Khurasan Road From Al-Rayy To Naysabur on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Greater Khorāsān,Dabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 or Khorāsān ( pal, Xwarāsān; fa, خراسان ), is a historical eastern region in the
Humbach, Helmut, and Djelani Davari, "Nāmé Xorāsān"
, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz; Persian translation by Djelani Davari, published in Iranian Languages Studies Website. MacKenzie, D. (1971). ''A Concise Pahlavi Dictionary'' (p. 95). London: Oxford University Press. The Persian word ''Khāvar-zamīn'' ( fa, خاور زمین), meaning "the eastern land", has also been used as an equivalent term
The name was first given to the eastern province of
 By the late Middle Ages, the term lost its administrative significance, in the west only being loosely applied among the Turko-Persian dynasties of modern Iran to all its territories that lay east and north-east of the
By the late Middle Ages, the term lost its administrative significance, in the west only being loosely applied among the Turko-Persian dynasties of modern Iran to all its territories that lay east and north-east of the 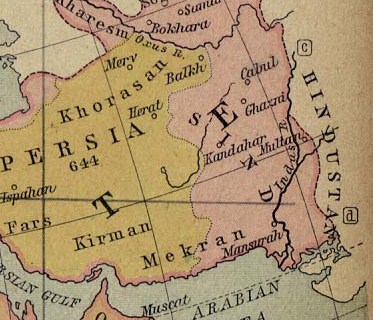

 Khorasan in the east saw some conflict with the Hephthalites who became the new rulers in the area but the borders remained stable. Being the eastern parts of the Sassanids and further away from
Khorasan in the east saw some conflict with the Hephthalites who became the new rulers in the area but the borders remained stable. Being the eastern parts of the Sassanids and further away from
vol. 1A, p. 102. Eds. Peter M. Holt, Ann K.S. Lambton and Bernard Lewis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995.
 Between the early 16th and early 18th centuries, parts of Khorasan were contested between the
Between the early 16th and early 18th centuries, parts of Khorasan were contested between the
Iranian Plateau
The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature in Western Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. It comprises part of the Eurasian Plate and is wedged between the Arabian Plate and the Indian Plate; situated between the Zagros ...
between Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. The name ''Khorāsān'' is Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and means "where the sun arrives from" or "the Eastern Province".Sykes, M. (1914). "Khorasan: The Eastern Province of Persia". ''Journal of the Royal Society of Arts'', 62(3196), 279-286.A compound of ''khwar'' (meaning "sun") and ''āsān'' (from ''āyān'', literally meaning "to come" or "coming" or "about to come"). Thus the name ''Khorasan'' (or ''Khorāyān'' ) means "sunrise", viz. " Orient, East"Humbach, Helmut, and Djelani Davari, "Nāmé Xorāsān"
, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz; Persian translation by Djelani Davari, published in Iranian Languages Studies Website. MacKenzie, D. (1971). ''A Concise Pahlavi Dictionary'' (p. 95). London: Oxford University Press. The Persian word ''Khāvar-zamīn'' ( fa, خاور زمین), meaning "the eastern land", has also been used as an equivalent term
The name was first given to the eastern province of
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
during the Sasanian Empire and was used from the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
in distinction to neighbouring Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
. ''Greater Khorasan'' is today sometimes used to distinguish the larger historical region from the former Khorasan Province of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(1906–2004), which roughly encompassed the western half of the historical Greater Khorasan.
Khorasan comprised the present territories of northeastern Iran, parts of Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
and southern parts of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. The province was often subdivided into four quarters, such that Nishapur (present-day Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
), Marv (present-day Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
), Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
and Balkh (present-day Afghanistan) were the centers, respectively, of the westernmost, northernmost, central, and easternmost quarters.Minorsky, V. (1938). "Geographical Factors in Persian Art". ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental Studies'', University of London, 9(3), 621-652. In a strict sense of the term, Khorasan stretched as far as the Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
(Oxus) river. However, the name has often been used in a loose sense to include a wider region that included most of Transoxiana (encompassing Bukhara and Samarqand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top: Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zin ...
in present-day Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
), extended westward to the Caspian coast and to the Dasht-e Kavir
Dasht-e Kavir ( fa, دشت كوير, lit=Low Plains in classical Persian, from ''khwar'' (low), and ''dasht'' (plain, flatland)), also known as Kavir-e Namak () and the Great Salt Desert, is a large desert lying in the middle of the Iranian Plat ...
(Great Salt Desert), southward to Sistan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan ( ...
, and eastward to the Pamir Mountains.
Khorasan was first established as an administrative division in the 6th century (approximately after 520) by the Sasanians
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
, during the reign of Kavad I
Kavad I ( pal, 𐭪𐭥𐭠𐭲 ; 473 – 13 September 531) was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 488 to 531, with a two or three-year interruption. A son of Peroz I (), he was crowned by the nobles to replace his deposed and unpopular un ...
