Ise Jingū on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The , located in Ise,
 According to the ''
According to the ''
 The architectural style of the Ise shrine is known as ''
The architectural style of the Ise shrine is known as ''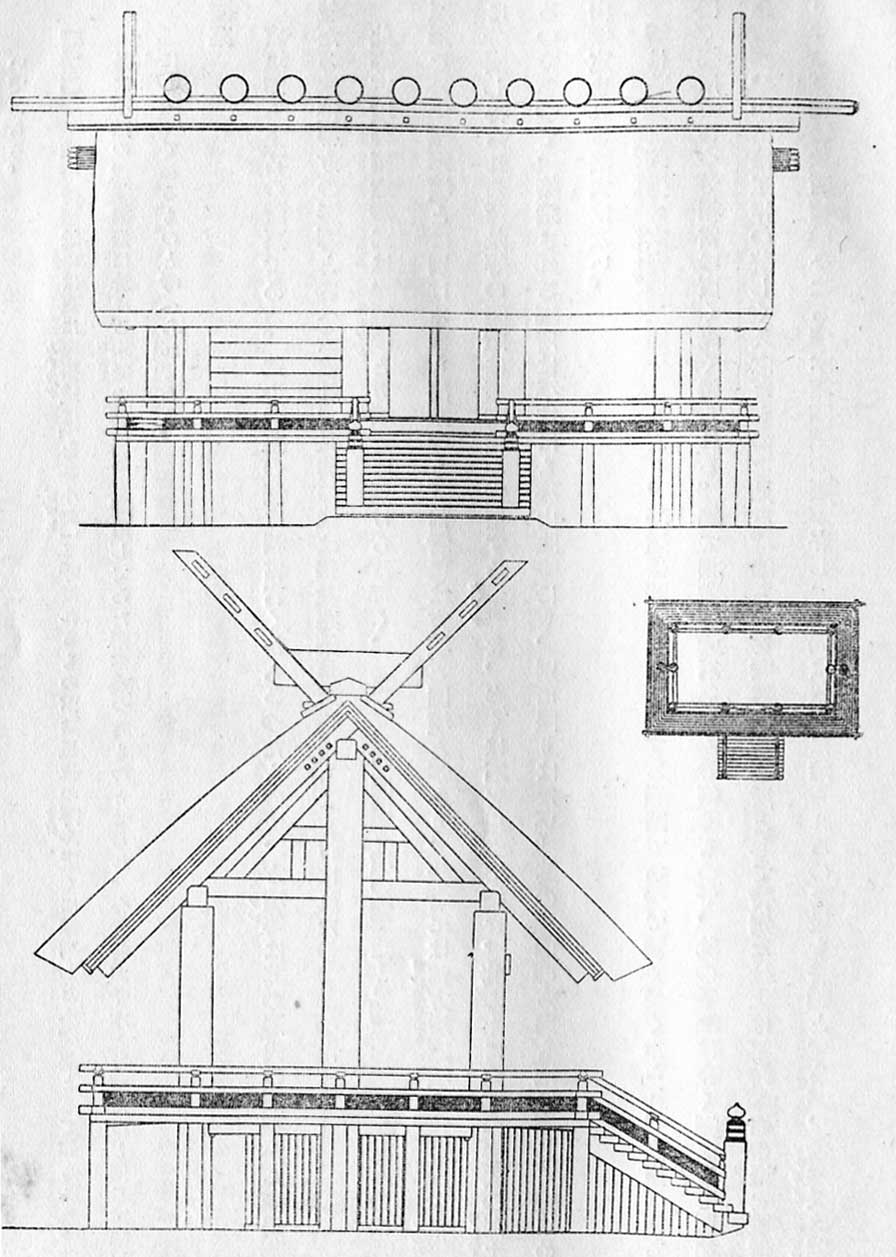 The shrine at Naikū is constructed of Japanese cypress. Built on pillars set directly in the ground, the shrine building measures 10.9 by 5.5 meters and includes a raised floor, verandas all the way around the building and a staircase leading to a single central doorway. The Naikū does not have any windows. The roof is made of thatched reed with ten billets (''
The shrine at Naikū is constructed of Japanese cypress. Built on pillars set directly in the ground, the shrine building measures 10.9 by 5.5 meters and includes a raised floor, verandas all the way around the building and a staircase leading to a single central doorway. The Naikū does not have any windows. The roof is made of thatched reed with ten billets (''
 In August, in a long-standing tradition, the people who live in Ise are allowed to enter the area around the Inner Sanctum of the Naiku as well as the Geku. Some villages drag a wooden carriage laden with white stones up the Isuzu River onto the grounds of the Naiku. Each participant gets two white stones in a white handkerchief and these allow them to place the stones in the area around the Inner Sanctum. Other villages drag a huge wooden cart or Noburi Kuruma laden with white stones to the Uji bridge at the entrance of the grounds of the Naiku. Participants receive two white stones which are also placed in the sacred space around the Inner Sanctum. The entire tradition is called Shiraisshiki and it is very colourful with every participant wearing a happi coat representing a particular village. The rebuilding of the main shrine takes place on a site adjacent to the old, and each rebuilding alternates between the two sites. The next scheduled rebuilding of Naikū is due in 2033 on the lower, northern site. Various other religious ceremonies are held with the completion of the shrine, each serving different purposes.
