KrakĂłw Army on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
KrakĂłw Army () was one of the

 Its main task was to delay advancing German troops and withdraw eastwards along the northern line of the
Its main task was to delay advancing German troops and withdraw eastwards along the northern line of the
Armie i samodzielne grupy operacyjne Wojska Polskiego 1939
Polish armies
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
* Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin ...
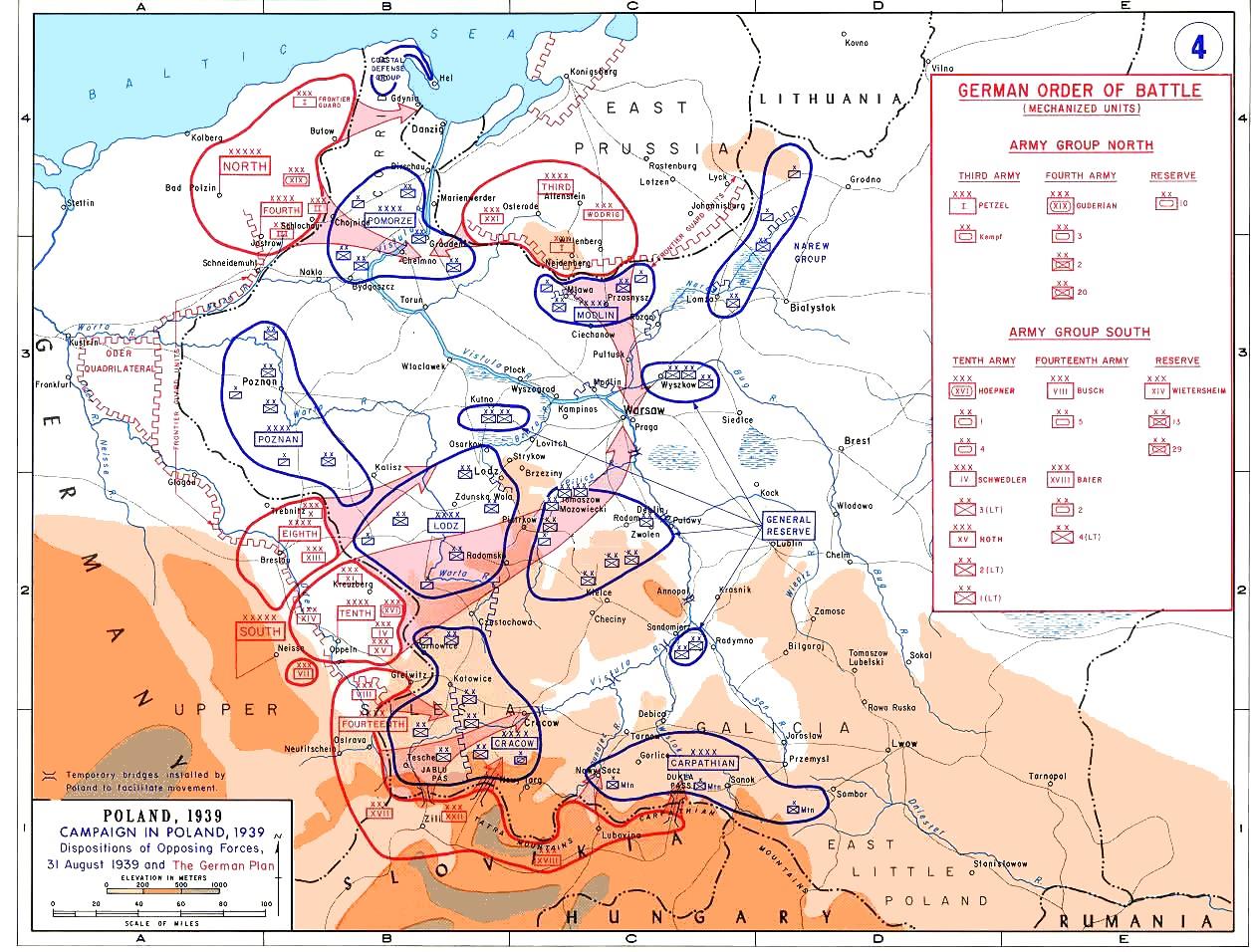
which took part in the Polish Defensive War of 1939. It was officially created on March 23, 1939 as the main pivot of Polish defence. It was commanded by Gen. Antoni Szylling. Originally, KrakĂłw Army was to be made of seven infantry divisions, two cavalry brigades and one mountain brigade. On September 1, 1939, General Szylling had the force which consisted of five infantry divisions, two cavalry brigades and one brigade of mountain infantry. Altogether, the army was made of 59 battalions, 29 squadrons, 352 cannons, 90 tanks, two armoured trains and 44 planes. These forces were not enough to halt German advance, especially in the area north of CzÄstochowa
CzÄstochowa ( , ) is a city in southern Poland on the Warta with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship. However, CzÄstochowa is historically part of Lesser Poland, not Si ...
