Joseph Smith Jr. on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious and political leader and the founder of
 According to Smith's later accounts, while praying one night in 1823, he was visited by an angel named Moroni. Smith claimed this angel revealed the location of a buried book made of golden plates, as well as other artifacts including a breastplate and a set of interpreters composed of two seer stones set in a frame, which had been hidden in a hill near his home. Smith said he attempted to remove the plates the next morning, but was unsuccessful because Moroni returned and prevented him. He reported that during the next four years he made annual visits to the hill, but, until the fourth and final visit, each time he returned without the plates.
Meanwhile, Smith's family faced financial hardship, due in part to the death of his oldest brother Alvin. Family members supplemented their meager farm income by hiring out for odd jobs and working as treasure seekers, a type of magical supernaturalism common during the period. Smith was said to have an ability to locate lost items by looking into a seer stone, which he also used in treasure hunting, including, beginning in 1825, several unsuccessful attempts to find buried treasure sponsored by
According to Smith's later accounts, while praying one night in 1823, he was visited by an angel named Moroni. Smith claimed this angel revealed the location of a buried book made of golden plates, as well as other artifacts including a breastplate and a set of interpreters composed of two seer stones set in a frame, which had been hidden in a hill near his home. Smith said he attempted to remove the plates the next morning, but was unsuccessful because Moroni returned and prevented him. He reported that during the next four years he made annual visits to the hill, but, until the fourth and final visit, each time he returned without the plates.
Meanwhile, Smith's family faced financial hardship, due in part to the death of his oldest brother Alvin. Family members supplemented their meager farm income by hiring out for odd jobs and working as treasure seekers, a type of magical supernaturalism common during the period. Smith was said to have an ability to locate lost items by looking into a seer stone, which he also used in treasure hunting, including, beginning in 1825, several unsuccessful attempts to find buried treasure sponsored by  While boarding at the Hale house, located in the township of Harmony (now
While boarding at the Hale house, located in the township of Harmony (now
 Smith said that Moroni returned the plates to him in September 1828, and he then dictated some of the book to his wife Emma. In April 1829 he met
Smith said that Moroni returned the plates to him in September 1828, and he then dictated some of the book to his wife Emma. In April 1829 he met
 In Jackson County, existing Missouri residents resented the Latter Day Saint newcomers for both political and religious reasons. Additionally, their rapid growth aroused fears that they would soon constitute a majority in local elections, and thus "rule the county". Tension increased until July 1833, when non-Mormons forcibly evicted the Mormons and destroyed their property. Smith advised his followers to bear the violence patiently until after they had been attacked multiple times, after which they could fight back. Armed bands exchanged fire, killing one Mormon and two non-Mormons, until the old settlers forcibly expelled the Latter Day Saints from the county.
After petitions to Missouri governor Daniel Dunklin for aid were unsuccessful, Smith organized and led a small
In Jackson County, existing Missouri residents resented the Latter Day Saint newcomers for both political and religious reasons. Additionally, their rapid growth aroused fears that they would soon constitute a majority in local elections, and thus "rule the county". Tension increased until July 1833, when non-Mormons forcibly evicted the Mormons and destroyed their property. Smith advised his followers to bear the violence patiently until after they had been attacked multiple times, after which they could fight back. Armed bands exchanged fire, killing one Mormon and two non-Mormons, until the old settlers forcibly expelled the Latter Day Saints from the county.
After petitions to Missouri governor Daniel Dunklin for aid were unsuccessful, Smith organized and led a small  In January 1837, Smith and other churchleaders created a
In January 1837, Smith and other churchleaders created a
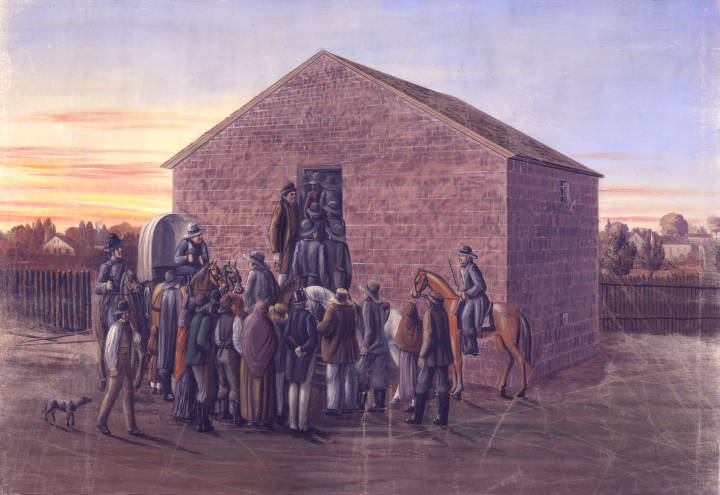 The following day, the Mormons surrendered to 2,500 state troops and agreed to forfeit their property and leave the state. Smith was immediately brought before a military court, accused of
The following day, the Mormons surrendered to 2,500 state troops and agreed to forfeit their property and leave the state. Smith was immediately brought before a military court, accused of
 Smith also attracted a few wealthy and influential converts, including John C. Bennett, the Illinois quartermaster general. Bennett used his connections in the Illinois state legislature to obtain an unusually liberal charter for the new city, which Smith renamed " Nauvoo". The charter granted the city virtual autonomy, authorized a university, and granted Nauvoo ''
Smith also attracted a few wealthy and influential converts, including John C. Bennett, the Illinois quartermaster general. Bennett used his connections in the Illinois state legislature to obtain an unusually liberal charter for the new city, which Smith renamed " Nauvoo". The charter granted the city virtual autonomy, authorized a university, and granted Nauvoo '' The early Nauvoo years were a period of doctrinal innovation. Smith introduced
The early Nauvoo years were a period of doctrinal innovation. Smith introduced  In December 1843, Smith petitioned
In December 1843, Smith petitioned
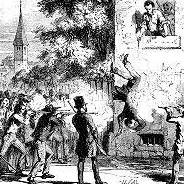 Destruction of the newspaper provoked a strident call to arms from Thomas C. Sharp, editor of the '' Warsaw Signal'' and longtime critic of Smith. Fearing mob violence, Smith mobilized the Nauvoo Legion on June 18 and declared
Destruction of the newspaper provoked a strident call to arms from Thomas C. Sharp, editor of the '' Warsaw Signal'' and longtime critic of Smith. Fearing mob violence, Smith mobilized the Nauvoo Legion on June 18 and declared  On June 27, 1844, an armed mob with blackened faces stormed Carthage Jail, where Joseph and Hyrum were being detained. Hyrum, who was trying to secure the door, was killed instantly with a shot to the face. Smith fired three shots from a pepper-box pistol that his friend, Cyrus H. Wheelock, had lent him, wounding three men, before he sprang for the window. (Smith and his companions were staying in the jailer's bedroom, which did not have bars on the windows.) He was shot multiple times before falling out of the window, crying, "Oh Lord my God!" He died shortly after hitting the ground, but was shot several more times by an improvised
On June 27, 1844, an armed mob with blackened faces stormed Carthage Jail, where Joseph and Hyrum were being detained. Hyrum, who was trying to secure the door, was killed instantly with a shot to the face. Smith fired three shots from a pepper-box pistol that his friend, Cyrus H. Wheelock, had lent him, wounding three men, before he sprang for the window. (Smith and his companions were staying in the jailer's bedroom, which did not have bars on the windows.) He was shot multiple times before falling out of the window, crying, "Oh Lord my God!" He died shortly after hitting the ground, but was shot several more times by an improvised

 According to Bushman, the "signal feature" of Smith's life was "his sense of being guided by revelation". Instead of presenting his ideas with logical arguments, Smith dictated authoritative scripture-like "revelations" and let people decide whether to believe, doing so with what Peter Coviello calls "beguiling offhandedness". Smith and his followers treated his revelations as being above teachings or opinions, and he acted as though he believed in his revelations as much as his followers. The revelations were written as if God himself were speaking through Smith, often opening with words such as, "Hearken O ye people which profess my name, saith the Lord your God".
According to Bushman, the "signal feature" of Smith's life was "his sense of being guided by revelation". Instead of presenting his ideas with logical arguments, Smith dictated authoritative scripture-like "revelations" and let people decide whether to believe, doing so with what Peter Coviello calls "beguiling offhandedness". Smith and his followers treated his revelations as being above teachings or opinions, and he acted as though he believed in his revelations as much as his followers. The revelations were written as if God himself were speaking through Smith, often opening with words such as, "Hearken O ye people which profess my name, saith the Lord your God".
 Smith never fully described how he produced the Book of Mormon, saying only that he translated by the power of God and implying that he had read its words. The Book of Mormon itself states only that its text will "come forth by the gift and power of God unto the interpretation thereof". Accordingly, there is considerable disagreement about the actual method used. For at least some of the earliest dictation, Smith's compatriots said he used the "Urim and Thummim", a pair of seer stones he said were buried with the plates. However, people close to Smith said that later in the process of dictation, he used a chocolate-colored stone he had found in 1822 that he had used previously for treasure hunting. Joseph Knight said that Smith saw the words of the translation while, after excluding all light, he gazed at the stone or stones in the bottom of his hat, a process similar to divining the location of treasure. Sometimes, Smith concealed the process by raising a curtain or dictating from another room; at other times he dictated in full view of witnesses while the plates lay covered on the table or were hidden elsewhere.
Smith never fully described how he produced the Book of Mormon, saying only that he translated by the power of God and implying that he had read its words. The Book of Mormon itself states only that its text will "come forth by the gift and power of God unto the interpretation thereof". Accordingly, there is considerable disagreement about the actual method used. For at least some of the earliest dictation, Smith's compatriots said he used the "Urim and Thummim", a pair of seer stones he said were buried with the plates. However, people close to Smith said that later in the process of dictation, he used a chocolate-colored stone he had found in 1822 that he had used previously for treasure hunting. Joseph Knight said that Smith saw the words of the translation while, after excluding all light, he gazed at the stone or stones in the bottom of his hat, a process similar to divining the location of treasure. Sometimes, Smith concealed the process by raising a curtain or dictating from another room; at other times he dictated in full view of witnesses while the plates lay covered on the table or were hidden elsewhere.