In the lead-up to the rebuilding of the shrines, a number of festivals are held to mark special events. The Okihiki Festival is held in the spring over two consecutive years and involves people from surrounding towns dragging huge wooden logs through the streets of Ise to Naikū and Gekū. In the lead-up to the 2013 rebuilding, the Okihiki festival was held in 2006 and 2007. A year after the completion of the Okihiki festival, carpenters begin preparing the wood for its eventual use in the Shrine.
In August, in a long-standing tradition, the people who live in Ise are allowed to enter the area around the Inner Sanctum of the Naiku as well as the Geku. Some villages drag a wooden carriage laden with white stones up the Isuzu River onto the grounds of the Naiku. Each participant gets two white stones in a white handkerchief and these allow them to place the stones in the area around the Inner Sanctum. Other villages drag a huge wooden cart or Noburi Kuruma laden with white stones to the Uji bridge at the entrance of the grounds of the Naiku. Participants receive two white stones which are also placed in the sacred space around the Inner Sanctum. The entire tradition is called Shiraisshiki and it is very colourful with every participant wearing a happi coat representing a particular village. The rebuilding of the main shrine takes place on a site adjacent to the old, and each rebuilding alternates between the two sites. The next scheduled rebuilding of Naikū is due in 2033 on the lower, northern site. Various other religious ceremonies are held with the completion of the shrine, each serving different purposes.
In the lead-up to the rebuilding of the shrines, a number of festivals are held to mark special events. The Okihiki Festival is held in the spring over two consecutive years and involves people from surrounding towns dragging huge wooden logs through the streets of Ise to Naikū and Gekū. In the lead-up to the 2013 rebuilding, the Okihiki festival was held in 2006 and 2007. A year after the completion of the Okihiki festival, carpenters begin preparing the wood for its eventual use in the Shrine.
 From the late seventh century, when the festivals and offerings of Ise Shrine became more formalised, a number of annual events have been performed at both Naikū and Gekū. The Tsukinamisai, which was held in June and December, as well as the Kannamesai Festival in September, were the only three offerings performed by the Saiō, an imperial princess who served as high priestess of the shrine until the 14th century. These offerings are based on the cycle of the agricultural year and are still performed today.
The first important ceremony of the modern calendar year is the Kinen-sai, where prayers are offered for a bountiful harvest. Kazahinomisai, where prayers for fair weather and sufficient rains are made, is held twice a year in May and August at both Naikū and Gekū.
The most important annual festival held at Ise Shrine is the . Held in October each year, this ritual makes offerings of the first harvest of crops for the season to Amaterasu. An imperial envoy carries the offering of rice harvested by the
From the late seventh century, when the festivals and offerings of Ise Shrine became more formalised, a number of annual events have been performed at both Naikū and Gekū. The Tsukinamisai, which was held in June and December, as well as the Kannamesai Festival in September, were the only three offerings performed by the Saiō, an imperial princess who served as high priestess of the shrine until the 14th century. These offerings are based on the cycle of the agricultural year and are still performed today.
The first important ceremony of the modern calendar year is the Kinen-sai, where prayers are offered for a bountiful harvest. Kazahinomisai, where prayers for fair weather and sufficient rains are made, is held twice a year in May and August at both Naikū and Gekū.
The most important annual festival held at Ise Shrine is the . Held in October each year, this ritual makes offerings of the first harvest of crops for the season to Amaterasu. An imperial envoy carries the offering of rice harvested by the
 This 100 meter wooden bridge, built in a traditional Japanese style, stretches across the Isuzu River at the entrance of Naikū. Like the shrine buildings of Naikū, it is rebuilt every 20 years as a part of the Shikinen Sengū ceremony. The bridge is typically built by carpenters with less experience to gain more skills before moving on to take on the task of working on the main shrine. On crossing the bridge, the path turns to the right along the banks of the Isuzu river and passes through large landscaped gardens.
