IĹ‚owa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
IĹ‚owa () is a
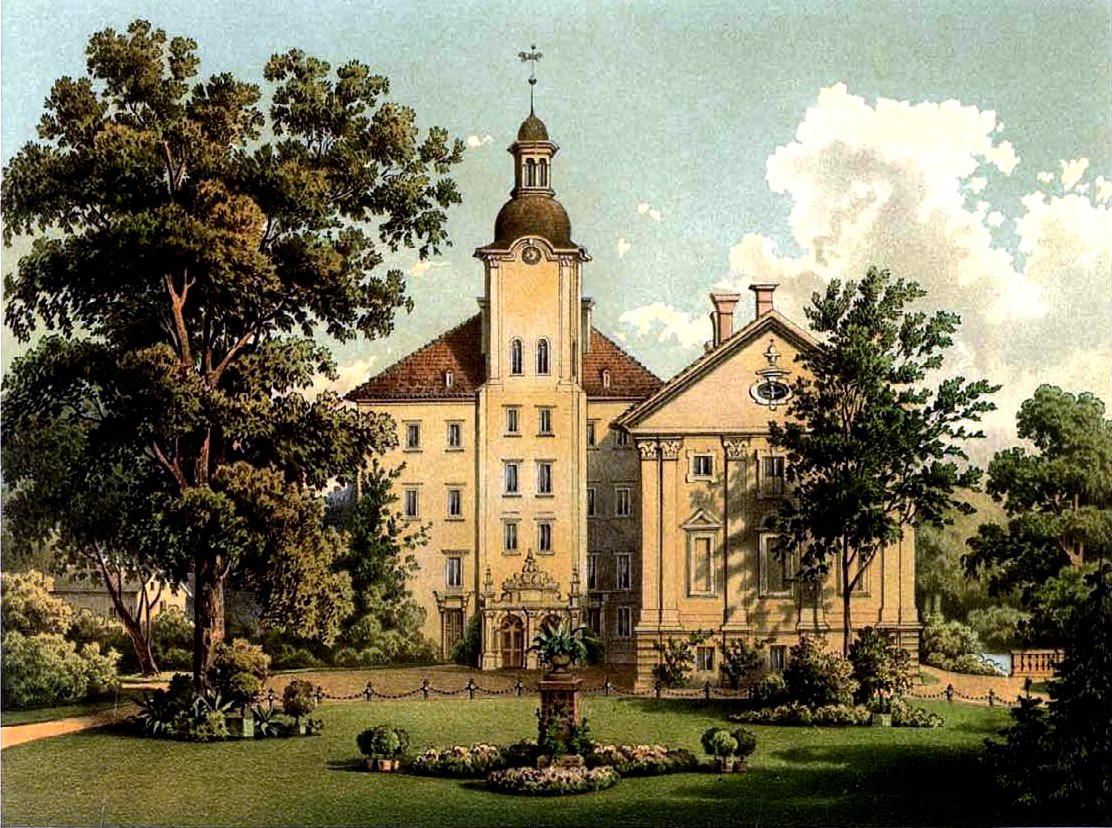 According to an annex to the 1635 Peace of Prague, IĹ‚owa together with Upper Lusatia passed from the
According to an annex to the 1635 Peace of Prague, IĹ‚owa together with Upper Lusatia passed from the
Official town webpage
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Lubusz Voivodeship Żagań County 10th-century establishments in Poland
town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city.
The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ...
in Żagań County
__NOTOC__
Żagań County () is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lubusz Voivodeship, western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its a ...
, in Lubusz Voivodeship
Lubusz Voivodeship ( ) is a voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) in western Poland with a population of 972,140. Its regional capitals are GorzĂłw Wielkopolski and Zielona GĂłra. The region is characterized by a landscape of forests, lake ...
, in western Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, the administrative seat of the Gmina IĹ‚owa
__NOTOC__
Gmina Iłowa is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Żagań County, Lubusz Voivodeship, in western Poland. Its seat is the town of Iłowa, which lies approximately south-west of Żagań and south-west of Zielona Góra.
Th ...
.
