Market Square (Alexandria, Virginia) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alexandria is an
 The city of Alexandria was named in honor of the Alexander family,
The city of Alexandria was named in honor of the Alexander family, 
 On October 21, 1669, a
On October 21, 1669, a
 In 1814, during the
In 1814, during the
 The first fatalities of the North and South in the
The first fatalities of the North and South in the
(2)
Ellsworth was publicized as a Union martyr, and the incident generated great excitement in the North, with many children being named for him. Jackson's death defending his home caused a similar sensation in the South. Alexandria remained under military occupation until the end of the Civil War. Fort Ward, one of a ring of forts built by the Union army for the defense of
/ref> In the waning years of the 19th century, Alexandria suffered its two documented
 Until 2014, local legislation mandated that all new north–south streets in the city be named for Confederate military leaders. Efforts have increased in recent years to expedite the renaming of these streets with Mayor Justin Wilson and the City Council setting a goal of renaming three of these streets annually. In 2019, the name of U.S. 1 was changed from
Until 2014, local legislation mandated that all new north–south streets in the city be named for Confederate military leaders. Efforts have increased in recent years to expedite the renaming of these streets with Mayor Justin Wilson and the City Council setting a goal of renaming three of these streets annually. In 2019, the name of U.S. 1 was changed from
 According to the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which is land and , or 2.85%, is water. Alexandria is bounded on the east by the
According to the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which is land and , or 2.85%, is water. Alexandria is bounded on the east by the
 Companies headquartered in Alexandria include Crooked Beat Records, Five Guys, the
Companies headquartered in Alexandria include Crooked Beat Records, Five Guys, the  Major employment sectors in Alexandria include management consulting, business and finance, office and administrative support, computer and mathematical, sales, and legal. Jobs in Alexandria are highly concentrated around the city's Washington Metro, Metrorail stations, primarily in Old Town North and the Braddock Road (Alexandria, Virginia), Braddock Road area, Old Town, and Carlyle near the
Major employment sectors in Alexandria include management consulting, business and finance, office and administrative support, computer and mathematical, sales, and legal. Jobs in Alexandria are highly concentrated around the city's Washington Metro, Metrorail stations, primarily in Old Town North and the Braddock Road (Alexandria, Virginia), Braddock Road area, Old Town, and Carlyle near the

 Alexandria has over of protected open space with 566 acres of city-owned park land and 11 recreation centers, of which Castanea pumila, Chinquapin is one of the largest. Chinquapin offers facilities for swimming, tennis, racquetball, and other sports. Additionally, on March 19th, 2024 a year round recreation center opened inside of the Minnie Howard campus of Alexandria City High School, with a competition size swimming pool and a therapeutic training pool. The city also organizes several sports leagues throughout the year including volleyball, softball and basketball.
The city is home to Cameron Run Regional Park, operated by NOVA Parks, which includes a water park, a miniature golf course, and batting cages. NOVA Parks also operates the Winkler Botanical Preserve in the city's Neighborhoods in Alexandria, Virginia#West End, West End. A portion of the Mount Vernon Trail, a popular bike and jogging path, runs through Old Town near the Potomac River on its way from the
Alexandria has over of protected open space with 566 acres of city-owned park land and 11 recreation centers, of which Castanea pumila, Chinquapin is one of the largest. Chinquapin offers facilities for swimming, tennis, racquetball, and other sports. Additionally, on March 19th, 2024 a year round recreation center opened inside of the Minnie Howard campus of Alexandria City High School, with a competition size swimming pool and a therapeutic training pool. The city also organizes several sports leagues throughout the year including volleyball, softball and basketball.
The city is home to Cameron Run Regional Park, operated by NOVA Parks, which includes a water park, a miniature golf course, and batting cages. NOVA Parks also operates the Winkler Botanical Preserve in the city's Neighborhoods in Alexandria, Virginia#West End, West End. A portion of the Mount Vernon Trail, a popular bike and jogging path, runs through Old Town near the Potomac River on its way from the
 As an Independent city (Virginia), independent city of Virginia (as opposed to an incorporated town within a county), Alexandria derives its governing authority from the
As an Independent city (Virginia), independent city of Virginia (as opposed to an incorporated town within a county), Alexandria derives its governing authority from the
 Alexandria Union Station, Union Station, the city's historic train station, has Amtrak intercity services and the Virginia Railway Express regional rail service. The station is directly adjacent to the King Street–Old Town Metro station. The traditional boundary between Old Town and the latterly annexed sections of the city follows the railway acquired by Virginia in 2021 and formerly owned by CSX Transportation. In addition, Norfolk Southern Railway operates a Rail freight transport, freight rail line and a Transloading, transload terminal in the city.
Capital Bikeshare, a Bicycle-sharing system, bicycle-sharing public transportation system, launched in Alexandria in 2012. The system has 62 rental locations throughout the city. The East Coast Greenway and Mount Vernon Trail cycle routes pass through Alexandria.
Alexandria Union Station, Union Station, the city's historic train station, has Amtrak intercity services and the Virginia Railway Express regional rail service. The station is directly adjacent to the King Street–Old Town Metro station. The traditional boundary between Old Town and the latterly annexed sections of the city follows the railway acquired by Virginia in 2021 and formerly owned by CSX Transportation. In addition, Norfolk Southern Railway operates a Rail freight transport, freight rail line and a Transloading, transload terminal in the city.
Capital Bikeshare, a Bicycle-sharing system, bicycle-sharing public transportation system, launched in Alexandria in 2012. The system has 62 rental locations throughout the city. The East Coast Greenway and Mount Vernon Trail cycle routes pass through Alexandria.
 *Diedrich Bader, actor
* Hannibal Brumskine III, internet entrepreneur
* Sandor Bustamante, soccer player
* Stewart Copeland, drummer for The Police
* Leon Day, Hall of Fame baseball pitcher who played in the Negro league baseball, Negro leagues
* Elena Delle Donne, forward-guard, Washington Mystics, WNBA champion, two-time league MVP
* Stefon Diggs, wide receiver for the Houston Texans
* Donna Dixon, former actress, model
* William O. Douglas, American jurist who served as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the US 1939–75, and environmentalist resided in Old Town for four decades
* Chad Dukes (radio personality), Chad Dukes, Alexandria, Virginia radio personality, pioneer in podcasting
* Marion Moncure Duncan, 25th President General of the Daughters of the American Revolution
*
*Diedrich Bader, actor
* Hannibal Brumskine III, internet entrepreneur
* Sandor Bustamante, soccer player
* Stewart Copeland, drummer for The Police
* Leon Day, Hall of Fame baseball pitcher who played in the Negro league baseball, Negro leagues
* Elena Delle Donne, forward-guard, Washington Mystics, WNBA champion, two-time league MVP
* Stefon Diggs, wide receiver for the Houston Texans
* Donna Dixon, former actress, model
* William O. Douglas, American jurist who served as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the US 1939–75, and environmentalist resided in Old Town for four decades
* Chad Dukes (radio personality), Chad Dukes, Alexandria, Virginia radio personality, pioneer in podcasting
* Marion Moncure Duncan, 25th President General of the Daughters of the American Revolution
*
The Chamber ALX - Alexandria Chamber of Commerce
Historic Alexandria Foundation
Visit Alexandria
{{Authority control Alexandria, Virginia, 1745 establishments in the Colony of Virginia Art gallery districts Cities in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area Cities in Virginia History of the District of Columbia Northern Virginia Majority-minority counties and independent cities in Virginia Populated places established in 1745 Virginia populated places on the Potomac River Washington metropolitan area
independent city
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor states ...
in Northern Virginia
Northern Virginia, locally referred to as NOVA or NoVA, comprises several County (United States), counties and independent city (United States), independent cities in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. ...
, United States. It lies on the western bank of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
approximately south of D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
The city's population of 159,467 at the 2020 census made it the sixth-most populous city in Virginia and 169th-most populous city in the U.S. Alexandria is a principal city
In the United States, a principal city is the largest incorporated place with a population of at least 10,000 in a core-based statistical area (CBSA) or New England city and town area (NECTA), or if no incorporated place of least 10,000 populati ...
of the Washington metropolitan area
The Washington metropolitan area, also referred to as the National Capital Region, Greater Washington, or locally as the DMV (short for Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia), is the metropolitan area comprising Washing ...
, which is part of the larger Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area
The Washington–Baltimore combined metropolitan statistical area is a combined statistical area, statistical area, including the overlapping metropolitan areas of Washington metropolitan area, Washington, D.C. and Baltimore metropolitan area, B ...
.
Like the rest of Northern Virginia and Central Maryland
The Baltimore–Columbia–Towson Metropolitan Statistical Area, also known as Central Maryland, is a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) in Maryland as defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB). It is part of the larger ...
, present-day Alexandria has been influenced by its proximity to the U.S. capital. It is largely populated by professionals working in the federal civil service, in the U.S. military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. U.S. federal law names six armed forces: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and the Coast Guard. Since 1949, all of the armed forces, except th ...
, or for one of the many private companies which contract to provide services to the U.S. federal government
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, execut ...
. The city's largest employers include the U.S. Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, t ...
and the Institute for Defense Analyses
The Institute for Defense Analyses (IDA) is an American non-profit corporation that administers three federally funded research and development centers (FFRDCs) – the Systems and Analyses Center (SAC), Science and Technology Policy Institute, t ...
. Alexandria is the highest-income independent city in Virginia.