This 100 meter wooden bridge, built in a traditional Japanese style, stretches across the Isuzu River at the entrance of Naikū. Like the shrine buildings of Naikū, it is rebuilt every 20 years as a part of the Shikinen Sengū ceremony. The bridge is typically built by carpenters with less experience to gain more skills before moving on to take on the task of working on the main shrine. On crossing the bridge, the path turns to the right along the banks of the Isuzu river and passes through large landscaped gardens.
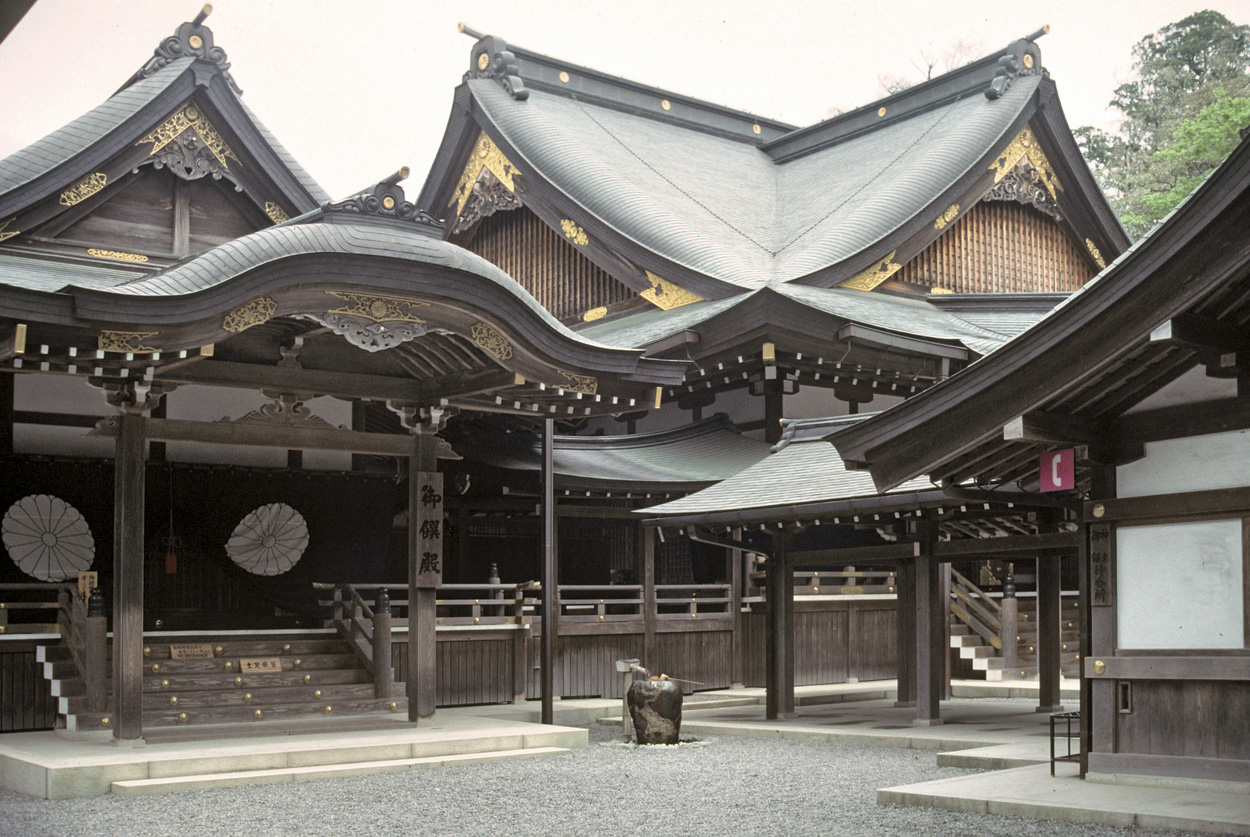 This hall for special prayer, located just after the second large torii gate, is open to the public for the offering of individual prayers to the kami, the giving of donations and the purchase of special talisman of protection, amulets and hanging scrolls of Amaterasu Omikami.
This hall for special prayer, located just after the second large torii gate, is open to the public for the offering of individual prayers to the kami, the giving of donations and the purchase of special talisman of protection, amulets and hanging scrolls of Amaterasu Omikami.

 This hall contains the sacred fire used to cook all of the food offerings to the kami of Ise Shrine. Rice and other offerings cooked on the sacred fire are stored in a box made of Japanese cypress, then purified at the Haraedo immediately in front of the Imibiyaden before being offered to the kami.
