Islamic science on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the
Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the
 The Islamic era began in 622. Islamic armies eventually conquered
The Islamic era began in 622. Islamic armies eventually conquered 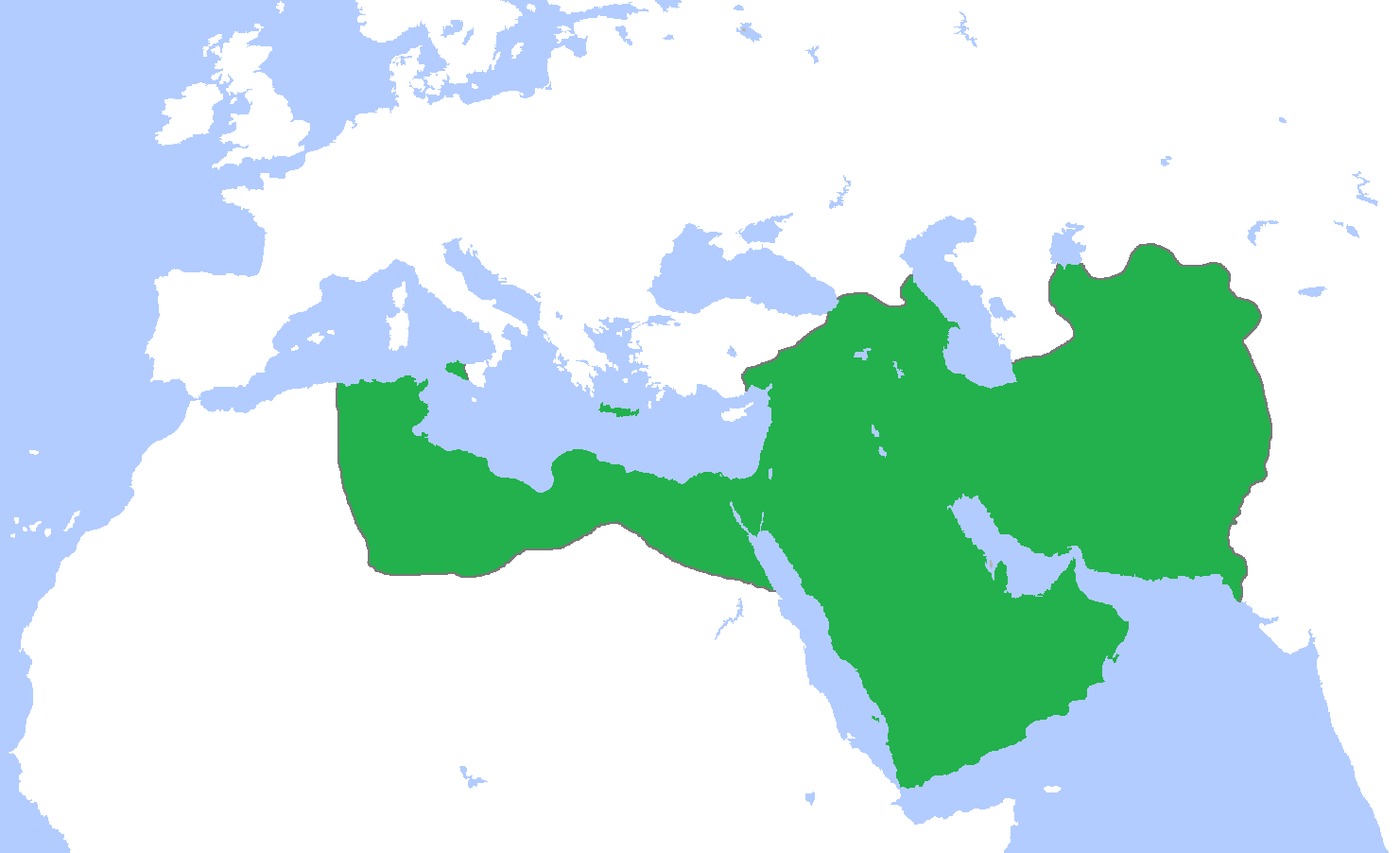 Islamic science survived the initial Christian reconquest of Spain, including the fall of
Islamic science survived the initial Christian reconquest of Spain, including the fall of
 Astronomy became a major discipline within Islamic science. Astronomers devoted effort both towards understanding the nature of the cosmos and to practical purposes. One application involved determining the ''Qibla'', the direction to face during prayer. Another was
Astronomy became a major discipline within Islamic science. Astronomers devoted effort both towards understanding the nature of the cosmos and to practical purposes. One application involved determining the ''Qibla'', the direction to face during prayer. Another was
 The spread of Islam across Western Asia and North Africa encouraged an unprecedented growth in trade and travel by land and sea as far away as Southeast Asia, China, much of Africa, Scandinavia and even Iceland. Geographers worked to compile increasingly accurate maps of the known world, starting from many existing but fragmentary sources.
The spread of Islam across Western Asia and North Africa encouraged an unprecedented growth in trade and travel by land and sea as far away as Southeast Asia, China, much of Africa, Scandinavia and even Iceland. Geographers worked to compile increasingly accurate maps of the known world, starting from many existing but fragmentary sources.