, where KrakĂłw Army connected with ĆĂłdĆș Army. Main thrust of Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935â1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
panzer units was directed there, and this area was defended only by the Polish 7th I.D., which was destroyed in the early days of September 1939, opening the way towards central Poland.
Creation of KrakĂłw Army
On March 15, 1939, units of theWehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935â1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
entered Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
, and two days earlier at Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
, Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich-Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 â 16 October 1946) was a German Nazi politician and diplomat who served as Minister for Foreign Affairs (Germany), Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945. ...
in a conversation with Polish ambassador JĂłzef Lipski demanded definite answer to German demands of Free City of Danzig
The Free City of Danzig (; ) was a city-state under the protection and oversight of the League of Nations between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig (now GdaĆsk, Poland) and nearly 200 other small localities in the surrou ...
and a highway through the Polish Corridor. On March 23, a number of officers of the Polish Army was ordered to come to the General Inspector of the Armed Forces in Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
. Together with General Antoni Szylling, these officers (Colonel Jan Rzepecki, Major WĆadysĆaw Steblik, Major Kazimierz SzpÄ
drowski and Major Franciszek Chmura) were ordered to create staff of the newly created KrakĂłw Army. The army itself was created upon written order of Edward Rydz-ĆmigĆy
Marshal Edward ĆmigĆy-Rydz also called Edward Rydz-ĆmigĆy, (11 March 1886 â 2 December 1941) was a Polish people, Polish politician, statesman, Marshal of Poland and Commander-in-Chief of Poland's armed forces, as well as a painter and ...
, which was handed to General Szylling on the same day, together with more detailed demands. On March 25, staff officers of KrakĂłw Army arrived at KrakĂłw
, officially the Royal Capital City of KrakĂłw, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
, staying at the Jan III Sobieski barracks, where the 5th Military Police Unit was located. On the same day at noon, General Szylling met commanders of the divisions that came under his control, and on March 27, the officers took their oath.
Tasks


 Its main task was to delay advancing German troops and withdraw eastwards along the northern line of the
Its main task was to delay advancing German troops and withdraw eastwards along the northern line of the Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains ...
and defend the heavily industrialized Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
region, together with western counties of Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''MaĆopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is KrakĂłw. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
and the Carpathian foothills. Altogether, KrakĂłw Army defended southwestern border of Poland, from Krzepice
Krzepice is a Polish town near CzÄstochowa, in KĆobuck County, Silesian Voivodeship, in northwestern Lesser Poland. It is near the historic border of Lesser Poland and Silesia, which goes along the Liswarta river. A few kilometers to the nort ...
near CzÄstochowa
CzÄstochowa ( , ) is a city in southern Poland on the Warta with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship. However, CzÄstochowa is historically part of Lesser Poland, not Si ...
, to Czorsztyn
Czorsztyn (German: ''Schorstin'') is a village in Poland, in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Nowy Targ County. The village lies in Pieniny, the mountain range on the current Polish- Slovak border. It is famous for the ruins of a 14th-17th-century c ...
