Augustin Le Prince (28 August 1841 – disappeared 16 September 1890, Presumption of death, declared dead 16 September 1897) was a French artist and the inventor of an early film, motion-picture camera, and director of ''Roundhay Ga ...
in 1888. He had built a 16 lens camera in 1887 at his workshop in Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
. The first 8 lenses would be triggered in rapid succession by an electromagnetic shutter on the sensitive film; the film would then be moved forward allowing the other 8 lenses to operate on the film. After much trial and error, he was finally able to develop a single-lens camera in 1888, which he used to shoot sequences of moving pictures on paper film, including the ''Roundhay Garden Scene
''Roundhay Garden Scene'' is a short film, short silent film, silent motion picture filmed by French inventor Louis Le Prince at Oakwood, Leeds, Oakwood Grange in Roundhay, Leeds, in Yorkshire on 14 October 1888. It is believed to be the olde ...
'' and '' Leeds Bridge''.
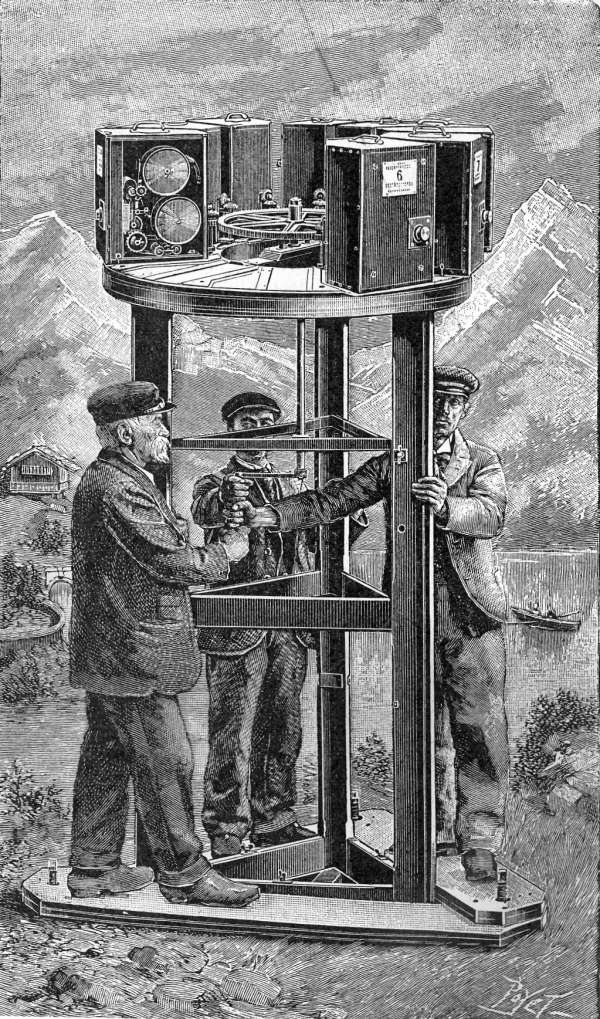
In June 1878, Eadweard Muybridge
Eadweard Muybridge ( ; 9 April 1830 – 8 May 1904, born Edward James Muggeridge) was an English photographer known for his pioneering work in photographic studies of motion, and early work in motion-picture Movie projector, projection.
He ...
created sequential series of photographs with a battery of 12 cameras along the race track at Stanford's Palo Alto Stock Farm (now the campus of Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
). The shutters were automatically triggered when the wheel of a cart or the breast or legs of a horse tripped wires connected to an electromagnetic circuit.
Another early pioneer was the British inventor William Friese-Greene
William Friese-Greene (born William Edward Green, 7 September 1855 – 5 May 1921) was a prolific English inventor and professional photographer. He was known as a pioneer in the field of motion pictures, having devised a series of cameras bet ...
. In 1887, he began to experiment with the use of paper film, made transparent through oiling, to record motion pictures. He also said he attempted using experimental celluloid
Celluloids are a class of materials produced by mixing nitrocellulose and camphor, often with added dyes and other agents. Once much more common for its use as photographic film before the advent of safer methods, celluloid's common present-day ...
, made with the help of Alexander Parkes. In 1889, Friese-Greene took out a patent for a moving picture camera that was capable of taking up to ten photographs per second. Another model, built in 1890, used rolls of the new Eastman celluloid film, which he had perforated. A full report on the patented camera was published in the British ''Photographic News'' on February 28, 1890. He showed his cameras and film shot with them on many occasions, but never projected his films in public. He also sent details of his invention to the American inventor Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February11, 1847October18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, ...
in February 1890, which was also seen by Dickson (see below).
