Main Line Elevated on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Orange Line is a rapid transit line operated by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) as part of the MBTA subway system. The line runs south on the surface from
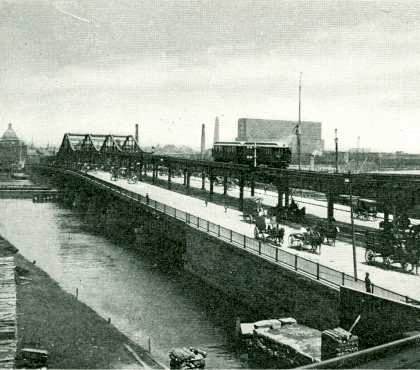 The Main Line of the electric Boston Elevated Railway opened in segments, starting in 1901. It proceeded from Sullivan Square along the Charlestown Elevated to the Canal Street incline near North Station. It was carried underground by the Tremont Street subway (now part of the
The Main Line of the electric Boston Elevated Railway opened in segments, starting in 1901. It proceeded from Sullivan Square along the Charlestown Elevated to the Canal Street incline near North Station. It was carried underground by the Tremont Street subway (now part of the
 Following a 1928 accident at a tight curve on Beach Street, the southern portion of the Atlantic Avenue Elevated, between South Station and Tower D on Washington Street, was closed (except for rush-hour trips from Dudley to North Station via the Elevated), breaking the loop; non-rush-hour Atlantic Avenue service was reduced to a shuttle between North and South Stations. In 1938, the remainder of the Atlantic Avenue Elevated was closed, leaving the subway as the only route through downtown – what is now the Orange Line between and stations.
Ownership of the railway was transferred from the private Boston Elevated Railway to the public Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA) in 1947; the MTA was itself reconstituted as the modern Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) in 1964.
Following a 1928 accident at a tight curve on Beach Street, the southern portion of the Atlantic Avenue Elevated, between South Station and Tower D on Washington Street, was closed (except for rush-hour trips from Dudley to North Station via the Elevated), breaking the loop; non-rush-hour Atlantic Avenue service was reduced to a shuttle between North and South Stations. In 1938, the remainder of the Atlantic Avenue Elevated was closed, leaving the subway as the only route through downtown – what is now the Orange Line between and stations.
Ownership of the railway was transferred from the private Boston Elevated Railway to the public Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA) in 1947; the MTA was itself reconstituted as the modern Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) in 1964.
 The line was known as the Main Line Elevated under the Boston Elevated Railway, and the Forest Hills–Everett Elevated (Route 2 on maps) under the Metropolitan Transportation Authority.
After taking over operations in August 1964, the MBTA began rebranding many elements of Boston's public transportation network. Colors were assigned to the rail lines on August 26, 1965, as part of a wider modernization developed by Cambridge Seven Associates.
The line was known as the Main Line Elevated under the Boston Elevated Railway, and the Forest Hills–Everett Elevated (Route 2 on maps) under the Metropolitan Transportation Authority.
After taking over operations in August 1964, the MBTA began rebranding many elements of Boston's public transportation network. Colors were assigned to the rail lines on August 26, 1965, as part of a wider modernization developed by Cambridge Seven Associates.
 Between April 30 and May 3, 1987, the Washington Street Elevated south of the
Between April 30 and May 3, 1987, the Washington Street Elevated south of the
 In the early 2000s,
In the early 2000s,
 Starting in 2015, the MBTA began implementing its $83.7 million Winter Resiliency Program, much of which focused on preventing similar issues with the Orange and Red lines. The Southwest Corridor section of the Orange Line is located in a trench and is protected from the worst weather, but the 1970s-built
Starting in 2015, the MBTA began implementing its $83.7 million Winter Resiliency Program, much of which focused on preventing similar issues with the Orange and Red lines. The Southwest Corridor section of the Orange Line is located in a trench and is protected from the worst weather, but the 1970s-built

 The Orange Line is standard-gauge
The Orange Line is standard-gauge
 In late 2008, the MBTA began the planning process for new Orange and Red Line vehicles. The agency originally planned for a simultaneous order for 146 Orange Line cars (to replace the whole fleet) and 74 Red Line cars (to replace the older 1500 and 1600 series cars). A similar order was used in the late 1970s for the current Orange Line cars and the old Blue Line cars, ordered at the same time and largely identical except for size and color. In October 2013, MassDOT announced plans for a $1.3 billion subway car order for the Orange and Red Lines, which would provide 152 new Orange Line cars to replace the existing 120-car fleet and add more frequent service.
