Keystone Corridor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Keystone Corridor is a 349-mile (562 km) railroad corridor between
 In 1999, the Keystone Corridor was formally recognized as a "designated high speed corridor" by the
In 1999, the Keystone Corridor was formally recognized as a "designated high speed corridor" by the
 The busiest part of the Keystone Corridor is the segment between Harrisburg and New York City, which sees multiple trains per day.
The busiest part of the Keystone Corridor is the segment between Harrisburg and New York City, which sees multiple trains per day.
 SEPTA Regional Rail operates commuter rail service on the Keystone Corridor between
SEPTA Regional Rail operates commuter rail service on the Keystone Corridor between
Plan the Keystone
– PennDOT
Keystone Corridor on Google Maps
{{High-speed rail Amtrak lines Electric railways in Pennsylvania High-speed railway lines in the United States Keystone Corridor Pennsylvania Railroad lines SEPTA Regional Rail
Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
and Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, that consists of two rail lines: Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
and SEPTA
SEPTA, the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority, is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly four million people througho ...
's Philadelphia-to-Harrisburg main line, which hosts SEPTA's Paoli/Thorndale Line commuter rail
Commuter rail or suburban rail is a Passenger train, passenger rail service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting Commuting, commuters to a Central business district, central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter town ...
service, and Amtrak's '' Keystone Service'' and ''Pennsylvanian'' inter-city
Inter-city rail services are Express train, express trains that run services that connect cities over longer distances than Commuter rail, commuter or Regional rail, regional trains. They include rail services that are neither short-distance co ...
trains; and the Norfolk Southern
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States. Headquartered in Atlanta, the company was formed in 1982 with the merger of the Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. The comp ...
Pittsburgh Line. The corridor was originally the Main Line of the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
.
Amtrak runs two intercity rail
Inter-city rail services are Express train, express trains that run services that connect cities over longer distances than Commuter rail, commuter or Regional rail, regional trains. They include rail services that are neither short-distance co ...
services along the Keystone Corridor: the Harrisburg-to-New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
'' Keystone Service'' and the Pittsburgh-to-New York City '' Pennsylvanian''. SEPTA operates daily Paoli/Thorndale commuter rail service between Philadelphia and Thorndale on the Philadelphia-to-Harrisburg main line. The towns along this stretch form a socio-cultural region called the " Philadelphia Main Line".
The tracks from Pittsburgh to Harrisburg
Harrisburg ( ; ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat, seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50, ...
are owned and maintained by Norfolk Southern
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States. Headquartered in Atlanta, the company was formed in 1982 with the merger of the Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. The comp ...
, which acquired them from Conrail
Conrail , formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do busine ...
. They include the Horseshoe Curve west of Altoona. The tracks between Harrisburg and Philadelphia are owned and maintained by Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
, and are the only part of the Keystone Corridor that is electrified. The tracks join the Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
at Zoo Interlocking near the Philadelphia Zoo
The Philadelphia Zoo is a zoo located in the Centennial District of Philadelphia on the west bank of the Schuylkill River. It was the first true zoo in the United States; it was chartered by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania on March 21, 1859 ...
and 30th Street Station
30th Street Station, officially William H. Gray III 30th Street Station, is a major intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transit station in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The station opened in 1933 as Pennsylvania Station– ...
.
History
The right-of-way that would become the Keystone Corridor was mainly laid by two railroads. The tracks east of Dillerville, just west of Lancaster, were originally the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad, part of the state-owned Main Line of Public Works. From Lancaster west to Harrisburg, the tracks were laid by the Harrisburg, Portsmouth, Mount Joy and Lancaster Railroad. Except for minor realignments, today's Keystone Corridor runs along the same path. Both lines eventually became part of thePennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
's (PRR) main line.
