Malmesbury Park 1st School, Charminster, Bournemouth (280346) (9453693423) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Malmesbury () is a

 The Abbey was founded in 675 by Maildubh, Mailduf or Maelduib, an Irishman. The town came to be named after Maildubh; the name Malmesbury is a combination of Maildubh and burh, meaning Maildubh's fortification. After his death around 700,
The Abbey was founded in 675 by Maildubh, Mailduf or Maelduib, an Irishman. The town came to be named after Maildubh; the name Malmesbury is a combination of Maildubh and burh, meaning Maildubh's fortification. After his death around 700,
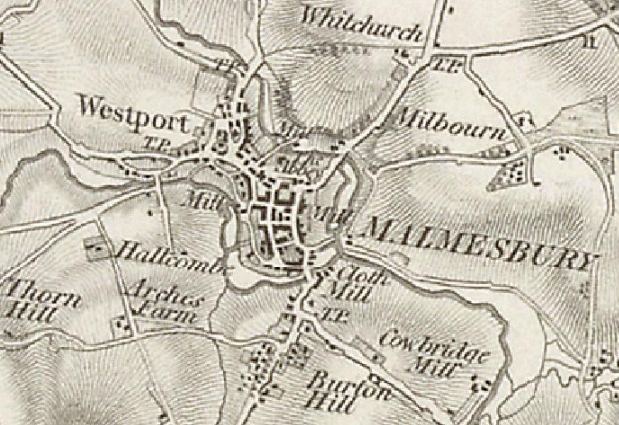 Westport, sometimes called Westport St. Mary, was a village and civil parish immediately west of Malmesbury, outside the confines of the hilltop. The philosopher
Westport, sometimes called Westport St. Mary, was a village and civil parish immediately west of Malmesbury, outside the confines of the hilltop. The philosopher
 What made Malmesbury successful as a town—water and excellent defences—led to its current layout and the presence of over 300
What made Malmesbury successful as a town—water and excellent defences—led to its current layout and the presence of over 300

 There are two primary schools in Malmesbury: Malmesbury Church of England Primary School and St Joseph's
There are two primary schools in Malmesbury: Malmesbury Church of England Primary School and St Joseph's
Malmesbury Town CouncilHistoric Malmesbury photos
at
Aerial view of Malmesbury, 1930
– from the English Heritage "Britain from Above" archive {{Authority control Malmesbury Market towns in Wiltshire Civil parishes in Wiltshire Towns in Wiltshire Cotswolds
town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city.
The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ...
and civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of parishes, w ...
in north Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated to Wilts) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It borders Gloucestershire to the north, Oxfordshire to the north-east, Berkshire to the east, Hampshire to the south-east, Dorset to the south, and Somerset to ...
, England, which lies approximately west of Swindon
Swindon () is a town in Wiltshire, England. At the time of the 2021 Census the population of the built-up area was 183,638, making it the largest settlement in the county. Located at the northeastern edge of the South West England region, Swi ...
, northeast of Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
, and north of Chippenham
Chippenham is a market town in north-west Wiltshire, England. It lies north-east of Bath, Somerset, Bath, west of London and is near the Cotswolds Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The town was established on a crossing of the River Avon, ...
. The older part of the town is on a hilltop which is almost surrounded by the upper waters of the Bristol Avon
The River Avon ( ) is a river in the southwest of England. To distinguish it from a number of other rivers of the same name, it is often called the Bristol Avon. The name 'Avon' is loaned from an ancestor of the Welsh word , meaning 'rive ...
and one of its tributaries.
Once the site of an Iron Age fort, in the early medieval period Malmesbury became the site of Malmesbury Abbey
Malmesbury Abbey, at Malmesbury in Wiltshire, England, is a former Benedictine abbey dedicated to Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul. It was one of the few English religious houses with a continuous history from the 7th century throug ...
, a monastery famed for its learning. It was later home to one of Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfr ...
's fortified burh
A burh () or burg was an Anglo-Saxon fortification or fortified settlement. In the 9th century, raids and invasions by Vikings prompted Alfred the Great to develop a network of burhs and roads to use against such attackers. Some were new constru ...
s for defence against the Vikings. Æthelstan
Æthelstan or Athelstan (; ; ; ; – 27 October 939) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 924 to 927 and King of the English from 927 to his death in 939. He was the son of King Edward the Elder and his first wife, Ecgwynn. Modern histori ...
, the first king of all England, was buried in the abbey when he died in 939. As a market town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rura ...
, it became prominent in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
as a centre for learning, focused on and around the abbey.
In modern times, Malmesbury is best known for its abbey, the bulk of which forms a rare survival of the dissolution of the monasteries. The economy benefits mostly from agriculture, as well as tourism to the Cotswolds
The Cotswolds ( ) is a region of central South West England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper River Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and the Vale of Evesham. The area is defined by the bedroc ...
; Dyson Dyson may refer to:
* Dyson (surname), people with the surname Dyson
* Dyson (company), a Singaporean multinational home appliances company founded by James Dyson
* Dyson (crater), a crater on the Moon
* Dyson (operating system), a Unix general- ...
is the town's main employer. At the 2021 census, the population of the parish was almost 6,000.
History
The hilltop contains several freshwater springs, which helped early settlements. It was the site of anIron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
fort
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
, and in the Anglo-Saxon period it had a monastery famed as a centre of learning. The town is listed in the Burghal Hidage
The Burghal Hidage () is an Anglo-Saxon document providing a list of over thirty fortified places (burhs), the majority being in the ancient Kingdom of Wessex, and the taxes (recorded as numbers of hides) assigned for their maintenance.Hill/ Rumb ...
as one of Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfr ...
's defended burh
A burh () or burg was an Anglo-Saxon fortification or fortified settlement. In the 9th century, raids and invasions by Vikings prompted Alfred the Great to develop a network of burhs and roads to use against such attackers. Some were new constru ...
s assessed at 1200 hides, its Iron Age defences helping to provide protection against Viking attack. The town was described in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
of 1086 as a borough. Also within the Domesday Book it is reported to be within the Hundred (county division)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County in the British Colony o ...
of Cicementone. Alfred's grandson, Æthelstan
Æthelstan or Athelstan (; ; ; ; – 27 October 939) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 924 to 927 and King of the English from 927 to his death in 939. He was the son of King Edward the Elder and his first wife, Ecgwynn. Modern histori ...
, the first king of England, was buried in Malmesbury Abbey in 939.
Malmesbury Abbey

St Aldhelm
Aldhelm (, ; 25 May 709), Abbot of Malmesbury Abbey, Bishop of Sherborne, and a writer and scholar of Latin poetry, was born before the middle of the 7th century. He is said to have been the son of Kenten, who was of the royal house of Wessex. ...
became the first abbot and built the first church organ
Carol Williams performing at the West_Point_Cadet_Chapel.html" ;"title="United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel">United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel.
In music, the organ is a keyboard instrument of one or mo ...
in England, which was described as a "mighty instrument with innumerable tones, blown with bellows, and enclosed in a gilded case." Having founded other churches in the area, including at Bradford on Avon
Bradford-on-Avon (sometimes Bradford on Avon) is a town and civil parish in west Wiltshire, England, near the border with Somerset. The town's canal, historic buildings, shops, pubs and restaurants make it popular with tourists. The parish had ...