The historic center of Alexandria is known as Old Town Alexandria, or simply "Old Town". With its concentration of boutiques, restaurants, antique shop
An antique shop (or antiques shop) is a retail store specializing in the selling of antiques. Antiques shops generally have a physical presence in a shop where the wares are stored and displayed, but some antique shops are online, with no phy ...
s and theaters, it is a major draw for city residents and visitors. Like Old Town, many Alexandria neighborhoods are compact and walkable. A large portion of adjacent Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous county in Virginia, the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington ...
, mostly south but also west of the city, has Alexandria mailing addresses. However, this area is under the jurisdiction of Fairfax County's government and separate from the independent city. The city is therefore sometimes referred to as the "City of Alexandria" to avoid confusion.
Etymology
 The city of Alexandria was named in honor of the Alexander family,
The city of Alexandria was named in honor of the Alexander family, Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
merchants who owned much of the land where the city now stands. In 1749, the Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, and the first elected legislative assembly in the New World. It was established on July 30, ...
established Alexandria as a new port town on the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
to accommodate increasing commercial activity and relieve congestion in the port of Dumfries
Dumfries ( ; ; from ) is a market town and former royal burgh in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, near the mouth of the River Nith on the Solway Firth, from the Anglo-Scottish border. Dumfries is the county town of the Counties of Scotland, ...
. The Alexanders
''Smyrnium olusatrum'', common name alexanders (or alisander) is an edible flowering plant of the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae), which grows on waste ground and in hedges around the Mediterranean and Atlantic coastal regions of Europe. It was ...
particularly John Alexander, who had purchased a large tract of land in the area in 1669 were instrumental in its early development, and the name “Alexandria” was chosen to reflect their influence.
From its inception, Alexandria was envisioned as a planned commercial center. Its grid street system, waterfront location, and proximity to major colonial trade routes helped it quickly become one of the most important ports in the Chesapeake region. During the late 18th and early 19th
19 (nineteen) is the natural number following 18 and preceding 20. It is a prime number.
Mathematics
Nineteen is the eighth prime number.
Number theory
19 forms a twin prime with 17, a cousin prime with 23, and a sexy prime with 13. ...
centuries, Alexandria served as a bustling hub for the export of tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, and other goods, and was integrated into the thriving economy of the newly established United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
Alexandria became part of the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
in 1791 when the federal capital was established. However, in 1846, amid concerns over economic neglect and the growing abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the political movement to end slavery and liberate enslaved individuals around the world.
The first country to fully outlaw slavery was Kingdom of France, France in 1315, but it was later used ...
movement in D.C., Alexandria residents at the time voted to retrocede the city and the rest of Alexandria County (present day Arlington County
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the nati ...
) back to Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
which was a rare reversal of a U.S. boundary change inspired by a desire to hold on to southern culture and beliefs during the time.
The city played a prominent role during the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
, serving as a Union-occupied logistics and hospital center due to its strategic location. Today, Old Town Alexandria preserves much of its colonial and Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
-era architecture, helping define the city's reputation as a historic and culturally vibrant destination.

Definition
Covering roughly 15 square miles and identified by ZIP codes 22301 through 22315, the city of Alexandria is politically separate fromFairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous county in Virginia, the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington ...
but closely integrated with the region's transportation, economic, and cultural networks.
Many surrounding areas such as Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franco ...
, Hybla Valley, and Kingstowne use “Alexandria” mailing addresses despite being located in unincorporated Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous county in Virginia, the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington ...
not the city of Alexandria. These communities are often referred to as “South Alexandria,” and share ZIP codes like 22306, 22307, 22309, and 22310, and are frequently grouped with the city for planning and identity purposes.
Together, the City of Alexandria and the broader South Alexandria region of Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous county in Virginia, the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington ...
form a densely populated and historically rich section of the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area. The area is known for its walkable neighborhoods, preserved colonial architecture, and a mix of residential and commercial development anchored by strong transit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1980 film), a 1980 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (1986 film), a Canadian short film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countrie ...
connections.
History
Early history
According to archaeologists' estimates, a succession ofindigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
began to occupy the Chesapeake Chesapeake most often refers to:
*Chesapeake people, a Native American tribe also known as the Chesepian
*Chesapeake Bay
*Delmarva Peninsula, also known as the Chesapeake Peninsula
Chesapeake may also refer to:
Populated places In Virginia
* ...
and Tidewater
Tidewater may refer to:
* Tidewater (region), a geographic area of southeast Virginia, southern Maryland, and northeast North Carolina.
** Tidewater accent, an accent of American English associated with the Tidewater region of Virginia
* Tidewater ...
region about 3,000 to 10,000 years ago. Various Algonquian-speaking peoples inhabited the lands in the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
drainage area since at least the early 14th century
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCCI) to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Euro ...
.
In the summer of 1608, English settler John Smith explored the Potomac River and came into contact with the Patawomeck
The Patawomeck are a Native American tribe based in Stafford County, Virginia, along the Potomac River. ''Patawomeck'' is another spelling of Potomac.
The Patawomeck Indian Tribe of Virginia is a state-recognized tribe in Virginia that identif ...
(loosely affiliated with the Powhatan
Powhatan people () are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands who belong to member tribes of the Powhatan Confederacy, or Tsenacommacah. They are Algonquian peoples whose historic territories were in eastern Virginia.
Their Powh ...
) and Doeg tribes who lived on the Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
side, as well as on Theodore Roosevelt Island
Theodore Roosevelt Island is an island and national memorial located in the Potomac River in Washington, D.C. During the Civil War, it was used as a training camp for the United States Colored Troops. The island was given to the federal gov ...
, and the Piscataway Piscataway may refer to:
*Maryland (place)
**Piscataway, Maryland, an unincorporated community
** Piscataway Creek, Maryland
** Piscataway Park, historical park at the mouth of Piscataway Creek
** Siege of Piscataway, siege of Susquehannock fort sou ...
(also known as the Conoy), who resided on the Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
side. On this visit, Smith recorded the presence of a settlement called ''Assaomeck'' near the south bank of what is now Hunting Creek.
Colonial era
 On October 21, 1669, a
On October 21, 1669, a patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
granted to Robert Howsing for transporting 120 people to the Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia was a British Empire, British colonial settlement in North America from 1606 to 1776.
The first effort to create an English settlement in the area was chartered in 1584 and established in 1585; the resulting Roanoke Colo ...
. That tract later became the City of Alexandria. Virginia's comprehensive Tobacco Inspection Law of 1730 mandated that all tobacco grown in the colony must be brought to locally designated public warehouses for inspection before sale. One of the sites designated for a warehouse on the upper Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
was at the mouth of Hunting Creek. However, the ground proved to be unsuitable, and the warehouse was built half a mile up-river, where the water was deep near the shore.
Following the 1745 settlement of the Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia was a British Empire, British colonial settlement in North America from 1606 to 1776.
The first effort to create an English settlement in the area was chartered in 1584 and established in 1585; the resulting Roanoke Colo ...
's 10-year dispute with Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron
Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron (22 October 16939 December 1781) was a British-born planter. The only member of the British peerage to permanently reside in British America, Fairfax owned the Northern Neck Proprietary in the Colony ...
over the western boundary of the Northern Neck Proprietary
The Northern Neck Proprietary – also called the Northern Neck land grant, Fairfax Proprietary, or Fairfax Grant – was a land grant first contrived by the exiled English King Charles II in 1649 and encompassing all the lands bounded by the Pot ...
, when the Privy Council in London found in favor of Lord Fairfax's expanded claim, some of the Fairfax County gentry formed the Ohio Company
The Ohio Company, formally known as the Ohio Company of Virginia, was a land speculation company organized for the settlement by Virginians of the Ohio Country (approximately the present U.S. state of Ohio) and to trade with the Native Ameri ...
of Virginia. They intended to conduct trade into the interior of America, and they required a trading center near the head of navigation on the Potomac. The best location was Hunting Creek tobacco warehouse, since the deep water could easily accommodate sailing ships. Many local tobacco planters, however, wanted a new town further up Hunting Creek, away from nonproductive fields along the river.
Around 1746, Captain Philip Alexander II (1704–1753) moved to what is south of present Duke Street in Alexandria. His estate, which consisted of , was bounded by Hunting Creek, Hooff's Run, the Potomac River, and approximately the line which would become Cameron Street. At the opening of Virginia's 1748–49 legislative session, there was a petition submitted in the House of Burgesses
The House of Burgesses () was the lower house of the Virginia General Assembly from 1619 to 1776. It existed during the colonial history of the United States in the Colony of Virginia in what was then British America. From 1642 to 1776, the Hou ...
on November 1, 1748, that the "inhabitants of Fairfax (Co.) praying that a town may be established at Hunting Creek Warehouse on Potowmack River," since Hugh West was the owner of the warehouse. The petition was introduced by Lawrence Washington, the representative for Fairfax County, the son-in-law of William Fairfax
William Fairfax (1691–1757) was a political appointee of the British Crown in several colonies as well as a planter and politician in the Colony of Virginia. Fairfax served as Collector of Customs in Barbados, Chief Justice and governor of the ...
, and a founding member of the Ohio Company. To support the company's push for a town on the river, Lawrence's younger brother George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
, an aspiring surveyor, made a sketch of the shoreline touting the advantages of the tobacco warehouse site.
Since the river site was amidst his estate, Philip opposed the idea and strongly favored a site at the head of Hunting Creek (also known as Great Hunting Creek). It has been said that in order to avoid a predicament the petitioners offered to name the new town ''Alexandria'', in honor of Philip's family. As a result, Philip and his cousin Captain John Alexander (1711–1763) gave land to assist in the development of Alexandria and are thus listed as the founders. This John was the son of Robert Alexander II (1688–1735). On May 2, 1749, the House of Burgesses approved the river location and ordered "Mr. Washington do go up with a Message to the Council
A council is a group of people who come together to consult, deliberate, or make decisions. A council may function as a legislature, especially at a town, city or county/shire level, but most legislative bodies at the state/provincial or natio ...
and acquaint them that this House have agreed to the Amendments titled An Act for erecting a Town at Hunting Creek Warehouse, in the County of Fairfax." A "Public Vendue" (auction) was advertised for July, and the county surveyor laid out street lanes and town lots. The auction was conducted on July 13–14, 1749.
