Momchil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
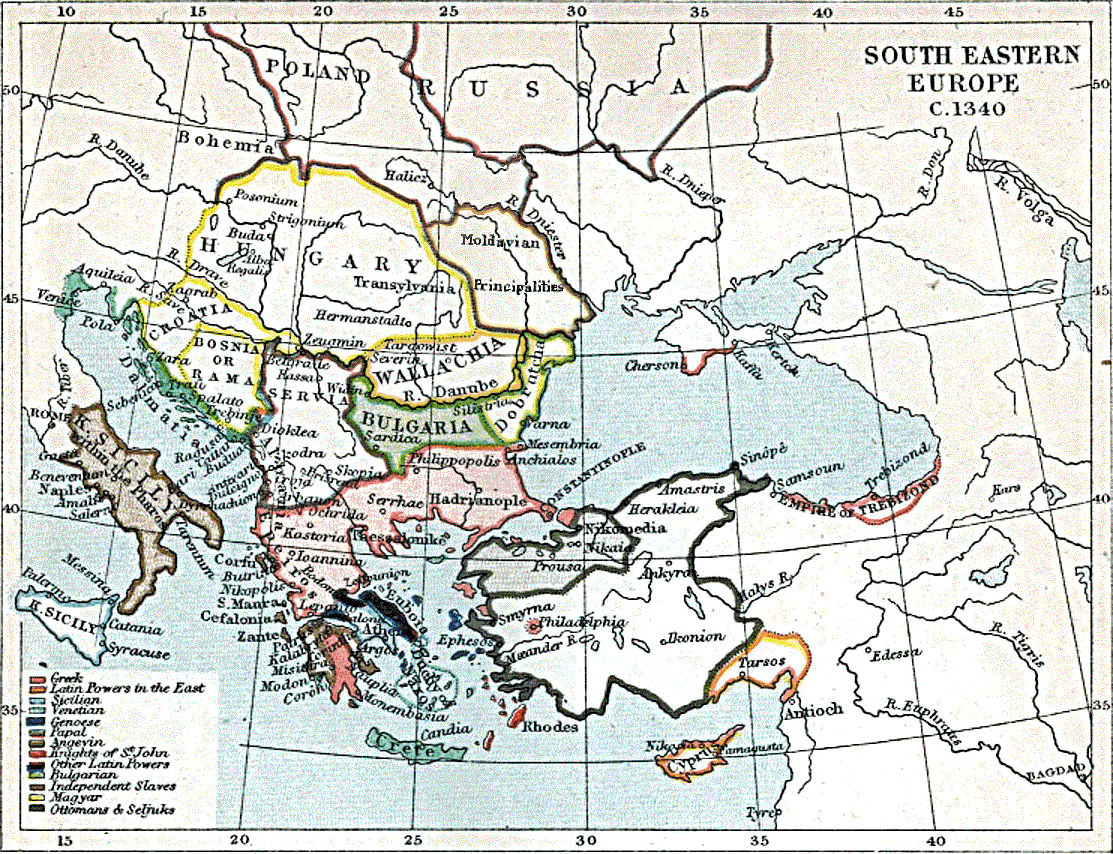
Momchil (, , ; – 7 July 1345) was a 14th-century Bulgarian brigand and local ruler. Initially a member of a bandit gang in the borderlands of
 Contemporary and near-contemporary accounts describe Momchil physically as "imposing in appearance", "as tall as two men" and, in the words of a Turkish poet, "resembling a
Contemporary and near-contemporary accounts describe Momchil physically as "imposing in appearance", "as tall as two men" and, in the words of a Turkish poet, "resembling a
 The two armies met near Peritheorion on 7 July 1345. Momchil tried to seek refuge behind the city's walls — scholars debate whether he actually held the city or not — but they were shut against him and his men by the locals.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1391 The locals did let in Momchil's cousin Rayko along with 50 men, which they hoped would persuade Momchil not to take vengeance on the city if he defeated his opponents. In the subsequent battle before the city walls, Momchil's forces used the Peritheorion's ruined old fortifications as a first line of defence, with the city walls behind them.Андреев (1999), pp. 285–286
After the foremost Turkish troops crossed the fortifications and dealt with the Bulgarian defenders, they began plundering the vicinity. However, to the surprise of Kantakouzenos and Umur Bey, the majority of Momchil's men were standing in front of the city walls and had not yet participated in the skirmishes. As the Byzantine–Turkish force advanced towards the defenders, Momchil led his troops ahead into battle. His cavalry was promptly eliminated by Turkish sharpshooters and his remaining troops were surrounded on three sides by heavily armed horsemen. Momchil's remaining men continued the fight on foot and for the most part did not surrender until Momchil himself perished.
