Macedonian Question on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The region of
The region of
 The Macedonians (, ''Makedónes'') were an ancient tribe that lived on the
The Macedonians (, ''Makedónes'') were an ancient tribe that lived on the
 Taking advantage of the desolation left by the nomadic tribes,
Taking advantage of the desolation left by the nomadic tribes,
 The initial period of Ottoman rule led a depopulation of the plains and river valleys of Macedonia. The Christian population there fled to the mountains. Ottomans were largely brought from Asia Minor and settled parts of the region. Towns destroyed in
The initial period of Ottoman rule led a depopulation of the plains and river valleys of Macedonia. The Christian population there fled to the mountains. Ottomans were largely brought from Asia Minor and settled parts of the region. Towns destroyed in
 The rise of European nationalism in the 18th century led to the expansion of the Hellenic idea in Macedonia. Its main pillar throughout the centuries of Ottoman rule had been the indigenous Greek population of historical Macedonia. Under the influence of the Greek schools and the
The rise of European nationalism in the 18th century led to the expansion of the Hellenic idea in Macedonia. Its main pillar throughout the centuries of Ottoman rule had been the indigenous Greek population of historical Macedonia. Under the influence of the Greek schools and the
 In Europe, the classic non-national states were the ''multi-ethnic empires'' such as the Ottoman Empire, ruled by a
In Europe, the classic non-national states were the ''multi-ethnic empires'' such as the Ottoman Empire, ruled by a
 The
The
 A great contribution to the Serbian cause was made by an astronomer and historian from
A great contribution to the Serbian cause was made by an astronomer and historian from
 It was established by the end of the 19th century that the majority of the population of central and Southern Macedonia (vilaets of Monastiri and Thessaloniki) were predominantly an ethnic Greek population, while the Northern parts of the region (vilaet of Skopje) were predominantly Slavic. Jews and Ottoman communities were scattered all over. Because of Macedonia's such polyethnic nature, the arguments which Greece used to promote its claim to the whole region were usually of historical and religious character. The Greeks consistently linked nationality to the allegiance to the Patriarchate of Constantinople. "Bulgarophone", "Albanophone" and "Vlachophone" Greeks were coined to describe the population who were Slavic, Albanian or
It was established by the end of the 19th century that the majority of the population of central and Southern Macedonia (vilaets of Monastiri and Thessaloniki) were predominantly an ethnic Greek population, while the Northern parts of the region (vilaet of Skopje) were predominantly Slavic. Jews and Ottoman communities were scattered all over. Because of Macedonia's such polyethnic nature, the arguments which Greece used to promote its claim to the whole region were usually of historical and religious character. The Greeks consistently linked nationality to the allegiance to the Patriarchate of Constantinople. "Bulgarophone", "Albanophone" and "Vlachophone" Greeks were coined to describe the population who were Slavic, Albanian or
 Romanian influence in the area made some success in Bitola, Kruševo, and in the Aromanian villages in the districts of Bitola and Ohrid. Most Aromanians regard and regarded themselves as a separate ethnic group, and Romanians view such nations as subgroups of a wider Romanian ethnicity. Some Aromanians do identify as part of the Romanian nation however. Currently, among anti-Romanian groups of Aromanians, particularly in Greece, these acts are referred to as "the Romanian propaganda".
Romanian influence in the area made some success in Bitola, Kruševo, and in the Aromanian villages in the districts of Bitola and Ohrid. Most Aromanians regard and regarded themselves as a separate ethnic group, and Romanians view such nations as subgroups of a wider Romanian ethnicity. Some Aromanians do identify as part of the Romanian nation however. Currently, among anti-Romanian groups of Aromanians, particularly in Greece, these acts are referred to as "the Romanian propaganda".
 Bulgarian troops were welcomed as liberators in 1941 but mistakes of the Bulgarian administration made a growing number of people resent their presence by 1944. It must also to be noted that the
Bulgarian troops were welcomed as liberators in 1941 but mistakes of the Bulgarian administration made a growing number of people resent their presence by 1944. It must also to be noted that the
- Лидерот на ВМРО-ДПМНЕ и Премиер на Република Македонија, Љубчо Георгиевски одговара и полемизира на темата за национално помирување. After the war the region received the status of a constituent republic within Yugoslavia and in 1945 a separate,
 The Bulgarian population in
The Bulgarian population in 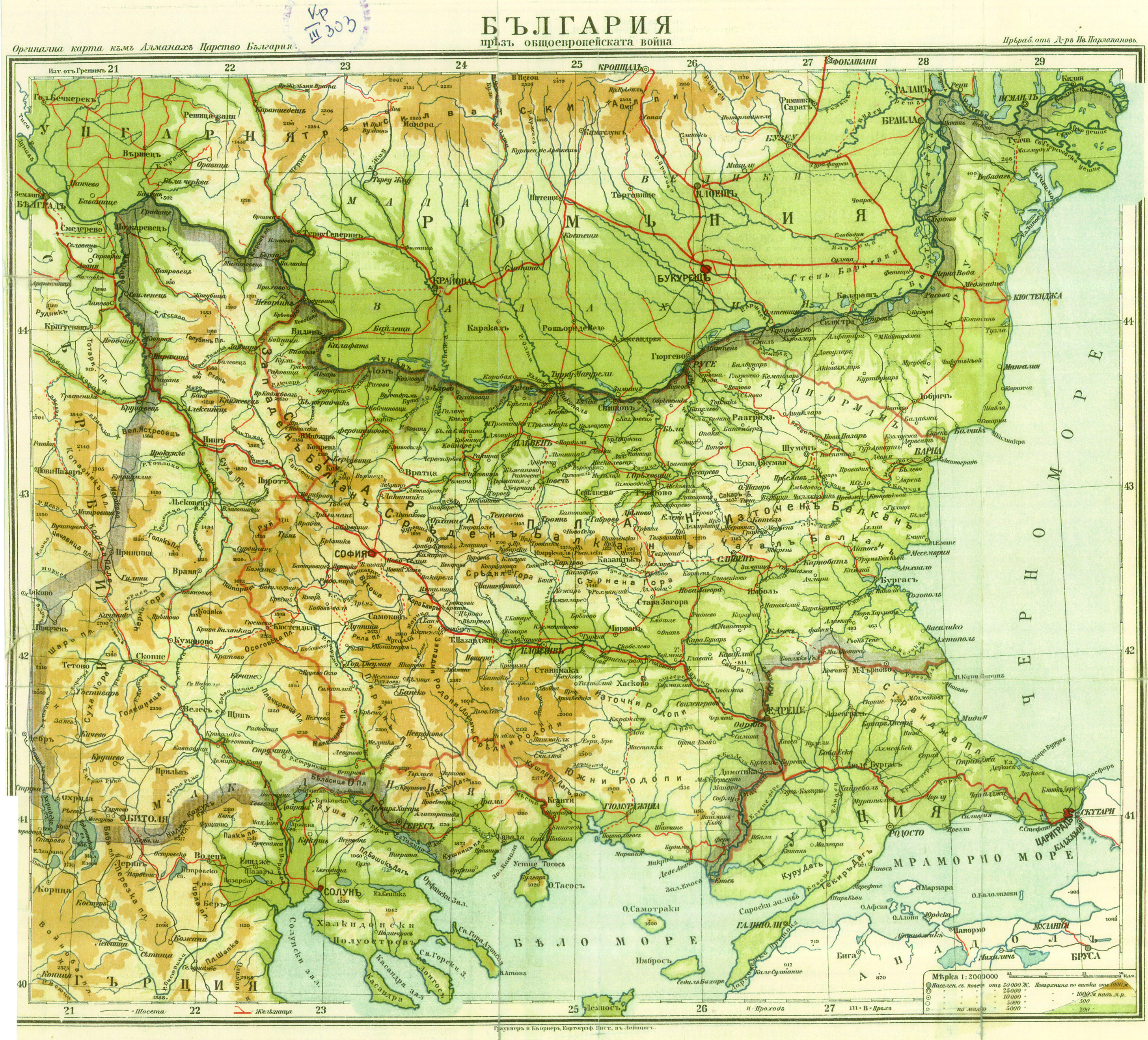 The movement of the Bulgarian army in Yugoslavia started on April 19, and in Greece on April 20. The prominent force which occupied most of Vardar Macedonia, was the Bulgarian 5th Army. The 6th and 7th Infantry Divisions were active in invading the Vardar Banovina between 19 and 24 April 1941. The Bulgarian troops were mainly present in the western part of Vardar Macedonia, close to the Italian occupational zone, because of some border clashes with Italians, who implemented Albanian interests and terrorized the local peasants. So the most of
The movement of the Bulgarian army in Yugoslavia started on April 19, and in Greece on April 20. The prominent force which occupied most of Vardar Macedonia, was the Bulgarian 5th Army. The 6th and 7th Infantry Divisions were active in invading the Vardar Banovina between 19 and 24 April 1941. The Bulgarian troops were mainly present in the western part of Vardar Macedonia, close to the Italian occupational zone, because of some border clashes with Italians, who implemented Albanian interests and terrorized the local peasants. So the most of
Македония 1941 Възкресение
' (''Macedonia 1941 Resurrection''), Сотир Нанев (Sotir Nanev), 1942, reprinted 1993 with , publisher Труд (Trud). Memoirs of a Macedonia-born Bulgarian lieutenant participating in the occupation of the Yugoslavian and Greek parts of Macedonia.
Between Past and Future: Civil-Military Relations in Post-Communist Balkan States
', by Biljana Vankovska, 2003, , page 270. Extract from
Dimitre Mičev (Dimiter Minchev). Hosted on Kroraina.com, retrieved 2007-08-21. charged with taking over the local authorities. Bulgarian Action Committees propagated a proclamation to the Bulgarians in North Macedonia on occasion of the invasion of the Bulgarian Army in the Vardar Banovina. As regards the Serbian colonists, the members of the campaign committees were adamant—they had to be deported as soon as possible and their properties to be returned to the locals. With the arrival of the Bulgarian army mass expulsion of Serbs from the area of the Vardar Macedonia took place. First, the city dwellers were deported in 1941, then all of the suspected pro-Serbs. Metodi Shatarov-Šarlo, who was a local leader of the Yugoslav Communist Party, also refused to define the Bulgarian forces as occupiers (contrary to instructions from Meanwhile, the Bulgarian government was responsible for the round-up and deportation of over 7,000 Jews in Skopje and Bitola. It refused to deport the Jews from Bulgarian proper but later under German pressure those Jews from the new annexed territories, without a Bulgarian
Meanwhile, the Bulgarian government was responsible for the round-up and deportation of over 7,000 Jews in Skopje and Bitola. It refused to deport the Jews from Bulgarian proper but later under German pressure those Jews from the new annexed territories, without a Bulgarian  A total of 3,100 people in the Blagoevgrad District declared themselves Macedonian in the 2001 census (0.9% of the population of the region). According to the European Court of Human Rights ethnic Macedonians in Bulgaria have endured Ethnic Macedonians in Bulgaria#European Court of Human Rights Decisions and European Parliament, violations of human rights by the Bulgarian government.
In Bulgaria today, the Macedonian question has been understood largely as a result of the violation of national integrity, beginning with the revision of the
A total of 3,100 people in the Blagoevgrad District declared themselves Macedonian in the 2001 census (0.9% of the population of the region). According to the European Court of Human Rights ethnic Macedonians in Bulgaria have endured Ethnic Macedonians in Bulgaria#European Court of Human Rights Decisions and European Parliament, violations of human rights by the Bulgarian government.
In Bulgaria today, the Macedonian question has been understood largely as a result of the violation of national integrity, beginning with the revision of the
, Albanian Helsinki Committee with the support of the Finnish Foundation ‘KIOS’ and "Finnish NGO Foundation for Human Rights" was officially recognized. Schools and radio stations in Macedonian were founded in the area. Albania has recognised around 5,000 strong Macedonian minority. In Albania are both Bulgarian and Macedonian organizations. Each of them claims that the local Slavic population is either Bulgarian or Macedonian. The population itself, which is predominantly
Radko
as "promoting racial and religious hate and intolerance". In 2009 the European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg, condemned Republic of Macedonia because of violations of the European Convention of Human Rights in this case. Nevertheless, during the last few years, rising economic prosperity and the EU membership of Bulgaria has seen around 60,000 Macedonians applying for Bulgarian
Banac, Ivo. (1984). The National Question in Yugoslavia. Origins, History, Politics. Cornell University Press: Ithaca/London University Press: Ithaca/London (online version of relevant pages)
* Boué, Ami. (1840). Le Turquie d’Europe. Paris: Arthus Bertrand.
* Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. (1914). Report of the International Commission To Inquire into the Causes and Conduct of the Balkan Wars. Washington: The Carnegie Endowment from https://web.archive.org/web/20110927153709/http://vmro.150m.com/en/carnegie/ * * Gopčević, Spiridon. (1889). Makedonien und Alt-Serbien. Wien: L. W. Seidel & Sohn. - Стара Србија и Македонија, превод: Милан Касумовић. Београд, 1890.
Jezernik, Bozhidar. Macedonians: Conspicuous By Their Absence
Misirkov, Krste P. (1903). Za makedonckite raboti. Sofia: Liberalni klub.
(In Macedonian and English)
The Emergence of Macedonian National Thought and the Formation of a National Programme (up to 1878) by Blaže Ristovski
* Kunčov, Vasil. (1900). Makedonija. Etnografija i statistika. Sofia: Državna pečatnica (Кънчов, В. 1900, Македония. Етнография и статистика. София: Държавна печатница). * Lange-Akhund, Nadine. (1998). The Macedonian Question, 1893–1908 from Western Sources. Boulder, Colo. : New York. * MacKenzie, Georgena Muir and Irby, I.P. (1971). Travels in the Slavonic Provinces of Turkey in Europe. New York, Arno Press. * Poulton, Hugh. (1995). Who are the Macedonians? C. Hurst & Co. (Publishers) Ltd., London * Roudometoff, Victor. (2000). The Macedonian Question: Culture, Historiography, Politics. Boulder, CO: East European Monographs. * quoted in . * Weigand, Gustav. (1924). ETHNOGRAPHIE VON MAKEDONIEN, Geschichtlich-nationaler, spraechlich-statistischer Teil von Prof. Dr. Gustav Weigand, Leipzig, Friedrich Brandstetter. * Wilkinson, H.R. (1951). Maps and Politics; a review of the ethnographic cartography of Macedonia, Liverpool University Press. * Kuhn's Zeitschrift für vergleichende Sprachforschung XXII (1874), Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht

Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
is known to have been inhabited since Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
times.
Еarliest historical inhabitants
The earliest historical inhabitants of the region were thePelasgians
The name Pelasgians (, ) was used by Classical Greek writers to refer either to the predecessors of the Greeks, or to all the inhabitants of Greece before the emergence of the Greeks. In general, "Pelasgian" has come to mean more broadly all ...
