Laos–Thailand Border on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
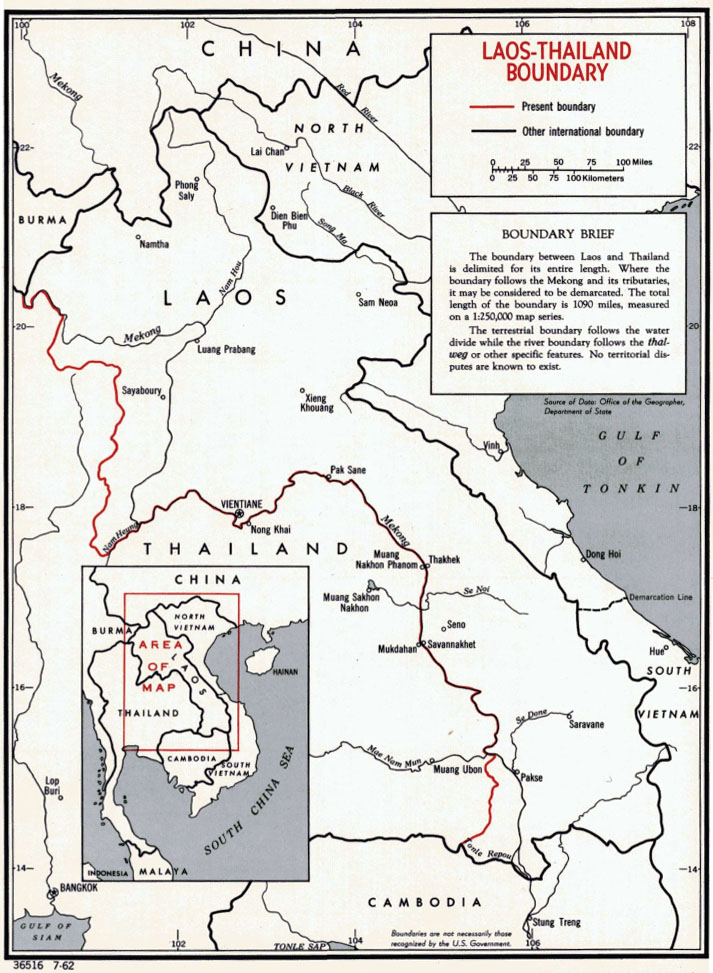 The Laos–Thailand border is the international border between the territory of
The Laos–Thailand border is the international border between the territory of
 The border starts in the north at the tripoint with Myanmar at the confluence of the Kok and
The border starts in the north at the tripoint with Myanmar at the confluence of the Kok and
 From the 1860s,
From the 1860s,
''Laos: a country study''
(Andrea Matles Savada, ed).
 The Laos–Thailand border is the international border between the territory of
The Laos–Thailand border is the international border between the territory of Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
and Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
. The border is 1,845 km (1,146 mi) in length, over half of which follows the Mekong River
The Mekong or Mekong River ( , ) is a transboundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's List of rivers by length, twelfth-longest river and List of longest rivers of Asia, the third-longest in Asia with an estimated l ...
, and runs from the tripoint
A triple border, tripoint, trijunction, triple point, or tri-border area is a geography, geographical point at which the boundaries of three countries or Administrative division, subnational entities meet. There are 175 international tripoints ...
with Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
in the north to tripoint with Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
in the south.
Description
 The border starts in the north at the tripoint with Myanmar at the confluence of the Kok and
The border starts in the north at the tripoint with Myanmar at the confluence of the Kok and Mekong river
The Mekong or Mekong River ( , ) is a transboundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's List of rivers by length, twelfth-longest river and List of longest rivers of Asia, the third-longest in Asia with an estimated l ...
s, following the latter towards the south-east. It then leaves the river and proceeds overland in a broadly southwards direction over various hill ridges, down to the Hueang River. It then follows this river to the north-east up to the confluence with the Mekong, from where it follows the Mekong for the majority of the border's length. Just north-west of Pakse
Pakse (or ''Pakxe''; French: ''Paksé''; Laotian: ປາກເຊ 'mouth of the river') is the capital and most populous city of the southern Laotian province of Champasak. Located at the confluence of the Xe Don and Mekong Rivers, the distri ...
the border leaves the Mekong and then follows the ridge of the Dângrêk Mountains
The Dângrêk Mountains (; , ; , , ), also the Dângrêk Range, is a mountain range forming a natural border between Cambodia and Thailand. Anlong Veng became the final headquarters of the Khmer Rouge of Democratic Kampuchea and Pol Pot ...
south the tripoint with Cambodia.
History
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
began establishing a presence in the region, initially in modern Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
and Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
, and the colony of French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China), officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1941 as the Indochinese Federation, was a group of French dependent territories in Southeast Asia from 1887 to 1954. It was initial ...
was created in 1887. The Lao kingdoms were at this point tributary states of the Kingdom of Siam (the old name for Thailand), however all areas east of the Mekong were annexed to French Indochina in 1893 following the Franco-Siamese crisis
The Franco-Siamese crisis of 1893, known in Thailand as the Incident of Rattanakosin Era 112 (,
, ) was a conflict between the French Third Republic and the Kingdom of Siam. Auguste Pavie, French vice-consul in Luang Prabang in 1886, was the c ...
