local government in Canada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Local government in Canada can be defined as all elected local authorities which are legally empowered to make decisions on behalf of its electors, excluding the
. Government of Australia. Retrieved May 24, 2009.
Nick Swift. Retrieved May 24, 2009. and when the government is not funded by the provincial government, taxes need to be imposed. * Public utilities and other services. Usually, parks are taken care of by the municipal government and occasionally sewerage, water, etc. * In Quebec, Ontario and Alberta the range of local government services is broadened to include electricity, telephone and gas services.Local Government
The Canadian Encyclopedia. Retrieved May 24, 2009.Local Government in Canada
MapleLeafWeb. Retrieved May 24, 2009.
 Most local governments are formed by a
Most local governments are formed by a
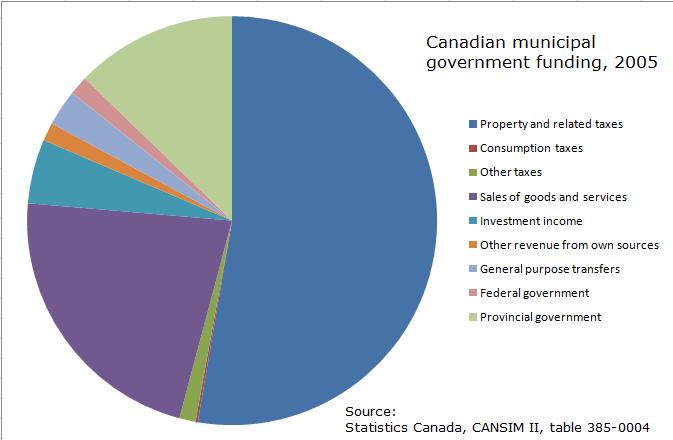
Example of council structure. Retrieved May 24, 2009. In Canada, 83% of the municipal government revenue is raised through their own sources, and legally their accounts cannot go into deficit, safeguarding the provinces from unintentionally guaranteeing their municipal governments' debts. The majority of funding for Canadian municipal governments comes from
.
- Andrew Sancton, Professor, University of Western Ontario. In 1849, the
Local Government in Canada: Organization & Basic Institutions , Mapleleafweb.com
{{North America topic, Local government in
federal government
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
, provincial and territorial governments, and First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
, Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
and Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
governments. This can include municipalities, school board
A board of education, school committee or school board is the board of directors or board of trustees of a school, local school district or an equivalent institution.
The elected council determines the educational policy in a small regional area, ...
s, health authorities, and so on.
The most prominent form of local government in Canada is municipal government, which is a local council authority which provides local services, facilities, safety and infrastructure for communities. Municipal governments are local general-purpose authorities which provide services to all residents within a defined geographic area called a municipality.
According to Section 92(8) of the ''Constitution Act, 1867
The ''Constitution Act, 1867'' ( 30 & 31 Vict. c. 3) (),''The Constitution Act, 1867'', 30 & 31 Victoria (U.K.), c. 3, http://canlii.ca/t/ldsw retrieved on 2019-03-14. originally enacted as the ''British North America Act, 1867'' (BNA Act), ...
'', ''"''In each Province the Legislature may exclusively make Laws in relation to … Municipal Institutions in the Province." There are about 3,700 municipal governments in Canada. Municipal governments are established under provincial/territorial authority.
The powers granted to municipal governments are delegated by each of the provinces and territories of Canada
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Constitution of Canada, Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North Amer ...
according to governing legislation. Therefore, the legislation passed by municipalities has the status of subordinate legislation under provincial and territorial jurisdiction. However, rather than being "mere 'creatures of the provinces,'" municipal governments are "democratically elected by members of the general public and are accountable to their constituents in a manner analogous to that in which Parliament and the provincial legislatures are accountable to the electorates." Therefore, while municipalities do not have independent constitutional status, they are considered a separate level of government.
Municipal government
The organisation of local government is complex. For instance, in some provinces there are several tiers of local government: regional governments, county governments and municipal governments. There are also special service districts in some unincorporated areas. Municipal local governments take various forms including cities, towns and villages. There are also innumerable specific purpose authorities. In Ontario alone there are at least 2000 of these bodies, including 'police commissions, health units, conservation authorities, public utilities commissions, parks boards and school boards.’ Schools are usually provided locally by school boards, with the 'school trustees' being elected.Chapter 7 : Special report: local government in Canada. Government of Australia. Retrieved May 24, 2009.
Regional municipalities
In some provinces, several municipalities in a particular area are also part of an upper tier of municipal government, which provides more regionally oriented services. Depending on the province, this second tier may be called acounty
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
, regional municipality
A regional municipality (or region) is a type of Canadian municipal government similar to and at the same municipal government level as a county, although the specific structure and servicing responsibilities may vary from place to place. R ...
, regional district or regional county municipality
The term regional county municipality or RCM (, , MRC) is used in Quebec, Canada to refer to one of 87 county-like political entities. In some older English translations they were called county regional municipality.
Regional county municipalit ...
.
In Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
, three municipalities are designated as "regional municipalities". A regional municipality is a single municipal government covering an entire historical county including all formerly incorporated towns and cities within the county. Within the three regional municipalities, designations such as "city" and "town" exist only as informal signifiers for historically chartered towns and cities that used to exist prior to the establishment of the regional municipality.
Local municipalities
In Canada, the types of municipal government vary between provinces, although they all perform the same functions. The general hierarchy was established in 1849 with the passing of the Municipal Corporations Act in United Canada. The largest municipalities are usually calledcities
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
, and their governments, city councils. Smaller governments are commonly called town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city.
The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ...
s, village
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban v ...
s, parishes
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or ...
, rural municipalities, township
A township is a form of human settlement or administrative subdivision. Its exact definition varies among countries.
Although the term is occasionally associated with an urban area, this tends to be an exception to the rule. In Australia, Canad ...
s or hamlets
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. This is often simply an informal description of a smaller settlement or possibly a subdivision or satellite entity to a larger settlement. Sometimes a hamlet is defined f ...
. Some may also be directly designated as municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
rather than as a particular type of municipality, but this term is still considered inclusive of all local governments regardless of their status.
The term "borough" was previously used in Metropolitan Toronto
The Municipality of Metropolitan Toronto was an upper-tier level of municipal government in Ontario, Canada, from 1953 to 1998. It was made up of the old city of Toronto and numerous townships, towns and villages that surrounded Toronto, whic ...
, Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, to denote suburban municipalities. The Borough of East York
East York is a district and former municipality within Toronto, Ontario, Canada. From 1967 to 1998, it was officially the Borough of East York, a borough within the upper-tier municipality of Metropolitan Toronto. The borough was dissolved ...
was the last municipality to hold this status, relinquishing it upon becoming part of the City of Toronto on January 1, 1998.
In Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, there is no legal distinction between cities and towns – although an informal and subjective distinction may be observed by English speakers, legally all "cities" and "towns" in Quebec have the same status of '' ville''.
Sublocal divisions
InQuebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, the term borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
is generally used as the English translation of arrondissement
An arrondissement (, , ) is any of various administrative divisions of France, Belgium, Haiti, and certain other Francophone countries, as well as the Netherlands.
Europe
France
The 101 French departments are divided into 342 ''arrondissem ...
, referring to an administrative division of a municipality. Only eight municipalities in Quebec are divided into boroughs. (See List of boroughs in Quebec
This is a list of boroughs (''arrondissements'') in Quebec. Boroughs are provincially organized recognized sub-municipal administrative divisions of Quebec, administrative divisions that have mayors and councillors.
List Grenville-sur-la-Rouge, ...
.)
Unincorporated areas
Some areas in Canada are unincorporated, meaning that they do not have a municipal government at all. Any government services in an unincorporated area are provided either by a local agency, such as a Local services board or local service district, or by the province itself.Powers and functions
While many municipal governments have different functions to others (urban vs. rural, etc.), and vary from province to province, most of the services and functions they perform are effectively the same. Functions of municipal governments can include: * Management of the local policing and firefighting stations. Whilst this sometimes comes under the jurisdiction of the provincial government, there is often municipal police and fire services. * Transportation. Whilst municipal governments may not be responsible for provincial and federally designated highways, roads may come under their control. Additionally, municipal governments may operate local transit services. * Education management or funding school boards. In many municipalities, the school board is voted by the people and funded by the municipal government itself from the taxes it collects. * Planning and development. Municipal government is responsible for local planning and approvals based on legislative requirements. They are also responsible for enforcing compliance with local requirements. * Finance and collecting municipality taxes. Most municipalities (with the exception of some rural ones) have the power to collect taxes in order to provide the services mentioned in this list. Almost 10% of the national GDP is spent on municipal government services,Canada offers its people an array of local governmentsNick Swift. Retrieved May 24, 2009. and when the government is not funded by the provincial government, taxes need to be imposed. * Public utilities and other services. Usually, parks are taken care of by the municipal government and occasionally sewerage, water, etc. * In Quebec, Ontario and Alberta the range of local government services is broadened to include electricity, telephone and gas services.Local Government
The Canadian Encyclopedia. Retrieved May 24, 2009.Local Government in Canada
MapleLeafWeb. Retrieved May 24, 2009.
Structure and funding
 Most local governments are formed by a
Most local governments are formed by a charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the ...
or act granted by the province or territory. Local governments are not mentioned in the Canadian Constitution other than to say they are the responsibility of the provinces. Consequently, municipalities can be created, amalgamated, or disbanded by the provincial government. Mayors frequently interact with their federal and provincial counterparts over areas of shared responsibility. The federal government does fund quite a few projects in many cities, like major transit and roads. These funds come from a variety of federal programs like P3 Canada, where a private company/consortia does a percentage of a project, construction, operations, maintenance, financing and designing, the Building Canada Fund, where major projects can receive federal funds for a project. Unlike many US projects and cities, most projects only get approximately a quarter of their funds from the federal government, and they are not obligated Buy American Act to have a certain amount of the work done by Canadians or Canadian companies.