Out of respect for Momchil, Kantakouzenos spared his wife, a Bulgarian woman he had captured during his conquest of Xanthi. He allowed her to flee to Bulgaria along with all of her property. However, it is unknown whether Momchil had any children from this marriage or a previous one, if any. Pavlov presents the hypothesis that Momchil's wife was a noblewoman from the Bulgarian capital
The two armies met near Peritheorion on 7 July 1345. Momchil tried to seek refuge behind the city's walls — scholars debate whether he actually held the city or not — but they were shut against him and his men by the locals.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1391 The locals did let in Momchil's cousin Rayko along with 50 men, which they hoped would persuade Momchil not to take vengeance on the city if he defeated his opponents. In the subsequent battle before the city walls, Momchil's forces used the Peritheorion's ruined old fortifications as a first line of defence, with the city walls behind them.Андреев (1999), pp. 285–286
After the foremost Turkish troops crossed the fortifications and dealt with the Bulgarian defenders, they began plundering the vicinity. However, to the surprise of Kantakouzenos and Umur Bey, the majority of Momchil's men were standing in front of the city walls and had not yet participated in the skirmishes. As the Byzantine–Turkish force advanced towards the defenders, Momchil led his troops ahead into battle. His cavalry was promptly eliminated by Turkish sharpshooters and his remaining troops were surrounded on three sides by heavily armed horsemen. Momchil's remaining men continued the fight on foot and for the most part did not surrender until Momchil himself perished.
Out of respect for Momchil, Kantakouzenos spared his wife, a Bulgarian woman he had captured during his conquest of Xanthi. He allowed her to flee to Bulgaria along with all of her property. However, it is unknown whether Momchil had any children from this marriage or a previous one, if any. Pavlov presents the hypothesis that Momchil's wife was a noblewoman from the Bulgarian capital
SCAR Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica
Momchil Peak. His life served as the basis for an
Who was Duke Momcilo?
Dusko Lopandic, No 3114, 2011 {{Authority control 1345 deaths 14th-century births 14th-century Bulgarian people Medieval Bulgarian military personnel Medieval Serbian military leaders Byzantine mercenaries Byzantine governors Byzantine rebels People from the Serbian Empire Medieval Thrace Rhodope Mountains Sebastokrators Bulgarian military personnel killed in action Medieval mercenaries Medieval rebels 14th-century soldiers Boyars of Stefan Dušan
Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
and Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, Momchil was recruited by the Byzantines as a mercenary. Through his opportunistic involvement in the Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347
The Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347, sometimes referred to as the Second Palaiologan Civil War, was a conflict that broke out in the Byzantine Empire after the death of Andronikos III Palaiologos over the guardianship of his nine-year-old son ...
, where he played the various sides against each other, he became ruler of a large area in the Rhodopes and western Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
.
Momchil achieved initial successes against Turks and Byzantines alike, setting Turkish ships on fire and almost managing to kill one of his main opponents at the time, John VI Kantakouzenos
John VI Kantakouzenos or Cantacuzene (; ; – 15 June 1383) was a Byzantine Greek nobleman, statesman, and general. He served as grand domestic under Andronikos III Palaiologos and regent for John V Palaiologos before reigning as Byza ...
. Despite this, he was defeated and killed by a joint Byzantine–Turkish army in 1345. Due to his opposition to the Turks, he is remembered in popular South Slavic legend as a fighter against the Turkish invasion of the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
.
Brigandage and role in the Byzantine civil war
 Contemporary and near-contemporary accounts describe Momchil physically as "imposing in appearance", "as tall as two men" and, in the words of a Turkish poet, "resembling a
Contemporary and near-contemporary accounts describe Momchil physically as "imposing in appearance", "as tall as two men" and, in the words of a Turkish poet, "resembling a minaret
A minaret is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer (''adhan'') from a muezzin, but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can h ...
". According to a contemporary source, Momchil was a native of the "border area of Bulgarians and Serbs", which at the time straddled the Rhodopes and the Pirin
The Pirin Mountains ( ) are a mountain range in southwestern Bulgaria, with the highest peak, Vihren, at an altitude of .