, the Bryges
Bryges or Briges () is the historical name given to a people of the ancient Balkans. They are generally considered to have been related to the Phrygians, who during classical antiquity lived in western Anatolia. Both names, ''Bryges'' and ''Phryg ...
and the Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
. The Pelasgians occupied Emathia and the Bryges occupied northern Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, as well as Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
, mainly west of the Axios River and parts of Mygdonia
Mygdonia (; ) was an ancient territory, part of ancient Thrace, later conquered by Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon, which comprised the plains around Therma (Thessalonica) together with the valleys of Klisali and Besikia, including the ar ...
. Thracians, in early times occupied mainly the eastern parts of Macedonia, (Mygdonia
Mygdonia (; ) was an ancient territory, part of ancient Thrace, later conquered by Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon, which comprised the plains around Therma (Thessalonica) together with the valleys of Klisali and Besikia, including the ar ...
, Crestonia
Crestonia (or Crestonice) () was an ancient region immediately north of Mygdonia. The Echeidorus river, which flowed through Mygdonia into the Thermaic Gulf, had its source in Crestonia. It was partly occupied by a remnant of the Pelasgi, who spo ...
, Bisaltia). The Ancient Macedonians
The Macedonians (, ) were an ancient tribe that lived on the alluvial plain around the rivers Haliacmon and lower Vardar, Axios in the northeastern part of Geography of Greece#Mainland, mainland Greece. Essentially an Ancient Greece, ancient ...
are missing from early historical accounts because they had been living in the southern extremities of the region – the Orestian highlands – since before the Dark Ages. The Macedonian tribes subsequently moved down from Orestis in the upper Haliacmon due to pressure from the Orestae.
Ancient Macedonians
The name of the region ofMacedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
(, ''Makedonia'') derives from the tribal name of the ancient Macedonians (, ''Makedónes''). According to the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
historian Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
, the ''Makednoi'' () were a Dorian tribe that stayed behind during the great southward migration of the Dorian Greeks. The word "Makednos" is cognate with the Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greec ...
word "Μάκος" ''Μakos'' (Attic
An attic (sometimes referred to as a '' loft'') is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building. It is also known as a ''sky parlor'' or a garret. Because they fill the space between the ceiling of a building's t ...
form Μήκος – "mékos"), which is Greek for "length". The ancient Macedonians took this name either because they were physically tall, or because they settled in the mountains. The latter definition would translate "Macedonian" as "Highlander".
 The Macedonians (, ''Makedónes'') were an ancient tribe that lived on the
The Macedonians (, ''Makedónes'') were an ancient tribe that lived on the alluvial plain
An alluvial plain is a plain (an essentially flat landform) created by the deposition of sediment over a long period by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A ''floodplain'' is part of the process, bei ...
around the rivers Haliacmon
The Haliacmon (, ''Aliákmonas''; formerly: , ''Aliákmon'' or ''Haliákmōn'') is the longest river flowing entirely in Greece, with a total length of . In Greece there are three rivers longer than Haliacmon: Maritsa (), Struma (Strymónas), bot ...
and lower Axios
Axios commonly refers to:
* Axios (river), a river that runs through Greece and North Macedonia
* ''Axios'' (website), an American news and information website
Axios may also refer to:
Brands and enterprises
* Axios, a brand of suspension produ ...
in the northeastern part of mainland Greece
Greece is a country in Southeastern Europe, on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. It is bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cret ...
. Essentially an ancient Greek people,; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; . they gradually expanded from their homeland along the Haliacmon valley on the northern edge of the Greek world, absorbing or driving out neighbouring non-Greek tribes, primarily Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
and Illyrian. They spoke Ancient Macedonian, which was either a sibling language to Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
or a Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greec ...
dialect, although the prestige language
Prestige may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Films
* ''Prestige'' (film), a 1932 American film directed by Tay Garnett: woman travels to French Indochina to meet up with husband
* ''The Prestige'' (film), a 2006 American thriller direct ...
of the region was at first Attic
An attic (sometimes referred to as a '' loft'') is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building. It is also known as a ''sky parlor'' or a garret. Because they fill the space between the ceiling of a building's t ...
and then Koine Greek
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the koiné language, common supra-regional form of Greek language, Greek spoken and ...
. Their religious beliefs mirrored those of other Greeks, following the main deities of the Greek pantheon
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancie ...
, although the Macedonians continued Archaic burial practices that had ceased in other parts of Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
after the 6th century BC. Aside from the monarchy, the core of Macedonian society was its nobility. Similar to the aristocracy of neighboring Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, their wealth was largely built on herding horses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 milli ...
and cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
.
Roman Macedonia
After the defeat ofAndriscus
Andriscus (, ''Andrískos''; 154/153 BC – 146 BC), also often referenced as Pseudo-Philip, was a Greek pretender who became the last independent king of Macedon in 149 BC as Philip VI (, ''Philipos''), based on his claim of being Philip, a n ...
in 148 BC, Macedonia officially became a province of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
in 146 BC. Hellenization of the non-Greek population was not yet complete in 146 BC, and many of the Thracian and Illyrian tribes had preserved their languages. It is also possible that the ancient Macedonian tongue was still spoken, alongside Koine
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-regional form of Greek spoken and written during the Hellenistic ...
, the common Greek language of the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
era. From an early period, the Roman province of Macedonia included Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, parts of Thrace and Illyria
In classical and late antiquity, Illyria (; , ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; , ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.
The Ancient Gree ...
, thus making the region of Macedonia permanently lose any connection with its ancient borders, and now be the home of a greater variety of inhabitants.
Middle Ages
Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
settled in the Balkan Peninsula from the 6th century AD.
''(see also: South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, ...
)''. Aided by the Avars and by Turkic Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
, Slavic tribes in the 6th century started a gradual invasion into the lands of Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
. They infiltrated into Macedonia and reached as far south as Thessaly and the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
, settling in isolated regions that the Byzantines called ''Sclavinias'', until they were gradually pacified. Many Slavs came to serve as soldiers in Byzantine armies and settled in other parts of the Byzantine Empire. Slavic settlers assimilated many among the Romanised and Hellenised Paeonian, Illyrian and Thracian population of Macedonia, but pockets of tribes that fled to the mountains remained independent. A number of scholars today consider that present-day Aromanians
The Aromanians () are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgari ...
(Vlachs), Sarakatsani
The Sarakatsani (), also called Karakachani (), are an ethnic Greeks, Greek population subgroup who were traditionally Transhumance, transhumant shepherds, native to Greece, with a smaller presence in neighbouring Bulgaria, southern Albania, an ...
and Albanians
The Albanians are an ethnic group native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, Albanian culture, culture, Albanian history, history and Albanian language, language. They are the main ethnic group of Albania and Kosovo, ...
originate from these mountainous populations. The interaction between Romanised and non-Romanised indigenous peoples and the Slavs resulted in linguistic similarities which are reflected in modern Bulgarian, Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
, Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
and Macedonian, all of them members of the Balkan language area. The Slavs also occupied the hinterland of Thessaloniki, launching consecutive attacks on the city in 584, 586, 609, 620, and 622 AD, but never taking it. Detachments of Avars often joined the Slavs in their onslaughts, but the Avars did not form any lasting settlements in the region. A branch of the Bulgars led by khan Kuber
Kuber (also Kouber or Kuver) was a Bulgar leader who, according to the '' Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', liberated a mixed Bulgar and Byzantine Christian population in the 670s, whose ancestors had been transferred from the Eastern Roman Empi ...
, however, settled in western Macedonia and eastern Albania around 680 AD and also engaged in attacks on Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
together with the Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
. By this time, several different ethnicities inhabited the whole Macedonia region, with South Slavs forming the overall majority in the northern fringes of Macedonia while Greeks dominated the highlands of western Macedonia, the central plains, and the coastline.
Ottoman rule
Muslims and Christians
 The initial period of Ottoman rule led a depopulation of the plains and river valleys of Macedonia. The Christian population there fled to the mountains. Ottomans were largely brought from Asia Minor and settled parts of the region. Towns destroyed in
The initial period of Ottoman rule led a depopulation of the plains and river valleys of Macedonia. The Christian population there fled to the mountains. Ottomans were largely brought from Asia Minor and settled parts of the region. Towns destroyed in Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia (Macedonian language, Macedonian and ) is a historical term referring to the central part of the broader Macedonian region, roughly corresponding to present-day North Macedonia. The name derives from the Vardar, Vardar River and i ...
during the conquest were renewed, this time populated exclusively by Muslims. The Ottoman element in Macedonia was especially strong in the 17th and the 18th century with travellers defining the majority of the population, especially the urban one, as Muslim. The Ottoman population, however, sharply declined at the end of the 18th and the beginning of the 19th century on account of the incessant wars led by the Ottoman Empire, the low birth rate and the higher death toll of the frequent plague epidemics among Muslims than among Christians.
The Ottoman–Habsburg War (1683–1699), the subsequent flight of a substantial part of the Serbian population in Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
to Austria and the reprisals and looting during the Ottoman counteroffensive led to an influx of Albanian Muslims into Kosovo, northern and northwestern Macedonia. Being in the position of power, the Albanian Muslims managed to push out their Christian neighbours and conquered additional territories in the 18th and the 19th centuries. Pressures from central government following the first Russo-Turkish war that ended in 1774 and in which Ottoman Greeks were implicated as a "fifth column" led to the superficial Islamization of several thousand Greek-speakers in western Macedonia. These Greek Muslims
Greek Muslims, also known as Grecophone Muslims, are Muslims of Greeks, Greek ethnic origin whose adoption of Islam (and often the Turkish language and identity in more recent times) dates either from the contact of early Arabic dynasties of th ...
retained their Greek language and identity, remained Crypto-Christians
Crypto-Christianity is the secret adherence to Christianity, while publicly professing to be another faith; people who practice crypto-Christianity are referred to as "crypto-Christians". In places and time periods where Christians were persecuted ...
, and were subsequently called Vallahades
The Vallahades () or Valaades () are a Greek-speaking Muslim population who lived along the river Haliacmon in southwest Greek Macedonia, in and around Anaselitsa (modern Neapoli) and Grevena. They numbered about 17,000 in the early 20th centur ...
by local Greek Orthodox Christians because apparently the only Turkish-Arabic they ever bothered to learn was how to say "wa-llahi" or "by Allah". The destruction and abandoning of the Christian Aromanian city of Moscopole and other important Aromanian settlements in the southern Albania (Epirus-Macedonia) region in the second half of the 18th century caused a large-scale migration of thousands of Aromanians to the cities and villages of Western Macedonia, most notably to Bitola
Bitola (; ) is a city in the southwestern part of North Macedonia. It is located in the southern part of the Pelagonia valley, surrounded by the Baba, Nidže, and Kajmakčalan mountain ranges, north of the Medžitlija-Níki border crossing ...
, Krushevo and surrounding regions. Thessaloniki also became the home of a large Jewish population following Spain's expulsions of Jews after 1492. The Jews later formed small colonies in other Macedonian cities, most notably Bitola and Serres
Serres ( ) is a city in Macedonia, Greece, capital of the Serres regional unit and second largest city in the region of Central Macedonia, after Thessaloniki.
Serres is one of the administrative and economic centers of Northern Greece. The c ...
.
Hellenic idea
 The rise of European nationalism in the 18th century led to the expansion of the Hellenic idea in Macedonia. Its main pillar throughout the centuries of Ottoman rule had been the indigenous Greek population of historical Macedonia. Under the influence of the Greek schools and the
The rise of European nationalism in the 18th century led to the expansion of the Hellenic idea in Macedonia. Its main pillar throughout the centuries of Ottoman rule had been the indigenous Greek population of historical Macedonia. Under the influence of the Greek schools and the Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (, ; ; , "Roman Orthodox Patriarchate, Ecumenical Patriarchate of Istanbul") is one of the fifteen to seventeen autocephalous churches that together compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is headed ...
, however, it started to spread among the other orthodox subjects of the Empire as the urban Christian population of Slavic and Albanian origin started to view itself increasingly as Greek. The Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
became a symbol of civilization and a basic means of communication between non-Muslims. The process of Hellenization was additionally reinforced after the abolition of the Bulgarian Archbishopric of Ohrid
The Archbishopric of Ohrid, also known as the Bulgarian Archbishopric of Ohrid
*T. Kamusella in The Politics of Language and Nationalism in Modern Central Europe, Springer, 2008, p. 276
*Aisling Lyon, Decentralisation and the Management of Ethn ...
in 1767. Though with a predominantly Greek clergy, the Archbishopric did not yield to the direct order of Constantinople and had autonomy in many vital domains. However, the poverty of the Christian peasantry and the lack of proper schooling in villages preserved the linguistic diversity of the Macedonian countryside. The Hellenic idea reached its peak during the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
(1821–1829) which received the active support of the Greek Macedonian population as part of their struggle for the resurrection of Greek statehood. According to the ''Istituto Geografiko de Agostini'' of Rome, in 1903 in the vilayet
A vilayet (, "province"), also known by #Names, various other names, was a first-order administrative division of the later Ottoman Empire. It was introduced in the Vilayet Law of 21 January 1867, part of the Tanzimat reform movement initiated b ...
s of Selanik and Monastir Greek was the dominant language of instruction in the region:
Macedonian question
 In Europe, the classic non-national states were the ''multi-ethnic empires'' such as the Ottoman Empire, ruled by a
In Europe, the classic non-national states were the ''multi-ethnic empires'' such as the Ottoman Empire, ruled by a Sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
and the population belonged to many ethnic groups, which spoke many languages. The idea of nation state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
was an increasing emphasis during the 19th century, on the ethnic
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
and racial
Race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 16th century, when it was used to refer to groups of va ...
origins of the nations. The most noticeable characteristic was the degree to which nation-states use the state as an instrument of ''national unity'', in economic, social and cultural life. By the 19th century, the Ottomans had fallen well behind the rest of Europe in science, technology, and industry.
Bulgarian propaganda
By that time Bulgarians had initiated a purposeful struggle against theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
clerics. Bulgarian religious leaders had realised that any further struggle for the rights of the Bulgarians
Bulgarians (, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its neighbouring region, who share a common Bulgarian ancestry, culture, history and language. They form the majority of the population in Bulgaria, ...
in the Ottoman Empire could not succeed unless they managed to obtain at least some degree of autonomy from the Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (, ; ; , "Roman Orthodox Patriarchate, Ecumenical Patriarchate of Istanbul") is one of the fifteen to seventeen autocephalous churches that together compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is headed ...
