County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a
county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
in the
Eastern and Midland Region
The Eastern and Midland Region has been defined as a region in Ireland since 1 January 2015. It is a NUTS Level II statistical region of Ireland (coded IE06).
NUTS 2 Regions may be classified as ''less developed regions'', ''transition ...
of
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
, within the
province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of
Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland.
The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century ...
. It is bordered by
County Dublin
County Dublin ( or ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and holds its capital city, Dublin. It is located on the island's east coast, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Until 1994, County Dubli ...
to the southeast,
Louth Louth may refer to:
Australia
*Hundred of Louth, a cadastral unit in South Australia
* Louth, New South Wales, a town
* Louth Bay, a bay in South Australia
** Louth Bay, South Australia, a town and locality
Canada
* Louth, Ontario
Ireland
* Cou ...
to the northeast,
Kildare
Kildare () is a town in County Kildare, Ireland. , its population was 10,302, making it the 7th largest town in County Kildare. It is home to Kildare Cathedral, historically the site of an important abbey said to have been founded by Saint ...
to the south,
Offaly
County Offaly (; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain ...
to the southwest,
Westmeath
County Westmeath (; or simply ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It formed part of the historic Kingdom of ...
to the west,
Cavan
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road (Ireland), N3 road that links Dublin ( ...
to the northwest, and
Monaghan
Monaghan ( ; ) is the county town of County Monaghan, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It also provides the name of its Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish and Monaghan (barony), Monaghan barony.
The population of the town as of the 2022 cen ...
to the north. To the east, Meath also borders the
Irish Sea
The Irish Sea is a body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Celtic Sea in the south by St George's Channel and to the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland in the north by the North Ch ...
along a narrow strip between the rivers
Boyne and
Delvin
Delvin () is a village in County Westmeath, Ireland; it is located on the N52 road at a junction with the N51 to Navan. The town is from Mullingar (along the N52).
The word Delvin comes from Delbhna. That tribe settled in what is present- ...
, giving it the
second shortest coastline of any county.
Meath County Council
Meath County Council () is the local authority of County Meath, Ireland. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and de ...
is the
local authority
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of a higher-level political or administrative unit, such a ...
for the county.
Meath is the
14th-largest of Ireland's 32 traditional counties by land area, and the
8th-most populous, with a total population of 220,826 according to the
2022 census.
The county town and largest settlement in Meath is
Navan
Navan ( ; , meaning "the Cave") is the county town and largest town of County Meath, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is at the confluence of the River Boyne and Leinster Blackwater, Blackwater, around 50 km northwest of Dublin. At the ...
, located in the centre of the county along the River Boyne. Other towns in the county include
Trim
Trim or TRIM may refer to:
Cutting
* Cutting or trimming small pieces off something to remove them
** Book trimming, a stage of the publishing process
** Pruning, trimming as a form of pruning often used on trees
Decoration
* Trim (sewing), or ...
,
Kells,
Laytown
Laytown () is a village in County Meath, Ireland, located on the R150 regional road and overlooking the Irish Sea. Historically it was called ''Ninch'', after the townland it occupies. Together with the neighbouring villages of Mornington, ...
,
Ashbourne,
Dunboyne
Dunboyne () is a town in County Meath, Ireland, north-west of Dublin city centre. It is a commuter town for Dublin. In the 20 years between the 1996 and 2016 censuses, the population of Dunboyne more than doubled from 3,080 to 7,272 inhabitan ...
,
Slane
Slane () is a village in County Meath, in Ireland. The village stands on a steep hillside on the left bank of the River Boyne at the intersection of the N2 (Dublin to Monaghan road) and the N51 (Drogheda to Navan road). As of the 2022 census ...
and
Bettystown
Bettystown (), previously known as Betaghstown and transliterated to ''Beattystown/Bettystown'', is a village in County Meath, Ireland. Together with the neighbouring villages of Laytown, Mornington and Donacarney, it comprises the urban ar ...
.
Colloquially known as "The Royal County", the historic
Kingdom of Meath
Meath ( ; ; ) was a kingdom in Ireland from the 1st to the 12th century AD. Its name means "middle," denoting its location in the middle of the island.
At its greatest extent, it included all of County Meath (which takes its name from the k ...
was the seat of the
High King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and was later sometimes assigned anachronously or to leg ...
and, for a time, was also the island's
fifth province. Ruled for centuries by the
Southern Uí Néill
The Southern Uí Néill (, ) were a branch of the Uí Néill dynasty that invaded and settled in the Kingdom of Mide and its associated kingdoms.
Two sons of Niall Noigiallach, Lóegaire () and Coirpre (), initially led the dynasty. As did th ...
dynasty, in the late 1100s the kingdom was invaded by the
Anglo-Norman conqueror
Hugh de Lacy Hugh de Lacy or Hugh Lacy may refer to:
*Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Lassy (c. 1020–1085), first recorded member of the Norman noble family de Lacy
*Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath (died 1186), 4th Baron Lacy
*Hugh de Lacy, Abbot of Shrewsbury (died c. 121 ...
, who ousted the Uí Néill and established himself as the
Lord of Meath. This lordship gradually diminished in size before being formally shired as County Meath in 1297, which was further sub-divided into Meath and
Westmeath
County Westmeath (; or simply ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It formed part of the historic Kingdom of ...
in 1542. The county took its present boundaries in 1977, when much of
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth ...
was transferred to
County Louth
County Louth ( ; ) is a coastal Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Louth is bordered by the counties of County Meath, Meath to the ...
.
Meath has an abundance of historical sites, including the
Hill of Tara
The Hill of Tara ( or ) is a hill and ancient ceremonial and burial site near Skryne in County Meath, Ireland. Tradition identifies the hill as the inauguration place and seat of the High Kings of Ireland; it also appears in Irish mythology. ...
,
Hill of Slane,
Newgrange
Newgrange () is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, placed on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, west of the town of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3100 BC, makin ...
,
Knowth
Knowth (; ) is a prehistoric tomb overlooking the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland. It comprises a large passage tomb surrounded by 17 smaller tombs, built during the Neolithic era around 3200 BC. It contains the largest assemblage of megali ...
,
Dowth
Dowth () is the site of Neolithic passage tombs near the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland. It is one of the three main tombs of the ''Brú na Bóinne'' World Heritage Site, along with Newgrange and Knowth. Its features align it with the ot ...
,
Loughcrew
Loughcrew or Lough Crew () is an area of historical importance near Oldcastle, County Meath, Ireland. It is home to a group of ancient tombs from the 4th millennium BC, some decorated with rare megalithic art, which sit on top of a range of hi ...
, the
Abbey of Kells
The Abbey of Kells () or Kells Priory is a former monastery in Kells, County Meath, Ireland, north-west of Dublin. It was founded in the early 9th century, and the Book of Kells was kept there during the later medieval and early modern perio ...
,
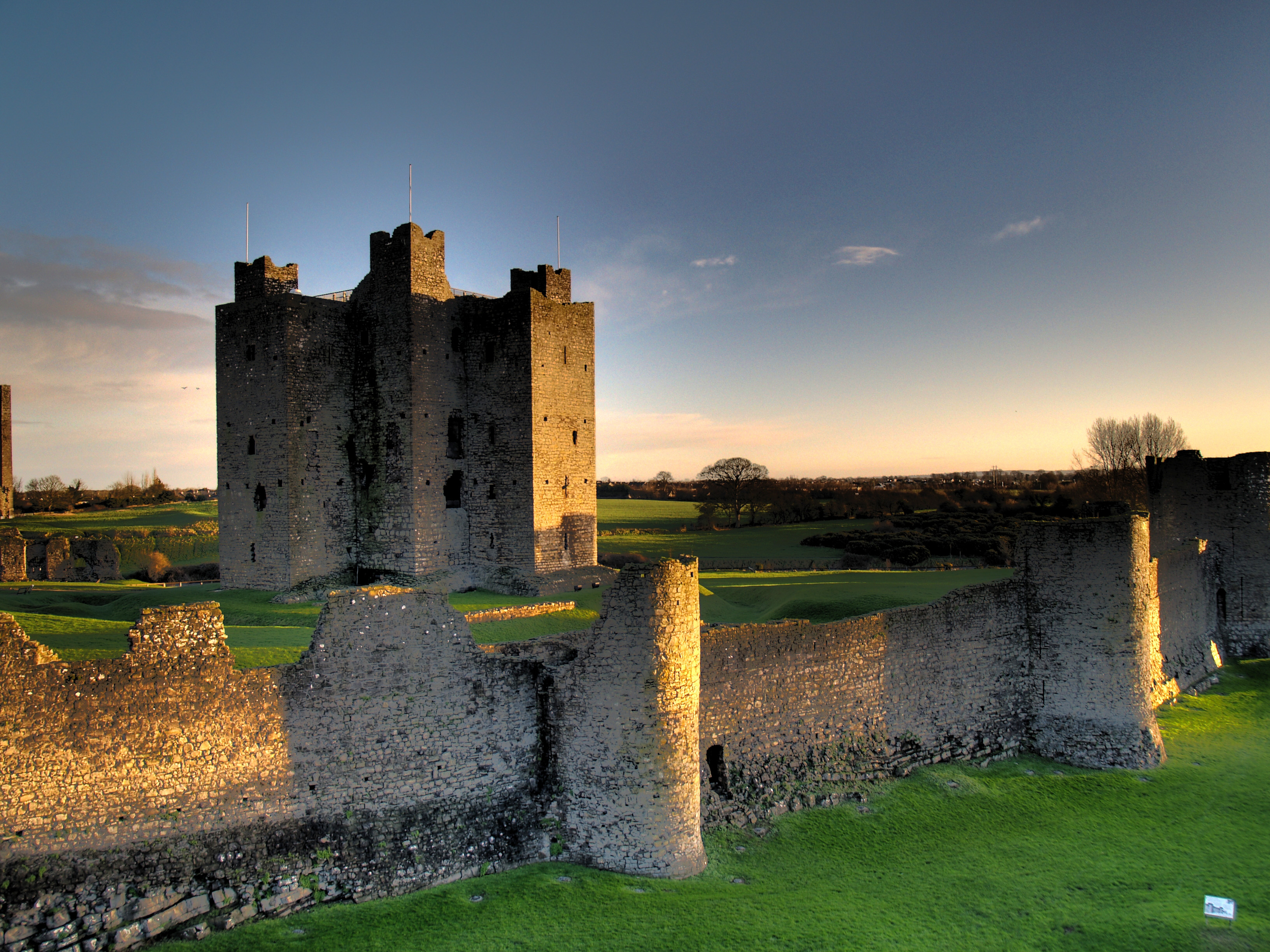
Trim Castle
Trim Castle () is a castle on the south bank of the River Boyne in Trim, County Meath, Ireland, with an area of 30,000 m2. Over a period of 30 years, it was built by Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, Hugh de Lacy and his son Walter de Lacy, ...
and
Slane Castle
Slane Castle () is located in the village of Slane, within the Boyne Valley of County Meath, Ireland. The castle has been the family seat of the Conyngham family since it was built in the late 18th century, on land first purchased in 1703 by ...
. The county was also the site of the seminal
Battle of the Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne ( ) took place in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II, and those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and James's daughter), had acceded to the Crowns of England and Sc ...
, which was fought near
Oldbridge
Oldbridge () is a townland near Drogheda in County Meath, Ireland. The area is home to the Boyne Navigation, the Battle of the Boyne Interpretive Centre and the southern half of the Mary McAleese Boyne Valley Bridge (which carries the M1 motor ...
in 1690, ending in the defeat of
James II and his flight to
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. It is the only county in Leinster to have
Gaeltacht
A ( , , ) is a district of Ireland, either individually or collectively, where the Irish government recognises that the Irish language is the predominant vernacular, or language of the home.
The districts were first officially recognised ...
regions, at
Ráth Chairn
Ráth Chairn () is a small village and Gaeltacht ( Irish-speaking area) in County Meath, Ireland. It is about 55 km northwest of Dublin. Ráth Chairn Gaeltacht was founded in 1935 when 27 families from Connemara, mostly from Ceantar na n ...
and
Baile Ghib
Baile Ghib () is a small village and Gaeltacht ( Irish-speaking area) in County Meath, Ireland. It is about 70km northwest of Dublin.
The Baile Ghib Gaeltacht was founded in 1937 when 52 families were settled on land previously acquired by the ...
, and is also one of only two counties outside of the west of Ireland to have an official Gaeltacht (the other being
County Waterford
County Waterford () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. It is named after the city of Waterford. ...
).
Geography and subdivisions
Meath is the 14th-largest of Ireland's 32 counties by area, and the eighth-largest in terms of population. It is the second-largest of Leinster's 12 counties in size, and the third-largest in terms of population. Meath borders seven counties –
Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
and
Louth Louth may refer to:
Australia
*Hundred of Louth, a cadastral unit in South Australia
* Louth, New South Wales, a town
* Louth Bay, a bay in South Australia
** Louth Bay, South Australia, a town and locality
Canada
* Louth, Ontario
Ireland
* Cou ...
to the east,
Westmeath
County Westmeath (; or simply ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It formed part of the historic Kingdom of ...
and
Offaly
County Offaly (; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain ...
to the west,
Kildare
Kildare () is a town in County Kildare, Ireland. , its population was 10,302, making it the 7th largest town in County Kildare. It is home to Kildare Cathedral, historically the site of an important abbey said to have been founded by Saint ...
to the south, and
Cavan
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road (Ireland), N3 road that links Dublin ( ...
and
Monaghan
Monaghan ( ; ) is the county town of County Monaghan, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It also provides the name of its Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish and Monaghan (barony), Monaghan barony.
The population of the town as of the 2022 cen ...
to the north. Meath's coastline stretches for roughly along the
Irish Sea
The Irish Sea is a body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Celtic Sea in the south by St George's Channel and to the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland in the north by the North Ch ...
between the
Boyne and
Delvin
Delvin () is a village in County Westmeath, Ireland; it is located on the N52 road at a junction with the N51 to Navan. The town is from Mullingar (along the N52).
The word Delvin comes from Delbhna. That tribe settled in what is present- ...
rivers, making it the
second shortest coastline of any coastal county. The county town, Navan, is the largest settlement in Meath, and is situated on the River Boyne in the middle of the county. Navan is approximately from
Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
and from
Belfast
Belfast (, , , ; from ) is the capital city and principal port of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan and connected to the open sea through Belfast Lough and the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel ...
.
Physical geography
Owing to the fertile agricultural plains along the Boyne valley, which dominate the county, Meath's landscape is largely rural in nature. However, it is also one of the most densely populated counties in Ireland, with a population density of 94 people per km2. Centuries of exhaustive harvesting and reclamation for agriculture have severely reduced the extent of
bogland
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muske ...
in the county, especially in comparison to the neighbouring
Midland counties. However, small areas of bogland survived, such as Jamestown Bog, Girley Bog and Killyconny Bog, and are currently protected as either
Special Areas of Conservation
A special area of conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and ap ...
(SACs) or Natural Heritage Areas (NHAs).
The River Boyne, at in length, is Meath's dominant geographic feature and is synonymous with the county, having defined its history and culture over millennia. The two most prominent tributaries of the Boyne are the
Leinster Blackwater
The Kells Blackwater (), also called the River Blackwater or Leinster Blackwater, is a river that flows through the counties of Cavan and Meath in Ireland. It is a tributary of the River Boyne which flows into the Irish Sea at Drogheda. (This ...
, which has its source in Cavan and flows south for before joining the Boyne at Navan, and the
Enfield Blackwater, which has its source in Kildare and flows north for before joining the Boyne at Donore. In the east of the county, both the
River Nanny and the
Delvin River flow to the Irish sea, with the latter demarcating the border with County Dublin.
As of 2017, there is a total of of forest cover in the county, representing 5.7% of the total land area. This is an increase from just (4.8%) in 2006. Nevertheless, Meath is Ireland's third-least forested county and remains well below the national average of 11% forest cover. Historically, Meath was extensively forested, but experienced a near total deforestation between the 16th and 18th centuries. Although it has rebounded in recent years, the low forest cover compared to other counties can be explained by the lack of a significant commercial forestry industry within the county. Meath is one of the smallest contributors to the national timber supply, and over two-thirds of Meath's forests are
broadleaf – the highest of any county – as opposed to more commercially viable
conifers
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All e ...
. Additionally, three-quarters of forests within the county are privately owned.
Climate
Under
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
, Meath experiences a maritime
temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
with cool winters, mild humid summers, and a lack of temperature extremes.
Met Éireann
Met Éireann (; meaning "Meteorology, Met of Ireland") is the state meteorology, meteorological service of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, part of the Department of Housing, Local Government and Heritage.
History
The history of modern meteorolog ...
records the climate data for Meath from their station at
Dunsany Dunsany may refer to:
* Dunsany Castle and Demesne, County Meath, Ireland
* Baron of Dunsany, "Lord Dunsany" or "Dunsany", the holders of the Dunsany estate
* Dunsany, County Meath, a townland and hamlet, named for the adjacent castle and demesne
...
, situated above sea level. The average maximum January temperature is , while the average maximum July temperature is . On average, the sunniest months are May and June, while the wettest month is October with of rain, and the driest month is June with . Humidity is high year-round and rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year. A number of
synoptic stations which record rainfall are located throughout the county. The driest parts of the county are in the east and south, while the wettest are in the west.
Julianstown
Julianstown () is a village in County Meath, Ireland. It is located near Drogheda on the R132 regional road. In 1641, the Battle of Julianstown was fought here during the Irish Rebellion of 1641.
History
The parish of Julianstown is situated ...
near the east coast receives of rainfall per year, while
Oldcastle in the west receives . The annual precipitation at Dunsany is .
Snow showers generally occur between November and March, but prolonged or heavy snow events are rare. Although frost is common in the central and western areas of the county, temperatures typically fall below 0 °C (32 °F) on just a few days per year. The lowest ever temperature in Meath was recorded in December 2010, at . Summer daytime temperatures range between and , with temperatures rarely going beyond . As with rainfall, the sunniest areas of the county are located along the coast. The climate gets progressively duller and wetter inland due to the convective development of clouds over land.
Geology