, he died in 709 and was canonised
Canonization is the declaration of a deceased person as an officially recognized saint, specifically, the official act of a Christian communion declaring a person worthy of public veneration and entering their name in the canon catalogue of sai ...
. The Abbey's architecture is listed in the highest category and it is a Scheduled Ancient Monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage, visu ...
.
Across the River Avon's Sherston branch via the footpath by 18 Gloucester Street (leading south-west) is a depression called Daniels Well, and a farm beyond it is named after this. This derives from a monk called Daniel named after an earlier Daniel of Winchester
Daniel (Danihel) of Winchester (died 745) was Bishop of the West Saxons, and Bishop of Winchester from c. 705 to 744.Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 223
Life
The prominent position which he held among the English clergy of ...
. This former bishop, on losing his sight, lived at the abbey briefly until death in 745 and was educated there. The later monk is said to have submerged himself in the cold water every day for decades to quell fiery passions.
The Abbey was the site of an early attempt at human flight in 1010, when, as noted by historian William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury (; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as "a gifted historical scholar and a ...
, the monk Eilmer of Malmesbury
Eilmer of Malmesbury (also known as Oliver due to a scribe's miscopying, or Elmer, or Æthelmær) was an 11th-century English Benedictine monk best known for his early attempt at a gliding flight using wings.
Life
Eilmer was a monk of Malme ...
flew a primitive hang glider
Hang gliding is an air sport or recreational activity in which a pilot flies a light, non-motorised, fixed-wing heavier-than-air aircraft called a hang glider. Most modern hang gliders are made of an aluminium alloy or composite frame covered ...
from a tower. Eilmer flew over 180 metres before landing, breaking both his legs.
By the time of the Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 9th and 10th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norma ...
invasion in 1066, Malmesbury was one of the most significant towns in England. It is listed first (thus most important) in the Wiltshire section of the Domesday Book. King Henry I's chancellor, Roger of Salisbury
Roger of Salisbury (died 1139), was a Norman medieval bishop of Salisbury and the seventh Lord Chancellor and Lord Keeper of England.
Life
Roger was originally priest of a small chapel near Caen in Normandy. He was called "Roger, priest of t ...
, seized the monastery under his bishopric in 1118, and held it for 20 years. Renowned as a great builder, he rebuilt the wooden town walls wholly in stone rather than wood, constructing the short-lived Malmesbury Castle
Malmesbury Castle was a castle in the town of Malmesbury, Wiltshire, England.
Details
The town of Malmesbury was an important settlement in the early medieval period, both as a trading centre and as the site of Malmesbury Abbey. Early in the 12 ...
at the same time.
By the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, the north of the town was heavily developed as a religious centre, resulting in the construction of the third Abbey on the site, the 12th-century Malmesbury Abbey
Malmesbury Abbey, at Malmesbury in Wiltshire, England, is a former Benedictine abbey dedicated to Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul. It was one of the few English religious houses with a continuous history from the 7th century throug ...
, which had a spire
A spire is a tall, slender, pointed structure on top of a roof of a building or tower, especially at the summit of church steeples. A spire may have a square, circular, or polygonal plan, with a roughly conical or pyramidal shape. Spire ...
taller than the one of Salisbury Cathedral
Salisbury Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary, is an Church of England, Anglican cathedral in the city of Salisbury, England. The cathedral is regarded as one of the leading examples of Early English architecture, ...
. In 1220 this resulted in the construction of the Abbey guest house, which is now The Old Bell hotel and claims to be the oldest hotel in England. The Abbey's spire collapsed in either the late 15th or early 16th century. Under his English Reformation
The English Reformation began in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away first from the authority of the pope and bishops Oath_of_Supremacy, over the King and then from some doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church ...
, King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
, sold the substantial land, but retaining a minor choice portion, to a local clothier William Stumpe
William Stumpe (by 1498 – 22 July 1552) of Malmesbury, Wiltshire, was a clothier, Sheriff of Wiltshire, and briefly a member of parliament.
Career
Stumpe was a leading Wiltshire clothier and one of England's most successful merchants in the ...
. The extant part of the Abbey is now the parish church; the remains containing a parvise
A parvis or parvise is the open space in front of and around a cathedral or church, especially when surrounded by either colonnades or porticoes, as at St. Peter's Basilica in Rome. It is thus a church-specific type of forecourt, front yard or ...
which still holds some fine examples of books from the former Abbey library.
Malmesbury natives are sometimes nicknamed Jackdaw
Jackdaws are two species of bird in the genus ''Coloeus'' closely related to, but generally smaller than, crows and ravens ('' Corvus''). They have a blackish crown, wings, and tail, with the rest of their plumage paler.Madge & Burn (1994) 136� ...
s, originating from the avian colony of these that inhabit the Abbey walls and roof.
Battles
The community was the ancient frontier of two kingdoms—Tetbury
Tetbury is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish inside the Cotswold (district), Cotswold district in Gloucestershire, England. It lies on the site of an ancient hill fort, on which an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon monastery was found ...
to the north was in Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlan ...
, while Malmesbury was in the West Saxon Kingdom
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886.
The Anglo-Saxons belie ...
—resulting in centuries of animosity between the two towns. The location and defensive position of Malmesbury on the latterly important Oxford to Bristol route made it a strategic military point. During the 12th century civil war between Stephen of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne '' jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 113 ...
and his cousin the Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda (10 September 1167), also known as Empress Maud, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter and heir of Henry I, king of England and ruler of Normandy, she went to ...
, the succession agreement between Stephen and Henry of Anjou (later Henry II) was reached after their armies faced each other across the impassable River Avon at Malmesbury in the winter of 1153, with Stephen losing by refusing battle.
During the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
the town changed hands seven times; the south face of Malmesbury Abbey still today bears pock-marks from cannon and gunshot. In 1646 Parliament ordered that the town walls be destroyed. As peace came to inland England, and the need to defend the developing coastal port towns became more important, Malmesbury, without its Abbey, lost its importance. As developing transport and trade routes passed it by, it regressed to a regional market town.
Malmesbury Commoners
At theBattle of Brunanburh
The Battle of Brunanburh was fought in 937 between Æthelstan, King of Kingdom of England, England, and an alliance of Olaf Guthfrithson, King of Kingdom of Dublin, Dublin; Constantine II of Scotland, Constantine II, King of Scotland; and O ...
in 937, King Æthelstan
Æthelstan or Athelstan (; ; ; ; – 27 October 939) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 924 to 927 and King of the English from 927 to his death in 939. He was the son of King Edward the Elder and his first wife, Ecgwynn. Modern histori ...
of Wessex
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy, kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886.