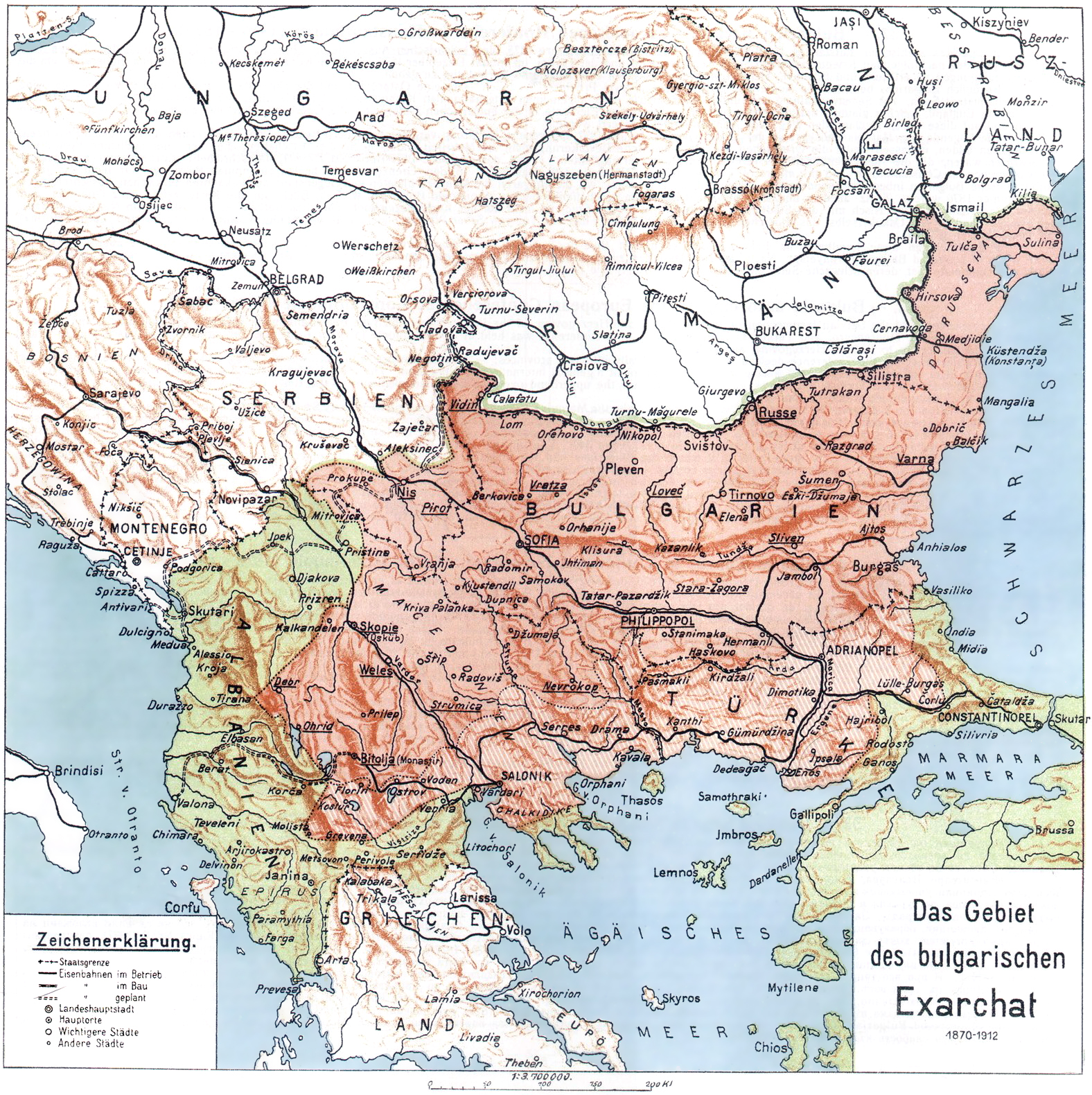
. The foundation of the Bulgarian Exarchate in 1870, which included most of Macedonia by a firman
A firman (; ), at the constitutional level, was a royal mandate or decree issued by a sovereign in an Islamic state. During various periods such firmans were collected and applied as traditional bodies of law. The English word ''firman'' co ...
of Sultan Abdülaziz
Abdulaziz (; ; 8 February 18304 June 1876) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 25 June 1861 to 30 May 1876, when he was 1876 Ottoman coup d'état, overthrown in a government coup. He was a son of Sultan Mahmud II and succeeded his brother ...
was the direct result of the struggle of the Bulgarian Orthodox against the domination of the Greek Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (, ; ; , "Roman Orthodox Patriarchate, Ecumenical Patriarchate of Istanbul") is one of the fifteen to seventeen autocephalous churches that together compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is headed ...
in the 1850s and 1860s.
Afterward, in 1876 the Bulgarians revolted in the ''April uprising
The April Uprising () was an insurrection organised by the Bulgarians in the Ottoman Empire from April to May 1876. The rebellion was suppressed by irregular Ottoman bashi-bazouk units that engaged in indiscriminate slaughter of both rebels ...
''. The emergence of Bulgarian national sentiments was closely related to the re-establishment of the independent Bulgarian church. This rise of national awareness became known as the Bulgarian National Revival
The Bulgarian Revival (, ''Balgarsko vazrazhdane'' or simply: Възраждане, ''Vazrazhdane'', and ), sometimes called the Bulgarian National Revival, was a period of socio-economic development and national integration among Bulgarian pe ...
. However, the uprising was crushed by the Ottomans. As a result, on the Constantinople Conference in 1876 the predominant Bulgarian character of the Slavs in Macedonia reflected in the borders of future autonomous Bulgaria as it was drawn there. The Great Powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
eventually gave their consent to variant, which excluded historical Macedonia and Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
, and denied Bulgaria access to the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
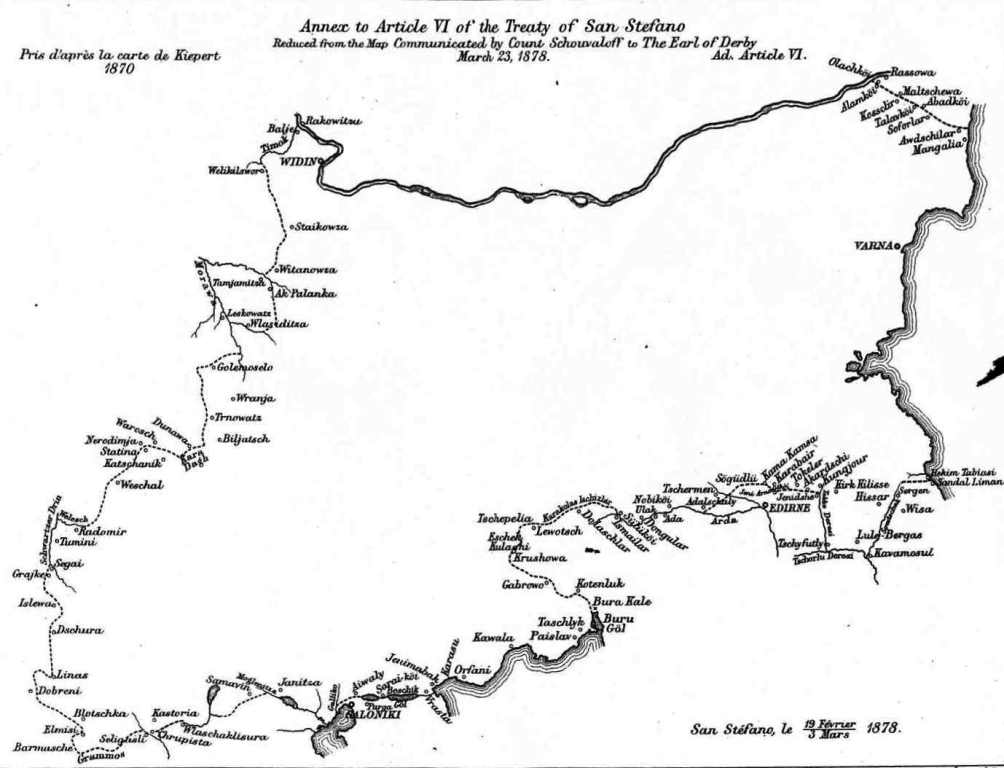
, but otherwise incorporated all other regions in the Ottoman Empire inhabited by Bulgarians. At the last minute, however, the Ottomans rejected the plan with the secret support of Britain. Having its reputation at stake, Russia had no other choice but to declare war on the Ottomans in April 1877. The Treaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Preliminary Treaty of San Stefano (; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878. It was signed at San Ste ...
from 1878, which reflected the maximum desired by Russian expansionist policy, gave Bulgaria the whole of Macedonia except Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
, the Chalcidice
Chalkidiki (; , alternatively Halkidiki), also known as Chalcidice, is a peninsula and regional units of Greece, regional unit of Greece, part of the region of Central Macedonia, in the Geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedon ...
peninsula and the valley of the Aliakmon.
 The
The Congress of Berlin
At the Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878), the major European powers revised the territorial and political terms imposed by the Russian Empire on the Ottoman Empire by the Treaty of San Stefano (March 1878), which had ended the Rus ...
in the same year redistributed most Bulgarian territories that the previous treaty had given to the Principality of Bulgaria
The Principality of Bulgaria () was a vassal state under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire. It was established by the Treaty of Berlin in 1878.
After the Russo-Turkish War ended with a Russian victory, the Treaty of San Stefano was signed ...
back to the Ottoman Empire. This included the whole of Macedonia. As a result, in late 1878, the Kresna–Razlog uprising – an unsuccessful Bulgarian revolt against the Ottoman rule in the region of Macedonia – broke out. However the decision taken at the Congress of Berlin
At the Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878), the major European powers revised the territorial and political terms imposed by the Russian Empire on the Ottoman Empire by the Treaty of San Stefano (March 1878), which had ended the Rus ...
soon turned the Macedonian question into "the apple of constant discord" between Serbia, Greece and Bulgaria. The Bulgarian national revival
The Bulgarian Revival (, ''Balgarsko vazrazhdane'' or simply: Възраждане, ''Vazrazhdane'', and ), sometimes called the Bulgarian National Revival, was a period of socio-economic development and national integration among Bulgarian pe ...
in Macedonia was not unopposed. The Greeks and Serbs, too, had national ambitions in the region, and believed that these could be furthered by a policy of cultural and linguistic dissimilation of the Macedonian Slavs, to be achieved through educational and church propaganda. Nonetheless, by the 1870s the Bulgarians were clearly the dominant national party in Macedonia. It was widely anticipated that the Macedonian Slavs would continue to evolve as an integral part of the Bulgarian nation, and that, in the event of the Ottoman Empire's demise, Macedonia would be included in a Bulgarian successor-state. That these anticipations proved false was due not to any intrinsic peculiarities of the Macedonian Slavs, setting them apart from the Bulgarians, but to a series of catastrophic events, which, over a period of seventy years, diverted the course of Macedonian history away from its presumed trend.
Serbian propaganda

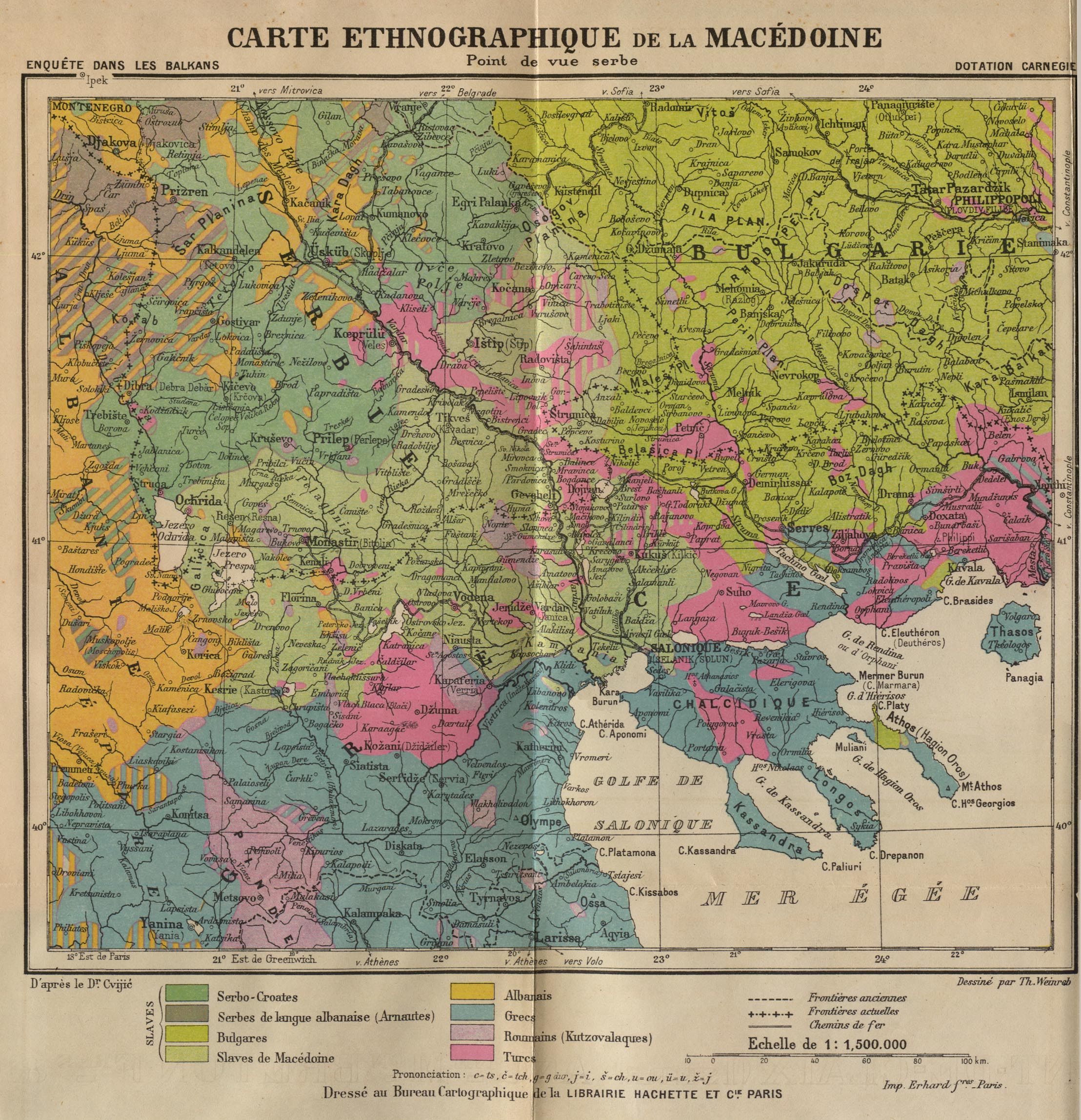
 A great contribution to the Serbian cause was made by an astronomer and historian from
A great contribution to the Serbian cause was made by an astronomer and historian from Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
, Spiridon Gopčević (also known as Leo Brenner). Gopčević published in 1889 the ethnographic research ''Macedonia and Old Serbia'', which defined more than three-quarters of the Macedonian population as Serbian.
The work of Gopčević was further developed by two Serbian scholars, geographer Jovan Cvijić
Jovan Cvijić ( sr-Cyrl, Јован Цвијић, ; 1865 – 16 January 1927) was a Serbs, Serbian geographer, Ethnology, ethnologist, university professor and academic.
He was the president of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts, S ...
and linguist Aleksandar Belić
Aleksandar Belić (Serbian Cyrillic: Александар Белић, ; 15 August 1876 – 26 February 1960) was a Serbian linguist and academic.
Biography
Belić was born in Belgrade. After studying Slavic languages in Belgrade, Odessa, and ...
. Less extreme than Gopčević, Cvijić and Belić claimed only the Slavs of northern Macedonia were Serbian whereas those of southern Macedonia were identified as "Macedonian Slavs", an amorphous Slavic mass that was neither Bulgarian, nor Serbian but could turn out either Bulgarian or Serbian if the respective people were to rule the region.