Almost immediately upon establishment, the town founders called the new town "Belhaven", believed to be in honor of a Scottish patriot, John Hamilton, 2nd Lord Belhaven and Stenton
John Hamilton, 2nd Lord Belhaven and Stenton (5 July 1656 – 21 June 1708) was a Scottish peer, landowner and politician.
Life
He was the eldest son of Robert Hamilton, Lord Presmennan (d. 1696). Having married Margaret, granddaughter of John H ...
, the Northern Neck tobacco trade being then dominated by Scots. The name Belhaven was used in official lotteries to raise money for a Church and Market House, but it was never approved by the legislature and fell out of favor in the mid-1750s. The town of Alexandria did not become incorporated until 1779.
In 1755, General Edward Braddock
Edward Braddock (January 1695 – 13 July 1755) was a British officer and commander-in-chief for the Thirteen Colonies during the start of the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the North American front of what is known in Europe and Canada as ...
organized his fatal expedition against Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne ( , ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed ...
at Carlyle House
Carlyle House is a historic mansion in Alexandria, Virginia, United States, built by Scottish merchant John Carlyle from 1751 to 1752 in the Georgian style.
It is situated in the city's Old Town at 121 North Fairfax Street between Cameron a ...
in Alexandria. In April 1755, the governors of Virginia, and the provinces of Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
met to determine upon concerted action against the French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
in America.
In March 1785, commissioners from Virginia and Maryland met in Alexandria to discuss the commercial relations of the two states, finishing their business at Mount Vernon
Mount Vernon is the former residence and plantation of George Washington, a Founding Father, commander of the Continental Army in the Revolutionary War, and the first president of the United States, and his wife, Martha. An American landmar ...
. The Mount Vernon Conference
The Mount Vernon Conference was a meeting of delegates from Virginia and Maryland held at Mount Vernon on March 21–28, 1785, to discuss navigational rights in the states' common waterways. On March 28, 1785, the group drew up a thirteen-point pr ...
concluded on March 28 with an agreement for freedom of trade and freedom of navigation of the Potomac River. The Maryland legislature, in ratifying this agreement on November 22, proposed a conference among representatives from all the states to consider the adoption of definite commercial regulations. This led to the calling of the Annapolis Convention of 1786, which in turn led to the calling of the Federal Convention of 1787.
As part of the District of Columbia
 In 1814, during the
In 1814, during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
, the British military
The British Armed Forces are the unified military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, support international peacekeeping e ...
carried out a successful raid on Alexandria, which surrendered without a fight. In order to avoid the town's destruction, twenty-two merchant ships and large quantities of flour
Flour is a powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredie ...
, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
, and sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
were handed over by Alexandria's municipal authorities to the British. In 1823 William Holland Wilmer
William Holland Wilmer (October 9, 1782 – July 24, 1827) was an Episcopal Church (USA), Episcopal priest, teacher and writer in Maryland and Virginia who served briefly as the eleventh president of the College of William and Mary.
Early lif ...
, Francis Scott Key
Francis Scott Key (August 1, 1779January 11, 1843) was an American lawyer, author, and poet from Frederick, Maryland, best known as the author of the poem "Defence of Fort M'Henry" which was set to a popular British tune and eventually became t ...
, and others founded the Virginia Theological Seminary
Virginia Theological Seminary (VTS), formally the Protestant Episcopal Theological Seminary in Virginia, is an Episcopal Church (United States), Episcopal seminary in Alexandria, Virginia. It is the largest and second-oldest such accredited se ...
. From 1828 to 1836, Alexandria was home to the Franklin & Armfield
Franklin may refer to:
People and characters
* Franklin (given name), including list of people and characters with the name
* Franklin (surname), including list of people and characters with the name
* Franklin (class), a member of a historica ...
Slave Market, one of the largest slave trading companies in the country. By the 1830s, they were sending more than 1,000 slaves annually from Alexandria to their Natchez, Mississippi
Natchez ( ) is the only city in and the county seat of Adams County, Mississippi, United States. The population was 14,520 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Located on the Mississippi River across from Vidalia, Louisiana, Natchez was ...
, New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
, and later Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
markets to help meet the demand for slaves in Mississippi and nearby states. Later owned by Price, Birch & Co., the slave pen
Slave markets and slave jails in the United States were places used for the slave trade in the United States from the founding in 1776 until the total abolition of slavery in 1865. ''Slave pens'', also known as slave jails, were used to temporar ...
became a jail under Union occupation.
A portion of the City of Alexandria—most of the area now known as Old Town
In a city or town, the old town is its historic or original core. Although the city is usually larger in its present form, many cities have redesignated this part of the city to commemorate its origins. In some cases, newer developments on t ...
as well as the areas of the city northeast of what is now King Street—and all of today's Arlington County
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the nati ...
share the distinction of having been the portion of Virginia ceded to the U.S. Government in 1791 to help form the new District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
. Over time, a movement grew to separate what was called "Alexandria County
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the national capital.
Arlington ...
" from the District of Columbia. As competition grew with the port of Georgetown and the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal
The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, abbreviated as the C&O Canal and occasionally called the Grand Old Ditch, operated from 1831 until 1924 along the Potomac River between Washington, D.C., and Cumberland, Maryland. It replaced the Patowmack Canal ...
fostered development on the north side of the Potomac River, Alexandria's economy stagnated; at the same time, residents had lost any representation in Congress and the right to vote and were disappointed with the negligible economic benefit (on the Alexandria side) of being part of the national capital. Alexandria still had an important port and market in the slave trade Slave trade may refer to:
* History of slavery - overview of slavery
It may also refer to slave trades in specific countries, areas:
* Al-Andalus slave trade
* Atlantic slave trade
** Brazilian slave trade
** Bristol slave trade
** Danish sl ...
, and as talk increased of abolishing slavery in the national capital, there was concern that Alexandria's economy would suffer greatly if this step were taken. After a referendum, voters petitioned Congress and Virginia to return the portion of the District of Columbia south of the Potomac River (Alexandria County) to Virginia. On July 9, 1846, Congress retroceded Alexandria County to Virginia. The City of Alexandria was re-chartered in 1852 and became independent of Alexandria County in 1870. The remaining portion of Alexandria County changed its name to Arlington County
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the nati ...
in 1920.
Late 19th century
 The first fatalities of the North and South in the
The first fatalities of the North and South in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
occurred in Alexandria. Within a month of the Battle of Fort Sumter
The Battle of Fort Sumter (also the Attack on Fort Sumter or the Fall of Fort Sumter) (April 12–13, 1861) was the bombardment of Fort Sumter near Charleston, South Carolina, by the South Carolina militia. It ended with the surrender of the ...
, the Civil War's first battle, Union Army troops occupied Alexandria, landing troops at the base of King Street on the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
on May 24, 1861. A few blocks up King Street from their landing site, the commander of the New York Fire Zouaves, Colonel Elmer E. Ellsworth, sortied with a small detachment to remove a large Confederate flag
The flags of the Confederate States of America have a history of three successive designs during the American Civil War. The flags were known as the "Stars and Bars", used from 1861 to 1863; the "Stainless Banner", used from 1863 to 1865; and ...
displayed on the roof of the Marshall House Inn that had been visible from the White House. While descending from the roof, Ellsworth was shot dead by James W. Jackson, the hotel's proprietor. One of Ellsworth's soldiers immediately killed Jackson.(1) (2)
Ellsworth was publicized as a Union martyr, and the incident generated great excitement in the North, with many children being named for him. Jackson's death defending his home caused a similar sensation in the South. Alexandria remained under military occupation until the end of the Civil War. Fort Ward, one of a ring of forts built by the Union army for the defense of
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, is located inside the boundaries of present-day Alexandria. There were five military prisons in the city, the largest being the Washington Street Military Prison. After the creation by Washington of the state of West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
in 1863 and until the close of the war, Alexandria was the seat of the so-called Restored Government of Virginia
The Restored (or Reorganized) Government of Virginia was the Unionist government of Virginia during the American Civil War (1861–1865) in opposition to the government which had approved Virginia's seceding from the United States and join ...
, also known as the "Alexandria Government". During the Union occupation, a recurring contention between the Alexandria citizenry and the military occupiers was the Union army's periodic insistence that church services include prayers for the President of the United States. Failure to do so resulted in incidents including the arrest of ministers in their church.
In 1861 and 1862, escaped African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
slaves poured into Alexandria. Safely behind Union lines, the cities of Alexandria and Washington offered comparative freedom and employment. Alexandria became a major supply depot and transport and hospital center for the Union army. Until the Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War. The Proclamation had the eff ...
of January 1, 1863, escaped slaves legally remained the property of their owners. Therefore, they were labeled contrabands to avoid returning them to their masters. Contrabands worked for the Union army in various support roles.
After all slaves in the seceding states were liberated, even more African Americans came to Alexandria. By the fall of 1863, the population of Alexandria had exploded to 18,000an increase of 10,000 people in 16 months.