The Anglo-Sa ...
defeated an army of northern English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
and Scots and made a claim to become the first 'King of All England'. Helped by many men from Malmesbury, in gratitude he gave the townsfolk their freedom, along with 600 hides of land to the south of the town. The status of freemen of Malmesbury was passed down through the generations and remains to this day. Since at least the 17th century, the right has been only handed down from father to son or son-in-law. There is a maximum of 280 commoners. To be a commoner, one has to be born to a freeman or marry the daughter of one. Since 2000, women were admitted for the first time—the daughters of freemen. The organisation, The Warden and Freemen of Malmesbury, still owns the land to the south of the town, along with dozens of properties, pubs
A pub (short for public house) is in several countries a drinking establishment licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption Licensing laws of the United Kingdom#On-licence, on the premises. The term first appeared in England in the ...
and shops within the town itself, providing affordable housing to townsfolk.
Westport St Mary
 Westport, sometimes called Westport St. Mary, was a village and civil parish immediately west of Malmesbury, outside the confines of the hilltop. The philosopher
Westport, sometimes called Westport St. Mary, was a village and civil parish immediately west of Malmesbury, outside the confines of the hilltop. The philosopher Thomas Hobbes
Thomas Hobbes ( ; 5 April 1588 – 4 December 1679) was an English philosopher, best known for his 1651 book ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', in which he expounds an influential formulation of social contract theory. He is considered t ...
was born in Westport in 1588; his father, also Thomas, lived at Westport while serving as curate of Brokenborough
Brokenborough is a village and civil parish about northwest of Malmesbury, Wiltshire in England. The course of the Fosse Way Roman road forms the northwest boundary of the parish, and also the county boundary with neighbouring Gloucestershire. ...
.
Westport no longer exists as a separate village and is not named on modern maps. The built-up area was incorporated in the borough of Malmesbury in 1934, and the rural parts of the parish were incorporated in 1896 into the parish of St Paul Malmesbury Without.
Government
Malmesbury was amunicipal borough
A municipal borough was a type of local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of ...
until 1974, when Malmesbury Town Council was formed as a successor
Successor may refer to:
* An entity that comes after another (see Succession (disambiguation))
Film and TV
* ''The Successor'' (1996 film), a film including Laura Girling
* The Successor (2023 film), a French drama film
* ''The Successor'' ( ...
to it. The council is made up of sixteen councillors, who annually elect a town mayor and deputy town mayor from their number. The town council meets at Malmesbury Town Hall
Malmesbury Town Hall is a municipal building in Cross Hayes in Malmesbury, Wiltshire, England. The structure, which is the meeting place of Malmesbury Town Council and the home of the Athelstan Museum, is a Grade II listed building.
History
Af ...
.
Malmesbury was in the area of Wiltshire County Council
Wiltshire Council, known between 1889 and 2009 as Wiltshire County Council, is the local authority for the non-metropolitan county of Wiltshire in South West England, and has its headquarters at County Hall in Trowbridge. Since 2009 it has bee ...
from its creation in 1889 until it was disbanded in 2009. In 1974, the municipal borough was merged into the North Wiltshire
North Wiltshire was a Districts of England, local government district in Wiltshire, England, between 1974 and 2009, when it was superseded by the unitary area of Wiltshire (district), Wiltshire.
The district was formed on 1 April 1974 by a me ...
district
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municip ...
.
In 2009, Wiltshire Council
Wiltshire Council, known between 1889 and 2009 as Wiltshire County Council, is the Local government in England, local authority for the non-metropolitan county of Wiltshire (district), Wiltshire in South West England, and has its headquarters a ...
succeeded the county council and district council as a unitary authority
A unitary authority is a type of local government, local authority in New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Unitary authorities are responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are ...
. For elections to Wiltshire Council, Malmesbury forms one electoral division
An electoral (congressional, legislative, etc.) district, sometimes called a constituency, riding, or ward, is a geographical portion of a political unit, such as a country, state or province, city, or administrative region, created to provid ...
, returning a single unitary councillor. Gavin Grant, a Liberal Democrat
Several political parties from around the world have been called the Liberal Democratic Party, Democratic Liberal Party or Liberal Democrats. These parties have usually followed liberalism as ideology, although they can vary widely from very progr ...
, was re-elected in 2021, following his initial election in 2017.
At UK Government
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
level in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
, Malmesbury is part of the South Cotswolds
South Cotswolds is a newly created constituency of the House of Commons in the UK Parliament. Further to the completion of the 2023 review of Westminster constituencies, it was first contested at the 2024 general election, when it was won by Roz Sa ...
constituency, represented since 2024 by Roz Savage
Rosalind Elizabeth Adriana Savage (born 23 December 1967), known as Roz Savage, is an English ocean rower, environmental advocate, writer, speaker and politician. She was elected as a Liberal Democrat MP for the new South Cotswolds constituen ...
for the Liberal Democrats.
Public services
Malmesbury is policed by theWiltshire Police
Wiltshire Police, formerly known as Wiltshire Constabulary, is the territorial police force responsible for policing the county of Wiltshire (including the Borough of Swindon) in South West England.
The force serves 722,000 people over an area ...
force and is in the Royal Wootton Bassett
Royal Wootton Bassett , formerly Wootton Bassett, is a market town and civil parish in Wiltshire, England, with a population of 13,570 at the 2021 Census. In the north of the county, it lies to the west of the town of Swindon and northeast of ...
Community Policing Team area. Fire services are provided by the Dorset & Wiltshire Fire and Rescue Service
Dorset & Wiltshire Fire and Rescue Service is a statutory emergency fire and rescue service covering the local authority areas of Wiltshire, Swindon, Dorset and Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole in England.
The service was created on 1 April 2 ...
, and ambulance services by the South Western Ambulance Service
The South Western Ambulance Service NHS Foundation Trust (SWASFT) is the organisation responsible for providing ambulance services for the National Health Service (NHS) across South West England. It serves the council areas of Bath and North East ...
. Malmesbury is also served by the charity-funded Wiltshire Air Ambulance
Wiltshire and Bath Air Ambulance Charity is a helicopter emergency medical service (HEMS) serving Wiltshire, Bath and surrounding areas of England. The service was launched in 1990, and since 2015 has been run as a registered charity.
Histor ...
.
A GP surgery
Ambulatory care or outpatient care is Health care, medical care provided on an outpatient basis, including diagnosis, observation, consultation, treatment, intervention, and rehabilitation services. This care can include advanced medical technolog ...
—Malmesbury Primary Care Centre—is located in the town and is overseen by the Bath and North East Somerset, Swindon, and Wiltshire Integrated Care Board. The NHS
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern ...
hospitals overseen by the board are Great Western Hospital
The Great Western Hospital is a large hospital in Swindon, Wiltshire, England, near junction 15 of the M4 motorway. It opened in 2002 and is run by the Great Western Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
History
The original hospital in Swindon wa ...
in Swindon
Swindon () is a town in Wiltshire, England. At the time of the 2021 Census the population of the built-up area was 183,638, making it the largest settlement in the county. Located at the northeastern edge of the South West England region, Swi ...
, Royal United Hospital
The Royal United Hospital (RUH) is a major acute-care district general hospital in the Weston suburb of Bath, England, which lies approximately west of the city centre. The hospital has 565 beds and occupies a site. It is the area's major acci ...
in Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, and Salisbury Hospital
Salisbury District Hospital is a large hospital on Odstock Road, Britford, Wiltshire, England, about south of the centre of the city of Salisbury. It is managed by the Salisbury NHS Foundation Trust.