In 1915, the PRR electrified the line from Philadelphia's Broad Street Station to Paoli, then the west end of commuter service. Electrification west of Paoli to Harrisburg came in the 1930s, after the PRR completed electrifying its New York-Washington, D.C. section (the present-day Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
). The total cost of electrification topped $200 million, which was financed by government-supported loans from the Reconstruction Finance Corporation
The Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC) was an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the United States federal government that served as a lender of last resort to US banks and businesses. Established in ...
and the Public Works Administration
The Public Works Administration (PWA), part of the New Deal of 1933, was a large-scale public works construction agency in the United States headed by United States Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of the Interior Harold L. Ickes. It was ...
.
Passenger service remained unprofitable, returned to profitability during World War II, and then slumped again. The PRR overhauled much of the right-of-way in the 1950s, but chose to keep paying a stable dividend rather than reinvest in infrastructure. The result was dilapidated stations, slow, disjointed track conditions, and antiquated rolling stock which frequently broke down.
In 1968, the PRR merged with the New York Central
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midw ...
to become Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals, the Pennsylvania, New York Central and the ...
, which declared bankruptcy in 1970. In 1976, Amtrak took ownership of the line between Philadelphia and Harrisburg while Conrail (the merger of Penn Central, the Reading Company, and several other Class I railroads) took ownership of the remaining part of the line and the many branches, both electrified and non-electrified, that the Penn Central had owned. Amtrak took over the express Harrisburg-New York intercity rail service in 1971, while Conrail, under SEPTA auspices, continued Harrisburg-Philadelphia commuter services. In 1983, SEPTA took over all commuter services and extended operations to Parkesburg (later truncated in 1996 to Downingtown, but later extended to Thorndale).
Penn Central made an agreement with the federal government to provide a high-speed service called the Metroliner, which upgraded the Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
tracks between New York and Washington by 1969, but neglected other areas such as the Keystone Corridor, a lack of maintenance that continued after Amtrak's takeover in 1976. The Keystone Corridor eventually served as a "depository" for the problem-prone Metroliner electric multiple unit
A multiple-unit train (or multiple unit (MU)) is a self-propelled train composed of one or more Coach (rail), carriages joined, and where one or more of the carriages have the means of propulsion built in. By contrast, a locomotive-hauled ...
cars. Amtrak also used electric locomotive-hauled trains for Harrisburg-New York service. Before the introduction of ''Acela
The ''Acela'' ( ; originally the ''Acela Express'' until September 2019) is Amtrak's flagship passenger train service along the Northeast Corridor (NEC) in the Northeastern United States between Washington, D.C. and Boston via 13 intermedia ...
'' electric high-speed service over the Northeast Corridor, and after facing a shortage of electric locomotives (both E60 and AEM-7 models), Amtrak used GE Genesis
The GE Genesis (officially trademarked GENESIS) is a series of passenger diesel locomotives built by GE Transportation for Amtrak, Metro-North, and Via Rail between 1992 and 2001. A total of 321 units were produced.
Designed to meet Amtrak's ...
diesel locomotives between Harrisburg and Philadelphia, with an engine change to an electric (usually AEM-7) locomotive at 30th Street Station
30th Street Station, officially William H. Gray III 30th Street Station, is a major intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transit station in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The station opened in 1933 as Pennsylvania Station– ...
. Due to the slower schedules combined with higher ticket prices and competition from SEPTA, ridership declined.