. In the area of CzÄstochowa, the 7th I.D. (General Janusz GÄ
siorowski) was placed, with its right wing supported by the KrakĂłw Cavalry Brigade KrakĂłw Cavalry Brigade (') was a unit of the Polish Army, created on April 1, 1937. Its headquarters were located in KrakĂłw, but some units were stationed in other places:
* 3rd Silesian Uhlan Regiment, in Tarnowskie GĂłry
* 8th Uhlan Regiment o ...
of General Zygmunt Piasecki. The remaining units were divided into two operational groups. ''Operational Group Silesia'' (under General Jan Jagmin Sadowski) was made of the 23rd I.D. (Colonel WĆadysĆaw Powierza), together with the 55th (reserve) I.D. (Colonel StanisĆaw KalabiĆski), and soldiers manning the Fortified Area of Silesia. ''Operational Group Bielsko'' (under General MieczysĆaw Boruta-Spiechowicz) was made of the 21st I.D. (General JĂłzef KustroĆ), and the 1st Brigade of Mountain Infantry (Colonel Janusz GaĆadyk). This group was located in the area of Ć»ywiec
Ć»ywiec () is a town on the River SoĆa in southern Poland with 31,194 inhabitants (2019). It is situated within the Silesian Voivodeship, near the Ć»ywiec Lake and Ć»ywiec Landscape Park, one of the eight protected areas in the voivodeship. H ...
, ChabĂłwka, and Bielsko-BiaĆa
Bielsko-BiaĆa (; ; , ; ) is a city in southern Poland, with a population of approximately 166,765 as of December 2022, making it the List of cities and towns in Poland#Largest cities and towns by population, 22nd largest city in Poland, and an a ...
. Furthermore, in the area of Pszczyna was the 6th I.D. (General Bernard Mond), and in the area of KrakĂłw
, officially the Royal Capital City of KrakĂłw, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
, the 10th Motorized Cavalry Brigade (Colonel StanisĆaw Maczek
Lieutenant General StanisĆaw WĆadysĆaw Maczek (; 31 March 1892 â 11 December 1994) was a Polish tank commander of World War II, whose division was instrumental in the Allied liberation of France, closing the Falaise pocket, resulting in the ...
).
KrakĂłw Army's tasks were as follows:
* to defend Upper Silesia,
* to protect the general direction towards the city of KrakĂłw from southwest,
* to defend the strategic rail line from DÄ
browa GĂłrnicza
DÄ
browa GĂłrnicza () is a city in ZagĆÄbie DÄ
browskie, southern Poland, near Katowice and Sosnowiec. It is located in eastern part of the Silesian Voivodeship, on the Czarna Przemsza and BiaĆa Przemsza rivers (tributaries of the Vistula Rive ...
ZÄ
bkowice to CzÄstochowa
CzÄstochowa ( , ) is a city in southern Poland on the Warta with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship. However, CzÄstochowa is historically part of Lesser Poland, not Si ...
,
* final line of defence was as follows: Fortified Area of Silesia - MikoĆĂłw
MikoĆĂłw (, ) is a town in Silesia, in southern Poland, near the city of Katowice. Outer town of the Metropolis GZM, a metropolis with a population of over 2 million, and is within a greater Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan area populated by abou ...
- Pszczyna - Bielsko-BiaĆa - Ć»ywiec.
Operational history
Battle of the Border
KrakĂłw Army fought against GermanArmy Group South
Army Group South () was the name of one of three German Army Groups during World War II.
It was first used in the 1939 September Campaign, along with Army Group North to invade Poland. In the invasion of Poland, Army Group South was led by Ge ...