History
The first Odstock Hospital was con ...
. There are also nearby minor injuries unit
A minor injuries unit (MIU) is a type of walk-in clinic service provided in some hospitals in the United Kingdom. Units are generally staffed by emergency nurse practitioners (ENPs) who can work autonomously to treat minor injuries such as lacerati ...
s in Tetbury
Tetbury is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish inside the Cotswold (district), Cotswold district in Gloucestershire, England. It lies on the site of an ancient hill fort, on which an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon monastery was found ...
and Chippenham
Chippenham is a market town in north-west Wiltshire, England. It lies north-east of Bath, Somerset, Bath, west of London and is near the Cotswolds Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The town was established on a crossing of the River Avon, ...
.
Waste management
Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. This includes the collection, transport, treatment, and disposal of waste, together with monitor ...
services are overseen by Wiltshire Council
Wiltshire Council, known between 1889 and 2009 as Wiltshire County Council, is the Local government in England, local authority for the non-metropolitan county of Wiltshire (district), Wiltshire in South West England, and has its headquarters a ...
, which provides recycling, refuse and garden waste collection.
Western Power Distribution
Western Power Distribution is a trade name formerly used by four electricity distribution companies in the United Kingdom: WPD South West (operating in South West England), WPD South Wales (in South Wales) and WPD Midlands (two companies, in t ...
is the electricity distribution network operator
A distribution network operator (DNO), also known as a distribution system operator (DSO), is the operator of the electric power distribution system which delivers electricity to most end users. Each country may have many local distribution netwo ...
which supplies the area.
Wessex Water
Wessex Water Services Limited, known as Wessex Water, is a water supply and sewerage utility company serving an area of South West England, covering 10,000 square kilometres including Bristol, most of Dorset, Somerset and Wiltshire and parts of ...
is responsible for the provision of drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
and sewerage
Sewerage (or sewage system) is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff ( stormwater, meltwater, rainwater) using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, and scr ...
in the area.
Geography
Malmesbury sits on a flat Cotswolds hilltop at the convergence of two rivers. The town has a maximum elevation of and a minimum of ; the average elevation is above sea level. From the west, the infant (Bristol) Avon flows from Sherston, and from the north west, a tributary either known as theTetbury Avon
The Tetbury Avon, also known as the River Avon (Tetbury Branch), Little Avon or Ingleburn (Anglo-Saxon – English river), is a tributary of the Bristol Avon in south-west England. It rises at Tetbury in Gloucestershire and flows in a generally ...
, River Avon (Tetbury branch), or—locally—The Ingleburn. They flow within of each other but are separated by a narrow and high isthmus
An isthmus (; : isthmuses or isthmi) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea count ...
which forces the Bristol Avon south and the Tetbury Avon east. This creates a rocky outcrop as a south-facing, gently sloping hilltop, until the two rivers meet on the southern edge of the town. With steep sides, in places cliff-like, the town was described by Sir William Waller
Sir William Waller JP (c. 159819 September 1668) was an English soldier and politician, who commanded Parliamentarian armies during the First English Civil War. Elected MP for Andover to the Long Parliament in 1640, Waller relinquished ...
as the best naturally defended inland location he had seen.
In the 19th and 20th centuries the town expanded to the northwest, occupying land between the two rivers which was formerly in Westport and Brokenborough
Brokenborough is a village and civil parish about northwest of Malmesbury, Wiltshire in England. The course of the Fosse Way Roman road forms the northwest boundary of the parish, and also the county boundary with neighbouring Gloucestershire. ...
parishes. In the later 20th and early 21st, development was to the north, as far as the area known as Filands which is bounded by the B4014 road.
Demography
At the 2011 census the population was 5,380 in 2,280 homes. In the table below, the additional figures in the 19th century are for The Abbey, the supplementalecclesiastical parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish pries ...
added to that of St Paul. Figures for 1901 are for the parishes of St Paul Within, St Paul Without and Abbey, respectively. Figures from 1911 are for the municipal borough, and after 1961 for the ward
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a pris ...
.
Economy
Traditionally amarket town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rura ...
serving the rural area of north west Wiltshire, farming has been the main industry. Even today, the High Street
High Street is a common street name for the primary business street of a city, town, or village, especially in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth. It implies that it is the focal point for business, especially shopping. It is also a metonym fo ...
has numerous independent shops and a weekly farmers' market
A farmers' market (or farmers market according to the AP stylebook, also farmer's market in the Cambridge Dictionary) is a physical retail marketplace intended to sell foods directly by farmers to consumers. Farmers' markets may be indoors or ...
.
The Reformation of 1539 brought about a change in the economy of Malmesbury: having no income from the Abbey, the town turned to the wool spinning and weaving industry, having access to large quantities of wool and water. It then became a centre of the lace
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is split into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted o ...
-making industry. But, what had made it successful and important as a religious and strategic defensive centre—water on three sides and steep cliffs—precluded easy access for the modern bulk transport
Bulk cargo is product cargo that is transported unpackaged in large quantities.
Description
Bulk cargo refers to material in either liquid or granular, particulate (as a mass of relatively small solids) form, such as petroleum/crude oil, ...
methods of canals and railways. Hence the Kennet and Avon Canal
The Kennet and Avon Canal is a waterway in southern England with an overall length of , made up of two lengths of Navigability, navigable river linked by a canal. The name is used to refer to the entire length of the navigation rather than sol ...
and the later Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
passed well to the south of the town; while local quarrying of cotswold stone
The Cotswolds ( ) is a region of central South West England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper River Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and the Vale of Evesham. The area is defined by the bedroc ...
provided often transient booms in employment, Malmesbury saw little expansion compared to, for example, Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ...
, by not being a commuter suburb or major production centre of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
.
The town's main employer today is Dyson Dyson may refer to:
* Dyson (surname), people with the surname Dyson
* Dyson (company), a Singaporean multinational home appliances company founded by James Dyson
* Dyson (crater), a crater on the Moon
* Dyson (operating system), a Unix general- ...
, which has a site on the edge of the town which employs around 4,000. This is mainly a research, development and design site; manufacturing is carried out in Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
. The site was the company's headquarters until 2019, when it was announced that the company registration would be moved to Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
.
The town's economy profits from tourism, divided among Cotswold Hills
The Cotswolds ( ) is a region of central South West England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper River Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and the Vale of Evesham. The area is defined by the be ...
retreats (ranging from B&Bs to golf/spa resorts), visits and tours of the abbey, nearby landmarks and festivals or by interest in the counter-modernism 1960s work of poet laureate, John Betjeman
Sir John Betjeman, (; 28 August 190619 May 1984) was an English poet, writer, and broadcaster. He was Poet Laureate from 1972 until his death. He was a founding member of The Victorian Society and a passionate defender of Victorian architect ...
.
Malmesbury had a nine-day wonder media event
A media event, also known as a pseudo-event, is an event, activity, or experience conducted for the purpose of creating media publicity. It may also be any event that is covered in the mass media or was hosted largely with the media in mind.