As of ratification of the Fifteenth Amendment, Alexandria County's black population was more than 8,700, or about half the total number of residents in the county. This newly enfranchised constituency provided the support necessary to elect the first black Alexandrians to the City Council and the Virginia Legislature./ref> In the waning years of the 19th century, Alexandria suffered its two documented
lynching
Lynching is an extrajudicial killing by a group. It is most often used to characterize informal public executions by a mob in order to punish an alleged or convicted transgressor or to intimidate others. It can also be an extreme form of i ...
s. The first, in 1897, was Joseph H. McCoy and the second, in 1899, was Benjamin Thomas. Both were Black male teenagers accused, but never convicted, of assaulting young white girls that were known to them. They were both kidnapped from jail and hanged by mobs.
20th century
At the turn of the 20th century the most common production in the city was glass, fertilizer, beer, and leather. The glass often went into beer bottles. Much of the Virginia Glass Company effort went to supply the demands of the Robert Portner Brewing Company, until fire destroyed the St. Asaph Street plant on February 18, 1905. The Old Dominion Glass Company also had a glass works fall to fire, then built a new one. The Belle Pre Bottle Company held a monopoly on amilk bottle
From the second half of the 19th century, milk has been packaged and delivered in Reusable packaging, reusable and returnable glass bottles. They are used mainly for doorstep delivery of fresh milk by milkman, milkmen. Once customers have f ...
that they patented, yet that organization only lasted 10 years. Most businesses were smaller where the business occupied the first floor of a building and the owner and family lived above. Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
closed Portner Brewing in 1916.
President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
visited the Virginia Shipbuilding Corporation on May 30, 1918, to drive the first rivet into the keel of the . In 1930, Alexandria annexed the town adjacent to Potomac Yard
Potomac Yard is a neighborhood in Northern Virginia that straddles southeastern Arlington County and northeastern Alexandria, Virginia, located principally in the area between U.S. Route 1 and the Washington Metro Blue Line / Yellow Line tr ...
incorporated in 1908 named Potomac. In 1938 the Mt. Vernon Drive-In cinema opened. In 1939, the segregated public library experienced a sit-in
A sit-in or sit-down is a form of direct action that involves one or more people occupying an area for a protest, often to promote political, social, or economic change. The protestors gather conspicuously in a space or building, refusing to mo ...
organized by Samuel Wilbert Tucker
Samuel Wilbert Tucker (June 18, 1913 – October 19, 1990) was an American lawyer and a cooperating attorney with the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP). His civil rights career began as he organized a 1939 sit-in ...
. In 1940, both the Robert Robinson Library, which is now the Alexandria Black History Museum
The Alexandria Black History Museum, located at 902 Wythe St., Alexandria, Virginia, is operated by the City of Alexandria. The building was formerly the Robert Robinson Library, originally constructed in 1940 as the first "separate but equal" libr ...
, and the Vernon Theatre opened Jim Morrison
James Douglas Morrison (December 8, 1943 – July 3, 1971) was an American singer, songwriter, and poet who was the lead vocalist and primary lyricist of the rock band the Doors. Due to his charismatic persona, poetic lyrics, distinctive vo ...
of The Doors
The Doors were an American rock band formed in Los Angeles in 1965, comprising vocalist Jim Morrison, keyboardist Ray Manzarek, guitarist Robby Krieger and drummer John Densmore. They were among the most influential and controversial rock acts ...
, as well as Cass Elliot
Ellen Naomi Cohen (September 19, 1941 – July 29, 1974), known professionally as Cass Elliot, was an American singer. She was also known as "Mama Cass", a name she reportedly disliked. Elliot was a member of the singing group the Mamas & the P ...
and John Phillips of The Mamas & The Papas
The Mamas & the Papas were an American folk rock vocal group that recorded and performed from 1965 to 1968, with a brief reunion in 1971. The group was a defining force in the music scene of the counterculture of the 1960s. Formed in New York C ...
attended the George Washington High School in the 1950s.
In 1955, then- Representative and future President Gerald R. Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. (born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was the 38th president of the United States, serving from 1974 to 1977. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, Ford assumed the p ...
and his family moved to Alexandria from Georgetown. The Fords remained in their Alexandria home during Ford's tenure as Vice President
A vice president or vice-president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vi ...
(1973–1974), as the vice president did not yet have an official residence. Following the resignation of Richard Nixon, Ford spent his first 10 days as President in the house before moving to the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest (Washington, D.C.), NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president ...
.
In March 1959, Lieutenant Colonel William Henry Whalen
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is ...
, the "highest-ranking American ever recruited as a mole
Mole (or Molé) may refer to:
Animals
* Mole (animal) or "true mole"
* Golden mole, southern African mammals
* Marsupial mole
Marsupial moles, the Notoryctidae family, are two species of highly specialized marsupial mammals that are found i ...
by the Russian Intelligence Service
The Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation �СБ, ФСБ России (FSB) is the principal security agency of Russia and the main successor agency to the Soviet Union's KGB; its immediate predecessor was the Federal Counteri ...
", provided Colonel Sergei A. Edemski three classified
Classified may refer to:
General
*Classified information, material that a government body deems to be sensitive
*Classified advertising or "classifieds"
Music
*Classified (rapper) (born 1977), Canadian rapper
* The Classified, a 1980s American ro ...
Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
manuals in exchange for $3,500 at a shopping center parking lot within the city. Agents of the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
later arrested Whalen on July 12, 1966, at his home in the city. In 1961 the original Woodrow Wilson Bridge
The Woodrow Wilson Memorial Bridge, also known as the Woodrow Wilson Bridge or the Wilson Bridge, is a bascule bridge that spans the Potomac River between Alexandria, Virginia and Oxon Hill, Maryland in Prince George's County, Maryland. The ...
opened.
In 1965, the city integrated schools. In 1971, the city consolidated all high school junior and senior students into T. C. Williams High School. Freshman and sophomore students were assigned to attend either Francis C Hammond or George Washington, formerly four-year high schools, as part of a system-wide overhaul of the public school system, beginning with kindergarten classes, in an attempt to racially "balance" student population throughout the city's public schools to better reflect the city's racial makeup. The plan was known as the "K-6, 2, 2, 2 plan". Classes were broken out, beginning with kindergarten through sixth grade; then seventh through eighth; then freshman and sophomore classes; and finally junior and senior classes, with the changes including being moved to a different school building. The same year that head coach Herman Boone
Herman Ike Boone (October 28, 1935 – December 18, 2019) was an American high school football coach who coached the 1971 T. C. Williams High School football team to a 13–0 season, state championship, and national runner-up. That season late ...
joined the school and lead the football team to a 13–0 season, a state championship, and a national championship runner-up; the basis for the 2000 film ''Remember the Titans
''Remember the Titans'' is a 2000 American biographical sports drama film produced by Jerry Bruckheimer and directed by Boaz Yakin. The screenplay by Gregory Allen Howard is loosely based on the true story of coach Herman Boone, portrayed b ...
'' where Boone was portrayed by Denzel Washington
Denzel Hayes Washington Jr. (born December 28, 1954) is an American actor, producer, and director. Known for his dramatic roles Denzel Washington on screen and stage, on stage and screen, Washington has received List of awards and nominations ...
.
In 1972, Clifford T. Cline purchased the 1890 Victorian
Victorian or Victorians may refer to:
19th century
* Victorian era, British history during Queen Victoria's 19th-century reign
** Victorian architecture
** Victorian house
** Victorian decorative arts
** Victorian fashion
** Victorian literatur ...
house at 219 King Street and converted it into the Creole serving Two-Nineteen Restaurant. In 1973, Nora Lamborne and Beverly Beidler became the first women elected to the city council. In 1974, the Torpedo Factory Art Center
The Torpedo Factory Art Center is the former U.S. Naval Torpedo Station, a naval munitions factory on the banks of the Potomac River in Old Town, Alexandria, Virginia which was converted into an art center in 1974. The facility is located at 1 ...
opened. In 1983, the King Street–Old Town station
King Street–Old Town station (also known by its former name, King Street) is a Washington Metro station in Alexandria, Virginia, United States. The station opened on December 17, 1983, and is operated by the Washington Metropolitan Area Transi ...
, Braddock Road station, and Eisenhower Avenue station
Eisenhower Avenue station is a rapid transit station on the Yellow Line of the Washington Metro in Alexandria, Virginia. It opened on December 17, 1983.
Location
The station is located at Eisenhower Avenue near Stovall Street, next to the C ...
opened as the Washington Metro
The Washington Metro, often abbreviated as the Metro and formally the Metrorail, is a rapid transit system serving the Washington metropolitan area of the United States. It is administered by the Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority ...
system expanded. In 1991, the Van Dorn Street station
Van Dorn Street station is a Washington Metro station straddling the boundary between Fairfax County and the independent city of Alexandria in Virginia, United States. The station's island platform lies in unincorporated Rose Hill in Fairfax ...
opened and Patricia Ticer became the first woman to be elected mayor.
21st century
 Until 2014, local legislation mandated that all new north–south streets in the city be named for Confederate military leaders. Efforts have increased in recent years to expedite the renaming of these streets with Mayor Justin Wilson and the City Council setting a goal of renaming three of these streets annually. In 2019, the name of U.S. 1 was changed from
Until 2014, local legislation mandated that all new north–south streets in the city be named for Confederate military leaders. Efforts have increased in recent years to expedite the renaming of these streets with Mayor Justin Wilson and the City Council setting a goal of renaming three of these streets annually. In 2019, the name of U.S. 1 was changed from Jefferson Davis Highway
The Jefferson Davis Highway, also known as the Jefferson Davis Memorial Highway, was a transcontinental highway in the United States in the 1910s and 1920s that began in Arlington County, Virginia, and extended south and west to San Diego, Cali ...
to Richmond Highway.
In November 2020, the school board unanimously voted to rename T. C. Williams High School and Matthew Maury Elementary School. The high school was renamed Alexandria City High School and Maury Elementary was renamed Naomi L. Brooks Elementary School, effective July 1, 2021.
