MacAdam ellipse on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the study of 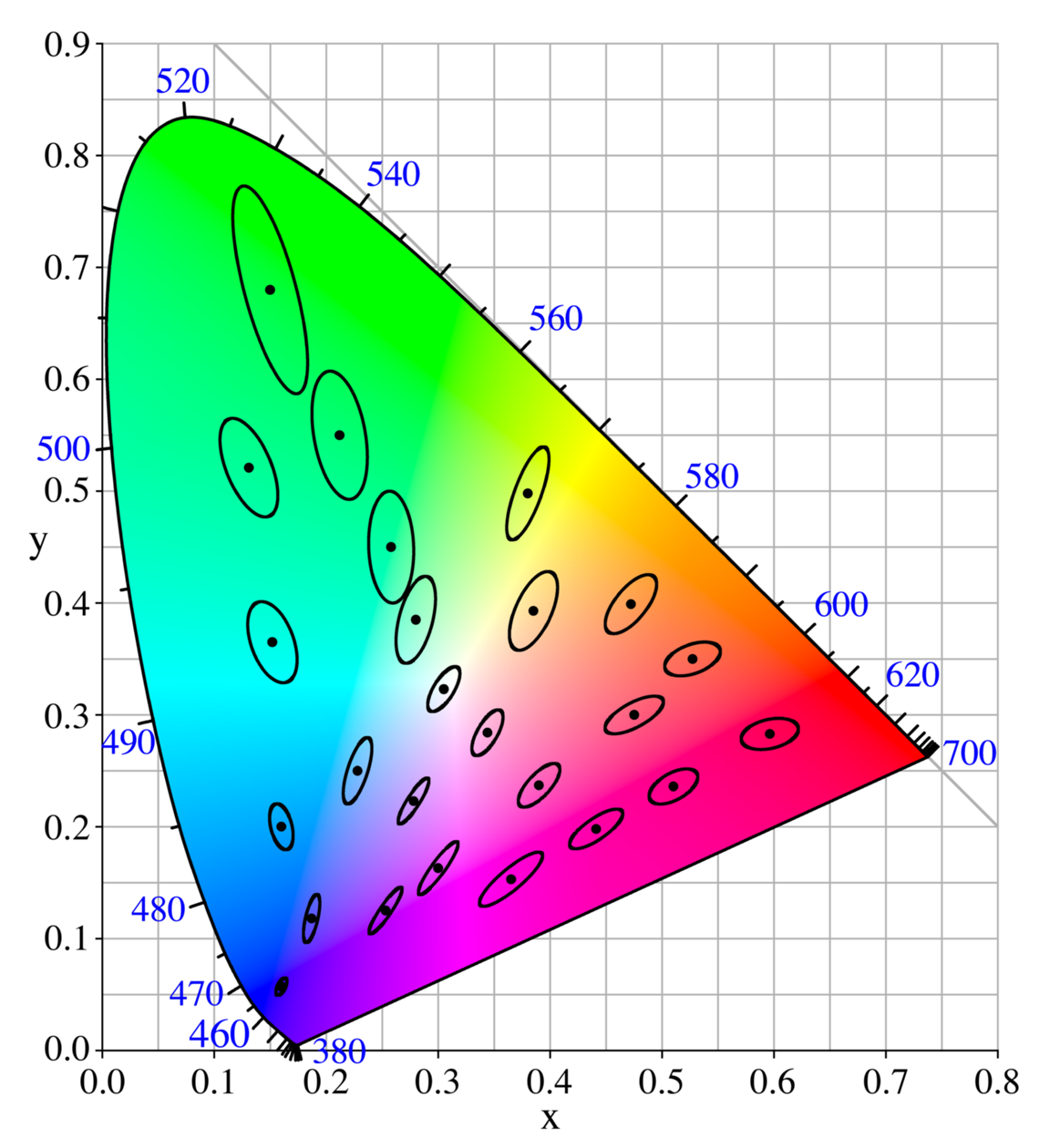
in CIE 1960 UCS
Color space Vision
color vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
, a MacAdam ellipse is a region on a chromaticity diagram
Chromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance. Chromaticity consists of two independent parameters, often specified as hue (h) and colorfulness (s), where the latter is alternatively called s ...
which contains all colors which are indistinguishable, to the average human eye, from the color at the center of the ellipse. The contour of the ellipse therefore represents the just-noticeable difference
In the branch of experimental psychology focused on sense, sensation, and perception, which is called psychophysics, a just-noticeable difference or JND is the amount something must be changed in order for a difference to be noticeable, detectab ...
s of chromaticity
Chromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance. Chromaticity consists of two independent parameters, often specified as hue (h) and colorfulness (s), where the latter is alternatively called ...