Etym ...
in January 1998, when two Tamworth pig
The Tamworth is a British breed of domestic pig. It is the only red-coloured British pig. Its origins are unknown, but it appears to have developed near the town of Tamworth in south-eastern Staffordshire, close to Warwickshire border. It is on ...
s known as the Tamworth Two
The Tamworth Two were a pair of pigs that escaped while being unloaded from a lorry at an abattoir in the English town of Malmesbury, Wiltshire in January 1998. The pigs (later named Butch and Sundance after ''Butch Cassidy and the Sundance K ...
escaped from the town's abattoir. They swam the Tetbury branch of the River Avon, across a few fields and lived in an orchard for a week. The story made international headlines with tabloid newspapers and TV news stations fighting each other to sight and then capture the pigs. The pigs were recaptured, and lived out their lives in an animal rescue centre.
EKCO factory
At the beginning of theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the electronics company EKCO moved part of its operations from Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in south-eastern Essex, England. It lies on the nor ...
to Cowbridge House
Cowbridge House, southeast of Malmesbury, Wiltshire, England, was an 18th-century country house that was demolished in 2007.
During the Second World War, the EKCO company used the house as a shadow factory for the manufacture of radar equip ...
, southeast of the town, to avoid the danger of bombing. The company established a shadow factory
A shadow is a dark area on a surface where light from a light source is blocked by an object. In contrast, shade occupies the three-dimensional volume behind an object with light in front of it. The cross-section of a shadow is a two-dimensional ...
to produce radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
equipment, then a new technology. The factory continued production after the war, was taken over by Pye TMC and then Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), simply branded Philips, is a Dutch multinational health technology company that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, its world headquarters have been situated in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarter ...
, and later became part of AT&T
AT&T Inc., an abbreviation for its predecessor's former name, the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the w ...
. The site was in use as offices until 2004 when the owners, Lucent Technologies
Lucent Technologies, Inc. was an American Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications equipment company headquartered in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey. It was established on September 30, 1996, through the div ...
, moved their operations to Swindon
Swindon () is a town in Wiltshire, England. At the time of the 2021 Census the population of the built-up area was 183,638, making it the largest settlement in the county. Located at the northeastern edge of the South West England region, Swi ...
and the building was converted to housing.
Culture and community
Malmesbury has an annualcarnival
Carnival (known as Shrovetide in certain localities) is a festive season that occurs at the close of the Christian pre-Lenten period, consisting of Quinquagesima or Shrove Sunday, Shrove Monday, and Shrove Tuesday or Mardi Gras.
Carnival typi ...
, which takes place throughout August. This consists of various events throughout the month, culminating in a procession through the town, typically held on the last Saturday. Since its inception in 1917, it has grown to include more than 30 events, ranging from music events to an attempt on the world record
A world record is usually the best global and most important performance that is ever recorded and officially verified in a specific skill, sport, or other kind of activity. The book ''Guinness World Records'' and other world records organizatio ...
for the largest pillow fight
A pillow fight is a common game mostly played by young children (but also by teens and adults) in which they engage in mock physical conflict, using pillows as weapons.
Pillow fights often occur during children's sleepovers. Since pillows ...
. A new Carnival Committee was formed in 2019 with the aim of raising money for the local community.
Since 2007, the annual world music
"World music" is an English phrase for styles of music from non-English speaking countries, including quasi-traditional, Cross-cultural communication, intercultural, and traditional music. World music's broad nature and elasticity as a musical ...
festival WOMAD Charlton Park
WOMAD Charlton Park or WOMAD UK is the name given to the World of Music Arts and Dance (WOMAD) festival held in Charlton Park near Malmesbury, Wiltshire, England, since 2007. It is the direct successor to WOMAD Reading, which was held in the to ...
has been held in Charlton Park. This usually takes place over the last weekend of July, spanning approximately three and a half days from the Thursday evening to Monday morning.
Community facilities
Malmesbury has a number of public parks and gardens. Three of these (St Aldhelm's Mead, Cuckingstool Mead and White Lion Recreation Park) were registered in 2013 asFields in Trust
Fields in Trust is a British charity set up in 1925 as the National Playing Fields Association (NPFA), by Brigadier-General Reginald Kentish and the Duke of York, later King George VI, who was the first president, which protects parks and green s ...
, giving them long-lasting protection as free, open recreational spaces. Malmesbury also has a leisure centre (The Activity Zone) and a public library
A public library is a library, most often a lending library, that is accessible by the general public and is usually funded from public sources, such as taxes. It is operated by librarians and library paraprofessionals, who are also Civil servic ...
, both of which are managed by Wiltshire Council
Wiltshire Council, known between 1889 and 2009 as Wiltshire County Council, is the Local government in England, local authority for the non-metropolitan county of Wiltshire (district), Wiltshire in South West England, and has its headquarters a ...
. A mobile library
A bookmobile, or mobile library, is a vehicle designed for use as a library. They have been known by many names throughout history, including traveling library, library wagon, book wagon, book truck, library-on-wheels, and book auto service. Boo ...
also services the town.
Sport and leisure
Malmesbury has anon-League football
Non-League football describes association football, football leagues played outside the top leagues of a country. Usually, it describes leagues which are not fully professional. The term is primarily used for football in England, where it is ...
team Malmesbury Victoria F.C., who play at The Flying Monk Ground. The team plays in the Hellenic Football League
The Hellenic Football League, currently known as the uhlsport Hellenic Football League for sponsorship reasons, is an English men's association football, football league covering an area including the English Counties of the United Kingdom, cou ...
. A swimming club, 'Malmesbury Marlins', train at The Activity Zone leisure centre. Malmesbury Cricket Club are an ECB Clubmark accredited sports club who play at The Wortheys sports ground, with adult and junior teams playing in the Wiltshire Leagues.
Twin towns
Malmesbury is twinned with the following places: *Gien
Gien () is a Communes of France, commune in the Loiret Departments of France, department in north-central France.
Gien is on the river Loire, from Orléans. Gien station has rail connections to Montargis, Nevers and Paris. The town was bought ...
, France
* Niebüll
Niebüll (; ; ) is a town in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated near the North Sea coast and the border with Denmark, approx. 35 km northwest of Husum.
Local districts and settlements include Deezb� ...
, Germany
Malmesbury also has friendship agreements with three other towns and cities:
* Bad Hersfeld
The festival and spa town of Bad Hersfeld (''Bad'' is "spa" in German; the Old High German name of the city was ''Herolfisfeld'') is the district seat of the Hersfeld-Rotenburg district in northeastern Hesse, Germany, roughly 50 km southeast ...
, Germany
* Cherkasy
Cherkasy (, ) is a city in central Ukraine. Cherkasy serves as the administrative centre of Cherkasy Oblast as well as Cherkasy Raion within the oblast. The city has a population of
Cherkasy is the cultural, educational and industrial centre ...
, Ukraine
* Malmesbury
Malmesbury () is a town and civil parish in north Wiltshire, England, which lies approximately west of Swindon, northeast of Bristol, and north of Chippenham. The older part of the town is on a hilltop which is almost surrounded by the upp ...