File:TabulaRogeriana upside-down.jpg, Modern copy of al-Idrisi's 1154 '' Tabula Rogeriana'', upside-down, north at top

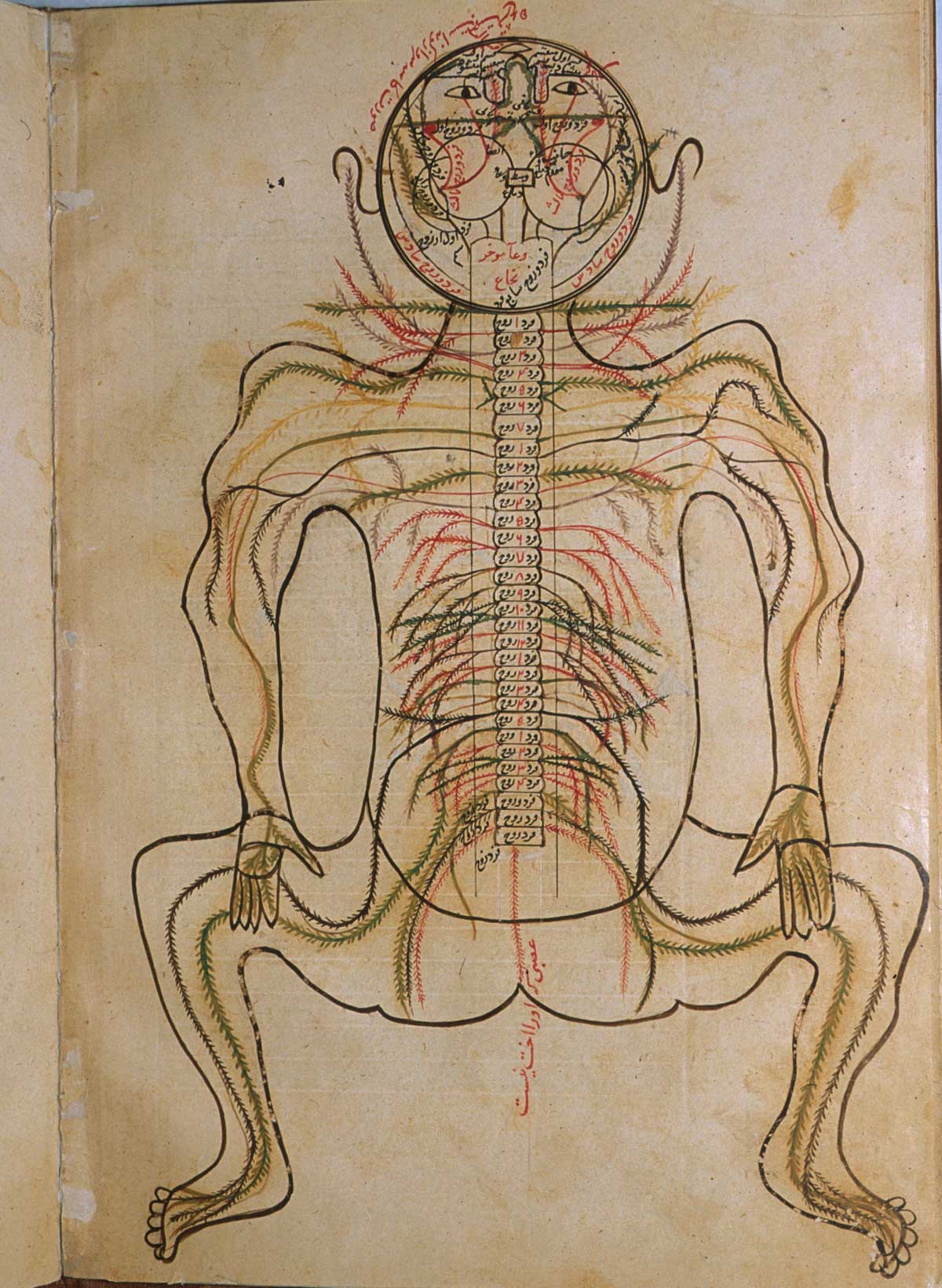 Islamic society paid careful attention to medicine, following a ''
Islamic society paid careful attention to medicine, following a ''

 Optics developed rapidly in this period. By the ninth century, there were works on physiological, geometrical and physical optics. Topics covered included mirror reflection.
Hunayn ibn Ishaq (809–873) wrote the book ''Ten Treatises on the Eye''; this remained influential in the West until the 17th century.
Optics developed rapidly in this period. By the ninth century, there were works on physiological, geometrical and physical optics. Topics covered included mirror reflection.
Hunayn ibn Ishaq (809–873) wrote the book ''Ten Treatises on the Eye''; this remained influential in the West until the 17th century.
Review on JSTOR, Toomer's 1964 review of Matthias Schramm (1963) ''Ibn Al-Haythams Weg Zur Physik''
Toomer p.464: "Schramm sums up bn Al-Haytham'sachievement in the development of scientific method."
 Advances in
Advances in
 The fields of physics studied in this period, apart from optics and astronomy which are described separately, are aspects of
The fields of physics studied in this period, apart from optics and astronomy which are described separately, are aspects of
 Many classical works, including those of Aristotle, were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle's zoology remained dominant in its field for two thousand years. The '' Kitāb al-Hayawān'' (كتاب الحيوان, English: ''Book of Animals'') is a 9th-century
Many classical works, including those of Aristotle, were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle's zoology remained dominant in its field for two thousand years. The '' Kitāb al-Hayawān'' (كتاب الحيوان, English: ''Book of Animals'') is a 9th-century
"How Greek Science Passed to the Arabs"
by De Lacy O'Leary * *Habibi, Golareh
is there such a thing as Islamic science? the influence of Islam on the world of science
''Science Creative Quarterly''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Science In Medieval Islam .Science Medieval history of the Middle East
 Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the
Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.