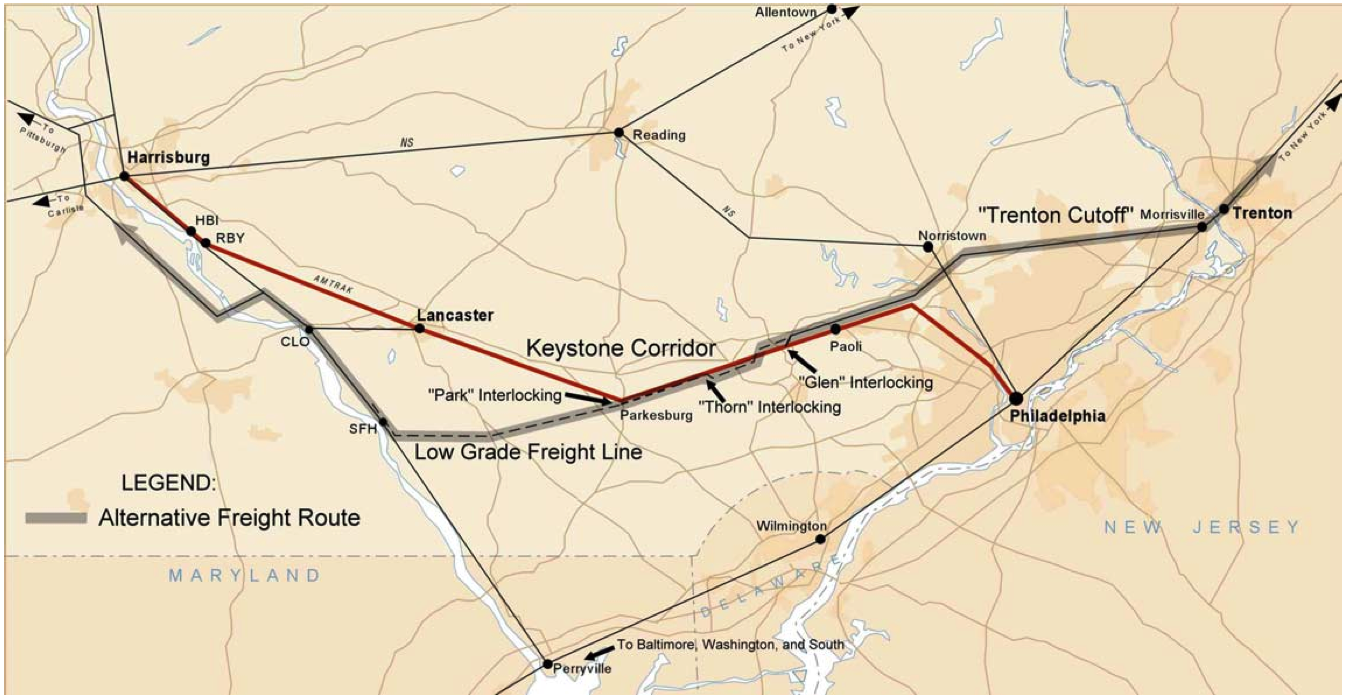
The line between Philadelphia and Lancaster was four tracks until the 1960s, when the PRR removed two of the tracks west of Paoli. The line is now two tracks from Paoli to Harrisburg, save for a three-track section between the Glen and Park interlockings, and a four-track section between the Downs and Thorn interlockings.
most of the track was limited to a maximum speed of , except for a few sections between Downingtown and Lancaster. There are also curves which require slower speeds (especially in the section between Merion and Overbrook), and speed restrictions within interlocking limits.
High-speed corridor
Federal Railroad Administration
The Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) is an agency in the United States Department of Transportation (DOT). The agency was created by the Department of Transportation Act of 1966. The purpose of the FRA is to promulgate and enforce railroa ...
(FRA), as part of the TEA-21 transportation bill. The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania will fund half of the project's costs, and Amtrak will fund the other half.
The goals of this project include:
* 90-minute travel time between Harrisburg and Philadelphia on express trains
* 105-minute travel time on normal trains
* Raising track speed to where possible
* Increasing the number of daily round trips from 11 to 14
* Replacing diesel trains with electric on ''Keystone Service''
A summary appears in an FRA report.
Construction on the USD $145 million project began on March 7, 2005, and was completed in Fall, 2006. Amtrak's press releases have summarized the improvements as:
* Installation of 80 track miles (128 km) of new concrete ties
* Installation of more than 40 new track switches
* A new signal system between Lancaster and Harrisburg
* Upgrade of 16 existing bridges and culverts
* Upgrade of overhead electrical wires (catenary)
* Upgrade of electrical substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station an ...
s to support use of electric locomotives.