Official LDS Church site about Joseph Smith
JosephSmithPapers.org
��An LDS Church project compiling
Recently-discovered photo of Smith
{{DEFAULTSORT:Smith, Joseph 1805 births 1844 deaths 19th-century American male writers 19th-century American non-fiction writers 19th-century apocalypticists 19th-century Christian mystics Politicians assassinated in the 1840s Abolitionists from Illinois American city founders American faith healers American founders American Freemasons American Latter Day Saint leaders American Latter Day Saint missionaries American male non-fiction writers American militia generals American murder victims American people of English descent Angelic visionaries Apostles of the Church of Christ (Latter Day Saints) Assassinated American politicians Assassinated mayors Assassinated religious leaders Book of Mormon witnesses Burials at the Smith Family Cemetery Candidates in the 1844 United States presidential election Child marriage in the United States Christian abolitionists Christian miracle workers Deaths by firearm in Illinois Dispensationalism Doctrine and Covenants people Editors of Latter Day Saint publications Founders of new religious movements History of the Latter Day Saint movement Latter Day Saint martyrs Latter Day Saint missionaries in Canada Latter Day Saint missionaries in the United States Latter Day Saints from Illinois Latter Day Saints from Missouri Latter Day Saints from New York (state) Latter Day Saints from Ohio Latter Day Saints from Vermont Lynching deaths in Illinois Mayors of Nauvoo, Illinois Mormon mystics Nauvoo Legion People from Ontario County, New York People from Palmyra, New York People from Windsor County, Vermont People murdered in Illinois Presidents of the Church (LDS Church) Prophet-Presidents of the Community of Christ Smith Religious leaders from New York (state) Religious leaders from Vermont Seership in Mormonism Smith family (Latter Day Saints) Tarring and feathering in the United States Treasure hunters Victims of religiously motivated violence in the United States People murdered in 1844
Mormonism
Mormonism is the theology and religious tradition of the Latter Day Saint movement of Restorationism, Restorationist Christianity started by Joseph Smith in Western New York in the 1820s and 1830s. As a label, Mormonism has been applied to va ...
and the Latter Day Saint movement
The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian Restorationist movement founded by ...
. Publishing the Book of Mormon
The Book of Mormon is a religious text of the Latter Day Saint movement, first published in 1830 by Joseph Smith as ''The Book of Mormon: An Account Written by the Hand of Mormon upon Plates Taken from the Plates of Nephi''.
The book is one of ...
at the age of 24, Smith attracted tens of thousands of followers by the time of his death fourteen years later. The religious movement he founded is followed by millions of global adherents and several churches, the largest of which is the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
(LDS Church).
Born in Sharon, Vermont, Smith moved with his family to Western New York
Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all so ...
, following a series of crop failures in 1816. Living in an area of intense religious revivalism during the Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Protestant religious revival during the late 18th to early 19th century in the United States. It spread religion through revivals and emotional preaching and sparked a number of reform movements. Revivals were a k ...
, Smith reported experiencing a series of visions. The first of these was in 1820, when he saw "two personages" (whom he eventually described as God the Father
God the Father is a title given to God in Christianity. In mainstream trinitarian Christianity, God the Father is regarded as the first Person of the Trinity, followed by the second person, Jesus Christ the Son, and the third person, God th ...
and Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
). In 1823, he said he was visited by an angel who directed him to a buried book of golden plates inscribed with a Judeo-Christian history of an ancient American civilization. In 1830, Smith published the Book of Mormon, which he described as an English translation of those plates. The same year he organized the Church of Christ Church of Christ may refer to:
Church groups
* Christianity, the Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ
* Christian Church, an ecclesiological term used by denominations to describe the true body of Christia ...
, calling it a restoration of the early Christian Church
Early Christianity, otherwise called the Early Church or Paleo-Christianity, describes the historical era of the Christian religion up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325. Christianity spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and bey ...
. Members of the church were later called Latter Day Saints or Mormons.
In 1831, Smith and his followers moved west, planning to build a communal Zion
Zion (; ) is a placename in the Tanakh, often used as a synonym for Jerusalem as well as for the Land of Israel as a whole.
The name is found in 2 Samuel (), one of the books of the Tanakh dated to approximately the mid-6th century BCE. It o ...
in the American heartland. They first gathered in Kirtland, Ohio
Kirtland is a city in Lake County, Ohio, United States. The population was 6,937 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Kirtland is known for being the early headquarters of the Latter Day Saint movement from 1831 to 1837 and the site of ...
, and established an outpost in Independence, Missouri
Independence is a city in and one of two county seats of Jackson County, Missouri, United States. It is a satellite city of Kansas City, Missouri, and is the largest suburb on the Missouri side of the Kansas City metropolitan area. In 2020 Unite ...
, which was intended to be Zion's central location. During the 1830s, Smith sent out missionaries, published revelations, and supervised construction of the Kirtland Temple. Smith and his followers left Ohio and Missouri after the collapse of the church-sponsored Kirtland Safety Society and violent skirmishes with non-Mormon Missourians escalated into the Mormon extermination order. They established a new settlement at Nauvoo, Illinois
Nauvoo ( ; from the ) is a small city in Hancock County, Illinois, United States, on the Mississippi River near Fort Madison, Iowa. The population of Nauvoo was 950 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Nauvoo attracts visitors for its h ...
which quickly grew to be the second-largest city in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
during Smith’s mayoralty.
Joseph Smith launched a presidential campaign in 1844. During his campaign, Smith and the Nauvoo City Council ordered the destruction of the '' Nauvoo Expositor''‘s printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
after it criticized Smith's power and his practice of polygamy
Polygamy (from Late Greek , "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marriage, marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, it is called polygyny. When a woman is married to more tha ...
. This inflamed anti-Mormon sentiment. Fearing an invasion of Nauvoo, Smith rode to Carthage, Illinois
Carthage is a city in and the county seat of Hancock County, Illinois, United States. Its population was 2,490 as of the 2020 census. Carthage is best known for being the site of the 1844 murder of Joseph Smith, who founded the Latter Day Saint ...
, to stand trial, but was shot and killed by a mob that stormed the jailhouse. During his ministry, Smith published numerous documents and texts, many of which he attributed to divine inspiration and revelation from God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
. He dictated the majority of these in the first-person, saying they were the writings of ancient prophets or expressed the voice of God. His followers accepted his teachings as prophetic and revelatory, and several of these texts were canonized
Canonization is the declaration of a deceased person as an officially recognized saint, specifically, the official act of a Christian communion declaring a person worthy of public veneration and entering their name in the canon catalogue of sa ...
by denominations of the Latter Day Saint movement, which continue to treat them as scripture
Religious texts, including scripture, are texts which various religions consider to be of central importance to their religious tradition. They often feature a compilation or discussion of beliefs, ritual practices, moral commandments and ...
. Smith's teachings discuss God's nature, cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
, family structures, political organization, and religious community and authority. Mormons generally regard Smith as a prophet comparable to Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
and Elijah
Elijah ( ) or Elias was a prophet and miracle worker who lived in the northern kingdom of Israel during the reign of King Ahab (9th century BC), according to the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible.
In 1 Kings 18, Elijah defended the worsh ...
. Several religious denominations identify as the continuation of the church that he organized, including the LDS Church and the Community of Christ
Community of Christ, known legally and from 1872 to 2001 as the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (RLDS), is an American-based international church, and is the second-largest denomination in the Latter Day Saint movement ...
.
Life
Early years (1805–1827)
Joseph Smith was born on December 23, 1805, inVermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
, on the border between the villages of South Royalton and Sharon
Sharon ( 'plain'), also spelled Saron, is a given name as well as a Hebrew name.
In Anglosphere, English-speaking areas, Sharon is now predominantly a feminine given name, but historically it was also used as a masculine given name. In Israel, ...
, to Lucy Mack Smith
Lucy Mack Smith (July 8, 1775 – May 14, 1856) was the mother of Joseph Smith, founder of the Latter Day Saint movement. She is noted for writing the memoir, ''History of Joseph Smith by His Mother, Biographical Sketches of Joseph Smith, the Pr ...
and her husband Joseph Smith Sr., a merchant and farmer. He was one of eleven children. At the age of seven, Smith had a bone infection and, after receiving surgery, used crutches for three years. After an ill-fated business venture and three successive years of crop failures culminating in the 1816 Year Without a Summer
The year 1816 is known as the Year Without a Summer because of severe climate abnormalities that caused average global temperatures to decrease by . Summer temperatures in Europe were the coldest of any on record between 1766 and 2000, resultin ...
, the Smith family left Vermont and moved to Western New York
Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all so ...
, and took out a mortgage on a farm
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used fo ...
in the townships of Palmyra
Palmyra ( ; Palmyrene dialect, Palmyrene: (), romanized: ''Tadmor''; ) is an ancient city in central Syria. It is located in the eastern part of the Levant, and archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first menti ...
and Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
.
The region was a hotbed of religious enthusiasm during the Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Protestant religious revival during the late 18th to early 19th century in the United States. It spread religion through revivals and emotional preaching and sparked a number of reform movements. Revivals were a k ...
. Between 1817 and 1825, there were several camp meetings and revivals in the Palmyra area. Smith's parents disagreed about religion, but the family was caught up in this excitement. Smith later recounted that he had become interested in religion by age 12, and as a teenager, may have been sympathetic to Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother ...
. With other family members, he also engaged in religious folk magic, a relatively common practice in that time and place. Both his parents and his maternal grandfather reported having visions or dreams that they believed communicated messages from God. Smith said that, although he had become concerned about the welfare of his soul, he was confused by the claims of competing religious denominations.