, whose units crossed the border on September 1, 1939, at 4 a.m. In central part of the front, German 10th Army advanced, attacking in the sector from Tarnowskie GĂłry
Tarnowskie GĂłry (; ; ) is a city in Silesia, southern Poland, located in the Silesian Highlands near Katowice and seat city of Tarnowskie GĂłry County Located in the north of the Metropolis GZM, a megalopolis (city type), megalopolis, the great ...
to WieluĆ
WieluĆ () is a town in south-central Poland with 21,624 inhabitants (2021). The town is the seat of the Gmina WieluĆ and WieluĆ County, and is located within the ĆĂłdĆș Voivodeship. WieluĆ is a capital of the historical WieluĆ Land.
W ...
. North of the 10th Army was the 8th Army (advancing towards Sieradz
Sieradz (,) is a city on the Warta river in central Poland with 40,891 inhabitants (2021). It is the seat of the Sieradz County, situated in the ĆĂłdĆș Voivodeship. Sieradz is a capital of the historical Sieradz Land.
Sieradz is one of the olde ...
and ĆĂłdĆș
ĆĂłdĆș is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of ĆĂłdĆș Voivodeship, and is located south-west of Warsaw. ĆĂłdĆș has a population of 655,279, making it the country's List of cities and towns in Polan ...
), and in the south was and the 14th Army, advancing towards KrakĂłw
, officially the Royal Capital City of KrakĂłw, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
. On September 1, the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935â1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
failed to cause a breach Polish positions, but it was obvious that the Germans tried to bypass Fortified Area of Silesia, attacking both north and south of the fortifications. As early as the night of September 1/2, Polish situation became difficult, as the 7th I.D., operating near CzÄstochowa, found it hard to halt the advance of the panzers of the XVI Panzer Corps, which fought their way into central Poland. This division was located some 40 kilometers away from other Polish units; close to it was the Volhynian Cavalry Brigade, which itself was attacked by the Germans in the Battle of Mokra.
On September 2, German 1st Panzer Division bypassed CzÄstochowa north of the city, and supported by the Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ...
, managed to cross the Warta
The river Warta ( , ; ; ) rises in central Poland and meanders greatly through the Polish Plain in a north-westerly direction to flow into the Oder at Kostrzyn nad OdrÄ
on Poland's border with Germany. About long, it the second-longest riv ...
river. At the same time, KrakĂłw Cavalry Brigade KrakĂłw Cavalry Brigade (') was a unit of the Polish Army, created on April 1, 1937. Its headquarters were located in KrakĂłw, but some units were stationed in other places:
* 3rd Silesian Uhlan Regiment, in Tarnowskie GĂłry
* 8th Uhlan Regiment o ...
was attacked by the 2nd Light Division in the area of WoĆșniki. After heavy fighting, it withdrew towards Zawiercie
Zawiercie () () is a town in southern Poland located in the Silesian Voivodeship with 49,334 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in the KrakĂłw-CzÄstochowa Upland near the source of the Warta River. The town lies near the historical region of Sil ...
, which caused a breach in the defensive line, enabling the Germans both to bypass Polish fortifications in Upper Silesia, and to attack the 7th I.D. from the rear. As a result, the 7th I.D. was destroyed on Sept. 2, and its remaining units retreated to the forests near Koniecpol. This defeat enabled German XVI Panzer Corps to move towards Kielce
Kielce (; ) is a city in south-central Poland and the capital of the ĆwiÄtokrzyskie Voivodeship. In 2021, it had 192,468 inhabitants. The city is in the middle of the ĆwiÄtokrzyskie Mountains (Holy Cross Mountains), on the banks of the Silnic ...
without any problems. Since Polish Army did not have any reserve units east of CzÄstochowa, Edward ĆmigĆy-Rydz ordered a detachment of the PZL.23 KaraĆ bombers to attack the advancing panzers. The attack, however, did not result in a success, and the advance of the Wehrmacht continued.
In the south, the Wehrmacht attacked on Sept. 2 in two spots - MikoĆĂłw
MikoĆĂłw (, ) is a town in Silesia, in southern Poland, near the city of Katowice. Outer town of the Metropolis GZM, a metropolis with a population of over 2 million, and is within a greater Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan area populated by abou ...
/ Pszczyna, and Wysoka
Wysoka is a town in PiĆa County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Poland, with 2,736 inhabitants (2010).