() or Khosrow I (), which comprised the eastern and northeastern part of the empire. Early Islamic usage often regarded everywhere east of Jibal
Jibāl ( ar, جبال), also al-Jabal ( ar, الجبل), was the name given by the Arabs to a region and province located in western Iran, under the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates.
Its name means "the Mountains", being the plural of ''jabal'' (" ...
or what was subsequently termed Iraq Ajami (Persian Iraq), as being included in a vast and loosely-defined region of Khorasan, which might even extend to the Indus Valley and the Pamir Mountains. The boundary between these two was the region surrounding the cities of Gurgan
Gorgan ( fa, گرگان ; also romanized as ''Gorgān'', ''Gurgān'', and ''Gurgan''), formerly Esterabad ( ; also romanized as ''Astarābād'', ''Asterabad'', and ''Esterābād''), is the capital city of Golestan Province, Iran. It lies appro ...
and Qumis. In particular, the Ghaznavids, Seljuqs
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
and Timurids
The Timurid Empire ( chg, , fa, ), self-designated as Gurkani ( Chagatai: کورگن, ''Küregen''; fa, , ''Gūrkāniyān''), was a PersianateB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition, 2006 Turco-Mongol empire ...
divided their empires into Iraqi and Khorasani regions. Khorasan is believed to have been bounded in the southwest by desert and the town of Tabas
Tabas ( fa, طبس, also Romanized as Ṭabas), formerly known as Golshan, is the capital city of Tabas County in South Khorasan Province of Iran. At the 2011 census, its population was 35,150, in 9,903 families.
Tabas is located in central Iran ...
, known as "the Gate of Khorasan", from which it extended eastward to the mountains of central Afghanistan. Sources from the 10th century onwards refer to areas in the south of the Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
as the Khorasan Marches, forming a frontier region between Khorasan and Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( , from '' Hindū'' and ''-stān''), also sometimes spelt as Hindōstān ( ''Indo-land''), along with its shortened form ''Hind'' (), is the Persian-language name for the Indian subcontinent that later became commonly used by ...
.
Geography
First established in the 6th century as one of four administrative (military) divisions by the Sasanian Empire, the scope of the region has varied considerably during its nearly 1,500-year history. Initially, the Khorasan division of the Sasanian Empire covered the northeastern military gains of the empire, at its height including cities such as Nishapur,Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
, Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
, Faryab
Faryab (Dari: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, which is located in the north of the country bordering neighboring Turkmenistan. It has a population of about 1,109,223, which is multi-ethnic and mostly a tribal society. The pr ...
, Taloqan
Taloqan ( Persian, also transcribed Taleqan or Taluqan) is the capital of Takhar Province, in northeastern Afghanistan. It is located in the Taluqan District. The population was estimated as 196,400 in 2006.
In 2021, the Taliban gained contro ...
, Balkh, Bukhara, Badghis
Bādghīs ( Dari: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northwest of the country, on the border with Turkmenistan. It is considered to be one of the country's most underdeveloped provinces, with the highest povert ...
, Abiward, Gharjistan, Tus
Tus or TUS may refer to:
* Tus (biology), a protein that binds to terminator sequences
* Thales Underwater Systems, an international defence contractor
* Tuscarora language, an Iroquoian language, ISO 639-3 code
Education
* Technological Univ ...
and Sarakhs
Sarakhs ( fa, سرخس, Saraxs, also Romanized as Serakhs) is a city in Sarakhs County, Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran. Sarakhs was once a stopping point along the Silk Road, and in its 11th century heyday had many libraries. Much of the origina ...
.
With the rise of the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
, the designation was inherited and likewise stretched as far as their military gains in the east, starting off with the military installations at Nishapur and Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
, slowly expanding eastwards into Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan c ...
and Sogdia. Under the Caliphs
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
, Khorasan was the name of one of the three political zones under their dominion (the other two being ''Eraq-e Arab'' "Arabic Iraq" and ''Eraq-e Ajam'' "Non-Arabic Iraq or Persian Iraq"). Under the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
and Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
caliphates, Khorasan was divided into four major sections or quarters (''rub′''), each section based on a single major city: Nishapur, Merv, Herat and Balkh. By the 10th century, Ibn Khordadbeh
Abu'l-Qasim Ubaydallah ibn Abdallah ibn Khordadbeh ( ar, ابوالقاسم عبیدالله ابن خرداذبه; 820/825–913), commonly known as Ibn Khordadbeh (also spelled Ibn Khurradadhbih; ), was a high-ranking Persian bureaucrat and ...
and the Hudud al-'Alam mentions what roughly encompasses the previous regions of Abarshahr
Abarshahr (Persian:اَبَرشهر) or Nishapur (Persian:نیشاپور) was a Sasanian satrapy (province) in Late Antiquity, that lay within the kust of Khorasan. The province bordered Media in the west, Hyrcania in the north west, Margian ...
, Tokharistan and Sogdia as ''Khwarasan'' proper. They further report the southern part of the Hindu Kush, i.e. the regions of Sistan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan ( ...