The county's geological landscape is predominantly made up of
Lower Carboniferous
Lower may refer to:
* ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is sit ...
limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, which underlies approximately 75% of the county. These were laid down following the erosion of mountain ranges which formed due to the closure of the
Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean (; ) existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale (between 600 and 400 million years ago). It was in the southern hemisphere, between the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalon ...
. The eroded mountains became basins in which limestone sediments and carbonate
mud
Mud (, or Middle Dutch) is loam, silt or clay mixed with water. Mud is usually formed after rainfall or near water sources. Ancient mud deposits hardened over geological time to form sedimentary rock such as shale or mudstone (generally cal ...
were deposited. The oldest rocks in the county are
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
in age and are found in thin layers near
Slane
Slane () is a village in County Meath, in Ireland. The village stands on a steep hillside on the left bank of the River Boyne at the intersection of the N2 (Dublin to Monaghan road) and the N51 (Drogheda to Navan road). As of the 2022 census ...
and at
Stamullen
Stamullen () is a village in County Meath, Ireland on the border with County Dublin. It lies just off the M1 motorway 32 km north of Dublin city centre and beside the Delvin River. In the late 1990s and early 21st century, it expanded sig ...
, while the youngest rocks are of
Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
age, and were formed as a result of volcanic activity. These are found in small
dykes and
sills throughout the county.
Crustal stretching beneath Ireland during the Carboniferous allowed fluids to infiltrate through faults in the rock, and extensive mineralisation occurred. Most notably, zinc-bearing
Sphalerite
Sphalerite is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hoste ...
and lead-bearing
Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It crysta ...
were deposited in vast quantities, giving Ireland the highest concentration of zinc per square kilometre on Earth. The ubiquity of these minerals gave rise to the term "
Irish-type" lead-zinc deposits, which is a descriptive term for lead-zinc deposits hosted in carbonate rocks.
Meath's landscape was shaped during the
Last Glacial Period, which ended 11,700 years ago. The soils of the county are mostly derived from
glacial till
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
, consisting of a mix of clay, sand and gravel which were deposited by glacial melt-water. In the north of the county near the border with Cavan, a small series of
drumlin
A drumlin, from the Irish word ("little ridge"), first recorded in 1833, in the classical sense is an elongated hill in the shape of an inverted spoon or half-buried egg formed by glacial ice acting on underlying unconsolidated till or groun ...
s were formed from
boulder clay
Boulder clay is an unsorted agglomeration of clastic sediment that is unstratified and structureless and contains gravel of various sizes, shapes, and compositions distributed at random in a fine-grained matrix. The fine-grained matrix consists o ...
. Loughs typically form in between the poorly-drained inter-drumlin areas, however unlike in neighbouring Cavan and Westmeath, Meath has no sizable loughs, other than
Lough Sheelin
Lough Sheelin (), in standard Irish language, Irish ''Loch Síleann'', is a limestone freshwater lough (lake) in central Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The lake is a part of the River Inny (Leinster), River Inny course, and ultimately of the Riv ...
, on which the county shares a small coastline in its westernmost tip.
Meath is largely flat and much of the county lies below above sea-level. The minor hills in the far west of the county at
Loughcrew
Loughcrew or Lough Crew () is an area of historical importance near Oldcastle, County Meath, Ireland. It is home to a group of ancient tombs from the 4th millennium BC, some decorated with rare megalithic art, which sit on top of a range of hi ...
, and in the north at Carrickleck are the only upland areas of any significance.
Slieve na Calliagh
Slieve na Calliagh () are a range of hills and ancient burial site near Oldcastle, County Meath, Ireland. The summit is , the highest point in the county. On the hilltops are about twenty passage tombs, some decorated with rare megalithic art, ...
, at just in height, is the highest point in the county, making it the second lowest
county top
The mountains and hills of the British Isles are categorised into various lists based on different combinations of elevation, prominence, and other criteria such as isolation. These lists are used for peak bagging, whereby hillwalkers attempt ...
in Ireland. Carrickleck Hill, near the Cavan border, is the second highest peak in Meath, at .
The
Hill of Tara
The Hill of Tara ( or ) is a hill and ancient ceremonial and burial site near Skryne in County Meath, Ireland. Tradition identifies the hill as the inauguration place and seat of the High Kings of Ireland; it also appears in Irish mythology. ...
is located south of Navan and, although just in height, is the most prominent feature in the local topography, commanding a panoramic view of the surrounding area.
Baronies
There are eighteen historic
baronies Barony may refer to:
* Barony, the peerage, office of, or territory held by a baron
* Barony, the title and land held in fealty by a feudal baron
* Barony (county division), a type of administrative or geographical division in parts of the British ...
in the county. While baronies continue to be officially defined units, they are no longer used for many administrative purposes, and the barony boundaries in County Meath which continuously changed from the 16th to 19th centuries were last finalised in 1807. Their official status is illustrated by Placenames Orders made since 2003, where official Irish names of baronies are listed under "Administrative units". The largest barony in Meath is Kells Upper, at 49,552 acres (201 km2), and the smallest barony is Dunboyne, at 16,781 acres (68 km2).
* Deece Upper ()
* Deece Lower ()
* Duleek Upper ()
* Duleek Lower ()
* Dunboyne ()
* Fore ()
* Kells Upper ()
*
Kells Lower ()
* Lune (''Luíne'')
*
Morgallion
Morgallion (, "plain of the Gailenga") is one of the baronies that comprise county Meath, Ireland.
In 1172 King Henry II of England granted the Lordship of Meath to Hugh de Lacy to hold as King Murrough O Melaghlin held it. Once establish ...
()
* Moyfenrath Upper ()
* Moyfenrath Lower ()
* Navan Upper ()
* Navan Lower ()
*
Ratoath
Ratoath () is a commuter town in County Meath, Ireland. A branch of the Broad Meadow Water (Broadmeadow River) () flows through the town. The R125 and R155 roads meet in the village. At the 2022 census, there were 10,007 people living in Ra ...
()
*
Skreen
Skreen () is a small village and parish in County Sligo, Ireland. The village is in a civil parish of the same name.
History
St Adomnán, the first biographer of St Columba (Colmcille) and one of his successors at Iona, first served as abbot ...
()
* Slane Upper ()
* Slane Lower ()
Civil parishes and townlands
Townland
A townland (; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a traditional small land division used in Ireland and in the Western Isles of Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of medieval Gaelic origin, predating the Norman invasion, and mo ...
s are the smallest officially defined geographical divisions in Ireland, there are approximately 1,634 townlands in the county. Historic town boundaries are registered as their own townlands and much larger than rural townlands which, within County Meath, are typically small in size, ranging from just 1 acre to 2,681 acres, with the average size of a townland in the county (excluding towns) being 356 acres.
Towns and villages
European statistical region
For
statistical purposes at EU level, the county is part of the
Mid-East Region – a NUTS III entity – which is in turn part of the level II NUTS entity –
Eastern and Midland Region
The Eastern and Midland Region has been defined as a region in Ireland since 1 January 2015. It is a NUTS Level II statistical region of Ireland (coded IE06).
NUTS 2 Regions may be classified as ''less developed regions'', ''transition ...
.
Governance and politics
Local government
Meath County Council
Meath County Council () is the local authority of County Meath, Ireland. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and de ...
is the
local authority
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of a higher-level political or administrative unit, such a ...
governing County Meath. It has 40 councillors, and the county is divided into divided into six
local electoral area
A local electoral area (LEA; ) is an electoral area for elections to Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authorities in Ireland. All elections in the Republic of Ireland, elections use the single transferable vote. Republic of Ir ...
s, each of which also forms a municipal district: Ashbourne (6), Kells (7), Laytown–Bettystown (7), Navan (7), Ratoath (7) and Trim (6).
Fine Gael
Fine Gael ( ; ; ) is a centre-right, liberal-conservative, Christian democratic political party in Ireland. Fine Gael is currently the third-largest party in the Republic of Ireland in terms of members of Dáil Éireann. The party had a member ...
currently hold 11 seats,
Fianna Fáil
Fianna Fáil ( ; ; meaning "Soldiers of Destiny" or "Warriors of Fál"), officially Fianna Fáil – The Republican Party (), is a centre to centre-right political party in Ireland.
Founded as a republican party in 1926 by Éamon de ...
hold 9,
Sinn Féin
Sinn Féin ( ; ; ) is an Irish republican and democratic socialist political party active in both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The History of Sinn Féin, original Sinn Féin organisation was founded in 1905 by Arthur Griffit ...
hold 6,
Aontú
Aontú (; "Unity") is a conservative Irish republican political party active in both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland. It has been led by Peadar Tóibín since its foundation in January 2019. The party holds socially conservative ...
hold 2, and the
Social Democrats
Social democracy is a social, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, s ...
hold 1. There are 11 independent councillors. Council elections are held every 5 years, with the next election due to be held in June 2029. The
2024 Meath local elections had a voter turnout of 48.0%, a very slight decrease of 0.1% on the
2019 election. The highest turnout was at Kells (55.0%) and the lowest was at Trim (43.9%).
The council has three representatives on the
Eastern and Midland Regional Assembly
The Eastern and Midland Region has been defined as a region in Ireland since 1 January 2015. It is a NUTS Level II statistical region of Ireland (coded IE06).
NUTS 2 Regions may be classified as ''less developed regions'', ''transition ...
.
The county town is Navan, where the county hall and government are located, although
Trim
Trim or TRIM may refer to:
Cutting
* Cutting or trimming small pieces off something to remove them
** Book trimming, a stage of the publishing process
** Pruning, trimming as a form of pruning often used on trees
Decoration
* Trim (sewing), or ...
, the former county town, has historical significance and remains a sitting place of the
circuit court
Circuit courts are court systems in several common law jurisdictions. It may refer to:
* Courts that literally sit 'on circuit', i.e., judges move around a region or country to different towns or cities where they will hear cases;
* Courts that s ...
.
Former districts
County Meath was divided under the
Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898
The Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898 ( 61 & 62 Vict. c. 37) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland that established a system of local government in Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots diale ...
into the
rural district
A rural district was a type of local government area – now superseded – established at the end of the 19th century in England, Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. I ...
s of Ardee No. 2, Dunshaughlin, Kells, Meath, Navan, Oldcastle, Trim, and Edenderry No. 3, and the
urban districts of An Uaimh (
Navan
Navan ( ; , meaning "the Cave") is the county town and largest town of County Meath, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is at the confluence of the River Boyne and Leinster Blackwater, Blackwater, around 50 km northwest of Dublin. At the ...
), Ceannanus Mór (
Kells), and
Trim
Trim or TRIM may refer to:
Cutting
* Cutting or trimming small pieces off something to remove them
** Book trimming, a stage of the publishing process
** Pruning, trimming as a form of pruning often used on trees
Decoration
* Trim (sewing), or ...
. The rural districts were abolished in 1925. The urban districts became
town councils
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, borough counci ...
in 2002. All town councils in Ireland were abolished in 2014.
National elections

County Meath is within four
Dáil constituencies
There are 43 multi-member electoral districts, known as Dáil constituencies, to elect 174 Teachta Dála, TDs to Dáil Éireann, the house of representatives of the Oireachtas, Republic of Ireland, Ireland's parliament, on the system of propor ...
:
*
Cavan–Monaghan – comprises the entirety of counties
Cavan
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road (Ireland), N3 road that links Dublin ( ...
and
Monaghan
Monaghan ( ; ) is the county town of County Monaghan, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It also provides the name of its Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish and Monaghan (barony), Monaghan barony.
The population of the town as of the 2022 cen ...
, with a small portion of northern County Meath;
*
Louth Louth may refer to:
Australia
*Hundred of Louth, a cadastral unit in South Australia
* Louth, New South Wales, a town
* Louth Bay, a bay in South Australia
** Louth Bay, South Australia, a town and locality
Canada
* Louth, Ontario
Ireland
* Cou ...
– comprises the entirety of
County Louth
County Louth ( ; ) is a coastal Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Louth is bordered by the counties of County Meath, Meath to the ...
, with the electoral divisions of Julianstown and St. Marys (Part) in County Meath;
*
Meath East
County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, County ...
– lies entirely within the borders of the county;
*
Meath West – comprises the western portion of the county and includes a part of the neighbouring county of
Westmeath
County Westmeath (; or simply ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It formed part of the historic Kingdom of ...
;
From 1923 to 1937, and again from 1948 to 2007, there was one
Meath
County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, County ...
constituency. From 1937 to 1948 the county was within the
Meath–Westmeath constituency. Between 1923 and 2007 a total of 31
general elections
A general election is an electoral process to choose most or all members of a governing body at the same time. They are distinct from by-elections, which fill individual seats that have become vacant between general elections. General elections ...
and
by-election
A by-election, also known as a special election in the United States and the Philippines, or a bypoll in India, is an election used to fill an office that has become vacant between general elections.
A vacancy may arise as a result of an incumben ...
s were held. Following the demise of
Cumann na nGaedheal
Cumann na nGaedheal (; ) was a political party in the Irish Free State, which formed the government from 1923 to 1932. It was named after the original Cumann na nGaedheal organisation which merged with the Dungannon Clubs and the National Co ...
in the 1930s, national politics in the Meath and Meath–Westmeath constituencies was dominated by Fianna Fáil, Fine Gael and Labour Party. During those years, the Meath and Meath–Westmeath constituencies returned a total of 106
TDs to
Dáil Éireann
Dáil Éireann ( ; , ) is the lower house and principal chamber of the Oireachtas, which also includes the president of Ireland and a senate called Seanad Éireann.Article 15.1.2° of the Constitution of Ireland reads: "The Oireachtas shall co ...
, of which 54 were from Fianna Fáil, 34 from Fine Gael and 11 from Labour; with Cumann na nGaedheal and the
Farmers' Party returning 6 and 1 TDs respectively in the 1920s and 1930s. No other party would win a Dáil seat in Meath until 2011, when
Peadar Tóibín
Peadar Tóibín (; born 19 June 1974) is an Irish politician who has served as leader of Aontú since January 2019. He has been a Teachta Dála (TD) for the Meath West constituency since 2011. He previously served as Chair of the Committee on ...
was elected to
Meath West for Sinn Féin.
Meath East and Meath West return 6 TDs to the Dáil. In the most recent
general election in 2020, Sinn Féin won 2 of the 6 seats, Fine Gael won 2, and Fianna Fáil and Aontú both won 1 seat each. The voter turnout at the 2016 general election was 61.5% in Meath West, and 63.4% in Meath East.
European elections
The county is part of the 4-seat
Midlands–North-West constituency for elections to the
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
.
History
The county is colloquially known by the nickname "The Royal County", owing to its history as the seat of the
High King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and was later sometimes assigned anachronously or to leg ...
. It formed from the eastern part of the former
Kingdom of Mide
Meath ( ; ; ) was a kingdom in Ireland from the 1st to the 12th century AD. Its name means "middle," denoting its location in the middle of the island.
At its greatest extent, it included all of County Meath (which takes its name from the k ...
but now forms part of the
province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of
Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland.
The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century ...
. Historically, the kingdom and its successor territory the
Lordship of Meath
The Lordship of Meath was an extensive seigneurial liberty in medieval Ireland that was awarded to Hugh de Lacy by King Henry II of England by the service of fifty knights and with almost royal authority. The Lordship was roughly co-extensive wit ...
included all of the counties Meath,
Fingal
Fingal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which ...
and Westmeath as well as parts of counties
Cavan
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road (Ireland), N3 road that links Dublin ( ...
,
Longford
Longford () is the county town of County Longford in Ireland. It had a population of 10,952 at the 2022 census. It is the biggest town in the county and about one third of the county's population lives there. Longford lies at the meeting of ...
,
Louth Louth may refer to:
Australia
*Hundred of Louth, a cadastral unit in South Australia
* Louth, New South Wales, a town
* Louth Bay, a bay in South Australia
** Louth Bay, South Australia, a town and locality
Canada
* Louth, Ontario
Ireland
* Cou ...
,
Offaly
County Offaly (; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain ...
and
Kildare
Kildare () is a town in County Kildare, Ireland. , its population was 10,302, making it the 7th largest town in County Kildare. It is home to Kildare Cathedral, historically the site of an important abbey said to have been founded by Saint ...
. The seat of the High King of Ireland was at
Tara. The archaeological complex of ''
Brú na Bóinne
(, "mansion or palace of the Boyne"), also called the Boyne Valley tombs, is an ancient monument complex and ritual landscape in County Meath, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, located in a bend of the River Boyne. It is one of the world's most im ...
'' in the north-east of the county is 5,000 years old and is a
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
-designated
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
.