This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign o ...
under the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
of Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
, the Umayyads of Córdoba, the Abbadids of Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, ...
, the Samanids, the Ziyarids and the Buyids in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and beyond, spanning the period roughly between 786 and 1258. Islamic scientific achievements encompassed a wide range of subject areas, especially astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
, mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, and medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included alchemy and chemistry, botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
and agronomy
Agronomy is the science and technology of producing and using plants by agriculture for food, fuel, fiber, chemicals, recreation, or land conservation. Agronomy has come to include research of plant genetics, plant physiology, meteorology, and ...
, geography and cartography, ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a ...
, pharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur betwee ...
, physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, and zoology
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the anatomy, structure, embryology, Biological classification, classification, Ethology, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinction, extinct, and ...
.
Medieval Islamic science had practical purposes as well as the goal of understanding. For example, astronomy was useful for determining the ''Qibla
The qibla () is the direction towards the Kaaba in the Great Mosque of Mecca, Sacred Mosque in Mecca, which is used by Muslims in various religious contexts, particularly the direction of prayer for the salah. In Islam, the Kaaba is believed to ...
'', the direction in which to pray, botany had practical application in agriculture, as in the works of Ibn Bassal
Ibn Bassal () was an 11th-century Andalusian Arab botanist and agronomist in Toledo and Seville, Spain who wrote about horticulture and arboriculture. He is best known for his book on agronomy, the ''Dīwān al-filāha'' (An Anthology of Husb ...
and Ibn al-'Awwam
Ibn al-'Awwam (), also called Abu Zakariya Ibn al-Awwam (), was an Al-Andalus agriculturist who flourished at Seville (modern-day southern Spain) in the later 12th century. He wrote a lengthy handbook on agriculture entitled in Arabic '' Kitāb al ...
, and geography enabled Abu Zayd al-Balkhi
Abu Zayd Ahmed ibn Sahl Balkhi () was a Persian Muslim polymath: a geographer, mathematician, physician, psychologist and scientist. Born in 850 CE in Shamistiyan, in the province of Balkh, Greater Khorasan, he was a disciple of al-Kindi. He a ...
to make accurate maps. Islamic mathematicians such as Al-Khwarizmi
Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi , or simply al-Khwarizmi, was a mathematician active during the Islamic Golden Age, who produced Arabic-language works in mathematics, astronomy, and geography. Around 820, he worked at the House of Wisdom in B ...
, Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
and Jamshīd al-Kāshī
Ghiyāth al-Dīn Jamshīd Masʿūd al-Kāshī (or al-Kāshānī) ( ''Ghiyās-ud-dīn Jamshīd Kāshānī'') (c. 1380 Kashan, Iran – 22 June 1429 Samarkand, Transoxiana) was a Persian astronomer and mathematician during the reign of Tamerlane.
...
made advances in algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic ope ...
, trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The fiel ...
, geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician w ...
and Arabic numerals
The ten Arabic numerals (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9) are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation number with a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with Roman numera ...
. Islamic doctors described diseases like smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
and measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
, and challenged classical Greek medical theory. Al-Biruni, Avicenna and others described the preparation of hundreds of drugs
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestio ...
made from medicinal plants
Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including Plant defense against h ...
and chemical compounds. Islamic physicists such as Ibn Al-Haytham
Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham (Latinization of names, Latinized as Alhazen; ; full name ; ) was a medieval Mathematics in medieval Islam, mathematician, Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world, astronomer, and Physics in the medieval Islamic world, p ...
, Al-Bīrūnī and others studied optics and mechanics as well as astronomy, and criticised Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
's view of motion.
During the Middle Ages, Islamic science flourished across a wide area around the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
and further afield, for several centuries, in a wide range of institutions.
Context and history
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, and successfully displaced the Persian and Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
s from the region within a few decades. Within a century, Islam had reached the area of present-day Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
in the west and Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
in the east. The Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.
This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign o ...
(roughly between 786 and 1258) spanned the period of the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
(750–1258), with stable political structures and flourishing trade. Major religious and cultural works of the Islamic empire were translated into Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
and occasionally Persian. Islamic culture inherited Greek, Indic, Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n and Persian influences. A new common civilisation formed, based on Islam. An era of high culture
In a society, high culture encompasses culture, cultural objects of Objet d'art, aesthetic value that a society collectively esteems as exemplary works of art, as well as the literature, music, history, and philosophy a society considers represen ...
and innovation ensued, with rapid growth in population and cities. The Arab Agricultural Revolution in the countryside brought more crops and improved agricultural technology, especially irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
. This supported the larger population and enabled culture to flourish.McClellan and Dorn 2006, pp.103–115 From the 9th century onwards, scholars such as Al-Kindi translated India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
n, Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n, Sasanian (Persian) and Greek knowledge, including the works of Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, into Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
. These translations supported advances by scientists across the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
.
 Islamic science survived the initial Christian reconquest of Spain, including the fall of
Islamic science survived the initial Christian reconquest of Spain, including the fall of Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, ...
in 1248, as work continued in the eastern centres (such as in Persia). After the completion of the Spanish reconquest in 1492, the Islamic world went into an economic and cultural decline. The Abbasid caliphate was followed by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
( 1299–1922), centred in Turkey, and the Safavid Empire
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
(1501–1736), centred in Persia, where work in the arts and sciences continued.
Fields of inquiry
Medieval Islamic scientific achievements encompassed a wide range of subject areas, especiallymathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
, and medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, alchemy and chemistry, ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a ...
, and geography and cartography.