William Kennedy Laurie Dickson
William Kennedy Laurie Dickson (3 August 1860 – 28 September 1935) was a British- American inventor who devised an early motion picture camera under the employment of Thomas Edison.
Early life
William Kennedy Dickson was born on 3 Augu ...
, a Scottish inventor and employee of Edison, designed the Kinetograph
The Kinetoscope is an early motion picture exhibition device, designed for films to be viewed by one person at a time through a peephole viewer window. The Kinetoscope was not a movie projector, but it introduced the basic approach that woul ...
Camera in 1891. The camera was powered by an electric motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to gene ...
and was capable of shooting with the new sprocketed film. To govern the intermittent movement of the film in the camera, allowing the strip to stop long enough so each frame could be fully exposed and then advancing it quickly (in about 1/460 of a second) to the next frame, the sprocket wheel that engaged the strip was driven by an escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to t ...
disc mechanism—the first practical system for the high-speed stop-and-go film movement that would be the foundation for the next century of cinematography
Cinematography () is the art of motion picture (and more recently, electronic video camera) photography.
Cinematographers use a lens (optics), lens to focus reflected light from objects into a real image that is transferred to some image sen ...
.
The Lumière Domitor camera, owned by brothers Auguste and Louis Lumière
The Lumière brothers (, ; ), Auguste Marie Louis Nicolas Lumière (19 October 1862 – 10 April 1954) and Louis Jean Lumière (5 October 1864 – 6 June 1948), were French manufacturers of photography equipment, best known for their ' motion ...
, was created by Charles Moisson, the chief mechanic at the Lumière works in Lyon
Lyon (Franco-Provençal: ''Liyon'') is a city in France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, Switzerland, north ...
in 1894. The camera used paper film 35 millimeters wide, but in 1895, the Lumière brothers shifted to celluloid film, which they bought from New-York's Celluloid Manufacturing Co. This they covered with their own Etiquette-bleue emulsion, had it cut into strips and perforated.
In 1894, the Polish inventor Kazimierz Prószyński
Kazimierz Prószyński (4 April 1875 – 13 March 1945) was a Polish inventor active in the field of cinematography. He patented his first film camera, called Pleograph, before the Auguste and Louis Lumière, Lumière brothers, and later went o ...
constructed a projector and camera in one, an invention he called the Pleograph
Pleograph () was an early type of movie camera constructed in 1894, before those made by the Lumière brothers,Maciej Iłowiecki, "Dzieje nauki polskiej", Wydawnictwo Interpress, Warszawa 1981, , p.202 (Polish). by Polish inventor Kazimierz Prósz ...
."Polska. Informator", Wydawnictwo Interpress, Warszawa 1977 (in Polish)
Mass-market
 Due to the work of Le Prince, Friese-Greene, Edison, and the Lumière brothers, the movie camera had become a practical reality by the mid-1890s. The first firms were soon established for the manufacture of movie camera, including
Due to the work of Le Prince, Friese-Greene, Edison, and the Lumière brothers, the movie camera had become a practical reality by the mid-1890s. The first firms were soon established for the manufacture of movie camera, including Birt Acres
Birt Acres (23 July 1854 – 27 December 1918) was an American and British photographer and film pioneer. Among his contributions to the early film industry are the first working 35 mm camera in Britain (Wales), and ''Birtac'', the firs ...
, Eugene Augustin Lauste, Dickson, Pathé frères, Prestwich, Newman & Guardia, de Bedts, Gaumont-Démény, Schneider, Schimpf, Akeley, Debrie, Bell & Howell, Leonard-Mitchell, Ertel, Ernemann, Eclair, Stachow, Universal, Institute, Wall, Lytax, and many others.
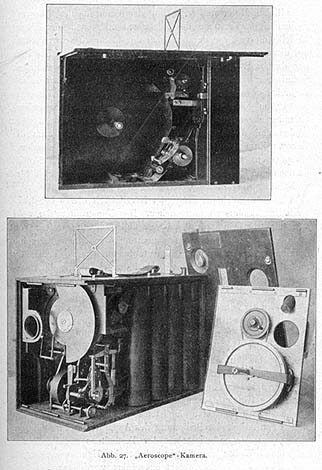
The Aeroscope was built and patented in England in the period 1909–1911 by Polish inventor Kazimierz Prószyński
Kazimierz Prószyński (4 April 1875 – 13 March 1945) was a Polish inventor active in the field of cinematography. He patented his first film camera, called Pleograph, before the Auguste and Louis Lumière, Lumière brothers, and later went o ...