History
The oldest known mention Wysoka comes from 1260, when it was granted by Duke BolesĆaw the Pious from the Piast dynasty to MikoĆaj ...
/ Rabka. Near Pszczyna, Polish 6th I.D. failed to halt the 5th Panzer Division, and in the morning of the same day, the 2nd Panzer Division
The 2nd Panzer Division (English: 2nd Tank Division) was an armoured division in the German Army, the Heer, during World War II.
Created as one of the original three German tank divisions in 1935, it was stationed in Austria after the Anschluss ...
was stopped in the Battle of JordanĂłw. At the same time, however, the Germans won the Battle of WÄgierska GĂłrka
The Battle of WÄgierska GĂłrka was a two-day-long defence of a Polish fortified area in south of Ć»ywiec Region (Lesser Poland) during the opening stages of the Invasion of Poland of 1939.
Although the Polish position was not completed and onl ...
. In the afternoon of September 2, the situation of KrakĂłw Army turned critical. German panzers attacked in large formations in the area of KoziegĆowy in the north, and in the area of JordanĂłw in the south. Furthermore, breach of the Polish lines near Pszczyna caused another problem, as it gave the Germans an opportunity to bypass the Upper Silesian fortifications. As a result, General Szylling, in a conversation with Marshall ĆmigĆy-Rydz stated that it was necessary to withdraw from Upper Silesia and Trans-Olza
Trans-Olza (, ; , ''ZĂĄolĆĄĂ''; ), also known as Trans-Olza Silesia (), is a territory in the Czech Republic which was disputed between Poland and Czechoslovakia during the Interwar Period. Its name comes from the Olza River.
The history of ...
, and to retreat towards KrakĂłw. The Marshall gave tentative permission at 16:00 on Sept. 2, urging Szylling to press his soldiers to do their best. In the evening of September 2, the situation deteriorated further, as KrakĂłw Cavalry Brigade was pushed behind the Warta, and the distance to the retreating remnants of the 7th I.D. was some 30 kilometres. German 2nd Light Division entered this gap, advancing towards Ć»arki. The Luftwaffe bombed Polish towns and rail junctions, General Szylling was unable to locate the positions of his divisions, and to get in touch with their commandants. At 18:00, Szylling once again talked with ĆmigĆy-Rydz, and 30 minutes later, the Marshall agreed to the withdrawal of KrakĂłw Army to the line marked by the Nida and Dunajec
The Dunajec (; Goral dialects: ''DĂłnajec''; ) is a river running through northeastern Slovakia and southern Poland. It is also regarded as the main river of the Goral Lands. It is a right tributary of the Vistula River. It begins in Nowy Targ at ...
rivers. It was a difficult decision, as it meant that the pre-war Polish defensive plan (see Plan West) was abandoned. ĆmigĆy-Rydz, however, hoped that the retreat would save KrakĂłw Army from complete destruction.
The Retreat
In the evening of Saturday, Sept. 2, the order to retreat reached Polish units. KrakĂłw Cavalry Brigade, together with the 7th I.D. was to move towards JÄdrzejĂłw, halting the advance of the 2nd Light Division. 22nd Mountain I.D. was to withdraw towardsOlkusz
Olkusz ( ''Elkish'') is a town in southern Poland with 36,607 inhabitants (2014). Situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Katowice Voivodeship (1975â1998), it is the capital of Olkusz County. Olkusz is known for its ...
, and to support ''Operational Group Silesia'' (renamed into ''Operational Group Jagmin''), which itself was to retreat behind the Przemsza
The Przemsza () is a river in the south of Poland, and a tributary of the Vistula. According to one view, it originates at the confluence of the Black () Przemsza and White (''BiaĆa'') Przemsza, between the towns of MysĆowice and Jaworzno. For ...