Alchemy and chemistry
The early Islamic period saw the development of theoretical frameworks inalchemy
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first ...
and chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, laying the foundation for later advancements in both fields. The sulfur-mercury theory of metals, first found in '' Sirr al-khalīqa'' ("The Secret of Creation", c. 750–850, falsely attributed to Apollonius of Tyana), and in the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan
Abū Mūsā Jābir ibn Ḥayyān (Arabic: , variously called al-Ṣūfī, al-Azdī, al-Kūfī, or al-Ṭūsī), died 806−816, is the purported author of a large number of works in Arabic, often called the Jabirian corpus. The treatises that ...
(written c. 850–950), vol. II, p. 1, note 1; remained the basis of theories of metallic composition until the 18th century. The '' Emerald Tablet'', a cryptic text that all later alchemists up to and including Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
saw as the foundation of their art, first occurs in the ''Sirr al-khalīqa'' and in one of the works attributed to Jabir. In practical chemistry, the works of Jabir, and those of the Persian alchemist and physician Abu Bakr al-Razi (c. 865–925), contain the earliest systematic classifications of chemical substances. Alchemists were also interested in artificially creating such substances. Jabir describes the synthesis of ammonium chloride
Ammonium chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula , also written as . It is an ammonium salt of hydrogen chloride. It consists of ammonium cations and chloride anions . It is a white crystalline salt (chemistry), sal ...
( sal ammoniac) from organic substances, and Abu Bakr al-Razi experimented with the heating of ammonium chloride, vitriol, and other salts, which would eventually lead to the discovery of the mineral acids by 13th-century Latin alchemists such as pseudo-Geber
Pseudo-Geber (or "Middle Latin, Latin pseudo-Geber") is the presumed author or group of authors responsible for a corpus of pseudepigraphic alchemical writings dating to the late 13th and early 14th centuries. These writings were falsely attrib ...
.
Astronomy and cosmology
 Astronomy became a major discipline within Islamic science. Astronomers devoted effort both towards understanding the nature of the cosmos and to practical purposes. One application involved determining the ''Qibla'', the direction to face during prayer. Another was
Astronomy became a major discipline within Islamic science. Astronomers devoted effort both towards understanding the nature of the cosmos and to practical purposes. One application involved determining the ''Qibla'', the direction to face during prayer. Another was astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
, predicting events affecting human life and selecting suitable times for actions such as going to war or founding a city. Al-Battani (850–922) accurately determined the length of the solar year. He contributed to the Tables of Toledo, used by astronomers to predict the movements of the sun, moon and planets across the sky. Copernicus (1473–1543) later used some of Al-Battani's astronomic tables.
Al-Zarqali (1028–1087) developed a more accurate astrolabe
An astrolabe (; ; ) is an astronomy, astronomical list of astronomical instruments, instrument dating to ancient times. It serves as a star chart and Model#Physical model, physical model of the visible celestial sphere, half-dome of the sky. It ...
, used for centuries afterwards. He constructed a water clock in Toledo, discovered that the Sun's apogee moves slowly relative to the fixed stars, and obtained a good estimate of its motion for its rate of change. Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ibn al-Ḥasan al-Ṭūsī (1201 – 1274), also known as Naṣīr al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī (; ) or simply as (al-)Tusi, was a Persians, Persian polymath, architect, Early Islamic philosophy, philosopher, Islamic medicine, phy ...
(1201–1274) wrote an important revision to Ptolemy's 2nd-century celestial model. When Tusi became Helagu's astrologer, he was given an observatory and gained access to Chinese techniques and observations. He developed trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The fiel ...
as a separate field, and compiled the most accurate astronomical tables available up to that time.
Botany and agronomy
The study of the natural world extended to a detailed examination of plants. The work done proved directly useful in the unprecedented growth ofpharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur betwee ...
across the Islamic world. Al-Dinawari (815–896) popularised botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
in the Islamic world with his six-volume ''Kitab al-Nabat'' (''Book of Plants''). Only volumes 3 and 5 have survived, with part of volume 6 reconstructed from quoted passages. The surviving text describes 637 plants in alphabetical order from the letters ''sin'' to ''ya'', so the whole book must have covered several thousand kinds of plants. Al-Dinawari described the phases of plant growth
Important structures in plant development are buds, Shoot (botany), shoots, roots, leaf, leaves, and flowers; plants produce these tissues and structures throughout their life from meristems located at the tips of organs, or between mature tissues. ...
and the production of flowers and fruit. The thirteenth century encyclopedia compiled by Zakariya al-Qazwini
Zakariyya' al-Qazwini ( , ), also known as Qazvini (), (born in Qazvin, Iran, and died 1283), was a Cosmography, cosmographer and Geography in medieval Islam, geographer.
He belonged to a family of jurists originally descended from Anas bin Mal ...
(1203–1283) – ''ʿAjā'ib al-makhlūqāt'' (The Wonders of Creation) – contained, among many other topics, both realistic botany and fantastic accounts. For example, he described trees which grew birds on their twigs in place of leaves, but which could only be found in the far-distant British Isles., in Morelon & Rashed 1996, pp.813–852Turner 1997, pp.138–139 The use and cultivation of plants was documented in the 11th century by Muhammad bin Ibrāhīm Ibn Bassāl of Toledo in his book ''Dīwān al-filāha'' (The Court of Agriculture), and by Ibn al-'Awwam al-Ishbīlī (also called Abū l-Khayr al-Ishbīlī) of Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, ...
in his 12th century book ''Kitāb al-Filāha'' (Treatise on Agriculture). Ibn Bassāl had travelled widely across the Islamic world, returning with a detailed knowledge of agronomy
Agronomy is the science and technology of producing and using plants by agriculture for food, fuel, fiber, chemicals, recreation, or land conservation. Agronomy has come to include research of plant genetics, plant physiology, meteorology, and ...
that fed into the Arab Agricultural Revolution. His practical and systematic book describes over 180 plants and how to propagate and care for them. It covered leaf- and root-vegetables, herbs, spices and trees.
