Mildew on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Mildew is a form of
Mildew is a form of
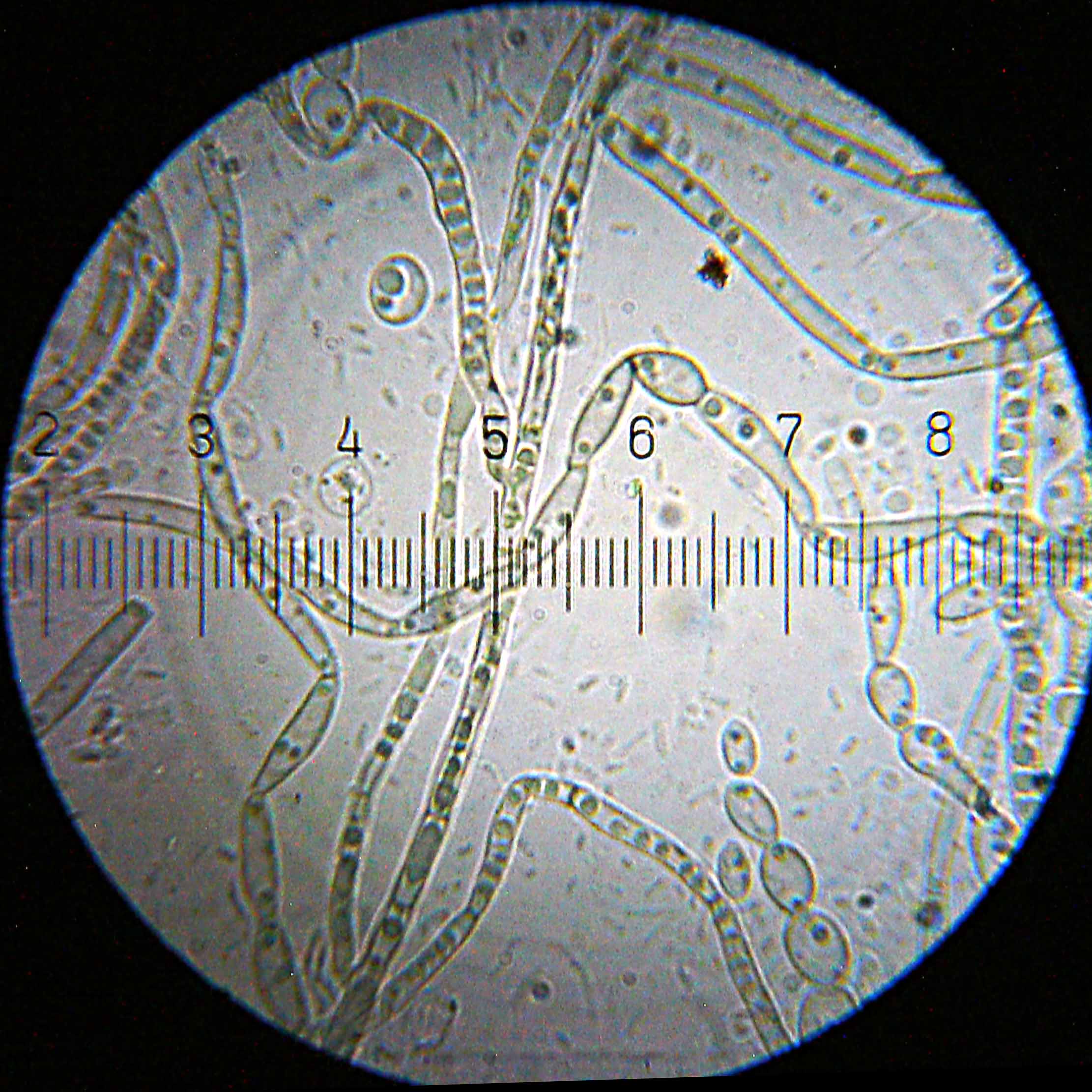 The term mildew is often used generically to refer to mold growth, usually with a flat growth habit. Molds can thrive on many organic materials, including clothing, leather, paper, and the ceilings, walls and floors of homes or offices with poor moisture control. Mildew can be cleaned using specialized mildew remover, or substances such as bleach (though they may discolour the surface).
The term mildew is often used generically to refer to mold growth, usually with a flat growth habit. Molds can thrive on many organic materials, including clothing, leather, paper, and the ceilings, walls and floors of homes or offices with poor moisture control. Mildew can be cleaned using specialized mildew remover, or substances such as bleach (though they may discolour the surface).
 There are many species of mold. The black mold which grows in attics, on window sills, and other places where moisture levels are moderate often is ''
There are many species of mold. The black mold which grows in attics, on window sills, and other places where moisture levels are moderate often is ''
fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
. It is distinguished from its closely related counterpart, mold
A mold () or mould () is one of the structures that certain fungus, fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of Spore#Fungi, spores containing Secondary metabolite#Fungal secondary metabolites, fungal ...
, largely by its colour: molds appear in shades of black, blue, red, and green, whereas mildew is white. It appears as a thin, superficial growth consisting of minute hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one o ...
(fungal
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the tradit ...
filaments) produced especially on living plants or organic matter such as wood, paper or leather. Both mold and mildew produce distinct offensive odours, and both have been identified as the cause of certain human ailments.