, Rukhkhudh, Zabulistan
Zabulistan ( fa, زابلستان ''Zābulistān''/''Zābolistān''/''Zāwulistān'' or simply ''Zābul'', ps, زابل ''Zābəl''), was a historical region in southern Afghanistan roughly corresponding to the modern provinces of Zabul and ...
and Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
etc. to make up the ''Khorasan'' ''marches'', a frontier region between Khorasan and Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( , from '' Hindū'' and ''-stān''), also sometimes spelt as Hindōstān ( ''Indo-land''), along with its shortened form ''Hind'' (), is the Persian-language name for the Indian subcontinent that later became commonly used by ...
. By the late Middle Ages, the term lost its administrative significance, in the west only being loosely applied among the Turko-Persian dynasties of modern Iran to all its territories that lay east and north-east of the
By the late Middle Ages, the term lost its administrative significance, in the west only being loosely applied among the Turko-Persian dynasties of modern Iran to all its territories that lay east and north-east of the Dasht-e Kavir
Dasht-e Kavir ( fa, دشت كوير, lit=Low Plains in classical Persian, from ''khwar'' (low), and ''dasht'' (plain, flatland)), also known as Kavir-e Namak () and the Great Salt Desert, is a large desert lying in the middle of the Iranian Plat ...
desert. It was therefore subjected to constant change, as the size of their empires changed. In the east, ''Khwarasan'' likewise became a term associated with the great urban centers of Central Asia. It is mentioned in the Memoirs of Babur that:
In modern times, the term has been source of great nostalgia and nationalism, especially amongst the Tajiks
Tajiks ( fa, تاجيک، تاجک, ''Tājīk, Tājek''; tg, Тоҷик) are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest ethnicity in Taj ...
of Central Asia. Many Tajiks regard Khorasan as an integral part of their national identity, which has preserved an interest in the term, including its meaning and cultural significance, both in common discussion and academia, despite its falling out of political use in the region. According to Ghulam Mohammad Ghobar, Afghanistan's current Persian-speaking territories formed the major portion of Khorasān, Ghubar, Mir Ghulam Mohammad (1937). ''Khorasan'', Kabul Printing House. Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, Afghanistan. as two of the four main capitals of Khorasān (Herat and Balkh) are now located in Afghanistan. Ghobar uses the terms ''"Proper Khorasan"'' and "''Improper Khorasan"'' in his book to distinguish between the usage of Khorasān in its strict sense and its usage in a loose sense. According to him, Proper Khorasan contained regions lying between Balkh in the east, Merv in the north, Sistan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan ( ...
in the south, Nishapur in the west and Herat, known as the ''Pearl of Khorasan'', in the center. Improper Khorasan's boundaries extended to as far as Hazarajat
Hazaristan ( fa, هزارستان, Hazāristān), or Hazarajat ( fa, هزارهجات, Hazārajāt) is a mostly mountainous region in the central highlands of Afghanistan, among the Koh-i-Baba mountains in the western extremities of the ...
and Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
in the east, Baluchistan in the south, Transoxiana and Khwarezm in the north, and Damghan
Damghan ( fa, دامغان, translit=Dāmghān) is the capital of Damghan County, Semnan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 57,331, in 15,849 families. It is situated east of Tehran on the high-road to Mashad, at an elevat ...
and Gorgan
Gorgan ( fa, گرگان ; also romanized as ''Gorgān'', ''Gurgān'', and ''Gurgan''), formerly Esterabad ( ; also romanized as ''Astarābād'', ''Asterabad'', and ''Esterābād''), is the capital city of Golestan Province, Iran. It lies appro ...
in the west.
History

Ancient era
Before the region fell toAlexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in 330 BC, it was part of the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Achaemenid Empire and prior to that it was occupied by the Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
. The land that became known as Khorasan in geography of Eratosthenes was recognized as Ariana
Ariana was a general geographical term used by some Greek and Roman authors of the ancient period for a district of wide extent between Central Asia and the Indus River, comprising the eastern provinces of the Achaemenid Empire that covered the ...
by Greeks at that time, which made up Greater Iran or the land where Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
was the dominant religion. The southeastern region of Khorasan fell to the Kushan Empire in the 1st century AD. The Kushan rulers built a capital in modern-day Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
at Bagram
Bagram (; Pashto/ fa, بگرام) is a town and seat in Bagram District in Parwan Province of Afghanistan, about 60 kilometers north of the capital Kabul. It is the site of an ancient city located at the junction of the Ghorband and Panjshir ...
and are believed to have built the famous Buddhas of Bamiyan
The Buddhas of Bamiyan (or Bamyan) were two 6th-century monumental statues carved into the side of a cliff in the Bamyan valley of Hazarajat region in central Afghanistan, northwest of Kabul at an elevation of . Carbon dating of the structural ...