Geography and cartography
 The spread of Islam across Western Asia and North Africa encouraged an unprecedented growth in trade and travel by land and sea as far away as Southeast Asia, China, much of Africa, Scandinavia and even Iceland. Geographers worked to compile increasingly accurate maps of the known world, starting from many existing but fragmentary sources.
The spread of Islam across Western Asia and North Africa encouraged an unprecedented growth in trade and travel by land and sea as far away as Southeast Asia, China, much of Africa, Scandinavia and even Iceland. Geographers worked to compile increasingly accurate maps of the known world, starting from many existing but fragmentary sources. Abu Zayd al-Balkhi
Abu Zayd Ahmed ibn Sahl Balkhi () was a Persian Muslim polymath: a geographer, mathematician, physician, psychologist and scientist. Born in 850 CE in Shamistiyan, in the province of Balkh, Greater Khorasan, he was a disciple of al-Kindi. He a ...
(850–934), founder of the Balkhī school of cartography in Baghdad, wrote an atlas called ''Figures of the Regions'' (Suwar al-aqalim).
Al-Biruni (973–1048) measured the radius of the Earth using a new method. It involved observing the height of a mountain at Nandana (now in Pakistan). Al-Idrisi (1100–1166) drew a map of the world for Roger
Roger is a masculine given name, and a surname. The given name is derived from the Old French personal names ' and '. These names are of Germanic languages">Germanic origin, derived from the elements ', ''χrōþi'' ("fame", "renown", "honour") ...
, the Norman King of Sicily (ruled 1105–1154). He also wrote the '' Tabula Rogeriana'' (Book of Roger), a geographic study of the peoples, climates, resources and industries of the whole of the world known at that time. The Ottoman admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in many navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force. Admiral is ranked above vice admiral and below admiral of ...
Piri Reis ( 1470–1553) made a map of the New World and West Africa in 1513. He made use of maps from Greece, Portugal, Muslim sources, and perhaps one made by Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
. He represented a part of a major tradition of Ottoman cartography.
Mathematics
Islamic mathematicians gathered, organised and clarified the mathematics they inherited from ancient Egypt, Greece, India, Mesopotamia and Persia, and went on to make innovations of their own. Islamic mathematics coveredalgebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic ope ...
, geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician w ...
and arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms.
...
. Algebra was mainly used for recreation: it had few practical applications at that time. Geometry was studied at different levels. Some texts contain practical geometrical rules for surveying and for measuring figures. Theoretical geometry was a necessary prerequisite for understanding astronomy and optics, and it required years of concentrated work. Early in the Abbasid caliphate (founded 750), soon after the foundation of Baghdad in 762, some mathematical knowledge was assimilated by al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ; 714 – 6 October 775) usually known simply as by his laqab al-Manṣūr () was the second Abbasid caliph, reigning from 754 to 775 succeeding his brother al-Saffah (). He is known ...
's group of scientists from the pre-Islamic Persian tradition in astronomy. Astronomers from India were invited to the court of the caliph in the late eighth century; they explained the rudimentary trigonometrical techniques used in Indian astronomy. Ancient Greek works such as Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
's '' Almagest'' and Euclid's ''Elements'' were translated into Arabic. By the second half of the ninth century, Islamic mathematicians were already making contributions to the most sophisticated parts of Greek geometry. Islamic mathematics reached its apogee in the Eastern part of the Islamic world between the tenth and twelfth centuries. Most medieval Islamic mathematicians wrote in Arabic, others in Persian.

Al-Khwarizmi
Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi , or simply al-Khwarizmi, was a mathematician active during the Islamic Golden Age, who produced Arabic-language works in mathematics, astronomy, and geography. Around 820, he worked at the House of Wisdom in B ...
(8th–9th centuries) was instrumental in the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system (also known as the Indo-Arabic numeral system, Hindu numeral system, and Arabic numeral system) is a positional notation, positional Decimal, base-ten numeral system for representing integers; its extension t ...
and the development of algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic ope ...
, introduced methods of simplifying equations, and used Euclidean geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry, ''Euclid's Elements, Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set ...
in his proofs. He was the first to treat algebra as an independent discipline in its own right,, page 263–277: "In a sense, al-Khwarizmi is more entitled to be called "the father of algebra" than Diophantus because al-Khwarizmi is the first to teach algebra in an elementary form and for its own sake, Diophantus is primarily concerned with the theory of numbers". and presented the first systematic solution of linear
In mathematics, the term ''linear'' is used in two distinct senses for two different properties:
* linearity of a '' function'' (or '' mapping'');
* linearity of a '' polynomial''.
An example of a linear function is the function defined by f(x) ...
and quadratic equation
In mathematics, a quadratic equation () is an equation that can be rearranged in standard form as
ax^2 + bx + c = 0\,,
where the variable (mathematics), variable represents an unknown number, and , , and represent known numbers, where . (If and ...
s.Maher, P. (1998). From Al-Jabr to Algebra. Mathematics in School, 27(4), 14–15.