Pre-history

The earliest known evidence of human settlement in the county is the
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
flints found at Randalstown north of Navan, which were uncovered during the construction of the
tailings
In mining, tailings or tails are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different from overburden, which is the waste rock or other material ...
pond for Tara Mines in the 1970s. These flints have been dated to 9,500 BC and are one of the earliest traces of
pre-historic humans in Ireland. The excavation site at Randalstown also revealed other evidence of
hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
society, such as a
fulacht fiadh
A burnt mound is an archaeological feature consisting of a mound of shattered stones and charcoal, normally with an adjacent hearth and trough. The trough could be rock-cut, wood-lined or clay-lined to ensure it was watertight. Radiocarbon ...
and mounds of burnt soil and stone.
Farming was established in the area during the
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period. This provided a surplus of time and resources which was spent constructing great stone monuments to the dead, such as
passage grave
A passage grave or passage tomb consists of one or more burial chambers covered in earth or stone and having a narrow access passage made of large stones. These structures usually date from the Neolithic Age and are found largely in Western Europ ...
s,
court cairns and
wedge tombs. There are hundreds of surviving examples of these dotted across the landscape, however, the most famous Neolithic monuments in Ireland are those at
Brú na Bóinne
(, "mansion or palace of the Boyne"), also called the Boyne Valley tombs, is an ancient monument complex and ritual landscape in County Meath, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, located in a bend of the River Boyne. It is one of the world's most im ...
–
Newgrange
Newgrange () is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, placed on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, west of the town of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3100 BC, makin ...
,
Knowth
Knowth (; ) is a prehistoric tomb overlooking the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland. It comprises a large passage tomb surrounded by 17 smaller tombs, built during the Neolithic era around 3200 BC. It contains the largest assemblage of megali ...
and
Dowth
Dowth () is the site of Neolithic passage tombs near the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland. It is one of the three main tombs of the ''Brú na Bóinne'' World Heritage Site, along with Newgrange and Knowth. Its features align it with the ot ...
. These tombs were constructed prior to 3,000 BC making them older than
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric Megalith, megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, to ...
and the
Egyptian pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Most were built as tombs for the pharaohs and their consorts during the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old and Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom periods. At least 138 identi ...
. The site is believed to have been of religious significance and is decorated with
megalithic art
Megalithic art refers to art either painted or carved onto megaliths in prehistoric Europe and found on the structural elements, like the kerbstones, orthostats, or capstones of megalithic tombs, but recent investigations have included decorati ...
. Newgrange, the largest pre-historic tomb in Ireland, is most famous for its alignment with the
equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun appears directly above the equator, rather than to its north or south. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise directly east and set directly west. This occurs twice each year, arou ...
es, when sunlight shines through a '
roofbox {{Short description, Archaeological feature
In archaeology, a roofbox is a term for a specially contrived opening above a doorway, that is constructed in such way that at particular times of the year e.g. the winter or summer solstices, the Sun wo ...
' and floods the inner chamber.
In constructing the tomb the early settlers displayed an advanced knowledge of
astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
and a
calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is ...
system. However, a writing system would not be developed until the 1st century BC, with the emergence of
Ogham
Ogham (also ogam and ogom, , Modern Irish: ; , later ) is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the early Irish language (in the "orthodox" inscriptions, 4th to 6th centuries AD), and later the Old Irish language ( scholastic ...
.
The arrival of the
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
to Ireland around 500 BC heralded the beginning of the
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
and the establishment of most of what would define Gaelic Irish culture for millennia; including
Primitive Irish
Primitive Irish or Archaic Irish (), also called Proto-Goidelic, is the oldest known form of the Goidelic languages, and the ancestor of all languages within this family.
This phase of the language is known only from fragments, mostly persona ...
,
Irish mythology
Irish mythology is the body of myths indigenous to the island of Ireland. It was originally Oral tradition, passed down orally in the Prehistoric Ireland, prehistoric era. In the History of Ireland (795–1169), early medieval era, myths were ...
,
Celtic paganism
Ancient Celtic religion, commonly known as Celtic paganism, was the religion of the ancient Celtic peoples of Europe. Because there are no extant native records of their beliefs, evidence about their religion is gleaned from archaeology, Greco ...
and an early form of the
Gaelic calendar. The ancient monuments of the Boyne Valley were assimilated into Celtic culture and mythology, with
Cú Chulainn
Cú Chulainn ( ), is an Irish warrior hero and demigod in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology, as well as in Scottish and Manx folklore. He is believed to be an incarnation of the Irish god Lugh, who is also his father. His mother is the ...
said to have been conceived at Newgrange. Furthermore, tradition states that
Sláine mac Dela
Sláine (Sláinge, Slánga), son of Dela, of the Fir Bolg was the legendary first High King of Ireland, who cleared the forest around Brú na Bóinne. He reportedly came ashore at Wexford Harbour at the mouth of the River Slaney.
The Fir Bo ...
, of the
Fir Bolg
In medieval Irish myth, the Fir Bolg (also spelt Firbolg and Fir Bholg) are the fourth group of people to settle in Ireland. They are descended from the Muintir Nemid, an earlier group who abandoned Ireland and went to different parts of Europe. ...
, cleared the forest at Brú na Bóinne and built the monuments, becoming the first High King of Ireland. It was during the Celtic period that Meath was divided into 8
túath
''Túath'' (plural ''túatha'') is the Old Irish term for the basic political and jurisdictional unit of Gaelic Ireland. ''Túath'' can refer to both a geographical territory as well the people who lived in that territory. The smallest ''túath ...
a, the primary political unit of
Celtic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland () was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late prehistoric era until the 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Irelan ...
. The túatha were independent
petty kingdoms
A petty kingdom is a kingdom described as minor or "petty" (from the French 'petit' meaning small) by contrast to an empire or unified kingdom that either preceded or succeeded it (e.g. the numerous kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England unified into t ...
ruled by a chief who was elected by members of their extended family.
Early Christian period (400–1169)
Kingdom of Meath


Due to a lack of extensive written historical records prior to the 5th century AD, the early history of Meath is murky and largely mythologised.
Irish legend purports that the title of "
High King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and was later sometimes assigned anachronously or to leg ...
" stretches back millennia, however, it is today known that the Hill of Tara did not become a seat of power until the early centuries AD.
Dáibhí Ó Cróinín
Dáibhí Iarla Ó Cróinín (born 29 August 1954) is an Irish historian and authority on Hiberno-Latin texts, noted for his significant mid-1980s discovery in a manuscript in Padua of the "lost" Irish 84-year Easter table. Ó Cróinín was Pro ...
, "Ireland, 400–800", in Dáibhí Ó Cróinín (ed.), ''A New History of Ireland 1: Prehistoric and Early Ireland'', Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
, 2005, pp. 182–234. In the 400s,
Niall of the Nine Hostages
Niall Noígíallach (; Old Irish "having nine hostages"), or Niall of the Nine Hostages, was a legendary, semi-historical Irish king who was the ancestor of the Uí Néill dynasties that dominated Ireland from the 6th to the 10th centuries. ...
, King of the
Uí Néill
The Uí Néill (; meaning "descendants of Niall") are Irish dynasties that claim descent from Niall Noígíallach (Niall of the Nine Hostages), a historical King of Tara who is believed to have died around c. 405. They are generally divided ...
, conquered southward from
Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
and established a kingdom in Meath. As was commonplace in Ireland at the time, the achievements of Niall and his sons were propagandised and
mythicised by
bards
In Celtic cultures, a bard is an oral repository and professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron (such as a monarch or chieftain) to commemorate one or more of the patron's an ...
to such an extent that much of what is known about them is considered fictional. Nevertheless, the dynasty of the Uí Néill had become firmly established in the centre of Ireland and they proclaimed themselves the
Kings of Tara
The term Kingship of Tara () was a title of authority in ancient Ireland - the title is closely associated with the archaeological complex at the Hill of Tara. The position was considered to be of eminent authority in medieval Irish literature ...
and
Kings of Uisnech
The Kings of Uisnech were of the Uí Néill and one of its major southern branches, the Clann Cholmáin. The Hill of Uisnech is located in what is now County Westmeath
County Westmeath (; or simply ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Re ...
. The Uí Néill dynasty subsequently divided into two septs, the
Northern Uí Néill
The Northern Uí Néill was any of several dynasties in north-western medieval Ireland that claimed descent from a common ancestor, Niall of the Nine Hostages. Other dynasties in central and eastern Ireland who also claimed descent from Niall ar ...
who remained in Ulster, and the
Southern Uí Néill
The Southern Uí Néill (, ) were a branch of the Uí Néill dynasty that invaded and settled in the Kingdom of Mide and its associated kingdoms.
Two sons of Niall Noigiallach, Lóegaire () and Coirpre (), initially led the dynasty. As did th ...
who now ruled over several small, disjointed kingdoms established throughout modern-day Meath, Westmeath and Dublin.
Following the split, a series of internecine conflicts erupted between members of the Uí Néill septs. The feud was eventually resolved, and as part of the resolution, it was decided that the position of King of Tara would alternate between the northern and southern Uí Néill septs. The title alternated between the two septs for over 500 years, with every second king travelling south from Ulster for an inauguration ceremony at Tara. By 740,
Domnall Midi
Domhnall Mac Murchada (born c. 700, died 20 November 763), called Domnall Midi (Donald of Meath), was High King of Ireland. He belonged to the Clann Cholmáin branch of the Uí Néill. Clann Cholmáin's pre-eminence among the southern Uí Néill ...
of the
Clann Cholmáin
Clann Cholmáin is the dynasty descended from Colmán Már mac Diarmato, son of Diarmait mac Cerbaill. Part of the Southern Uí Néill — they were the kings of Mide (Meath) — they traced their descent to Niall Noígiallach and hi ...
dynasty, the most powerful branch of the southern Uí Néill, had conquered or subdued all neighbouring clans in Meath, and the Uí Néill were recognised as their
suzerain
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy and economic relations of another subordinate party or polity, but allows i ...
. Domnall was now in possession of both Tara, the seat of the Uí Néill, and the
Hill of Uisneach
The Hill of Uisneach or Ushnagh ( or ) is a hill and ancient ceremonial site in the barony of Rathconrath in County Westmeath, Ireland. It is a protected national monument. It consists of numerous monuments and earthworks—prehistoric and medi ...
, which held symbolic significance as the
geographical centre of Ireland
The Geographical Centre of Ireland, according to an investigation and calculation carried out by the Official Irish Government Mapping Agency, Ordnance Survey Ireland (OSI) published on the official OSI website on 24 February 2022 is near the ...
. Having secured his power in the heart of the island, Domnall now presided over a unified
Kingdom of Mide
Meath ( ; ; ) was a kingdom in Ireland from the 1st to the 12th century AD. Its name means "middle," denoting its location in the middle of the island.
At its greatest extent, it included all of County Meath (which takes its name from the k ...
(''Meath''), a name derived from the
Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic (, Ogham, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ; ; or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic languages, Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive written texts. It was used from 600 to 900. The ...
meaning "middle".
The first
annalistic mention of a "''High King of Ireland''" or "''Ard-Rí''" was
Máel Sechnaill mac Máele Ruanaid, King of Mide, who died in 862 AD, having achieved many victories against both the
Norse and the kingdoms of Ulster. Later historians would retroactively apply the title of "High King" to the earlier Kings of Tara, although there were no contemporary references to either the Kings of Tara or Mide being referred to as ''Ard-Rí'' prior to the 9th century. During the reign of
Máel Sechnaill mac Domnaill
Máel Sechnaill mac Domnaill (), also called Máel Sechnaill Mór or Máel Sechnaill II (949 – 2 September 1022), was a King of Mide and High King of Ireland. His great victory at the Battle of Tara against Olaf Cuaran in 980 resulted i ...
in the 970s, the fort of Dun-na-Scia near
Lough Ennell
Lough Ennell () is a lake near the town of Mullingar, County Westmeath, Ireland. It is situated beside the N52 road, off the Mullingar/ Kilbeggan road. The lake is part of the Lough Ennell Special Protection Area. It is long by wide, with an ...
became the permanent royal residence, thereby creating two seats of power within the kingdom – one for the High King and one for the King of Mide.

In the late 10th century, the Dalcassians to the south, led by Brian Boru, consolidated their hold over Munster, with Boru establishing himself as King of Munster. The ascendancy of this longtime rival kingdom posed a serious threat to High King
Máel Sechnaill mac Domnaill
Máel Sechnaill mac Domnaill (), also called Máel Sechnaill Mór or Máel Sechnaill II (949 – 2 September 1022), was a King of Mide and High King of Ireland. His great victory at the Battle of Tara against Olaf Cuaran in 980 resulted i ...
, so the two leaders met at Clonfert in 997 and agreed upon a truce, whereby Boru was granted overlordship of the southern half of the island. The Kingdom of Leinster immediately rebelled against Boru and allied with the Norse Kingdom of Dublin. Mide and Munster formed a defensive alliance and, after a series of campaigns throughout 998–999, crushed the forces of Leinster and Dublin, which both became Vassal state, vassals of Munster.
Boru now believed that Munster was the most powerful kingdom in Ireland and therefore he, and not Máel Sechnaill, should be the High King. Máel Sechnaill's claim to the kingship was challenged by Boru in 1002 at the Hill of Tara. The Meath king requested a month-long truce to rally his subordinates to his side, which Boru accepted, however, Máel Sechnaill was quickly abandoned by his northern Uí Néill kinsmen. Having failed to raise enough troops to challenge Boru, he was forced to abdicate, thus ending the hereditary right of the Uí Néill to the title of High King. Although they remained Kings of Meath, the power and prestige of the southern Uí Néill would never recover.
Monastic settlement
Traditional accounts of the arrival of Saint Patrick and Christianity to Ireland are centred on Meath and its legendary High Kings. Folklore states that he travelled to the kingdom to light a Easter Fire, Paschal Fire on the
Hill of Slane, in defiance of High-King Lóegaire mac Néill, who was on the nearby Hill of Tara celebrating a pagan festival. Patrick was then summoned to the king's court and so impressed Lóegaire with his teachings that he was allowed to continue preaching Christianity across Ireland. While Christian missionaries were documented in Ireland long before the time of Saint Patrick, and accounts of his activities are heavily shrouded in myth, what is known is that by the late 6th century AD Christianity had supplanted Ancient Celtic religion, Celtic Paganism in every corner of the island. In a similar manner to how the Celts assimilated prehistoric traditions into their beliefs, many Celtic pagan beliefs and festivities were adapted to Celtic Christianity, such as Samhain, which became Halloween, and Imbolc, which became St. Brigid's Day.
By the 7th century a network of monasteries and religious settlements had been set up throughout Ireland and Dál Riata, Western Scotland, supported by local kings and chieftains. Beginning at this time, the "''Golden Age of Irish Christianity''" lasted for several centuries. Irish Scholars preserved invaluable Classical Latin, Latin texts and Gaelic monasteries developed into centres of learning which attracted theologians from across Europe. These monasteries sent missionaries to northern and central Europe to re-ignite Christianity and Latin tradition in areas where it had lapsed following the fall of the Western Roman Empire. One of Ireland's national nicknames, "''the land of saints and scholars''", is in reference to this period.
Patronage of the Church was also used as a political tool to project wealth and prestige in Irish kingdoms until the 16th century. Successive High Kings and Kings of Meath supported the establishment of prominent religious settlements and institutions, such as Abbey of Kells, Kells and Clonard Abbey, the latter of which taught Ireland's most significant saints, dubbed the Twelve Apostles of Ireland. During the golden age, the monasteries of Meath were associated with several of Ireland's most famous artefacts, which are considered to be among the finest examples of Insular art, Insular and medieval Christian art in existence.
File:Ireland 2010 etc 029 (2).jpg, Tara Brooch,
c. 7th century
File:Donore Handle.jpg, Donore, County Meath, Donore Handle,
c. 8th century
File:KellsFol032vChristEnthroned.jpg, Book of Kells,
c. 9th century
File:Britishmuseumkellscrozier.jpg, Kells Crozier,
c. 10th century
File:The_Bell_of_Saint_Patrick_Shrine_MET_tem07651s1.jpg, St. Patrick's Shrine,
c. 11th century
As knowledge of the importance and wealth of the Irish monasteries became more widely known, they began to attract the attention of Vikings, who were raiding throughout Britain and Ireland in the 8th century. The most distinctive feature of Irish monasteries, their Irish round tower, round towers, were built in response to these Viking raids. Eventually, the Vikings established kingdoms and founded History of Ireland (800–1169)#Second Viking age (914–980), Ireland's first cities along coastal areas, including in neighbouring
Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
. The High Kings and lesser kingdoms waged near-continuous war with these Norse-Gael settlers for over two centuries.
Lordship of Ireland (1169–1542)
Norman period

In 1166, Diarmait Mac Murchada was banished from Ireland by the High King Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair for the abduction of Lady of Meath Derbforgaill ingen Maeleachlainn, wife of Tigernán Ua Ruairc, King of Breifne. Mac Murchada returned with Norman allies and landed at Bannow in County Wexford, Wexford in 1169, after which they conquered northward throughout 1169–70, initiating the Norman Invasion of Ireland. In response, the High King assembled an alliance which included King Magnus Ua Máel Sechlainn of Meath as well as soldiers from Connacht, Breifne and Kingdom of Dublin, Dublin along with their respective kings. They confronted Mac Murchada's forces at Ferns, County Wexford, Ferns and an agreement was reached whereby Mac Murchada was acknowledged as king of Leinster, in return for acknowledging Ruaidrí as his overlord and agreeing to send his foreign allies away permanently. However, Mac Murchada breached the agreement and enlisted more Normans to his side before continuing his conquests, capturing
Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
in 1171 and forcing the capitulation of Magnus Ua Máel Sechlainn.