Greek propaganda
 It was established by the end of the 19th century that the majority of the population of central and Southern Macedonia (vilaets of Monastiri and Thessaloniki) were predominantly an ethnic Greek population, while the Northern parts of the region (vilaet of Skopje) were predominantly Slavic. Jews and Ottoman communities were scattered all over. Because of Macedonia's such polyethnic nature, the arguments which Greece used to promote its claim to the whole region were usually of historical and religious character. The Greeks consistently linked nationality to the allegiance to the Patriarchate of Constantinople. "Bulgarophone", "Albanophone" and "Vlachophone" Greeks were coined to describe the population who were Slavic, Albanian or
It was established by the end of the 19th century that the majority of the population of central and Southern Macedonia (vilaets of Monastiri and Thessaloniki) were predominantly an ethnic Greek population, while the Northern parts of the region (vilaet of Skopje) were predominantly Slavic. Jews and Ottoman communities were scattered all over. Because of Macedonia's such polyethnic nature, the arguments which Greece used to promote its claim to the whole region were usually of historical and religious character. The Greeks consistently linked nationality to the allegiance to the Patriarchate of Constantinople. "Bulgarophone", "Albanophone" and "Vlachophone" Greeks were coined to describe the population who were Slavic, Albanian or Vlach
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula) ...
( Aromanian)-speaking. There was also pressure on Aromanians to become linguistically dissimilated from the 18th century, when dissimilation efforts were encouraged by the Greek missionary Cosmas of Aetolia (1714–1779) who taught that Aromanians should speak Greek because as he said "it's the language of our Church" and established over 100 Greek schools in northern and western Greece. The offensive of the clergy against the use of Aromanian was by no means limited to religious issues but was a tool devised in order to convince the non-Greek speakers to abandon what they regarded as a "worthless" idiom and adopt the superior Greek speech: "There we are Metsovian brothers, together with those who are fooling themselves with this sordid and vile Aromanian language... forgive me for calling it a language", "repulsive speech with a disgusting diction".
Ethnic Macedonian propaganda
The ethnic Macedonian ideology during the second half of the 19th century was at its inception. One of the first preserved accounts is an article The Macedonian question by Petko Slaveykov, published on 18 January 1871 in the "Macedonia" newspaper inConstantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. In this article Petko Slaveykov writes: "We have many times heard from the Macedonists that they are not Bulgarians, but they are rather Macedonians, descendants of the Ancient Macedonians". In a letter written to the Bulgarian Exarch in February 1874 Petko Slaveykov reports that discontentment with the current situation "has given birth among local patriots to the disastrous idea of working independently on the advancement of their own local dialect and what’s more, of their own, separate Macedonian church leadership."
In 1875 Gjorgjija Pulevski published in Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
a book called ''Dictionary of Three Languages'' (''Rečnik od tri jezika''). The text of the ''Rečnik'' contains programmatic statements where Pulevski argues for an independent Slavic Macedonian nation and language. It was the first work that publicly claimed Macedonian to be a separate language. In 1880 he published ''Slognica Rechovska'' in Sofia
Sofia is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain, in the western part of the country. The city is built west of the Is ...
as an attempt at a grammar of the language of the Slavs who lived in Macedonia. Although he had no formal education, Pulevski published several other books, including three dictionaries and a collection of songs from Macedonia, customs, and holidays.
The first significant manifestation of ethnic Macedonian nationalism was the book On Macedonian Matters (''Za Makedonskite Raboti'') published in Sofia in 1903 by Krste Misirkov
Krste Petkov Misirkov (, ; ; Serbian Cyrillic: Крста Петковић Мисирков; ; 18 November 1874 – 26 July 1926) was a philologist, journalist, historian and ethnographer from the region of Macedonia.
In the period between 1903 ...
. In the book Misirkov advocated that the Slavs of Macedonia should take a separate way from the Bulgarians and the Bulgarian language. Misirkov considered that the term "Macedonian" should be used to define the whole Slavic population of Macedonia, obliterating the existing division between Greeks, Bulgarians and Serbians. The adoption of a separate "Macedonian language" was also advocated as a means of unification of the Ethnic Macedonians with Serbian, Bulgarian and Greek consciousness. ''On Macedonian Matters'' was written in the South Slavic dialect spoken in central Macedonia ( Veles-Prilep
Prilep ( ) is the List of cities in North Macedonia, fourth-largest city in North Macedonia. According to 2021 census, it had a population of 63,308.
Name
The name of Prilep appeared first as ''Πρίλαπος'' in Greek (''Prilapos'') in 1 ...
-Bitola
Bitola (; ) is a city in the southwestern part of North Macedonia. It is located in the southern part of the Pelagonia valley, surrounded by the Baba, Nidže, and Kajmakčalan mountain ranges, north of the Medžitlija-Níki border crossing ...
-Ohrid
Ohrid ( ) is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording a population of over 42,000 inhabitants as of ...
). This dialect was proposed by Misirkov as the basis for the future language, and, as Misirkov says, a dialect which is most different from all other neighboring languages (as the eastern dialect was too close to Bulgarian and the northern one too close to Serbian). Misirkov calls this language Macedonian.
While Misirkov talked about the Macedonian consciousness and the Macedonian language as a future goal, he described the wider region of Macedonia in the early 20th century as inhabited by Bulgarians, Greeks, Serbs, Turks, Albanians, Aromanians, and Jews. As regards to the ethnic Macedonians themselves, Misirkov maintained that they had called themselves Bulgarians until the publication of the book and were always called Bulgarians by independent observers until 1878 when the Serbian views also started to get recognition. He also explained that the reason for that was because local Slavs were allies with the Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
in the wars against Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
and because of that Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Medieval Greek, Greek-speaking Eastern Romans throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople and Asia ...
renamed them into "Bulgarians", in that way the term became an identification for Macedonian Slavs in the future. Misirkov rejected the ideas in ''On Macedonian Matters'' later and turned into a staunch advocate of the Bulgarian cause. He returned to the ethnic Macedonian idea again in the 1920s.
Another prominent activist for the ethnic Macedonian national revival was Dimitrija Čupovski, who was one of the founders and the president of the Macedonian Literary Society established in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
in 1902. During the 1913–14 period, Čupovski published the newspaper ''Makedonski Golos (Македонскi Голосъ) (meaning ''Macedonian voice'') in which he and fellow members of the Petersburg Macedonian Colony propagandized the existence of a separate Macedonian people different from Greeks, Bulgarians and Serbs, and were struggling for popularizing the idea for an independent Macedonian state.
During the 1920s and 30s the idea was promoted by some of the leftist
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social hierarchies. Left-wing politi ...
members of the Macedonian Federative Organization and later IMRO (United) and also by some members of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia
The League of Communists of Yugoslavia, known until 1952 as the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, was the founding and ruling party of SFR Yugoslavia. It was formed in 1919 as the main communist opposition party in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats a ...
. In 1934 the Comintern
The Communist International, abbreviated as Comintern and also known as the Third International, was a political international which existed from 1919 to 1943 and advocated world communism. Emerging from the collapse of the Second Internatio ...
in coordination with IMRO (United) published a resolution on the Macedonian question in which for the first time, an authoritative international organization has recognized the existence of a separate Macedonian nation and Macedonian language
Macedonian ( ; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch. Sp ...
.
The ideas of Misirkov, Pulevski and other Macedonians would remain largely unnoticed until World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
when they were adopted by the Macedonian Partisans movement which in 1944 set up the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia
The Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (, ''Antifašističko sobranie za narodno osloboduvanje na Makedonija''; Serbo-Croatian: ''Antifašističko sobranje narodnog oslobođenja Makedonije''; abbr. ASNOM) was the supr ...
and proclaimed a Macedonian nation-state of ethnic Macedonians. They made Macedonian the official language of the Macedonian state further influencing its codification in 1945. The state was later incorporated in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (commonly abbreviated as SFRY or SFR Yugoslavia), known from 1945 to 1963 as the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as Socialist Yugoslavia or simply Yugoslavia, was a country ...
.
The present-day historians from North Macedonia claim that IMRO was split into two factions: the first aimed an ethnic Macedonian state, and the second believed in a Macedonia as a part of wider Bulgarian entity.
These claims of present-day historians from North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
that the "Autonomists" in IMRO who defended a Macedonian position are largely ungrounded. IMRO regarded itself – and was regarded by the Ottoman authorities, the Greek guerilla groups, the contemporary press in Europe and even by Misirkov -as an exclusively Bulgarian organization.
Romanian propaganda
Development of the name "Macedonian Slavs"
The name "Macedonian Slavs" started to appear in publications at the end of the 1880s and the beginning of the 1890s. Though the successes of the Serbian propaganda effort had proved that the Slavic population of Macedonia was not only Bulgarian, they still failed to convince that this population was, in fact, Serbian. Rarely used until the end of the 19th century compared to 'Bulgarians', the term 'Macedonian Slavs' served more to conceal rather than define the national character of the population of Macedonia. Scholars resorted to it usually as a result of Serbian pressure or used it as a general term for the Slavs inhabiting Macedonia regardless of their ethnic affinities. The Serbian politician Stojan Novaković proposed in 1887 employing the Macedonistic ideas as they means to counteract the Bulgarian influence in Macedonia, thereby promoting Serbian interests in the region.Absent national consciousness
What stood behind the difficulties to properly define the nationality of the Slavic population of Macedonia was the apparent levity with which this population regarded it. The existence of a separate Macedonian national consciousness prior to the 1940s is disputed. This confusion is illustrated by Robert Newman in 1935, who recounts discovering in a village inVardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia (Macedonian language, Macedonian and ) is a historical term referring to the central part of the broader Macedonian region, roughly corresponding to present-day North Macedonia. The name derives from the Vardar, Vardar River and i ...
two brothers, one who considered himself a Serb, and the other considered himself a Bulgarian. In another village he met a man who had been, "a Macedonian peasant all his life", but who had varyingly been called a Turk, a Serb and a Bulgarian.Newman, R. (1952) ''Tito's Yugoslavia'' (London) However anti-Serb and pro-Bulgarian feelings among the local population at this period prevailed.
Statistical data
Ottoman statistics
The basis of the Ottoman censuses was themillet system
In the Ottoman Empire, a ''millet'' (; ) was an independent court of law pertaining to "personal law" under which a confessional community (a group abiding by the laws of Muslim sharia, Christian canon law, or Jewish halakha) was allowed to rule ...
. People were assigned to ethnic categories according to religious affiliation. So all Sunni Muslims were categorised as Turks, all members of Greek Orthodox church as Greeks, while rest being divided between Bulgarian and Serb Orthodox churches.Ortaylı, İlber. ''Son İmparatorluk Osmanlı (The Last Empire: Ottoman Empire)'', İstanbul, Timaş Yayınları (Timaş Press), 2006. pp. 87–89. . All censuses concluded that the province is of Christian majority, among whom the Bulgarians prevail.
1882 Ottoman census in Macedonia:
1895 census:
Special survey in 1904 of Hilmi Pasha of the three Macedonian vilayets of Selanik
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
, Manastir and Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
(648 thousand followes of the Ecumenical Patriarchate
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (, ; ; , "Roman Orthodox Patriarchate, Ecumenical Patriarchate of Istanbul") is one of the fifteen to seventeen Autocephaly, autocephalous churches that together compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. ...
and 557 thousand faithful of the Bulgarian Exarchate
The Bulgarian Exarchate (; ) was the official name of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church before its autocephaly was recognized by the Ecumenical See in 1945 and the Bulgarian Patriarchate was restored in 1953.
The Exarchate (a de facto autocephaly) ...
, but an additional 250 thousand of the former) had identified as Bulgarian speakers. The survey also extends to parts of the three vilayets which are not part of the region of Macedonia, i.e., Sandžak
Sandžak (Serbian Cyrillic: ; ) is a historical and geo-political region in the Balkans, located in the southwestern part of Serbia and the eastern part of Montenegro. The Bosnian/ Serbian term ''Sandžak'' derives from the Sanjak of Novi Paza ...
, Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
, parts of eastern Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
and Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
.
Census 1906:
Rival statistical data
''Encyclopædia Britannica''
The 1911 edition of the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' gave the following statistical estimates about the population of Macedonia: *Slavs (described in the encyclopaedia as a "Slavonic population, the bulk of which is regarded by almost all independent sources as Bulgarians"): approximately 1,150,000, whereof, 1,000,000 Orthodox and 150,000Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s (called Pomaks
Pomaks (; Macedonian: Помаци ; ) are Bulgarian-speaking Muslims inhabiting Bulgaria, northwestern Turkey, and northeastern Greece. The strong ethno-confessional minority in Bulgaria is recognized officially as Bulgarian Muslims by th ...
)
*Turks: ca. 500,000 (Muslims)
*Greeks: ca. 250,000, whereof ca. 240,000 Orthodox and 14,000 Muslims
*Albanians: ca. 120,000, whereof 10,000 Orthodox and 110,000 Muslims
*Vlachs: ca. 90,000 Orthodox and 3,000 Muslims
*Jews: ca. 75,000
*Roma: ca. 50,000, whereof 35,000 Orthodox and 15,000 Muslims
In total 1,300,000 Christians (almost exclusively Orthodox), 800,000 Muslims, 75,000 Jews, a total population of ca. 2,200,000 for the whole of Macedonia.
It needs to be taken into account that part of the Slavic-speaking population in southern Macedonia regarded itself as ethnically Greek and a smaller percentage, mostly in northern Macedonia, as Serbian. All Muslims (except the Albanians) tended to view themselves and were viewed as Turks, irrespective of their mother tongue.
Statistical data of Greek Macedonia
According to aLeague of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
report in 1912, Greek Macedonia
Macedonia ( ; , ) is a geographic and former administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and geographic region in Greece, with a population of 2.36 million (as of 2020). It is highly mountainous, wit ...
's national makeup in 1913 was 42.6% Greek (513,000), 39.4% Muslim (475,000; including ''Vallahades
The Vallahades () or Valaades () are a Greek-speaking Muslim population who lived along the river Haliacmon in southwest Greek Macedonia, in and around Anaselitsa (modern Neapoli) and Grevena. They numbered about 17,000 in the early 20th centur ...
''), 9.9% Bulgarian (119,000) and 8.1% others (98,000). According to a Carnegie survey based on the ethnographic map of Southern Macedonia, representing the ethnic distribution on the eve of the 1912 Balkan war, published in 1913 by Mr. J. Ivanov, lecturer at the University of Sofia. The total numbers belonging to the various nationalities in a territory a little larger than the portion in the same region ceded to the Greeks by the Turks was 1,042,029 inhabitants, of whom 329,371 Bulgarians, 314,854 Turks, 236,755 Greeks, 68,206 Jews, 44,414 Wallachians, 25,302 Gypsies, 15,108 Albanians, 8,019 Miscellaneous.
According to a later League of Nations report, at the 1928 census the population consisted of 1,341,000 Greeks (88.8%), 77,000 Bulgarians (5%), 2,000 Turks and 91,000 others, but according to Greek archival sources the total number of the Slavic speakers may have been 200,000.
20th and 21st centuries
TheBalkan Wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, M ...