In horticulture, mildews are species of fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
in the order Erysiphales, or fungus-like organisms in the family '' Peronosporaceae''. It is also used more generally to mean mold growth. In Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
, mildew meant honeydew (a substance secreted by aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly ...
s on leaves, formerly thought to distill from the air like dew
Dew is water in the form of droplets that appears on thin, exposed objects in the morning or evening due to condensation.
As the exposed surface cools by thermal radiation, radiating its heat, atmospheric moisture condenses at a rate grea ...
), and later came to mean mold or fungus.
Household varieties
 The term mildew is often used generically to refer to mold growth, usually with a flat growth habit. Molds can thrive on many organic materials, including clothing, leather, paper, and the ceilings, walls and floors of homes or offices with poor moisture control. Mildew can be cleaned using specialized mildew remover, or substances such as bleach (though they may discolour the surface).
The term mildew is often used generically to refer to mold growth, usually with a flat growth habit. Molds can thrive on many organic materials, including clothing, leather, paper, and the ceilings, walls and floors of homes or offices with poor moisture control. Mildew can be cleaned using specialized mildew remover, or substances such as bleach (though they may discolour the surface).
 There are many species of mold. The black mold which grows in attics, on window sills, and other places where moisture levels are moderate often is ''
There are many species of mold. The black mold which grows in attics, on window sills, and other places where moisture levels are moderate often is ''Cladosporium
''Cladosporium'' is a genus of fungi including some of the most common indoor and outdoor molds. Some species are endophytes or plant pathogens, while others parasitize fungi.
Description
Species produce olive-green to brown or black colonie ...
''. Colour alone is not always a reliable indicator of the species of mold. Proper identification requires a microbiologist or mycologist. Mold growth found on cellulose-based substrates or materials where moisture levels are high (90 per cent or greater) is often '' Stachybotrys chartarum.'' "Black mold," also known as "toxic black mold", properly refers to ''S. chartarum''. This species is commonly found indoors on wet materials containing cellulose, such as wallboard (drywall), jute, wicker, straw baskets, and other paper materials. ''S. chartarum'' does not, however, grow on plastic, vinyl, concrete, glass, ceramic tile, or metals. A variety of other mold species, such as ''Penicillium
''Penicillium'' () is a genus of Ascomycota, ascomycetous fungus, fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
Some members of th ...
'' or ''Aspergillus
' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide.
''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Miche ...
'', may appear to grow on non-cellulosic surfaces but are actually growing on the biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
that adheres to these surfaces. Glass, plastic, and concrete provide no food for organic growth and as such cannot support mold or mildew growth alone without biofilm present. In places with stagnant air, such as basements, molds can produce a strong musty odour.
The pink "mildew" often found on plastic shower curtains and bathroom tile is a red yeast, ''Rhodotorula
''Rhodotorula'' is a genus of fungi in the class (biology), class Microbotryomycetes. Most species are known in their yeast states which produce orange to red colony (biology), colonies when grown on Sabouraud agar, Sabouraud's dextrose agar (SD ...
''.
Environmental conditions
Mildew requires certain factors to develop. Without any one of these, it cannot reproduce and grow. The requirements are a food source (any organic material), sufficient ambient moisture (arelative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
of 62–93%), and reasonable warmth () is optimal. Still, some growth can occur anywhere between freezing and . Slightly acidic conditions are also preferred. At warmer temperatures, air can hold a greater volume of water; as air temperatures drop, so does the ability of air to hold moisture, which then tends to condense on cool surfaces. This can work to bring moisture onto surfaces where mildew is then likely to grow (such as an exterior wall).
Preventing the growth of mildew therefore requires a balance between moisture and temperature. This can be achieved by minimizing the moisture available in the air.
Air temperatures at or below will inhibit growth, but only if the relative humidity is low enough to prevent water condensation (i.e., the dew point
The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to produce a relative humidity of 100%. This temperature depends on the pressure and water content of the air. When the air at a temperature above the ...
is not reached).
With warmer temperatures, the water holding capacity of the air increases. This means that if the amount of water vapour in the warming air remains the same, the air will become drier (i.e. it has a lower relative humidity). This again inhibits fungal growth. However, warm, growth-favoring temperatures coupled with high relative humidity will support mildew growth.
Air conditioners are one effective tool for removing moisture and heat from otherwise humid warm air. The coils of an air conditioner cause moisture in the air to condense on them, eventually losing this excess moisture through a drain and placing it back into the environment. They can also inhibit mildew growth by lowering indoor temperatures. For them to be effective, air conditioners must recirculate the existing indoor air and not be exposed to warm, humid outside air. Some energy efficient air conditioners may cool a room so quickly that they do not have an opportunity to also effectively collect and drain significant ambient water vapour.
See also
*Downy mildew
Downy mildew refers to any of several types of oomycete microbes that are obligate parasites of plants. Downy mildews exclusively belong to the Peronosporaceae family. In commercial agriculture, they are a particular problem for growers of c ...
* Phase I environmental site assessment
* Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungus, fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of Ascomycota, ascomycete fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant disea ...
* Obligate parasite
References
{{Reflist Building defects Plant pathogens and diseases Fungus common names