, South Africa
Religion
Church of England
In theChurch of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
, Malmesbury Abbey
Malmesbury Abbey, at Malmesbury in Wiltshire, England, is a former Benedictine abbey dedicated to Saint Peter and Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul. It was one of the few English religious houses with a continuous history from the 7th century throug ...
has served as the parish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the Church (building), church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in com ...
since 1541, following on from the former parish church of St Paul. Malmesbury forms part of the modern ecclesiastical parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish pries ...
of Malmesbury and Brokenborough, which joins with the ecclesiastical parish of Corston with Rodbourne to form the benefice
A benefice () or living is a reward received in exchange for services rendered and as a retainer for future services. The Roman Empire used the Latin term as a benefit to an individual from the Empire for services rendered. Its use was adopted by ...
of Malmesbury and Upper Avon. The parish is in the Deanery of North Wiltshire, a sub-division of the larger Archdeaconry of Malmesbury in the Diocese of Bristol
The Diocese of Bristol is an ecclesiastical jurisdiction or diocese of the Church of England in the Province of Canterbury, England. It is based in the city of Bristol and covers South Gloucestershire and parts of north Wiltshire, as far east ...
. The Abbey is dedicated to Saint Peter
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the Jewish Christian#Jerusalem ekklēsia, e ...
and Saint Paul
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is generally ...
.
Roman Catholic Church
The localRoman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
church in Malmesbury is St Aldhelm's Church, which serves the ecclesiastical parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish pries ...
of ''St Aldhelm, Malmesbury''. The Catholic parish covers a larger area than the Church of England parish, and falls within the St Aldhelm pastoral area of the Diocese of Clifton
The Diocese of Clifton is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church centred at the Cathedral Church of Saints Peter and Paul in Clifton, England.
The diocese covers the City and County of Bristol and the ceremonial counties of Gloucester ...
. The church is dedicated to St Aldhelm
Aldhelm (, ; 25 May 709), Abbot of Malmesbury Abbey, Bishop of Sherborne, and a writer and scholar of Latin poetry, was born before the middle of the 7th century. He is said to have been the son of Kenten, who was of the royal house of Wessex. ...
, who lived in Malmesbury.
Other churches
Malmesbury is also home to MalmesburyUnited Reformed Church
The United Reformed Church (URC) is a Protestant Christian church in the United Kingdom. As of 2024 it had approximately 44,000 members in around 1,250 congregations with 334 stipendiary ministers.
The URC is a Trinitarian church whose theolog ...
and ''The King's Church''. There are also a number of former churches in the town, including an old Moravian church
The Moravian Church, or the Moravian Brethren ( or ), formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestant denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohemian Reformation of the 15th century and the original ...
which is now owned by Athelstan Museum and called ''The Julia & Hans Rausing Building.''
Planning
In 2011 Malmesbury was chosen by theDepartment for Communities and Local Government
The Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government (MHCLG) is a ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for housing, communities, and local government in England. It was established in May 200 ...
as a "front-runner" area to test Neighbourhood Planning powers introduced in the Localism Act 2011
The Localism Act 2011 (c. 20) is an Act of Parliament that changes the powers of local government in England. The aim of the act is to facilitate the devolution of decision-making powers from central government control to individuals and commun ...
. As part of the neighbourhood planning process in February 2012 a series of seminars and workshops involving residents and stakeholders were run in Malmesbury by The Prince's Foundation for Building Community
The King's Foundation (formerly the Prince of Wales's Institute of Architecture until 2001, the Prince's Foundation for the Built Environment until 2012, the Prince's Foundation for Building Community until 2018, and the Prince's Foundation until 2 ...
. In March 2012 issues of planning in Malmesbury were featured as part of the wider national debate about changes to the planning system and the balance of power between communities and developers.
Landmarks
listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
s within its boundaries. Roger of Salisbury
Roger of Salisbury (died 1139), was a Norman medieval bishop of Salisbury and the seventh Lord Chancellor and Lord Keeper of England.
Life
Roger was originally priest of a small chapel near Caen in Normandy. He was called "Roger, priest of t ...
reconstructed the town after his accession to Bishop of Salisbury
The Bishop of Salisbury is the Ordinary (officer), ordinary of the Church of England's Diocese of Salisbury in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese covers much of the counties of Wiltshire and Dorset. The Episcopal see, see is in the Salisbur ...
in 1102, and the Saxon layout he rebuilt is retained in the centre today. The geography also precluded easy development for mass transport and hence hindered industrial development, leaving the architecture and ancient buildings largely untouched. The result is a higher proportion of Grade I and Grade II buildings than in many other English towns.
Grade I listed
The parish has six Grade I listed structures, all of them within the hilltop town.Malmesbury Abbey
The surviving nave of the 12th-centuryabbey church
A church, church building, church house, or chapel is a building used for Christian worship services and Christian activities. The earliest identified Christian church is a house church founded between 233 AD and 256 AD.
''Church'' is also ...
, built in limestone ashlar with stone tiles, serves as the parish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the Church (building), church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in com ...
. In the period 1350–1450 the building was enlarged and a clerestory, crossing spire and west towers were added; the spire fell in 1479. After the Dissolution, William Stumpe
William Stumpe (by 1498 – 22 July 1552) of Malmesbury, Wiltshire, was a clothier, Sheriff of Wiltshire, and briefly a member of parliament.
Career
Stumpe was a leading Wiltshire clothier and one of England's most successful merchants in the ...
reduced and altered the building to form the parish church. The west tower fell c. 1662.
Features of the building include the south porch, richly carved with Biblical scenes, which Pevsner describes as "among the best pieces of Norman sculpture and decoration in England".
The abbey was placed on Historic England's Heritage at Risk Register
An annual ''Heritage at Risk Register'' is published by Historic England. The survey is used by national and local government, a wide range of individuals and heritage groups to establish the extent of risk and to help assess priorities for acti ...
in November 2022, owing to the condition of its roofs.
Market Cross
In the centre of the town stands themarket cross
A market cross, or in Scots, a mercat cross, is a structure used to mark a market square in market towns, where historically the right to hold a regular market or fair was granted by the monarch, a bishop or a baron.
History
Market crosses ...
, built , possibly using stone salvaged from the recently ruined part of the abbey. It was described by John Leland, writing in the 1540s, as a "right fair and costely peace of worke", which was built to shelter the "poore market folkes" when "rayne cummith". An elaborately carved octagonal structure, it is recognised as one of the best preserved of its kind in England. It still serves as a public shelter today, nicknamed "The Birdcage" because of its appearance.
Numbers 1 and 3 Market Cross are also listed buildings, as is the former Abbey Brewery opposite.
St Paul's bell tower
The 15th-century three-stage tower is all that remains of St Paul's church, which stood adjacent to the abbey and was the town's parish church until 1541, when that role was transferred to the former abbey church. The nave of St Paul's had collapsed by the early 16th century, and the remainder was used for a time as a private house and town hall; the chancel was pulled down in 1852. Today it serves as the bell tower for the abbey.Abbey House
Abbey House was rebuilt byWilliam Stumpe
William Stumpe (by 1498 – 22 July 1552) of Malmesbury, Wiltshire, was a clothier, Sheriff of Wiltshire, and briefly a member of parliament.