The installation of concrete ties also included replacement of the old jointed rail with new continuous welded rail (136 RE), track surfacing, and alignment. Track surfacing is adjusting the vertical profile of the two rails, leveling the rails on straight track and introducing superelevation (banking) in curves. The are broken down as:
* on track 4 from Park (Parkesburg) to Cork (Lancaster) interlockings
* on track 1 from Cork (Lancaster) to Park (Parkesburg) interlockings
* on track 3 from Paoli to Overbrook
* on track 2 from Overbrook to Paoli
Amtrak replaced the signal and communications system and rebuilt the overhead catenary wire and upgraded electrical substations to provide the power needed to operate several electric trains simultaneously on this line. Since October 2006, Amtrak, having sufficient ''Acela'' high-speed trainsets, started using electric push-pull trainsets for the first time since the mid-1990s. Using AEM7 locomotives and former Metroliner m.u. coaches modified into a push-pull cab-coach (with the locomotive "pulling" westbound trains and "pushing" eastbound), the electrified service is currently used on the Harrisburg-New York ''Keystone Service'', while the Genesis diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover (locomotive), power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is con ...
s are still used for the Pittsburgh-New York ''Pennsylvanian'' service. As on the Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
, Amtrak trains between Paoli and Overbrook use the high-speed inner rails for normal operations.
In March 2011, Pennsylvania received a $750,000 grant from the High-Speed Intercity Passenger Rail Program to investigate extending high-speed electrified service from Harrisburg to Pittsburgh.
At-grade crossings with roads between Philadelphia and Harrisburg remained until 2014. One of the crossings was in Elizabethtown and another in Mount Joy. The third, between Mount Joy and Lancaster, was blocked off using fencing and jersey barrier
A Jersey barrier, Jersey wall, or Jersey bump is a modular concrete or plastic barrier employed to separate lanes of traffic. It is designed to minimize vehicle damage in cases of incidental contact while still preventing vehicle crossovers resu ...
s. Additional funding from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) (), nicknamed the Recovery Act, was a Stimulus (economics), stimulus package enacted by the 111th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama in February 2009. Developed ...
was used to complete the elimination of all at-grade crossings. The last was closed in 2014. Private crossings remain between Philadelphia and Harrisburg. There are still grade crossings between Harrisburg and Pittsburgh.
Earlier studies
There have been earlier studies by theUSDOT
The United States Department of Transportation (USDOT or DOT) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is headed by the secretary of transportation, who reports directly to the president of the United States a ...
and FRA of the Keystone Corridor, and these studies contain proposals or speculations which might not be in the currently funded projects. Some of these ideas are below.
Amtrak service to Suburban Station, which is in Center City Philadelphia, ended in 1988. An early study says that PennDOT used Suburban Station as the Philadelphia endpoint for the 90-minute service to Harrisburg. Restoring service to Suburban Station may increase ridership but would require using the upper level of 30th Street Station and either scheduling trains to turn at Suburban Station or to continue through the Center City Commuter Tunnel with Amtrak trains turning around at Wayne Junction.
Bypassing 30th Street Station by using the New York-Pittsburgh Subway would allow trains to skip a time-consuming stop and reverse of directions at 30th Street Station and allow fast service between New York and Harrisburg. Historically, the PRR fast trains going to NY from the west would bypass 30th Street Station, and passengers for Philadelphia would change trains at North Philadelphia. One study suggested two daily electric-train round-trips between New York and Harrisburg with stops in North Philadelphia and Ardmore, a routing last used by Keystone trains in 1994.