Geography
It lies in the easternmost part of the historicUpper Lusatia
Upper Lusatia (, ; , ; ; or ''Milsko''; ) is a historical region in Germany and Poland. Along with Lower Lusatia to the north, it makes up the region of Lusatia, named after the Polabian Slavs, Slavic ''Lusici'' tribe. Both parts of Lusatia a ...
region, at the border with Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a historical and geographical region mostly located in Poland with small portions in the Czech Republic and Germany. It is the western part of the region of Silesia. Its largest city is Wrocław.
The first ...
. The settlement is located on the Czerna Mała river, a tributary to the Bóbr
The BĂłbr (; ; ) is a river which flows through the north of the Czech Republic and the southwest of Poland. It is a left tributary of the Oder. Its Polish name translates directly to ' beaver'.
Course
The BĂłbr has a length of (3 in Czech ...
, in the Silesian-Lusatian Lowlands
Silesian-Lusatian Lowlands (or Silesian-Lusatian Uplands, ) are lowlands located in Silesia, Poland and Germany.
See also
* Silesian Highlands
* Silesian Lowlands
* Silesian Foothills
Silesian Foothills (, , ) are foothills located in Silesian ...
. It is situated on the rim of the Lower Silesian Wilderness
Lower Silesian Forest () is the largest continuous forest of Poland, with total area of 1650 square kilometers. It is located in southwestern Poland, in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship and the Lubusz Voivodeship, near border with Germany. Western ...
and just south of the A18 autostrada.
History
The settlement arose in the 10th century, at the crossroad of the trade routes fromGörlitz
Görlitz (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, East Lusatian: , , ) is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is on the river Lusatian Neisse and is the largest town in Upper Lusatia, the second-largest town in the region of Lusatia after ...
to Żagań
Żagań (French language, French and , ) is a town in western Poland, on the Bóbr river, with 25,731 inhabitants (2019), capital of Żagań County in the Lubusz Voivodeship, located in the historic region of Lower Silesia.
Founded in the 12th ce ...
and from Gubin to Legnica
Legnica (; , ; ; ) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River and the Czarna Woda. As well as being the seat of the county, since 1992 the city has been the seat of the Diocese of Legnica. Le ...
. The medieval chronicler Thietmar of Merseburg
Thietmar (also Dietmar or Dithmar; 25 July 9751 December 1018), Prince-Bishop of Merseburg from 1009 until his death in 1018, was an important chronicler recording the reigns of German kings and Holy Roman Emperors of the Ottonian (Saxon) dynas ...
(975–1018) mentioned a castle of ''Ilva'', where in 1000 AD the Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
* Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin ...
duke Bolesław I Chrobry
Bolesław or Boleslav may refer to:
People
* Bolesław (given name) (also ''Boleslav'' or ''Boleslaus''), including a list of people with this name
Geography
* Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland
* Bolesław, Olkusz Coun ...
met with Emperor Otto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was the Holy Roman emperor and King of Italy from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was c ...
on his journey from the canonization of Bishop Adalbert of Prague
Adalbert of Prague (, , , , ; 95623 April 997), known in the Czech Republic, Poland and Slovakia by his birth name Vojtěch (), was a Czech missionary and Christian saint. He was the Bishop of Prague and a missionary to the Hungarians, Poles, ...
to the Congress of Gniezno
The Congress of Gniezno (, or ''Gnesener Übereinkunft'') was an amicable meeting between the Polish Duke Bolesław I the Brave and Emperor Otto III, which took place at Gniezno in Poland on 11 March 1000. Scholars disagree over the details o ...
. As a result of the fragmentation of Poland, from the 12th century onwards, the border fortress was controlled by the Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of King Casimir III the Great.
Branches of ...
dukes of Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
. IĹ‚owa's inhabitants took part in the 1241 Battle of Legnica
The Battle of Legnica (), also known as the Battle of Liegnitz () or Battle of Wahlstatt (), was fought between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces at the village of Legnickie Pole (''Wahlstatt''), approximately southeast of the ci ...
against the invading Mongols.
IĹ‚owa itself is first documented in a 1356 deed by the Bohemian
Bohemian or Bohemians may refer to:
*Anything of or relating to Bohemia
Culture and arts
* Bohemianism, an unconventional lifestyle, originally practised by 19th–20th century European and American artists and writers.