On October 22, 2014, the MassDOT Board awarded a $566.6 million contract to a
In late 2008, the MBTA began the planning process for new Orange and Red Line vehicles. The agency originally planned for a simultaneous order for 146 Orange Line cars (to replace the whole fleet) and 74 Red Line cars (to replace the older 1500 and 1600 series cars). A similar order was used in the late 1970s for the current Orange Line cars and the old Blue Line cars, ordered at the same time and largely identical except for size and color. In October 2013, MassDOT announced plans for a $1.3 billion subway car order for the Orange and Red Lines, which would provide 152 new Orange Line cars to replace the existing 120-car fleet and add more frequent service.
On October 22, 2014, the MassDOT Board awarded a $566.6 million contract to a Were you hoping for an Orange Line train diner? It's not likely as MBTA scraps old cars
/ref>
 The Orange Line has two tracks for most of its length; a third track is present between Wellington station and the Charles River portal. This track is used to bypass construction on the other two tracks and for testing newly delivered cars for the Orange Line. The primary maintenance and storage facility is at Wellington station. Had the Orange Line been extended to Reading, the third track would have been the northbound local track, and the present-day northbound track would likely have become a bi-directional express track.
The Orange Line has two tracks for most of its length; a third track is present between Wellington station and the Charles River portal. This track is used to bypass construction on the other two tracks and for testing newly delivered cars for the Orange Line. The primary maintenance and storage facility is at Wellington station. Had the Orange Line been extended to Reading, the third track would have been the northbound local track, and the present-day northbound track would likely have become a bi-directional express track.
Official MBTA Orange Line information
* ttp://world.nycsubway.org/us/boston/orange.html Orange Linefrom nycsubway.org – Includes detailed description and photos of current Orange Line
* ttp://www.cityofboston.gov/news/default.aspx?id=5823 "An Elevated View: The Orange Line", Boston Public Library exhibit about Orange Line elevated line history, October 2012 – January 2013
BPL description
) {{DEFAULTSORT:Orange Line (Mbta) Railway lines opened in 1901 1901 establishments in Massachusetts Standard gauge railways in the United States 600 V DC railway electrification
Oak Grove station
Oak Grove station is a Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) intermodal transit station in the northern section of Malden, Massachusetts, just south of the Melrose border. It is the northern terminus of the rapid transit Orange L ...
in Malden, Massachusetts
Malden is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. At the time of the 2020 U.S. Census, the population was 66,263 people.
History
Malden, a hilly woodland area north of the Mystic River, was settled by Puritans in 1640 on la ...
through Malden and Medford, paralleling the Haverhill Line, then crosses the Mystic River on a bridge into Somerville
Somerville may refer to:
*Somerville College, Oxford, a constituent college of the University of Oxford
Places
*Somerville, Victoria, Australia
* Somerville, Western Australia, a suburb of Kalgoorlie, Australia
* Somerville, New Zealand, a subur ...
, then into Charlestown. It passes under the Charles River and runs through Downtown Boston in the Washington Street Tunnel. The line returns to the surface in the South End, then follows the Southwest Corridor southwest in a cut through Roxbury Roxbury may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Roxbury, Nova Scotia
* Roxbury, Prince Edward Island
;United States
* Roxbury, Connecticut
* Roxbury, Kansas
* Roxbury, Maine
* Roxbury, Boston, a municipality that was later integrated into the city of Bosto ...
and Jamaica Plain to Forest Hills station.