In December 2023, Virginia Governor Glenn Youngkin
Glenn Allen Youngkin (born December 9, 1966) is an American politician and businessman serving as the 74th governor of Virginia since 2022. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he spent 25 years at the Private equi ...
and Monumental Sports & Entertainment
Monumental Sports & Entertainment (MSE) is an American sports management, sports and venue management company founded by Ted Leonsis in June 2010. Monumental owns and operates the NHL team Washington Capitals, the NBA team Washington Wizards, t ...
founder Ted Leonsis
Theodore John Leonsis (born January 8, 1957) is an American businessman. He is a former senior executive with America Online (AOL) and the founder, chairman, and CEO of Monumental Sports & Entertainment, which owns the NHL's Washington Capitals, ...
announced plans to develop a 70-acre area in Potomac Yards to include a concert venue, businesses, and a new arena that would have been home to the Washington Capitals
The Washington Capitals (colloquially known as the Caps) are a professional ice hockey team based in Washington, D.C. The Capitals compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division in the Eastern Conference (NH ...
and Washington Wizards. The proposal failed in March 2024 with the announcement Virginia negotiations were ending and Monumental planning to sign an additional lease with Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
after it did not advance in the Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, and the first elected legislative assembly in the New World. It was established on July 30, ...
.
Geography
 According to the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which is land and , or 2.85%, is water. Alexandria is bounded on the east by the
According to the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which is land and , or 2.85%, is water. Alexandria is bounded on the east by the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
(which forms the boundary between the city and Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
and Prince George's County, Maryland), on the north and northwest by Arlington County, and on the south by Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous county in Virginia, the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington ...
. The western portions of the city were annexed from those two entities beginning in the 1930s.
The address (geography), addressing system in Alexandria is not uniform and reflects the consolidation of several originally separate communities into a single city. In Old Town Alexandria, building numbers are assigned north and south from King Street (Alexandria, Virginia), King Street and west (only) from the Potomac River. In the areas formerly in the town of Potomac, such as Del Ray and St. Elmo, building numbers are assigned east and west from Commonwealth Avenue and north (only) from King Street. In the western parts of the city, building numbers are assigned north and south from Virginia State Route 236, Duke Street.
The ZIP Code prefix 223 uniquely identifies the Alexandria postal area. However, the Alexandria postal area extends into Fairfax County and includes addresses outside of the city. Delivery areas have ZIP Codes 22301, 22302, 22303, 22304, 22305, 22306, 22307, 22308, 22309, 22310, 22311, 22312, 22314, and 22315, with other ZIP Codes in use for post office boxes and large mailers (22313, 22331, 22332, 22333).
Part of the George Washington Memorial Parkway is the one national protected area within the borders of Alexandria.
Neighborhoods and planning areas
As of 2024, the City of Alexandria is divided into 19 "Small Area Plans" and 11 additional overlapping plans. These areas and their component neighborhoods include: Many areas outside the city have an Alexandria mailing address yet are a part ofFairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous county in Virginia, the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington ...
including: Hollin Hills, Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franco ...
, Groveton, Virginia, Groveton, Hybla Valley, Huntington, Virginia, Huntington, Lincolnia, Virginia, Lincolnia, Belle Haven, Fairfax County, Virginia, Belle Haven, Mount Vernon, Virginia, Mount Vernon, Fort Hunt, Virginia, Fort Hunt, Engleside, Burgundy Village, Waynewood, Wilton Woods, Rose Hill, Fairfax County, Virginia, Rose Hill, Virginia Hills, Hayfield, Fairfax County, Virginia, Hayfield, and Kingstowne. Some refer to these areas as Lower Alexandria, South Alexandria, or Alexandria, Fairfax County.
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen climate classification system, Alexandria has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.Demographics
2020 census
2010 census
At the 2010 census, there were 139,966 people, 68,082 households and 30,978 families residing in the city. The population density was . There were 68,082 housing units at an average density of . The racial/ethnic mix of the population was: * 60.9% White Americans, White * 21.8% African Americans, African American * 6.0% Asian Americans, Asian (1.3% Indian Americans, Indian, 1.0% Filipino Americans, Filipino, 0.9% Chinese Americans, Chinese, 0.8% Korean Americans, Korean, 0.5% Thai Americans, Thai, 0.3% Vietnamese Americans, Vietnamese, 0.2% Japanese Americans, Japanese, 1.0% Other) * 0.4% Native Americans in the United States, Native American * 0.1% Pacific Islands Americans, Pacific Islander * 3.7% from Multiracial Americans, two or more races * 16.1% of the population were Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanics or Latinos of any national origin (4.6% Salvadoran Americans, Salvadoran, 1.7% Mexican Americans, Mexican, 1.6% Honduran Americans, Honduran, 1.1% Guatemalan Americans, Guatemalan, 1.1% Puerto Ricans, Puerto Rican, 0.9% Bolivian Americans, Bolivian, 0.8% Peruvian Americans, Peruvian, 0.4% Colombian Americans, Colombian) In 2000, there were 61,889 households, of which 18.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 32.2% were Marriage, married couples living together, 9.2% had a female householder with no husband present, and 55.2% were non-families. 43.4% of all households were made up of individuals, and 6.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.04 and the average family size was 2.87. The age distribution was 16.8% under the age of 18, 9.2% from 18 to 24, 43.5% from 25 to 44, 21.5% from 45 to 64, and 9.0% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females, there were 93.5 males. For every 100 females aged 18 and over, there were 91.7 males. According to 2019 United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau data, the median household income was $103,284 and median family income was $130,395. Additionally, 8.6% of the population of the population were below the poverty line. 14.2% of those under the age of 18 and 3.1% of those 65 and older were living below the poverty line. According to 2022 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates, 69.9% of Alexandria residents aged 25 and older have attained a bachelor's degree or higher, compared with 42.2% statewide.Economy
 Companies headquartered in Alexandria include Crooked Beat Records, Five Guys, the
Companies headquartered in Alexandria include Crooked Beat Records, Five Guys, the Institute for Defense Analyses
The Institute for Defense Analyses (IDA) is an American non-profit corporation that administers three federally funded research and development centers (FFRDCs) – the Systems and Analyses Center (SAC), Science and Technology Policy Institute, t ...
(IDA), The Motley Fool, Oblon law firm, Pentagon Federal Credit Union (PenFed), Port City Brewing Company, Purple Strategies, ThinkFun, and VSE Corporation, VSE. Several federal agencies are based in Alexandria, including the National Credit Union Administration, United States Patent and Trademark Office, National Science Foundation, Office of the Inspector General, U.S. Department of Defense, and the Food and Nutrition Service. The Department of Defense Education Activity (DoDEA), the federal school system for military dependents, is headquartered in Alexandria.
Alexandria is home to many Charitable organization, charities and Nonprofit organization, non-profit organizations including the national headquarters of Catholic Charities, USA, Catholic Charities, Citizens for the Republic, Global Impact, Good360, International Centre for Missing & Exploited Children, Islamic Relief USA, United Way of America, United Way, and Volunteers of America. Trade associations located in the city include the American Counseling Association, the Professional in Human Resources, Human Resource Certification Institute, the Society for Human Resource Management, the National Society of Professional Engineers, the National Beer Wholesalers Association, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, National Industries for the Blind, American Physical Therapy Association, the National Association of Convenience Stores, and the American International Automobile Dealers Association. Alexandria also has a Chamber of commerce, Chamber of Commerce and other business associations including the West End Business Association, the Del Ray Business Association and the Old Town Business Association.
 Major employment sectors in Alexandria include management consulting, business and finance, office and administrative support, computer and mathematical, sales, and legal. Jobs in Alexandria are highly concentrated around the city's Washington Metro, Metrorail stations, primarily in Old Town North and the Braddock Road (Alexandria, Virginia), Braddock Road area, Old Town, and Carlyle near the
Major employment sectors in Alexandria include management consulting, business and finance, office and administrative support, computer and mathematical, sales, and legal. Jobs in Alexandria are highly concentrated around the city's Washington Metro, Metrorail stations, primarily in Old Town North and the Braddock Road (Alexandria, Virginia), Braddock Road area, Old Town, and Carlyle near the Eisenhower Avenue station
Eisenhower Avenue station is a rapid transit station on the Yellow Line of the Washington Metro in Alexandria, Virginia. It opened on December 17, 1983.
Location
The station is located at Eisenhower Avenue near Stovall Street, next to the C ...
, as well as along the I-395 corridor on the west side of the city.
13% of people that work in Alexandria live in the city, while 87% commute in, with 37% of those commuters being from Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous county in Virginia, the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington ...
. An additional 61,000 people commute out of Alexandria to work. 35% commute to Washington, D.C., and 29% commute to Fairfax County. As of March 2024, 2.0% of Alexandria residents are unemployed.