Years later, Smith wrote that he had received a vision
''A Vision: An Explanation of Life Founded upon the Writings of Giraldus and upon Certain Doctrines Attributed to Kusta Ben Luka'', privately published in 1925, is a book-length study of various philosophical, historical, astrological, and poet ...
that resolved his religious confusion. He said that in 1820, while he had been praying in a wooded area near his home, God the Father
God the Father is a title given to God in Christianity. In mainstream trinitarian Christianity, God the Father is regarded as the first Person of the Trinity, followed by the second person, Jesus Christ the Son, and the third person, God th ...
and Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
together appeared to him, told him his sins were forgiven, and said that all contemporary churches had "turned aside from the gospel". Smith said he recounted the experience to a Methodist minister, who dismissed the story "with great contempt". According to historian Steven C. Harper, "There is no evidence in the historical record that Joseph Smith told anyone but the minister of his vision for at least a decade", and Smith might have kept it private because of how uncomfortable that first dismissal was. During the 1830s, Smith orally described the vision to some of his followers, though it was not widely published among Mormons until the 1840s. This vision later grew in importance to Smith's followers, who eventually regarded it as the first event in the restoration of Christ's church to Earth. Smith himself may have originally considered the vision to be a personal conversion.
 According to Smith's later accounts, while praying one night in 1823, he was visited by an angel named Moroni. Smith claimed this angel revealed the location of a buried book made of golden plates, as well as other artifacts including a breastplate and a set of interpreters composed of two seer stones set in a frame, which had been hidden in a hill near his home. Smith said he attempted to remove the plates the next morning, but was unsuccessful because Moroni returned and prevented him. He reported that during the next four years he made annual visits to the hill, but, until the fourth and final visit, each time he returned without the plates.
Meanwhile, Smith's family faced financial hardship, due in part to the death of his oldest brother Alvin. Family members supplemented their meager farm income by hiring out for odd jobs and working as treasure seekers, a type of magical supernaturalism common during the period. Smith was said to have an ability to locate lost items by looking into a seer stone, which he also used in treasure hunting, including, beginning in 1825, several unsuccessful attempts to find buried treasure sponsored by
According to Smith's later accounts, while praying one night in 1823, he was visited by an angel named Moroni. Smith claimed this angel revealed the location of a buried book made of golden plates, as well as other artifacts including a breastplate and a set of interpreters composed of two seer stones set in a frame, which had been hidden in a hill near his home. Smith said he attempted to remove the plates the next morning, but was unsuccessful because Moroni returned and prevented him. He reported that during the next four years he made annual visits to the hill, but, until the fourth and final visit, each time he returned without the plates.
Meanwhile, Smith's family faced financial hardship, due in part to the death of his oldest brother Alvin. Family members supplemented their meager farm income by hiring out for odd jobs and working as treasure seekers, a type of magical supernaturalism common during the period. Smith was said to have an ability to locate lost items by looking into a seer stone, which he also used in treasure hunting, including, beginning in 1825, several unsuccessful attempts to find buried treasure sponsored by Josiah Stowell Josiah Stowell Sr. (also spelled Stoal; 1770–1844) was an associate of Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious and political leader and the founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint ...
, a wealthy farmer in Chenango County.; ; ; ; ; In 1826, Smith was brought before a Chenango County court for "glass-looking", or pretending to find lost treasure; Stowell's relatives accused Smith of tricking Stowell and faking an ability to perceive hidden treasure, though Stowell attested that he believed Smith had such abilities. The result of the proceeding remains unclear because primary sources report conflicting outcomes.
 While boarding at the Hale house, located in the township of Harmony (now
While boarding at the Hale house, located in the township of Harmony (now Oakland
Oakland is a city in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area in the U.S. state of California. It is the county seat and most populous city in Alameda County, with a population of 440,646 in 2020. A major West Coast port, Oakland is ...
) in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, Smith met and courted Emma Hale. When he proposed marriage, her father, Isaac Hale, objected; he believed Smith had no means to support his daughter. Hale also considered Smith a stranger who appeared "careless" and "not very well educated". Smith and Emma eloped
Elopement is a marriage which is conducted in a sudden and secretive fashion, sometimes involving a hurried flight away from one's place of residence together with one's beloved with the intention of getting married without parental approval. A ...
and married on January 18, 1827, after which the couple began boarding with Smith's parents in Manchester. Later that year, when Smith promised to abandon treasure seeking, his father-in-law offered to let the couple live on his property in Harmony and help Smith get started in business.
Smith made his last visit to the hill shortly after midnight on September 22, 1827, taking Emma with him. This time, he said he successfully retrieved the plates. Smith said Moroni commanded him not to show the plates to anyone else, but to translate them and publish their translation. He also said the plates were a religious record of Middle-Eastern indigenous Americans and were engraved in an unknown language, called reformed Egyptian. He told associates that he was capable of reading and translating them.
Although Smith had abandoned treasure hunting, former associates believed he had double crossed them and had taken the golden plates for himself, property they believed should be jointly shared. After they ransacked places where they believed the plates might have been hidden, Smith decided to leave Palmyra.
Founding a church (1827–1830)
In October 1827, Smith and Emma permanently moved to Harmony, aided by a relatively prosperous neighbor, Martin Harris, who began serving as Smith's scribe in April 1828. Although he and his wife,Lucy
Lucy is an English language, English feminine given name derived from the Latin masculine given name Lucius with the meaning ''as of light'' (''born at dawn or daylight'', maybe also ''shiny'', or ''of light complexion''). Alternative spellings ar ...
, were early supporters of Smith, by June 1828 they began to have doubts about the existence of the golden plates. Harris persuaded Smith to let him take 116 pages of manuscript to Palmyra to show a few family members, including his wife. While Harris had the manuscript in his possession—of which there was no other copy—it was lost. Smith was devastated by this loss, especially since it came at the same time as the death of his first son, who died shortly after birth. Smith said that as punishment for his having lost the manuscript, Moroni returned, took away the plates, and revoked his ability to translate. During this period, Smith briefly attended Methodist meetings with his wife, until a cousin of hers objected to inclusion of a "practicing necromancer
Necromancy () is the practice of magic involving communication with the dead by summoning their spirits as apparitions or visions for the purpose of divination; imparting the means to foretell future events and discover hidden knowledge. ...
" on the Methodist class roll.
 Smith said that Moroni returned the plates to him in September 1828, and he then dictated some of the book to his wife Emma. In April 1829 he met
Smith said that Moroni returned the plates to him in September 1828, and he then dictated some of the book to his wife Emma. In April 1829 he met Oliver Cowdery
Oliver H. P. Cowdery (October 3, 1806 – March 3, 1850) was an American religious leader who, with Joseph Smith, was an important participant in the formative period of the Latter Day Saint movement between 1829 and 1836. He was the first bapt ...
, who had also dabbled in folk magic; and with Cowdery as scribe, Smith began a period of "rapid-fire translation". Between April and early June 1829, the two worked full time on the manuscript, then moved to Fayette, New York
Fayette is a town in Seneca County, New York, United States. The population was 3,617 at the 2020 census. The town is in the north-central part of the county and is southeast of Geneva, New York.
A post office is located in the Town of Fayette ...
, where they continued the work at the home of Cowdery's friend, Peter Whitmer. When the narrative described an institutional church and a requirement for baptism
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water eit ...
, Smith and Cowdery baptized each other. Dictation was completed about July 1, 1829. According to Smith, Moroni took back the plates once Smith finished using them.
The completed work, titled the Book of Mormon
The Book of Mormon is a religious text of the Latter Day Saint movement, first published in 1830 by Joseph Smith as ''The Book of Mormon: An Account Written by the Hand of Mormon upon Plates Taken from the Plates of Nephi''.
The book is one of ...
, was published in Palmyra by printer Egbert Bratt Grandin and was first advertised for sale on March 26, 1830. Less than two weeks later, on April 6, 1830, Smith and his followers formally organized the Church of Christ Church of Christ may refer to:
Church groups
* Christianity, the Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ
* Christian Church, an ecclesiological term used by denominations to describe the true body of Christia ...
, and small branches were established in Manchester, Fayette, and Colesville, New York. The Book of Mormon brought Smith regional notoriety and renewed the hostility of those who remembered the 1826 Chenango County trial. After Cowdery baptized several new church members, Smith's followers were threatened with mob violence. Before Smith could confirm the newly baptized, he was arrested and charged with being a "disorderly person". Although he was acquitted
In common law jurisdictions, an acquittal means that the criminal prosecution has failed to prove that the accused is guilty beyond a reasonable doubt of the charge presented. It certifies that the accused is free from the charge of an o ...
, both he and Cowdery fled to Colesville to escape a gathering mob. Smith later claimed that, probably around this time, Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a su ...
, James, and John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
had appeared to him and had ordained him and Cowdery to a higher priesthood.
Smith's authority was undermined when Cowdery, Hiram Page
Hiram Page ( 1800 August 12, 1852) was an early member of the Latter Day Saint movement and one of the Eight Witnesses to the Book of Mormon's golden plates.
Early life
Page was born in Vermont. Earlier in his life, he studied medicine whic ...
, and other church members also claimed to receive revelations. In response, Smith dictated a revelation which clarified his office as a prophet and an apostle
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary. The word is derived from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", itself derived from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to se ...
, stating that only he had the ability to declare doctrine and scripture for the church. Smith then dispatched Cowdery, Peter Whitmer, and others on a mission to proselytize Native Americans. Cowdery was also assigned the task of locating the site of the New Jerusalem
In the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible, New Jerusalem (, ''YHWH šāmmā'', YHWH sthere") is Ezekiel's prophetic vision of a city centered on the rebuilt Holy Temple, to be established in Jerusalem, which would be the capital of the ...
, which was to be "on the borders" of the United States with what was then Indian territory.
On their way to Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
, Cowdery's party passed through northeastern Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
, where Sidney Rigdon and over a hundred followers of his variety of Campbellite Restorationism
Restorationism, also known as Christian primitivism, is a religious perspective according to which the early beliefs and practices of the followers of Jesus were either lost or adulterated after Crucifixion of Jesus, his death and required a "r ...
converted to the Church of Christ, swelling the ranks of the new organization dramatically. After Rigdon visited New York, he soon became Smith's primary assistant. With growing opposition in New York, Smith announced a revelation that his followers should gather to Kirtland, Ohio
Kirtland is a city in Lake County, Ohio, United States. The population was 6,937 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Kirtland is known for being the early headquarters of the Latter Day Saint movement from 1831 to 1837 and the site of ...
, establish themselves as a people and await word from Cowdery's mission.