This hall contains the sacred fire used to cook all of the food offerings to the kami of Ise Shrine. Rice and other offerings cooked on the sacred fire are stored in a box made of Japanese cypress, then purified at the Haraedo immediately in front of the Imibiyaden before being offered to the kami.
 The pilgrimage to the Ise shrine, also known as ''Sangū'', gained immense popularity during the Edo Period, where hundreds of thousands of pilgrims would travel there every year. The growth was exponential, 5 million pilgrims visiting the shrine in the year 1830 alone. By the late 19th century, tourists from abroad began to visit and document Ise. The popularity of making a trip to Ise resulted in vast networks and groups of travelers, which ultimately led to businesses working to benefit from this influx of interest for the shrine. Travel guidebooks were made to aid travelers in their navigation, as well to let them know of specific important places to visit while at Ise. They also included woodblock prints of the shrine that were very appealing to those who had made the long trek to the shrine. Additionally, people wanted souvenirs, which resulted in a variety of vendors at Ise selling general goods and specialty items. There were also various post stations which had specific gifts, many of which were woodblock prints. The pilgrimage had multiple purposes and appeals. It was seen as a purification process, and by visiting Ise, pilgrims were purified and aided in receiving a good afterlife. It also was seen as a vacation, the journey to the shrine itself being almost as important as actually getting there. In the 21st century, Ise is still an important destination both to foreign tourists and especially to the Japanese community; 9 million Japanese tourists visited the shrine in 2013.
The pilgrimage to the Ise shrine, also known as ''Sangū'', gained immense popularity during the Edo Period, where hundreds of thousands of pilgrims would travel there every year. The growth was exponential, 5 million pilgrims visiting the shrine in the year 1830 alone. By the late 19th century, tourists from abroad began to visit and document Ise. The popularity of making a trip to Ise resulted in vast networks and groups of travelers, which ultimately led to businesses working to benefit from this influx of interest for the shrine. Travel guidebooks were made to aid travelers in their navigation, as well to let them know of specific important places to visit while at Ise. They also included woodblock prints of the shrine that were very appealing to those who had made the long trek to the shrine. Additionally, people wanted souvenirs, which resulted in a variety of vendors at Ise selling general goods and specialty items. There were also various post stations which had specific gifts, many of which were woodblock prints. The pilgrimage had multiple purposes and appeals. It was seen as a purification process, and by visiting Ise, pilgrims were purified and aided in receiving a good afterlife. It also was seen as a vacation, the journey to the shrine itself being almost as important as actually getting there. In the 21st century, Ise is still an important destination both to foreign tourists and especially to the Japanese community; 9 million Japanese tourists visited the shrine in 2013.
OCLC 399449
*
New York Public Library Digital Gallery, early photograph of Ise Shrine compound
Photographs of the Ise Shrine by Yoshio Watanabe
Canadian Centre for Architecture
Smithsonian Magazine – This Japanese Shrine
Wheelchair Accessibility of Shrine
* {{Shinmei shrines 7th-century establishments in Japan Jingū Shinto shrines in Mie Prefecture Asuka period Yayoi period Sun temples Japanese imperialism and colonialism Rebuilt buildings and structures in Japan 692 establishments Religious buildings and structures completed in the 690s 7th-century Shinto shrines Ise, Mie Twenty-Two Shrines Shinmei shrines Shikinai Taisha Shinmei-zukuri
Mie Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region of Honshu. Mie Prefecture has a population of 1,781,948 () and has a geographic area of . Mie Prefecture is bordered by Gifu Prefecture to the north, Shiga Prefecture an ...
of Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, is a Shinto shrine
A Stuart D. B. Picken, 1994. p. xxiii is a structure whose main purpose is to house ("enshrine") one or more kami, , the deities of the Shinto religion.
The Also called the . is where a shrine's patron is or are enshrined.Iwanami Japanese dic ...
dedicated to the solar goddess Amaterasu
, often called Amaterasu () for short, also known as and , is the goddess of the sun in Japanese mythology. Often considered the chief deity (''kami'') of the Shinto pantheon, she is also portrayed in Japan's earliest literary texts, the () ...
Ōmikami and the grain goddess Toyouke-hime
Toyouke-hime is the goddess of agriculture, industry, food, clothing, and houses in the Shinto religion. Originally enshrined in the Tanba region of Japan, she was called to reside at Gekū, Ise Shrine, about 1,500 years ago at the age of Empe ...
(Toyouke Omikami). Also known simply as , Ise Shrine is a shrine complex composed of many Shinto shrines centered on two main shrines, and .