Following Mac Murchada's death in May 1171, Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, Strongbow succeeded him as King of Leinster and, once again, Magnus joined the High-King's coalition army to oust the Normans, however, their forces were routed during an unsuccessful siege of Dublin. Fearing that Strongbow was growing too powerful and might set up his own independent kingdom in Ireland, Henry II of England landed in Ireland in October 1171 to establish control over both the Irish and the Normans. Henry's campaign in Ireland was largely successful and he managed to reign in the Normans as well as a few Irish kingdoms which also submitted to him. Most crucially, he retained the city of Dublin, and Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, Baron Hugh de Lacy was made its bailiff. Henry's appointment of de Lacy was intended to act as a counterbalance to Strongbow. However, in order to achieve this, de Lacy would need a strong holding on Irish soil and it was decided that the Kingdom of Meath was to be granted to de Lacy.
This grant posed an issue for Henry as the previous decade had been a tumultuous time in Meath. There were four rival heirs to the kingship and each claimant held a different part of the kingdom. The strongest claim came from the King of Breifne, Tigernán Ua Ruairc, who – through conquest, marriage and an alliance with the church – had subsumed almost all of eastern Meath into his kingdom by the time of the Norman arrival. Strongbow also had nominal claim to Meath as King of Leinster. A war of succession within the
Clann Cholmáin
Clann Cholmáin is the dynasty descended from Colmán Már mac Diarmato, son of Diarmait mac Cerbaill. Part of the Southern Uí Néill — they were the kings of Mide (Meath) — they traced their descent to Niall Noígiallach and hi ...
dynasty meant that both Magnus and Art Ua Máel Sechlainn were also vying for the kingship of Meath. To circumvent this problem, Henry defined the borders of Meath as they had been in 1153 in Ireland, 1153 and ignored all subsequent subdivisions. In March 1172 he granted control of Meath to de Lacy on the condition that de Lacy could personally retain the kingdom with near total autonomy if he could conquer it.
Shortly after Henry left Ireland, Hugh de Lacy invaded Meath, setting up countless motte and bailey fortifications throughout the kingdom. de Lacy made the ecclesiastic centre of Trim his stronghold, constructing a huge ringwork castle defended by a stout double palisade and external ditch on top of the hill. With de Lacy now at the border of Ua Ruairc's outermost settlement of Kells, a parlay was arranged and the two leaders met on the Hill of Ward for negotiations. During these negotiations, a dispute erupted and de Lacy's men killed Ua Ruairc. Both sides blamed the other, with the Irish annals reporting that Ua Ruairc was "''treacherously slain''".
[Martin (2008), p.99]
By 1175, de Lacy had conquered the entire territory, executing Magnus Ua Máel Sechlainn that year. He expanded existing settlements into charter towns throughout Meath, including Trim, Athboy, Kells and Navan; and he married Rose Ní Conchobair, the High-King's daughter, in order to cement his claim as Lord of Meath.
Hugh de Lacy died in 1186 and several informal divisions and feuds among de Lacy's descendants over control of the lordship followed over the next century. The Lordship was formally shired in 1297 into the County of Meath. Following this, Meath developed into the largest and wealthiest shire in Ireland, with the eastern portion characterized by well-populated market towns, nucleated villages and a strong commercial focus on labour-intensive cereal cultivation, with one English official noting that Meath was "as well inhabited as any shire in England". Many of the Lordship of Ireland's judges, barristers and government officials such as Lord Chief Justice of Ireland, Chief Baron of the Irish Exchequer and Chief Justice of the Common Pleas for Ireland hailed from the county.
Between the 13th and 15th centuries, English power diminished significantly in Ireland for three primary reasons. Firstly, there was a reconsolidation and resurgence in the power of the Irish kingdoms which had been shattered during the Norman invasion. Secondly, the onset of the Black Death devastated nucleated settlements such as walled Anglo-Norman towns but had a significantly smaller impact in more sparsely populated Gaelic kingdoms. Lastly, and of most concern to the English crown, the gradual More Irish than the Irish themselves, gaelicisation of the Normans meant that many of the most prominent Anglo-Norman families, who were meant to act as England's viceroys in Ireland, no longer followed English laws or customs.
[The introduction to the text of the Statutes of Kilkenny, 1366, (pp.4–7)]
English authority continued to retreat eastward until Trim, Athboy and Kells were the outermost settlements of The Pale, an area centred around
Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
where English law was still obeyed. This situation meant that by the 1500s part of County Meath was within the Pale while other areas – which were inhabited by both the Gaelic Irish as well as Normans who were once loyal to the Crown – were now outside the control of the authorities in Dublin.
Kingdom of Ireland (1542–1800)
Tudor conquest

The papal bull ''Laudabiliter'' of Pope Adrian IV, issued in 1155, recognised the House of Plantagenet, Angevin monarch as ''Dominus Hibernae'' (Latin for "Lord of Ireland"). When Pope Clement VII excommunicated Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII in 1533, the constitutional position of the lordship in Ireland became uncertain. Following Henry's split with the church, the Tudors heralded the end of monastic Meath. Church Lands which comprised roughly one-third of the county were seized and granted to Protestant English statesmen and soldiers as a form of payment. Monasteries were suppressed and their treasures were either looted or scattered by Irish scholars to protect them.
Meath was invaded by Tír Eoghain, Tyrone and its allies in 1539 who raided as far south as Navan, which was razed to the ground. King Conn O'Neill, 1st Earl of Tyrone, Conn O'Neill had been recognized as "''King of our realm in Ireland''" by Pope Paul III and was encouraged to expel Protestant influence from the island. However, the conflict stoked an unexpectedly swift reaction from the typically lethargic Dublin government, and Tyrone was defeated by Leonard Grey, 1st Viscount Grane, Lord Deputy Grey and forced to sue for peace in 1541.
Henry had broken away from the Holy See and declared himself the head of the Church in England, and subsequently refused to recognise the Roman Catholic Church's vestigial sovereignty over Ireland. For this reason, and also to address England's waning power in Ireland, Henry proclaimed the Kingdom of Ireland in 1542, with himself as its monarch. The following year, the Counties of Meath and Westmeath Act 1543, Counties of Meath and Westmeath Act was passed by the Parliament of Ireland and Meath was officially divided in two. The act was intended to allow a more effective administration in both counties, particularly in Westmeath, which England had lost control of. A new shire town at Mullingar was established along with four new
baronies Barony may refer to:
* Barony, the peerage, office of, or territory held by a baron
* Barony, the title and land held in fealty by a feudal baron
* Barony (county division), a type of administrative or geographical division in parts of the British ...
, while Trim retained its status as the shire town of Meath.
Despite the general loyalty of the "Normans in Ireland#"Old English" vs. New English, Old English" of Meath to the government in Dublin, the introduction of new Anglican English settlers, seen as more reliable by the English government, undermined the power of the Anglo-Norman aristocracy who had remained overwhelmingly Catholic following the Reformation. Although there was a fervent anti-Catholic sentiment in England at this time, no punitive laws were enacted out of fear that they would provoke further rebellion. However, this changed following England's victory over the Irish kingdoms in the Nine Years' War (Ireland), Nine Years' War in 1603. With Ireland subdued, the English pursued a series of Penal Laws against Irish Catholics, Penal Laws restricting the rights of Catholics, which were accelerated following the Gunpowder Plot of 1605.
Protestant Ascendancy
The uneasy peace that had persisted between Catholics and Protestants for several decades unravelled when the anti-Catholic Long Parliament gained traction in England in 1640. Fearing further persecution, the dispossessed Irish of
Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
went into Irish Rebellion of 1641, rebellion in 1641 to regain the lands they had lost to the Plantation of Ulster, plantations. Exaggerated news of brutal Catholic massacres against Protestants spurred the English into aggressive action, and the peaceful lands of Meath were indiscriminately ransacked by Puritans, puritanical armies in retribution. In response, the lords of Meath met at Trim and issued their remonstrance to Charles I of England, King Charles I. Sir John Read was sent to deliver it; however, gripped by anti-Catholic hysteria, officials in Dublin seized Read and tortured him, questioning whether the King and his Catholic wife Henrietta Maria of France, Henrietta were in league with the Irish rebels.
As the rebellion intensified, the Ulstermen once again conquered southward into Meath, crushing an English garrison at the Battle of Julianstown. A contingent of Old English lords led by Viscount Gormanston rode out to halt their advance. A parlay was arranged at the Hill of Crufty and the Irish, led by Rory O'Moore, O'Moore and Philip O'Reilly (Cavan County MP), O'Reilly, met with the Anglo-Norman gentry of Meath. Seeing that they fought for a common cause, the leaders of the two sides embraced amid the acclamation of their followers, and the lords of Meath rode home to rally their forces against the English.
On 22 March 1642 the Catholic hierarchy held a synod at Kells and almost unanimously agreed that the rebellion was a Just war theory, just war. They drafted a Confederate Oath of Association in May and Meath lawyer Nicholas Plunkett encouraged Catholic nobles to take up the oath. After the outbreak of the English Civil War, an assembly was held in Kilkenny and the provisional government of Confederate Ireland was established, which took up arms with the Cavalier, Royalists against the Roundhead, Parliamentarians. The Royalists were crushed by Oliver Cromwell, who then set about ending the Irish Confederate Wars by engaging in an unquestionably brutal Cromwellian conquest of Ireland, conquest of Ireland, resulting in the death of up to 40% of the island's population.
[Genocidal or near-genocidal: Brendan O'Leary and John McGarry, "Regulating nations and ethnic communities", in Breton Albert (ed.) (1995). ''Nationalism and Rationality'', Cambridge University Press. p. 248.]
Following the conquest, further Penal Laws were enacted and Catholics were forbidden to hold government office and stripped of their lands under the Down Survey. Former aristocratic families were forced to send their children abroad for education to Irish seminaries in
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and the Spanish Netherlands. The "New English" along with those who had converted to Anglicanism occupied the Parliament, becoming what would later be termed the Protestant Ascendancy. This period also saw an influx of Huguenots into Meath, and surnames such as Beaufort and Metge appeared in the county for the first time.
Some Old English families were able to recover their lands and return to Meath following the restoration of James II of England, King James II. Although James did little to improve the overall situation of Irish Catholics, he was backed by them during the Glorious Revolution, while Protestants overwhelmingly backed William III of England, William of Orange during the Williamite War in Ireland. The defeat of the Jacobitism, Jacobites at the
Battle of the Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne ( ) took place in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II, and those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and James's daughter), had acceded to the Crowns of England and Sc ...
in July 1690 forced James to flee to France, ending the prospect of an autonomous Irish kingdom. This battle is seen as a seminal event in Irish history and is still The Twelfth, celebrated every year by Unionism in Ireland, Ulster Unionists.
Towards the end of the 18th century the Penal Laws were relaxed and Catholic merchant families such as Fay (surname), Fay and Connolly (surname), Connolly were granted trading privileges in Trim and Navan. Celebrated Meath sculptor Edward Smyth (sculptor), Edward Smyth was commissioned by Catholics in Navan to produce a crucifix for the town's new chapel in 1792, which is still located in the church to this day.
As sectarian tensions eased, liberal ideas began to spread among members of the Protestant Ascendancy, such as Wolfe Tone and Henry Grattan, and many came to see themselves as citizens of an Irish nation and championed Catholic emancipation. Ireland briefly secured parliamentary independence through the Constitution of 1782 which ushered in Ireland's first economic boom in centuries, as trade flourished and the population grew exponentially. However, these freedoms were abruptly ended with the Act of Union 1800, when Ireland was subsumed into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom.
19th century