Track reconfiguration between Zoo and Overbrook interlockings can increase track speeds which are usually due to the need to take diverging routes through switches. Reducing the number of diverging moves and the use of switches can increase speeds. Also, the reconfiguration can allow for the removal of the overhead bridge that the R6 Cynwyd trains use. Some other interlockings may be removed or reconfigured. With the reconfiguration near Zoo, the Overbrook interlocking can be removed and replaced with 4 through tracks. Bryn Mawr interlocking may have storage tracks added west of the station to allow R5 Bryn Mawr locals to turn without occupying an express track. Paoli interlocking may be removed if the four-track configuration were to continue west of the station. Paoli station may be reconfigured with high-level island platforms serving all four tracks, as part of a new Paoli transportation center. Frazer interlocking may be reconfigured for turning SEPTA trains and as the point where four tracks become two.
Electrification may be converted to use commercial 60 Hz AC power instead of the special 25 Hz single-phase AC currently in use, although this is doubtful due to the costs involved, lack of real benefits and dedicated 25 Hz hydro-electric capacity at the Safe Harbor Dam. The Safe Harbor Dam also generates electricity for the Northeast Corridor itself, the power going from the dam to the NEC (at Perryville, Maryland
Perryville is a town in Cecil County, Maryland, United States. The population was 4,361 at the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. The town is located near an exit for Interstate 95 in Maryland, Interstate 95, on the north side of the outlet ...
), via a pylon network. Between Paoli and 30th Street Station, most of the overhead electric wire and other electrification system components date back to the original 1915 electrification, although the 1915 substations have been retired. West of Paoli the electrification dates from the late 1930s, and west of Downingtown the system is still controlled by the original 1939 power dispatching office in Harrisburg, utilizing electromechanical systems.
Construction progress
The four-track section between Overbrook and Paoli is numbered sequentially from the southernmost track (number 1 track) to the northernmost track (number 4 track). Between March 7 and June 27, 2005, Amtrak worked on the number 4 track between Lancaster and Parkesburg, and from June 27 to September 2, 2005, they worked on number 1 track. A work gang with a track laying system (TLS) installed concrete crossties, new continuous welded rail, and new ballast, allowing for . The track layout at Lancaster station was simplified so that trains no longer have to take a diverging route to access the station platforms. Because tracks 2 and 3 have been removed, tracks 1 and 4 are the only tracks in this section. Between October 3, 2005, and mid-December, Amtrak worked on the number 2 track from Paoli to a point between Narberth and Merion stations. On March 20, 2006, Amtrak started working on the number 3 track, starting within Paoli interlocking and working east towards Overbrook. As of April 6, 2006, a track laying system (TLS) has completed work to approximately milepost 16.7. 110-mph service started on October 30, 2006, following completion of a $145 million upgrade of the 104-mile line. Push-pull express trains will cut journey time from the current two hours to 90 minutes. Local service will improve to 105 minutes. Three weekday and two weekend roundtrips will be added as well.Services
 The busiest part of the Keystone Corridor is the segment between Harrisburg and New York City, which sees multiple trains per day.
The busiest part of the Keystone Corridor is the segment between Harrisburg and New York City, which sees multiple trains per day.
Amtrak
The following Amtrak rail lines serve Keystone Corridor stations: *'' Capitol Limited'' – to/fromChicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
and Washington D.C. stops at Pittsburgh, the westernmost stop on the Pennsylvanian route.
* '' Keystone Service'' – local service along the Northeast Corridor between New York and Philadelphia, and along the Keystone Corridor between Philadelphia and Harrisburg. Timings vary by day of the week in each direction, and some trains to/from Harrisburg terminate at and start from Philadelphia.
* '' Pennsylvanian'' – between Pittsburgh and Philadelphia along the Keystone Corridor and between Philadelphia and New York on the Northeast Corridor.
Commuter rail
 SEPTA Regional Rail operates commuter rail service on the Keystone Corridor between
SEPTA Regional Rail operates commuter rail service on the Keystone Corridor between 30th Street Station
30th Street Station, officially William H. Gray III 30th Street Station, is a major intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transit station in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The station opened in 1933 as Pennsylvania Station– ...
and Thorndale as the Paoli/Thorndale Line service. Efforts to re-extend the line to Parkesburg and even to Atglen were under discussion by state Congressman Jim Gerlach, R-PA 6, and the Delaware Valley Regional Planning Commission. On March 7, 2019, it was announced that SEPTA service would be extended back to Coatesville "in the near future", with a new Coatesville station to be built.