. ''Operational Group Bielsko'' (renamed into ''Operational Group Boruta'') was to withdraw behind the Skawa, and to take positions between Zator and Wadowice
Wadowice () is a town in southern Poland, southwest of KrakĂłw with 17,455 inhabitants (2022), situated on the Skawa river, confluence of Vistula, in the eastern part of Silesian Foothills (PogĂłrze ĆlÄ
skie). Wadowice is known for being the bir ...
. General retreat towards the Dunajec
The Dunajec (; Goral dialects: ''DĂłnajec''; ) is a river running through northeastern Slovakia and southern Poland. It is also regarded as the main river of the Goral Lands. It is a right tributary of the Vistula River. It begins in Nowy Targ at ...
and the Nida was to begin in the night of September 2/3.. General Szylling specified that units located in the centre of the front were to retreat first, to avoid being surrounded by German panzers advancing fast both in the north and the south. This plan failed, as Polish 7th I.D. was completely destroyed in the morning of Sunday, September 3, by the 14th Infantry Division, the 4th Infantry Division, and the 2nd Light Division.
The retreat itself did not improve the situation of KrakĂłw Army, as it lost its fortified defensive positions, together with heavy equipment, which was abandoned. Polish historians CzesĆaw Grzelak and Henryk StaĆczyk in their book "Kampania polska 1939 roku" write that several historians question the decision of General Szylling, as in their opinion the decision to withdraw eastwards on the second day of the war was premature. Tadeusz Jurga wrote: "To remain in defensive positions would result in halting the advance of the German 10th Army, which later destroyed Prusy Army
The Prusy Army () was one of the Polish armies to fight during the Invasion of Poland in 1939. Created in the summer of 1939 as the main reserve of the Commander in Chief, it was commanded by Gen. Stefan DÄ
b-Biernacki. The word ''Prusy'' in the ...
(...) Furthermore, defensive positions of KrakĂłw Army were based on fortifications, which had been built before the war. These fortifications eliminated technological superiority of the Wehrmacht. To abandon them and to fight in the open lowered defensive abilities of KrakĂłw Army".Tadeusz Jurga, Obrona Polski 1939. Warsaw 1990, page 313
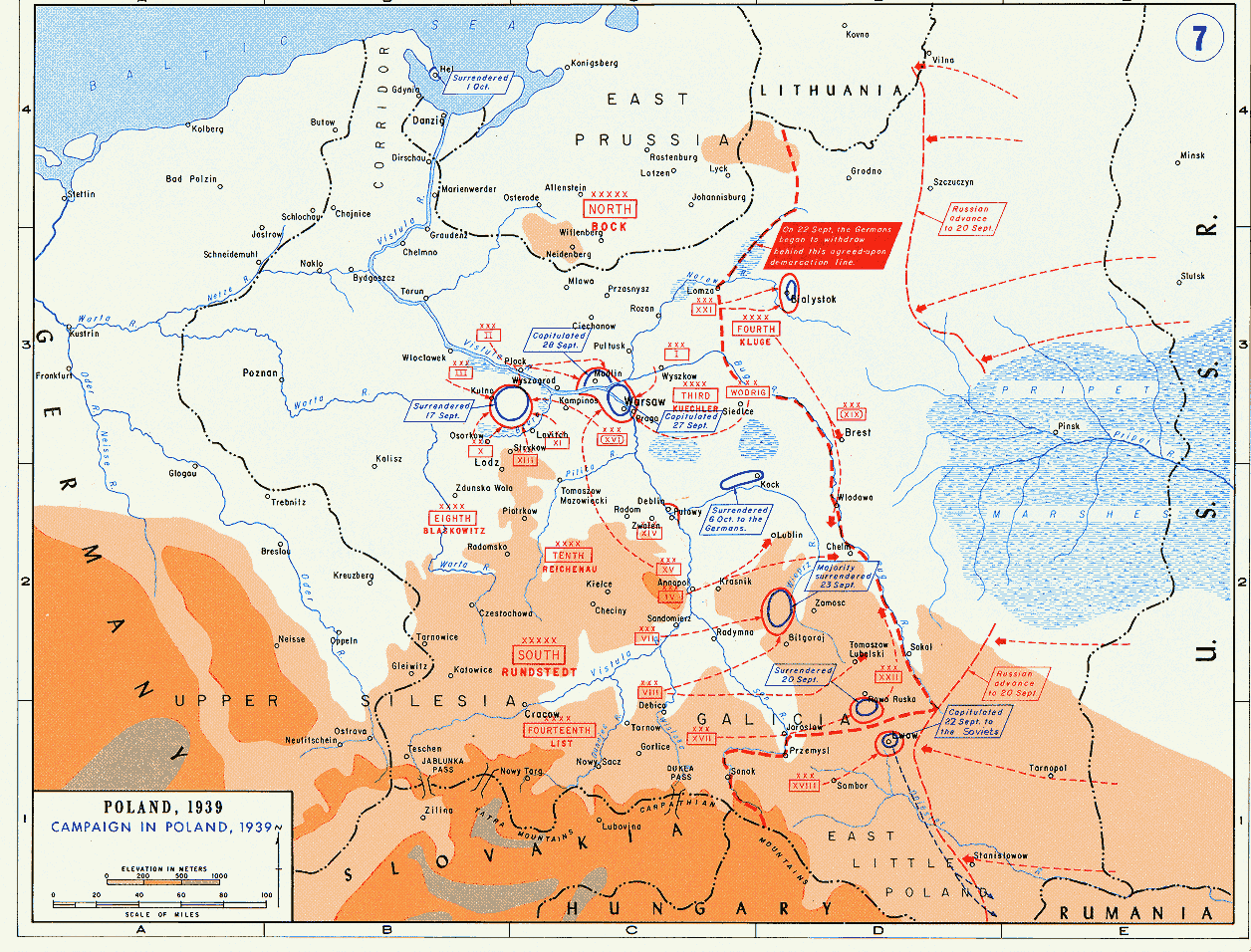