The Orange Line operates during normal MBTA service hours (all times except late nights) with six-car trains. A 120-car fleet built in 1979–1981 is being replaced with a 152-car CRRC fleet from 2018 to 2023. The Orange Line is fully grade-separated; trains are driven by operators with automatic train control for safety. Wellington Carhouse in Medford is used for heavy maintenance and storage; a small yard at Forest Hills is also used for storage. All 20 Orange Line stations are fully accessible. Averaging 201,000 weekday passengers in 2019, the Orange Line has the second-highest ridership of the MBTA subway lines.
The Orange Line originated as the Main Line Elevated of the Boston Elevated Railway, which was built in 1901. It consisted of the Charlestown Elevated, Atlantic Avenue Elevated, Washington Street Elevated, and a portion of the previously-built Tremont Street subway. All of the original route has been replaced, beginning with the Washington Street Tunnel replacing the Tremont Street subway in 1908. The Washington Street Elevated was extended from to Forest Hills in 1909, with an infill station at in 1912; the Charlestown Elevated was extended from to in 1919. The Atlantic Avenue Elevated was closed in 1938.
The newly formed MBTA assigned colors to its subway lines in 1965, with the Main Line becoming the Orange Line. The Charlestown Elevated was closed in 1975; it was replaced by the Haymarket North Extension
The Haymarket North Extension is a section of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's rapid transit Orange Line which currently constitutes the northern section of the line. It runs from North Station through an underground crossing of th ...
, which opened in phases from 1975 to 1977. The Southwest Corridor replaced the Washington Street Elevated in 1987, using an alignment originally intended for Interstate 95
Interstate 95 (I-95) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the East Coast of the United States, running from U.S. Route 1, US Route 1 (US 1) in Miami, Miami, Florida, to the Houlton–Woodstock Border Crossing between M ...
, completing the modern Orange Line alignment. The downtown stations were lengthened in the 1980s to allow six-car trains. Accessibility modifications began with some of those stations and were completed in 2005. opened as an infill station in 2014.
The Orange Line has struggled with reliability issues, including aging infrastructure and trains, since the 2010s. Despite the ongoing fleet replacement, several prominent incidents occurred in 2022. The entire Orange Line was replaced with buses from August 19 to September 18, 2022, to allow for accelerated repairs.
History
Construction
 The Main Line of the electric Boston Elevated Railway opened in segments, starting in 1901. It proceeded from Sullivan Square along the Charlestown Elevated to the Canal Street incline near North Station. It was carried underground by the Tremont Street subway (now part of the
The Main Line of the electric Boston Elevated Railway opened in segments, starting in 1901. It proceeded from Sullivan Square along the Charlestown Elevated to the Canal Street incline near North Station. It was carried underground by the Tremont Street subway (now part of the Green Line
Green Line may refer to:
Places Military and political
* Green Line (France), the German occupation line in France during World War II
* Green Line (Israel), the 1949 armistice line established between Israel and its neighbours
** City Line ( ...
), returning above ground at the Pleasant Street incline (now closed, located just south of Boylston station). A temporary link connected from there to the Washington Street Elevated, which in 1901 ran from this point via Washington Street to Dudley Square (which is most of what is now Phase 1 of the Silver Line).
Also in 1901, the Atlantic Avenue Elevated opened, branching at Causeway Street to provide an alternate route through downtown Boston (along the shoreline, where today there is no rail transit) to the Washington Street Elevated.
In 1908, a new Washington Street Tunnel opened, allowing Main Line service to travel from the Charlestown Elevated, underground via an additional new portal at the Canal Street incline, under downtown Boston and back up again to meet the Washington Street Elevated and Atlantic Avenue Elevated near Chinatown
A Chinatown () is an ethnic enclave of Chinese people located outside Greater China, most often in an urban setting. Areas known as "Chinatown" exist throughout the world, including Europe, North America, South America, Asia, Africa and Austra ...
. The stations were richly decorated with tile work, mosaics, and copper; after criticism of the large Tremont Street subway headhouses, most entrances were comparatively modest and set into buildings. Use of the parallel Tremont Street subway was returned exclusively to streetcars.
By 1909, the Washington Street Elevated had been extended south to . Trains from Washington Street were routed through the new subway, either all the way to Sullivan Square, or back around in a loop via the subway and then the Atlantic Avenue Elevated.