The economic boom of the late 18th century came to a sudden and catastrophic halt following the end of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815. During the war, Ireland had become known as the "''Food larder of Europe''", and the tenant farmers and landlords of Meath relied heavily on tillage, which fetched an artificially high price due to a surge in wartime demand. Further, a substantial number of Irish soldiers who comprised as much as 25% of the entire British Army and Royal Navy, Navy during the war were now made redundant. As post-war trade between Britain and Europe recovered, demand for Irish tillage collapsed; however, rents remained the same and the population continued to boom. As economic stagnation set in, the once well-managed, prosperous estates of Meath gave way to mismanagement and Absentee landlord, absenteeism, and the tenant farmers were pushed further into poverty.
This dire economic state resulted in a surge of Irish nationalism and demands to repeal the disastrous Act of Union. Nationalist sentiment was widespread in Meath, as reflected in the Meath (UK Parliament constituency), Meath Parliamentary constituency, which returned several of 19th century Ireland's most prominent nationalist politicians, including Daniel O'Connell, Charles Stewart Parnell and Michael Davitt. Owing to its symbolic place in the national psyche, Daniel O'Connell held a rally on the
Hill of Tara
The Hill of Tara ( or ) is a hill and ancient ceremonial and burial site near Skryne in County Meath, Ireland. Tradition identifies the hill as the inauguration place and seat of the High Kings of Ireland; it also appears in Irish mythology. ...
in August 1843 which was attended by between 500,000 and 1 million people, making it one of the largest crowd gatherings in Irish history.
To address rising poverty and growing unrest in Ireland, the British government set up workhouses in the 1830s and began constructing Rail transport in Ireland, railroads. However, these efforts were largely unsuccessful and the impoverished of Meath, pushed to the brink by high rents and mass unemployment, were wiped out by the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845–49. Having reached over 183,000 in 1841, the population of Meath would fall to 67,000 by 1900. The famine had a lasting cultural, societal and linguistic effect on the county. Pre-famine census records show that Meath had been a region with an "''undoubted Irish speaking majority''", but by the late 1800s the Irish language was virtually extinct within the county. The famine-era workhouse and mass grave at Dunshaughlin is today a memorial to its victims.
The famine shed light on the detrimental effects that Ireland's land laws were having on the economic and social well-being of the country, and the British government's lacklustre response to the crisis further strengthened the cause of Irish nationalists. The Protestant Ascendancy went into steep decline following the famine and many landholders were effectively bankrupt, leading to the ad hoc sale of lands to unproductive use. The push for reform escalated in the 1870s into a period of sporadic violence and civil unrest known as the Land Wars.
Thomas Brennan (Irish Land League), Thomas Brennan, of Yellow Furze, co-founded the Irish National Land League in 1879 alongside Michael Davitt. His staunch Irish republicanism, republicanism and socialist leanings put him at odds with the League's executive, and he was excluded from the Irish National League set up by Parnell in 1882. Brennan moved to the United States and raised money for the republican cause, advocating total Irish independence as opposed to Home Rule to the Irish-American diaspora. This revealed an ideological divide within the nationalist movement, between those who favoured greater legislative independence under the British crown, as had been achieved in the 1780s, and those who advocated for completely severing ties with the United Kingdom.
Some of the political reforms desired by the nationalists were finally realised under the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898, Local Government Act of 1898. The act set up urban and rural districts as well as county councils to take over local government from landlords. Under the reforms, small sub-councils and boroughs were abolished and
Meath County Council
Meath County Council () is the local authority of County Meath, Ireland. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and de ...
was granted full control over the jurisdiction. The council sat at Navan, which became the new county town of Meath, ending Trim's 600-year status as Meath's shire town.
20th century
The reforms proposed by the UK government failed to stem the rising tide of nationalism, which spilled over into the 20th century as the 1916 Easter Rising. The Battle of Ashbourne was one of the few skirmishes which took place outside of Dublin during the rising and was its sole success. On 28 April 1916, members of the Irish Volunteers, Dublin Volunteers Fifth (
Fingal
Fingal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which ...
) battalion, led by Thomas Ashe, surrounded a Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) police station in
Ashbourne and demanded their surrender. RIC reinforcements were dispatched from Navan and upon arriving at the scene a firefight ensued during which 8 RIC members were killed and 15 wounded, forcing them to retreat. On the orders of Patrick Pearse, Ashe and his battalion surrendered the following day.
Meath's Eamonn Duggan served as the Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), IRA's director of intelligence during and after the rising and was a signatory of the Anglo-Irish treaty in 1921. Meath largely sided with the pro-treaty forces during the Irish Civil War, Civil War, with the Louth–Meath (Dáil constituency), Louth–Meath constituency returning one anti-treaty and four pro-treaty
TDs in the 1922 Irish general election, 1922 general election. Duggan later joined
Cumann na nGaedheal
Cumann na nGaedheal (; ) was a political party in the Irish Free State, which formed the government from 1923 to 1932. It was named after the original Cumann na nGaedheal organisation which merged with the Dungannon Clubs and the National Co ...
and held various ministerial offices until his death in 1936. Following independence, various government-backed Gaelic revival efforts were centred on the county and its history, including the foundation of 5
Gaeltacht
A ( , , ) is a district of Ireland, either individually or collectively, where the Irish government recognises that the Irish language is the predominant vernacular, or language of the home.
The districts were first officially recognised ...
areas within Meath, and the symbolic hosting of the Tailteann Games (ancient), Tailteann Games.
The declining population of Meath gradually stabilised as emigration balanced with high natural birth rates. Outward migration from the county remained substantial until the reforms of Seán Lemass in the 1960s strengthened industry by injecting capital into the economy and abandoning the policy of autarky. These reforms, coupled with EEC membership in 1973, brought jobs and investment into the county, and the extraction and textile industries prospered. By the 1971 census, Meath's population had surpassed 70,000 for the first time in eighty years. Despite a Economic history of the Republic of Ireland#1980 to early 1990s, severe recession in the 1980s, the growth of Meath's economy and population became exponential in the late 1990s and early 2000s during the Celtic Tiger era.
As places such as Trim, Navan and Kells developed into major commuter towns of Dublin, the county grew increasingly reliant on the Overheating (economics), overheated construction sector, leaving Meath hard-hit by the Irish property bubble, property collapse in Post-2008 Irish banking crisis, 2008. From 2014 onward, the economy experienced a robust recovery, and by 2016 Meath had the third lowest unemployment rate in Ireland. Meath surpassed its pre-famine population in 2011, becoming one of only five counties in the State to do so.
Places of interest
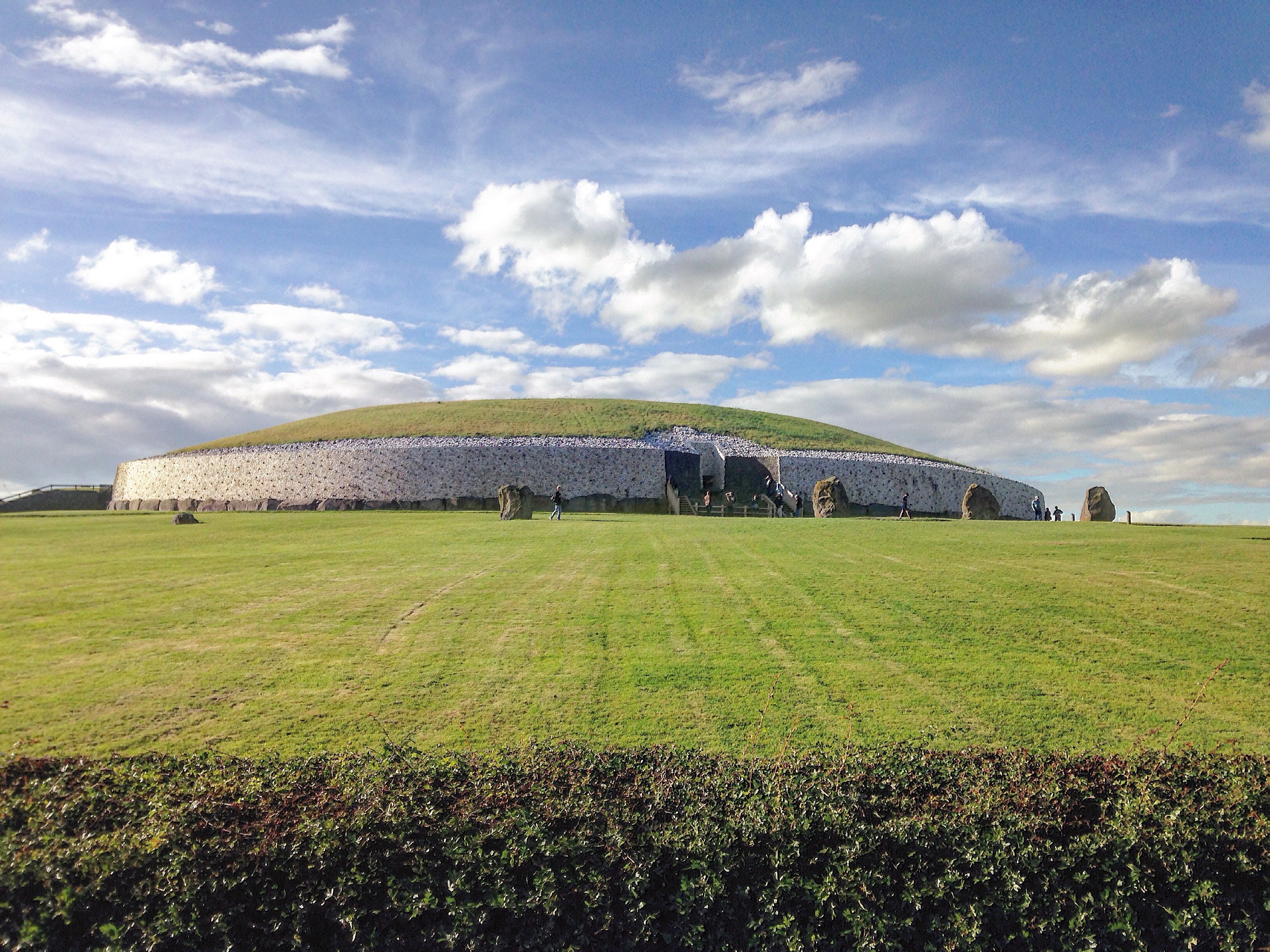

As a consequence of its location in the centre of Ireland, Meath has an abundance of historic sites.
All periods of Irish history are represented in the landmarks of the county, spanning from the prehistoric tombs at
Brú na Bóinne
(, "mansion or palace of the Boyne"), also called the Boyne Valley tombs, is an ancient monument complex and ritual landscape in County Meath, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, located in a bend of the River Boyne. It is one of the world's most im ...
, the early Christian monasteries at Kells and Bective, the Norman-era fortifications at Trim and Dunmoe, the manor houses and estates of the 17th and 18th centuries such as those at Bellinter and Slane, the famine-era workhouse and graveyard at Dunshaughlin, all the way up to the Battle of Ashbourne historic site, which commemorates the sole victory of the Irish Volunteers during the 1916 Easter Rising.
In terms of natural attractions, the county has a relatively tame landscape compared to other parts of Ireland, with no mountains, a short coastline and generally little forest cover. There are however a number of National Parks and Wildlife Service (Ireland), National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) protected sites within the county. The River Nanny Estuary & Shore and the River Boyne & River Blackwater are listed as Special Protection Areas.
Additionally, all bogs within the county; those being Mount Hevey, Girley, Killyconny, Molerick and Jamestown are listed as either Special Area of Conservation, Special Areas of Conservation or Natural Heritage Areas. Lough Bane, Lough Glass, White Lough, Ben Loughs and Lough Doo are all also protected by the NPWS.
Landmarks
* Athcarne Castle
* Athlumney Castle
* Ballinlough Castle
*
Battle of the Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne ( ) took place in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II, and those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and James's daughter), had acceded to the Crowns of England and Sc ...
Visitor Centre
* Bective Abbey
* Bellinter House
* Boyne Hill Estate
* Clonard Abbey
* Dangan Castle
* Dardistown Castle
* Donaghmore Round Tower
*
Dowth
Dowth () is the site of Neolithic passage tombs near the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland. It is one of the three main tombs of the ''Brú na Bóinne'' World Heritage Site, along with Newgrange and Knowth. Its features align it with the ot ...
* Dunsany Castle and Demesne
* Dunmoe Castle
* Dunshaughlin Famine Workhouse
* Fairyhouse Racecourse
* Fourknocks Passage Tomb
* Gormanston College, Gormanston Castle
*
Hill of Slane
*
Hill of Tara
The Hill of Tara ( or ) is a hill and ancient ceremonial and burial site near Skryne in County Meath, Ireland. Tradition identifies the hill as the inauguration place and seat of the High Kings of Ireland; it also appears in Irish mythology. ...
* Hill of Ward
* Irish Military War Museum
* Abbey of Kells, Kells Abbey
* Killeen Castle, Dunsany, Killeen Castle
*
Knowth
Knowth (; ) is a prehistoric tomb overlooking the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland. It comprises a large passage tomb surrounded by 17 smaller tombs, built during the Neolithic era around 3200 BC. It contains the largest assemblage of megali ...
*
Loughcrew
Loughcrew or Lough Crew () is an area of historical importance near Oldcastle, County Meath, Ireland. It is home to a group of ancient tombs from the 4th millennium BC, some decorated with rare megalithic art, which sit on top of a range of hi ...
*
Newgrange
Newgrange () is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, placed on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, west of the town of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3100 BC, makin ...
* Oldcastle World War I Prisoner-of-war camp, POW Camp
* Robertstown Castle
* St. Mary's Abbey, Trim, St. Mary's Abbey
* Skryne Castle
* Skryne Monastic Site
*
Slane Castle
Slane Castle () is located in the village of Slane, within the Boyne Valley of County Meath, Ireland. The castle has been the family seat of the Conyngham family since it was built in the late 18th century, on land first purchased in 1703 by ...
* Spire of Lloyd
* Tailteann Games (ancient), Tailteann
* Tattersalls Country House
*
Trim Castle
Trim Castle () is a castle on the south bank of the River Boyne in Trim, County Meath, Ireland, with an area of 30,000 m2. Over a period of 30 years, it was built by Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, Hugh de Lacy and his son Walter de Lacy, ...
* Trim Cathedral
Natural attractions
* Balrath Woods
* Bettystown Beach
* River Boyne, Boyne Valley
* Girley Bog
* Grove Gardens
* Jamestown Bog
* Killyconny Bog
* Larchill Arcadian Gardens
* Loughs of the Upper Boyne Valley
*
Leinster Blackwater
The Kells Blackwater (), also called the River Blackwater or Leinster Blackwater, is a river that flows through the counties of Cavan and Meath in Ireland. It is a tributary of the River Boyne which flows into the Irish Sea at Drogheda. (This ...
*
Lough Sheelin
Lough Sheelin (), in standard Irish language, Irish ''Loch Síleann'', is a limestone freshwater lough (lake) in central Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The lake is a part of the River Inny (Leinster), River Inny course, and ultimately of the Riv ...
* Loughcrew Historic Gardens
* Molerick Bog
* Mount Hevey Bog
* Nanny (river), Nanny Estuary
* Rathbeggan Lakes
*
Slieve na Calliagh
Slieve na Calliagh () are a range of hills and ancient burial site near Oldcastle, County Meath, Ireland. The summit is , the highest point in the county. On the hilltops are about twenty passage tombs, some decorated with rare megalithic art, ...
* Sonairte National Ecology Centre
Demographics
Meath had a population of 220,826 according to the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 Census; an increase of 25,252 (+13.2 percent) since the 2016 census of Ireland, making it the second fastest growing county in Ireland, after County Longford. Population growth from 2016 to 2022 included a natural increase of 3,558 people (+1.62 percent) since the last census, coupled with an increase of 22,078 people (10.0%) due to net Human migration, migration into the county. Immigration from people born outside of the Republic of Ireland resulted in a net increase of 10,687 people. Migration of those from other Irish counties, primarily from neighbouring
County Dublin
County Dublin ( or ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and holds its capital city, Dublin. It is located on the island's east coast, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Until 1994, County Dubli ...
, produced a net increase of 11,391 people. Owing to its proximity to
Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
, Meath is the least indigenous county in Ireland, with just 71,356 usual residents (32.4 percent) recorded as being born within the county. Just under half of all Meath residents (49.2 percent) were born elsewhere in the State, and the remaining 18.3 percent were born abroad. The county's population density was 94 people/km2 in 2022, making it one of just 8 counties in Ireland with a population density above the all-island average density of 83.5 people/km2.
In 2022, 6.4 per cent of the county's population was reported as younger than 5 years old, 23.5 per cent were between 5 and 19, 57.8 per cent were between 20 and 65, and 12.3 per cent of the population was older than 65. 5,661 people (2.6 per cent) were over the age of 80. Across all age groups, there was a roughly even split between females (50.2 per cent) and males (49.8 per cent).
In 2021, there were 2,847 births within the county, and the average age of a first time mother was 31.6 years.
Population trends
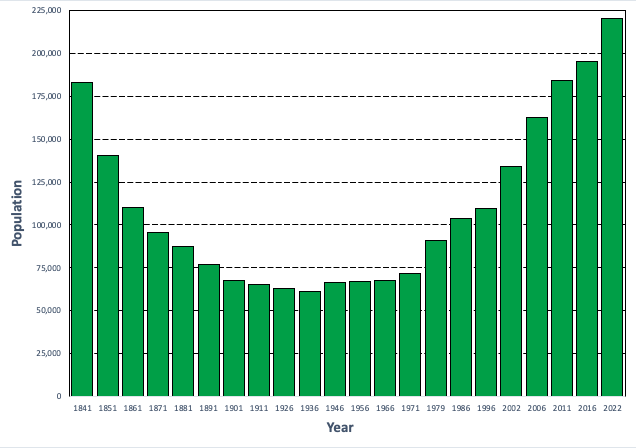
The population of Meath suffered a significant decline between 1841 and 1901, decreasing by almost two-thirds (183,828 to 67,497); it stabilised between 1901 and 1971 (67,497 to 71,729), and there was a substantial increase between 1971 and 1981 to 95,419. This increase was mainly due to a baby boom locally. The population then continued to increase at a constant rate, before increasing at an explosive rate between 1996 and 2002, from 109,732 to 134,005. This is due primarily to economic factors, with the return of residents to live in the county, and also an echo effect of the 1970s baby boom. The census of 2022 gives a figure of 220,296, including a dramatic increase in inward migration to the county. Meath is one of only 5 counties in the state which has a population higher than its 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 pre-famine peak.
This population growth has seen divergent trends emerge in recent years, with mild depopulation in the north and west of the county more than offset by large increases in the population of the eastern and south-eastern parts of the county, principally owing to inward migration to districts that have good proximity via road to the business parks on the western outskirts of Dublin. The accession of Poland and the Baltic States to the European Union in 2004 resulted in a significant influx of workers from these countries to work in sectors such as agriculture, quarrying, construction and catering.
Migration
The five largest foreign national groups in Meath are: Polish people, Polish (2.2 percent), British people, British (1.9 percent), Romanians, Romanian (1.6 percent), Lithuanians, Lithuanian (1.3 percent), Americans, American (0.6 percent), Latvians, Latvian (0.6 percent), and Nigerians, Nigerian (0.6 percent).
Ethnicity
In 2022, the racial composition of the county was:
* 89.9% White people, White (78.7% White Irish, 10.7% Other White Background, 0.5% Irish Traveler)
* 2.6% Asian people, Asian
* 1.8% Black people in Ireland, Black
* 1.9% Others including mixed
* 3.8% Not stated
Religion
According to the 2022 Census, published by the Central Statistics Office (Ireland), Central Statistics Office, 82.6% of County Meath's residents identify with a religion. 80.0% affiliate with Christianity and its various denominations, and the other 2.6% are adherents of non-Christian religions. The remaining 13.1% have no religion, with 4.3% of people not stating their religion.
The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2022 were the Roman Catholic Church with 159,410; followed Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity with 6,512; the Church of Ireland, Church of England, England, Anglican and Episcopalian with 4,446; and all other Christian denominations including Presbyterian, Pentecostal, Lutheran and Evangelicalism, Evangelical with 5,176 adherents. Among the non-Christian denominations, Islam, Muslims are by far the largest group, with 3,153 adherents, followed by Hinduism with 881 and Buddhism with 330. Additionally, 9,495 people did not state their religion.
The Trim Cathedral, Cathedral of Saint Patrick in Trim was the seat of the former Diocese of Meath, which is now the Diocese of Meath and Kildare in the Church of Ireland. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Meath has its seat at Mullingar, County Westmeath. A former cathedral was located at Clonard Abbey, however, it was destroyed by fire in 1206. Thomas Deenihan is the current Bishop of Meath. The county's largest Presbyterian church is located in Kells, and the Navan Muslim Community Centre, which is primarily used as a mosque, is located on Kennedy Road in Navan.
Continuing the trend which has been observed throughout Ireland since the Census of 2006, a significant increase in the number of people who identified as having no religion was observed in the 2022 census. This demographic has increased by 260% since 2011, from 7,990 to 28,771. People with no religion now account for 13.1% of the county's population, up from 8.1% in 2016.
Irish language