The decision to abandon southwestern Poland had far-reaching consequences, as KrakĂłw Army was the centre point of the defensive plan. Its new line of defence along the Dunajec and the Nida was ill-prepared, and the retreat itself turned out to be very difficult, as Polish units were under constant pressure of the Luftwaffe and German motorized divisions. In the morning of September 3, General Szylling ordered general retreat east of KrakĂłw, dividing his army into ''Operational Group Jagmin'' (north of the Vistula, consisting of the 23rd, the 55th and the 22th I.D.'s, together with KrakĂłw Cavalry Brigade, and soldiers of Fortified Group Silesia), and ''Operational Group Boruta'' (south of the Vistula, consisting of the 6th and the 21st I.D.'s, the 10th Motorized Brigade, and the 1st Mountain Brigade). Szylling hoped to reach the defensive line by September 7, and first days of retreat were relatively calm, as the Wehrmacht concentrated its efforts in the area of PiotrkĂłw Trybunalski
PiotrkĂłw Trybunalski (; also known by #Etymology, alternative names), often simplified to PiotrkĂłw, is a city in central Poland with 71,252 inhabitants (2021). It is the capital of PiotrkĂłw County and the second-largest city in the ĆĂłdĆș Voi ...
.
The End of KrakĂłw Army
On September 5, German 2nd Panzer Division, together with the 3rd Mountain Division and the 7th Infantry Division broke through Polish lines near Pcim, capturingMyĆlenice
MyĆlenice is a town in southern Poland situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship, 30 km south of KrakĂłw. The town is divided into six districts. The most popular of them, Zarabie, is a famous tourist destination. It is located behind the Ra ...
, Bochnia
Bochnia is a town on the river Raba in southern Poland, administrative seat of Bochnia County in Lesser Poland Voivodeship. The town lies approximately halfway between TarnĂłw (east) and the regional capital KrakĂłw (west). Bochnia is most noted ...
and WiĆnicz, thus positioning themselves in the rear of the retreating units of ''Operational Group Boruta''. On the same day, ''Fall 5 September'' instruction was issued by the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht
The (; abbreviated OKW Ë kaËËveArmed Forces High Command) was the Command (military formation), supreme military command and control Staff (military), staff of Nazi Germany during World War II, that was directly subordinated to Adolf ...