The Inner Shrine, Naikū (also officially known as "Kōtai Jingū"), is dedicated to the worship of Amaterasu and is located in the town of Uji-tachi, south of central Ise, where she is believed to dwell. The shrine buildings are made of solid cypress wood and use no nails but instead joined wood. The Outer Shrine, ''Gekū'' (also officially known as "Toyouke Daijingū"), is located about six kilometers from Naikū and dedicated to Toyouke-Ōmikami, the god of agriculture, rice harvest and industry. Besides Naikū and Gekū, there are an additional 123 Shinto shrines in Ise City and the surrounding areas, 91 of them connected to Naikū and 32 to Gekū.
Purportedly the home of the Sacred Mirror, the shrine is one of Shinto's holiest and most important sites. Access to both sites is strictly limited, with the general public not allowed beyond sight of the thatched roofs of the central structures, hidden behind four tall wooden fences. However, visitors are free to roam the forest, including its ornamental walkways which date back to the Meiji period
The was an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868, to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonizatio ...
.
During the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
, it is estimated that one out of ten Japanese conducted an ''Okage Mairi'' pilgrimage to the shrine. Accordingly, pilgrimage to the shrine flourished in both commercial and religious frequency. According to historical documents, 3.62 million people visited the shrine in 50 days in 1625, and 1.18 million people visited the shrine in three days in 1829 when the grand festival held every 20 years was held. Because the shrine is considered sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred space, sacred place, such as a shrine, protected by ecclesiastical immunity. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This seconda ...
, no security checkpoints were conducted, as it was considered sacrilege
Sacrilege is the violation or injurious treatment of a sacred object, site or person. This can take the form of irreverence to sacred persons, places, and things. When the sacrilegious offence is verbal, it is called blasphemy, and when physical ...
by the faithful. The two main shrines of Ise are joined by a pilgrimage road that passes through the old entertainment district of Furuichi.
The chief priest or priestess of Ise Shrine must be related to the Imperial House of Japan
The is the reigning dynasty of Japan, consisting of those members of the extended family of the reigning emperor of Japan who undertake official and public duties. Under the present constitution of Japan, the emperor is "the symbol of the State ...
and is responsible for watching over the Shrine. The current High Priestess of the shrine is the daughter of Emperor Emeritus Akihito
Akihito (born 23 December 1933) is a member of the Imperial House of Japan who reigned as the 125th emperor of Japan from 1989 until 2019 Japanese imperial transition, his abdication in 2019. The era of his rule was named the Heisei era, Hei ...
, former Princess Sayako Kuroda
, formerly , is the youngest child and only daughter of Emperor Emeritus Akihito and Empress Emerita Michiko, and the younger sister of the current Emperor of Japan, Naruhito. She is an imperial Shinto priestess of the Ise Grand Shrine, curr ...
.
Establishment of the Shrine
Nihon Shoki
The or , sometimes translated as ''The Chronicles of Japan'', is the second-oldest book of classical Japanese history. It is more elaborate and detailed than the , the oldest, and has proven to be an important tool for historians and archaeol ...
'', around 2000 years ago the divine Yamatohime-no-mikoto, daughter of the Emperor Suinin, set out from Mt. Miwa in modern Nara Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region of Honshu. Nara Prefecture has a population of 1,321,805 and has a geographic area of . Nara Prefecture borders Kyoto Prefecture to the north, Osaka Prefecture to the ...
in search of a permanent location to worship the goddess Amaterasu, wandering for 20 years through the regions of Omi and Mino. Her search eventually brought her to Ise, in modern Mie Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region of Honshu. Mie Prefecture has a population of 1,781,948 () and has a geographic area of . Mie Prefecture is bordered by Gifu Prefecture to the north, Shiga Prefecture an ...
, where she is said to have established Naikū after hearing the voice of Amaterasu saying "(Ise) is a secluded and pleasant land. In this land I wish to dwell." Before Yamatohime-no-mikoto's journey, Amaterasu
, often called Amaterasu () for short, also known as and , is the goddess of the sun in Japanese mythology. Often considered the chief deity (''kami'') of the Shinto pantheon, she is also portrayed in Japan's earliest literary texts, the () ...
had been worshiped at the imperial residence in Yamato
was originally the area around today's Sakurai, Nara, Sakurai City in Nara Prefecture of Japan, which became Yamato Province and by extension a Names of Japan, name for the whole of Japan.
Yamato is also the dynastic name of the ruling Imperial ...