In 1919, the same year that the Atlantic Avenue Elevated was partially damaged in Boston's Great Molasses Flood
The Great Molasses Flood, also known as the Boston Molasses Disaster, was a disaster that occurred on January 15, 1919, in the North End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts.
A large storage tank filled with of molasses, weighing approximat ...
, the Charlestown Elevated was extended north from Sullivan Square to Everett, over surface right-of-way parallel to Alford Street/Broadway, with a drawbridge
A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of moveable bridge typically at the entrance to a castle or tower surrounded by a moat. In some forms of English, including American English, the word ''drawbridge'' commonly refers to all types of moveable ...
over the Mystic River. The Boston Elevated had long-term plans to continue this extension further north to Malden, a goal which would only be achieved decades later, under public ownership and not via the Everett route.
Closure of Atlantic Avenue Elevated and ownership changes
 Following a 1928 accident at a tight curve on Beach Street, the southern portion of the Atlantic Avenue Elevated, between South Station and Tower D on Washington Street, was closed (except for rush-hour trips from Dudley to North Station via the Elevated), breaking the loop; non-rush-hour Atlantic Avenue service was reduced to a shuttle between North and South Stations. In 1938, the remainder of the Atlantic Avenue Elevated was closed, leaving the subway as the only route through downtown – what is now the Orange Line between and stations.
Ownership of the railway was transferred from the private Boston Elevated Railway to the public Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA) in 1947; the MTA was itself reconstituted as the modern Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) in 1964.
Following a 1928 accident at a tight curve on Beach Street, the southern portion of the Atlantic Avenue Elevated, between South Station and Tower D on Washington Street, was closed (except for rush-hour trips from Dudley to North Station via the Elevated), breaking the loop; non-rush-hour Atlantic Avenue service was reduced to a shuttle between North and South Stations. In 1938, the remainder of the Atlantic Avenue Elevated was closed, leaving the subway as the only route through downtown – what is now the Orange Line between and stations.
Ownership of the railway was transferred from the private Boston Elevated Railway to the public Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA) in 1947; the MTA was itself reconstituted as the modern Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) in 1964.
Orange Line naming
 The line was known as the Main Line Elevated under the Boston Elevated Railway, and the Forest Hills–Everett Elevated (Route 2 on maps) under the Metropolitan Transportation Authority.
After taking over operations in August 1964, the MBTA began rebranding many elements of Boston's public transportation network. Colors were assigned to the rail lines on August 26, 1965, as part of a wider modernization developed by Cambridge Seven Associates.
The line was known as the Main Line Elevated under the Boston Elevated Railway, and the Forest Hills–Everett Elevated (Route 2 on maps) under the Metropolitan Transportation Authority.
After taking over operations in August 1964, the MBTA began rebranding many elements of Boston's public transportation network. Colors were assigned to the rail lines on August 26, 1965, as part of a wider modernization developed by Cambridge Seven Associates. Peter Chermayeff
Peter Chermayeff LLC is a Massachusetts-based architectural firm which specializes in aquarium architecture and exhibit design, from conceptual planning to the details of final realization.
History
The two principals, Peter Chermayeff and Bobb ...
assigned red, green, and blue to the other three lines based on geographic features; however, according to Chermayeff, the Main Line El "ended up being orange for no particular reason beyond color balance." The firm originally planned for yellow instead of orange, but yellow was rejected after testing because yellow text was difficult to read on a white background. (Yellow was later used for MBTA bus
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) operates List of MBTA bus routes, 170 bus routes in the Greater Boston area. The MBTA has a policy objective to provide transit service within walking distance (defined as ) for all residents ...
service). The MBTA and transit historians later claimed that orange came from Orange Street, an early name for what is now part of Washington Street.
In January and February 1967, the four original Washington Street Tunnel stations were renamed. Transfer stations were given the same name for all lines: Winter and Summer stations plus Washington on the Red Line became Washington, Milk and State plus Devonshire on the Blue Line became after the cross street, and Union and Friend plus Haymarket Square on the Green Line became after Haymarket Square. Boylston Street was renamed Essex to avoid confusion with nearby Boylston station on the Green Line.