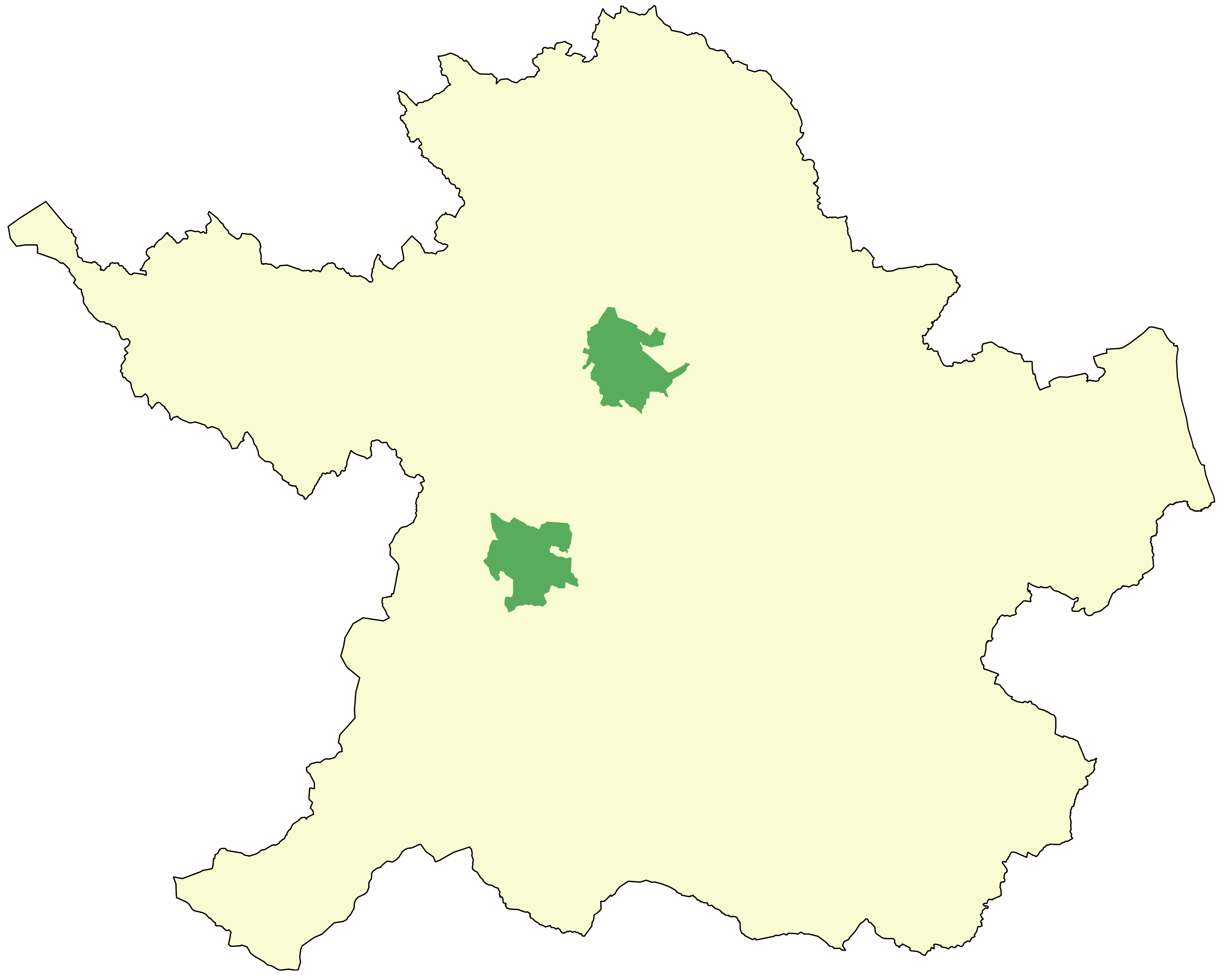
Meath contains
Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland.
The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century ...
's only
Gaeltacht
A ( , , ) is a district of Ireland, either individually or collectively, where the Irish government recognises that the Irish language is the predominant vernacular, or language of the home.
The districts were first officially recognised ...
areas, at
Ráth Chairn
Ráth Chairn () is a small village and Gaeltacht ( Irish-speaking area) in County Meath, Ireland. It is about 55 km northwest of Dublin. Ráth Chairn Gaeltacht was founded in 1935 when 27 families from Connemara, mostly from Ceantar na n ...
, close to Athboy, and
Baile Ghib
Baile Ghib () is a small village and Gaeltacht ( Irish-speaking area) in County Meath, Ireland. It is about 70km northwest of Dublin.
The Baile Ghib Gaeltacht was founded in 1937 when 52 families were settled on land previously acquired by the ...
, located northwest of Navan. With a combined area of 44 km
2, they are the two smallest Gaeltachts in Ireland. As of 2022, there were 2,093 people living within the Meath Gaeltacht areas, of which 1,179 (56.3 percent) stated that they were Irish speakers.
Unlike the Gaeltachts of the west of Ireland, the Meath Gaeltachts are the result of a government gaelicisation scheme to reintroduce the Irish language to the east of the country. In total, 5 Irish-speaking settlements were set up in Meath between 1935 and 1939 – Ráth Chairn, Baile Ghib, Cill Bhríde, Cluain an Ghaill and Baile Ailin. They were established on fertile land which had been allowed to fall into disrepair by absentee landlords and was consequently repossessed by the Irish Land Commission. In total, 122 Irish-speaking families moved to the county. They were primarily from Connemara, but some families were also from County Kerry.
Over the years Cill Bhríde was subsumed into Ráth Chairn, and Cluain an Ghaill was subsumed into Baile Ghib. The fifth and final Gaeltacht to be set up – Baile Ailin – failed after a generation, as several Irish-speaking families moved away and day-to-day use of the Irish language failed to take hold amongst the children of those who remained. The two surviving settlements were officially recognised as Gaeltacht areas in 1967.
According to the 2022 Census, 39.8 per cent of Meath residents were able to speak Irish, up from 38.6 percent in 2016. Of that, there were 2,594 ''Gaeilgeoirí'' (people who speak Irish everyday outside of the education system) in County Meath. In addition, 27,566 people stated that they speak Irish daily within the education system only. The Greater Dublin Area has the highest number of Irish-medium schools in Ireland, and there are seven Gaelscoileanna outside the Gaeltacht areas within Meath.
Urban areas
Navan is the county town and by far the largest settlement in Meath. It is also the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, 4th largest town in the state, excluding City status in Ireland, cities.
Meath is predominantly an urban county, although a large percentage of its residents live in rural areas. According to the 2022 Census, 56 percent of the county lived in urban areas, and the remaining 44 percent lived in rural areas. Just over half of the county's population (52.1 percent) live in the ten largest towns. Historically, the largest towns in Meath were located in the north and west of the county, such as Trim, Navan and Kells. However, in recent years settlements in the south and east of the county such as Ashbourne, Dunboyne, and the coastal agglomeration of
Bettystown
Bettystown (), previously known as Betaghstown and transliterated to ''Beattystown/Bettystown'', is a village in County Meath, Ireland. Together with the neighbouring villages of Laytown, Mornington and Donacarney, it comprises the urban ar ...
,
Laytown
Laytown () is a village in County Meath, Ireland, located on the R150 regional road and overlooking the Irish Sea. Historically it was called ''Ninch'', after the townland it occupies. Together with the neighbouring villages of Mornington, ...
, Mornington, County Meath, Mornington and Donacarney have expanded significantly, and the majority of the county's fastest growing towns are now located in these areas.
Economy
The Central Statistics Office (Ireland), Central Statistics Office estimates that Meath's Total Household Income in 2017 was €5.253 billion, ranking 6th among Irish counties. Meath also ranks 6th in the country by per capita disposable income, at €20,493 or 95.8% of the State average. Meath residents are also the 6th highest per capita tax contributors to the State, returning a total of €1.311 billion in taxes in 2017 – roughly equivalent to the entire Midland Region, Ireland, Midlands Region. Major industries include services, retail, agriculture and food processing, mining, manufacturing and tourism.
Services, retail and hospitality
Services, retail and the hospitality industry are the primary employers in the county. Navan was historically a manufacturing town, and involved in the household goods sector. Navan was also a centre in the Irish carpet-making industry, before this was lost to overseas competition.
Tourism benefits from the abundance of historically important pre-historic and early Christian sites, as well as castles and manor houses within the county, many of which are currently in use as hotels. Due to its rich history, Meath is marketed by Fáilte Ireland, the country's national tourism agency, as "Ireland's Heritage Capital". Good local infrastructure means that most of Meath's tourist attractions are located within a one-and-a-half-hour drive from Dublin Airport. Despite this, Meath received just 162,000 overseas tourists in 2017 – placing it 17th out of 26 counties. Tourism is worth in excess of €50 million to the local economy each year.
In addition to historic attractions, Meath is home to scenic lakes, beaches, wooded areas and several European-designated areas of ecological significance. The only permanent amusement park in Ireland is Emerald Park, located in Ashbourne, which has 3 roller coasters, including ''Cú Chulainn'', Ireland's largest roller-coaster.
Meath also has a growing science and biotechnology field. In 2018, Shire (pharmaceutical company), Shire, one of the world's largest pharmaceutical companies, opened a €350 million international disease research centre in Dunboyne, which was sold to Merck & Co. in 2020.
Agriculture

The agricultural products of the county are beef, pork, dairy, poultry, vegetables and cereals. Meath has a strong farming tradition and up until the Census of Ireland, 1911, 1911 Census the most commonly listed occupation in the county was Farmworker, farm labourer. Meath is ranked 2nd in the country for the production of vegetables and 2nd for the production of Rapeseed, rapeseed oil.
As of 2018, Meath has the country's 8th largest cattle herd with 275,301 cows. Dairy production was the largest and most profitable agricultural sector in the county and 63.7% of all cattle were Dairy cattle, dairy cows. The remaining 36.3% were beef cattle. The county also has Ireland's 9th largest sheep herd (150,571 sheep) and 14th largest pig herd (40,259). Meat processors such as Kepak and Dawn Meats are large employers within the county.
There are 4,620 farms in the county, with a total farmed area of , accounting for 83% of land area. Of this, was under tillage, the 3rd highest in the country. Although Irish agriculture is heavily dominated by pasture farming, Meath's favourable climate and easterly location give it a much greater capacity than most counties for agricultural diversification, reflected in its robust tillage and vegetable production sectors. The average size of a farm in the county is , well above the national average of .
Agriculture supports thousands of jobs within the county and, according to the Irish Farmers' Association, the total value of agricultural produce from Meath in 2018 was €541 million, ranking it 6th in Ireland.
Extraction and energy
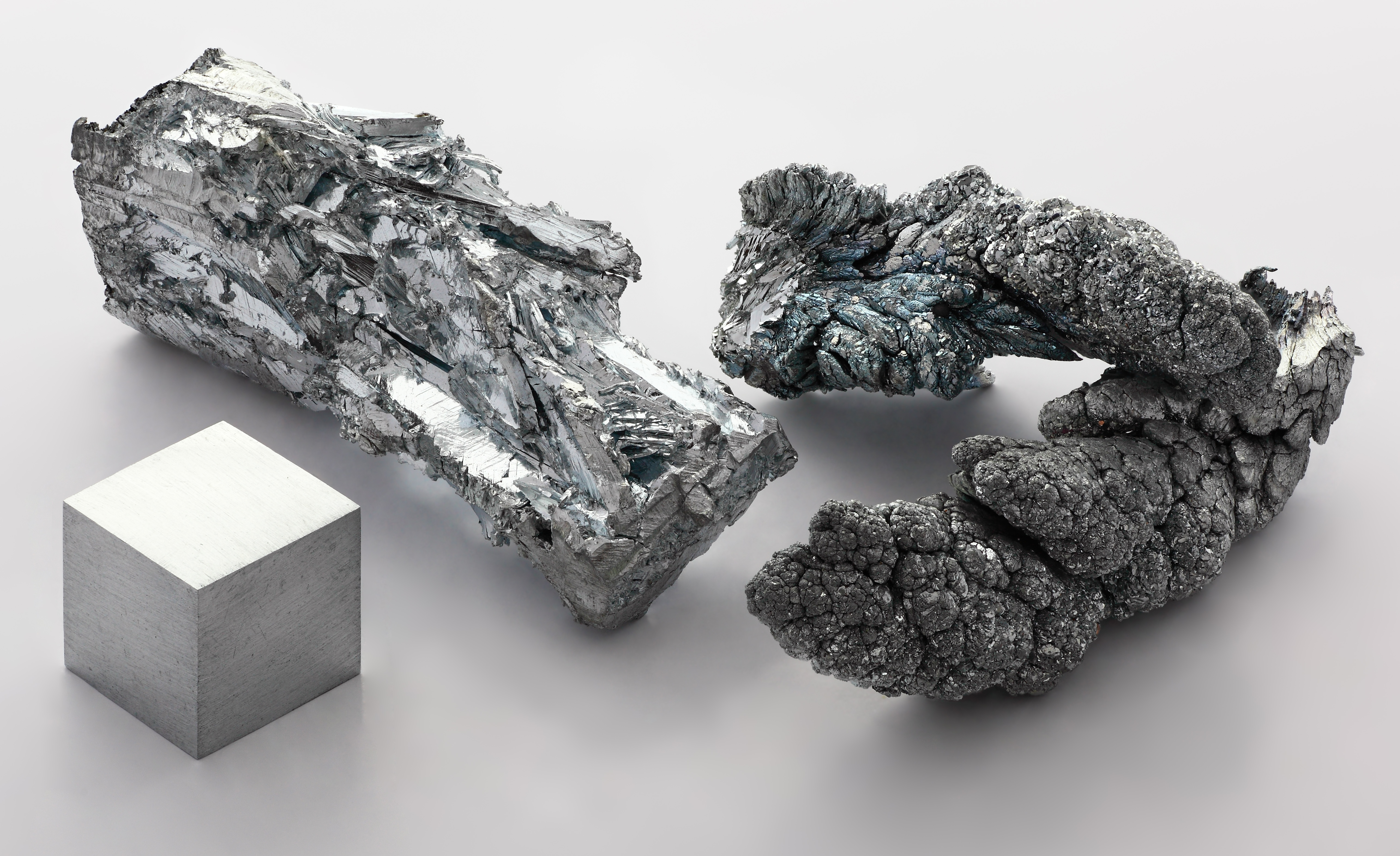

Due to the geology of the area, Meath has enormous reserves of Lead and Zinc, which are extracted at Tara Mine in Navan. Tara is both Europe's largest and deepest mine and is currently owned by Boliden AB. The mine commenced operations in 1977, and a total of 85 million tonnes of ore has been extracted from it, producing an average of 2.6 million tonnes of zinc ore annually.
Glacial deposits of gravel exist in a band stretching from the Offaly border at Edenderry, to the sea at Laytown. This is the basis of a long quarrying tradition. The local availability of large deposits of limestone and shale also gave rise to a significant cement production industry within the county. The two largest cement facilities are at Kinnegad and Platin, the latter of which is owned by CRH plc, Irish Cement and has the capacity to produce 2.8 million tonnes of cement per annum, which is primarily transported via rail to Dublin for use or export.
Ireland's first waste-to-energy plant opened in Duleek in 2011 and produces 17 MW of electricity per annum. SSE plc, SSE Airtricity aim to build a 208 MW gas-fired power plant south of Drogheda. Meath has a small but growing biomass industry, however other forms of renewable energy such as wind power and hydroelectricity have stalled due to widespread objections. There is an abundance of natural subterranean Fault (geology), faults where water from hot springs, such as those Enfield, rise to the surface at 25 °C. There is potential for these to be used for Geothermal power, Shallow Geothermal Energy generation.
Infrastructure
Road
The county is served by four Motorways in the Republic of Ireland, motorway routes. The N3 road (Ireland), M3 connects Navan to Dublin and runs from just south of Kells to Clonee, a distance of . The N4 road (Ireland), M4 passes through the south of the county and serves as the main road to both Sligo and Galway, when it divides at Kinnegad into the N4 and the M6 motorway (Ireland), M6. The M1 motorway (Republic of Ireland), M1 Dublin to
Belfast
Belfast (, , , ; from ) is the capital city and principal port of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan and connected to the open sea through Belfast Lough and the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel ...
route traverses East Meath for before bypassing
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth ...
.
A stretch of the N2 road (Ireland), N2 from Ashbourne to the Dublin border at Ward Cross was upgraded to the M2 motorway in 2009.
Two National primary road, national primary routes pass through the county, The N3 and the N2. The M3 becomes the N3 south of Kells before continuing on to County Cavan, a distance of . The N2 begins at Ashbourne and crosses the county for roughly before entering
County Louth
County Louth ( ; ) is a coastal Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Louth is bordered by the counties of County Meath, Meath to the ...
near Collon. Two National secondary road, national secondary routes pass through the county. The majority of the N51 road (Ireland), N51 Drogheda to Mullingar route is located within Meath, and crosses the county for , passing through Slane, Navan and Athboy.
The N52 road (Ireland), N52 which stretches from Nenagh, where it joins the M7 motorway (Ireland), M7, to Dundalk, where it joins the N1, crosses the county for and passes through Kells. Bus Éireann, as well as private coach operators, provide bus services to villages and towns across the county. Areas close to Dublin city in southern and eastern Meath such as Clonee and Dunboyne are also served by Dublin Bus.
Rail