, then briefly at Kasanui in the eastern Nara basin. When Princess Yamatohime-no-mikoto arrived at the village of Uji-tachi, she set up fifty bells to designate the area as enshrined for the goddess Amaterasu, which is why the river is called the Isuzu
, commonly known as Isuzu (, ), is a Japanese multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Yokohama, Kanagawa Prefecture. Its principal activity is the production, marketing and sale of Isuzu commercial vehicles and diesel engines ...
, or "fifty bells".
Geku was founded after Emperor Yuryaku dreamt that he saw Amaterasu
, often called Amaterasu () for short, also known as and , is the goddess of the sun in Japanese mythology. Often considered the chief deity (''kami'') of the Shinto pantheon, she is also portrayed in Japan's earliest literary texts, the () ...
. She said she was unable to get food and asked him to bring Toyouke-hime
Toyouke-hime is the goddess of agriculture, industry, food, clothing, and houses in the Shinto religion. Originally enshrined in the Tanba region of Japan, she was called to reside at Gekū, Ise Shrine, about 1,500 years ago at the age of Empe ...
from Tanba help her with food.
Besides the traditional establishment date of 4 BC,''Encyclopædia Britannica Ise Shrine'' https://www.britannica.com/ebc/article-9368233 other dates of the 3rd and 5th centuries have been put forward for the establishment of Naikū and Gekū respectively. The first shrine building at Naikū was erected by Emperor Tenmu
was the 40th Emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 天武天皇 (40) retrieved 2013-8-22. according to the traditional order of succession. Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan'', p. 53. He ascended ...
(678–686), with the first ceremonial rebuilding being carried out by his wife, Empress Jitō
was the 41st emperor of Japan, monarch of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 持統天皇 (41)/ref> according to the traditional List of Emperors of Japan, order of succession.
Jitō's reign spanned the years from Jitō period, 68 ...
, in 692.''Sacred Places Ise Shrine'' http://witcombe.sbc.edu/sacredplaces/ise.html
The shrine was foremost among a group of shrines which became objects of imperial patronage in the early Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kammu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means in Japanese. It is a ...
. In 965, Emperor Murakami
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother/grandmother ( empress dowager/ grand empress dowager), or a woman who rul ...
ordered imperial messengers to be sent to report important events to the guardian kami
are the Deity, deities, Divinity, divinities, Spirit (supernatural entity), spirits, mythological, spiritual, or natural phenomena that are venerated in the traditional Shinto religion of Japan. ''Kami'' can be elements of the landscape, forc ...
of Japan. These ''heihaku'' were initially presented to 16 shrines including the Ise Shrine.
Chief priestess / chief priest
From the late 7th century until the 14th century, the role of chief priestess of Ise Shrine was carried out by a female member of theImperial House of Japan
The is the reigning dynasty of Japan, consisting of those members of the extended family of the reigning emperor of Japan who undertake official and public duties. Under the present constitution of Japan, the emperor is "the symbol of the State ...
known as a Saiō. According to the ''Man'yōshū
The is the oldest extant collection of Japanese (poetry in Classical Japanese), compiled sometime after AD 759 during the Nara period. The anthology is one of the most revered of Japan's poetic compilations. The compiler, or the last in ...
'', the first saiō to serve at the shrine was Princess Ōku, daughter of Emperor Tenmu
was the 40th Emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 天武天皇 (40) retrieved 2013-8-22. according to the traditional order of succession. Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan'', p. 53. He ascended ...
, during the Asuka period
The was a period in the history of Japan lasting from 538 to 710, although its beginning could be said to overlap with the preceding Kofun period. The Yamato period, Yamato polity evolved greatly during the Asuka period, which is named after the ...
. Mention of Ise Shrine's saiō is also made in the Aoi, Sakaki and Yugao chapters of ''The Tale of Genji
is a classic work of Japanese literature written by the noblewoman, poet, and lady-in-waiting Murasaki Shikibu around the peak of the Heian period, in the early 11th century. It is one of history's first novels, the first by a woman to have wo ...
'' as well as in the 69th chapter of ''The Tales of Ise
is a Japanese '' uta monogatari'', or collection of '' waka'' poems and associated narratives, dating from the Heian period. The current version collects 125 sections, with each combining poems and prose, giving a total of 209 poems in most vers ...
''. The saiō system ended during the turmoil of the Nanboku-chō period
The , also known as the Northern and Southern Courts period, was a period in Japanese history between 1336-1392 CE, during the formative years of the Ashikaga shogunate, Muromachi (Ashikaga) shogunate. Ideologically, the two courts fought for 50 ...
.