. Numerous Buddhist temples
A Buddhist temple or Buddhist monastery is the place of worship for Buddhists, the followers of Buddhism. They include the structures called vihara, chaitya, stupa, wat and pagoda in different regions and languages. Temples in Buddhism represen ...
and buried cities have been found in Afghanistan. However, the region of Khorasan remained predominantly Zoroastrian but there were also Manichaeists, sun worshippers, Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
, Pagans, Shamanists, Buddhists, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
and others. One of the three great fire-temples of the Sassanids "Azar-burzin Mehr" is situated near Sabzevar
Sabzevar ( fa, سبزوار ), previously known as Beyhagh (also spelled "Beihagh"; fa, بيهق), is a city and capital of Sabzevar County, in Razavi Khorasan Province, approximately west of the provincial capital Mashhad, in northeastern ...
in Iran. The boundary of the region began changing until the Kushans and Sassanids
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
merged to form the Kushano-Sassanian civilization.
During the Sasanian era, likely in the reign of Khusrow I, Persia was divided into four regions (known as ''kust'' Middle Persian), Khwārvarān in the west, apāxtar in the north, nīmrūz in the south and Khorasan in the east. Since the Sasanian territories were more or less remained stable up to Islamic conquests, it can be concluded that Sasanian Khorasan was bordered to the south by Sistan and Kerman, to the west by the central deserts of modern Iran, and to the east by China and India.
In the Sasanian era, Khorasan was further divided into four smaller regions, and each region was ruled by a marzban
Marzbān, or Marzpān (Middle Persian transliteration: mrzwpn, derived from ''marz'' "border, boundary" and the suffix ''-pān'' "guardian"; Modern Persian: ''Marzbān'') were a class of margraves, warden of the marches, and by extension milita ...
. These four regions were Nishapur, Marv, Herat and Balkh.
 Khorasan in the east saw some conflict with the Hephthalites who became the new rulers in the area but the borders remained stable. Being the eastern parts of the Sassanids and further away from
Khorasan in the east saw some conflict with the Hephthalites who became the new rulers in the area but the borders remained stable. Being the eastern parts of the Sassanids and further away from Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
, Khorasan region was conquered after the remaining Persia. The last Sassanid king of Persia, Yazdgerd III
Yazdegerd III (also spelled Yazdgerd III and Yazdgird III; pal, 𐭩𐭦𐭣𐭪𐭥𐭲𐭩) was the last Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II.
Ascending the throne at the ...
, moved the throne to Khorasan following the Arab invasion in the western parts of the empire. After the assassination of the king, Khorasan was conquered by Arab Muslims in 647 AD. Like other provinces of Persia it became a province of the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
.
Medieval era
The first movement against the Arab conquest was led by Abu Muslim Khorasani between 747 and 750. Originally from Isfahan, scholars believe Abu Muslim was probably Persian. It's possible he may have been born a slave. According to the Ancient Persian historianAl-Shahrastani
Tāj al-Dīn Abū al-Fath Muhammad ibn `Abd al-Karīm ash-Shahrastānī ( ar, تاج الدين أبو الفتح محمد بن عبد الكريم الشهرستاني; 1086–1153 CE), also known as Muhammad al-Shahrastānī, was an influenti ...
, he was a Kaysanite. This revolutionary Shi'a movement rejected the three Caliphs that had preceded Ali
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam ...
.
Abu Muslim helped the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
s come to power but was later killed by Al-Mansur, an Abbasid Caliph. The first kingdom independent from Arab rule was established in Khorasan by Tahir Phoshanji in 821, but it seems that it was more a matter of political and territorial gain. Tahir had helped the Caliph subdue other nationalistic movements in other parts of Persia such as Maziar's movement in Tabaristan
Tabaristan or Tabarestan ( fa, طبرستان, Ṭabarestān, or mzn, تبرستون, Tabarestun, ultimately from Middle Persian: , ''Tapur(i)stān''), was the name applied to a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. ...
.
Other major independent dynasties who ruled over Khorasan were the Saffarids
The Saffarid dynasty ( fa, صفاریان, safaryan) was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1003. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emer ...
from Zaranj
Zaranj or Zarang ( Persian/Pashto/ bal, زرنج) is a city in southwestern Afghanistan, near the border with Iran, which has a population of 160,902 people as of 2015. It is the capital of Nimruz Province and is linked by highways with Lashkarga ...
(861–1003), Samanids People
Samanid
Samanid
Samanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan orig ...
from Bukhara (875–999), Ghaznavids from Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, غزنی, ps, غزني), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, Αλεξάνδρεια Ωπιανή), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
(963–1167), Seljuqs
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
(1037–1194), Khwarezmids (1077–1231), Ghurids
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; fa, دودمان غوریان, translit=Dudmân-e Ğurīyân; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty and a clan of presumably eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the ...
(1149–1212), and Timurids
The Timurid Empire ( chg, , fa, ), self-designated as Gurkani ( Chagatai: کورگن, ''Küregen''; fa, , ''Gūrkāniyān''), was a PersianateB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition, 2006 Turco-Mongol empire ...