(1912–1913) and World War I (1914–1918) left the region of Macedonia divided among Greece, Serbia, Bulgaria, and Albania and resulted in significant changes in its ethnic composition. 51% of the region's territory went to Greece, 38% to Serbia and 10% to Bulgaria. At least several hundred thousand left their homes, while the rest were also subjected to assimilation as all "liberators" after the Balkan War wanted to assimilate as many inhabitants as possible and colonize with settlers from their respective nation. The Greeks become the largest population in the region. The formerly leading Muslim and Bulgarian communities were reduced either by deportation (through population exchange) or by change of identity.
Greece
The Slavic population was viewed as Slavophone Greeks and prepared to be reeducated in Greek. Any vestiges of Bulgarian and Slavic Macedonia in Greece have been eliminated from the Balkan Wars, continuing to the present. The Greeks detested the Bulgarians (Slavs of Macedonia), considering them less than human "bears, practising systematic and inhumane methods of extermination and assimilation. The use of Bulgarian language had been prohibited, for which the persecution by the police peaked, while during the regime of Metaxas a vigorous assimilation campaign was launched. The civilians have been persecuted solely for identifying as Bulgarian with the slogans "If you want to be free, be Greek" "We shall cut your tongues to teach you to speak Greek." "become Greeks again, that being the condition of a peaceful life.""Are you Christians or Bulgarians?" "The voice of Alexander the Great calls to you from the tomb; do you not hear it? You sleep on and go on calling yourselves Bulgarians!" "Wast thou born at Sofia; there are no Bulgarians in Macedonia; the whole population is Greek." "He who goes to live in Bulgaria," was the reply to the protests, "is Bulgarian. No more Bulgarians in Greek Macedonia." The remaining Bulgarians threatened by use of force were made to become Greeks and to sign a declaration stating that they had been Greek since ancient times, but by the influence of komitadji they became Bulgarians only fifteen years ago, but nevertheless there was no real change in consciousness. In many villages people were put to prison and then were released after having proclaimed themselves Greeks. The Slavic dialect was considered as being of lowest intelligence with the assumptions that it "consists" only a thousand words of vocabulary. There are official records showing that children professing Bulgarian identity were also murdered for declining to profess Greek identity. After the Treaty of Bucharest, some 51% of the ''modern'' region that was known as Macedonia was won by the Greek state (also known as Aegean or Greek Macedonia). This was the only part of Macedonia that Greece was directly interested in. Greeks regarded this land as the only true region of Macedonia as it geographically corresponded to ancientMacedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
and contained an ethnically Greek majority of population. Bulgarian and other non-Greek schools in southern (Greek) Macedonia were closed and Bulgarian teachers and priests were deported as early as the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and involved actions of the Balkan League (the Kingdoms of Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Greece, Greece and Kingdom of Montenegro, Montenegro) agai ...
simultaneous to deportation of Greeks from Bulgaria. The bulk of the Slavic population of southeastern Macedonia fled to Bulgaria during the Second Balkan War or was resettled there in the 1920s by virtue of a population exchange agreement. The Slavic minority in Greek Macedonia, who were referred to by the Greek authorities as "Slavomacedonians", "Slavophone Greeks" and "Bulgarisants", were subjected to a gradual assimilation by the Greek majority. Their numbers were reduced by a large-scale emigration to North America in the 1920s and the 1930s and to Eastern Europe and Yugoslavia following the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
(1944–1949). At the same time a number of Macedonian Greeks from Monastiri
Bitola (; ) is a city in the southwestern part of North Macedonia. It is located in the southern part of the Pelagonia valley, surrounded by the Baba, Nidže, and Kajmakčalan mountain ranges, north of the Medžitlija-Níki border crossing ...
(modern Bitola) entered Greece.
The 1923 Compulsory population exchange between Greece and Turkey
The 1923 population exchange between Greece and Turkey stemmed from the "Convention Concerning the Exchange of Greek and Turkish Populations" signed at Lausanne, Switzerland, on 30 January 1923, by the governments of Greece and Turkey. It involv ...
led to a radical change in the ethnic composition of Greek Macedonia. Some 380,000 Turks and other Muslims left the region and were replaced by 538,253 Greeks from Asia Minor and Eastern Thrace
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically in Southeast Europe. Turkish Thrace accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest c ...
, including Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks (; or ; , , ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group indigenous to the region of Pontus, in northeastern Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). They share a common Pontic Greek culture that is di ...
from northeastern Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and Caucasus Greeks from the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
.
Greece was attacked and occupied by Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
-led Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
during World War II. By the beginning of 1941 the whole of Greece was under a tripartite German, Italian and Bulgarian occupation. The Bulgarians were permitted to occupy western Thrace
Western Thrace or West Thrace (, '' ytikíThráki'' ), also known as Greek Thrace or Aegean Thrace, is a geographical and historical region of Greece, between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country; East Thrace, which lie ...
and parts of Greek Macedonia, where they persecuted and committed massacre
A massacre is an event of killing people who are not engaged in hostilities or are defenseless. It is generally used to describe a targeted killing of civilians Glossary of French words and expressions in English#En masse, en masse by an armed ...
s and other atrocities against the Greek population. The once thriving Jewish community of Thessaloniki was decimated by the Nazis, who deported 60,000 of the city's Jews to the German death camps in Germany and German-occupied Poland. Large Jewish populations in the Bulgarian occupied zone were deported by the Bulgarian army and had an equal death rate to the German zone.
The Bulgarian Army occupied the whole of Eastern Macedonia and Western Thrace, where it was greeted from a part of a Slav-speakers as liberators. Unlike Germany and Italy, Bulgaria officially annexed the occupied territories, which had long been a target of Bulgarian irridentism. A massive campaign of " Bulgarisation" was launched, which saw all Greek officials deported. This campaign was successful especially in Eastern and later in Central Macedonia, when Bulgarians entered the area in 1943. All Slav-speakers there were regarded as Bulgarians. However it was not so effective in German-occupied Western Macedonia. A ban was placed on the use of the Greek language, the names of towns and places changed to the forms traditional in Bulgarian.
With the help of Bulgarian officers several pro-Bulgarian and anti-Greek armed detachments ( Ohrana) were organized in the Kastoria
Kastoria (, ''Kastoriá'' ) is a city in northern Greece in the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Macedonia. It is the capital of Kastoria (regional unit), Kastoria regional unit, in the Geographic regions of Greece, geographic region ...
, Florina
Florina (, ''Flórina''; known also by some alternative names) is a town and municipality in the mountainous northwestern Macedonia, Greece. Its motto is, 'Where Greece begins'.
The town of Florina is the capital of the Florina regional uni ...
and Edessa
Edessa (; ) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, in what is now Urfa or Şanlıurfa, Turkey. It was founded during the Hellenistic period by Macedonian general and self proclaimed king Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Sel ...
districts of occupied Greek Macedonia in 1943. These were led by Bulgarian officers originally from Greek Macedonia; Andon Kalchev and Georgi Dimchev. Ohrana (meaning Defense) was an autonomist
Autonomism or ''autonomismo'', also known as autonomist Marxism or autonomous Marxism, is an anti-capitalist
Anti-capitalism is a political ideology and Political movement, movement encompassing a variety of attitudes and ideas that oppose ...
pro-Bulgarian organization fighting for unification with Greater Bulgaria. Uhrana was supported from IMRO leader Ivan Mihaylov too. It was apparent that Mihailov had broader plans which envisaged the creation of a Macedonian state under a German control. It was also anticipated that the IMRO volunteers would form the core of the armed forces of a future Independent Macedonia in addition to providing administration and education in the Florina, Kastoria and Edessa districts. In the summer of 1944, Ohrana constituted some 12,000 fighters and volunteers from Bulgaria charged with protection of the local population. During 1944, whole Slavophone villages were armed by the occupation authorities and developed into the most formidable enemy of the Greek People's Liberation Army
The Greek People's Liberation Army (, ''Ellinikós Laïkós Apeleftherotikós Stratós''; ELAS) was the military arm of the left-wing National Liberation Front (EAM) during the period of the Greek resistance until February 1945, when, followi ...
(ELAS). Ohrana was dissolved in late 1944 after the German and Bulgarian withdrawal from Greece and Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito ( ; , ), was a Yugoslavia, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and politician who served in various positions of national leadership from 1943 unti ...
's Partisans movement hardly concealed its intention of expanding. After World War II, many former "Ohranists" were convicted of a military crimes as collaborationists. It was from this period, after Bulgaria's conversion to communism, that some Slav-speakers in Greece who had referred to themselves as "Bulgarians" increasingly began to identify as "Macedonians".
Following the defeat of the Axis powers and the evacuation of the Nazi occupation forces many members of the Ohrana joined the SNOF where they could still pursue their goal of secession. The advance of the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
into Bulgaria in September 1944, the withdrawal of the German armed forces from Greece in October, meant that the Bulgarian Army had to withdraw from Greek Macedonia and Thrace. A large proportion of Bulgarians and Slavic speakers emigrated there. In 1944 the declarations of Bulgarian nationality were estimated by the Greek authorities, on the basis of monthly returns, to have reached 16,000 in the districts of German-occupied Greek Macedonia, but according to British sources, declarations of Bulgarian nationality throughout Western Macedonia reached 23,000.
By 1945 World War II had ended and Greece was in open civil war. It has been estimated that after the end of World War II over 40,000 people fled from Greece to Yugoslavia and Bulgaria. To an extent the collaboration of the peasants with the Germans, Italians, Bulgarians or the Greek People's Liberation Army
The Greek People's Liberation Army (, ''Ellinikós Laïkós Apeleftherotikós Stratós''; ELAS) was the military arm of the left-wing National Liberation Front (EAM) during the period of the Greek resistance until February 1945, when, followi ...
(ELAS) was determined by the geopolitical position of each village. Depending upon whether their village was vulnerable to attack by the Greek communist guerrillas or the occupation forces, the peasants would opt to support the side in relation to which they were most vulnerable. In both cases, the attempt was to promise "freedom" (autonomy or independence) to the formerly persecuted Slavic minority as a means of gaining its support.
The National Liberation Front (NOF) was organized by the political and military groups of the Slavic minority in Greece, active from 1945 to 1949. The interbellum
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
was the time when part of them came to the conclusion that they are Macedonians. Greek hostility to the Slavic minority produced tensions that rose to separatism. After the recognition in 1934 from the Comintern of the Macedonian ethnicity, the Greek communists have also recognized Macedonian national identity. Soon after the first "free territories" were created it was decided that ethnic Macedonian schools would open in the area controlled by the DSE. Books written in the ethnic Macedonian language were published, while ethnic Macedonians theatres and cultural organizations operated. Also within the NOF, a female organization, the Women's Antifascist Front (AFZH), and a youth organization, the National Liberation Front of Youth (ONOM), were formed.
The creation of the ethnic Macedonian cultural institutions in the Democratic Army of Greece
The Democratic Army of Greece (DAG; , ΔΣΕ; ''Dimokratikós Stratós Elládas'', DSE) was the army founded by the Communist Party of Greece during the Greek Civil War (1946–1949). At its height, it had a strength of around 50,000 men and w ...
(DSE)-held territory, newspapers and books published by NOF, public speeches and the schools opened, helped the consolidation of the ethnic Macedonian conscience and identity among the population. According to information announced by Paskal Mitrovski on the I plenum of NOF in August 1948 – about 85% of the Slavic-speaking population in Greek Macedonia has ethnic Macedonian self-identity. The language that was thought in the schools was the official language of the Socialist Republic of Macedonia
The Socialist Republic of Macedonia (), or SR Macedonia, commonly referred to as Socialist Macedonia, Yugoslav Macedonia or simply Macedonia, was one of the six constituent republics of the post-World War II Socialist Federal Republic of Y ...
. About 20,000 young ethnic Macedonians learned to read and write using that language, and learned their own history.
From 1946 until the end of the Civil War in 1949, the NOF was loyal to Greece and was fighting for minimal human rights within the borders of a Greek republic. But in order to mobilize more ethnic Macedonians into the DSE it was declared on 31 January 1949 at the 5th Meeting of the KKE Central Committee that when the DSE took power in Greece there would be an independent Macedonian state, united in its geographical borders. This new line of the KKE affected the mobilisation rate of ethnic Macedonians (which even earlier was considerably high), but did not manage, ultimately, to change the course of the war.
The government forces destroyed every village that was on their way, and expelled the civilian population. Leaving as a result of force or on their own accord (in order to escape oppression and retaliation), 50,000 people left Greece together with the retreating DSE forces. All of them were sent to Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries. It was not until the 1970s that some of them were allowed to come to the Socialist Republic of Macedonia. In the 1980s, the Greek parliament
The Parliament of the Hellenes (), commonly known as the Hellenic Parliament (), is the unicameral legislature of Greece, located in the Old Royal Palace, overlooking Syntagma Square in Athens. The parliament is the supreme democratic instit ...
adopted the law of national reconciliation which allowed DSE members "of Greek origin" to repatriate to Greece, where they were given land. Ethnic Macedonian DSE remembers remained excluded from the terms of this legislation.
On August 20, 2003, the Rainbow Party hosted a reception for the "child refugees", ethnic Macedonian children who fled their homes during the Greek Civil War who were permitted to enter Greece for a maximum of 20 days. Now elderly, this was the first time many of them saw their birthplaces and families in some 55 years. The reception included relatives of the refugees who are living in Greece and are members of Rainbow Party. However, many were refused entry by Greek border authorities because their passports listed the former names of their places of birth.
The present number of the "Slavophones" in Greece has been subject to much speculation with varying numbers. As Greece does not hold census based on self-determination and mother tongue, no official data is available. It should be noted, however, that the official Macedonian Slav party in Greece receives at an average only 1000 votes. For more information about the region and its population see Slavic speakers of Greek Macedonia
Slavic speakers are a minority population in the Geographic regions of Greece, northern Greek region of Macedonia, Greece, Macedonia, who are mostly concentrated in certain parts of the Peripheries of Greece, peripheries of West Macedonia, West ...
.
Serbia and Yugoslavia
After theBalkan Wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, M ...
(1912–1913) the Slavs in Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia (Macedonian language, Macedonian and ) is a historical term referring to the central part of the broader Macedonian region, roughly corresponding to present-day North Macedonia. The name derives from the Vardar, Vardar River and i ...
were regarded as southern Serbs and the language they spoke a southern Serbian dialect. Serbian rule ensured that all ethnic Macedonian symbolism and identity were henceforth proscribed, and only standard Serbian was permitted to be spoken by the locals of Macedonia. In addition, Serbia did not refer to its southern land as ''Macedonia'', a legacy which remains in place today among some Serbian nationalists (e.g. the Serbian Radical Party
The Serbian Radical Party (, abbr. SRS) is a Far-right politics in Serbia, far-right, Ultranationalism, ultranationalist List of political parties in Serbia, political party in Serbia. Founded in 1991, its co-founder, first and only leader is ...