, ordering German divisions to continue their advance towards TarnĂłw
TarnĂłw () is a city in southeastern Poland with 105,922 inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of 269,000 inhabitants. The city is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship. It is a major rail junction, located on the strategic eastâ ...
and RzeszĂłw
RzeszĂłw ( , ) is the largest city in southeastern Poland. It is located on both sides of the WisĆok River in the heartland of the Sandomierz Basin. RzeszĂłw is the capital of the Subcarpathian Voivodeship and the county seat, seat of RzeszĂłw C ...
. On September 6, German 4th Light Division attacked Polish 24th I.D. near TarnĂłw, crossing the Dunajec south of Zakliczyn. Polish unit managed to halt the Germans, and its commandant, Colonel BolesĆaw KrzyĆŒanowski hoped to keep the line of the Dunajec for ''Operational Group Boruta''. In the evening of September 6, General Kazimierz Fabrycy ordered him to retreat to the WisĆoka
The WisĆoka is a river in south-eastern Poland, and a tributary of Vistula River. It is long and has a basin area of . Its highest elevation is , while the lowest point in the valley of the river WisĆoka lies at an elevation of above sea ...
river. On the same day, Polish units abandoned KrakĂłw.
On September 6, Marshall ĆmigĆy-Rydz reorganized the units fighting in southern Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''MaĆopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is KrakĂłw. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
. ''Operational Group Boruta'' was moved to Karpaty Army
Karpaty Army () was formed on 11 July 1939 under Major General Kazimierz Fabrycy after Nazi Germany created a puppet state of Slovakia and the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia was proclaimed after the events that lead to the breakup of Czechos ...
, and soon afterwards, Karpaty Army was merged with ''Operational Group Jagmin'', creating MaĆopolska Army, under General Fabrycy. ĆmigĆy-Rydz was well aware of the fact that it was impossible to hold the line of the Dunajec and the Nida, and that further retreat towards the San was the only option.
Organization
The Army was commanded by general Antoni Szylling; his chief of staff was Colonel StanisĆaw Wiloch. It consisted of five infantry divisions, one motorized cavalry brigade, one mountain brigade and one cavalry brigade. The 22nd Mountain Infantry Division (Colonel Leopold Endel-Ragis) was supposed to be the reserve of ĆĂłdĆș Army, but due to destruction of rail connections, this division never reached its destination in central Poland. It concentrated nearKrzeszowice
Krzeszowice () is a town in southern Poland, situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship. As of 2004, its population was 9,993. Krzeszowice belongs to ''KrakĂłw Metropolitan Area'', and lies 25 kilometers west of the center of the city of KrakĂł ...
and Trzebinia
Trzebinia (; ''Tchebin'') is a town in ChrzanĂłw County, Lesser Poland, Poland with an Orlen oil refinery and a major rail junction of the KrakĂłw - Katowice line, with connections to OĆwiÄcim and Spytkowice. The town became part of Lesser Pola ...
, and on September 2 joined KrakĂłw Army, replacing the 7th I.D., which had been destroyed near CzÄstochowa.
References
Armie i samodzielne grupy operacyjne Wojska Polskiego 1939
WIEM Encyklopedia
WIEM Encyklopedia (full name in - "Great Interactive Multimedia Encyclopedia"; in Polish, ''wiem'' also means 'I know') is a Polish Internet encyclopedia.
The encyclopedia was based on the first printed edition was released in mid-1990s (with Vo ...
* CzesĆaw Grzelak, Henryk StaĆczyk Kampania polska 1939 roku. Oficyna Wydawnicza RYTM Warszawa, 2005.
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Krakow Army Military units and formations of Poland in World War II Polish armies Military units and formations established in 1939 Military units and formations disestablished in 1939 KrakĂłw in World War II