* Bohemian style, a ...
king and Emperor Charles IV, when he granted the fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
of ''das halbe Dorf an der Czirne'' (i.e. half the village on the Czerna River, later called ''Halbau'') at the border with the Silesian Duchy of Żagań
The Duchy of Żagań (, ) or Duchy of Sagan () was one of the duchies of Silesia ruled by the Silesian Piasts. Its capital was Żagań in Lower Silesia, the territory stretched to the town of Nowogród Bobrzański in the north and reached the Lusa ...
to the Kotowice noble family. Mining and smelting of bog iron
Bog iron is a form of impure iron deposit that develops in bogs or swamps by the chemical or biochemical oxidation of iron carried in solution. In general, bog ores consist primarily of iron oxyhydroxides, commonly goethite (FeO(OH)).
Iron-beari ...
in the area is documented since the 15th century. The Kotowice family had a castle built here, that later became a notorious robber baron stronghold and was later destroyed by armed forces of the Lusatian League
The Lusatian League () was a historical alliance of six towns in the region of Upper Lusatia from 1346 until 1815, when the region was controlled first by Bohemia (1346–1635) and later by the Electorate of Saxony (1635–1815). The member towns ...
at the behest of the Görlitz citizens in 1440. The Kotowice dynasty sold the estates of Halbau together with neighbouring Konin
Konin () is a city in central Poland, on the Warta River. It is the capital of Konin County and is located within the Greater Poland Voivodeship. In 2021 the population of the city was 71,427, making it the fourth-largest city in Greater Poland af ...
to the Upper Lusatian state country
State country (; ; ) was a unit of administrative and territorial division in the Bohemian crown lands of Silesia and Upper Lusatia, existing from 15th to 18th centuries. These estates were exempt from feudal tenure by privilege of the Bohemian ...
of Königsbrück
Königsbrück (Upper Sorbian language, Upper Sorbian name: ''Kinspork'', ) is a town in the Bautzen (district), Bautzen district, in Saxony, in eastern Germany. It is situated west of Kamenz, and northeast of the Saxon capital Dresden. Königsbrà ...
in 1567.
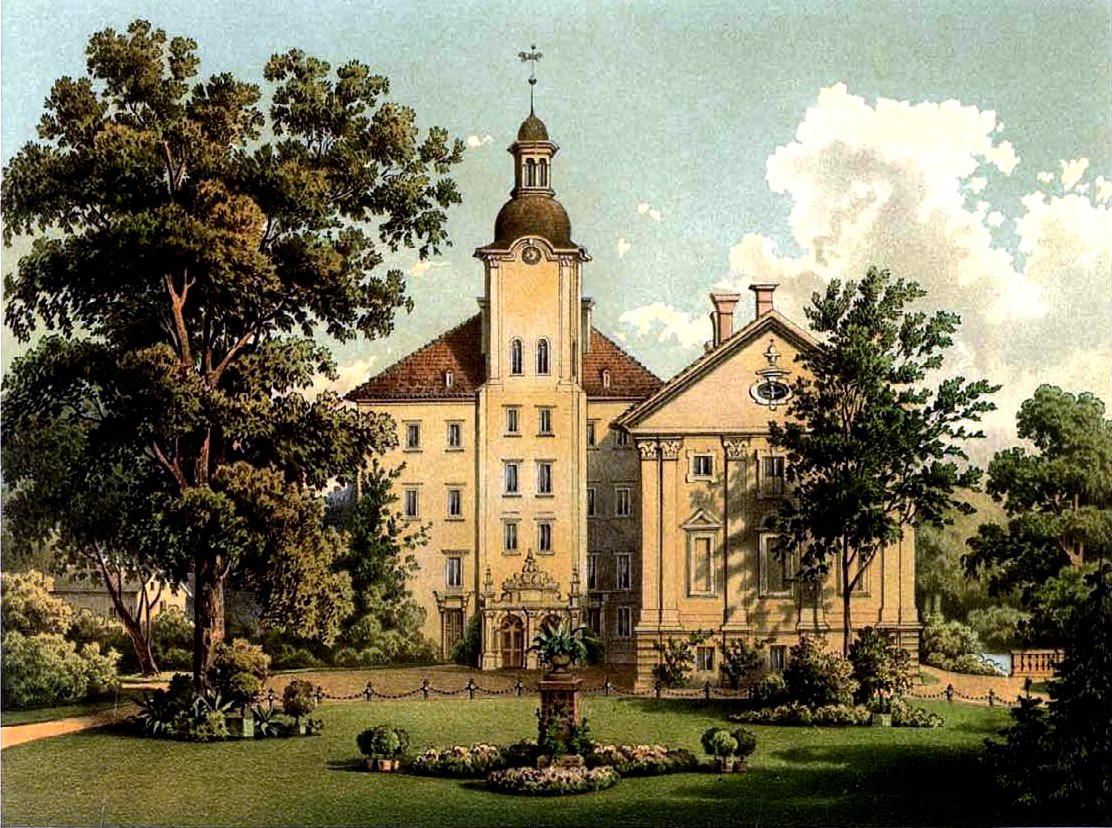 According to an annex to the 1635 Peace of Prague, IĹ‚owa together with Upper Lusatia passed from the
According to an annex to the 1635 Peace of Prague, IĹ‚owa together with Upper Lusatia passed from the Lands of the Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were the states in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and early modern periods with feudalism, feudal obligations to the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted o ...