Life in Ohio (1831–1838)
When Smith moved to Kirtland in January 1831, he encountered a religious culture that included enthusiastic demonstrations ofspiritual gift
In Christianity, a spiritual gift or charism (plural: charisms or charismata; in Greek singular: χάρισμα
''charisma'', plural: χαρίσματα ''charismata'') is an extraordinary power given by the Holy Spirit."Spiritual gifts". ''A ...
s, including fits and trances, rolling on the ground, and speaking in tongues
Speaking in tongues, also known as glossolalia, is an activity or practice in which people utter words or speech-like sounds, often thought by believers to be languages unknown to the speaker. One definition used by linguists is the fluid voc ...
. Rigdon's followers were practicing a form of communalism. Smith brought the Kirtland congregation under his authority and tamed ecstatic outbursts. He had promised church elders that in Kirtland they would receive an endowment of heavenly power, and at the June 1831 general conference, he introduced the greater authority of a High ("Melchizedek") Priesthood to the church hierarchy.
Converts poured into Kirtland. By the summer of 1835, there were fifteen hundred to two thousand Latter Day Saints in the vicinity, many expecting Smith to lead them shortly to the Millennial kingdom. Though his mission to the Native Americans had been a failure, Cowdery and the other missionaries with him were charged with finding a site for "a holy city". They found Jackson County, Missouri
Jackson County is located in the western portion of the U.S. state of Missouri, on the border with Kansas. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 717,204. making it the second-most populous county in the state (af ...
. After Smith visited in July 1831, he pronounced the frontier hamlet of Independence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of ...
the "center place" of Zion
Zion (; ) is a placename in the Tanakh, often used as a synonym for Jerusalem as well as for the Land of Israel as a whole.
The name is found in 2 Samuel (), one of the books of the Tanakh dated to approximately the mid-6th century BCE. It o ...
.
For most of the 1830s, the church was effectively based in Ohio. Smith lived there, though he visited Missouri again in early 1832 to prevent a rebellion of prominent church members who believed the church in Missouri was being neglected. Smith's trip was expedited by a mob of Ohio residents who were outraged over the church's presence and Smith's political power. The mob beat Smith and Rigdon unconscious, tarred and feathered
Tarring and feathering is a form of public torture where a victim is stripped naked, or stripped to the waist, while wood tar (sometimes hot) is either poured or painted onto the person. The victim then either has feathers thrown on them or is ...
them, and left them for dead.
 In Jackson County, existing Missouri residents resented the Latter Day Saint newcomers for both political and religious reasons. Additionally, their rapid growth aroused fears that they would soon constitute a majority in local elections, and thus "rule the county". Tension increased until July 1833, when non-Mormons forcibly evicted the Mormons and destroyed their property. Smith advised his followers to bear the violence patiently until after they had been attacked multiple times, after which they could fight back. Armed bands exchanged fire, killing one Mormon and two non-Mormons, until the old settlers forcibly expelled the Latter Day Saints from the county.
After petitions to Missouri governor Daniel Dunklin for aid were unsuccessful, Smith organized and led a small
In Jackson County, existing Missouri residents resented the Latter Day Saint newcomers for both political and religious reasons. Additionally, their rapid growth aroused fears that they would soon constitute a majority in local elections, and thus "rule the county". Tension increased until July 1833, when non-Mormons forcibly evicted the Mormons and destroyed their property. Smith advised his followers to bear the violence patiently until after they had been attacked multiple times, after which they could fight back. Armed bands exchanged fire, killing one Mormon and two non-Mormons, until the old settlers forcibly expelled the Latter Day Saints from the county.
After petitions to Missouri governor Daniel Dunklin for aid were unsuccessful, Smith organized and led a small paramilitary
A paramilitary is a military that is not a part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. The Oxford English Dictionary traces the use of the term "paramilitary" as far back as 1934.
Overview
Though a paramilitary is, by definiti ...
expedition, called Zion's Camp, to aid the Latter Day Saints in Missouri. As a military endeavor, the expedition was a failure. The men of the expedition were disorganized, suffered from a cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
outbreak and were severely outnumbered. By the end of June, Smith deescalated the confrontation, sought peace with Jackson County's residents, and disbanded Zion's Camp. Nevertheless, Zion's Camp transformed Latter Day Saint leadership because many future church leaders came from among the participants.
After the Camp returned to Ohio, Smith drew heavily from its participants to establish various governing bodies in the church. He gave a revelation announcing that in order to redeem Zion, his followers would have to receive an endowment in the Kirtland Temple, which he and his followers constructed. In March 1836, at the temple's dedication, many who received the endowment reported seeing visions of angels and engaged in prophesying and speaking in tongues.
 In January 1837, Smith and other churchleaders created a
In January 1837, Smith and other churchleaders created a joint stock company
A joint-stock company (JSC) is a business entity in which shares of the company's capital stock, stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their share (finance), shares (certifi ...
, called the Kirtland Safety Society, to act as a quasi-bank; the company issued banknote
A banknote or bank notealso called a bill (North American English) or simply a noteis a type of paper money that is made and distributed ("issued") by a bank of issue, payable to the bearer on demand. Banknotes were originally issued by commerc ...
s partly capitalized
Capitalization ( North American spelling; also British spelling in Oxford) or capitalisation (Commonwealth English; all other meanings) is writing a word with its first letter as a capital letter (uppercase letter) and the remaining letters in ...
by real estate. Smith encouraged his followers to buy the notes, in which he invested heavily himself. The bank failed within a month. As a result, Latter Day Saints in Kirtland suffered extreme high volatility and intense pressure from debt collectors. Smith was held responsible for the failure, and there were widespread defections from the church, including many of Smith's closest advisers.
The failure of the bank was one part of a series of internal disputes led to the demise of the Kirtland community. Cowdery had accused Smith of engaging in a sexual relationship with a teenage servant in his home, Fanny Alger. Construction of the Kirtland Temple had only added to the church's debt, and Smith was hounded by creditors. After a warrant was issued for Smith's arrest on a charge of banking fraud
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
As ban ...
, he and Rigdon fled for Missouri in January 1838.
Life in Missouri (1838–39)
By 1838, Smith had abandoned plans to redeem Zion in Jackson County, and instead declared the town of Far West, Missouri, in Caldwell County, as the new "Zion". In Missouri, the church also took the name "Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints", and construction began on a new temple. In the weeks and months after Smith and Rigdon arrived at Far West, thousands of Latter Day Saints followed them from Kirtland. Smith encouraged the settlement of land outside Caldwell County, instituting a settlement in Adam-ondi-Ahman, in Daviess County. Political and religious differences between old Missourians and newly arriving Latter Day Saint settlers provoked tensions between the two groups, much as they had in Jackson County. By this time, Smith's experiences with mob violence led him to believe that his faith's survival required greater militancy against anti-Mormons. Tensions between the Mormons and the native Missourians escalated quickly until, on August 6, 1838, non-Mormons in Gallatin, Missouri, tried to prevent Mormons from voting, and a brawl ensued. The election day scuffles initiated the 1838 Mormon War. Non-Mormonvigilantes
Vigilantism () is the act of preventing, investigating, and punishing perceived offenses and crimes without legal authority.
A vigilante is a person who practices or partakes in vigilantism, or undertakes public safety and retributive justice ...
raided and burned Mormon farms, while Danites and other Mormons pillaged non-Mormon towns. In the Battle of Crooked River, a group of Mormons attacked the Missouri state militia, mistakenly believing them to be anti-Mormon vigilantes. Governor Lilburn Boggs
Lilburn Williams Boggs (December 14, 1796March 14, 1860) was the sixth Governor of Missouri, from 1836 to 1840. He is now most widely remembered for his interactions with Joseph Smith and Porter Rockwell, and Missouri Executive Order 44, kno ...
then ordered that the Mormons be "exterminated or driven from the state". On October 30, a party of Missourians surprised and killed seventeen Mormons in the Haun's Mill massacre.
 The following day, the Mormons surrendered to 2,500 state troops and agreed to forfeit their property and leave the state. Smith was immediately brought before a military court, accused of
The following day, the Mormons surrendered to 2,500 state troops and agreed to forfeit their property and leave the state. Smith was immediately brought before a military court, accused of treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state (polity), state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to Coup d'état, overthrow its government, spy ...
, and sentenced to be executed the next morning, but Alexander Doniphan, who was Smith's former attorney and a brigadier general in the Missouri militia, refused to carry out the order. Smith was then sent to a state court for a preliminary hearing
In common law jurisdictions, a preliminary hearing, preliminary examination, preliminary inquiry, evidentiary hearing or probable cause hearing is a proceeding, after a criminal complaint has been filed by the prosecutor, to determine whether the ...
, where several of his former allies testified against him. Smith and five others, including Rigdon, were charged with treason, and transferred to the jail
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol, penitentiary, detention center, correction center, correctional facility, or remand center, is a facility where people are imprisoned under the authority of the state, usually as punishment for various cr ...
at Liberty, Missouri
Liberty is a city in and the county seat of Clay County, Missouri, United States and is a suburb of Kansas City, located in the Kansas City Metro Area. As of the 2020 United States census the population was 30,167. Liberty is home to Willia ...
, to await trial.
Smith bore his imprisonment stoically. Understanding that he was effectively on trial before his own people, many of whom considered him a fallen prophet, he wrote a personal defense and an apology for the activities of his followers. "The keys of the kingdom", he wrote, "have not been taken away from us". Though he directed his followers to collect and publish their stories of persecution, he also urged them to moderate their antagonism toward non-Mormons. On April 6, 1839, after a grand jury
A grand jury is a jury empowered by law to conduct legal proceedings, investigate potential criminal conduct, and determine whether criminal charges should be brought. A grand jury may subpoena physical evidence or a person to testify. A grand ju ...
hearing in Daviess County, Smith and his companions escaped custody, almost certainly with the connivance of the sheriff and guards.
Life in Nauvoo, Illinois (1839–1844)
Many American newspapers criticized Missouri for the Haun's Mill massacre and the state's expulsion of the Mormons. Illinois then accepted Mormon refugees who gathered along the banks of theMississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
, where Smith purchased high-priced, swampy woodland in the hamlet of Commerce
Commerce is the organized Complex system, system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered large-scale exchange (distribution through Financial transaction, transactiona ...
