Kearns–Sayre Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kearns–Sayre syndrome (KSS), oculocraniosomatic disorder or oculocranionsomatic neuromuscular disorder with ragged red fibers is a
 A neuro-ophthalmologist is usually involved in the diagnosis and management of KSS. An individual should be suspected of having KSS based upon clinical exam findings. Suspicion for myopathies should be increased in patients whose ophthalmoplegia does not match a particular set of cranial nerve palsies ( oculomotor nerve palsy, fourth nerve palsy, sixth nerve palsy). Initially, imaging studies are often performed to rule out more common pathologies. Diagnosis may be confirmed with muscle biopsy, and may be supplemented with PCR determination of mtDNA mutations.
A neuro-ophthalmologist is usually involved in the diagnosis and management of KSS. An individual should be suspected of having KSS based upon clinical exam findings. Suspicion for myopathies should be increased in patients whose ophthalmoplegia does not match a particular set of cranial nerve palsies ( oculomotor nerve palsy, fourth nerve palsy, sixth nerve palsy). Initially, imaging studies are often performed to rule out more common pathologies. Diagnosis may be confirmed with muscle biopsy, and may be supplemented with PCR determination of mtDNA mutations.
mitochondrial myopathy
Mitochondrial myopathies are types of myopathy, myopathies associated with mitochondrial disease. Adenosine triphosphate (Adenosine triphosphate, ATP), the chemical used to provide energy for the cell, cannot be produced sufficiently by oxidative ...
with a typical onset before 20 years of age. KSS is a more severe syndromic variant of chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (abbreviated CPEO), a syndrome that is characterized by isolated involvement of the muscles controlling movement of the eyelid (levator palpebrae, orbicularis oculi) and eye (extra-ocular muscles). This results in ptosis and ophthalmoplegia respectively. KSS involves a combination of the already described CPEO as well as pigmentary retinopathy in both eyes and cardiac conduction abnormalities. Other symptoms may include cerebellar ataxia, proximal muscle weakness, deafness
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is writte ...
, diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
, growth hormone deficiency, hypoparathyroidism, and other endocrinopathies. In both of these diseases, muscle involvement may begin unilaterally but always develops into a bilateral deficit, and the course is progressive. This discussion is limited specifically to the more severe and systemically involved variant.
Signs and symptoms
Individuals with KSS present initially in a similar way to those with typical CPEO. Onset is in the first and second decades of life. The first symptom of this disease is a unilateral ptosis, or difficulty opening the eyelids, that gradually progresses to a bilateral ptosis. As the ptosis worsens, the individual commonly extends their neck, elevating their chin in an attempt to prevent the eyelids from occluding the visual axis. Along with the insidious development of ptosis, eye movements eventually become limited causing a person to rely more on turning the head side to side or up and down to view objects in the peripheralvisual field
The visual field is "that portion of space in which objects are visible at the same moment during steady fixation of the gaze in one direction"; in ophthalmology and neurology the emphasis is mostly on the structure inside the visual field and it i ...
.
Mitochondrial retinopathy
Kearns and Sayre described patients with "pigmentary degeneration" on funduscopy, night vision abnormalities, and some histologic similarities, but also clinical differences, to retinitis pigmentosa Subsequently, the retinal phenotype of KSS was described as retinitis pigmentosa, atypical retinitis pigmentosa, tapetoretinal degeneration, salt-and-pepper retinopathy, and pigmentary retinopathy. As the clinical characterization, however, was not always comprehensive the term "mitochondrial retinopathy" appears most accurate and the diagnosis of RP may have been imprecise. Patients with KSS show widespread granular pigmented alterations in the posterior fundus which correspond to granular patterns on fundus autofluorescence imaging. Associated changes on optical coherence tomography (OCT) include reflectivity changes predominantly at the level of the ellipsoid and interdigitation zone and an increased distance between the ellipsoid band and theretinal pigment epithelium
The pigmented layer of retina or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is the pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), ...
. Night blindness may be seen in patients with KSS. Visual acuity loss is usually mild and only occurs in 40–50% of patients.
Cardiac conduction abnormalities
These most often occur years after the development of ptosis and ophthalmoplegia. Atrioventricular (abbreviated "AV") block is the most common cardiac conduction deficit. This often progresses to a Third-degree atrioventricular block, which is a complete blockage of the electrical conduction from the atrium to the ventricle. Symptoms of heart block include syncope,exercise intolerance
Exercise intolerance is a condition of inability or decreased ability to perform physical exercise at the normally expected level or duration for people of that age, size, sex, and muscle mass. It also includes experiences of unusually severe pos ...
, and bradycardia
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathological processes, it is commonly a physiological response to cardiovascular conditioning or due ...
.