(1370–1506). In 1221, Genghis Khan's son Tolui
Tolui (also Toluy, Tului; , meaning: "the mirror"; – 1232) was a Mongol khan, the fourth son of Genghis Khan by his chief khatun, Börte. At his father's death in 1227, his ''ulus'', or territorial inheritance, was the Mongol homelands on t ...
oversaw the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
subjugation of Khorasan, carrying out the task "with a thoroughness from which that region has never recovered."
Rashidun era (651–661)
UnderCaliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
(), the Rashidun Caliphate seized nearly the entire Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
from the Sasanian Empire. However, the areas of Khorasan weren't conquered until during the caliphate of Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic prop ...
(). The Rashidun commanders Ahnaf ibn Qays and Abd Allah ibn Amir were assigned to lead the invasion of Khorasan.The Muslim Conquest of Persia By A.I. Akram. Ch:17 , In late 651, the Rashidun army defeated the combined forces of the Sasanian and the First Turkic Khaganate in the Battle of the Oxus River. The next year, Ibn Amir concluded a peace treaty with Kanadbak Kanadbak, also known as Kanara, was an Iranian nobleman, who was the ''kanarang'' during the reign of the Sasanian king Khosrau II (r. 590–628), and various other Sasanian monarchs, which includes Yazdegerd III (r. 632–651), the last Sasanian ki ...
, an Iranian nobleman and the ''kanarang
The ''kanārang'' ( fa, کنارنگ) was a unique title in the Sasanian military, given to the commander of the Sasanian Empire's northeasternmost frontier province, Abarshahr (encompassing the cities of Nishapur, Tus and Abiward). In Byzant ...
'' of Tus
Tus or TUS may refer to:
* Tus (biology), a protein that binds to terminator sequences
* Thales Underwater Systems, an international defence contractor
* Tuscarora language, an Iroquoian language, ISO 639-3 code
Education
* Technological Univ ...
. The Sasanian rebel Burzin Shah Burzin Shah, also known by the Arabicized form of Barzan Jah, was an Iranian nobleman from the House of Karen. A descendant of Sukhra, he was the governor of Nishapur during the reign of the Sasanian king Yazdegerd III (r. 632–651).
Biography
...
, of the Karen family, revolted against Ibn Amir, though the latter crushed the rebels in the Battle of Nishapur. The Rashidun troops marched towards Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
and seized the city, concluding another treaty with its governor.
Umayyad era (661–750)
After the invasion of Persia under Rashidun was completed in five years and almost all of the Persian territories came under Arab control, it also inevitable created new problems for the caliphate. Pockets of tribal resistance continued for centuries in the Afghan territories. During the 7th century, Arab armies made their way into the region of Afghanistan from Khorasan. A second problem was as a corollary to the Muslim conquest of Persia, the Muslims became neighbors of the city states ofTransoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
. Although Transoxiana was included in the loosely defined "Turkestan" region, only the ruling elite of Transoxiana was partially of Turkic origins whereas the local population was mostly a diverse mix of local Iranian populations. As the Arabs reached Transoxiana following the conquest of the Sassanid Persian Empire, local Iranian-Turkic and Arab armies clashed over the control of Transoxiana's Silk Road cities. In particular, the Turgesh under the leadership of Suluk, and Khazars under Barjik clashed with their Arab neighbours in order to control this economically important region. Two notable Umayyad generals, Qutayba ibn Muslim
Abū Ḥafṣ Qutayba ibn Abī Ṣāliḥ Muslim ibn ʿAmr al-Bāhilī ( ar, أبو حفص قتيبة بن أبي صالح مسلم بن عمرو الباهلي; 669–715/6) was an Arab commander of the Umayyad Caliphate who became governor of ...
and Nasr ibn Sayyar, were instrumental in the eventual conquest. In July 738, at the age of 74, Nasr was appointed as governor of Khorasan. Despite his age, he was widely respected both for his military record, his knowledge of the affairs of Khorasan and his abilities as a statesman. Julius Wellhausen wrote of him that "His age did not affect the freshness of his mind, as is testified not only by his deeds, but also by the verses in which he gave expression to his feelings till the very end of his life". However, in the climate of the times, his nomination owed more to his appropriate tribal affiliation than his personal qualities. The problems of Transoxiana could be resolved, although the Umayyad was on decline and being replaced by the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
.
In 724, immediately after the rise of Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik (r. 724–743) to the throne, Asad's brother Khalid al-Qasri
Khālid ibn ʿAbdallāh al-Qasrī (; died 743) was an Arab who served the Umayyad Caliphate as governor of Mecca in the 8th century and of Iraq from 724 until 738. The latter post, entailing as it did control over the entire eastern Caliphate, mad ...
was appointed to the important post of governor of Iraq, with responsibility over the entire Islamic East, which he held until 738. Khalid in turn named Asad as governor of Khorasan. The two brothers thus became, according to Patricia Crone
Patricia Crone (March 28, 1945July 11, 2015) was a Danish historian specializing in early Islamic history. Crone was a member of the Revisionist school of Islamic studies and questioned the historicity of the Islamic traditions about the beginni ...