The range extends about from the north-west to the south-east and is about wide, spanning a territory of . To the north ...
mountains. The claim that Momchil was born in that region may be reinforced by 15th-century Ottoman registers, according to which his name was the most popular male name in that area. There exist at least a few legends which tie his birth to a particular place, for example the village of Fakia in Strandzha
Strandzha (, also transliterated as ''Strandja'', ; , or ) is a mountain massif in southeastern Bulgaria and East Thrace, the European part of Turkey. It is in the southeastern part of the Balkans between the plains of Thrace to the west, th ...
, though evidence is nonexistent. In any case, Momchil was born of humble origin. This was a main factor in his decision to join a band of brigands (''hajduk
A hajduk (, plural of ) is a type of Irregular military, irregular infantry found in Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and parts of Southeast Europe from the late 16th to mid 19th centuries, especially from Hajdú–Bihar Count ...
s'') which was active in the scarcely governed border areas between Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
and Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
.Андреев (1999), p. 282Павлов (2005)
Persecuted by the Bulgarian authorities, some time before 1341 Momchil fled to Byzantium. He was accepted into the service of Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos
Andronikos III Palaiologos (; 25 March 1297 – 15 June 1341), commonly Latinized as Andronicus III Palaeologus, was the Byzantine emperor from 1328 to 1341. He was the son of Michael IX Palaiologos and Rita of Armenia. He was proclaimed c ...
(r. 1328–1341) as a mercenary and tasked with the protection of the territories he previously plundered. However, his brigand activities did not cease. Momchil regularly raided Bulgarian lands, which negatively impacted Byzantine–Bulgarian relations. Undesired by the Byzantines and "detestable to the Bulgarians",Андреев (1999), pp. 282–283 he deserted the Byzantine army and fled to Serbia to serve its ruler Stephen Dušan.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1390Soulis (1984), p. 149 In Serbia, he formed a company of 2,000 trusted men, both Bulgarians and Serbs.Андреев (1999), p. 283
During the Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347
The Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347, sometimes referred to as the Second Palaiologan Civil War, was a conflict that broke out in the Byzantine Empire after the death of Andronikos III Palaiologos over the guardianship of his nine-year-old son ...
, Momchil joined the forces of John VI Kantakouzenos
John VI Kantakouzenos or Cantacuzene (; ; – 15 June 1383) was a Byzantine Greek nobleman, statesman, and general. He served as grand domestic under Andronikos III Palaiologos and regent for John V Palaiologos before reigning as Byza ...
(r. 1341–1354), who had perhaps known Momchil during his flight to Serbia in 1342, at the beginning of the war. In 1343, as per the wishes of the local population, Kantakouzenos gave Momchil governance of the region of Merope in the Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; , ; , ''Rodopi''; ) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak ...
, a virtual no man's land plagued by nomadic Slavic brigands.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1390Soulis (1984), p. 149 In the words of Kantakouzenos himself, the appointment was because " omchilwas of the same race these nomads would be favourably disposed toward him, but also because he was not lacking in courage and boldness in battle and was a first-rate expert in robbery and plunder."Soulis (1984), p. 149 As the governor of Merope, Momchil gathered of an army of 300 cavalry and 5,000 infantry from different nationalities. Though he considered himself able to "set against any side in the Byzantine war", along with Umur Bey
Umur Ghazi, Ghazi Umur, or Umur The LionDonald MacGillivray Nicol, ''The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261–1453'', Cambridge University Press, 1993, p. 144./ref> ( Modern Turkish: ''Aydınoğlu Umur Bey'', c. 1309–1348), also known as Umur Pa ...