Cerebral folate deficiency
Kearns-Sayre patients are consistently found to have cerebral folate deficiency, a syndrome in which 5-MTHF levels are decreased in thecerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
despite being normal in serum. Treatment with folinic acid
Folinic acid, also known as leucovorin, is a medication used to decrease the toxic effects of methotrexate and pyrimethamine. It is also used in combination with 5-fluorouracil to treat colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer, may be used to ...
can in some cases alleviate the associated symptoms and partially correct associated brain abnormalities, especially if started early in the course of illness. The proposed cause of cerebral folate deficiency in the Kearns–Sayre syndrome is the failure of the mechanisms in the choroid plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central ...
that are responsible for passage of folates from the serum to the cerebrospinal fluid.
Cause and prevalence
As characterized in Kearns's original publication in 1965 and in later publications, inconsistent features of KSS that may occur are weakness of facial, pharyngeal, trunk, and extremity muscles,hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spo ...
, small stature, electroencephalographic changes, cerebellar ataxia and elevated levels of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
protein.
Kearns–Sayre syndrome occurs spontaneously in the majority of cases. In some cases it has been shown to be inherited through mitochondrial, autosomal dominant, or autosomal recessive inheritance. There is no predilection for race or sex, and there are no known risk factors. As of 1992 there were only 226 cases reported in published literature. Although NIH and other studies estimate occurrence in the population to be 1–3 and some as high as 9 in 100,000 individuals but a failure to be referred to specialist centres and recognise the disease symptoms is common
Genetics
KSS is the result of deletions inmitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
(mtDNA) that cause a particular constellation of medical sign
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
s and symptoms. mtDNA is transmitted exclusively from the mother's ovum. Mitochondrial DNA is composed of 37 genes
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
found in the single circular chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
measuring 16,569 base pairs
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
in length. Among these, 13 genes encode proteins of the electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
(abbreviated "ETC"), 22 encode transfer RNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the gene ...
(tRNA), and two encode the large and small subunits that form ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
(rRNA). The 13 proteins involved in the ETC of the mitochondrion are necessary for oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order ...
. Mutations in these proteins results in impaired energy production by mitochondria. This cellular energy deficit manifests most readily in tissues that rely heavily upon aerobic metabolism such as the brain, skeletal and cardiac muscles, sensory organs, and kidneys. This is one factor involved in the presentation of mitochondrial diseases.
There are other factors involved in the manifestation of a mitochondrial disease besides the size and location of a mutation. Mitochondria replicate during each cell division during gestation and throughout life. Because the mutation in mitochondrial disease most often occurs early in gestation in these diseases, only those mitochondria in the mutated lineage are defective. This results in an uneven distribution of dysfunctional mitochondria within each cell, and among different tissues of the body. This describes the term heteroplasmic which is characteristic of mitochondrial diseases including KSS. The distribution of mutated mtDNA in each cell, tissue, and organ, is dependent on when and where the mutation occurs. This may explain why two patients with an identical mutation in mtDNA can present with entirely different phenotypes and in turn different syndromes. A publication in 1992 by Fischel-Ghodsian et al. identified the same 4,977-bp deletion in mtDNA in two patients presenting with two entirely different diseases. One of the patients had characteristic KSS, while the other patient had a very different disease known as Pearson marrow pancreas syndrome. Complicating the matter, in some cases Pearson's syndrome has been shown to progress into KSS later in life.
More recent studies have concluded that mtDNA duplications may also play a significant role in determining what phenotype is present. Duplications of mtDNA seem to be characteristic of all cases of KSS and Pearson's syndrome, while they are absent in CPEO.
Deletions of mtDNA in KSS vary in size (1.3–8kb), as well as position in the mitochondrial genome. The most common deletion is 4.9kb and spans from position 8469 to position 13147 on the genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
. This deletion is present in approximately ⅓ of people with KSS
Diagnosis
 A neuro-ophthalmologist is usually involved in the diagnosis and management of KSS. An individual should be suspected of having KSS based upon clinical exam findings. Suspicion for myopathies should be increased in patients whose ophthalmoplegia does not match a particular set of cranial nerve palsies ( oculomotor nerve palsy, fourth nerve palsy, sixth nerve palsy). Initially, imaging studies are often performed to rule out more common pathologies. Diagnosis may be confirmed with muscle biopsy, and may be supplemented with PCR determination of mtDNA mutations.
A neuro-ophthalmologist is usually involved in the diagnosis and management of KSS. An individual should be suspected of having KSS based upon clinical exam findings. Suspicion for myopathies should be increased in patients whose ophthalmoplegia does not match a particular set of cranial nerve palsies ( oculomotor nerve palsy, fourth nerve palsy, sixth nerve palsy). Initially, imaging studies are often performed to rule out more common pathologies. Diagnosis may be confirmed with muscle biopsy, and may be supplemented with PCR determination of mtDNA mutations.