, "among the most prominent men of the Marwanid period". Asad's arrival in Khorasan found the province in peril: his predecessor, Muslim ibn Sa'id al-Kilabi
Muslim ibn Sa'id ibn Aslam ibn Zur'ah ibn Amr ibn Khuwaylid al-Sa'iq al-Kilabi () was governor of Khurasan for the Umayyad Caliphate in 723–724. He is best known for his efforts to conciliate the native population of Transoxiana and for the major ...
, had just attempted a campaign against Ferghana and suffered a major defeat, the so-called "Day of Thirst
The "Day of Thirst" ( ar, ﻳﻮﻢ ﺍلعطش, Yawm al-aṭash) is the name traditionally given in Arabic historiography to a battle fought in 724 between the Turkic Türgesh Khaganate and the Umayyad Caliphate on the banks of the Syr Darya ri ...
", at the hands of the Turgesh Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
and the Soghdia
Sogdia ( Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Em ...
n principalities of Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
that had risen up against Muslim rule.
From the early days of the Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
, Arab armies were divided into regiments drawn from individual tribes or tribal confederations (''butun'' or ''‘asha‘ir''). Despite the fact that many of these groupings were recent creations, created for reasons of military efficiency rather than any common ancestry, they soon developed a strong and distinct identity. by the beginning of the Umayyad period, this system progressed to the formation of ever-larger super-groupings, culminating in the two super-groups: the northern Arab Mudaris or Qays
Qays ʿAylān ( ar, قيس عيلان), often referred to simply as Qays (''Kais'' or ''Ḳays'') were an Arab tribal confederation that branched from the Mudar group. The tribe does not appear to have functioned as a unit in the pre-Islamic e ...
is, and the south Arabs or "Yemenis" (''Yaman''), dominated by the Azd and Rabi'ah
Rabīʿa ibn Nizar ( ar, ربيعة بن نزار) is the patriarch of one of two main branches of the "North Arabian" (Adnanite) tribes, the other branch being founded by Mudhar.
Branches
According to the classical Arab genealogists, the foll ...
tribes. By the 8th century, this division had become firmly established across the Caliphate and was a source of constant internal instability, as the two groups formed in essence two rival political parties, jockeying for power and separated by a fierce hatred for each other. During Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik's reign, the Umayyad government appointed Mudaris as governors in Khorasan, except for Asad ibn Abdallah al-Qasri's tenure in 735–738. Nasr's appointment came four months after Asad's death. In the interim, the sources report variously that the province was run either by the Syrian general Ja'far ibn Hanzala al-Bahrani or by Asad's lieutenant Juday' al-Kirmani. At any rate, the sources agree that al-Kirmani stood at the time as the most prominent man in Khorasan and should have been the clear choice for governor. His Yemeni roots (he was the leader of the Azd in Khorasan), however, made him unpalatable to the Caliph.
Abbasid era (750–861)
Khorasan became the headquarters of theAbbasid Revolution
The Abbasid Revolution, also called the Movement of the Men of the Black Raiment, was the overthrow of the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE), the second of the four major Caliphates in early Islamic history, by the third, the Abbasid Caliphate ...
against the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
s. It was led by Abu Muslim, who himself belonged to Khorasan. This province was part of Iranian world that had been heavily colonised by Arab tribes following the Muslim conquest
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He esta ...
with the intent of replacing Umayyad dynasty which is proved to be successful under the sign of the Black Standard
The Black Banner or Black Standard ( ar, الراية السوداء, ar-rāyat as-sawdāʾ, also known as (, "banner of the eagle" or simply as , , "the banner") is one of the flags flown by the Islamic prophet Muhammad according to Muslim tr ...
.The Cambridge History of Islamvol. 1A, p. 102. Eds. Peter M. Holt, Ann K.S. Lambton and Bernard Lewis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995.
Modern era
 Between the early 16th and early 18th centuries, parts of Khorasan were contested between the
Between the early 16th and early 18th centuries, parts of Khorasan were contested between the Safavids
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
and the Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
. A part of the Khorasan region was conquered in 1722 by the Ghilji
The Ghiljī ( ps, غلجي, ; fa, خیلجی, Xelji) also spelled Khilji, Khalji, or Ghilzai or Ghilzay (), are one of the largest Pashtun tribes. Their traditional homeland is Ghazni and Qalati Ghilji in Afghanistan but they have also sett ...