). Despite their attempts of forceful assimilation, Serb colonists in Vardar Macedonia numbered only 100,000 by 1942, so there was not that colonization and expulsion as in Greek Macedonia. Ethnic cleansing was unlikely in Serbia, Bulgarians were given to sign declaration for being Serbs since ancient times, those who refused to sign faced assimilation through terror, while Muslims faced similar discrimination. However, in 1913 Bulgarian revolts broke out in Tikvesh, Negotino
Negotino (, ) is a town in North Macedonia, the seat of the Negotino Municipality. Its population is about 13,000.
Geography
Negotino is located on the right side of the river Vardar.
It is about Above mean sea level, above sea level.
Negotin ...
, Kavadarci
Kavadarci ( ) is a town in the Tikveš region of North Macedonia. In the heart of North Macedonia's wine country, it is home to the largest winery in Southeast Europe, named after the Tikveš plain. The town of Kavadarci is the seat of Kavadarc ...
, Vartash, Ohrid
Ohrid ( ) is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording a population of over 42,000 inhabitants as of ...
, Debar and Struga
Struga ( ; , sq-definite, Struga) is a town and popular tourist destination situated in the south-western region of North Macedonia, lying on the shore of Lake Ohrid. The town of Struga is the seat of Struga Municipality.
Name
The name Struga ...
, and more than 260 villages were burnt down. Serbian officials are documented to have buried alive three Bulgarian civilians from Pehčevo then. Bulgarians were forced to sign a petition "Declare yourself a Serb or die." 90,000 Serbian troops were deployed in Macedonia to keep down resistance from Serbianization, Serbian colonists were unsuccessfully encouraged to immigrate with the slogan "for the good of Serbs", but the Albanians and Turks to emigrate. In the next centuries, a sense of a distinct Macedonian nation emerged partly as a result of the resistance of IMRO
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO; ; ), was a secret revolutionary society founded in the Ottoman territories in Europe, that operated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Founded in 1893 in Salonica, it init ...
, despite it was split into one Macedonist and one pro-Bulgarian wing. In 1918 the use of Bulgarian and Macedonian language was prohibited in Serbian Macedonia.
The Bulgarian, Greek and Romanian schools were closed, the Bulgarian priests and all non-Serbian teachers were expelled. Bulgarian surname endings '-ov/-ev' were replaced with the typically Serbian ending '-ich' and the population which considered itself Bulgarian was heavily persecuted. The policy of Serbianization in the 1920s and 1930s clashed with popular pro-Bulgarian sentiment stirred by IMRO detachments infiltrating from Bulgaria, whereas local communists favoured the path of self-determination suggested by the Yugoslav Communist Party in the 1924 May Manifesto.
In 1925, D. J. Footman, the British vice consul at Skopje, addressed a lengthy report for the Foreign Office
Foreign may refer to:
Government
* Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries
** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government
** Foreign office and foreign minister
* United ...
. He wrote that "the majority of the inhabitants of ''Southern Serbia'' are Orthodox Christian Macedonians, ethnologically more akin to the Bulgarians than to the Serbs." He acknowledged that the Macedonians were better disposed toward Bulgaria because, Bulgarian education system in Macedonia in the time of the Turks, was widespread and effective; and because Macedonians at the time perceived Bulgarian culture and prestige to be higher than those of its neighbors. Moreover, large numbers of Macedonians educated in Bulgarian schools had sought refuge in Bulgaria before and especially after the partitions of 1913. "There is therefore now a large Macedonian element in Bulgaria, continued represented in all Government Departments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
* Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
and occupying high positions in the army and in the civil service...." He characterized this element as "Serbophobe, tmostly desires the incorporation of Macedonia in Bulgaria, and generally supports the IMRO." However, he also pointed to the existence of the tendency to seek an independent Macedonia with Salonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
as its capital. "This movement also had adherents among the Macedonian colony in Bulgaria."
 Bulgarian troops were welcomed as liberators in 1941 but mistakes of the Bulgarian administration made a growing number of people resent their presence by 1944. It must also to be noted that the
Bulgarian troops were welcomed as liberators in 1941 but mistakes of the Bulgarian administration made a growing number of people resent their presence by 1944. It must also to be noted that the Bulgarian army
The Bulgarian Army (), also called Bulgarian Armed Forces, is the military of Bulgaria. The commander-in-chief is the president of Bulgaria. The Ministry of Defense is responsible for political leadership, while overall military command is in ...
during the annexation of the region, was partially recruited from the local population, which formed as much as 40%-60% of the soldiers in certain battalions. Some recent data has announced that even the National Liberation War of Macedonia has resembled ethno-political motivated civil war.КОЈ СО КОГО ЌЕ СЕ ПОМИРУВА- Лидерот на ВМРО-ДПМНЕ и Премиер на Република Македонија, Љубчо Георгиевски одговара и полемизира на темата за национално помирување. After the war the region received the status of a constituent republic within Yugoslavia and in 1945 a separate,
Macedonian language
Macedonian ( ; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch. Sp ...
was codified. The population was declared Macedonian, a nationality different from both Serbs and Bulgarians. The decision was politically motivated and aimed at weakening the position of Serbia within Yugoslavia and of Bulgaria with regard to Yugoslavia. Surnames were again changed to include the ending '-ski', which was to emphasise the unique nature of the ethnic Macedonian population.
From the start of the new Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (commonly abbreviated as SFRY or SFR Yugoslavia), known from 1945 to 1963 as the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as Socialist Yugoslavia or simply Yugoslavia, was a country ...
(SFRY), accusations surfaced that new authorities in Macedonia were involved in retribution against people who did not support the formation of the new Yugoslav Macedonian republic. The numbers of dead "counter-revolutionaries" due to organized killings, however is unclear. Besides, many people went throughout the Labor camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see British and American spelling differences, spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are unfree labour, forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have ...
of Goli Otok in the middle 1940s. This chapter of the partisan's history was a taboo
A taboo is a social group's ban, prohibition or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, offensive, sacred or allowed only for certain people.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
subject for conversation in the SFRY until the late 1980s, and as a result, decades of official silence created a reaction in the form of numerous data manipulations for nationalist communist propaganda purposes.
At the times of Croatian ruling-class of Yugoslavia, Vardar Banovina
The Vardar Banovina, or Vardar Banate ( Macedonian and ; ), was a province ( banate) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941.
History
It was located in the southernmost part of the country, encompassing the whole of today's North Mace ...
Province was turned into autonomous Macedonia with a majority of the population declaring on census as ethnic Macedonians, and a Macedonian language
Macedonian ( ; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch. Sp ...
as the official, recognized as distinct from Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually i ...
. The capital was placed in a Torlakian-speaking region. Persecution of Bulgarian identity by the state continued, along with propaganda.
After the creation of Macedonian Republic the Presidium of ASNOM
The Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (, ''Antifašističko sobranie za narodno osloboduvanje na Makedonija''; Serbo-Croatian: ''Antifašističko sobranje narodnog oslobođenja Makedonije''; abbr. ASNOM) was the supr ...
which was the highest political organ in Macedonia made several statements and actions that were de facto boycotting the decisions of AVNOJ
The Anti-Fascist Council for the National Liberation of Yugoslavia,; ; commonly abbreviated as the AVNOJ, was a deliberative and legislative body that was established in Bihać, Yugoslavia, in November 1942. It was established by Josip Broz ...
. Instead of obeying the order of Tito's General Headquarters to send the main forces of the NOV of Macedonia to participate in the fighting in the Srem
Syrmia ( Ekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srem, Срем, separator=" / " or Ijekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srijem, Сријем, label=none, separator=" / ") is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is ...
area for the final liberation of Yugoslavia, the cadre close to President Metodija Andonov – Cento gave serious thoughts whether it is better to order the preparation for an advance of the 100.000 armed men under his command toward northern Greece in order to "unify the Macedonian people" into one country. Officers loyal to Chento's ideas made a mutiny in the garrison stationed on Skopje's fortress, but the mutiny was suppressed by armed intervention. A dozen officers were shot on place, others sentenced to life imprisonment. Also Chento and his close associates were trying to minimize the ties with Yugoslavia as far as possible and were constantly mentioning the unification of the Macedonian people into one state, which was against the decisions of AVNOJ. Chento was even talking about the possibility to create an independent Macedonia backed by the US. The Yugoslav secret police made a decisive action and managed to arrest Metodija Andonov - Chento and his closest men and prevent his policies. Chento's place was taken by Lazar Kolishevski, who started fully implementing the pro-Yugoslav line.
Later the authorities organised frequent purges and trials of Macedonian people charged with autonomist deviation. Many of the former IMRO (United) government officials, were purged from their positions then isolated, arrested, imprisoned or executed on various (in many cases fabricated) charges including: pro-Bulgarian leanings, demands for greater or complete independence of Yugoslav Macedonia, forming of conspirative political groups or organisations, demands for greater democracy, etc. People as Panko Brashnarov
Panko Brashnarov ( Bulgarian and '';'' 27 July 1883 – 13 July 1951) was a revolutionary and member of the left wing of the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMARO) and IMRO (United) later. As with many other IMARO mem ...
, Pavel Shatev, Dimitar Vlahov and Venko Markovski were quickly ousted from the new government, and some of them assassinated. On the other hand, former IMRO-members, followers of Ivan Mihailov, were also persecuted by the Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
-controlled authorities on accusations of collaboration with the Bulgarian occupation. Metodi Shatorov's supporters in Vardar Macedonia, called ''Sharlisti'', were systematically exterminated by the Yugoslav Communist Party
The League of Communists of Yugoslavia, known until 1952 as the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, was the founding and ruling party of SFR Yugoslavia. It was formed in 1919 as the main communist opposition party in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats a ...
(YCP) in the autumn of 1944, and repressed for their anti-Yugoslav and pro-Bulgarian political positions.
The encouragement and evolution of the culture of the Republic of Macedonia has had a far greater and more permanent impact on Macedonian nationalism than has any other aspect of Yugoslav policy. While development of national music, films and the graphic arts has been encouraged in the Republic of Macedonia, the greatest cultural effect has come from the codification of the Macedonian language and literature, the new Macedonian national interpretation of history and the establishment of a Macedonian Orthodox Church
The Macedonian Orthodox Church – Archdiocese of Ohrid (MOC-AO; ), or simply the Macedonian Orthodox Church (MOC) or the Archdiocese of Ohrid (AO), is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in North Macedonia. The Macedonian Orthodox Church ...
in 1967 by Central Committee of the Communist Party of Macedonia.
Bulgaria
 The Bulgarian population in
The Bulgarian population in Pirin Macedonia
Pirin Macedonia or Bulgarian Macedonia () (''Pirinska Makedoniya or Bulgarska Makedoniya''), which today is in southwestern Bulgaria, is the third-biggest part of the geographical region of Macedonia. This part coincides with the borders of Blag ...
remained Bulgarian after 1913. The "Macedonian question" became especially prominent after the Balkan wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, M ...
in 1912–1913, followed from the withdraw of the Ottoman Empire and the subsequent division of the region of Macedonia between Greece, Bulgaria and Serbia. The Slav – speakers in Macedonia tended to be Christian peasants, but the majority of them were under the influence of the Bulgarian Exarchate
The Bulgarian Exarchate (; ) was the official name of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church before its autocephaly was recognized by the Ecumenical See in 1945 and the Bulgarian Patriarchate was restored in 1953.
The Exarchate (a de facto autocephaly) ...
and its education system, thus considered themselves as Bulgarians. Moreover, Bulgarians in Bulgaria believed that most of the population of Macedonia was Bulgarian. Before the Balkan Wars the regional Macedonian dialects were treated as Bulgarian and the Exarchate school system taught the locals in Bulgarian. Following the Balkan wars the Bulgarian Exarchate activity in most of the region was discontinued. After World War I, the territory of the present-day North Macedonia came under the direct rule of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () h ...
and was sometimes termed "Southern Serbia". Together with a portion of today's Serbia, it belonged officially to the newly formed Vardar Banovina. An intense program of Serbianization
Serbianisation or Serbianization, also known as Serbification, and Serbisation or Serbization ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", srbizacija, србизација or sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=none, separator=" / ", posrbljavanje, посрбљавање; ...
was implemented during the 1920s and 1930s when Belgrade enforced a Serbian cultural assimilation process on the region. Between the two world wars in Vardar Banovina, the regional Macedonian dialects were declared as Serbian and the Serbian language
Serbian (, ) is the standard language, standardized Variety (linguistics)#Standard varieties, variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Serbs. It is the official and national language of Serbia, one of the three official languages of ...
was introduced in the schools and administration as official language. There was implemented a governmental policy of assassinations and assimilation. The Serbian administration in Vardar Banovina felt insecure and that provoked its brutal reprisals on the local peasant population.
Greece, like all other Balkan states, adopted restrictive policies towards its minorities, namely towards its Slavic population in its northern regions, due to its experiences with Bulgaria's wars, including the Second Balkan War, and the Bulgarian inclination of sections of its Slavic minority.
 The movement of the Bulgarian army in Yugoslavia started on April 19, and in Greece on April 20. The prominent force which occupied most of Vardar Macedonia, was the Bulgarian 5th Army. The 6th and 7th Infantry Divisions were active in invading the Vardar Banovina between 19 and 24 April 1941. The Bulgarian troops were mainly present in the western part of Vardar Macedonia, close to the Italian occupational zone, because of some border clashes with Italians, who implemented Albanian interests and terrorized the local peasants. So the most of
The movement of the Bulgarian army in Yugoslavia started on April 19, and in Greece on April 20. The prominent force which occupied most of Vardar Macedonia, was the Bulgarian 5th Army. The 6th and 7th Infantry Divisions were active in invading the Vardar Banovina between 19 and 24 April 1941. The Bulgarian troops were mainly present in the western part of Vardar Macedonia, close to the Italian occupational zone, because of some border clashes with Italians, who implemented Albanian interests and terrorized the local peasants. So the most of Vardar Banovina
The Vardar Banovina, or Vardar Banate ( Macedonian and ; ), was a province ( banate) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941.
History
It was located in the southernmost part of the country, encompassing the whole of today's North Mace ...
, (including Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia (Macedonian language, Macedonian and ) is a historical term referring to the central part of the broader Macedonian region, roughly corresponding to present-day North Macedonia. The name derives from the Vardar, Vardar River and i ...
), was annexed by Bulgaria and along with various other regions became Greater Bulgaria. The westernmost parts of Vardar Macedonia was occupied by the fascist Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
. As the Bulgarian Army entered Vardar Macedonia on 19 April 1941, it was greeted by the local population as liberators as it meant the end of Serbian rule.Македония 1941 Възкресение
' (''Macedonia 1941 Resurrection''), Сотир Нанев (Sotir Nanev), 1942, reprinted 1993 with , publisher Труд (Trud). Memoirs of a Macedonia-born Bulgarian lieutenant participating in the occupation of the Yugoslavian and Greek parts of Macedonia.