. He attempted to portray the Mormons as an oppressed minority and unsuccessfully petitioned the federal government
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
for help in obtaining reparations. During the summer of 1839, while Mormons in Illinois suffered from a malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
epidemic, Smith sent Young and other apostles to missions in Europe, where they made numerous converts, many of them poor factory workers.
 Smith also attracted a few wealthy and influential converts, including John C. Bennett, the Illinois quartermaster general. Bennett used his connections in the Illinois state legislature to obtain an unusually liberal charter for the new city, which Smith renamed " Nauvoo". The charter granted the city virtual autonomy, authorized a university, and granted Nauvoo ''
Smith also attracted a few wealthy and influential converts, including John C. Bennett, the Illinois quartermaster general. Bennett used his connections in the Illinois state legislature to obtain an unusually liberal charter for the new city, which Smith renamed " Nauvoo". The charter granted the city virtual autonomy, authorized a university, and granted Nauvoo ''habeas corpus
''Habeas corpus'' (; from Medieval Latin, ) is a legal procedure invoking the jurisdiction of a court to review the unlawful detention or imprisonment of an individual, and request the individual's custodian (usually a prison official) to ...
'' power—which allowed Smith to fend off extradition
In an extradition, one Jurisdiction (area), jurisdiction delivers a person Suspect, accused or Conviction, convicted of committing a crime in another jurisdiction, into the custody of the other's law enforcement. It is a cooperative law enforc ...
to Missouri. Though Latter Day Saint authorities controlled Nauvoo's civil government, the city guaranteed religious freedom
Freedom of religion or religious liberty, also known as freedom of religion or belief (FoRB), is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice ...
for its residents. The charter also authorized the Nauvoo Legion
The Nauvoo Legion was a state-authorized Latter-day Saints Militias and Military Units, militia of Nauvoo, Illinois, United States from February 4, 1841 until January 29, 1845. Its main function was the defense of Nauvoo and surrounding Latte ...
, a militia whose actions were limited only by state and federal constitutions. Smith and Bennett became its commanders, and were styled Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was norma ...
and Major General respectively. As such, they controlled by far the largest body of armed men in Illinois. Smith appointed Bennett as Assistant President of the Church, and Bennett was elected Nauvoo's first mayor.
 The early Nauvoo years were a period of doctrinal innovation. Smith introduced
The early Nauvoo years were a period of doctrinal innovation. Smith introduced baptism for the dead
Baptism for the dead, vicarious baptism or proxy baptism today commonly refers to the religious practice of baptizing a person on behalf of one who is dead—a living person receiving the rite on behalf of a deceased person.
Baptism for the dea ...
in 1840, and in 1841 construction began on the Nauvoo Temple as a place for recovering lost ancient knowledge. An 1841 revelation promised the restoration of the "fullness of the priesthood"; and in May 1842, Smith inaugurated a revised endowment or "first anointing". The endowment resembled the rites of Freemasonry
Freemasonry (sometimes spelled Free-Masonry) consists of fraternal groups that trace their origins to the medieval guilds of stonemasons. Freemasonry is the oldest secular fraternity in the world and among the oldest still-existing organizati ...
that Smith had observed two months earlier when he had been initiated " at sight" into the Nauvoo Masonic lodge. At first, the endowment was open only to men, who were initiated into a special group called the Anointed Quorum The Anointed Quorum, also known as the Quorum of the Anointed, or the Holy Order, was a select body of men and women who Joseph Smith initiated into Mormon Temple (Latter Day Saints), temple Ordinance (Latter Day Saints), ordinances at Nauvoo, Illin ...
. For women, Smith introduced the Relief Society
The Relief Society is a philanthropic and educational women's organization of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). It was founded in 1842 in Nauvoo, Illinois, United States, and has more than 7 million members in over 1 ...
, a service club
A service club or service organization is a Volunteering, voluntary nonprofit organization where members meet regularly to perform Charity (practice), charitable works either by direct hands-on efforts or by raising money for other organizations. ...
and sorority
In North America, fraternities and sororities ( and ) are social clubs at colleges and universities. They are sometimes collectively referred to as Greek life or Greek-letter organizations, as well as collegiate fraternities or collegiate sorori ...
within which Smith predicted women would receive "the keys of the kingdom". Smith also elaborated on his plan for a Millennial kingdom; no longer envisioning the building of Zion in Nauvoo, he viewed Zion as encompassing all of North and South America, with Mormon settlements being " stakes" of Zion's metaphorical tent. Zion also became less a refuge from an impending tribulation
In Christian eschatology, the Great Tribulation () is a period mentioned by Jesus in the Olivet Discourse as a sign that would occur in the time of the end.
At , "the Great Tribulation" () is used to indicate the period spoken of by Jesus. u ...
than a great building project. In the summer of 1842, Smith revealed a plan to establish the millennial Kingdom of God, which would eventually establish theocratic
Theocracy is a form of autocracy or oligarchy in which one or more deities are recognized as supreme ruling authorities, giving divine guidance to human intermediaries, with executive and legislative power, who manage the government's daily a ...
rule over the whole Earth.
It was around this time that Smith began secretly marrying additional wives, a practice called plural marriage
Polygamy (called plural marriage by Latter-day Saints in the 19th century or the Principle by modern fundamentalist practitioners of polygamy) was practiced by leaders of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) for more ...
. He introduced the doctrine to a few of his closest associates, including Bennett, who used it as an excuse to seduce numerous women, wed and unwed. When rumors of polygamy (called "spiritual wifery" by Bennett) got abroad, Smith forced Bennett's resignation as Nauvoo mayor. In retaliation, Bennett left Nauvoo and began publishing sensational accusations against Smith and his followers.
By mid-1842, popular opinion in Illinois had turned against the Mormons. After an unknown assailant shot and wounded Missouri governor Lilburn Boggs in May 1842, anti-Mormons circulated rumors that Smith's bodyguard, Porter Rockwell, was the gunman. Though the evidence was circumstantial, Boggs ordered Smith's extradition. Certain he would be killed if he ever returned to Missouri, Smith went into hiding twice during the next five months, until the U.S. Attorney for Illinois argued that his extradition would be unconstitutional. (Rockwell was later tried and acquitted.) In June 1843, enemies of Smith convinced a reluctant Illinois Governor Thomas Ford to extradite Smith to Missouri on an old charge of treason. Two law officers arrested Smith but were intercepted by a party of Mormons before they could reach Missouri. Smith was then released on a writ of ''habeas corpus'' from the Nauvoo municipal court. While this ended the Missourians' attempts at extradition, it caused significant political fallout in Illinois.
 In December 1843, Smith petitioned
In December 1843, Smith petitioned Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
to make Nauvoo an independent territory with the right to call out federal troops in its defense. Smith then wrote to the leading presidential candidates, asking what they would do to protect the Mormons. After receiving noncommittal or negative responses, he announced his own independent candidacy for president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
, suspended regular proselytizing, and sent out the Quorum of the Twelve and hundreds of other political missionaries. In March 1844—following a dispute with a federal bureaucrat—he organized the secret Council of Fifty
"The Council of Fifty" (also known as "the Living Constitution", "the Kingdom of God", or its name by revelation, "The Kingdom of God and His Laws with the Keys and Power thereof, and Judgment in the Hands of His Servants, Ahman Christ") was a Lat ...
, which was given the authority to decide which national or state laws Mormons should obey, as well as establish its own government for Mormons. Before his death the Council also voted unanimously to elect Smith "Prophet, Priest, and King". The Council was likewise appointed to select a site for a large Mormon settlement in the Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas (), or simply Texas, was a country in North America that existed for close to 10 years, from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846. Texas shared borders with Centralist Republic of Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande, an ...
, Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
, or California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
(then controlled by Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
), where Mormons could live under theocratic law beyond the control of other governments.
Smith launched a presidential campaign in 1844 on a platform which proposed gradually ending slavery, protecting the liberties of Latter Day Saints and other minorities, reducing the size of Congress, reestablishing a national bank, reforming prisons, and annexing Texas, California, and Oregon.
Death
By early 1844, a rift developed between Smith and a half dozen of his closest associates. Most notably,William Law
William Law (16869 April 1761) was a Church of England priest who lost his position at Emmanuel College, Cambridge, when his conscience would not allow him to take the required oath of allegiance to the first Hanoverian monarch, George I of Grea ...
, his trusted counselor, and Robert Foster, a general
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air force, air and space forces, marines or naval infantry.
In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colone ...
of the Nauvoo Legion, disagreed with Smith about how to manage Nauvoo's economy. Both also said that Smith had proposed marriage to their wives. Believing these men were plotting against his life, Smith excommunicated them on April 18, 1844. Law and Foster subsequently formed a competing "reform church", and in the following month, at the county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or parish (administrative division), civil parish. The term is in use in five countries: Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, and the United States. An equiva ...
in Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, they procured indictments against Smith for perjury
Perjury (also known as forswearing) is the intentional act of swearing a false oath or falsifying an affirmation to tell the truth, whether spoken or in writing, concerning matters material to an official proceeding."Perjury The act or an insta ...
(as Smith publicly denied having more than one wife) and polygamy.
On June 7, the dissidents published the first (and only) issue of the '' Nauvoo Expositor'', calling for reform within the church but also appealing politically to non-Mormons. The paper alluded to Smith's theocratic aspirations, called for a repeal of the Nauvoo city charter, and decried his new "doctrines of many Gods". (Smith had recently given his King Follett discourse, in which he said that God was once a man, and that men and women could become gods.) It also attacked Smith's practice of polygamy, implying that he was using religion as a pretext to draw unassuming women to Nauvoo to seduce and marry them.
Fearing the ''Expositor'' would provoke a new round of violence against the Mormons, the Nauvoo City Council declared the newspaper a public nuisance, and Smith ordered the Nauvoo Legion to assist the police force in destroying its printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
. During the council debate, Smith vigorously urged the council to order the press destroyed, not realizing that destroying a newspaper was more likely to incite an attack than any of the newspaper's accusations.