The Cynwyd Line service also uses the line between 30th Street Station and the Valley interlocking. The proposed Schuylkill Valley Metro service to Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of symbols, often specifically those of a written language, by means of Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifacete ...
would have also used this line. There is also a proposal to shift the line to eliminate a deteriorating truss bridge.
A project to bring commuter rail service between Harrisburg and Lancaster called the Capital Red Rose Corridor proposed to bring rail service to South Central Pennsylvania. In 2011, after numerous proposals, the project was canceled due to a lack of political will and funding.
SEPTA's capital budget for fiscal year
A fiscal year (also known as a financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. La ...
2006 financed an $80.594 million project with Amtrak to improve infrastructure along the line."R5 Paoli Line Improvements – Amtrak," page 54. SEPTA's effort to improve tracks 1 and 4 between Zoo and Paoli interlockings, included:
* Installation of 85,000 concrete crossties, track surfacing, and alignment
* Replacement of jointed rail with continuous welded rail
* Upgraded signal and communication systems
* Replacement of Bryn Mawr interlocking tracks
* Reconfiguration and replacement of Paoli interlocking tracks
* Improvements to pedestrian underpasses and ROW retaining walls
Freight service

Norfolk Southern
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States. Headquartered in Atlanta, the company was formed in 1982 with the merger of the Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. The comp ...
operates overnight freight service between the western junction of the Trenton Cutoff (a former Penn Central electrified "through-freight" line) and just west of Parkesburg via trackage rights, mainly supplying the ArcelorMittal
ArcelorMittal S.A. is a Luxembourg-based multinational steel manufacturing corporation, headquartered in Luxembourg City. It is ranked second on the list of steel producers behind Baowu, and had an annual crude steel production of 58 millio ...
steel plate manufacturing plant in Coatesville. Norfolk Southern also operates Enola Yard, a major freight classification yard near Harrisburg. Two other electrified through-freight lines, the Atglen and Susquehanna Branch (a.k.a. the Low-Grade Line) and the Philadelphia and Thorndale Branch, were abandoned by Conrail before its purchase by Norfolk Southern, with NS still maintaining the Low-Grade Line due to the catenary poles servicing the Keystone Corridor between Lancaster and Middletown, while the former has been looked at by the Delaware Valley Regional Planning Commission as a possible "''Cross-County Metro''" project connecting Thorndale with Trenton, New Jersey
Trenton is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of New Jersey and the county seat of Mercer County, New Jersey, Mercer County. It was the federal capital, capital of the United States from November 1 until D ...
. Although there is electrified service on portions of the line all freight traffic is served using diesel locomotives
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover (locomotive), power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is con ...
.
Former services
The '' Broadway Limited'', a train that operated betweenChicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
and New York, used the Keystone Corridor between Pittsburgh and Philadelphia and the Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
between Philadelphia and New York. Originally a Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
train, this route was discontinued by Amtrak in 1995 but later restarted by the passenger rail company and renamed the ''Three Rivers''. The '' Three Rivers'' was discontinued in 2005. (Amtrak's current Chicago-to-Washington, D.C. service, the Capitol Limited, uses the rail line west of Pittsburgh).
Stations
See also
*High-speed rail in the United States
High-speed rail in the United States dates back to the High-Speed Ground Transportation Act of 1965. Various state and federal proposals have followed. Despite being one of the world's first countries to get high-speed trains (the ''Metroliner ...
References
Further reading
*External links
Plan the Keystone
– PennDOT
Keystone Corridor on Google Maps
{{High-speed rail Amtrak lines Electric railways in Pennsylvania High-speed railway lines in the United States Keystone Corridor Pennsylvania Railroad lines SEPTA Regional Rail