In May 1987, Essex was renamed after the adjacent Chinatown neighborhood, and Washington renamed after the adjacent shopping district. In March 2010, New England Medical Center station was renamed as two years after the eponymous hospital changed its name.
Rerouting of Charlestown and Everett service
The Boston Transportation Planning Review looked at the line in the 1970s, considering extensions to reach the Route 128 beltway, with termini at Reading in the north and Dedham in the south. As a result of this review, the Charlestown Elevated – which served the Charlestown neighborhood north of downtown Boston and the inner suburb of Everett – was demolished and replaced in 1975. The Haymarket North Extension rerouted the Orange Line through an underwater crossing of the Charles River. Service in Charlestown was replaced with service along Boston and Maine tracks routed partially beneath an elevated section ofInterstate 93
Interstate 93 (I-93) is an Interstate Highway in the New England states of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont in the United States. Spanning approximately along a north–south axis, it is one of three primary Interstate Highways ...
, ultimately to and then to in Malden, Massachusetts
Malden is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. At the time of the 2020 U.S. Census, the population was 66,263 people.
History
Malden, a hilly woodland area north of the Mystic River, was settled by Puritans in 1640 on la ...
, instead of Everett. Rail service to Everett was replaced with buses.
The extension was unique among Boston transit lines as it contained a third express track between Wellington and Community College stations. These stations, along with Sullivan Sq, have two island platform stations as opposed to the more normal single island stations found on the southern side of the Orange Line. This express track was designed for the never-built extension north of Oak Grove to Reading. The third track would have allowed peak-direction express service as well as places to terminate trains. Service north of Oak Grove was planned to have longer headways to account for the lower projected ridership. This extension was opposed by residents of Melrose who preferred restored commuter rail service. Because of this, the express track ends at Wellington and a single commuter rail track continues parallel to the Orange Line north to Reading.
Closure of Washington Street Elevated
Construction ofInterstate 95
Interstate 95 (I-95) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the East Coast of the United States, running from U.S. Route 1, US Route 1 (US 1) in Miami, Miami, Florida, to the Houlton–Woodstock Border Crossing between M ...
into downtown Boston was cancelled in 1972 after local protest over the necessary demolition. However, land for I-95's Southwest Corridor through Roxbury Roxbury may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Roxbury, Nova Scotia
* Roxbury, Prince Edward Island
;United States
* Roxbury, Connecticut
* Roxbury, Kansas
* Roxbury, Maine
* Roxbury, Boston, a municipality that was later integrated into the city of Bosto ...
had already been cleared of buildings; moreover, the state had already committed to using this vacant land for transportation purposes. As a result, instead of an 8-lane Interstate highway with a relocated Orange Line running in its median (in a manner similar to the Chicago Transit Authority's Dan Ryan, Congress, and O'Hare branches), the space would be occupied by the realigned Orange Line, a reconstructed three-track mainline for Amtrak's Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston through Providence, New Haven, Stamford, New York City, Philadelphia, Wilmington, a ...
and MBTA Commuter Rail
The MBTA Commuter Rail system serves as the commuter rail arm of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's transportation coverage of Greater Boston in the United States. Trains run over of track to 141 different stations, with 58 statio ...
trains, and a linear park. After this re-routing was accomplished in 1987, the Washington Street Elevated was torn down, the last major segment of the original elevated line to be demolished.
Chinatown station Chinatown Station may refer to transit stations in:
;United States
* Chinatown station (MBTA), a subway station in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cermak–Chinatown station, an "L" station in Chicago, Illinois
* Chinatown station (HART), a planned ligh ...
was closed to allow the Orange Line to be tied into the new Southwest Corridor. On May 4, 1987, the Orange Line was rerouted from the southern end of the Washington Street Tunnel onto the new Southwest Corridor. Instead of rising up to elevated tracks, it now veered west at the Massachusetts Turnpike and followed the Pike and the old Boston and Albany Railroad right-of-way to the existing MBTA Commuter Rail
The MBTA Commuter Rail system serves as the commuter rail arm of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's transportation coverage of Greater Boston in the United States. Trains run over of track to 141 different stations, with 58 statio ...
stop at . It then continued along new tracks, partially covered and partially open but depressed, to . This MBTA right-of-way is also shared by Amtrak as part of the national Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston through Providence, New Haven, Stamford, New York City, Philadelphia, Wilmington, a ...
intercity passenger rail service.