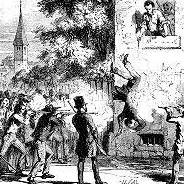 Destruction of the newspaper provoked a strident call to arms from Thomas C. Sharp, editor of the '' Warsaw Signal'' and longtime critic of Smith. Fearing mob violence, Smith mobilized the Nauvoo Legion on June 18 and declared
Destruction of the newspaper provoked a strident call to arms from Thomas C. Sharp, editor of the '' Warsaw Signal'' and longtime critic of Smith. Fearing mob violence, Smith mobilized the Nauvoo Legion on June 18 and declared martial law
Martial law is the replacement of civilian government by military rule and the suspension of civilian legal processes for military powers. Martial law can continue for a specified amount of time, or indefinitely, and standard civil liberties ...
. Officials in Carthage responded by mobilizing a small detachment of the state militia, and Governor Ford intervened, threatening to raise a larger militia unless Smith and the Nauvoo City Council surrendered themselves. Smith initially fled across the Mississippi River, but shortly returned and surrendered to Ford. On June 25, Smith and his brother Hyrum arrived in Carthage to stand trial for inciting a riot. Once the Smiths were in custody, the charges were increased to treason, preventing them from posting bail
Bail is a set of pre-trial restrictions that are imposed on a suspect to ensure that they will not hamper the judicial process. Court bail may be offered to secure the conditional release of a defendant with the promise to appear in court when ...
. John Taylor and Willard Richards voluntarily accompanied the Smiths in Carthage Jail.
 On June 27, 1844, an armed mob with blackened faces stormed Carthage Jail, where Joseph and Hyrum were being detained. Hyrum, who was trying to secure the door, was killed instantly with a shot to the face. Smith fired three shots from a pepper-box pistol that his friend, Cyrus H. Wheelock, had lent him, wounding three men, before he sprang for the window. (Smith and his companions were staying in the jailer's bedroom, which did not have bars on the windows.) He was shot multiple times before falling out of the window, crying, "Oh Lord my God!" He died shortly after hitting the ground, but was shot several more times by an improvised
On June 27, 1844, an armed mob with blackened faces stormed Carthage Jail, where Joseph and Hyrum were being detained. Hyrum, who was trying to secure the door, was killed instantly with a shot to the face. Smith fired three shots from a pepper-box pistol that his friend, Cyrus H. Wheelock, had lent him, wounding three men, before he sprang for the window. (Smith and his companions were staying in the jailer's bedroom, which did not have bars on the windows.) He was shot multiple times before falling out of the window, crying, "Oh Lord my God!" He died shortly after hitting the ground, but was shot several more times by an improvised firing squad
Firing may refer to:
* Dismissal (employment), sudden loss of employment by termination
* Firemaking, the act of starting a fire
* Burning; see combustion
* Shooting, specifically the discharge of firearms
* Execution by firing squad, a method of ...
before the mob dispersed. Smith was the first U.S. presidential candidate to be assassinated.
Legacy

Immediate aftermath
Following Smith's death, non-Mormon newspapers were nearly unanimous in portraying Smith as a religious fanatic. Conversely, within the Latter Day Saint community, Smith was viewed as a prophet,martyred
A martyr (, ''mártys'', 'witness' stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an external party. In colloquial ...
to seal the testimony of his faith.
After a public funeral and viewing of the deceased brothers, Smith's widow—who feared hostile non-Mormons might try to desecrate the bodies—had their remains buried at night in a secret location, with substitute coffins filled with sandbag
A sandbag or dirtbag is a bag or sack made of Hessian (cloth), hessian (burlap), polypropylene or other sturdy materials that is filled with sand or soil and used for such purposes as flood control, military fortification in trenches and bunke ...
s interred in the publicly attested grave. The bodies were later moved and reburied under an outbuilding on the Smith property off the Mississippi River. Members of the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (RLDS Church), under the direction of then-RLDS Church president Frederick M. Smith (Smith's grandson) searched for, located, and disinterred the Smith brothers' remains in 1928 and reinterred them, along with Smith's wife, in Nauvoo at the Smith Family Cemetery.
Impact and assessment
Modern biographers and scholars—Mormon and non-Mormon alike—agree that Smith was one of the most influential, charismatic, and innovative figures in American religious history.; ; In a 2015 compilation of the 100 Most Significant Americans of All Time, ''Smithsonian'' ranked Smith first in the category of religious figures. In popular opinion, non-Mormons in the U.S. generally consider Smith a "charlatan, scoundrel, and heretic", while outside the U.S. he is "obscure". Within the Latter Day Saint movement, Smith's legacy varies between denominations:The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
(LDS Church) and its members consider Smith the founding prophet of their church, on par with Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
and Elijah
Elijah ( ) or Elias was a prophet and miracle worker who lived in the northern kingdom of Israel during the reign of King Ahab (9th century BC), according to the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible.
In 1 Kings 18, Elijah defended the worsh ...
. Meanwhile, Smith's reputation is ambivalent in the Community of Christ
Community of Christ, known legally and from 1872 to 2001 as the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (RLDS), is an American-based international church, and is the second-largest denomination in the Latter Day Saint movement ...
, which continues "honoring his role" in the church's founding history but deemphasizes his human leadership. Conversely, Woolleyite Mormon fundamentalism
Mormon fundamentalism (also called fundamentalist Mormonism) is a belief in the validity of selected fundamentalism, fundamental aspects of Mormonism as taught and practiced in the nineteenth century, particularly during the administrations of J ...
has deified Smith within a cosmology of many gods.
Memorials to Smith include the Joseph Smith Memorial Building in Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City, often shortened to Salt Lake or SLC, is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah. It is the county seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in the state. The city is the core of the Salt Lake Ci ...
the former Joseph Smith Memorial building on the campus of Brigham Young University
Brigham Young University (BYU) is a Private education, private research university in Provo, Utah, United States. It was founded in 1875 by religious leader Brigham Young and is the flagship university of the Church Educational System sponsore ...
as well as the Joseph Smith Building there, a granite obelisk marking Smith's birthplace, and a fifteen-foot-tall bronze statue of Smith in the World Peace Dome in Pune
Pune ( ; , ISO 15919, ISO: ), previously spelled in English as Poona (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1978), is a city in the state of Maharashtra in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan plateau in Western ...
, India.
Successors and denominations
Smith's death resulted in a succession crisis within the Latter Day Saint movement. He had proposed several ways to choose his successor, but never clarified his preference. The two strongest succession candidates were Young, senior member and president of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles, and Rigdon, the senior remaining member of the First Presidency. In a church-wide conference on August 8, most of the Latter Day Saints present elected Young. They eventually left Nauvoo and settled theSalt Lake Valley
Salt Lake Valley is a valley in Salt Lake County, Utah, Salt Lake County in the north-central portion of the U.S. state of Utah. It contains Salt Lake City, Utah, Salt Lake City and many of its suburbs, notably Murray, Utah, Murray, Sandy, Uta ...
, Utah Territory
The Territory of Utah was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from September 9, 1850, until January 4, 1896, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Utah, the 45th st ...
.
Nominal membership in Young's denomination, which became the LDS Church, surpassed 17 million in 2023. Smaller groups followed Rigdon and James J. Strang, who had based his claim on a letter of appointment ostensibly written by Smith but which some scholars believe was forged
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compression (physics), compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die (manufacturing), die. Forging is often classif ...
. Some hundreds followed Lyman Wight
Lyman Wight (May 9, 1796 – March 31, 1858) was an early leader in the Latter Day Saint movement. He was the leader of the Latter Day Saints in Daviess County, Missouri, in 1838. In 1841, he was ordained a member of the Quorum of the Twelve Apo ...
to establish a community in Texas. Others followed Alpheus Cutler. Many members of these smaller groups, including most of Smith's family, eventually coalesced in 1860 under the leadership of Joseph Smith III
Joseph Smith III (November 6, 1832 – December 10, 1914) was the eldest surviving son of Joseph Smith (founder of the Latter Day Saint movement) and Emma Hale Smith. Joseph Smith III was the Prophet-President of what became the Reorganized Chu ...
and formed the RLDS Church (Community of Christ), which has about 250,000 members.
Family and descendants
The first of Smith's wives, Emma Hale, gave birth to nine children during their marriage, five of whom died before the age of two. The eldest, Alvin (born in 1828), died within hours of birth, as did twins Thaddeus and Louisa (born in 1831). When the twins died, the Smiths adopted another set of twins, Julia and Joseph Murdock, whose mother had recently died in childbirth; the adopted Smith died ofmeasles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
in 1832. In 1841, Don Carlos, who had been born a year earlier, died of malaria, and five months later, in 1842, Emma gave birth to a stillborn son.
Joseph and Emma had five children who lived to maturity: adopted Julia Murdock, Joseph Smith III, David Hyrum Smith, Frederick Granger Williams Smith, and Alexander Hale Smith. Some historians have speculated—based on journal entries and family stories—that Smith fathered children with his plural wives. However, in cases where DNA testing of potential Smith descendants from plural wives has been possible, results have been negative.
After Smith's death, Emma was quickly alienated from Young and the LDS leadership. Emma feared and despised Young, who in turn was suspicious of Emma's desire to preserve the family's assets from inclusion with those of the church. He also disliked her open opposition to plural marriage. Young excluded Emma from ecclesiastical meetings and from social gatherings. When most Mormons moved west, Emma stayed in Nauvoo and married a non-Mormon, Major Lewis C. Bidamon. She withdrew from religion until 1860, when she affiliated with the RLDS Church headed by her son, Joseph III. Emma maintained her belief that Smith had been a prophet, and she never repudiated her belief in the authenticity of the Book of Mormon.
Polygamy
By some accounts, Smith had been teaching a polygamy doctrine as early as 1831, and there is evidence that he may have been a polygamist by 1835. Although the church had publicly repudiated polygamy, in 1837 there was a rift between Smith and Cowdery over the issue. Cowdery suspected Smith had engaged in a relationship with Fanny Alger, who worked in the Smith household as a serving girl. Smith did not deny having a relationship, but he insisted that he had never admitted toadultery
Adultery is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral, or legal grounds. Although the sexual activities that constitute adultery vary, as well as the social, religious, and legal consequences, the concept ...
. "Presumably", historian Bushman argues, "because he had married Alger" as a plural wife.