Ibn Ishaq al-Kindi (801–873) worked on cryptography for the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
, and gave the first known recorded explanation of cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic se ...
and the first description of the method of frequency analysis.
Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
( 980–1037) contributed to mathematical techniques such as casting out nines.Masood 2009, pp.104–105 Thābit ibn Qurra (835–901) calculated the solution to a chessboard problem involving an exponential series.
Al-Farabi
file:A21-133 grande.webp, thumbnail, 200px, Postage stamp of the USSR, issued on the 1100th anniversary of the birth of Al-Farabi (1975)
Abu Nasr Muhammad al-Farabi (; – 14 December 950–12 January 951), known in the Greek East and Latin West ...
( 870–950) attempted to describe, geometrically, the repeating patterns popular in Islamic decorative motifs in his book ''Spiritual Crafts and Natural Secrets in the Details of Geometrical Figures''. Omar Khayyam
Ghiyāth al-Dīn Abū al-Fatḥ ʿUmar ibn Ibrāhīm Nīshābūrī (18 May 1048 – 4 December 1131) (Persian language, Persian: غیاث الدین ابوالفتح عمر بن ابراهیم خیام نیشابورﻯ), commonly known as Omar ...
(1048–1131), known in the West as a poet, calculated the length of the year to within 5 decimal places, and found geometric solutions to all 13 forms of cubic equations, developing some quadratic equation
In mathematics, a quadratic equation () is an equation that can be rearranged in standard form as
ax^2 + bx + c = 0\,,
where the variable (mathematics), variable represents an unknown number, and , , and represent known numbers, where . (If and ...
s still in use. Jamshīd al-Kāshī
Ghiyāth al-Dīn Jamshīd Masʿūd al-Kāshī (or al-Kāshānī) ( ''Ghiyās-ud-dīn Jamshīd Kāshānī'') (c. 1380 Kashan, Iran – 22 June 1429 Samarkand, Transoxiana) was a Persian astronomer and mathematician during the reign of Tamerlane.
...
(c. 1380–1429) is credited with several theorems of trigonometry, including the law of cosines
In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. For a triangle with sides , , and , opposite respective angles , , and (see ...
, also known as Al-Kashi's Theorem. He has been credited with the invention of decimal fractions, and with a method like Horner's to calculate roots. He calculated π correctly to 17 significant figures.
Sometime around the seventh century, Islamic scholars adopted the Hindu–Arabic numeral system
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system (also known as the Indo-Arabic numeral system, Hindu numeral system, and Arabic numeral system) is a positional notation, positional Decimal, base-ten numeral system for representing integers; its extension t ...
, describing their use in a standard type of text ''fī l-ḥisāb al hindī'', (On the numbers of the Indians). A distinctive Western Arabic variant of the Eastern Arabic numerals
The Eastern Arabic numerals, also called Indo-Arabic numerals or Arabic-Indic numerals as known by Unicode, are the symbols used to represent numerical digits in conjunction with the Arabic alphabet in the countries of the Mashriq (the east o ...
began to emerge around the 10th century in the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
and Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
(sometimes called ''ghubar'' numerals, though the term is not always accepted), which are the direct ancestor of the modern Arabic numerals
The ten Arabic numerals (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9) are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation number with a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with Roman numera ...
used throughout the world.
Medicine
 Islamic society paid careful attention to medicine, following a ''
Islamic society paid careful attention to medicine, following a ''hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ...
'' enjoining the preservation of good health. Its physicians inherited knowledge and traditional medical beliefs from the civilisations of classical Greece, Rome, Syria, Persia and India. These included the writings of Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
such as on the theory of the four humours, and the theories of Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one o ...
. al-Razi ( 865–925) identified smallpox and measles, and recognized fever as a part of the body's defenses. He wrote a 23-volume compendium of Chinese, Indian, Persian, Syriac and Greek medicine. al-Razi questioned the classical Greek medical theory of how the four humours regulate life processes. He challenged Galen's work on several fronts, including the treatment of bloodletting
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) was the deliberate withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and othe ...
, arguing that it was effective.
al-Zahrawi
Abū al-Qāsim Khalaf ibn al-'Abbās al-Zahrāwī al-Ansari (; c. 936–1013), popularly known as al-Zahrawi (), Latinisation of names, Latinised as Albucasis or Abulcasis (from Arabic ''Abū al-Qāsim''), was an Arabs, Arab physician, su ...
(936–1013) was a surgeon whose most important surviving work is referred to as '' al-Tasrif'' (Medical Knowledge). It is a 30-volume set mainly discussing medical symptoms, treatments, and pharmacology. The last volume, on surgery, describes surgical instruments, supplies, and pioneering procedures. Avicenna (c. 980–1037) wrote the major medical textbook, ''The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' () is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Avicenna (, ibn Sina) and completed in 1025. It is among the most influential works of its time. It presents an overview of the contemporary medical knowle ...
''. Ibn al-Nafis (1213–1288) wrote an influential book on medicine; it largely replaced Avicenna's ''Canon'' in the Islamic world. He wrote commentaries on Galen and on Avicenna's works. One of these commentaries, discovered in 1924, described the circulation of blood through the lungs.
Optics and ophthalmology

 Optics developed rapidly in this period. By the ninth century, there were works on physiological, geometrical and physical optics. Topics covered included mirror reflection.
Hunayn ibn Ishaq (809–873) wrote the book ''Ten Treatises on the Eye''; this remained influential in the West until the 17th century.
Optics developed rapidly in this period. By the ninth century, there were works on physiological, geometrical and physical optics. Topics covered included mirror reflection.