Pashtuns from Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the c ...
and became part of the Hotaki dynasty
The Hotak dynasty ( ps, fa, ) was an Afghan monarchy founded by Ghilji Pashtuns that briefly ruled portions of Iran and Afghanistan during the 1720s. It was established in April 1709 by Mirwais Hotak, who led a successful revolution against t ...
from 1722 to 1729. Nader Shah recaptured Khorasan in 1729 and chose Mashhad as the capital of Persia. Following his assassination in 1747, the eastern parts of Khorasan, including Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
was annexed with the Durrani Empire. Mashhad area was under control of Nader Shah's grandson Shahrukh Afshar
Shahrokh Mirza ( fa, شاهرُخمیرزا; 1734–1796), better known by his dynastic title of Shahrokh Shah () was the Afsharid king (shah) of the western part of Khorasan (corresponding to the present-day Khorasan Province) from 1750 to 17 ...
until it was captured by the Qajar dynasty in 1796. In 1856, the Iranians, under the Qajar dynasty, briefly recaptured Herat; by the Treaty of Paris of 1857, signed between Iran and the British Empire to end the Anglo-Persian War
The Anglo-Persian War or the Anglo-Iranian War () lasted between 1 November 1856 and 4 April 1857, and was fought between the United Kingdom and Iran, which was ruled by the Qajar dynasty. The war had the British oppose an attempt by Iran to ...
, the Iranian troops withdrew from Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
. Later, in 1881, Iran relinquished its claims to a part of the northern areas of Khorasan to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, principally comprising Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
, by the Treaty of Akhal (also known as the ''Treaty of Akhal-Khorasan'').
Cultural importance
Khorasan has had a great cultural importance among other regions in Greater Iran. The literaryNew Persian
New Persian ( fa, فارسی نو), also known as Modern Persian () and Dari (), is the current stage of the Persian language spoken since the 8th to 9th centuries until now in Greater Iran and surroundings. It is conventionally divided into thr ...
language developed in Khorasan and Transoxiana and gradually supplanted the Parthian language. The New Persian literature
Persian literature ( fa, ادبیات فارسی, Adabiyâte fârsi, ) comprises oral compositions and written texts in the Persian language and is one of the world's oldest literatures. It spans over two-and-a-half millennia. Its sources h ...
arose and flourished in Khorasan and Transoxiana where the early Iranian dynasties such as Tahirids
The Tahirid dynasty ( fa, طاهریان, Tâheriyân, ) was a culturally Arabized Sunni Muslim dynasty of Persian dehqan origin, that ruled as governors of Khorasan from 821 to 873 as well as serving as military and security commanders in A ...
, Samanids People
Samanid
Samanid
Samanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan orig ...
, Saffirids and Ghaznavids (a Turco-Persian dynasty) were based. The early Persian poets such as Rudaki
Rudaki (also spelled Rodaki; fa, رودکی; 858 – 940/41) was a Persian poet, singer and musician, who served as a court poet under the Samanids. He is regarded as the first major poet to write in New Persian. Said to have composed more tha ...
, Shahid Balkhi, Abu al-Abbas Marwazi, Abu Hafas Sughdi, and others were from Khorasan. Moreover, Ferdowsi and Rumi were also from Khorasan.
Until the devastating Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
invasion of the 13th century, Khorasan remained the cultural capital of Persia. It has produced scientists such as Avicenna, Al-Farabi
Abu Nasr Muhammad Al-Farabi ( fa, ابونصر محمد فارابی), ( ar, أبو نصر محمد الفارابي), known in the West as Alpharabius; (c. 872 – between 14 December, 950 and 12 January, 951)PDF version was a renowned early Isl ...
, Al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
, Omar Khayyam
Ghiyāth al-Dīn Abū al-Fatḥ ʿUmar ibn Ibrāhīm Nīsābūrī (18 May 1048 – 4 December 1131), commonly known as Omar Khayyam ( fa, عمر خیّام), was a polymath, known for his contributions to mathematics, astronomy, philosophy, an ...
, Al-Khwarizmi
Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī ( ar, محمد بن موسى الخوارزمي, Muḥammad ibn Musā al-Khwārazmi; ), or al-Khwarizmi, was a Persian polymath from Khwarazm, who produced vastly influential works in mathematics, astronom ...
, Abu Ma'shar al-Balkhi
Abu Ma'shar al-Balkhi, Latinized as Albumasar (also ''Albusar'', ''Albuxar''; full name ''Abū Maʿshar Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿUmar al-Balkhī'' ;
, AH 171–272), was an early Persian Muslim astrologer, thought to be the greatest ast ...
(known as Albumasar or Albuxar in the west), Alfraganus, Abu Wafa, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Sharaf al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī
Sharaf al-Dīn al-Muẓaffar ibn Muḥammad ibn al-Muẓaffar al-Ṭūsī ( fa, شرفالدین مظفر بن محمد بن مظفر توسی; 1135 – 1213) was an Iranian mathematician and astronomer of the Islamic Golden Age (during the ...
, and many others who are widely well known for their significant contributions in various domains such as mathematics, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, medicine, physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
, geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
, and geology.Starr, S. Frederick, ''Lost Enlightenment. Central Asia's golden age from the Arab conquest to Tamerlane'', Princeton University Press (2013) Khorasan artisans contributed to the spread of technology and goods along the ancient trade routes have been traced to this ancient culture, including art objects, textiles and zoomorphic
The word ''zoomorphism'' derives from the Greek ζωον (''zōon''), meaning "animal", and μορφη (''morphē''), meaning "shape" or "form". In the context of art, zoomorphism could describe art that imagines humans as non-human animals. It c ...
metalworks. Decorative antecedents of the famous "singing bowls" of Asia may have been invented in ancient Khorasan.