Between Past and Future: Civil-Military Relations in Post-Communist Balkan States
', by Biljana Vankovska, 2003, , page 270. Extract from
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical charac ...
retrieved 2007-08-21. Former IMRO and IMRO (United) members were active in organizing Bulgarian Action CommitteesBulgarian Campaign Committees in Macedonia - 1941Dimitre Mičev (Dimiter Minchev). Hosted on Kroraina.com, retrieved 2007-08-21. charged with taking over the local authorities. Bulgarian Action Committees propagated a proclamation to the Bulgarians in North Macedonia on occasion of the invasion of the Bulgarian Army in the Vardar Banovina. As regards the Serbian colonists, the members of the campaign committees were adamant—they had to be deported as soon as possible and their properties to be returned to the locals. With the arrival of the Bulgarian army mass expulsion of Serbs from the area of the Vardar Macedonia took place. First, the city dwellers were deported in 1941, then all of the suspected pro-Serbs. Metodi Shatarov-Šarlo, who was a local leader of the Yugoslav Communist Party, also refused to define the Bulgarian forces as occupiers (contrary to instructions from
Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
) and called for the incorporation of the local Macedonian Communist organizations within the Bulgarian Communist Party
The Bulgarian Communist Party ( Bulgarian: Българска комунистическа партия (БΚП), Romanised: ''Bŭlgarska komunisticheska partiya''; BKP) was the founding and ruling party of the People's Republic of Bulgaria f ...
(BCP). The Macedonian Regional Committee refused to remain in contact with Communist Party of Yugoslavia
The League of Communists of Yugoslavia, known until 1952 as the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, was the founding and ruling party of SFR Yugoslavia. It was formed in 1919 as the main communist opposition party in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats a ...
(CPY) and linked up with BCP as soon as the invasion of Yugoslavia started. The CPY formally decided to launch an armed uprising on 4 July 1941 but Šarlo refused to distribute the proclamation of calling for military actions against Bulgarians. More than 12,000 Yugoslav Macedonian prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
(POWs) who had been conscripted into the Yugoslav army were released by a German, Italian and Hungarian Armies. The Slav-speakers in the part of Greek Macedonia occupied by the Bulgarian Army also greeted it as liberation.
Before the German invasion in the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, there had not been any resistance in Vardar Banovina. At the start of World War II, the Comintern supported a policy of non-intervention, arguing that the war was an imperialist war between various national ruling classes, but when the Soviet Union itself was invaded on 22 June 1941, the Comintern changed its position. The German attack on the Soviet Union sparked the rage of the Communists in Bulgaria. The same day the BCP spread a brochure among the people urging "To hinder by all means the usage of Bulgarian land and soldiers for the criminal purposes of German fascism". Two days later, on 24 June, the BCP called for an armed resistance against the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
and the Bogdan Filov government. After that, and when already months ago Yugoslavia was annexed by Axis Powers, Macedonian Communist partisans, which included Macedonians, Aromanians, Serbs, Albanians, Jews and Bulgarians had begun organizing their resistance. The First Skopje Partisan Detachment was founded and had been attacked Axis soldiers on 8 September 1941 in Bogomila, near Skopje. The revolt on 11 October 1941 by the Prilep Partisan Detachment is considered to be the symbolic beginning of the resistance. Armed insurgents from the Prilep Partisan Detachment attacked Axis occupied zones in the city of Prilep
Prilep ( ) is the List of cities in North Macedonia, fourth-largest city in North Macedonia. According to 2021 census, it had a population of 63,308.
Name
The name of Prilep appeared first as ''Πρίλαπος'' in Greek (''Prilapos'') in 1 ...
, notably a police station, killing one Bulgarian policeman of local origin, which led to attacks in Kruševo
Kruševo ( ; "Crușuva") is a town in North Macedonia. In Macedonian language, Macedonian the name means the 'place of pear trees'. It is the highest town in North Macedonia and one of the highest in the Balkans, situated at an altitude of over ...
and to the creation of small rebel detachments in other regions of North Macedonia. Partisan detachments were formed also in Greek Macedonia and today's Bulgarian Macedonia under the leadership of Communist Party of Greece
The Communist Party of Greece (, ΚΚΕ; ''Kommounistikó Kómma Elládas'', KKE) is a Marxist–Leninist political party in Greece. It was founded in 1918 as the Socialist Workers' Party of Greece (SEKE) and adopted its current name in Novem ...
and Bulgarian Communist Party.
In April 1942 a map titled "The Danube area" was published in Germany, where the so-called "new annexed territories" of Bulgaria in Vardar
The Vardar (; , , ) or Axios (, ) is the longest river in North Macedonia and a major river in Greece, where it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . The maximum depth of ...
and Greek Macedonia and Western Thrace
Western Thrace or West Thrace (, '' ytikíThráki'' ), also known as Greek Thrace or Aegean Thrace, is a geographical and historical region of Greece, between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country; East Thrace, which lie ...
were described as "territories under temporary Bulgarian administration". This was a failure for Sofia
Sofia is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain, in the western part of the country. The city is built west of the Is ...
's official propaganda, which claimed to have completed the National unification of the Bulgarians and showed the internal contradiction among Italy, Bulgaria and Germany. With the ongoing war, new anti-fascist
Anti-fascism is a political movement in opposition to fascist ideologies, groups and individuals. Beginning in European countries in the 1920s, it was at its most significant shortly before and during World War II, where the Axis powers were op ...
partisan units were constantly formed and in 1942 a total of nine small partisan detachments were active in Vardar Macedonia and had maintained control of mountainous territories around Prilep
Prilep ( ) is the List of cities in North Macedonia, fourth-largest city in North Macedonia. According to 2021 census, it had a population of 63,308.
Name
The name of Prilep appeared first as ''Πρίλαπος'' in Greek (''Prilapos'') in 1 ...
, Skopje, Kruševo
Kruševo ( ; "Crușuva") is a town in North Macedonia. In Macedonian language, Macedonian the name means the 'place of pear trees'. It is the highest town in North Macedonia and one of the highest in the Balkans, situated at an altitude of over ...
and Veles. The clash between the Yugoslav and Bulgarian Communists about possession over North Macedonia was not ended. While the Bulgarian Communists avoided organizing mass armed uprising against the Bulgarian authorities, the Yugoslav Communists insisted that no liberation could be achieved without an armed revolt. With the help of the Comintern and of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
himself a decision was taken and the Macedonian Communists were attached to CPY. Because of the unwillingness of local Communists for earnest struggle against the Bulgarian Army, the Supreme Staff of CPY took measurements for strengthening of the campaign.
Otherwise the policy of minimal resistance changed towards 1943 with the arrival of the Montenegrin Svetozar Vukmanović-Tempo Svetozar (Cyrillic script: Светозар) is a Slavic origin given name and may refer to:
* Svetozar Boroević (1856–1920), Austro-Hungarian Field Marshal
* Svetozar Čiplić (born 1965), Serbian politician
* Svetozar Đanić (1917–1941), S ...
, who began to organize an energetic struggle against the Bulgarian occupants. Tempo served on the Supreme Staff of CPY and became Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito ( ; , ), was a Yugoslavia, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and politician who served in various positions of national leadership from 1943 unti ...
's personal representative in the Vardar Banovina.
 Meanwhile, the Bulgarian government was responsible for the round-up and deportation of over 7,000 Jews in Skopje and Bitola. It refused to deport the Jews from Bulgarian proper but later under German pressure those Jews from the new annexed territories, without a Bulgarian
Meanwhile, the Bulgarian government was responsible for the round-up and deportation of over 7,000 Jews in Skopje and Bitola. It refused to deport the Jews from Bulgarian proper but later under German pressure those Jews from the new annexed territories, without a Bulgarian citizenship
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationalit ...
were deported, as these from Vardar Macedonia and Western Thrace. The Bulgarian authorities created a special Gendarmerie
A gendarmerie () is a paramilitary or military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term ''gendarme'' () is derived from the medieval French expression ', which translates to " men-at-arms" (). In France and so ...
forces which received almost unlimited power to pursue the Communist partisans on the whole territory of the kingdom. The gendarmes became notorious for carrying out atrocities against captured partisans and their supporters. Harsh rule by the occupying forces and a number of Allied victories indicated that the Axis might lose the war and that encouraged more Macedonians to support the communist Partisan
Partisan(s) or The Partisan(s) may refer to:
Military
* Partisan (military), paramilitary forces engaged behind the front line
** Francs-tireurs et partisans, communist-led French anti-fascist resistance against Nazi Germany during WWII
** Ital ...
resistance movement of Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito ( ; , ), was a Yugoslavia, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and politician who served in various positions of national leadership from 1943 unti ...
.
Many former IMRO members assisted the Bulgarian authorities in fighting Tempo's partisans. With the help of Bulgarian government and former IMRO members, several pro-Bulgarian and anti-Greek detachments – Uhrana were organized in occupied Greek Macedonia in 1943. These were led by Bulgarian officers originally from Greek Macedonia and served for protection of the local population in the zone under German and Italian control. After the capitulation of Fascist Italy
Fascist Italy () is a term which is used in historiography to describe the Kingdom of Italy between 1922 and 1943, when Benito Mussolini and the National Fascist Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictatorship. Th ...
in September 1943, the Italian zone in Macedonia was taken over by the Germans. Uhrana was supported from Ivan Mihailov. It was apparent that Mihailov had broader plans which envisaged the creation of a Macedonian state under a German control. He was follower of the idea about a United Macedonia
United Macedonia (), or Greater Macedonia (), is an irredentist concept among ethnic Macedonian nationalists that aims to unify the transnational region of Macedonia in Southeastern Europe (which they claim as their homeland and which they asser ...
n state with prevailing Bulgarian element. It was also anticipated that the IMRO volunteers would form the core of the armed forces of a future Independent Macedonia in addition to providing administration and education in the Florina
Florina (, ''Flórina''; known also by some alternative names) is a town and municipality in the mountainous northwestern Macedonia, Greece. Its motto is, 'Where Greece begins'.
The town of Florina is the capital of the Florina regional uni ...
, Kastoria
Kastoria (, ''Kastoriá'' ) is a city in northern Greece in the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Macedonia. It is the capital of Kastoria (regional unit), Kastoria regional unit, in the Geographic regions of Greece, geographic region ...
and Edessa
Edessa (; ) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, in what is now Urfa or Şanlıurfa, Turkey. It was founded during the Hellenistic period by Macedonian general and self proclaimed king Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Sel ...
districts.
Then in the resistance movement in Vardar Macedonia were clearly visible two political tendencies. The first one was represented by Tempo and the newly established Macedonian Communist Party, gave priority to battling against any form of manifest or latent pro-Bulgarian sentiment and to bringing the region into the new projected Communist Yugoslav Federation. Veterans of the pro-Bulgarian IMRO and IMRO (United) who had accepted the solution of the Macedonian question as an ethnic preference, now regarded the main objective as being the unification of Macedonia into a single state, whose postwar future was to involve not necessarily inclusion in a Yugoslav federation. They foresaw in it a new form of Serbian dominance over North Macedonia, and prefer rather membership of a Balkan federation or else independence. These two tendencies would have struck in the next few years. In Spring of 1944 the Macedonian National Liberation Army launched an operation called "The Spring Offensive" engaging German and Bulgarian Armies, which had over 60,000 military and administrative personnel in the area. In Strumica
Strumica (, ) is the largest city2002 census results
in English and Macedonian (PDF) in so ...
, approximately 3,800 fighters took part in the formation of military movements of the region; The 4th, 14th and 20th Macedonian Action Brigades, the Strumica Partisan Detachment and the 50th and 51st Macedonian Divisions were formed. Since the formation of an army in 1943, Macedonian Communist partisans were aspiring to create an autonomous government.
On 2 August 1944, on the 41st anniversary of the Ilinden-Preobrazhenie Uprising, the first session of the newly created Anti-Fascist Assembly of the National Liberation of Macedonia (in English and Macedonian (PDF) in so ...
ASNOM
The Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (, ''Antifašističko sobranie za narodno osloboduvanje na Makedonija''; Serbo-Croatian: ''Antifašističko sobranje narodnog oslobođenja Makedonije''; abbr. ASNOM) was the supr ...
) was held at the St. Prohor Pčinjski monastery
The Monastery of Venerable Prohor of Pčinja (), commonly known as Prohor Pčinjski () is an 11th-century Serbian Orthodox monastery in the deep south in Serbia, located in the village of Klenike, south of Vranje, near the border with North Mac ...
. А manifesto
A manifesto is a written declaration of the intentions, motives, or views of the issuer, be it an individual, group, political party, or government. A manifesto can accept a previously published opinion or public consensus, but many prominent ...
was written outlining the future plans of ASNOM for an independent Macedonian state and for creation of the Macedonian language as the official language of the Macedonian state. However, a decision was later reached that Vardar Macedonia will become a part of new Communist Yugoslavia. In the summer of 1944, Ohrana constituted some 12,000 fighters and volunteers from Bulgaria. Whole Slavophone villages were armed and developed into the most formidable enemy of the Greek People's Liberation Army
The Greek People's Liberation Army (, ''Ellinikós Laïkós Apeleftherotikós Stratós''; ELAS) was the military arm of the left-wing National Liberation Front (EAM) during the period of the Greek resistance until February 1945, when, followi ...
(ELAS). At this time Ivan Mihailov arrived in German-occupied Skopje, where the Germans hoped that he could form an Independent State of Macedonia with their support on the base of IMRO and Ohrana. Seeing that the war is lost to Germany and to avoid further bloodshed, he refused.
At this time the new Bulgarian government of Ivan Bagryanov began secret negotiations with the Allies aiming to find separate peace with repudiating any alliance with Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
and declaring neutrality, ending all anti-Jewish laws and ordering the withdrawal of the Bulgarian troops from Macedonia. Through its Macedonia-born minister of Internal Affairs , the government tried to negotiate with the Macedonian partisans promising that after Bulgarian army withdrawal from Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia (Macedonian language, Macedonian and ) is a historical term referring to the central part of the broader Macedonian region, roughly corresponding to present-day North Macedonia. The name derives from the Vardar, Vardar River and i ...
its arms would be given up to the partisans. It would be possible by condition that partisans guaranteed the establishment of pro-Bulgarian Macedonian state without the frame of future Yugoslavia. The negotiations failed and on 9 September 1944 the Fatherland Front in Sofia made a coup d'état and deposed the government. After the declaration of war by Bulgaria on Nazi Germany, the withdrawing Bulgarian troops in Macedonia surrounded by German forces, fought their way back to the old borders of Bulgaria. Under the leadership of a new Bulgarian pro-Communist government, three Bulgarian armies, 455,000 strong in total, entered occupied Yugoslavia in late September 1944 and moved from Sofia to Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names of European cities in different languages (M–P)#N, names in other languages), less often spelled in English as Nish, is the list of cities in Serbia, third largest city in Serbia and the administrative cente ...
and Skopje with the strategic task of blocking the German forces withdrawing from Greece. They operated here in interaction with local partisans. Southern and eastern Serbia and most of Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia (Macedonian language, Macedonian and ) is a historical term referring to the central part of the broader Macedonian region, roughly corresponding to present-day North Macedonia. The name derives from the Vardar, Vardar River and i ...
were liberated within an end of November. Toward the end of November and during early December, the main Bulgarian forces were assembled in liberated Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
prior to their return home. The 135,000-strong Bulgarian First Army continued to Hungary, aided by Yugoslav Partisans
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian language, Macedonian, and Slovene language, Slovene: , officially the National Liberation Army and Partisan Detachments of Yugoslavia sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska i partizanski odr ...