Hunayn ibn Ishaq (809–873) wrote the book ''Ten Treatises on the Eye''; this remained influential in the West until the 17th century.
Abbas ibn Firnas
Abū al-Qāsim ʿAbbās ibn Firnās ibn Wardūs al-Tākurnī (; c. 809/810 – 887 CE), known as ʿAbbās ibn Firnās () was an Andalusi polymath: Lynn Townsend White, Jr. (Spring, 1961). "Eilmer of Malmesbury, an Eleventh Century Aviator: A C ...
(810–887) developed lenses for magnification and the improvement of vision.
Ibn Sahl ( 940–1000) discovered the law of refraction known as Snell's law
Snell's law (also known as the Snell–Descartes law, the ibn-Sahl law, and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing th ...
. He used the law to produce the first Aspheric lenses that focused light without geometric aberrations.
In the eleventh century Ibn al-Haytham
Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham (Latinization of names, Latinized as Alhazen; ; full name ; ) was a medieval Mathematics in medieval Islam, mathematician, Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world, astronomer, and Physics in the medieval Islamic world, p ...
(Alhazen, 965–1040) rejected the Greek ideas about vision, whether the Aristotelian tradition that held that the form of the perceived object entered the eye (but not its matter), or that of Euclid and Ptolemy which held that the eye emitted a ray. Al-Haytham proposed in his ''Book of Optics'' that vision occurs by way of light rays forming a cone with its vertex at the center of the eye. He suggested that light was reflected from different surfaces in different directions, thus causing objects to look different. He argued further that the mathematics of reflection and refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one transmission medium, medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commo ...
needed to be consistent with the anatomy of the eye.Masood 2009, pp.173–175 He was also an early proponent of the scientific method
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has been referred to while doing science since at least the 17th century. Historically, it was developed through the centuries from the ancient and ...
, the concept that a hypothesis must be proved by experiments based on confirmable procedures or mathematical evidence, five centuries before Renaissance scientists. Haq, Syed (2009). "Science in Islam". Oxford Dictionary of the Middle Ages. . Retrieved 22 October 2014. G. J. ToomerReview on JSTOR, Toomer's 1964 review of Matthias Schramm (1963) ''Ibn Al-Haythams Weg Zur Physik''
Toomer p.464: "Schramm sums up bn Al-Haytham'sachievement in the development of scientific method."
Pharmacology
 Advances in
Advances in botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
and chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
in the Islamic world encouraged developments in pharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur betwee ...
. Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi (Rhazes) (865–915) promoted the medical uses of chemical compounds. Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi (Abulcasis) (936–1013) pioneered the preparation of medicines by sublimation and distillation. His ''Liber servitoris'' provides instructions for preparing "simples" from which were compounded the complex drugs then used. Sabur Ibn Sahl (died 869) was the first physician to describe a large variety of drugs and remedies for ailments. Al-Muwaffaq
Abu Ahmad Ṭalḥa ibn Al-Mutawakkil, Jaʿfar ibn al-Mu'tasim, Muḥammad ibn Harun al-Rashid, Hārūn al-Muwaffaq bi'Llah (; 29 November 843 – 2 June 891), better known by his as Al-Muwaffaq Billah (), was an Abbasid dynasty, Abbasid prince ...
, in the 10th century, wrote ''The foundations of the true properties of Remedies'', describing chemicals such as arsenious oxide and silicic acid. He distinguished between sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate, and drew attention to the poisonous nature of copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
compounds, especially copper vitriol, and also of lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
compounds. Al-Biruni (973–1050) wrote the ''Kitab al-Saydalah'' (''The Book of Drugs''), describing in detail the properties of drugs, the role of pharmacy and the duties of the pharmacist. Ibn Sina (Avicenna) described 700 preparations, their properties, their mode of action and their indications. He devoted a whole volume to simples in ''The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' () is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Avicenna (, ibn Sina) and completed in 1025. It is among the most influential works of its time. It presents an overview of the contemporary medical knowle ...
''. Works by Masawaih al-Mardini ( 925–1015) and by Ibn al-Wafid (1008–1074) were printed in Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
more than fifty times, appearing as ''De Medicinis universalibus et particularibus'' by Mesue the Younger (died 1015) and as the ''Medicamentis simplicibus'' by Abenguefit (c. 997 – 1074) respectively. Peter of Abano (1250–1316) translated and added a supplement to the work of al-Mardini under the title ''De Veneris''. Ibn al-Baytar (1197–1248), in his ''Al-Jami fi al-Tibb'', described a thousand simples and drugs based directly on Mediterranean plants collected along the entire coast between Syria and Spain, for the first time exceeding the coverage provided by Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides (, ; 40–90 AD), "the father of pharmacognosy", was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of (in the original , , both meaning "On Materia medica, Medical Material") , a 5-volume Greek encyclopedic phar ...
in classical times. Islamic physicians such as Ibn Sina described clinical trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
for determining the efficacy of medical drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
s and substances.
Physics
 The fields of physics studied in this period, apart from optics and astronomy which are described separately, are aspects of
The fields of physics studied in this period, apart from optics and astronomy which are described separately, are aspects of mechanics
Mechanics () is the area of physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among Physical object, physical objects. Forces applied to objects may result in Displacement (vector), displacements, which are changes of ...
: statics
Statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque acting on a physical system that does not experience an acceleration, but rather is in mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium with its environment ...
, dynamics, kinematics
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics.