to the Wettin elector John George I of Saxony
John George I (5 March 1585 – 8 October 1656) was Elector of Saxony from 1611 to 1656. He led Saxony through the Thirty Years' War, which dominated his 45-year reign.
Biography
Born in Dresden, John George was the second son of the Elector C ...
. Under the rule of his successor Elector John George II, a Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
church was built and the settlement received town privileges
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the traditio ...
in 1679. From 1682 it was incorporated as a southern exclave into the Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the Germany, German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the south, Lower Lusa ...
n lordship of Żary
Żary (, , , ) is a town in western Poland with 37,502 inhabitants (2019), situated in the Lubusz Voivodeship. It is the administrative seat of the Żary County and of the Gmina Żary within the county, though the town is not part of the gmina (c ...
held by the Promnitz noble family. Between 1697 and 1815 it was also under rule of Polish monarchs in personal union.
After the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
the town was annexed by Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
in 1815, and became part of the province of Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the Germans operated the Dulag A and Dulag B transit camps for Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
* Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin ...
prisoners of war in the town in 1939–1940, and a subcamp
Subcamps were outlying detention centres (''Haftstätten'') that came under the command of a main Nazi concentration camps, concentration camp run by the SS in Nazi Germany and German-occupied Europe. The Nazis distinguished between the List of N ...
of the Gross-Rosen concentration camp
Gross-Rosen was a network of Nazi concentration camps built and operated by Nazi Germany during World War II. The main camp was located in the German village of Gross-Rosen, now the modern-day RogoĹşnica in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Poland, di ...
, whose prisoners were mostly Poles, but also Russians, Czechs, Italians, French, Greeks, Yugoslavs, Dutch and Germans, in 1944–1945. On 12 February 1945, most prisoners were sent on a death march
A death march is a forced march of prisoners of war, other captives, or deportees in which individuals are left to die along the way. It is distinct from simple prisoner transport via foot march. Article 19 of the Geneva Convention requires tha ...
to the Bergen-Belsen concentration camp
Bergen-Belsen (), or Belsen, was a Nazi concentration camp in what is today Lower Saxony in Northern Germany, northern Germany, southwest of the town of Bergen, Lower Saxony, Bergen near Celle. Originally established as a prisoner of war camp, ...
, whereas those sick or unable to march were left in the subcamp, where they were eventually liberated by 20 February. After Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
's defeat in the war, the abandoned town once again became part of Poland. IĹ‚owa's first post-war Polish wĂłjt
A wĂłjt is the highest administrative officer of a Polish ''rural gmina'', i.e., of a commune (''gmina'') comprising only villages. (The head of a town or city is called, respectively, the ''burmistrz'' or "president".)
History and etymology
T ...
was Stefan Urbański, a former forced labourer
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, or violence, including death or other forms of ...
returning from Germany.
After the war the village Żaków and the eastern part of the village Karolinów have been incorporated into the town limits. Town privileges were restored in 1962.
Notable people
* Friedrich Boser (1811–1881), artistTwin towns – sister cities
See twin towns of Gmina IĹ‚owa.References
External links
Official town webpage
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Lubusz Voivodeship Żagań County 10th-century establishments in Poland