Kantō Plain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


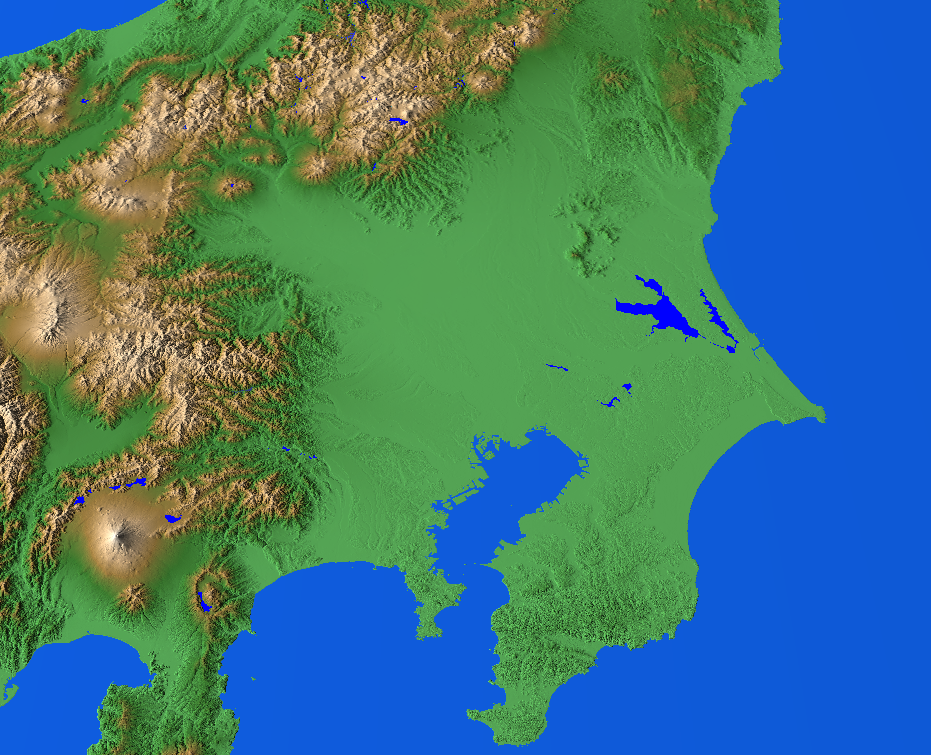 The , in the
The , in the

 The , in the
The , in the Kantō region
The is a geography, geographical region of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures of Japan, prefectures: Chiba Prefecture, Chiba, Gunma Prefe ...
of central Honshu
, historically known as , is the largest of the four main islands of Japan. It lies between the Pacific Ocean (east) and the Sea of Japan (west). It is the list of islands by area, seventh-largest island in the world, and the list of islands by ...
, is the largest plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. Its 17,000 km2 covers more than half of the region extending over Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
, Saitama Prefecture
is a Landlocked country, landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Saitama Prefecture has a population of 7,338,536 (January 1, 2020) and has a geographic area of 3,797 Square kilometre, km2 ( ...
, Kanagawa Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Kanagawa Prefecture is the List of Japanese prefectures by population, second-most populous prefecture of Japan at 9,221,129 (1 April 2022) and third-dens ...
, Chiba Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Chiba Prefecture has a population of 6,278,060 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of . Chiba Prefecture borders Ibaraki Prefecture to the north, Saitama ...
, Gunma Prefecture
is a landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Gunma Prefecture has a population of 1,937,626 (1 October 2019) and has a geographic area of . Gunma Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture and Fuk ...
, Tochigi Prefecture
is a landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Tochigi Prefecture has a population of 1,897,649 (1 June 2023) and has a geographic area of 6,408 Square kilometre, km2 (2,474 Square mile, sq mi ...
, and Ibaraki Prefecture.Encyclopedia of Japan, Kōdansha
Geography
The northern limit borders on the Abukuma Highlands, Yamizo Mountain Range, Ashio Mountain Range, and a volcanic field associated with the Nasu Volcanic Belt. The western coincides with the Kantō Mountain Range, and the southern edge is defined by the Bōsō Peninsula, the Miura Hills,Tokyo Bay
is a bay located in the southern Kantō region of Japan spanning the coasts of Tokyo, Kanagawa Prefecture, and Chiba Prefecture, on the southern coast of the island of Honshu. Tokyo Bay is connected to the Pacific Ocean by the Uraga Channel. Th ...
, and Sagami Bay. The Kashima Sea and Kujūkuri Beach define the eastern end of the plain. Most of its rivers originate in the northern or western mountain ranges and flow east or southeast into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
, Tokyo Bay
is a bay located in the southern Kantō region of Japan spanning the coasts of Tokyo, Kanagawa Prefecture, and Chiba Prefecture, on the southern coast of the island of Honshu. Tokyo Bay is connected to the Pacific Ocean by the Uraga Channel. Th ...
, or Sagami Bay. In the central part of the plain is the Tone River
The is a river in the Kantō region of Japan. It is in length (the second longest in Japan after the Shinano River) and has a drainage area of (the largest in Japan). It is nicknamed Bandō Tarō (); ''Bandō'' is an obsolete alias of the ...
