Mid-inguinal Point on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
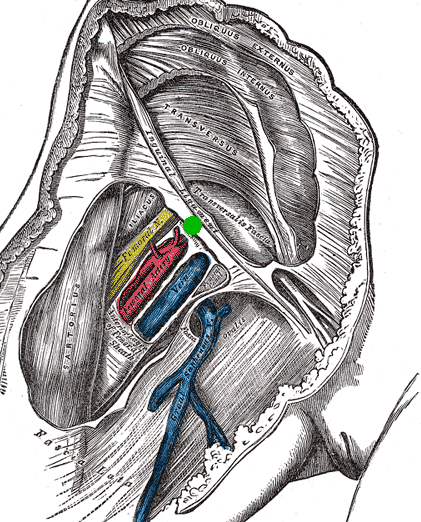 The mid-inguinal point (MIP) is located on the inguinal ligament, halfway between the
The mid-inguinal point (MIP) is located on the inguinal ligament, halfway between the
 The mid-inguinal point (MIP) is located on the inguinal ligament, halfway between the
The mid-inguinal point (MIP) is located on the inguinal ligament, halfway between the anterior superior iliac spine
The anterior superior iliac spine ( abbreviated: ASIS) is a bony projection of the iliac bone, and an important landmark of surface anatomy. It refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. It provides attachment for the in ...
(ASIS) and the pubic symphysis
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubi ...
. It is not to be confused with the midpoint of the inguinal ligament itself, which is located halfway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle
The pubic tubercle is a prominent tubercle on the superior ramus of the pubis bone of the pelvis.
Structure
The pubic tubercle is a prominent forward-projecting tubercle on the upper border of the medial portion of the superior ramus of th ...
.
Significance
Theexternal iliac artery
The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis.
Structure
The external iliac artery arises from the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. ...
becomes the femoral artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the f ...
when it passes deep to the inguinal ligament, at the mid-inguinal point. As such, the point is along the superior boundary of the femoral triangle.
References
{{Authority control Abdomen Ligaments