Culture

Events
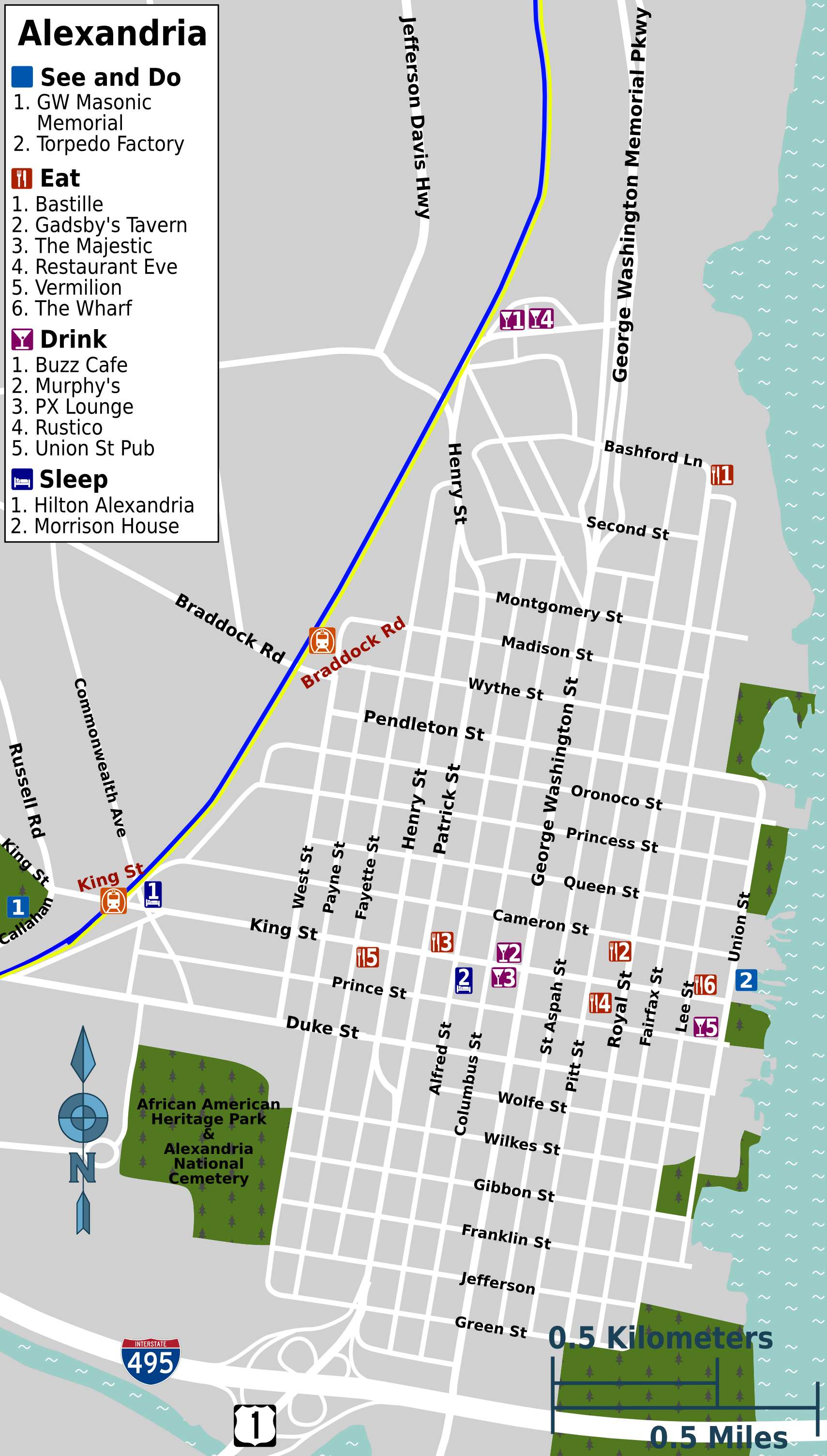
A popular Christmas time attraction in Alexandria is the Scottish Christmas Walk, which was established in 1969. The event, which involves a parade through the center of Old Town Alexandria, celebrates the city's Scottish Americans, Scottish heritage, and is the centerpiece of a yearly holiday festival. It serves as a fundraiser for social services in Alexandria. Other parades in Old Town celebrate Saint Patrick's Day and the Washington's Birthday, birthday of George Washington. Other annual events include the Red Cross Waterfront Festival in June, the city's birthday celebration with fireworks show in July, various ethnic heritage days at Tavern Square, and "First Night Alexandria" on New Year's Eve. These parades and other official events are typically led by Alexandria's town crier, who, often dressed in elaborately, by a tradition dating to the 18th century, in a Red coat (military uniform), red coat, breeches, black boots and a tricorne hat, welcomes participants.Sites of Interest
Landmarks within the city include the George Washington Masonic National Memorial (also known as the Freemasonry, Masonic Temple) and Observation Deck, Christ Church (Alexandria, Virginia), Christ Church, Gadsby's Tavern, Stabler-Leadbeater Apothecary Shop, John Carlyle House, Lee-Fendall House, Robert E. Lee's boyhood home, and the Alexandria City Hall with the adjacent Market Square. Other sites of historical interest in the city include Fort Ward (Virginia), Fort Ward Park and Museum, Phoenix Mill (Virginia), Phoenix Mill, and the Alexandria Canal lock re-creation at Canal Office Center. TheAlexandria Black History Museum
The Alexandria Black History Museum, located at 902 Wythe St., Alexandria, Virginia, is operated by the City of Alexandria. The building was formerly the Robert Robinson Library, originally constructed in 1940 as the first "separate but equal" libr ...
, Alexandria Archaeology Museum, and the Lyceum (Alexandria, Virginia), Lyceum display various aspects of the city's history.
The Torpedo Factory Art Center
The Torpedo Factory Art Center is the former U.S. Naval Torpedo Station, a naval munitions factory on the banks of the Potomac River in Old Town, Alexandria, Virginia which was converted into an art center in 1974. The facility is located at 1 ...
, located on the Old Town
In a city or town, the old town is its historic or original core. Although the city is usually larger in its present form, many cities have redesignated this part of the city to commemorate its origins. In some cases, newer developments on t ...
waterfront, is a former torpedo factory that now serves as an art center filled with independent art studios and exhibits. The Athenaeum (Alexandria, Virginia), Athenaeum is another center for the arts. Also located in Old Town is Little Theatre of Alexandria, a community theatre at 600 Wolfe Street. South of Old Town on the Potomac River is the Jones Point Light and the nearby List of Boundary Markers of the Original District of Columbia, south cornerstone of the original District of Columbia. Immediately west of Old Town is the United States Patent and Trademark Office which includes the ''National Inventors Hall of Fame Museum''. The Birchmere is a concert hall that features musical acts as well as ethnic and comedic performers. Site of interests with Alexandria addresses but located outside of the city include River Farm, Collingwood Library & Museum, Green Spring Gardens Park, Huntley Meadows Park, Historic Huntley, Pope-Leighey House (designed by Frank Lloyd Wright), Woodlawn (Alexandria, Virginia), Woodlawn Plantation, and George Washington's Grist Mill and Mount Vernon
Mount Vernon is the former residence and plantation of George Washington, a Founding Father, commander of the Continental Army in the Revolutionary War, and the first president of the United States, and his wife, Martha. An American landmar ...
Estate.
In 1830, John Hollensbury's home in Alexandria was one of two homes directly bordering an alleyway that received a large amount of Horse-drawn vehicle, horse-drawn wagon traffic and loiterers. In order to prevent people from using the alleyway, Hollensbury constructed a wide, deep, , two-story home using the existing brick walls of the adjacent homes for the sides of the new home. The brick walls of the Hollensbury Spite House living room have gouges from wagon-wheel hubs; the house is still standing, and is occupied.
The Oswald Durant Center in the Upper King Street neighborhood of the Old Town is named after Dr. Oswald Durant, one of the first African American doctors in Alexandria.
Media
Alexandria has two local weekly newspapers: the Alexandria Gazette Packet and the Alexandria Times. The Alexandria Gazette was once published in the city from 1834 to 1974.Sports
The city is home to the Alexandria Aces of the Cal Ripken Sr. Collegiate Baseball League. The team's home field is Frank Mann Field. Alexandria had previously been home of one professional sports team, the Alexandria Dukes, a minor league baseball team which moved to Woodbridge, Virginia, Woodbridge in 1984 to become Potomac Nationals, The Prince William Pirates (now known as the Fredericksburg Nationals).Parks and recreation
 Alexandria has over of protected open space with 566 acres of city-owned park land and 11 recreation centers, of which Castanea pumila, Chinquapin is one of the largest. Chinquapin offers facilities for swimming, tennis, racquetball, and other sports. Additionally, on March 19th, 2024 a year round recreation center opened inside of the Minnie Howard campus of Alexandria City High School, with a competition size swimming pool and a therapeutic training pool. The city also organizes several sports leagues throughout the year including volleyball, softball and basketball.
The city is home to Cameron Run Regional Park, operated by NOVA Parks, which includes a water park, a miniature golf course, and batting cages. NOVA Parks also operates the Winkler Botanical Preserve in the city's Neighborhoods in Alexandria, Virginia#West End, West End. A portion of the Mount Vernon Trail, a popular bike and jogging path, runs through Old Town near the Potomac River on its way from the
Alexandria has over of protected open space with 566 acres of city-owned park land and 11 recreation centers, of which Castanea pumila, Chinquapin is one of the largest. Chinquapin offers facilities for swimming, tennis, racquetball, and other sports. Additionally, on March 19th, 2024 a year round recreation center opened inside of the Minnie Howard campus of Alexandria City High School, with a competition size swimming pool and a therapeutic training pool. The city also organizes several sports leagues throughout the year including volleyball, softball and basketball.
The city is home to Cameron Run Regional Park, operated by NOVA Parks, which includes a water park, a miniature golf course, and batting cages. NOVA Parks also operates the Winkler Botanical Preserve in the city's Neighborhoods in Alexandria, Virginia#West End, West End. A portion of the Mount Vernon Trail, a popular bike and jogging path, runs through Old Town near the Potomac River on its way from the Mount Vernon
Mount Vernon is the former residence and plantation of George Washington, a Founding Father, commander of the Continental Army in the Revolutionary War, and the first president of the United States, and his wife, Martha. An American landmar ...