; in the northern part the Watarase River, Kinu River, Kokai River, Naka River, and Kuji River; and in the southern part the Arakawa River, Tama River, and Sagami River. Of these, the Tone River encompasses a large area of floodplain, for its drainage area of is the largest in Japan. The drainage areas covered by these rivers account for the alluvial lowland of the Kantō Plain.Encyclopedia of Japan Tokyo, Kōdansha
A collection of plateaus constitute a large part of the plain. Among them are the Ōmiya, Musashino, Sagamino, Jōsō, and Shimōsa Plateaus. These large plateaus are divided into smaller ones by shallow river valleys. A common feature of the plateaus is that their surfaces are covered with a thick layer of loam of volcanic origin. Volcanic ash from surrounding volcanoes, Mounts Asama, Haruna, and Akagi to the north and Mounts Hakone and Fuji to the southwest, are thought to have been deposited on these plateaus.Nihon Daihyakka Jiten, Shōgakkan
Among the plateaus, the Musashino Plateau has the largest stretch of land, extending from the western edge of Ōme to the eastern edge of Yamanote, which borders the alluvial plains of the Arakawa and Sumida Rivers. Its elevation gradually declines from west to east, measuring 190 m at Ōme and 20 m at Yamanote.
Hills in the Kantō Plain stand on Tertiary strata and rise higher than surrounding plateaus, exemplified by the Sayama Hills and Tama Hills, typically, undulating between 100 and 200 m above sea level. Hills located at the western edge of the Kantō Plain, the Hiki Hills, Koma Hills, Kusahana Hills, and Kaji Hills, also reach approximately above sea level.
The overall tilt of the plateaus and hills is noteworthy. In general, the whole area is slightly bent and forming a basin centered in the Tone River and Tokyo Bay. The ongoing process of tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
extension continues as the plain's central region gradually sinks.
The Kantō Plain witnessed its greatest devastation from an earthquake on 1 September 1923, with a death toll calculated of 142,807.
Geology
Kanto Plain was formed by the Kanto basin-forming movement, which has continued since the Neogene period. This movement is what caused sedimentation in the center of the present-day Kanto Plain and uplift of the surrounding mountains. As a result, sediment from the surrounding mountains was deposited very thickly (the Tertiary layer reaches as high as 3,000 meters) and further uplifted to form many hills and plateaus. Large tectonic lines such as the eastern margin of the Fossa Magna and the Median Tectonic Line are thought to exist in the central part of the plain, but this thick accumulation of soft sedimentary layers makes it difficult to find active faults that can cause earthquakes (faults exist in the base 3000m below the sedimentary layers). In addition, natural sediments such as sediment carried by rivers have been used to create land, and the terrain was almost the same as it is today in the Late Jomon to EarlyYayoi Period
The Yayoi period (弥生時代, ''Yayoi jidai'') (c. 300 BC – 300 AD) is one of the major historical periods of the Japanese archipelago. It is generally defined as the era between the beginning of food production in Japan and the emergence o ...
(more than 3,000 years ago).
Climate
The climate of the Kanto Plain is temperate, with a Pacific Ocean side climate. Winters are cold and summers are hot. The further inland, the greater the temperature difference between summer and winter, and within a day. There are relatively many hours of sunshine, especially in the northern part. Due to the influence of the Black Current (warm current) flowing along the coast, the climate is mild, especially in the southern part. In summer, rainfall is heavy due to the rainy season front caused by monsoon, and typhoons are often seen. Thunderclouds that form in the northern to western mountains areas before noon reach the plains in the early afternoon, often resulting in evening showers (thunderstorms). In years when Okhotsk anticyclone prevails, the winds from this anticyclone become northeasterly winds, and temperatures do not rise due to the cool air brought in by the Yamase, resulting in a cold summer. In winter, the monsoon from theSea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it ...
is blocked by the Mikuni Mountains, and the moisture falls as snow along the mountains to the north, and the monsoon that has lost its moisture blows through the Kanto Plain as a strong gale carrying dry air (such as Akagi Orosi in Gunma Prefecture
is a landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Gunma Prefecture has a population of 1,937,626 (1 October 2019) and has a geographic area of . Gunma Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture and Fuk ...
, Tsukuba Orosi in Ibaraki Prefecuture and Futaara Orosi). Snowfall has been decreasing year by year, but snow accumulation of around 10–20 cm is recorded several times during the winter.
Throughout the year, the entire Kanto Plain, especially the inland areas, are easily affected by radiative cooling
In the study of heat transfer, radiative cooling is the process by which a body loses heat by thermal radiation. As Planck's law describes, every physical body spontaneously and continuously emits electromagnetic radiation.
Radiative cooling has b ...
due to clear skies and north winds, so the minimum temperature before sunrise can drop to about 5 degrees below zero in winter. Even on days when the temperature drops at dawn, the daytime temperature rises to about 7 to 10 degrees Celsius on sunny days, and on days with strong dry north winds, the sensory temperature is lower than the actual temperature. The lowest temperatures in central Tokyo are higher than those in surrounding areas due to the heat island effect. Kumagaya tends to get hotter because of being inland, foehn phenomenon, which occurs when the wind in the sky above blows down after crossing the mountains on the north and west sides of the Kanto Plain, and the sea breeze that warms up while passing through central Tokyo.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kanto Plain Plains of Japan Landforms of Tokyo Landforms of Saitama Prefecture Landforms of Kanagawa Prefecture Landforms of Chiba Prefecture Landforms of Gunma Prefecture Landforms of Tochigi Prefecture Landforms of Ibaraki Prefecture