's Turkish forces he nevertheless assisted Kantakouzenos in his campaigns in 1344.Fine (1994), p. 304
At the time, Momchil was approached by agents of Kantakouzenos' opponents, the Constantinopolitan
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
regency, and persuaded to turn against him. Thinking that Kantakouzenos and his Turkish allies from the Emirate of Aydin were far away in eastern Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
, he attacked a Turkish fleet of 15 ships near Portolagos and sank three of them. He then overcame another Turkish force that arrived to exact retribution near the fortress of Peritheorion (also known as Burugrad), and plundered several cities in the area that refused to surrender.Soulis (1984), p. 149Fine (1994), p. 304 Afterwards, Momchil along with 1,000 horsemen attacked Kantakouzenos, who had set camp near Komotini with only 60 horsemen to protect him. The Byzantines were thoroughly routed: Kantakouzenos' horse was killed and he received a powerful hit to the head, which he survived thanks to his helmet. Momchil captured many of Kantakouzenos' men, but the claimant to the throne himself managed to escape in the turmoil.Андреев (1999), p. 284
Soon, however, Momchil sent messages to Kantakouzenos asking for forgiveness. The latter, loath to alienate Momchil and open another front in his rear, pardoned him in exchange for promises of future good conduct, and even awarded him the title of ''sebastokrator
''Sebastokrator'' (, ; ; ), was a senior court title in the late Byzantine Empire. It was also used by other rulers whose states bordered the Empire or were within its sphere of influence (Bulgarian Empire, Serbian Empire). The word is a compound ...
''. Momchil nevertheless continued to entertain parallel ties with the regency, and even secured the title of ''despotes
Despot or ''despotes'' () was a senior Byzantine court title that was bestowed on the sons or sons-in-law of reigning emperors, and initially denoted the heir-apparent of the Byzantine emperor.
From Byzantium it spread throughout the late medie ...
'' from the Empress Anna of Savoy
Anna of Savoy, born Giovanna (1306–1365), was a Byzantine Empress consort, as the second spouse of Andronikos III Palaiologos. She served as regent, with the titles '' augusta'' and '' autokratorissa'', during the minority of her son John V Pal ...
.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1390
Ruler in the Rhodopes and death
In the summer of 1344, Momchil finally broke with both parties and seceded from the Byzantine Empire. He proclaimed himself an independent ruler in the Rhodopes and the Aegean coast, "capturing cities and villages and appearing all-powerful and invincible". With his army he capturedXanthi
Xanthi is a city in the region of Western Thrace, northeastern Greece. It is the capital of the Xanthi regional unit of the region of East Macedonia and Thrace.
Amphitheatrically built on the foot of Rhodope mountain chain, the city is divided ...
, which became the capital of his domain.Fine (1994), p. 304Soulis (1984), p. 150 Bulgarian historian Plamen Pavlov theorises that Momchil was in friendly relations with Bulgarian emperor Ivan Alexander (r. 1331–1371), with whom he shared a lengthy border, and believes the two may have acted in co-ordination against the Byzantines.
In late spring 1345 however, Kantakouzenos, reinforced with allegedly 20,000 troops from Aydin under their ruler Umur Bey
Umur Ghazi, Ghazi Umur, or Umur The LionDonald MacGillivray Nicol, ''The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261–1453'', Cambridge University Press, 1993, p. 144./ref> ( Modern Turkish: ''Aydınoğlu Umur Bey'', c. 1309–1348), also known as Umur Pa ...
, marched against Momchil. Momchil tried to prevent this by asking again for pardon and offering to submit to Kantakouzenos, but the emperor refused to heed him.Fine (1994), p. 304Soulis (1984), p. 150
 The two armies met near Peritheorion on 7 July 1345. Momchil tried to seek refuge behind the city's walls — scholars debate whether he actually held the city or not — but they were shut against him and his men by the locals.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1391 The locals did let in Momchil's cousin Rayko along with 50 men, which they hoped would persuade Momchil not to take vengeance on the city if he defeated his opponents. In the subsequent battle before the city walls, Momchil's forces used the Peritheorion's ruined old fortifications as a first line of defence, with the city walls behind them.Андреев (1999), pp. 285–286
After the foremost Turkish troops crossed the fortifications and dealt with the Bulgarian defenders, they began plundering the vicinity. However, to the surprise of Kantakouzenos and Umur Bey, the majority of Momchil's men were standing in front of the city walls and had not yet participated in the skirmishes. As the Byzantine–Turkish force advanced towards the defenders, Momchil led his troops ahead into battle. His cavalry was promptly eliminated by Turkish sharpshooters and his remaining troops were surrounded on three sides by heavily armed horsemen. Momchil's remaining men continued the fight on foot and for the most part did not surrender until Momchil himself perished.