Career
Stumpe was a leading Wiltshire clothier and one of England's most successful merchants in the ...
or his son James, on the site of a 13th-century building within the abbey grounds; Harold Brakspear
Sir Harold Brakspear KCVO (10 March 1870 – 20 November 1934) was an English restoration architect and archaeologist.
He restored a number of ancient and notable buildings, including Bath Abbey, Windsor Castle, Brownston House in Devizes a ...
carried out 20th-century enlargement. The surrounding Abbey House Gardens were replanted in 2022 and are occasionally open to visitors.
The Old Bell hotel
The former guest house for the abbey dates from the early 13th century. The building was extended and altered in the late 15th century or early 16th, and from c. 1530 it was used as a cloth mill byWilliam Stumpe
William Stumpe (by 1498 – 22 July 1552) of Malmesbury, Wiltshire, was a clothier, Sheriff of Wiltshire, and briefly a member of parliament.
Career
Stumpe was a leading Wiltshire clothier and one of England's most successful merchants in the ...
. Further alterations were made in the 17th century and in 1908. There is a fine ashlar fire hood of c. 1220. Today the building is a hotel, The Old Bell. The hotel lays claim to the title of the oldest purpose-built hotel in England to still be in use today.
Former court house
From the 13th century or earlier, there was a hospital of St John the Baptist in the south of the town. In the 16th century the hospital was bought by the corporation, who used part of it for meetings of the borough court from 1616. The former court house, in limestone rubble with a 15th-century roof and retaining some 17th and 18th-century court fittings, is now part of a dwelling. Nearby is the 12th-century entrance arch of the hospital and the 16th-century almshouses, in use until 1948; now three cottages, Grade II* listed.Other buildings

Tower House
A large building of medieval origins, now a private home, Tower House stands at the end of Oxford Street. It contains a high-roofed main hall where it is said Henry VIII dined after hunting in nearby Bradon Forest. In the 1840s, a doctor living in the house, with a passion for astronomy, built a narrow tower protruding high from the roof. The Grade II* listed building dominates the skyline of the east of the town.St Aldhelm's Roman Catholic Church
St Aldhelm's Church is a Catholic church, built on Cross Hayes (the town's former marketplace, now a car park) in 1875. The church is named after the town's patron saint and associated with the local Catholic primary school, St Joseph's. Part of the church's presbytery is Grade II listed.War Memorial
Awar memorial
A war memorial is a building, monument, statue, or other edifice to celebrate a war or victory, or (predominating in modern times) to commemorate those who died or were injured in a war.
Symbolism
Historical usage
It has ...
was erected at The Triangle in 1921, following the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. This consists of a celtic cross
upright 0.75 , A Celtic cross symbol
The Celtic cross is a form of ringed cross, a Christian cross featuring a nimbus or ring, that emerged in the British Isles and Western Europe in the Early Middle Ages. It became widespread through its u ...
based on the Cross of St Martin on the island of Iona
Iona (; , sometimes simply ''Ì'') is an island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there are other buildings on the island. Iona Abbey was a centre of Gaeli ...
, where Aldhelm
Aldhelm (, ; 25 May 709), Abbot of Malmesbury Abbey, Bishop of Sherborne, and a writer and scholar of Latin poetry, was born before the middle of the 7th century. He is said to have been the son of Kenten, who was of the royal house of Wessex ...
had studied. The cross is built of Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
*Portland, Oregon, the most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon
*Portland, Maine, the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maine
*Isle of Portland, a tied island in the English Channel
Portland may also r ...
, blue pennant and Hopton Wood stone. The memorial is Grade II listed.
Transport
The A429 bypasses the town on its eastern edge; the road links Malmesbury with junction 17 of theM4 motorway
The M4, originally the London-South Wales Motorway, is the third longest motorway in the United Kingdom, running from west London to southwest Wales. The English section to the Severn Bridge was constructed between 1961 and 1971; the Welsh ele ...
to the south, and Kemble railway station
Kemble railway station is a railway station that serves the village of Kemble in Gloucestershire, England. The station is on the to "Golden Valley" line, from the zero point at . Despite its rural location, Kemble station has a high number ...
and Cirencester
Cirencester ( , ; see #Pronunciation, below for more variations) is a market town and civil parish in the Cotswold District of Gloucestershire, England. Cirencester lies on the River Churn, a tributary of the River Thames. It is the List of ...
to the north. Before the bypass was built in the later 20th century, the route followed the High Street, leaving the town to the north-east via Holloway. Three B roads meet at Malmesbury: the B4014 to Tetbury
Tetbury is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish inside the Cotswold (district), Cotswold district in Gloucestershire, England. It lies on the site of an ancient hill fort, on which an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon monastery was found ...
, the B4040 to Sherston and the B4042 to Royal Wootton Bassett
Royal Wootton Bassett , formerly Wootton Bassett, is a market town and civil parish in Wiltshire, England, with a population of 13,570 at the 2021 Census. In the north of the county, it lies to the west of the town of Swindon and northeast of ...
, near Swindon.
Malmesbury railway station opened on 17 December 1877. The Malmesbury branch
The Malmesbury branch was a six-and-a-half-mile-long single track branch railway line in Wiltshire, England; it ran from Dauntsey station on the Great Western Main Line to . Promoted locally, it opened with considerable assistance from the Grea ...
was built largely by the Malmesbury Railway Company, and was completed by the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
which absorbed the Malmesbury Railway Company in May 1877 when the latter could not raise sufficient funds to complete the line. The branch split from the main London-Bristol line at Dauntsey, although a later connection with the northern GWR 'mainline' to the Severn Tunnel
The Severn Tunnel () is a railway tunnel in the United Kingdom, linking South Gloucestershire in the west of England to Monmouthshire in south Wales under the estuary of the River Severn. It was constructed by the Great Western Railway (GWR) be ...
and South Wales
South Wales ( ) is a Regions of Wales, loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the Historic counties of Wales, historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire ( ...
was made at Little Somerford. Just short of its terminus, the line ran through a short tunnel: the only tunnel on the line between Malmesbury and Paddington
Paddington is an area in the City of Westminster, in central London, England. A medieval parish then a metropolitan borough of the County of London, it was integrated with Westminster and Greater London in 1965. Paddington station, designed b ...
. The station closed to passengers on 8 September 1951, and to freight in 1962. The tracks were used for a while to test new diesel locomotives built by Swindon railway works
Swindon Works was opened by the Great Western Railway in 1843 in Swindon, Wiltshire, England. It served as the principal west England maintenance centre until closed in 1986.
History
In 1835, Parliament approved the construction of the Great ...
, but lifted in the 1970s, and the site of the station is now home to an industrial estate.
The nearest stations today, all managed and served by Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
, are:
*Kemble on the Golden Valley Line
The Golden Valley line is the popular name for the railway line connecting , , and in England. Originally constructed as the Cheltenham and Great Western Union Railway, the line opened between Swindon and Kemble (with a branch to Cirencest ...