Irish Rail provides frequent rail services from Dunboyne railway station, Dunboyne and M3 Parkway railway station, M3 Parkway to Dublin city centre. Laytown railway station and Gormanston railway station have a commuter rail service and are located along Dublin's Dublin Suburban Rail, Northern Commuter Line which runs from Dundalk to Dublin. A commuter train service (Western Commuter Line) passes through Enfield railway station (Ireland), Enfield, although the service is less frequent as the station is primarily used for the long-distance Irish rail routes to Longford and Sligo.
Navan is currently served by a freight-only spur railway line from Drogheda on the Dublin-Belfast main line, for freight traffic (zinc and lead concentrate from Tara Mines in Navan to Dublin Port) connecting at Drogheda. Currently, the only commuter rail from Dublin to Navan must also pass through Drogheda. The direct Dublin–Navan railway line remains disused, though still intact. In June 2018, the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport, Department of Transport stated that it would review reopening the line by extending the link past the M3 parkway in 2021.
Air
For commercial and international flights, Meath is serviced by Dublin Airport, which is the closest international airport to the county and has good road links with most major towns. For light aircraft and recreational flying, there are several airstrips located throughout the county which serve as the base of operations for local flying clubs.
The Trim Aerodrome is primarily used for microlight flying. The Ballybog Airstrip opened in 1990 and provides a number of recreational aviation activities such as hot air balloon rides and air shows. There are also airfields at Navan and at Moyglare, across the river rye from Kilcock, County Kildare.
There is also a military landing strip at Gormanstown Camp which is not actively used for aircraft. However, the Irish Defence Forces continue to utilise the airstrip for ground-to-air combat training.
Sport
GAA

Gaelic football is the most popular sport in the county, and the Meath county football team competes annually in Division 2 of the National Football League (Ireland), National Football League, the provincial Leinster Senior Football Championship and the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship. Meath has long been the second power of Leinster football, behind Dublin–Meath Gaelic football rivalry, rivals Dublin GAA, Dublin, and 26 Leinster Senior Football Championship Finals have been contested between the two, of which Meath emerged victorious on 9 occasions. In total, Meath has won 21 Leinster titles, making the county the second most successful in the province after Dublin. Given the pre-eminence of Dublin in recent years, Meath's rivalry with Louth GAA, Louth is now often regarded as the most heated contest, especially after Meath's 2010 Leinster Senior Football Championship Final, highly controversial win over Louth in the 2010 Leinster Senior Football Championship, 2010 Leinster Final.
Meath has won the national football league 7 times, between 1933 and 1994, the fifth most titles in Ireland. Additionally, Meath has won the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, the most prestigious competition in Gaelic football, on 7 occasions between 1949 and 1999, also making it the fifth most successful county in Ireland. Meath has also won Leinster's O'Byrne Cup on 10 occasions, the joint-second most after Kildare GAA, Kildare.
Within the county, Gaelic football clubs compete annually in the Meath Senior Football Championship. The first championship was played in 1887, in which Dowdstown beat Kells by 1 goal to nothing. The most successful club in Meath is Navan O'Mahonys GAA, Navan O'Mahonys with 20 Senior Football Championship titles. The most successful club at the provincial level is Walterstown GFC, Walterstown, which has won 2 Leinster Senior Club Football Championship titles in 1980 and 1983. No team from Meath has ever won the All-Ireland Senior Club Football Championship.
In Hurling, the Meath county hurling team competes in Division 2 of the National Hurling League, as well as in the Leinster Senior Hurling Championship and the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. Meath is not a dual county, and has never won a provincial or national hurling title.
As with football, the Meath Senior Hurling Championship is held every year. The first championship in 1902 was won by the Navan Hibernians GAC, Navan Hibernians. The most successful hurling club in the county is Kilmessan GAA, Kilmessan, with 29 titles, followed by Trim GAA, Trim, with 28. No club team from Meath has ever won the Leinster Senior Club Hurling Championship, and has therefore never qualified for the All-Ireland Senior Club Hurling Championship.

Equestrian activities
Horse racing, horse breeding and horse training are popular in Meath. There are 54 studs within the county, including the Dollanstown Stud and Estate, which is one of the most expensive private properties in Ireland. Race courses within the county include Navan Racecourse, Navan, Fairyhouse Racecourse, Fairyhouse and Bellewstown, which host both National Hunt racing, National Hunt and Flat horse races, such as the Brownstown Stakes, the Bobbyjo Chase, the Lismullen Hurdle and the Irish Grand National. The latter has been held at Fairyhouse since 1870. Beach horse racing also takes place at the Laytown Racecourse.
The Tattersalls Country House and equestrian grounds, which hosts the International Horse Trials and Country Fair each year, is located opposite the Fairyhouse Racecourse near Ratoath.
Artist Letitia Marion Hamilton from Dunboyne won an Olympic bronze medal for Art competitions at the 1948 Summer Olympics, oils and watercolours in the 1948 Summer Olympics for her depiction of List of Irish National Hunt races, The Meath Hunt Point-to-Point Races.
Other sports

As with much of the rest of Ireland, association football is a popular spectator sport within Meath.
The lower-tier Meath and District League comprises clubs from counties Meath, Louth, Cavan and Monaghan.
Underage football in Meath is run by the NERL.
Despite being one of the most populous counties in Ireland, it took until 2018 for Dunboyne's Darragh Lenihan to become the first player from Meath to have represented the Republic of Ireland national football team. Since then, Jamie McGrath of Athboy and Evan Ferguson of
Bettystown
Bettystown (), previously known as Betaghstown and transliterated to ''Beattystown/Bettystown'', is a village in County Meath, Ireland. Together with the neighbouring villages of Laytown, Mornington and Donacarney, it comprises the urban ar ...
have represented the side.
Golf is also widely played, and there are numerous golf and Links (golf), links courses in Meath. Killeen Castle, Dunsany, Killeen Castle in Dunsany has an 18-hole championship golf course which was designed by Jack Nicklaus in 2009, and was the venue for the 2011 Solheim Cup. Knightsbrook Golf Club in Trim also has a championship golf course which was designed by Christy O'Connor Snr, Christy O'Connor in 2006. The County Meath Golf Club in Trim and Royal Tara Golf Club near Navan are two of the most popular golfing locations in the county. Links golf is also played adjacent to the Irish sea coast at the Laytown & Bettystown Golf Club.
Athletics (sport), Athletics within the county is organised by the Meath Athletics Board, which oversees the county's 18 athletics clubs. The board is based in Claremont Stadium in Navan, which is a 400m Tartan Athletics Track and Field Stadium. Sara Treacy of Dunboyne AC represented Ireland in the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro.
Several teams from Meath compete in the Leinster League in Rugby union, most notably Ashbourne RFC, Athboy RFC, Navan R.F.C. and North Meath RFC. Former Leinster Rugby, Leinster and Ireland national rugby union team, Ireland Wing (rugby union), wing Shane Horgan, from Bellewstown, played for Boyne RFC in
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth ...
at youth level.
Notable people
See also
*Counties of Ireland
*Lord Lieutenant of Meath
*High Sheriff of Meath
*Meath Archaeological and Historical Society
References
;Attribution
External links
Meath County CouncilMeath Tourism
{{Coord, 53, 40, N, 6, 40, W, region:IE_type:adm1st_source:GNS-enwiki, display=title
County Meath,
Leinster, Meath
Counties of the Republic of Ireland, Meath
Local government areas of the Republic of Ireland, Meath
 The county's geological landscape is predominantly made up of
The county's geological landscape is predominantly made up of  * Deece Upper ()
* Deece Lower ()
* Duleek Upper ()
* Duleek Lower ()
* Dunboyne ()
* Fore ()
* Kells Upper ()
* Kells Lower ()
* Lune (''Luíne'')
*
* Deece Upper ()
* Deece Lower ()
* Duleek Upper ()
* Duleek Lower ()
* Dunboyne ()
* Fore ()
* Kells Upper ()
* Kells Lower ()
* Lune (''Luíne'')
*  County Meath is within four
County Meath is within four 
 The earliest known evidence of human settlement in the county is the
The earliest known evidence of human settlement in the county is the  Due to a lack of extensive written historical records prior to the 5th century AD, the early history of Meath is murky and largely mythologised. Irish legend purports that the title of "
Due to a lack of extensive written historical records prior to the 5th century AD, the early history of Meath is murky and largely mythologised. Irish legend purports that the title of " In the late 10th century, the Dalcassians to the south, led by Brian Boru, consolidated their hold over Munster, with Boru establishing himself as King of Munster. The ascendancy of this longtime rival kingdom posed a serious threat to High King
In the late 10th century, the Dalcassians to the south, led by Brian Boru, consolidated their hold over Munster, with Boru establishing himself as King of Munster. The ascendancy of this longtime rival kingdom posed a serious threat to High King  In 1166, Diarmait Mac Murchada was banished from Ireland by the High King Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair for the abduction of Lady of Meath Derbforgaill ingen Maeleachlainn, wife of Tigernán Ua Ruairc, King of Breifne. Mac Murchada returned with Norman allies and landed at Bannow in County Wexford, Wexford in 1169, after which they conquered northward throughout 1169–70, initiating the Norman Invasion of Ireland. In response, the High King assembled an alliance which included King Magnus Ua Máel Sechlainn of Meath as well as soldiers from Connacht, Breifne and Kingdom of Dublin, Dublin along with their respective kings. They confronted Mac Murchada's forces at Ferns, County Wexford, Ferns and an agreement was reached whereby Mac Murchada was acknowledged as king of Leinster, in return for acknowledging Ruaidrí as his overlord and agreeing to send his foreign allies away permanently. However, Mac Murchada breached the agreement and enlisted more Normans to his side before continuing his conquests, capturing
In 1166, Diarmait Mac Murchada was banished from Ireland by the High King Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair for the abduction of Lady of Meath Derbforgaill ingen Maeleachlainn, wife of Tigernán Ua Ruairc, King of Breifne. Mac Murchada returned with Norman allies and landed at Bannow in County Wexford, Wexford in 1169, after which they conquered northward throughout 1169–70, initiating the Norman Invasion of Ireland. In response, the High King assembled an alliance which included King Magnus Ua Máel Sechlainn of Meath as well as soldiers from Connacht, Breifne and Kingdom of Dublin, Dublin along with their respective kings. They confronted Mac Murchada's forces at Ferns, County Wexford, Ferns and an agreement was reached whereby Mac Murchada was acknowledged as king of Leinster, in return for acknowledging Ruaidrí as his overlord and agreeing to send his foreign allies away permanently. However, Mac Murchada breached the agreement and enlisted more Normans to his side before continuing his conquests, capturing 
 Following Mac Murchada's death in May 1171, Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, Strongbow succeeded him as King of Leinster and, once again, Magnus joined the High-King's coalition army to oust the Normans, however, their forces were routed during an unsuccessful siege of Dublin. Fearing that Strongbow was growing too powerful and might set up his own independent kingdom in Ireland, Henry II of England landed in Ireland in October 1171 to establish control over both the Irish and the Normans. Henry's campaign in Ireland was largely successful and he managed to reign in the Normans as well as a few Irish kingdoms which also submitted to him. Most crucially, he retained the city of Dublin, and Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, Baron Hugh de Lacy was made its bailiff. Henry's appointment of de Lacy was intended to act as a counterbalance to Strongbow. However, in order to achieve this, de Lacy would need a strong holding on Irish soil and it was decided that the Kingdom of Meath was to be granted to de Lacy.
This grant posed an issue for Henry as the previous decade had been a tumultuous time in Meath. There were four rival heirs to the kingship and each claimant held a different part of the kingdom. The strongest claim came from the King of Breifne, Tigernán Ua Ruairc, who – through conquest, marriage and an alliance with the church – had subsumed almost all of eastern Meath into his kingdom by the time of the Norman arrival. Strongbow also had nominal claim to Meath as King of Leinster. A war of succession within the
Following Mac Murchada's death in May 1171, Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, Strongbow succeeded him as King of Leinster and, once again, Magnus joined the High-King's coalition army to oust the Normans, however, their forces were routed during an unsuccessful siege of Dublin. Fearing that Strongbow was growing too powerful and might set up his own independent kingdom in Ireland, Henry II of England landed in Ireland in October 1171 to establish control over both the Irish and the Normans. Henry's campaign in Ireland was largely successful and he managed to reign in the Normans as well as a few Irish kingdoms which also submitted to him. Most crucially, he retained the city of Dublin, and Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, Baron Hugh de Lacy was made its bailiff. Henry's appointment of de Lacy was intended to act as a counterbalance to Strongbow. However, in order to achieve this, de Lacy would need a strong holding on Irish soil and it was decided that the Kingdom of Meath was to be granted to de Lacy.
This grant posed an issue for Henry as the previous decade had been a tumultuous time in Meath. There were four rival heirs to the kingship and each claimant held a different part of the kingdom. The strongest claim came from the King of Breifne, Tigernán Ua Ruairc, who – through conquest, marriage and an alliance with the church – had subsumed almost all of eastern Meath into his kingdom by the time of the Norman arrival. Strongbow also had nominal claim to Meath as King of Leinster. A war of succession within the  The papal bull ''Laudabiliter'' of Pope Adrian IV, issued in 1155, recognised the House of Plantagenet, Angevin monarch as ''Dominus Hibernae'' (Latin for "Lord of Ireland"). When Pope Clement VII excommunicated Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII in 1533, the constitutional position of the lordship in Ireland became uncertain. Following Henry's split with the church, the Tudors heralded the end of monastic Meath. Church Lands which comprised roughly one-third of the county were seized and granted to Protestant English statesmen and soldiers as a form of payment. Monasteries were suppressed and their treasures were either looted or scattered by Irish scholars to protect them.
Meath was invaded by Tír Eoghain, Tyrone and its allies in 1539 who raided as far south as Navan, which was razed to the ground. King Conn O'Neill, 1st Earl of Tyrone, Conn O'Neill had been recognized as "''King of our realm in Ireland''" by Pope Paul III and was encouraged to expel Protestant influence from the island. However, the conflict stoked an unexpectedly swift reaction from the typically lethargic Dublin government, and Tyrone was defeated by Leonard Grey, 1st Viscount Grane, Lord Deputy Grey and forced to sue for peace in 1541.
Henry had broken away from the Holy See and declared himself the head of the Church in England, and subsequently refused to recognise the Roman Catholic Church's vestigial sovereignty over Ireland. For this reason, and also to address England's waning power in Ireland, Henry proclaimed the Kingdom of Ireland in 1542, with himself as its monarch. The following year, the Counties of Meath and Westmeath Act 1543, Counties of Meath and Westmeath Act was passed by the Parliament of Ireland and Meath was officially divided in two. The act was intended to allow a more effective administration in both counties, particularly in Westmeath, which England had lost control of. A new shire town at Mullingar was established along with four new
The papal bull ''Laudabiliter'' of Pope Adrian IV, issued in 1155, recognised the House of Plantagenet, Angevin monarch as ''Dominus Hibernae'' (Latin for "Lord of Ireland"). When Pope Clement VII excommunicated Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII in 1533, the constitutional position of the lordship in Ireland became uncertain. Following Henry's split with the church, the Tudors heralded the end of monastic Meath. Church Lands which comprised roughly one-third of the county were seized and granted to Protestant English statesmen and soldiers as a form of payment. Monasteries were suppressed and their treasures were either looted or scattered by Irish scholars to protect them.
Meath was invaded by Tír Eoghain, Tyrone and its allies in 1539 who raided as far south as Navan, which was razed to the ground. King Conn O'Neill, 1st Earl of Tyrone, Conn O'Neill had been recognized as "''King of our realm in Ireland''" by Pope Paul III and was encouraged to expel Protestant influence from the island. However, the conflict stoked an unexpectedly swift reaction from the typically lethargic Dublin government, and Tyrone was defeated by Leonard Grey, 1st Viscount Grane, Lord Deputy Grey and forced to sue for peace in 1541.
Henry had broken away from the Holy See and declared himself the head of the Church in England, and subsequently refused to recognise the Roman Catholic Church's vestigial sovereignty over Ireland. For this reason, and also to address England's waning power in Ireland, Henry proclaimed the Kingdom of Ireland in 1542, with himself as its monarch. The following year, the Counties of Meath and Westmeath Act 1543, Counties of Meath and Westmeath Act was passed by the Parliament of Ireland and Meath was officially divided in two. The act was intended to allow a more effective administration in both counties, particularly in Westmeath, which England had lost control of. A new shire town at Mullingar was established along with four new 
 The economic boom of the late 18th century came to a sudden and catastrophic halt following the end of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815. During the war, Ireland had become known as the "''Food larder of Europe''", and the tenant farmers and landlords of Meath relied heavily on tillage, which fetched an artificially high price due to a surge in wartime demand. Further, a substantial number of Irish soldiers who comprised as much as 25% of the entire British Army and Royal Navy, Navy during the war were now made redundant. As post-war trade between Britain and Europe recovered, demand for Irish tillage collapsed; however, rents remained the same and the population continued to boom. As economic stagnation set in, the once well-managed, prosperous estates of Meath gave way to mismanagement and Absentee landlord, absenteeism, and the tenant farmers were pushed further into poverty.
This dire economic state resulted in a surge of Irish nationalism and demands to repeal the disastrous Act of Union. Nationalist sentiment was widespread in Meath, as reflected in the Meath (UK Parliament constituency), Meath Parliamentary constituency, which returned several of 19th century Ireland's most prominent nationalist politicians, including Daniel O'Connell, Charles Stewart Parnell and Michael Davitt. Owing to its symbolic place in the national psyche, Daniel O'Connell held a rally on the
The economic boom of the late 18th century came to a sudden and catastrophic halt following the end of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815. During the war, Ireland had become known as the "''Food larder of Europe''", and the tenant farmers and landlords of Meath relied heavily on tillage, which fetched an artificially high price due to a surge in wartime demand. Further, a substantial number of Irish soldiers who comprised as much as 25% of the entire British Army and Royal Navy, Navy during the war were now made redundant. As post-war trade between Britain and Europe recovered, demand for Irish tillage collapsed; however, rents remained the same and the population continued to boom. As economic stagnation set in, the once well-managed, prosperous estates of Meath gave way to mismanagement and Absentee landlord, absenteeism, and the tenant farmers were pushed further into poverty.
This dire economic state resulted in a surge of Irish nationalism and demands to repeal the disastrous Act of Union. Nationalist sentiment was widespread in Meath, as reflected in the Meath (UK Parliament constituency), Meath Parliamentary constituency, which returned several of 19th century Ireland's most prominent nationalist politicians, including Daniel O'Connell, Charles Stewart Parnell and Michael Davitt. Owing to its symbolic place in the national psyche, Daniel O'Connell held a rally on the  As a consequence of its location in the centre of Ireland, Meath has an abundance of historic sites.
All periods of Irish history are represented in the landmarks of the county, spanning from the prehistoric tombs at
As a consequence of its location in the centre of Ireland, Meath has an abundance of historic sites.
All periods of Irish history are represented in the landmarks of the county, spanning from the prehistoric tombs at  The population of Meath suffered a significant decline between 1841 and 1901, decreasing by almost two-thirds (183,828 to 67,497); it stabilised between 1901 and 1971 (67,497 to 71,729), and there was a substantial increase between 1971 and 1981 to 95,419. This increase was mainly due to a baby boom locally. The population then continued to increase at a constant rate, before increasing at an explosive rate between 1996 and 2002, from 109,732 to 134,005. This is due primarily to economic factors, with the return of residents to live in the county, and also an echo effect of the 1970s baby boom. The census of 2022 gives a figure of 220,296, including a dramatic increase in inward migration to the county. Meath is one of only 5 counties in the state which has a population higher than its 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 pre-famine peak.
This population growth has seen divergent trends emerge in recent years, with mild depopulation in the north and west of the county more than offset by large increases in the population of the eastern and south-eastern parts of the county, principally owing to inward migration to districts that have good proximity via road to the business parks on the western outskirts of Dublin. The accession of Poland and the Baltic States to the European Union in 2004 resulted in a significant influx of workers from these countries to work in sectors such as agriculture, quarrying, construction and catering.
The population of Meath suffered a significant decline between 1841 and 1901, decreasing by almost two-thirds (183,828 to 67,497); it stabilised between 1901 and 1971 (67,497 to 71,729), and there was a substantial increase between 1971 and 1981 to 95,419. This increase was mainly due to a baby boom locally. The population then continued to increase at a constant rate, before increasing at an explosive rate between 1996 and 2002, from 109,732 to 134,005. This is due primarily to economic factors, with the return of residents to live in the county, and also an echo effect of the 1970s baby boom. The census of 2022 gives a figure of 220,296, including a dramatic increase in inward migration to the county. Meath is one of only 5 counties in the state which has a population higher than its 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 pre-famine peak.
This population growth has seen divergent trends emerge in recent years, with mild depopulation in the north and west of the county more than offset by large increases in the population of the eastern and south-eastern parts of the county, principally owing to inward migration to districts that have good proximity via road to the business parks on the western outskirts of Dublin. The accession of Poland and the Baltic States to the European Union in 2004 resulted in a significant influx of workers from these countries to work in sectors such as agriculture, quarrying, construction and catering.