While ending more or less at the same terminus (Forest Hills), the new routing passes significantly to the west of its previous route on Washington Street; local residents were promised replacement service. Originally, plans provided for light rail vehicles street running
A street running train is a train which runs on a track built on public streets. The rails are embedded in the roadway, and the train shares the street with other users, such as pedestrians, cars and cyclists, thus often being referred to as r ...
in mixed traffic, from Washington Street to Dudley Square, then diverting southeastward on Warren Street towards Dorchester. In 2002, Phase 1 of the Silver Line bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes ...
was added to connect Washington Street to the downtown subways, attempting to address this service need. This replacement service was controversial, as many residents preferred the return of rail transportation.
Station renovations
In the mid-1980s, the MBTA spent $80 million to extend the platforms of seven Red Line and three Orange Line stations (, Washington, and ) to allow the use of six-car trains. Washington and Essex were made fully accessible, as was the northbound platform at Essex. The Southwest Corridor station opened in 1987 were all fully accessible. Six-car trains entered service on August 18, 1987. was also renovated around 1987. This left only , five stations on the Haymarket North Extension, and the southbound platform at Chinatown inaccessible by the 1990 passage of theAmericans with Disabilities Act
The Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 or ADA () is a civil rights law that prohibits discrimination based on disability. It affords similar protections against discrimination to Americans with disabilities as the Civil Rights Act of 1964 ...
. Construction at and began in 1991. was retrofitted with elevators in 2000. The 1975-built was expanded into a "superstation" with a cross-platform transfer to the Green Line; elevators were in installed in 2001, though the Green Line did not use the station until 2004. The southbound platform at Chinatown was made accessible in 2002. Renovations to and were completed in 2005, making the Orange Line the first of the four original MBTA subway lines to become fully accessible.
Assembly
Somerville
Somerville may refer to:
*Somerville College, Oxford, a constituent college of the University of Oxford
Places
*Somerville, Victoria, Australia
* Somerville, Western Australia, a suburb of Kalgoorlie, Australia
* Somerville, New Zealand, a subur ...
began planning an infill station between and to serve the new Assembly Square
Assembly Square is a neighborhood in Somerville, Massachusetts. It is located along the west bank of the Mystic River, bordered by Ten Hills and Massachusetts Route 28 to the north and the Charlestown neighborhood of Boston to the south. The dis ...
development. The $57 million station was funded by the state's Executive Office of Housing and Economic Development, FTA Section 5309 New Starts program, and Federal Realty Investment Trust (the developer of Assembly Square). Construction began in late 2011 and finished in mid 2014. The new station, , opened on September 2, 2014. It was the first new station on the MBTA subway system since 1987.
Reliability issues and repairs
During the unusually brutal winter of 2014–2015, the entire MBTA system was shut down on several occasions by heavy snowfalls. The aboveground sections of the Orange and Red lines were particularly vulnerable due to their exposed third rail, which iced over during storms. When a single train stopped due to power loss, other trains soon stopped as well; without continually running trains pushing snow off the rails, the lines were quickly covered in snow. (Because the Blue Line was built with overhead lines on its surface section due to its proximity to corrosive salt air, it was not subject to icing issues.) Starting in 2015, the MBTA began implementing its $83.7 million Winter Resiliency Program, much of which focused on preventing similar issues with the Orange and Red lines. The Southwest Corridor section of the Orange Line is located in a trench and is protected from the worst weather, but the 1970s-built
Starting in 2015, the MBTA began implementing its $83.7 million Winter Resiliency Program, much of which focused on preventing similar issues with the Orange and Red lines. The Southwest Corridor section of the Orange Line is located in a trench and is protected from the worst weather, but the 1970s-built Haymarket North Extension
The Haymarket North Extension is a section of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's rapid transit Orange Line which currently constitutes the northern section of the line. It runs from North Station through an underground crossing of th ...
had older infrastructure and was in worse shape. From north, it is exposed to the weather and largely built on an embankment, rendering it more vulnerable. That section is receiving new heated third rail, switch heaters, and snow fences to reduce the impacts of inclement weather. The work requires bustitution of the line from Sullivan Square to Oak Grove on certain weeknights and weekends.