During the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
and the establishment of State Shinto
was Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan's ideological use of the Japanese folk religion and traditions of Shinto. The state exercised control of shrine finances and training regimes for Kannushi, priests to strongly encourage Shinto practices that ...
, the position of chief priest of the Ise Shrine was fulfilled by the reigning emperor and the Meiji, Taisho and Shōwa Emperors all played the role of chief priest during their reigns.
Since the disestablishment of State Shinto during the Occupation of Japan
Japan was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II from the surrender of the Empire of Japan on September 2, 1945, at the war's end until the Treaty of San Francisco took effect on April 28, 1952. The occupation, led by the ...
, the offices of chief priest and most sacred priestess have been held by former members of the imperial family or their descendants. The current chief priest of the shrine is , adoptive son of Takatsukasa Kazuko. He succeeded Kitashirakawa Michihisa, a great-grandson of Emperor Meiji
, posthumously honored as , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the List of emperors of Japan, traditional order of succession, reigning from 1867 until his death in 1912. His reign is associated with the Meiji Restoration of 1868, which ...
, in 2007. Takatsukasa Kazuko was succeeded by her younger sister, Ikeda Atsuko. In 2012, Ikeda was joined by her niece Sayako Kuroda
, formerly , is the youngest child and only daughter of Emperor Emeritus Akihito and Empress Emerita Michiko, and the younger sister of the current Emperor of Japan, Naruhito. She is an imperial Shinto priestess of the Ise Grand Shrine, curr ...
, sole daughter of Emperor Akihito
Akihito (born 23 December 1933) is a member of the Imperial House of Japan who reigned as the 125th emperor of Japan from 1989 until 2019 Japanese imperial transition, his abdication in 2019. The era of his rule was named the Heisei era, Hei ...
, to serve as a high priestess under her. On 19 June 2017, Sayako officially replaced her aunt as supreme priestess.
Shrine architecture
 The architectural style of the Ise shrine is known as ''
The architectural style of the Ise shrine is known as ''shinmei-zukuri
is an ancient Japanese architectural style typical of Ise Grand Shrine's ''honden'', the holiest of Shinto shrines.Encyclopedia of Shinto It is most common in Mie Prefecture.JAANUS
History
Ancient shrines were constructed according to the style ...
'', characterized by extreme simplicity and antiquity; its basic principles date back to the Kofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
(250–538 C.E.). The shrine buildings use a special variant of this style called , which may not be used in the construction of any other shrine. ''Yuitsu-shinmei-zukuri'' style replicates the architectural features of early rice granaries. The old shrines are dismantled and new ones built on an adjacent site to exacting specifications every 20 years at exorbitant expense, so that the buildings will be forever new and forever ancient and original. The present buildings, dating from 2013, are the 62nd iteration to date and are scheduled for rebuilding in 2033.
 The shrine at Naikū is constructed of Japanese cypress. Built on pillars set directly in the ground, the shrine building measures 10.9 by 5.5 meters and includes a raised floor, verandas all the way around the building and a staircase leading to a single central doorway. The Naikū does not have any windows. The roof is made of thatched reed with ten billets (''
The shrine at Naikū is constructed of Japanese cypress. Built on pillars set directly in the ground, the shrine building measures 10.9 by 5.5 meters and includes a raised floor, verandas all the way around the building and a staircase leading to a single central doorway. The Naikū does not have any windows. The roof is made of thatched reed with ten billets (''katsuogi
or are short, decorative logging, logs used in Japanese architecture, Japanese and Shinto architecture. They are placed at right angles to the ridgeline of roofs, and are usually featured in religious or imperial architecture. ''Katsuogi'' pred ...
'') located on the ridge of the roof, the bargeboards of which project beyond the roof to form the distinctive forked finials ('' chigi'') at the ends of the ridge. The ''chigi'' on the roof of the Naikū are flat on top, rather than pointed, which serves as a distinction for the gender of the deity being represented. In the case of Ise, Amaterasu, a female deity, is represented at the shrine, which is why the ''chigi'' are flat. The roof ridge is supported by two free-standing columns called the ''munamochi-bashira''. The ''katsuogi'', ''chigi'' and ''munamochi-bashira'' are stylised forms of older storehouse building techniques that pre-date the introduction of Buddhist architecture in Japan.
The empty site beside the shrine building, the site where the previous shrine once stood and where the next will be built, is called the ''kodenchi''. This area is strewn with large white pebbles and is left totally empty apart from the ''oi-ya'', a small wooden hut containing a wooden pole a little over 2 metres in height called the ''shin-no-mihashira'' (new sacred central pole). When a new shrine is built, it is built around the sacred central pole before the removal of the oi-ya, so that the central pole is never seen. The central pole of the old shrine will then have a new ''oi-ya'' erected so that the ''shin-no-mihashira'' also remains unseen.