 Meath contains
Meath contains  The agricultural products of the county are beef, pork, dairy, poultry, vegetables and cereals. Meath has a strong farming tradition and up until the Census of Ireland, 1911, 1911 Census the most commonly listed occupation in the county was Farmworker, farm labourer. Meath is ranked 2nd in the country for the production of vegetables and 2nd for the production of Rapeseed, rapeseed oil.
As of 2018, Meath has the country's 8th largest cattle herd with 275,301 cows. Dairy production was the largest and most profitable agricultural sector in the county and 63.7% of all cattle were Dairy cattle, dairy cows. The remaining 36.3% were beef cattle. The county also has Ireland's 9th largest sheep herd (150,571 sheep) and 14th largest pig herd (40,259). Meat processors such as Kepak and Dawn Meats are large employers within the county.
There are 4,620 farms in the county, with a total farmed area of , accounting for 83% of land area. Of this, was under tillage, the 3rd highest in the country. Although Irish agriculture is heavily dominated by pasture farming, Meath's favourable climate and easterly location give it a much greater capacity than most counties for agricultural diversification, reflected in its robust tillage and vegetable production sectors. The average size of a farm in the county is , well above the national average of .
Agriculture supports thousands of jobs within the county and, according to the Irish Farmers' Association, the total value of agricultural produce from Meath in 2018 was €541 million, ranking it 6th in Ireland.
The agricultural products of the county are beef, pork, dairy, poultry, vegetables and cereals. Meath has a strong farming tradition and up until the Census of Ireland, 1911, 1911 Census the most commonly listed occupation in the county was Farmworker, farm labourer. Meath is ranked 2nd in the country for the production of vegetables and 2nd for the production of Rapeseed, rapeseed oil.
As of 2018, Meath has the country's 8th largest cattle herd with 275,301 cows. Dairy production was the largest and most profitable agricultural sector in the county and 63.7% of all cattle were Dairy cattle, dairy cows. The remaining 36.3% were beef cattle. The county also has Ireland's 9th largest sheep herd (150,571 sheep) and 14th largest pig herd (40,259). Meat processors such as Kepak and Dawn Meats are large employers within the county.
There are 4,620 farms in the county, with a total farmed area of , accounting for 83% of land area. Of this, was under tillage, the 3rd highest in the country. Although Irish agriculture is heavily dominated by pasture farming, Meath's favourable climate and easterly location give it a much greater capacity than most counties for agricultural diversification, reflected in its robust tillage and vegetable production sectors. The average size of a farm in the county is , well above the national average of .
Agriculture supports thousands of jobs within the county and, according to the Irish Farmers' Association, the total value of agricultural produce from Meath in 2018 was €541 million, ranking it 6th in Ireland.
 Due to the geology of the area, Meath has enormous reserves of Lead and Zinc, which are extracted at Tara Mine in Navan. Tara is both Europe's largest and deepest mine and is currently owned by Boliden AB. The mine commenced operations in 1977, and a total of 85 million tonnes of ore has been extracted from it, producing an average of 2.6 million tonnes of zinc ore annually.
Glacial deposits of gravel exist in a band stretching from the Offaly border at Edenderry, to the sea at Laytown. This is the basis of a long quarrying tradition. The local availability of large deposits of limestone and shale also gave rise to a significant cement production industry within the county. The two largest cement facilities are at Kinnegad and Platin, the latter of which is owned by CRH plc, Irish Cement and has the capacity to produce 2.8 million tonnes of cement per annum, which is primarily transported via rail to Dublin for use or export.
Ireland's first waste-to-energy plant opened in Duleek in 2011 and produces 17 MW of electricity per annum. SSE plc, SSE Airtricity aim to build a 208 MW gas-fired power plant south of Drogheda. Meath has a small but growing biomass industry, however other forms of renewable energy such as wind power and hydroelectricity have stalled due to widespread objections. There is an abundance of natural subterranean Fault (geology), faults where water from hot springs, such as those Enfield, rise to the surface at 25 °C. There is potential for these to be used for Geothermal power, Shallow Geothermal Energy generation.
Due to the geology of the area, Meath has enormous reserves of Lead and Zinc, which are extracted at Tara Mine in Navan. Tara is both Europe's largest and deepest mine and is currently owned by Boliden AB. The mine commenced operations in 1977, and a total of 85 million tonnes of ore has been extracted from it, producing an average of 2.6 million tonnes of zinc ore annually.
Glacial deposits of gravel exist in a band stretching from the Offaly border at Edenderry, to the sea at Laytown. This is the basis of a long quarrying tradition. The local availability of large deposits of limestone and shale also gave rise to a significant cement production industry within the county. The two largest cement facilities are at Kinnegad and Platin, the latter of which is owned by CRH plc, Irish Cement and has the capacity to produce 2.8 million tonnes of cement per annum, which is primarily transported via rail to Dublin for use or export.
Ireland's first waste-to-energy plant opened in Duleek in 2011 and produces 17 MW of electricity per annum. SSE plc, SSE Airtricity aim to build a 208 MW gas-fired power plant south of Drogheda. Meath has a small but growing biomass industry, however other forms of renewable energy such as wind power and hydroelectricity have stalled due to widespread objections. There is an abundance of natural subterranean Fault (geology), faults where water from hot springs, such as those Enfield, rise to the surface at 25 °C. There is potential for these to be used for Geothermal power, Shallow Geothermal Energy generation.
 Irish Rail provides frequent rail services from Dunboyne railway station, Dunboyne and M3 Parkway railway station, M3 Parkway to Dublin city centre. Laytown railway station and Gormanston railway station have a commuter rail service and are located along Dublin's Dublin Suburban Rail, Northern Commuter Line which runs from Dundalk to Dublin. A commuter train service (Western Commuter Line) passes through Enfield railway station (Ireland), Enfield, although the service is less frequent as the station is primarily used for the long-distance Irish rail routes to Longford and Sligo.
Navan is currently served by a freight-only spur railway line from Drogheda on the Dublin-Belfast main line, for freight traffic (zinc and lead concentrate from Tara Mines in Navan to Dublin Port) connecting at Drogheda. Currently, the only commuter rail from Dublin to Navan must also pass through Drogheda. The direct Dublin–Navan railway line remains disused, though still intact. In June 2018, the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport, Department of Transport stated that it would review reopening the line by extending the link past the M3 parkway in 2021.
Irish Rail provides frequent rail services from Dunboyne railway station, Dunboyne and M3 Parkway railway station, M3 Parkway to Dublin city centre. Laytown railway station and Gormanston railway station have a commuter rail service and are located along Dublin's Dublin Suburban Rail, Northern Commuter Line which runs from Dundalk to Dublin. A commuter train service (Western Commuter Line) passes through Enfield railway station (Ireland), Enfield, although the service is less frequent as the station is primarily used for the long-distance Irish rail routes to Longford and Sligo.
Navan is currently served by a freight-only spur railway line from Drogheda on the Dublin-Belfast main line, for freight traffic (zinc and lead concentrate from Tara Mines in Navan to Dublin Port) connecting at Drogheda. Currently, the only commuter rail from Dublin to Navan must also pass through Drogheda. The direct Dublin–Navan railway line remains disused, though still intact. In June 2018, the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport, Department of Transport stated that it would review reopening the line by extending the link past the M3 parkway in 2021.
 Gaelic football is the most popular sport in the county, and the Meath county football team competes annually in Division 2 of the National Football League (Ireland), National Football League, the provincial Leinster Senior Football Championship and the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship. Meath has long been the second power of Leinster football, behind Dublin–Meath Gaelic football rivalry, rivals Dublin GAA, Dublin, and 26 Leinster Senior Football Championship Finals have been contested between the two, of which Meath emerged victorious on 9 occasions. In total, Meath has won 21 Leinster titles, making the county the second most successful in the province after Dublin. Given the pre-eminence of Dublin in recent years, Meath's rivalry with Louth GAA, Louth is now often regarded as the most heated contest, especially after Meath's 2010 Leinster Senior Football Championship Final, highly controversial win over Louth in the 2010 Leinster Senior Football Championship, 2010 Leinster Final.
Meath has won the national football league 7 times, between 1933 and 1994, the fifth most titles in Ireland. Additionally, Meath has won the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, the most prestigious competition in Gaelic football, on 7 occasions between 1949 and 1999, also making it the fifth most successful county in Ireland. Meath has also won Leinster's O'Byrne Cup on 10 occasions, the joint-second most after Kildare GAA, Kildare.
Within the county, Gaelic football clubs compete annually in the Meath Senior Football Championship. The first championship was played in 1887, in which Dowdstown beat Kells by 1 goal to nothing. The most successful club in Meath is Navan O'Mahonys GAA, Navan O'Mahonys with 20 Senior Football Championship titles. The most successful club at the provincial level is Walterstown GFC, Walterstown, which has won 2 Leinster Senior Club Football Championship titles in 1980 and 1983. No team from Meath has ever won the All-Ireland Senior Club Football Championship.
In Hurling, the Meath county hurling team competes in Division 2 of the National Hurling League, as well as in the Leinster Senior Hurling Championship and the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. Meath is not a dual county, and has never won a provincial or national hurling title.
As with football, the Meath Senior Hurling Championship is held every year. The first championship in 1902 was won by the Navan Hibernians GAC, Navan Hibernians. The most successful hurling club in the county is Kilmessan GAA, Kilmessan, with 29 titles, followed by Trim GAA, Trim, with 28. No club team from Meath has ever won the Leinster Senior Club Hurling Championship, and has therefore never qualified for the All-Ireland Senior Club Hurling Championship.
Gaelic football is the most popular sport in the county, and the Meath county football team competes annually in Division 2 of the National Football League (Ireland), National Football League, the provincial Leinster Senior Football Championship and the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship. Meath has long been the second power of Leinster football, behind Dublin–Meath Gaelic football rivalry, rivals Dublin GAA, Dublin, and 26 Leinster Senior Football Championship Finals have been contested between the two, of which Meath emerged victorious on 9 occasions. In total, Meath has won 21 Leinster titles, making the county the second most successful in the province after Dublin. Given the pre-eminence of Dublin in recent years, Meath's rivalry with Louth GAA, Louth is now often regarded as the most heated contest, especially after Meath's 2010 Leinster Senior Football Championship Final, highly controversial win over Louth in the 2010 Leinster Senior Football Championship, 2010 Leinster Final.
Meath has won the national football league 7 times, between 1933 and 1994, the fifth most titles in Ireland. Additionally, Meath has won the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, the most prestigious competition in Gaelic football, on 7 occasions between 1949 and 1999, also making it the fifth most successful county in Ireland. Meath has also won Leinster's O'Byrne Cup on 10 occasions, the joint-second most after Kildare GAA, Kildare.
Within the county, Gaelic football clubs compete annually in the Meath Senior Football Championship. The first championship was played in 1887, in which Dowdstown beat Kells by 1 goal to nothing. The most successful club in Meath is Navan O'Mahonys GAA, Navan O'Mahonys with 20 Senior Football Championship titles. The most successful club at the provincial level is Walterstown GFC, Walterstown, which has won 2 Leinster Senior Club Football Championship titles in 1980 and 1983. No team from Meath has ever won the All-Ireland Senior Club Football Championship.
In Hurling, the Meath county hurling team competes in Division 2 of the National Hurling League, as well as in the Leinster Senior Hurling Championship and the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. Meath is not a dual county, and has never won a provincial or national hurling title.
As with football, the Meath Senior Hurling Championship is held every year. The first championship in 1902 was won by the Navan Hibernians GAC, Navan Hibernians. The most successful hurling club in the county is Kilmessan GAA, Kilmessan, with 29 titles, followed by Trim GAA, Trim, with 28. No club team from Meath has ever won the Leinster Senior Club Hurling Championship, and has therefore never qualified for the All-Ireland Senior Club Hurling Championship.

 As with much of the rest of Ireland, association football is a popular spectator sport within Meath.
The lower-tier Meath and District League comprises clubs from counties Meath, Louth, Cavan and Monaghan.
Underage football in Meath is run by the NERL.
Despite being one of the most populous counties in Ireland, it took until 2018 for Dunboyne's Darragh Lenihan to become the first player from Meath to have represented the Republic of Ireland national football team. Since then, Jamie McGrath of Athboy and Evan Ferguson of
As with much of the rest of Ireland, association football is a popular spectator sport within Meath.
The lower-tier Meath and District League comprises clubs from counties Meath, Louth, Cavan and Monaghan.
Underage football in Meath is run by the NERL.
Despite being one of the most populous counties in Ireland, it took until 2018 for Dunboyne's Darragh Lenihan to become the first player from Meath to have represented the Republic of Ireland national football team. Since then, Jamie McGrath of Athboy and Evan Ferguson of