Estate to Theodore Roosevelt Island, Roosevelt Island in Washington, D.C. There is also a largely unbroken line of parks stretching along the Alexandria waterfront.
Government
 As an Independent city (Virginia), independent city of Virginia (as opposed to an incorporated town within a county), Alexandria derives its governing authority from the
As an Independent city (Virginia), independent city of Virginia (as opposed to an incorporated town within a county), Alexandria derives its governing authority from the Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, and the first elected legislative assembly in the New World. It was established on July 30, ...
using the Dillon Rule. In order to revise the power and structure of the city government, the city must request the General Assembly to amend the charter. The present charter was granted in 1950 and it has been amended in 1968, 1971, 1976, and 1982.
Alexandria adopted a council-manager form of government by way of referendum in 1921. This type of government empowers the elected City Council to pass legislation and appoint the City Manager. The City Manager is responsible for overseeing the city's administration.
The Mayor, who is chosen on a separate ballot, presides over meetings of the Council and serves as the ceremonial head of government. The Mayor does not have the power to veto Council action. Council members traditionally choose the person receiving the most votes in the election to serve as Vice Mayor. In the absence or disability of the Mayor, the Vice Mayor performs the mayoral duties.
In 2024, the city has 55 boards and commissions to advise the City Council on major issues affecting the community. The majority of members are appointed by the City Council. In addition, Alexandria City Public Schools has a school board with nine members. Three are elected from each of the city's three school board districts.
Alexandria has a Virginia Circuit Court, circuit court and a Virginia General District Court, general district court. The city also has a Virginia Juvenile and Domestic Relations District Court, juvenile and domestic relations district court. All of these courts are located in the Alexandria Courthouse at 520 King Street. The city is also the site of the Alexandria Division of the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Virginia.
In the Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, and the first elected legislative assembly in the New World. It was established on July 30, ...
, Alexandria is represented in the Virginia House of Delegates, House of Delegates as part of the Virginia's 3rd House of Delegates district, 3rd district, Virginia's 4th House of Delegates district, 4th district, and Virginia's 5th House of Delegates district, 5th district. In the Virginia Senate, the city is represented as part of the Virginia's 39th Senate district, 39th district. At the federal level, Alexandria is part of Virginia's 8th congressional district, represented by Democrat and Alexandria resident Don Beyer, elected in 2014. The state's senior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Mark Warner, first elected in 2008. The state's junior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Tim Kaine, first elected in 2012.
History
Since its foundation, Alexandria's government has had several different forms of government. Before 1921, Alexandria had an elected eight-member Board of Aldermen and a sixteen-member Common Council whose members were elected by ward. In addition, there was an elected mayor with the power to veto legislation from the two councils. Reformers within the city during the early 20th century hoped to adopt the then-popular council-manager system. As a means to implementing this new system, the reformists proposed a plan to create a single city council elected at-large. This new system was adopted in 1921 and the first at-large councilmen were elected in June 1922. In 1930, Alexandria annexed the town of Potomac fromArlington County
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the nati ...
. Alexandria and Potomac stood in stark contrast. The streetcar suburb commuter town of Potomac had, as part of Arlington, been heavily influenced by the anti-vice crusades of staunch Progressivism in the United States, progressive District attorney, Commonwealth's Attorney Crandal Mackey. In Potomac, slaughterhouses and saloons were banned. Residents of the former town of Potomac had a different identity from those in Alexandria, and after annexation former Potomac residents began to push for the reimplementation of the ward system. In a 1932 referendum, voters decided in favor of a new plan that would expand the city council to nine members; three elected at-large and six elected by ward. Support for the new plan was highest in the former town of Potomac.
City councils elected under the new ward system began to take a more direct role in city administration. The city council and city manager gave conflicting orders to city employees while spending increased to accommodate appropriations coming from both the council and manager. With over one million dollars spent on unauthorized projects, a movement to go back to at-large councilmen emerged. In 1944, a referendum to eliminate the ward system ended with a vote in favor of the ward system. Shortly afterwards, a number of high-ranking city officials resigned, and residents appealed to the Circuit Court for an order to force a referendum. Unbeknownst to the city government, Delegate Armistead L. Boothe, Armistead Boothe introduced a bill in Richmond to hold another referendum. This bill passed the General Assembly and a vote was held on March 2, 1948. The options in the referendum included retaining the extant system or replacing it with a council of seven at-large members. Voters approved the new system with 61% of votes in favor. More recently, a 1983 push by the Virginia NAACP to return to the ward system failed because of a lack of support from elected officials.
Ecocity
In 2008 the City Council approved a charter where "citizens, businesses, and city government participate in a vibrant community that is always mindful of the needs and lifestyles of the generations to come". That charter defined sustainability as "meeting our community's present needs while preserving our historic character and ensuring the ability of future generations to meet their own needs". An Eco-cities, ecocity is defined as "an ecologically healthy city". In 2022, Alexandria enacted a 5-cent Plastic bag ban, plastic bag tax consistent with the phase-out of lightweight plastic bags in the United States.Public safety
Alexandria's primary law enforcement is the Alexandria Police Department (APD) which is led by a Chief of police, Chief of Police who is appointed by city government. In April 2022, Don Hayes was appointed as Chief of Police. As of 2023, the APD employs roughly 300 officers that receive training at the Northern Virginia Criminal Justice Training Academy. Every four years, Alexandria residents elect a sheriff that leads the Sheriff's Office in overseeing roughly 200 deputies and a Alexandria City Jail, detention center for pre-trial and short-term inmates. This jail is used to house pre-trial inmates in federal espionage cases. The Alexandria Fire Department is the city's fire protection and emergency medical services provider and is led by Fire/EMS Chief Corey A. Smedley. The AFD operates 10 stations throughout the city and employs over 300 fire and EMS professionals.Education
Colleges and universities
Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Virginia Tech's Washington-Alexandria Architecture Center, also known as WAAC, is located on Prince Street in Old Town, offering graduate programs in Urban Affairs and Planning, Public and International Affairs, Architecture, and Landscape Architecture. In 2018, Virginia Tech announced the construction of an "Innovation Campus" in Potomac Yard with graduate programs in computer science and computer engineering. Virginia Commonwealth University operates a Northern Virginia branch of its School of Social Work and The George Washington University also has a campus near the station. This campus mainly offers professional and vocational programs, such as an executive MBA program, urban planning and security studies. The city also has a campus of the Northern Virginia Community College. The largest seminary in the Episcopal Church in the United States of America, Episcopal Church,Virginia Theological Seminary
Virginia Theological Seminary (VTS), formally the Protestant Episcopal Theological Seminary in Virginia, is an Episcopal Church (United States), Episcopal seminary in Alexandria, Virginia. It is the largest and second-oldest such accredited se ...
, is located on Seminary Road.
Primary and secondary schools
The city is served by the Alexandria City Public Schools system. Alexandria's public school system consists of twelve elementary schools for grades Kindergarten through 5th grade, with three of them also offering Pre-kindergarten, Pre-K. Two schools, Patrick Henry and Jefferson-Houston, are Pre-K through 8th grade schools while the middle schools, George Washington and Francis C. Hammond, serve 6th through 8th graders. Minnie Howard Ninth Grade Center serves 9th graders while the Alexandria City High School serves 10th through 12th for the entire city. The demographics of the public school system contrast with those of the city. In 2008, only 14% of the students at Francis C. Hammond Middle School were non-Hispanic whites, compared to about 60% when looking at the city as a whole. 27% were of Hispanic descent, and 48% were black. About 9% of the school was of Asian descent. In 2004, 62% of school-going children received National School Lunch Act, free lunches; by 2008, that number had decreased to 56%. At George Washington Middle School, 41% of students are non-Hispanic whites, 34% were Hispanic, 21% was black, and 2% of the students were Asian; 52% of students received free lunch. Alexandria City High School follows this trend as well; 23% of the students were classified as non-Hispanic whites, 25% as Hispanic, 44% as black, and 7% of the school was Asian; 47% of all students received free lunch. Alexandria is home to private schools such as St. Stephen's and St. Agnes School, Bishop Ireton High School, and Episcopal High School (Alexandria, Virginia), Episcopal High School. Also in the city are Alexandria Country Day School, Commonwealth Academy, the Basilica School of Saint Mary, St. Rita's Catholic School, Blessed Sacrament School, and Global Health College.Infrastructure
Healthcare
Alexandria is served by Inova Alexandria Hospital. The city's health department operates a clinic, health clinic at Mark Center in the city's Neighborhoods of Alexandria, Virginia#West End, West End and a teen wellness center at Alexandria City High School.Transportation
Concurrency (road), Concurrent highways Interstate 95 in Virginia, I-95 and I-495 (the Capital Beltway), including theWoodrow Wilson Bridge
The Woodrow Wilson Memorial Bridge, also known as the Woodrow Wilson Bridge or the Wilson Bridge, is a bascule bridge that spans the Potomac River between Alexandria, Virginia and Oxon Hill, Maryland in Prince George's County, Maryland. The ...
over the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
, roughly parallels the city's southern boundary with Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous county in Virginia, the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington ...
before very briefly passing through D.C. and entering Maryland. Interstate 395 (Virginia-District of Columbia), I-395 crosses north and south through the western part of the city. Alexandria is bisected east and west by Virginia State Route 7, SR 7 (King Street (Alexandria, Virginia), King Street). The most western section of King Street in the city was once the terminus of the Leesburg Turnpike. SR 7 terminates at Virginia State Route 400, SR 400 (Washington Street), which connects the northern and southern segments of the George Washington Memorial Parkway. Virginia State Route 236, SR 236 (Duke Street) runs east–west along the southern side of the city, also terminating at VA 400 in Old Town. Other primary state highways serving Alexandria include the short Limited-access road, limited-access Virginia State Route 241, SR 241 (Telegraph Road), as well as multiple thoroughfares serving the western side of the city, which are Virginia State Route 401, SR 401 (Van Dorn Street), Virginia State Route 402, SR 402 (Quaker Lane), and Virginia State Route 420, SR 420 (Seminary Road in the west, Janneys Lane in the east). U.S. Route 1 in Virginia, US 1 (Richmond Highway) passes north–south through the city, parallel and west of Washington Street and the George Washington Memorial Parkway. Through Old Town, the highway follows Patrick and Henry streets.