Since each province is responsible for creating local governments in its own territory, the names, functions, and powers of local bodies vary widely across the country. Local governments generally have limited powers, namely creating local by-laws and taxation (property tax
A property tax (whose rate is expressed as a percentage or per mille, also called ''millage'') is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or Wealth t ...
).
Typically, a municipal government is made up of one ''mayor'' (occasionally ''reeve'' or ''warden'') and a set number of ''councillors'' (occasionally ''alderman
An alderman is a member of a Municipal government, municipal assembly or council in many jurisdictions founded upon English law with similar officials existing in the Netherlands (wethouder) and Belgium (schepen). The term may be titular, denotin ...
''). There are usually 10−20 councillors in one council; however, an exception to this is Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
, with over 50 councillors. The councillors may represent districts called ''wards''.Regional Municipality of Wood BuffaloExample of council structure. Retrieved May 24, 2009. In Canada, 83% of the municipal government revenue is raised through their own sources, and legally their accounts cannot go into deficit, safeguarding the provinces from unintentionally guaranteeing their municipal governments' debts. The majority of funding for Canadian municipal governments comes from
property tax
A property tax (whose rate is expressed as a percentage or per mille, also called ''millage'') is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or Wealth t ...
es. Additional funding sources include the sale of goods and services, fines and tax transfers from the provincial government.Local general government revenue and expenditures, by province and territory.
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; ), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in ...
. Retrieved May 24, 2009.
Elections
Due to the control that the provinces have over their municipal governments, terms that councillors serve vary from province to province. Unlike most provincial elections, municipal elections are usually held on a fixed date.Dates of elections by province and territory
History
Like many Canadian political institutions, the municipal government has its roots in the medieval system of government in England. Famously, the city ofWinchester
Winchester (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs N ...
was given its charter in 1185, and the granting of freedoms became endorsed in Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter"), sometimes spelled Magna Charta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardin ...
, which was signed in 1215. The first formal municipality in Canada was the city of Saint John in New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
, which received royal approval in 1785. For municipal government, this began an almost 50-year hiatus of receiving approval from the government, ending in the 1830s when the issue was placed on the agenda once again. In 1835, the British parliament passed the Municipal Corporations Act, which specified how municipalities were to function and be elected. The ideas from this law were transferred to Canada by Lord Durham, who submitted a report to then- Governor General, Lord Sydenham. In late 1840 to early 1841, the governments of what was Canada at the time enacted various acts which established municipal government in all areas of the country.Canadian municipal history- Andrew Sancton, Professor, University of Western Ontario. In 1849, the
Legislative Assembly of the Province of Canada
The Legislative Assembly of the Province of Canada was the lower house of the Parliament of the Province of Canada. The Province of Canada consisted of the former province of Lower Canada, then known as Canada East (now Quebec), and Upper Canada ...
approved a Canadian version of the Municipal Corporations Act, often referred to as the Baldwin Act in honour of its creator, Robert Baldwin. It delegated authority to the municipal governments so they could raise taxes and enact by-laws. It also established a hierarchy of types of municipal governments, starting at the top with cities and continued down past towns, villages and finally townships. Changes to the boundaries of these new governments could be made by petitioning the provincial Municipal Board or by requesting a change through the legislature.
By the early 20th century, Canada was deeply involved in a period of municipal reform. An attempt to distinguish municipal government from the provincial legislature occurred, and the municipal governments were compared with a board of directors
A board of directors is a governing body that supervises the activities of a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government agency.
The powers, duties, and responsibilities of a board of directors are determined by government regulatio ...
– this form of government was not for advancing a certain political party's view, it was for sitting down and running it 'like a business'. As such, the idea that a larger municipality should have more councillors was the same as having a large board of directors for a larger company, i.e., not functionally possible.
Between the 1920s and the 1960s, the municipalities received increased funding from their provincial government parents. This was partly due to the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, but further discussion about reform reared its head in the 1970s. In many cities, the system of having a few very large wards encompassing many different walks of life was replaced with one ward for every area with different demographics; this was to ensure that councillors would not have conflicting interests between the well-off and those not so. The arguments over municipal government reform continue, seen in the recent '' City of Toronto Act'' 1997 dispute.
See also
*Government of Canada
The Government of Canada (), formally His Majesty's Government (), is the body responsible for the federation, federal administration of Canada. The term ''Government of Canada'' refers specifically to the executive, which includes Minister of t ...
* History of cities in Canada
* List of governments in Canada by annual expenditures
* List of municipalities in Canada
Canada has a total of 5,162 municipality, municipalities among its Provinces and territories of Canada, 10 provinces and 3 territories that are subject to some form of local government in Canada, local government.
Matrix of municipalities
Li ...
** List of cities in Canada
** List of towns in Canada
* Provinces and territories of Canada
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Constitution of Canada, Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North Amer ...
References
Further reading
* * * * ;Historical *External links
Local Government in Canada: Organization & Basic Institutions , Mapleleafweb.com
{{North America topic, Local government in