. Aeroscope was the first successful hand-held operated film camera. The cameraman
A camera operator, or depending on the context cameraman or camerawoman, is a professional operator of a film camera or video camera as part of a film crew. The term "cameraman" does not necessarily imply that a male is performing the task.
...
did not have to turn the crank to advance the film, as in all cameras of that time, so he could operate the camera with both hands, holding the camera and controlling the focus. This made it possible to film with the Aeroscope in difficult circumstances including from the air and for military purposes.
The first all-metal cine camera was the Bell & Howell Standard of 1911-12. One of the most complicated models was the Mitchell-Technicolor
Technicolor is a family of Color motion picture film, color motion picture processes. The first version, Process 1, was introduced in 1916, and improved versions followed over several decades.
Definitive Technicolor movies using three black-and ...
Beam Splitting Three-Strip Camera of 1932. With it, three colour separation originals are obtained behind a purple, a green, and a red light filter, the latter being part of one of the three different raw materials in use.
In 1923, Eastman Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company, referred to simply as Kodak (), is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in film photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorporated i ...
introduced a 16mm film
16 mm film is a historically popular and economical Film gauge, gauge of Photographic film, film. 16 mm refers to the width of the film (about inch); other common film gauges include 8 mm film, 8 mm and 35mm movie film, 35 mm. It ...
stock, principally as a lower-cost alternative to 35 mm and several camera makers launched models to take advantage of the new market of amateur movie-makers. Thought initially to be of inferior quality to 35 mm, 16 mm cameras continued to be manufactured until the 2000s by the likes of Bolex, Arri
Arri Group () (stylized as "ARRI") is a German manufacturer of motion picture film equipment. Based in Munich, the company was founded in 1917. It produces professional motion picture cameras, lenses, lighting and post-production equipment. It ...
, and Aaton.Digital movie cameras
 Digital movie cameras do not use analog
Digital movie cameras do not use analog film stock
Film stock is an analog medium that is used for recording motion pictures or animation. It is recorded on by a movie camera, developed,
edited, and projected onto a screen using a movie projector. It is a strip or sheet of transparent pl ...
to capture images, as had been the standard since the 1890s. Rather, an electronic image sensor An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into s ...
is employed and the images are typically recorded on hard drives or flash memory
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for t ...
using a variety of acquisition formats. Digital SLR cameras (DSLR) designed for consumer use have also been used for some low-budget independent productions.
Since the 2010s, digital movie cameras have become the dominant type of camera in the motion picture industry, being employed in film, television productions and even (to a lesser extent) video games. In response to this, movie director Martin Scorsese
Martin Charles Scorsese ( , ; born November17, 1942) is an American filmmaker. One of the major figures of the New Hollywood era, he has received List of awards and nominations received by Martin Scorsese, many accolades, including an Academ ...
started the non-profit organisation The Film Foundation to preserve the use of film in movie makingas many filmmakers feel digital cameras do not convey the depth or emotion that motion-picture film does. Other major directors involved in the organisation include Quentin Tarantino
Quentin Jerome Tarantino (; born March 27, 1963) is an American filmmaker, actor, and author. Quentin Tarantino filmography, His films are characterized by graphic violence, extended dialogue often featuring much profanity, and references to ...
, Christopher Nolan
Sir Christopher Edward Nolan (born 30 July 1970) is a British and American filmmaker. Known for his Cinema of the United States, Hollywood Blockbuster (entertainment), blockbusters with complex storytelling, he is considered a leading filmma ...
and many more.
Technical details
 Most of the optical and mechanical elements of a movie camera are also present in the
Most of the optical and mechanical elements of a movie camera are also present in the movie projector
A movie projector (or film projector) is an optics, opto-mechanics, mechanical device for displaying Film, motion picture film by projecting it onto a movie screen, screen. Most of the optical and mechanical elements, except for the illuminat ...