* on the Great Western Main Line
The Great Western Main Line (GWML) is a main line railway in England that runs between London Paddington and . It connects to other main lines such as those from Reading to Penzance and Swindon to Swansea. The GWML is presently a part of t ...
* on the Great Western Main Line
The town's bus network is run by Coachstyle, who run a town service in addition to services to and from Swindon, Yate, Chippenham and Cirencester.
Media
Local news and television programmes are provided byBBC West
BBC West is one of the BBC's English Regions serving Bristol, Somerset, the majority of Wiltshire and Gloucestershire and north of Dorset.
Services Television
BBC West's television service (broadcast on BBC One) consists of the flagship regio ...
and ITV West Country
ITV West Country is the British television service provided by ITV Broadcasting Limited for the South West England franchise area on the ITV network. Previously, between 2009 and 2013, the area was a non-franchise region, branded with the same ...
. Television signals are received from the Mendip TV transmitter. Local radio stations are BBC Radio Wiltshire
BBC Radio Wiltshire is the BBC's local radio station serving the English county of Wiltshire.
It broadcasts on FM, DAB, digital TV and via BBC Sounds from studios at Prospect Place in Swindon.
According to RAJAR, the station had a weekly au ...
, Heart West and Greatest Hits Radio South West
Greatest Hits Radio South West is a regional radio station serving the South West of England, as part of Bauer's Greatest Hits Radio network.
Coverage
The ten local stations broadcast across the South West of England to the areas of Bristol, Ba ...
. The town is served by these local newspapers: ''Gazette and Herald
The ''Gazette and Herald'' is a local weekly paid-for newspaper, established in Wiltshire, England in 1816 and published every Thursday. It serves the areas and communities of Devizes, Calne, Chippenham, Royal Wootton Bassett, Swindon, Marlbor ...
'' and ''Wilts and Gloucestershire Standard''.
Education
 There are two primary schools in Malmesbury: Malmesbury Church of England Primary School and St Joseph's
There are two primary schools in Malmesbury: Malmesbury Church of England Primary School and St Joseph's Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
Primary School. There is also a secondary school, Malmesbury School
Malmesbury School in Malmesbury, Wiltshire, England, was founded in 1971 with the merger of Malmesbury Grammar School at Filands with Bremhilam Secondary Modern at Corn Gastons.
History
Until 2002, the school operated on two sites, with the lo ...
, which was founded 1971.
In 2017, the Dyson Institute of Engineering and Technology
The Dyson Institute of Engineering and Technology is a private institution of higher education in England, founded in 2017 by James Dyson and based at the Dyson (company), Dyson technology campus in Malmesbury, Wiltshire. Students work in a posit ...
was founded by James Dyson
Sir James Dyson (born 2 May 1947) is a British inventor, industrial designer, farmer, and business magnate who founded the Dyson company. He is best known as the inventor of the bagless vacuum cleaner, which works on the principle of cyclonic ...
. This higher education
Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the educational level following the completion of secondary education.
The World Bank defines tertiary education as including universities, colleges, and vocational schools ...
institution is located on the Dyson Dyson may refer to:
* Dyson (surname), people with the surname Dyson
* Dyson (company), a Singaporean multinational home appliances company founded by James Dyson
* Dyson (crater), a crater on the Moon
* Dyson (operating system), a Unix general- ...
technology campus. The Dyson Institute Village
Dyson Institute Village was built in 2019 on the outskirts of Malmesbury, Wiltshire, England, to provide on-campus student housing for the Dyson Institute of Engineering and Technology. The village was designed as a number of stacked studio apar ...
was built in 2019 to provide on-campus student accommodation.
Notable people
''For a full list, see: :People from Malmesbury'' * Maildubh – Irish saint and monk, namesake of Malmesbury *Aldhelm
Aldhelm (, ; 25 May 709), Abbot of Malmesbury Abbey, Bishop of Sherborne, and a writer and scholar of Latin poetry, was born before the middle of the 7th century. He is said to have been the son of Kenten, who was of the royal house of Wessex ...
– Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
scholar, bishop, poet, musician; patron saint of Wessex and the abbey's first abbot
* King Æthelstan – first king of all England
*Eilmer of Malmesbury
Eilmer of Malmesbury (also known as Oliver due to a scribe's miscopying, or Elmer, or Æthelmær) was an 11th-century English Benedictine monk best known for his early attempt at a gliding flight using wings.
Life
Eilmer was a monk of Malme ...
– Benedictine monk, best known for his early attempt at a gliding flight using wings
*William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury (; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as "a gifted historical scholar and a ...
– monk and historian
*William Stumpe
William Stumpe (by 1498 – 22 July 1552) of Malmesbury, Wiltshire, was a clothier, Sheriff of Wiltshire, and briefly a member of parliament.
Career
Stumpe was a leading Wiltshire clothier and one of England's most successful merchants in the ...
– clothier and politician, best known for purchasing Malmesbury Abbey after the dissolution of the monasteries
*Alice Seeley Harris
Alice, Lady Harris ( Seeley; 24 May 1870 – 24 November 1970) was an English missionary and an early documentary photographer. Her photography helped to expose the human rights abuses in the Congo Free State under the regime of King Leopold ...
– missionary and photographer
*Thomas Hobbes
Thomas Hobbes ( ; 5 April 1588 – 4 December 1679) was an English philosopher, best known for his 1651 book ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', in which he expounds an influential formulation of social contract theory. He is considered t ...
– prominent British philosopher
* Samuel McDonald – footballer
* Hannah Twynnoy – barmaid; reputedly the first person killed by a tiger in Britain
* John Luce, senior Royal Navy officer during and after the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
* Basil Reed – cricketer
* James Scott Douglas – racing driver and the 6th Baronet Douglas
*Roger Scruton
Sir Roger Vernon Scruton, (; 27 February 194412 January 2020) was an English philosopher, writer, and social critic who specialised in aesthetics and political philosophy, particularly in the furtherance of Conservatism in the United Kingdom, c ...
– philosopher
*James Constable
James Ashley Constable (born 4 October 1984) is an English former semi-professional footballer and coach who played as a striker. He played in the Football League for Walsall, Shrewsbury Town and Oxford United. He is currently first-team pl ...
– footballer
See also
* Malmesbury Hundred *Malmesbury (UK Parliament constituency)
Malmesbury was a parliamentary borough in Wiltshire, which elected two Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons from 1275 until 1832, and then one member f ...
* St Paul Malmesbury Without
Notes
References
Sources
* *External links
Malmesbury Town Council
at
BBC Wiltshire
BBC Radio Wiltshire is the BBC's local radio station serving the English county of Wiltshire.
It broadcasts on FM, DAB, digital TV and via BBC Sounds from studios at Prospect Place in Swindon.
According to RAJAR, the station had a weekly au ...
Aerial view of Malmesbury, 1930
– from the English Heritage "Britain from Above" archive {{Authority control Malmesbury Market towns in Wiltshire Civil parishes in Wiltshire Towns in Wiltshire Cotswolds