In April 1841, Smith secretly wed Louisa Beaman, and during the next two-and-a-half years he secretly married or was sealed to about thirty or forty additional women. Ten of his plural wives were between the ages of fourteen and twenty; others were over fifty. Ten were already married to other men, though some of these polyandrous marriages were contracted with the consent of the first husbands. Evidence for whether and to what degree Smith's polygamous marriages involved sex is ambiguous and varies between marriages. Some polygamous marriages may have been considered solely religious marriages that would not take effect until after death. In any case, during Smith's lifetime, the practice of polygamy was kept secret from both non-Mormons and most members of the church. Polygamy caused a breach between Smith and his first wife, Emma; historian Laurel Thatcher Ulrich summarizes by stating that "Emma vacillated in her support for plural marriage, sometimes acquiescing to Joseph's sealings, sometimes resisting".
Revelations
 According to Bushman, the "signal feature" of Smith's life was "his sense of being guided by revelation". Instead of presenting his ideas with logical arguments, Smith dictated authoritative scripture-like "revelations" and let people decide whether to believe, doing so with what Peter Coviello calls "beguiling offhandedness". Smith and his followers treated his revelations as being above teachings or opinions, and he acted as though he believed in his revelations as much as his followers. The revelations were written as if God himself were speaking through Smith, often opening with words such as, "Hearken O ye people which profess my name, saith the Lord your God".
According to Bushman, the "signal feature" of Smith's life was "his sense of being guided by revelation". Instead of presenting his ideas with logical arguments, Smith dictated authoritative scripture-like "revelations" and let people decide whether to believe, doing so with what Peter Coviello calls "beguiling offhandedness". Smith and his followers treated his revelations as being above teachings or opinions, and he acted as though he believed in his revelations as much as his followers. The revelations were written as if God himself were speaking through Smith, often opening with words such as, "Hearken O ye people which profess my name, saith the Lord your God".
Book of Mormon
The Book of Mormon has been called the longest and most complex of Smith's revelations. Its language resembles theKing James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version (AV), is an Early Modern English Bible translations, Early Modern English translation of the Christianity, Christian Bible for the Church of England, wh ...
of the Bible, as does its organization as a compilation of smaller books, each named after prominent figures in the narrative. It tells the story of the rise and fall of a Judeo-Christian religious civilization in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, ...
,; beginning about 600 BC and ending in the fifth century. The book explains itself to be largely the work of Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into several ...
, a Nephite prophet and military figure. Christian themes permeate the work.
Some scholars have considered the Book of Mormon a response to pressing cultural and environmental issues in Smith's day. Historian Dan Vogel regards the book as autobiographical in nature, reflecting Smith's life and perceptions. Biographer Robert V. Remini calls the Book of Mormon "a typically American story" that "radiates the revivalist passion of the Second Great Awakening". Brodie suggested that Smith composed the Book of Mormon by drawing on sources of information available to him, such as the 1823 book '' View of the Hebrews.'' Other scholars argue the Book of Mormon is more biblical in inspiration than American. Bushman writes that "the Book of Mormon is not a conventional American book" and that its structure better resembles the Bible. According to historian Daniel Walker Howe, the book's "dominant themes are biblical, prophetic, and patriarchal, not democratic or optimistic" like the prevailing American culture. Shipps argues that the Book of Mormon's "complex set of religious claims" provided "the basis of a new mythos" or "story" which early converts accepted and lived in as their world, thus departing from "the early national period in America into a new dispensation of the fulness of times".
 Smith never fully described how he produced the Book of Mormon, saying only that he translated by the power of God and implying that he had read its words. The Book of Mormon itself states only that its text will "come forth by the gift and power of God unto the interpretation thereof". Accordingly, there is considerable disagreement about the actual method used. For at least some of the earliest dictation, Smith's compatriots said he used the "Urim and Thummim", a pair of seer stones he said were buried with the plates. However, people close to Smith said that later in the process of dictation, he used a chocolate-colored stone he had found in 1822 that he had used previously for treasure hunting. Joseph Knight said that Smith saw the words of the translation while, after excluding all light, he gazed at the stone or stones in the bottom of his hat, a process similar to divining the location of treasure. Sometimes, Smith concealed the process by raising a curtain or dictating from another room; at other times he dictated in full view of witnesses while the plates lay covered on the table or were hidden elsewhere.
Smith never fully described how he produced the Book of Mormon, saying only that he translated by the power of God and implying that he had read its words. The Book of Mormon itself states only that its text will "come forth by the gift and power of God unto the interpretation thereof". Accordingly, there is considerable disagreement about the actual method used. For at least some of the earliest dictation, Smith's compatriots said he used the "Urim and Thummim", a pair of seer stones he said were buried with the plates. However, people close to Smith said that later in the process of dictation, he used a chocolate-colored stone he had found in 1822 that he had used previously for treasure hunting. Joseph Knight said that Smith saw the words of the translation while, after excluding all light, he gazed at the stone or stones in the bottom of his hat, a process similar to divining the location of treasure. Sometimes, Smith concealed the process by raising a curtain or dictating from another room; at other times he dictated in full view of witnesses while the plates lay covered on the table or were hidden elsewhere.
Bible revision
In June 1830, Smith dictated a revelation in which Moses narrates a vision in which he sees "worlds without number" and speaks with God about the purpose of creation and the relation of humankind to deity. This revelation initiated a revision of the Bible which Smith worked on sporadically until 1833 but which remained unpublished until after his death.; He may have considered it complete, though according to Emma Smith, the biblical revision was still unfinished when Joseph died. In the course of producing the Book of Mormon, Smith declared that the Bible was missing "the most plain and precious parts of the gospel". He produced a "new translation" of the Bible, not by directly translating from manuscripts in another language, but by amending and appending to aKing James Bible
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version (AV), is an Early Modern English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by ...
in a process which he and Latter Day Saints believed was guided by inspiration; Smith asserted his translation would correct lacunae and restore what the contemporary Bible was missing. While many changes involved straightening out seeming contradictions or making small clarifications, other changes added large interpolations to the text. For example, Smith's revision nearly tripled the length of the first five chapters of Genesis into a text called the Book of Moses.
Book of Abraham
In 1835, Smith encouraged some Latter Day Saints in Kirtland to purchase rolls of ancient Egyptian papyri from a traveling exhibitor. He said they contained the writings of the ancient patriarchs Abraham andJoseph
Joseph is a common male name, derived from the Hebrew (). "Joseph" is used, along with " Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the modern-day Nordic count ...
. Over the next several years, Smith dictated to scribes what he reported was a revelatory translation of one of these rolls, which was published in 1842 as the Book of Abraham
The Book of Abraham is a religious text of the Latter Day Saint movement, first published in 1842 by Joseph Smith. Smith said the book was a translation from several Egyptian scrolls discovered in the early 19th century during an archeologic ...
. The Book of Abraham speaks of the founding of the Abrahamic nation, astronomy, cosmology, lineage and priesthood, and gives another account of the creation story. The papyri associated with the Book of Abraham were thought to have been lost in the Great Chicago Fire
The Great Chicago Fire was a conflagration that burned in the American city of Chicago, Illinois during October 8–10, 1871. The fire killed approximately 300 people, destroyed roughly of the city including over 17,000 structures, and left mor ...
, but several fragments were rediscovered in the 1960s. Egyptologists have subsequently determined them to be part of the Egyptian Book of Breathing with no connection to Abraham.
In his revisions of the Bible, and production of the Book of Abraham he taught that Black people
Black is a racial classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid- to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin and often additional phenotypical ...
were cursed by God with the curses placed on Cain and Ham, and linked the two curses by positioning Ham's Canaanite posterity as matrilinear descendants of Cain
Cain is a biblical figure in the Book of Genesis within Abrahamic religions. He is the elder brother of Abel, and the firstborn son of Adam and Eve, the first couple within the Bible. He was a farmer who gave an offering of his crops to God. How ...
. In another book of the Pearl of Great Price the descendants of Cain are described as dark-skinned. He referred to the curses as a justification for slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
.
Other revelations
According to Pratt, Smith dictated his revelations, which were recorded by a scribe without revisions or corrections. Revelations were immediately copied and then circulated among church members. Smith's revelations often came in response to specific questions. He described the revelatory process as having "pure Intelligence" flowing into him. Smith, however, never viewed the wording to be infallible. The revelations were not God's words verbatim, but "couched in language suitable to Joseph's time". In 1833, Smith edited and expanded many of the previous revelations, publishing them as the Book of Commandments, which later became part of theDoctrine and Covenants
The Doctrine and Covenants (sometimes abbreviated and cited as D&C or D. and C.) is a part of the open scriptural canon of several denominations of the Latter Day Saint movement. Originally published in 1835 as Doctrine and Covenants of the Chur ...
.
Smith gave varying types of revelations. Some were temporal, while others were spiritual or doctrinal. Some were received for a specific individual, while others were directed at the whole church. An 1831 revelation called "The Law" contained directions for missionary work, rules for organizing society in Zion, a reiteration of the Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments (), or the Decalogue (from Latin , from Ancient Greek , ), are religious and ethical directives, structured as a covenant document, that, according to the Hebrew Bible, were given by YHWH to Moses. The text of the Ten ...
, an injunction to "administer to the poor and needy" and an outline for the law of consecration. An 1832 revelation called "The Vision" added to the fundamentals of sin and atonement, and introduced doctrines of life after salvation, exaltation, and a heaven with degrees of glory. Another 1832 revelation was the first to explain priesthood doctrine.
In 1833, at a time of temperance agitation, Smith delivered a revelation called the " Word of Wisdom", which counseled a diet of wholesome herbs, fruits, grains and a sparing use of meat. It also recommended that Latter Day Saints avoid "strong" alcoholic drinks, tobacco, and "hot drinks" (later interpreted to mean tea and coffee). The Word of Wisdom was originally framed as a recommendation rather than a commandment and was not strictly followed by Smith and other early Latter Day Saints, though it later became a requirement in the LDS Church.