. The requirements for film tensioning, take-up, intermittent motion, loops, and rack positioning are almost identical. The camera will not have an illumination source and will maintain its film stock in a light-tight enclosure. A camera will also have exposure control via an iris aperture located on the lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
. The righthand side of the camera is often referred to by camera assistants as "the dumb side" because it usually lacks indicators or readouts and access to the film threading, as well as lens markings on many lens models. Later equipment often had done much to minimize these shortcomings, although access to the film movement block by both sides is precluded by basic motor and electronic design necessities. Advent of digital cameras reduced the above mechanism to a minimum removing much of the shortcomings.
 The standardized frame rate for commercial sound film is 24 frames per second. The standard commercial (i.e., movie-theater film) width is 35 millimeters, while many other
The standardized frame rate for commercial sound film is 24 frames per second. The standard commercial (i.e., movie-theater film) width is 35 millimeters, while many other film formats
A film format is a technical definition of a set of standard characteristics regarding image capture on photographic film for still images or film stock for filmmaking. It can also apply to projected film, either slides or movies. The primary ch ...
exist. The standard aspect ratios are 1.66:1, 1.85:1, and 2.39:1 (anamorphic
Anamorphic format is a cinematography technique that captures widescreen images using recording media with narrower native Aspect ratio (image), aspect ratios. Originally developed for 35 mm movie film, 35 mm film to create widescreen pres ...
). NTSC
NTSC (from National Television System Committee) is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170.
In 1953, a second ...
video (common in North America and Japan) plays at 29.97 frame/s; PAL
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a color encoding system for analog television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 ...
(common in most other countries) plays at 25 frames. These two television and video systems also have different resolutions and color encodings. Many of the technical difficulties involving film and video concern translation between the different formats. Video aspect ratios are 4:3 (1.33:1) for full screen and 16:9 (1.78:1) for widescreen.
Multiple cameras
 Multiple cameras may be placed side-by-side to record a single angle of a scene and repeated throughout the runtime. The film is then later projected simultaneously, either on a single three-image screen ( Cinerama) or upon multiple screens forming a complete circle, with gaps between screens through which the projectors illuminate an opposite screen. (See Circle-Vision 360°) Convex and concave mirrors are used in cameras as well as mirrors.
Multiple cameras may be placed side-by-side to record a single angle of a scene and repeated throughout the runtime. The film is then later projected simultaneously, either on a single three-image screen ( Cinerama) or upon multiple screens forming a complete circle, with gaps between screens through which the projectors illuminate an opposite screen. (See Circle-Vision 360°) Convex and concave mirrors are used in cameras as well as mirrors.
Sound synchronization
One of the problems in film is synchronizing a sound recording with the film. Most film cameras do not record sound internally; instead, the sound is captured separately by a precision audio device (see double-system recording). The exceptions to this are the single-system news film cameras, which had either an optical—or later—magnetic recording head inside the camera. For optical recording, the film only had a single perforation and the area where the other set of perforations would have been was exposed to a controlled bright light that would burn a waveform image that would later regulate the passage of light and playback the sound. For magnetic recording, that same area of the single perf 16 mm film that was prestriped with a magnetic stripe. A smaller balance stripe existed between the perforations and the edge to compensate the thickness of the recording stripe to keep the film wound evenly. Double-system cameras are generally categorized as either "sync" or "non-sync." Sync cameras use crystal-controlled motors that ensure that film is advanced through the camera at a precise speed. In addition, they're designed to be quiet enough to not hamper sound recording of the scene being shot. Non-sync or " MOS" cameras do not offer these features; any attempt to match location sound to these cameras' footage will eventually result in "sync drift", and the noise they emit typically renders location sound recording useless. To synchronize double-system footage, the clapper board which typically starts a take is used as a reference point for the editor to match the picture to the sound (provided the scene and take are also called out so that the editor knows which picture take goes with any given sound take). It also permits scene and take numbers and other essential information to be seen on the film itself. Aaton cameras have a system called AatonCode that can "jam sync" with a timecode-based audio recorder and prints a digital timecode directly on the edge of the film itself. However, the most commonly used system at the moment is unique identifier numbers exposed on the edge of the film by the film stock manufacturer (KeyKode is the name for Kodak's system). These are then logged (usually by a computer editing system, but sometimes by hand) and recorded along with audio timecode during editing. In the case of no better alternative, a handclap can work if done clearly and properly, but often a quick tap on the microphone (provided it is in the frame for this gesture) is preferred. One of the most common uses of non-sync cameras is the spring-wound cameras used in hazardous special effects, known as "crash cams". Scenes shot with these have to be kept short or resynchronized manually with the sound. MOS cameras are also often used forsecond unit
A second unit is a discrete team of filmmakers tasked with filming shots or sequences of a production, separate from the main or "first" unit. The second unit will often shoot simultaneously with the other unit or units, allowing the filming s ...
work or anything involving slow or fast-motion filming.