. In 1902, Siam
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
was forced to cede areas west of the Mekong to France, encompassing the modern province of Sainyabuli
Sainyabuli, (; alternatively spelled ''Sayaboury'', ''Xaignabouli'', ''Xayaburi'', or ''Xayaboury'') is the capital of Sainyabuli Province, Laos. It lies on Route 4 which along with Route 13 connects it to Luang Prabang, roughly 80 kilometres ...
and the western half of Champasak Province
Champasak (or Champassak, Champasack – Laotian language, Lao: ຈຳປາສັກ ) is a province in southwestern Laos, near the borders with Thailand and Cambodia. It is 1 of the 3 principalities that succeeded the Laos, Lao kingdom of Lan ...
. More land was ceded in another treaty in 1904, and again in 1907. A minor treaty in 1926 cleared up the outstanding issue of sovereignty over islets in the Mekong. Following Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
’s invasion
An invasion is a Offensive (military), military offensive of combatants of one geopolitics, geopolitical Legal entity, entity, usually in large numbers, entering territory (country subdivision), territory controlled by another similar entity, ...
of French Indochina in 1940, the ceded areas west of the Mekong and south-western Laos were returned to Thailand after it was occupied by Vichy France
Vichy France (; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was a French rump state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II, established as a result of the French capitulation after the Battle of France, ...
, however this arrangement was annulled following Japan's defeat and the pre-war border reinstated.
Laos obtained a partial independence from France in 1949, gaining complete independence in 1953, with the boundary then becoming one between two sovereign states. Thailand occasionally made claims on the territories ceded to Laos during the French colonial era, with tensions rising following the victory of the Communist Pathet Lao
The Pathet Lao (), officially the Lao People's Liberation Army, was a communist political movement and political organization, organization in Laos, formed in the mid-20th century. The group ultimately gained control over the entire country of ...
in the Laotian Civil War
The Laotian Civil War was waged between the Communist Pathet Lao and the Royal Lao Government from 23 May 1959 to 2 December 1975. The Kingdom of Laos was a covert Theatre (warfare), theater during the Vietnam War with both sides receiving heavy ...
in 1975, supported by Chairman Mao
Mao Zedong pronounced ; traditionally Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Mao Tse-tung. (26December 18939September 1976) was a Chinese politician, revolutionary, and political theorist who founded the People's Republic of China (PRC) in ...
and the People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the military of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the People's Republic of China (PRC). It consists of four Military branch, services—People's Liberation Army Ground Force, Ground Force, People's ...
as part of Maoist
Maoism, officially Mao Zedong Thought, is a variety of Marxism–Leninism that Mao Zedong developed while trying to realize a socialist revolution in the agricultural, pre-industrial society of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic o ...
government backing against not just the French, but the American imperialism. Friendship treaties were signed in 1976 and 1979 in attempt to calm tensions, with both sides recognising the territorial integrity of the other.Brown, MacAlister, and Joseph J. Zasloff. "Relations with Thailand"''Laos: a country study''
(Andrea Matles Savada, ed).
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., serving as the library and research service for the United States Congress and the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It also administers Copyright law o ...
Federal Research Division
The Federal Research Division (FRD) is the research and analysis unit of the United States Library of Congress.
The Federal Research Division provides directed research and analysis on domestic and international subjects to agencies of the Unite ...
(July 1994) However fighting broke out in 1984 over disputed villages adjacent to the frontier in Sainyabuli Province/ Uttaradit Province, and again in 1987–88 over a nearby area. A joint committee was established in 1991 which aimed to resolved the dispute peacefully, however discussions dragged on throughout the decade. The First Thai–Lao Friendship Bridge
The First Thai–Lao Friendship Bridge is a bridge over the Mekong, connecting Nong Khai Province and the city of Nong Khai in Thailand with Vientiane Prefecture in Laos. The Lao capital city Vientiane is approximately from the bridge.
The br ...
was opened on 4 April 1994. A joint boundary commission was established in 1997, however its work was suspended in 1998 following the Asian financial crisis
The 1997 Asian financial crisis gripped much of East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltd ...
. As of 2018 border demarcation is still ongoing.
Border crossings
, there were 20 permanent border crossings and 29 checkpoints forborder trade
Border trade, in general, refers to the flow of goods and services across the border between different jurisdictions. In this sense, border trade is a part of the normal trade that flows through the ordinary export/import legal and logistical fra ...
.
Permanent border crossings
Checkpoints for border trade
These border crossings are open for cross-border local trade only. There are 29 checkpoints for border trade officially recognized by the Ministry of Interior, located in provinces. Entering the opposite country beyond these checkpoints and their associated markets is illegal.See also
*Laos–Thailand relations
Laos and Thailand have had bilateral relations since the time of their precursor Lan Xang and Ayutthaya kingdoms in the 15th century. The two countries share a border and express linguistic and cultural similarities. The Lao kingdom of Lan Xang in ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Laos-Thailand borderborder
Borders are generally defined as geography, geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by polity, political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other administrative divisio ...
Borders of Thailand
Borders of Laos
International borders