Before 1832, most of Smith's revelations concerned establishing the church, gathering followers, and building the city of Zion. Later revelations dealt primarily with the priesthood, endowment, and exaltation. The pace of formal revelations slowed during the autumn of 1833 and again after the dedication of the Kirtland Temple. Smith moved away from formal written revelations spoken in God's voice, and instead taught more in sermons, conversations, and letters. For instance, the doctrines of baptism for the dead and the nature of God were introduced in sermons, and one of Smith's most famed statements, about there being "no such thing as immaterial matter", was recorded from a casual conversation with a Methodist preacher.
Views and teachings

Cosmology and theology
Smith taught that all existence wasmaterial
A material is a matter, substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an Physical object, object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical property, physical ...
, including a world of "spirit matter" so fine that it was invisible to all but the purest mortal eyes. Matter, in Smith's view, could be neither created nor destroyed; the creation involved only the reorganization of existing matter. Like matter, Smith saw "intelligence" as co-eternal with God, and he taught that human spirits had been drawn from a pre-existent pool of eternal intelligences. Nevertheless, according to Smith, spirits could not experience a "fullness of joy" unless joined with corporeal bodies. Therefore, the work and glory of God was to create worlds across the cosmos where inferior intelligences could be embodied.
Smith taught that God was an advanced and glorified man, embodied within time and space. He publicly taught that God the Father and Jesus were distinct beings with physical bodies. Nevertheless, he conceived of the Holy Spirit
The Holy Spirit, otherwise known as the Holy Ghost, is a concept within the Abrahamic religions. In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is understood as the divine quality or force of God manifesting in the world, particularly in acts of prophecy, creati ...
as a "personage of Spirit". Smith extended this materialist conception to all existence and taught that "all spirit is matter", meaning that a person's embodiment in flesh was not a sign of fallen carnality, but a divine quality that humans shared with deity. Humans are, therefore, not so much God's creations as they are God's "kin". There is also considerable evidence that Smith taught, at least to limited audiences, that God the Father was accompanied by God the Mother. In this conception, God fully understood is plural, embodied, gendered, and both male and female.
Through the gradual acquisition of knowledge, according to Smith, those who received exaltation could eventually become like God. These teachings implied a vast hierarchy of gods, with God himself having a father. In Smith's cosmology, those who became gods would reign, unified in purpose and will, leading spirits of lesser capacity to share immortality and eternal life.
In Smith's view, the opportunity to achieve godhood (also called exaltation) extended to all humanity. Those who died with no opportunity to accept saving ordinances could achieve exaltation by accepting them in the afterlife through proxy ordinances performed on their behalf. Smith said that children who died in their innocence would be guaranteed to rise at the resurrection and receive exaltation. Apart from those who committed the eternal sin
In Christian hamartiology, eternal sin, the unforgivable sin, unpardonable sin, or ultimate sin is the sin which will not be forgiven by God. One eternal or unforgivable sin (blasphemy against the Holy Spirit), also known as the sin unto death, ...
, Smith taught that even the wicked and disbelieving would achieve a degree of glory in the afterlife.
Religious authority and ritual
Smith's teachings were rooted in dispensationalrestorationism
Restorationism, also known as Christian primitivism, is a religious perspective according to which the early beliefs and practices of the followers of Jesus were either lost or adulterated after Crucifixion of Jesus, his death and required a "r ...
. He taught that the Church of Christ restored through him was a latter-day restoration of the early Christian faith, which had been lost in the Great Apostasy
The Great Apostasy is a concept within Christianity to describe a perception that mainstream Christian Churches have fallen away from the original faith founded by Jesus in Christianity, Jesus and promulgated through his Twelve Apostles.
A bel ...
. At first, Smith's church had little sense of hierarchy, and his religious authority was derived from his visions and revelations. Though he did not claim exclusive prophethood, an early revelation designated him as the only prophet allowed to issue commandments "as Moses". This religious authority included economic and political, as well as spiritual, matters. For instance, in the early 1830s, Smith temporarily instituted a form of religious communism, called the United Order, that required Latter Day Saints to give all their property to the church, to be divided among the faithful. He also envisioned that the theocratic institutions he established would have a role in the worldwide political organization of the Millennium.
By the mid-1830s, Smith began teaching a hierarchy of three priesthoods—the Melchizedek
In the Hebrew Bible, Melchizedek was the king of Salem and priest of (often translated as 'most high God'). He is first mentioned in Genesis 14:18–20, where he brings out bread and wine and then blesses Abraham, and El Elyon or "the Lord, Go ...
, the Aaronic, and the Patriarchal
Patriarchy is a social system in which positions of authority are primarily held by men. The term ''patriarchy'' is used both in anthropology to describe a family or clan controlled by the father or eldest male or group of males, and in fem ...
. Each priesthood was a continuation of biblical priesthoods through lineal succession or through ordination by biblical figures appearing in visions. Upon introducing the Melchizedek or "High" Priesthood in 1831, Smith taught that its recipients would be "endowed with power from on high", fulfilling a desire for a greater holiness and an authority commensurate with the New Testament apostles. This doctrine of endowment evolved through the 1830s until, in 1842, the Nauvoo endowment included an elaborate ceremony containing elements similar to those of Freemasonry and the Jewish Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ...
. Although the endowment was extended to women in 1843, Smith never clarified whether women could be ordained to priesthood offices.
Smith taught that the High Priesthood's endowment of heavenly power included the sealing powers of Elijah, allowing High Priests to perform ceremonies with effects that continued after death. For example, this power would enable proxy baptisms for the dead and marriages that would last into eternity. Elijah's sealing powers also enabled the second anointing, or "fulness of the priesthood", which, according to Smith, sealed married couples to their exaltation.
Theology of family
During the early 1840s, Smith unfolded a theology of family relations, called the "New and Everlasting Covenant", that superseded all earthly bonds. He taught that outside the covenant, marriages were simply matters of contract, and that in the afterlife, individuals who were unmarried or who married outside the covenant would be limited in their progression towards Godhood. To fully enter the covenant, a man and woman must participate in a "first anointing", a "sealing" ceremony, and a "second anointing" (also called "sealing by the Holy Spirit of Promise"). When fully sealed into the covenant, Smith said that no sin nor blasphemy (other than murder and apostasy) could keep them from their exaltation in the afterlife. According to a revelation Smith dictated, God appointed only one person on Earth at a time—in this case, Smith—to possess this power of sealing. According to Smith, men and women needed to be sealed to each other in this new and everlasting covenant (also called "celestial marriage") in order to be exalted in heaven after death and that such celestial marriage, perpetuated across generations, could reunite extended families of ancestors and descendants in the afterlife. Plural marriage, or polygamy, was Smith's "most famous innovation", according to historian Matthew Bowman. Once Smith introduced polygamy, it became part of his "Abrahamic project", in the phrasing of historian Benjamin Park, wherein the solution to humanity's chaos would be found through accepting the divine order of the cosmos, under God's authority, in a "fusion of ecclesiastical and civic authority". Smith also taught that the highest level of exaltation could be achieved through polygamy, the ultimate manifestation of the New and Everlasting Covenant. In Smith's theology, marrying in polygamy made it possible for practitioners to unlearn the Christian tradition which identified the physical body as carnal, and to instead recognize their embodied joy as sacred. Smith also taught that the practice allowed an individual to transcend the angelic state and become a god, accelerating the expansion of one's heavenly kingdom.; ; ;See also
*History of the Latter Day Saint movement
The Latter Day Saint movement is a religious movement within Christianity that arose during the Second Great Awakening in the early 19th century and that led to the set of doctrines, practices, and cultures called ''Mormonism'', and to the exis ...
* List of founders of religious traditions
These are historical figures credited with founding religions or religious philosophies, or who codified older known religious traditions. The list includes those who have founded a specific major denomination within a larger religion.
Legend ...
* Miracles attributed to Joseph Smith
* Mormonism in the 19th century
* Outline of Joseph Smith
* Smith family (Latter Day Saints)
The Smith family is the name of an American family with many members prominent in religion and politics. The family's most famous member was Joseph Smith, Joseph Smith Jr., founder of the Latter Day Saint movement. Many other members of the family ...
Notes
Citations
References
* . * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * SeeDoctrine and Covenants
The Doctrine and Covenants (sometimes abbreviated and cited as D&C or D. and C.) is a part of the open scriptural canon of several denominations of the Latter Day Saint movement. Originally published in 1835 as Doctrine and Covenants of the Chur ...
.
* See The History of Joseph Smith by His Mother
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
* * *Official LDS Church site about Joseph Smith
JosephSmithPapers.org
��An LDS Church project compiling
primary
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Work ...
documents relating to Joseph Smith
Recently-discovered photo of Smith
{{DEFAULTSORT:Smith, Joseph 1805 births 1844 deaths 19th-century American male writers 19th-century American non-fiction writers 19th-century apocalypticists 19th-century Christian mystics Politicians assassinated in the 1840s Abolitionists from Illinois American city founders American faith healers American founders American Freemasons American Latter Day Saint leaders American Latter Day Saint missionaries American male non-fiction writers American militia generals American murder victims American people of English descent Angelic visionaries Apostles of the Church of Christ (Latter Day Saints) Assassinated American politicians Assassinated mayors Assassinated religious leaders Book of Mormon witnesses Burials at the Smith Family Cemetery Candidates in the 1844 United States presidential election Child marriage in the United States Christian abolitionists Christian miracle workers Deaths by firearm in Illinois Dispensationalism Doctrine and Covenants people Editors of Latter Day Saint publications Founders of new religious movements History of the Latter Day Saint movement Latter Day Saint martyrs Latter Day Saint missionaries in Canada Latter Day Saint missionaries in the United States Latter Day Saints from Illinois Latter Day Saints from Missouri Latter Day Saints from New York (state) Latter Day Saints from Ohio Latter Day Saints from Vermont Lynching deaths in Illinois Mayors of Nauvoo, Illinois Mormon mystics Nauvoo Legion People from Ontario County, New York People from Palmyra, New York People from Windsor County, Vermont People murdered in Illinois Presidents of the Church (LDS Church) Prophet-Presidents of the Community of Christ Smith Religious leaders from New York (state) Religious leaders from Vermont Seership in Mormonism Smith family (Latter Day Saints) Tarring and feathering in the United States Treasure hunters Victims of religiously motivated violence in the United States People murdered in 1844