With the advent of digital cameras, synchronization became a redundant term, as both visual and audio is simultaneously captured electronically.
Home movie cameras
 Movie cameras were available before
Movie cameras were available before World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
often using the 9.5 mm film format or 16 mm format. The use of movie cameras had an upsurge in popularity in the immediate post-war period giving rise to the creation of home movies. Compared to the pre-war models, these cameras were small, light, fairly sophisticated and affordable.
An extremely compact 35 mm movie camera '' Kinamo'' was designed by Emanuel Goldberg
Emanuel Goldberg (; ; ; 31August 188113September 1970) was an Israeli physicist and inventor. He was born in Moscow and moved first to Germany and later to Israel. He described himself as "a chemist by learning, physicist by calling, and a mecha ...
for amateur and semi-professional movies in 1921. A spring motor attachment was added in 1923 to allow flexible handheld filming. The Kinamo was used by Joris Ivens and other avant-garde and documentary filmmakers in the late 1920s and early 1930s.''Ica and the Kinamo'' and ''Joris Evens''. In: Buckland, Michael: ''Emanuel Goldberg and his Knowledge Machine''. Libraries Unlimited, 2006. . pp. 85-92 and pp. 92-95
While a basic model might have a single fixed aperture/focus lens, a better version might have three or four lenses of differing apertures and focal lengths on a rotating turret. A good quality camera might come with a variety of interchangeable, focusable lenses or possibly a single zoom lens. The viewfinder was normally a parallel sight within or on top of the camera body. In the 1950s and for much of the 1960s these cameras were powered by clockwork motors, again with variations of quality. A simple mechanism might only power the camera for some 30 seconds, while a geared drive camera might work for as long as 75 – 90 seconds (at standard speeds).
The common film used for these cameras was termed Standard 8, which was a strip of 16-millimetre wide film which was only exposed down one half during shooting. The film had twice the number of perforations as film for 16 mm cameras and so the frames were half as high and half as wide as 16 mm frames. The film was removed and placed back in the camera to expose the frames on the other side once the first half had been exposed. Once the film was developed it was sliced down the middle and the ends attached, giving of Standard 8 film from a spool of of 16 mm film. 16 mm cameras, mechanically similar to the smaller format models, were also used in home movie making but were more usually the tools of semi professional film and news film makers.
In the 1960s a new film format, Super8, coincided with the advent of battery-operated electric movie cameras. The new film, with a larger frame print on the same width of film stock, came in a cassette that simplified changeover and developing. Another advantage of the new system is that they had the capacity to record sound, albeit of indifferent quality. Camera bodies, and sometimes lenses, were increasingly made in plastic rather than the metals of the earlier types. As the costs of mass production came down, so did the price and these cameras became very popular.
This type of format and camera was more quickly superseded for amateurs by the advent of digital video cameras in the 2000s. Since the 2010s, amateurs increasingly started preferring smartphone cameras.
See also
*Animation camera
An animation camera, a type of rostrum camera, is a movie camera specially adapted for frame (film), frame-by-frame shooting of animation. It consists of a camera body with lens and film magazines, and is most often placed on a stand that allows ...
* Camcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right side, hot-sw ...
* Camera stabilizer
* Digital movie camera
* Eyemo and Filmo
* History of cinema
* List of film formats
This list of motion picture film formats catalogues formats developed for shooting or viewing motion pictures, ranging from the Chronophotographe format from 1888, to mid-20th century formats such as the 1953 CinemaScope format, to more recent ...
* Konvas
Konvas () is the general name of portable 35mm motion-picture cameras that was manufactured in the USSR by KMZ (KRASNOGORSKIY MEKHANICHESKIY ZAVOD – Krasnogorsk Mechanical Works), known as ZENIT camera makers, and later on, MOSKINAP (MOSKOV ...
* Multiplane camera
* Debrie Parvo
* Prestwich Camera
* Professional video camera
A professional video camera (often called a television camera even though its use has spread beyond television) is a high-end device for creating electronic moving images (as opposed to a movie camera, that earlier recorded the images on film). O ...
* Video camera
A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos, as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film. Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of other ...
References
External links
{{Authority control 1876 introductions Film and video technology Cameras by type