The Alexandria city government operates its own Public transport, mass transit system, the DASH (bus), DASH bus, connecting points of interest with local transit hubs. Since 2021, DASH is Free public transport, fare-free. DASH also offers a "trolley" diesel bus service on King Street from the Metro station to the Waterfront. Metrobus (Washington, D.C.), Metrobus also serves Alexandria along with Washington Metro, Metrorail's Blue Line (Washington Metro), Blue and Yellow Line (Washington Metro), Yellow Lines with stops at , , King Street-Old Town, , and . Hornblower Cruises operates the Potomac Water Taxi to and from Georgetown and The Wharf (Washington, D.C.), The Wharf development in D.C. and the National Harbor development in Prince George's County, Maryland, Prince George's County.
 Alexandria Union Station, Union Station, the city's historic train station, has Amtrak intercity services and the Virginia Railway Express regional rail service. The station is directly adjacent to the King Street–Old Town Metro station. The traditional boundary between Old Town and the latterly annexed sections of the city follows the railway acquired by Virginia in 2021 and formerly owned by CSX Transportation. In addition, Norfolk Southern Railway operates a Rail freight transport, freight rail line and a Transloading, transload terminal in the city.
Capital Bikeshare, a Bicycle-sharing system, bicycle-sharing public transportation system, launched in Alexandria in 2012. The system has 62 rental locations throughout the city. The East Coast Greenway and Mount Vernon Trail cycle routes pass through Alexandria.
Alexandria Union Station, Union Station, the city's historic train station, has Amtrak intercity services and the Virginia Railway Express regional rail service. The station is directly adjacent to the King Street–Old Town Metro station. The traditional boundary between Old Town and the latterly annexed sections of the city follows the railway acquired by Virginia in 2021 and formerly owned by CSX Transportation. In addition, Norfolk Southern Railway operates a Rail freight transport, freight rail line and a Transloading, transload terminal in the city.
Capital Bikeshare, a Bicycle-sharing system, bicycle-sharing public transportation system, launched in Alexandria in 2012. The system has 62 rental locations throughout the city. The East Coast Greenway and Mount Vernon Trail cycle routes pass through Alexandria.
Notable people

 *Diedrich Bader, actor
* Hannibal Brumskine III, internet entrepreneur
* Sandor Bustamante, soccer player
* Stewart Copeland, drummer for The Police
* Leon Day, Hall of Fame baseball pitcher who played in the Negro league baseball, Negro leagues
* Elena Delle Donne, forward-guard, Washington Mystics, WNBA champion, two-time league MVP
* Stefon Diggs, wide receiver for the Houston Texans
* Donna Dixon, former actress, model
* William O. Douglas, American jurist who served as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the US 1939–75, and environmentalist resided in Old Town for four decades
* Chad Dukes (radio personality), Chad Dukes, Alexandria, Virginia radio personality, pioneer in podcasting
* Marion Moncure Duncan, 25th President General of the Daughters of the American Revolution
*
*Diedrich Bader, actor
* Hannibal Brumskine III, internet entrepreneur
* Sandor Bustamante, soccer player
* Stewart Copeland, drummer for The Police
* Leon Day, Hall of Fame baseball pitcher who played in the Negro league baseball, Negro leagues
* Elena Delle Donne, forward-guard, Washington Mystics, WNBA champion, two-time league MVP
* Stefon Diggs, wide receiver for the Houston Texans
* Donna Dixon, former actress, model
* William O. Douglas, American jurist who served as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the US 1939–75, and environmentalist resided in Old Town for four decades
* Chad Dukes (radio personality), Chad Dukes, Alexandria, Virginia radio personality, pioneer in podcasting
* Marion Moncure Duncan, 25th President General of the Daughters of the American Revolution
* Cass Elliot
Ellen Naomi Cohen (September 19, 1941 – July 29, 1974), known professionally as Cass Elliot, was an American singer. She was also known as "Mama Cass", a name she reportedly disliked. Elliot was a member of the singing group the Mamas & the P ...
and John Phillips of The Mamas & The Papas
The Mamas & the Papas were an American folk rock vocal group that recorded and performed from 1965 to 1968, with a brief reunion in 1971. The group was a defining force in the music scene of the counterculture of the 1960s. Formed in New York C ...
* Charles Esten, actor, singer
* Margaret Fetterolf, previously unidentified murder victim discovered in Woodlawn, Baltimore County, Maryland in 1976, identified in 2021
* Gerald R. Ford, former President of the United States, lived at 1521 Mount Eagle Place in Parkfairfax, Virginia, Parkfairfax, and later at 514 Crown View Drive, where he lived during his term as Vice President of the United States, vice president and for the first ten days of his presidency
* Rick Franklin, a Piedmont blues guitarist, singer and songwriter, was born in Alexandria
* Dave Grohl, founder and frontman of Foo Fighters, drummer for Nirvana (band), Nirvana
* Moses Hepburn, first African American town councilor of West Chester, Pennsylvania
* Sarah Gibson Jones, Black school, African American educator, journalist, poet, lecturer, and Woman's club movement in the United States, clubwoman
* Archie Kao, actor, who grew up in Alexandria and graduated from George Mason University in nearby Fairfax, Virginia.
* Thomas Kail, theater director
* Angus King, U.S. Senator for the state of Maine
* Gregory Lawler, mathematician who won the 2019 Wolf Prize in mathematics
* Henry Lee III, often known by his nickname "Light-Horse Harry", American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War Lieutenant colonel (United States), lieutenant colonel, Governor of Virginia, Virginia Governor, father of Robert E. Lee moved to Alexandria in 1810
* Robert E. Lee, Civil War general, grew up on Oronoco Street
* Thad Levine, general manager of Minnesota Twins, was born in Alexandria
* Emma Louise Lowe, American musician, educator, former First Lady of American Samoa and former First Ladies and Gentlemen of Guam, First Lady of Guam
* Noah Lyles, Olympian
* Scott McKenzie, musician
* Jim Morrison
James Douglas Morrison (December 8, 1943 – July 3, 1971) was an American singer, songwriter, and poet who was the lead vocalist and primary lyricist of the rock band the Doors. Due to his charismatic persona, poetic lyrics, distinctive vo ...
of The Doors
The Doors were an American rock band formed in Los Angeles in 1965, comprising vocalist Jim Morrison, keyboardist Ray Manzarek, guitarist Robby Krieger and drummer John Densmore. They were among the most influential and controversial rock acts ...
lived at 310 Woodland Terrace 1959–61
* David Lynch, filmmaker
* Dean Muhtadi, former American football player and former WWE wrestler
* Dermot Mulroney, American Actor, known for his role in ''My Best Friend's Wedding'', among others
* Mick Mulvaney, Director of the Office of Management and Budget and former United States House of Representatives, U.S. Congressman representing South Carolina, born in Alexandria
* Richard Nixon, former President of the United States, lived at 3426 Gunston Rd in Parkfairfax
* Sandie Pendleton, Lieutenant colonel (United States), Lieutenant Colonel in the Confederate States Army, C.S Army, Adjutant to Stonewall Jackson and other Confederate Generals.
* Eddie Royal, Chicago Bears wide receiver
* Willard Scott, national television personality, grew up in Rosemont
* Garren Stitt, actor known for his roles in ''General Hospital'' and ''Andi Mack''
* Nicholas Trist, Diplomat who negotiated the Treaty of Guadeloupe Hidalgo
* Kali Uchis, singer
* Wernher von Braun, NASA rocket scientist, residence on Vicar Lane, buried in Ivy Hill Cemetery
* Ella Wall Van Leer, American artist, architect and women's rights activist
* Mark Warner, United States Senate, U.S. Senator, 69th Governor of Virginia
* George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
, owned a house in Alexandria where he would stay while conducting business. He was also active in the local government and masonic lodge.
* Richard Hooker Wilmer, former Episcopal bishop, second Bishop of Alabama
* Megan Young, Miss World Philippines 2013 and Miss World 2013
Sister cities
Alexandria has four town twinning, sister cities: * Gyumri, Shirak Province, Armenia * Helsingborg, Skåne County, Sweden * Dundee, Scotland * Caen, Calvados (department), Calvados, France Alexandria was twinned with Gyumri as a means of showing goodwill in the wake of the 1988 Armenian earthquake.See also
* National Register of Historic Places listings in Alexandria, Virginia * Wales BreweryReferences
Further reading
* * Powell, Mary G., ''The History of Old Alexandria Virginia'', Richmond: William Byrd Press, 1928. * Seale, William. ''The Alexandria Library Company'', Alexandria, VA: Alexandria Library, 2007.External links
*The Chamber ALX - Alexandria Chamber of Commerce
Historic Alexandria Foundation
Visit Alexandria
{{Authority control Alexandria, Virginia, 1745 establishments in the Colony of Virginia Art gallery districts Cities in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area Cities in Virginia History of the District of Columbia Northern Virginia Majority-minority counties and independent cities in Virginia Populated places established in 1745 Virginia populated places on the Potomac River Washington metropolitan area