. Standard Deviation Color Matching in LED lighting
An LED lamp or LED light bulb is an electric light that produces light using light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED lamps are significantly more energy-efficient than equivalent incandescent lamps
and can be significantly more efficient than m ...
uses deviations relative to MacAdam ellipses to describe color precision of a light source.

History
In the study of color perception, the first question that usually comes to mind is, "Whatcolor
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are assoc ...
is it?" In other words, we wish to develop a method of specifying a particular color which allows us to differentiate it from all other colors. It has been found that three quantities are needed to specify a particular color. The relative amounts of red, green and blue in a color will serve to specify that color completely. This question was first approached by a number of researchers in the 1930s, and their results were formalized in the specification of the CIE XYZ color space
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that def ...
.
The second question we might ask, given two colors, is, "How different are these two colors?" Just as the first question was answered by developing a color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representa ...
in which three numbers specified a particular color, we are now asking effectively, how far apart these two colors are. This particular question was considered by researchers dating back to Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, ...
and Schrödinger, and later in industrial applications, but experiments by Wright and Pitt, and David MacAdam
David Lewis MacAdam (July 1, 1910 – March 9, 1998) was an American physicist and color scientist who made important contributions to color science and technology in the fields of colorimetry, color discrimination, color photography and televisi ...
provided much-needed empirical support.
Procedure
MacAdam set up an experiment in which a trained observer viewed two different colors, at a fixedluminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls withi ...
of about 48 cd/m2. One of the colors (the "test" color) was fixed, but the other was adjustable by the observer, and the observer was asked to adjust that color until it matched the test color. This match was, of course, not perfect, since the human eye, like any other instrument, has limited accuracy. It was found by MacAdam, however, that all of the matches made by the observer fell into an ellipse on the CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that defin ...
. The measurements were made at 25 points on the chromaticity diagram, and it was found that the size and orientation of the ellipses on the diagram varied widely depending on the test color. These 25 ellipses measured by MacAdam, for a particular observer, are shown on the chromaticity diagram above.
Extension to three dimensions
A more general concept is that of "discrimination ellipsoids" in the entire three-dimensional color space, which would include the ability of an observer to discriminate between two different luminances of the same color. Such measurements were carried out, among others, by Brown and MacAdam in 1949, Davidson in 1951, Brown in 1957, and by Wyszecki and Fielder in 1971. It was found that the discrimination ellipsoids yielded relatively unchanging discrimination ellipses in chromaticity space for luminances between 3 and 30 cd/m2.Effects in colour theory
{{missing information, section, attempts at reproduction, date=July 2021 MacAdam's results confirmed earlier suspicions that colour difference could be measured using ametric
Metric or metrical may refer to:
* Metric system, an internationally adopted decimal system of measurement
* An adjective indicating relation to measurement in general, or a noun describing a specific type of measurement
Mathematics
In mathem ...
in a chromaticity space. A number of attempts have been made to define a color space which is not as distorted as the CIE XYZ space. The most notable of these are the CIELUV
In colorimetry, the CIE 1976 ''L''*, ''u''*, ''v''* color space, commonly known by its abbreviation CIELUV, is a color space adopted by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1976, as a simple-to-compute transformation of the 1931 ...
and CIELAB
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'' , is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. (Referring to CIELAB as "Lab" without asterisks should be avoided to prevent confusi ...
color spaces. Although both of these spaces are less distorted than the CIE XYZ space, they are not completely free of distortion. This means that the MacAdam ellipses become nearly (but not exactly) circular in these spaces.
See also
*Metric tensor
In the mathematical field of differential geometry, a metric tensor (or simply metric) is an additional structure on a manifold (such as a surface) that allows defining distances and angles, just as the inner product on a Euclidean space allo ...
* Tissot's indicatrix
In cartography, a Tissot's indicatrix (Tissot indicatrix, Tissot's ellipse, Tissot ellipse, ellipse of distortion) (plural: "Tissot's indicatrices") is a mathematical contrivance presented by French mathematician Nicolas Auguste Tissot in 1859 a ...
, used to characterize distortions in map projections
* Mahalanobis distance The Mahalanobis distance is a measure of the distance between a point ''P'' and a distribution ''D'', introduced by P. C. Mahalanobis in 1936. Mahalanobis's definition was prompted by the problem of identifying the similarities of skulls based ...
, using covariance to create a metric
References
External links
* MacAdam ellipses plotted with the "colour-science" Python packagein CIE 1960 UCS
Color space Vision