Kinematics is concerned with s ...
and motion
In physics, motion is when an object changes its position with respect to a reference point in a given time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and frame of reference to an o ...
. In the sixth century John Philoponus () rejected the Aristotelian view of motion. He argued instead that an object acquires an inclination to move when it has a motive power impressed on it. In the eleventh century Ibn Sina adopted roughly the same idea, namely that a moving object has force which is dissipated by external agents like air resistance. Ibn Sina distinguished between "force" and "inclination" (''mayl''); he claimed that an object gained ''mayl'' when the object is in opposition to its natural motion. He concluded that continuation of motion depends on the inclination that is transferred to the object, and that the object remains in motion until the ''mayl'' is spent. He also claimed that a projectile in a vacuum would not stop unless it is acted upon. That view accords with Newton's first law of motion, on inertia. As a non-Aristotelian suggestion, it was essentially abandoned until it was described as "impetus" by Jean Buridan
Jean Buridan (; ; Latin: ''Johannes Buridanus''; – ) was an influential 14thcentury French scholastic philosopher.
Buridan taught in the faculty of arts at the University of Paris for his entire career and focused in particular on logic and ...
(c. 1295–1363), who was likely influenced by Ibn Sina's ''Book of Healing''.
In the ''Shadows'', Abū Rayḥān al-Bīrūnī (973–1048) describes non-uniform motion as the result of acceleration. Ibn-Sina's theory of ''mayl'' tried to relate the velocity and weight of a moving object, a precursor of the concept of momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. ...
. Aristotle's theory of motion stated that a constant force produces a uniform motion; Abu'l-Barakāt al-Baghdādī (c. 1080 – 1164/5) disagreed, arguing that velocity and acceleration are two different things, and that force is proportional to acceleration, not to velocity.
The Banu Musa brothers, Jafar-Muhammad, Ahmad and al-Hasan (c. early 9th century) invented automated devices described in their Book of Ingenious Devices. Advances on the subject were also made by al-Jazari and Ibn Ma'ruf.
Zoology
 Many classical works, including those of Aristotle, were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle's zoology remained dominant in its field for two thousand years. The '' Kitāb al-Hayawān'' (كتاب الحيوان, English: ''Book of Animals'') is a 9th-century
Many classical works, including those of Aristotle, were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle's zoology remained dominant in its field for two thousand years. The '' Kitāb al-Hayawān'' (كتاب الحيوان, English: ''Book of Animals'') is a 9th-century Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
translation of ''History of Animals'': 1–10, ''On the Parts of Animals'': 11–14, and ''Generation of Animals'': 15–19.
The book was mentioned by Al-Kindī (died 850), and commented on by Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
(Ibn Sīnā) in his '' The Book of Healing''. Avempace (Ibn Bājja) and Averroes
Ibn Rushd (14 April 112611 December 1198), archaically Latinization of names, Latinized as Averroes, was an Arab Muslim polymath and Faqīh, jurist from Al-Andalus who wrote about many subjects, including philosophy, theology, medicine, astron ...
(Ibn Rushd) commented on and criticised ''On the Parts of Animals'' and ''Generation of Animals''.
Significance
Muslim scientists helped in laying the foundations for anexperiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs whe ...
al science with their contributions to the scientific method
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has been referred to while doing science since at least the 17th century. Historically, it was developed through the centuries from the ancient and ...
and their empirical
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law.
There is no general agreement on how t ...
, experimental and quantitative approach to scientific inquiry
An inquiry (also spelled as enquiry in British English) is any process that has the aim of augmenting knowledge, resolving doubt, or solving a problem. A theory of inquiry is an account of the various types of inquiry and a treatment of the ...
. Durant, Will (1980). ''The Age of Faith ( The Story of Civilization, Volume 4)'', p. 162–186. Simon & Schuster. . Garrison, Fielding H., ''An Introduction to the History of Medicine: with Medical Chronology, Suggestions for Study and Bibliographic Data'', p. 86. In a more general sense, the positive achievement of Islamic science was simply to flourish, for centuries, in a wide range of institutions from observatories to libraries, madrasas
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , ), sometimes Romanization of Arabic, romanized as madrasah or madrassa, is the Arabic word for any Educational institution, type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whet ...
to hospitals and courts, both at the height of the Islamic golden age and for some centuries afterwards. It did not lead to a Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
like that in Early modern Europe
Early modern Europe, also referred to as the post-medieval period, is the period of European history between the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, roughly the mid 15th century to the late 18th century. Histori ...
, but such external comparisons are probably to be rejected as imposing "chronologically and culturally alien standards" on a successful medieval culture.
See also
* Continuity thesis * Indian influence on Islamic science * History of scientific method * History of Islamic economics *Islamic philosophy
Islamic philosophy is philosophy that emerges from the Islamic tradition. Two terms traditionally used in the Islamic world are sometimes translated as philosophy—''falsafa'' (), which refers to philosophy as well as logic, mathematics, and p ...
* Islamic attitudes towards science
* Scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval European philosophical movement or methodology that was the predominant education in Europe from about 1100 to 1700. It is known for employing logically precise analyses and reconciling classical philosophy and Ca ...
* Timeline of science and engineering in the Muslim world
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * (chapters 1–5 cover science, mathematics and medicine in Islam) * *External links
"How Greek Science Passed to the Arabs"
by De Lacy O'Leary * *Habibi, Golareh
is there such a thing as Islamic science? the influence of Islam on the world of science
''Science Creative Quarterly''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Science In Medieval Islam .Science Medieval history of the Middle East
Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...