In October 2018, the MBTA awarded a $218 million signal contract for the Red and Orange Lines, which was planned to allow 4.5-minute headways on the Orange Line beginning in 2022.
On July 22, 2022, an Orange Line train caught fire while crossing the Mystic River. Passengers had to jump out of the train onto the tracks, and one woman jumped into the river below. There were no injuries or casualties. A metal sill along the underside of the train came loose and came into contact with the third rail, igniting sparks.
Following various reliability issues on the Orange Line, the MBTA announced that it would close the entire line for renovations from August 19 to September 18, 2022. During the closure, the MBTA conducted accelerated repairs to track, ties, signals, and concrete walls, as well as replacing two crossovers. This was intended to remove speed restrictions and improve safety and reliability. The shutdown also gave time for more new CRRC cars to be delivered and put into service; after the closure, service on the line resumed with new trains almost all the time. However, the work was not enough to eliminate all slow zones, and temporary slow zones were added where work was performed. By early October, a round trip on the full line was 13 minutes slower than before the shutdown, and 20 minutes slower than it would be without any slow zones. On October 25, the MBTA sent a letter to Senator Ed Markey, who had been investigating the project, detailing work needed during November and December to lift remaining slow zones, ranging from always-planned to unexpectedly necessary tasks.
Historical routes
Station listing
Rolling stock

 The Orange Line is standard-gauge
The Orange Line is standard-gauge heavy rail
Various terms are used for passenger railway lines and equipment; the usage of these terms differs substantially between areas:
Rapid transit
A rapid transit system is an electric railway characterized by high speed (~) and rapid accelerati ...
and uses a third rail for power. As of 2022, the fleet is undergoing replacement. The newer cars are being built by CRRC in a newly-constructed plant in Springfield, Massachusetts
Springfield is a city in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, United States, and the seat of Hampden County. Springfield sits on the eastern bank of the Connecticut River near its confluence with three rivers: the western Westfield River, the ...
, with 152 cars on order, along with additional cars for the Red Line. The older fleet was built between 1979 and 1981 by Hawker Siddeley Canada of Thunder Bay, Ontario, Canada, and are based on the PA3 model used by PATH in New Jersey. There were 120 older cars prior to replacement, numbered 01200-01319. All in-service Orange Line trains run in six-car consists. Cars of both fleets are 65 feet (20 m) long and 9 ft 3 in (2.8 m) wide, with three pairs of doors on each side.
, weekday peak and afternoon service operates on 7-minute headways, with headways ranging from 8 to 10 minutes at other times. Vehicle utilization ranges between 8 trains (48 cars) and 15 trains (90 cars).
The "T" previously had a fleet of Pullman-Standard
The Pullman Company, founded by George Pullman, was a manufacturer of railroad cars in the mid-to-late 19th century through the first half of the 20th century, during the boom of railroads in the United States. Through rapid late-19th century ...
heavy rail cars for the Orange Line. These cars, known as 01100s, had been in service since the 1950s, and saw service on both the elevated and the northern extension before they were retired in 1981. Several remained on the property for some time before being scrapped. The 01100 cars were a favorite for fans, as the small motorman's cab enabled passengers to stand at the front for an operator's-eye view.
New CRRC trains
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
based manufacturer CNR (which became part of CRRC the following year) to build 152 replacement railcars for the Orange Line, as well as additional cars for the Red Line. The other bidders were Bombardier Transportation
Bombardier Transportation was a Canadian-German rolling stock and rail transport manufacturer, headquartered in Berlin, Germany.
It was one of the world's largest companies in the rail vehicle and equipment manufacturing and servicing industry ...
, Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Hyundai Rotem
Hyundai Rotem (founded in 1977) is a South Korean company that manufactures rolling stock, defense products and plant equipment. It is a part of the Hyundai Motor Group. Its name was changed from Rotem to Hyundai Rotem in December 2007 to refl ...
. CNR began building the cars at a new manufacturing plant in Springfield, Massachusetts
Springfield is a city in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, United States, and the seat of Hampden County. Springfield sits on the eastern bank of the Connecticut River near its confluence with three rivers: the western Westfield River, the ...
, with initial deliveries expected in 2018 and all cars in service by 2023. The Board forwent federal funding to allow the contract to specify the cars be built in Massachusetts, to create a local railcar manufacturing industry. In conjunction with the new rolling stock, the remainder of the $1.3 billion allocated for the project would pay for testing, signal improvements and expanded maintenance facilities, as well as other related expenses. Sixty percent of the car's components are sourced from the United States.
After delays due to issues with the train's control system, the first new train entered revenue service on August 14, 2019; Replacement of the signal system is expected to be complete by 2022 on the Orange Line; the total cost is $218 million for both the Red and Orange Lines.
While waiting for new cars, service has deteriorated due to maintenance problems with the old cars. The number of trains at rush hour was reduced from 17 (102 cars) to 16 (96 cars) in 2011; in the same year, daily ridership surpassed 200,000. Increased running times – largely due to longer dwell times from increased ridership – resulted in headways being lengthened from 5 minutes before 2011 to 6 minutes in 2016. The increased fleet size with the new trains will allow headways to be reduced to between 4 and 5 minutes at peak. In the interim, a 2016 test of platform markings at North Station which show boarding passengers where to stand to avoid blocking alighting passengers resulted in a one-third decrease in dwell times.
The new cars have faced several issues since their August entry into service. In November 2019, a car derailed while undergoing initial testing at the Wellington yard. The last car of a six car trainset had jumped the rails while going over a switch, however no major damage had been reported. Several months earlier, the first two trainsets were taken out of service due to safety issues following the inadvertent opening of a passenger door while the train was in motion. Cars were also rechecked in early December 2019, after issues with sounds combined with passenger overload necessitated removal from service. The first train was restored to service in January 2020. The trains were pulled again on March 16, 2021, after a derailment involving one of the cars. Buses replaced trains around the site of the derailment until April 12. The CRRC cars remained out of service as of July 2021; defective side bearer pads were identified as a contributing factor. These dampen the movements of the trucks (which include the wheels) with respect to the car bodies, but were found to be wearing in such a way as to produce too much friction. The first of the CRRC trainsets was returned to revenue service on August 20, after modifications were approved by the MBTA's Safety Department and the Department of Public Utilities. The new cars were again removed from service on May 19–23, 2022, after a braking issue on one car due to an incorrectly installed bolt, and again between June and July 2022 due to a battery failure.
The CRRC contract requires delivery of all Orange Line cars by January 2022, with a fine of $500 per day per car for late deliveries. Delays began to accumulate in 2019, and then facilities in China and Springfield had to shut down and operate at reduced capacity for parts of 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. As of September 2022, 78 of 152 new cars had been put in service on the Orange Line. This was enough for service almost all the time because of the rush hour service cap introduced after an FTA safety audit identified insufficient staffing of subway dispatchers. The MBTA indicated it would assess which delays were the fault of the contractor at the end of the contract.
The first #12 fleet cars were sent to scrap on September 22, 2022. Almost all will be processed by the contractor Costello to remove hazardous materials and be recycled; two have been offered to the Seashore Trolley Museum in Kennebunkport, Maine./ref>
Facilities
References
External links
Official MBTA Orange Line information
* ttp://world.nycsubway.org/us/boston/orange.html Orange Linefrom nycsubway.org – Includes detailed description and photos of current Orange Line
* ttp://www.cityofboston.gov/news/default.aspx?id=5823 "An Elevated View: The Orange Line", Boston Public Library exhibit about Orange Line elevated line history, October 2012 – January 2013
BPL description
) {{DEFAULTSORT:Orange Line (Mbta) Railway lines opened in 1901 1901 establishments in Massachusetts Standard gauge railways in the United States 600 V DC railway electrification