In Islamic theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
, jurisprudence
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning a ...
and philosophy, and in Hadith collection, many of the greatest Islamic scholars came from Khorasan, namely Imam Bukhari
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve ...
, Imam Muslim
Abū al-Ḥusayn ‘Asākir ad-Dīn Muslim ibn al-Ḥajjāj ibn Muslim ibn Ward ibn Kawshādh al-Qushayrī an-Naysābūrī ( ar, أبو الحسين عساكر الدين مسلم بن الحجاج بن مسلم بن وَرْد بن كوشاذ ...
, Abu Dawood
Abū Dāwūd (Dā’ūd) Sulaymān ibn al-Ash‘ath ibn Isḥāq al-Azdī al-Sijistānī ( ar, أبو داود سليمان بن الأشعث الأزدي السجستاني), commonly known simply as Abū Dāwūd al-Sijistānī, was a scholar o ...
, Al-Tirmidhi
Abū ʿĪsā Muḥammad ibn ʿĪsā as-Sulamī aḍ-Ḍarīr al-Būghī at-Tirmidhī ( ar, أبو عيسى محمد بن عيسى السلمي الضرير البوغي الترمذي; fa, , ''Termezī''; 824 – 9 October 892 CE / 209 - 2 ...
, Al-Nasa'i
Al-Nasāʾī (214 – 303 AH; 829 – 915 CE), full name Abū ʿAbd al-Raḥmān Aḥmad ibn Shuʿayb ibn ʿAlī ibn Sīnān al-Nasāʾī, (variant: Abu Abdel-rahman Ahmed ibn Shua'ib ibn Ali ibn Sinan ibn Bahr ibn Dinar Al-Khurasani ...
, Al-Ghazali
Al-Ghazali ( – 19 December 1111; ), full name (), and known in Persian-speaking countries as Imam Muhammad-i Ghazali (Persian: امام محمد غزالی) or in Medieval Europe by the Latinized as Algazelus or Algazel, was a Persian poly ...
, Al-Juwayni
Dhia' ul-Dīn 'Abd al-Malik ibn Yūsuf al-Juwaynī al-Shafi'ī ( fa, امام الحرمین ضیاءالدین عبدالملک ابن یوسف جوینی شافعی, 17 February 102820 August 1085; 419–478 AH) was a Persian Sunni Shafi'i j ...
, Abu Mansur Maturidi, Fakhruddin al-Razi, and others. Shaykh Tusi
Shaykh Tusi ( fa, شیخ طوسی), full name ''Abu Jafar Muhammad Ibn Hassan Tusi'' ( ar, ابو جعفر محمد بن حسن طوسی), known as Shaykh al-Taʾifah ( ar, links=no, شيخ الطائفة) was a prominent Persian scholar of the ...
, a Shi'a scholar, the grandfather of Imam Abu Hanifa
Nuʿmān ibn Thābit ibn Zūṭā ibn Marzubān ( ar, نعمان بن ثابت بن زوطا بن مرزبان; –767), commonly known by his '' kunya'' Abū Ḥanīfa ( ar, أبو حنيفة), or reverently as Imam Abū Ḥanīfa by Sunni Musl ...
was from Khorasan and Al-Zamakhshari
Abu al-Qasim Mahmud ibn Umar al-Zamakhshari (; 1074 –1143) was a medieval Muslim scholar of Iranian peoples, Iranian descent. He travelled to Mecca, Makkah and settled there for five years and has been known since then as Jar Allah ‘God's Ne ...
, the famous Mutazilite scholar, also lived in Khorasan.
See also
*Ariana
Ariana was a general geographical term used by some Greek and Roman authors of the ancient period for a district of wide extent between Central Asia and the Indus River, comprising the eastern provinces of the Achaemenid Empire that covered the ...
* Bactria
* Dahistan
* Khwarazm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
* Khurasan Road
* Margiana
Margiana ( el, ''Margianḗ'', Old Persian: ''Marguš'', Middle Persian: ''Marv'') is a historical region centred on the oasis of Merv and was a minor satrapy within the Achaemenid satrapy of Bactria, and a province within its successors, the Se ...
* Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
* Sogdia
* Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan c ...
* Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
* Turkestan
Turkestan, also spelled Turkistan ( fa, ترکستان, Torkestân, lit=Land of the Turks), is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and Xinjiang.
Overview
Known as Turan to the Persians, western Turk ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * *Further reading
{{Authority control Khorasan Geography of Central Asia Geography of Western Asia Regions of Afghanistan Regions of Iran Regions of Tajikistan Regions of Turkmenistan Regions of Uzbekistan History of Khorasan History of Western Asia Historical regions of Afghanistan Historical regions of Iran Iranian Plateau History of Balkh Province History of Herat History of Nishapur Geographic history of Tajikistan History of Turkmenistan Geographic history of Uzbekistan *