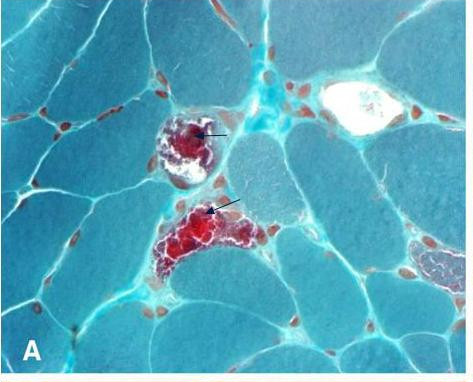
Biopsy findings
It is not necessary to biopsy an ocular muscle to demonstrate histopathologic abnormalities. Cross-section of muscle fibers stained with Gömöri trichrome stain is viewed using light microscopy. In muscle fibers containing high ratios of the mutated mitochondria, there is a higher concentration of mitochondria. This gives these fibers a darker red color, causing the overall appearance of the biopsy to be described as " ragged red fibers. Abnormalities may also be demonstrated in muscle biopsy samples using other histochemical studies such as mitochondrial enzyme stains, by electron microscopy, biochemical analyses of the muscle tissue (ie electron transport chain enzyme activities), and by analysis of muscle mitochondrial DNA."Laboratory studies
Blood lactate andpyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
levels usually are elevated as a result of increased anaerobic metabolism and a decreased ratio of ATP: ADP. CSF analysis shows an elevated protein level, usually >100 mg/dl, as well as an elevated lactate level.
Management
Currently there is no curative treatment for KSS. Because it is a rare condition, there are only case reports of treatments with very little data to support their effectiveness. Several promising discoveries have been reported which may support the discovery of new treatments with further research. Satellite cells are responsible for muscle fiber regeneration. It has been noted that mutant mtDNA is rare or undetectable insatellite cells
Myosatellite cells, also known as satellite cells, muscle stem cells or MuSCs, are small multipotent cells with very little cytoplasm found in mature muscle. Satellite cells are precursors to skeletal muscle cells, able to give rise to satellit ...
cultured from patients with KSS. Shoubridge et al. (1997) asked the question whether wildtype mtDNA could be restored to muscle tissue by encouraging muscle regeneration. In the forementioned study, regenerating muscle fibers were sampled at the original biopsy site, and it was found that they were essentially homoplasmic for wildtype mtDNA. Perhaps with future techniques of promoting muscle cell regeneration and satellite cell proliferation, functional status in KSS patients could be greatly improved.
One study described a patient with KSS who had reduced serum levels of coenzyme Q10. Administration of 60–120 mg of coenzyme Q10 for three months resulted in normalization of lactate and pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
levels, improvement of previously diagnosed first degree AV block, and improvement of ocular movements.
A screening ECG is recommended in all patients presenting with CPEO. In KSS, implantation of pacemaker is advised following the development of significant conduction disease, even in asymptomatic patients.
Screening for endocrinologic disorders should be performed, including measuring serum glucose levels, thyroid function tests
Thyroid function tests (TFTs) is a collective term for blood tests used to check the function of the thyroid.
TFTs may be requested if a patient is thought to suffer from hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) ...
, calcium and magnesium levels, and serum electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
levels. Hyperaldosteronism is seen in 3% of KSS patients.
In December 2022 researchers reported a study with modest results in five patients affected by either Pearson syndrome or Kearns–Sayre syndrome.
History
The triad of CPEO, bilateral pigmentary retinopathy, and cardiac conduction abnormalities was first described in a case report of two patients in 1958 by Thomas P. Kearns (1922–2011), MD., and George Pomeroy Sayre (1911–1992), MD. A second case was published in 1960 by Jager and co-authors reporting these symptoms in a 13-year-old boy. Previous cases of patients with CPEO dying suddenly had been published, occasionally documented as from a cardiac dysrhythmia. Other cases had noted a peculiar pigmentation of the retina, but none of these publications had documented these three pathologies occurring together as a genetic syndrome. Kearns published a defining case in 1965 describing nine unrelated cases with this triad. In 1988, the first connection was made between KSS and large-scale deletions of musclemitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
(abbreviated mtDNA) Since this discovery, numerous deletions in mitochondrial DNA have been linked to the development of KSS.
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Kearns-Sayre Syndrome Mitochondrial diseases Rare syndromes Syndromes affecting the endocrine system Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction Syndromes affecting the heart Syndromes affecting the eye Syndromes affecting hearing Syndromes including diabetes mellitus