.
However, the Bulgarian army during the annexation of the region was partially recruited from the local population, which formed as much as 40% of the soldiers in certain battalions. Some official comments of deputies in the Macedonian parliament and of former Premier, Ljubčo Georgievski
Ljubčo Georgievski (, ; ; born 17 January 1966) is a Macedonian politician and writer who served as the only Vice President of Macedonia from January to October 1991 and as the Prime Minister of Macedonia from 1998 to 2002. He advocated for th ...
after 1991 announced the "struggle was civil, but not a liberation war". According to official sources the number of Macedonian communist partisan's victims against the Bulgarian army during World War II was 539 men. Bulgarian historian and director of the Bulgarian National Historical Museum Dr. Bozhidar Dimitrov
Bozhidar Dimitrov Stoyanov (, 3 December 1945 – 1 July 2018) was a Bulgarian historian, politician, and polemicist in the sphere of Medieval Bulgarian history, the Ottoman rule of Bulgaria and the Macedonian Question. He was director of the ...
, in his 2003 book '' The Ten Lies of Macedonism'', has also questioned the extent of resistance of the local population of Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia (Macedonian language, Macedonian and ) is a historical term referring to the central part of the broader Macedonian region, roughly corresponding to present-day North Macedonia. The name derives from the Vardar, Vardar River and i ...
against the Bulgarian forces and describes the clash as political.
After the end of World War II, the creation of People's Republic of Macedonia
The Socialist Republic of Macedonia (), or SR Macedonia, commonly referred to as Socialist Macedonia, Yugoslav Macedonia or simply Macedonia, was one of the six constituent republics of the post-World War II Socialist Federal Republic of Y ...
and of a new Macedonian language, it started a process of ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is the formation and development of an ethnic group. This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th-century neologism that was later introduce ...
and distinct national Macedonian identity was formed. The new Yugoslav authorities began a policy of removing of any Bulgarian influence, making Macedonia connecting link for the establishment of new Balkan Federation and creating a distinct Slavic consciousness that would inspire identification with Yugoslavia. After World War II the ruling Bulgarian Communists declared the population in Bulgarian Macedonia as ethnic Macedonian and teachers were brought in from Yugoslavia to teach the locals in the new Macedonian language. The organizations of the IMRO in Bulgaria were completely destroyed. Former IMRO members were hunted by the Communist Militsiya
''Militsiya'' ( rus, милиция, 3=mʲɪˈlʲitsɨjə, 5=, ) were the police forces in the Soviet Union until 1991, in several Eastern Bloc countries (1945–1992), and in the Non-Aligned Movement, non-aligned Socialist Federal Republic ...
and many of them imprisoned, repressed, exiled or killed. Also internments of disagreeing with this political activities people at the Belene labor camp were organized. Tito and Georgi Dimitrov
Georgi Dimitrov Mihaylov (; ) also known as Georgiy Mihaylovich Dimitrov (; 18 June 1882 – 2 July 1949), was a Bulgarian communist politician who served as General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Bulgarian Communist Party from 1933 t ...
worked about the project to merge the two Balkan countries Bulgaria and Yugoslavia into a Balkan Federative Republic according to the projects of Balkan Communist Federation. This led to the 1947 cooperation and signing of Bled Agreement (1947), Bled Agreement. It foresaw unification between Vardar Macedonia and Pirin Macedonia and return of Western Outlands to Bulgaria. They also supported the Greek Communists and especially National Liberation Front (Macedonia), Slavic-Macedonian National Liberation Front in the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
with the idea of unification of Greek Macedonia and Western Thrace
Western Thrace or West Thrace (, '' ytikíThráki'' ), also known as Greek Thrace or Aegean Thrace, is a geographical and historical region of Greece, between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country; East Thrace, which lie ...
to the new state under Communist rule. According this project the bourgeoisie of the ruling nations in the three imperialist states among which Macedonia was partitioned, tried to camouflage its national oppression, denying the national features of the Macedonian people and the existence of the Macedonian nation. The policies resulting from the agreement were reversed after the Tito–Stalin split in June 1948, when Bulgaria, being subordinated to the interests of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
took a stance against Yugoslavia. This policy for projection and recognition of regional countries and nations since the 1930s as for example Macedonia, had been the norm in Comintern policies, displaying Soviet resentment of the nation-state in Eastern Europe and of the consequences of Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris Peace Conference. With the 1943 dissolution of Comintern and the subsequent advent of the Cominform in 1948 came Joseph Stalin's dismissal of the previous ideology, and adaptation to the conditions created for Soviet hegemony during the Cold War. The Dimitrov's sudden death in July 1949 was followed by a "Titoism, Titoists" witchhunt in Bulgaria.
After Greek Communists lost the Greek Civil War, many Slav speakers were expelled from Greece. Although the People's Republic of Bulgaria originally accepted very few refugees, government policy changed and the Bulgarian government actively sought out refugees from Greek Macedonia. It is estimated that approximately 2,500 children were sent to Bulgaria and 3,000 partisans fled there in the closing period of the war. There was a larger flow into Bulgaria of refugees as the Bulgarian Army pulled out of the Drama-Serres region in 1944. A large proportion of Slavic speakers emigrated there. The "Slavic Committee" in Sofia () helped to attract refugees that had settled in other parts of the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
. According to a political report in 1962 the number of political emigrants from Greece numbered at 6,529. The policy of communist Bulgaria towards the refugees from Greece was, at least initially, not discriminative with regard to their ethnic origin: Greek- and Slav-speakers were both categorized as Greek political emigrants and received equal treatment by state authorities. However, the end of the 1950s was marked by adecisive turn in the " Macedonistic" policy of Bulgaria, "which did not recognize anymore the existence of a Macedonian ethnicity different from the Bulgarian one". As a result, the trend to a discriminative policy, the refugees from Greece – more targeted at the Slav-speakers and less to "ethnic Greeks" – was given a certain proselytizing aspect. Eventually many of these migrants were assimilated into Bulgarian society.
At the end of the 1950s the Communist Party repealed its previous decision and adopted a position denying the existence of a "Macedonian" nation. The inconsistent Bulgarian policy has thrown most independent observers ever since into a state of confusion as to the real origin of the population in Bulgarian Macedonia. In 1960, the Bulgarian Communist Party
The Bulgarian Communist Party ( Bulgarian: Българска комунистическа партия (БΚП), Romanised: ''Bŭlgarska komunisticheska partiya''; BKP) was the founding and ruling party of the People's Republic of Bulgaria f ...
voted a special resolution explained "with the fact that almost all of the Macedonians have a ''clear Bulgarian national consciousness and consider Bulgaria their homeland''. As result international relations upon the Sofia–Belgrade line deteriorated, and in fact were broken. This led to a final victory of the anti-Bulgarian and pro-Yugoslav oriented Macedonian political circles and signified a definite decline of the very notion of a south Slavonic federation. In Macedonia the ''Bulgarophobia'' increased almost to the level of state ideology.
Bulgaria usually kept the right to declare ethnicity at census, but Bulgarian identity was minimized in the censuses of Yugoslavia and Blagoevgrad Province of Bulgaria. but between 1945 and 1965 forcefully Macedonians Blagoecgra Province 1946 and the 1956 census the population was forced to list as ethnic Macedonians against their will by the communist government in accordance with an agreement with Yugoslavia.
 A total of 3,100 people in the Blagoevgrad District declared themselves Macedonian in the 2001 census (0.9% of the population of the region). According to the European Court of Human Rights ethnic Macedonians in Bulgaria have endured Ethnic Macedonians in Bulgaria#European Court of Human Rights Decisions and European Parliament, violations of human rights by the Bulgarian government.
In Bulgaria today, the Macedonian question has been understood largely as a result of the violation of national integrity, beginning with the revision of the
A total of 3,100 people in the Blagoevgrad District declared themselves Macedonian in the 2001 census (0.9% of the population of the region). According to the European Court of Human Rights ethnic Macedonians in Bulgaria have endured Ethnic Macedonians in Bulgaria#European Court of Human Rights Decisions and European Parliament, violations of human rights by the Bulgarian government.
In Bulgaria today, the Macedonian question has been understood largely as a result of the violation of national integrity, beginning with the revision of the Treaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Preliminary Treaty of San Stefano (; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878. It was signed at San Ste ...
from 1878. Bulgaria denies the existence of a separate Macedonian identity. The Bulgarian denouncement is based on the strong sense of loss of the territory, history and language which it shared with present-day North Macedonia in the past. After the collapse of the Socialist Federative Republic of Yugoslavia and the consequent independence of the Macedonian state in 1991, Bulgaria continued to question of the legitimacy of Macedonian nationhood, yet at the same time recognised the new state. The Bulgarian government of 1991 promoted this political compromise as a constructive way of living with the national question, rather than suppressing them. Yet none of the fundamental tensions over the Macedonian question have been fully resolved, and the issue remains an important undercurrent in Sofia politics.
Albania
The South Slavs, South Slavic minority in Albania is concentrated in two regions, Mala Prespa and Golloborda. In the 1930s the orthodox Slavs living in Albania were regarded as Bulgarians by the local Albanian population. The new Albanian state did not attempt to assimilate this minority or to forcibly change the names of local towns and villages. During the second Balkan Conference in 1932 the Bulgarian and Albanian delegations signed a Protocol about the recognition of the ethnic Bulgarian minority in Albania. After World War II, the creation of People's Republic of Macedonia and the policy of the new communist states about the founding of Balkan Federative Republic changed the situation and an Macedonians in Albania, ethnic Macedonian minorityOn the status of minorities in the Republic of Albania, Albanian Helsinki Committee with the support of the Finnish Foundation ‘KIOS’ and "Finnish NGO Foundation for Human Rights" was officially recognized. Schools and radio stations in Macedonian were founded in the area. Albania has recognised around 5,000 strong Macedonian minority. In Albania are both Bulgarian and Macedonian organizations. Each of them claims that the local Slavic population is either Bulgarian or Macedonian. The population itself, which is predominantly
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, has, however, preferred to call itself Albanian in official censuses.
North Macedonia

North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
officially celebrates 1991 with regard to the referendum endorsing independence from Yugoslavia, albeit legalizing participation in "future union of the former states of Yugoslavia". The ethnic Macedonians of North Macedonia have demonstrated without any exception a strong and even aggressive at times Macedonian consciousness. Any ties with the Bulgarians have been denounced. During this period it has been claimed by Macedonian scholars that there exist large and oppressed ethnic Macedonian minorities in the region of Macedonia, located in neighboring states. Because of those claims, irredentist proposals are being made calling for the expansion of the borders of Macedonia to encompass the territories allegedly populated with ethnic Macedonians. The population of the neighboring regions is presented as "subdued" to the propaganda of the governments of those neighboring countries, and in need their incorporation into a United Macedonia
United Macedonia (), or Greater Macedonia (), is an irredentist concept among ethnic Macedonian nationalists that aims to unify the transnational region of Macedonia in Southeastern Europe (which they claim as their homeland and which they asser ...
. By the time Macedonia proclaimed its independence those who continued to look to Bulgaria were very few. Some 3,000–4,000 people that stuck to their Bulgarian identity met great hostility among the authorities and the rest of the population. Occasional trials against "Bulgarophiles" have continued until today. The Constitutional Court of Republic of Macedonia banned the organization of the Bulgarians in the Republic of Macedonia]Radko
as "promoting racial and religious hate and intolerance". In 2009 the European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg, condemned Republic of Macedonia because of violations of the European Convention of Human Rights in this case. Nevertheless, during the last few years, rising economic prosperity and the EU membership of Bulgaria has seen around 60,000 Macedonians applying for Bulgarian
citizenship
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationalit ...
; in order to obtain it they must sign a statement declaring they are ''Bulgarians by origin''. Probably the most prominent Macedonian that applied for and was granted Bulgarian citizenship is former Prime Minister Ljubčo Georgievski
Ljubčo Georgievski (, ; ; born 17 January 1966) is a Macedonian politician and writer who served as the only Vice President of Macedonia from January to October 1991 and as the Prime Minister of Macedonia from 1998 to 2002. He advocated for th ...
. An estimated 500 Macedonians receive Bulgarian citizenship every week. This aggregates to about 50,000 Macedonian nationals who have received Bulgarian citizenship in the past 20 years. Bulgarian governments justify this policy because they regard Macedonians as ''ethnopolitically disoriented Bulgarians.''
See also
* Macedonia (terminology) * Macedonia (region) * Demographic history of North Macedonia * Macedonia (Greece)#Demographic history, Macedonia (Greece) Demographic history * Blagoevgrad Province#Demographics, Blagoevgrad Province DemographicsNotes
References
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
Banac, Ivo. (1984). The National Question in Yugoslavia. Origins, History, Politics. Cornell University Press: Ithaca/London University Press: Ithaca/London (online version of relevant pages)
* Boué, Ami. (1840). Le Turquie d’Europe. Paris: Arthus Bertrand.
* Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. (1914). Report of the International Commission To Inquire into the Causes and Conduct of the Balkan Wars. Washington: The Carnegie Endowment from https://web.archive.org/web/20110927153709/http://vmro.150m.com/en/carnegie/ * * Gopčević, Spiridon. (1889). Makedonien und Alt-Serbien. Wien: L. W. Seidel & Sohn. - Стара Србија и Македонија, превод: Милан Касумовић. Београд, 1890.
Jezernik, Bozhidar. Macedonians: Conspicuous By Their Absence
Misirkov, Krste P. (1903). Za makedonckite raboti. Sofia: Liberalni klub.
(In Macedonian and English)
The Emergence of Macedonian National Thought and the Formation of a National Programme (up to 1878) by Blaže Ristovski
* Kunčov, Vasil. (1900). Makedonija. Etnografija i statistika. Sofia: Državna pečatnica (Кънчов, В. 1900, Македония. Етнография и статистика. София: Държавна печатница). * Lange-Akhund, Nadine. (1998). The Macedonian Question, 1893–1908 from Western Sources. Boulder, Colo. : New York. * MacKenzie, Georgena Muir and Irby, I.P. (1971). Travels in the Slavonic Provinces of Turkey in Europe. New York, Arno Press. * Poulton, Hugh. (1995). Who are the Macedonians? C. Hurst & Co. (Publishers) Ltd., London * Roudometoff, Victor. (2000). The Macedonian Question: Culture, Historiography, Politics. Boulder, CO: East European Monographs. * quoted in . * Weigand, Gustav. (1924). ETHNOGRAPHIE VON MAKEDONIEN, Geschichtlich-nationaler, spraechlich-statistischer Teil von Prof. Dr. Gustav Weigand, Leipzig, Friedrich Brandstetter. * Wilkinson, H.R. (1951). Maps and Politics; a review of the ethnographic cartography of Macedonia, Liverpool University Press. * Kuhn's Zeitschrift für vergleichende Sprachforschung XXII (1874), Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographic History Of Macedonia History of Macedonia (region) Demographic history by country or region, Macedonia Demographics of the Ottoman Empire Demographics of Bulgaria Demographics of Greece Demographics of Albania Demographics of North Macedonia