Out of respect for Momchil, Kantakouzenos spared his wife, a Bulgarian woman he had captured during his conquest of Xanthi. He allowed her to flee to Bulgaria along with all of her property. However, it is unknown whether Momchil had any children from this marriage or a previous one, if any. Pavlov presents the hypothesis that Momchil's wife was a noblewoman from the Bulgarian capital
The two armies met near Peritheorion on 7 July 1345. Momchil tried to seek refuge behind the city's walls — scholars debate whether he actually held the city or not — but they were shut against him and his men by the locals.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1391 The locals did let in Momchil's cousin Rayko along with 50 men, which they hoped would persuade Momchil not to take vengeance on the city if he defeated his opponents. In the subsequent battle before the city walls, Momchil's forces used the Peritheorion's ruined old fortifications as a first line of defence, with the city walls behind them.Андреев (1999), pp. 285–286
After the foremost Turkish troops crossed the fortifications and dealt with the Bulgarian defenders, they began plundering the vicinity. However, to the surprise of Kantakouzenos and Umur Bey, the majority of Momchil's men were standing in front of the city walls and had not yet participated in the skirmishes. As the Byzantine–Turkish force advanced towards the defenders, Momchil led his troops ahead into battle. His cavalry was promptly eliminated by Turkish sharpshooters and his remaining troops were surrounded on three sides by heavily armed horsemen. Momchil's remaining men continued the fight on foot and for the most part did not surrender until Momchil himself perished.
Out of respect for Momchil, Kantakouzenos spared his wife, a Bulgarian woman he had captured during his conquest of Xanthi. He allowed her to flee to Bulgaria along with all of her property. However, it is unknown whether Momchil had any children from this marriage or a previous one, if any. Pavlov presents the hypothesis that Momchil's wife was a noblewoman from the Bulgarian capital Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo (, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a city in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province. It is the historical and spiritual capital of Bulgaria.
Often referred to as the "''City of the Tsars''", Velik ...
, whom he married as part of an agreement with the Bulgarian court.
In popular culture
In Bulgarian and South Slavic folklore in general, Momchil is glorified in numerous songs and epic tales as a brigand, defender of the people and a prominent fighter against the Turks.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1391 Indeed, some of the earliest heroic songs in Bulgarian folklore tradition deal with Momchil's exploits. In some folklore material, Momchil, referred to as aduke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of Royal family, royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobi ...
, acts as the uncle of Prince Marko
Marko Mrnjavčević ( sr-Cyrl, Марко Мрњавчевић, ; – 17 May 1395) was the ''de jure'' Serbia in the Middle Ages, Serbian king from 1371 to 1395, while he was the ''de facto'' ruler of territory in western Macedonia (region) ...
, another legendary figure who in epic poetry is a fighter against the Turks. In the folklore version of Momchil's last battle, Vidosava, his wife, and not the citizens of Peritheorion, betrays him and is to blame for his death. On the other hand, Momchil's legendary sister Yevrosima is described as the mother of Prince Marko as well as a major influence on him.
The town of Momchilgrad
Momchilgrad ( , , Turkish language, Turkish: Mestanlı) is a town in the very south of Bulgaria, part of Kardzhali Province in the southern part of the Eastern Rhodopes. According to the 2011 census, Momchilgrad is the largest Bulgarian settlemen ...
and the village of Momchilovtsi in southern Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, as well as Momchil Peak on Greenwich Island
Greenwich Island (variant historical names ''Sartorius Island'', ''Berezina Island'') is an island long and from (average ) wide, lying between Robert Island and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The island's surface ...
of the South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands, Antarctic islands located in the Drake Passage with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the n ...
in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
are named after Momchil.Momchil Peak. His life served as the basis for an
opera
Opera is a form of History of theatre#European theatre, Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically ...
piece, eponymously named ''Momchil'' and written by Bulgarian composer Lyubomir Pipkov. Momchil's biography also inspired a 1988 children's comic book
A comic book, comic-magazine, or simply comic is a publication that consists of comics art in the form of sequential juxtaposed panel (comics), panels that represent individual scenes. Panels are often accompanied by descriptive prose and wri ...
, ''The Lord of Merope'', which tells a largely fictionalised version of his story.
References
Sources
* * * * *External links
Who was Duke Momcilo?
Dusko Lopandic, No 3114, 2011 {{Authority control 1345 deaths 14th-century births 14th-century Bulgarian people Medieval Bulgarian military personnel Medieval Serbian military leaders Byzantine mercenaries Byzantine governors Byzantine rebels People from the Serbian Empire Medieval Thrace Rhodope Mountains Sebastokrators Bulgarian military personnel killed in action Medieval mercenaries Medieval rebels 14th-century soldiers Boyars of Stefan Dušan