Rebuilding the Shrine
The shrine buildings at Naikū and Gekū, as well as the Uji Bridge, are rebuilt every 20 years as a part of the Shinto belief in ''tokowaka'' (常若), which means renewing objects to maintain a strong sense of divine prestige in pursuit of eternity, and as a way of passing building techniques from one generation to the next. The twenty-year renewal process is called the Shikinen Sengū. Although the goal of Sengū is to get the shrine built within the 20-year period, there have been some instances, especially because of war, where the shrine building process is postponed or delayed. The original physical purpose of the Sengu process is unknown. However, it is believed that it serves to maintain the longevity of the shrine, or possibly as a gesture to the deity enclosed within the shrine. Historically, this cyclical reconstruction has been practiced for many years in various shrines throughout Japan, meaning that it is not a process exclusive to Ise. The entire reconstruction process takes more or less 17 years, with the initial years focusing on project organization and general planning, and the last 8 years focusing on the physical construction of the shrine. The shrine has evolved throughout the years in its reconstruction, while maintaining some of its key features. The shrine was not originally constructed with gold copper adornments; however, because of advancements in technology as well as Buddhist influence, it gained them over the years. Another example of Buddhist influence on the shrine is the use of ''Suedama'', which are Buddhist orbs seen on various religious structures. It symbolizes a sacred jewel, and is comparable to '' nyoi-shu'', orbs which many Buddhist figures are displayed holding. Initially, the shrine was constructed of locally sourcedHinoki
''Chamaecyparis obtusa'' (Japanese cypress, hinoki cypress or hinoki; or , ) is a species of cypress native to central Japan in East Asia, and widely cultivated in the temperate northern hemisphere for its high-quality timber and ornamental qu ...
wood, which served as an ideal building material due to its physical properties. The abundance of local Hinoki wood was short lived, and the shrine currently obtains the wood through other domestic producers, who ensure that only the best wood is being used for the construction. Before the wood is usable in building the shrine, it must be put through a lengthy seasoning and drying process where it is in a pond for several years and then dried.
The team which builds the shrine is typically formed around a few factors. Since many of the building techniques haven't changed since the creation of the Ise Shrine, the workers who are hired to build the shrine must be skilled in specific techniques. Power tools are not allowed within the area of the shrine, which means that skilled artisans and carpenters known as ''miyadaiku'' are necessary in the construction process. The unit of workers is also organized around relative skill levels, and less experienced workers will work on smaller tasks than more experienced workers. The importance of hiring specifically local artisans has decreased throughout time, for the pool of available miyadaiku has thinned out. Specialized work and the specific materials come with a cost; in 2013, the shrine was built from private donations alone, totaling 57 billion Japanese Yen (US$550 million).
Annual festivals
 From the late seventh century, when the festivals and offerings of Ise Shrine became more formalised, a number of annual events have been performed at both Naikū and Gekū. The Tsukinamisai, which was held in June and December, as well as the Kannamesai Festival in September, were the only three offerings performed by the Saiō, an imperial princess who served as high priestess of the shrine until the 14th century. These offerings are based on the cycle of the agricultural year and are still performed today.
The first important ceremony of the modern calendar year is the Kinen-sai, where prayers are offered for a bountiful harvest. Kazahinomisai, where prayers for fair weather and sufficient rains are made, is held twice a year in May and August at both Naikū and Gekū.
The most important annual festival held at Ise Shrine is the . Held in October each year, this ritual makes offerings of the first harvest of crops for the season to Amaterasu. An imperial envoy carries the offering of rice harvested by the
From the late seventh century, when the festivals and offerings of Ise Shrine became more formalised, a number of annual events have been performed at both Naikū and Gekū. The Tsukinamisai, which was held in June and December, as well as the Kannamesai Festival in September, were the only three offerings performed by the Saiō, an imperial princess who served as high priestess of the shrine until the 14th century. These offerings are based on the cycle of the agricultural year and are still performed today.
The first important ceremony of the modern calendar year is the Kinen-sai, where prayers are offered for a bountiful harvest. Kazahinomisai, where prayers for fair weather and sufficient rains are made, is held twice a year in May and August at both Naikū and Gekū.
The most important annual festival held at Ise Shrine is the . Held in October each year, this ritual makes offerings of the first harvest of crops for the season to Amaterasu. An imperial envoy carries the offering of rice harvested by the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
himself to Ise, as well as five-coloured silk cloth and other materials, called ''heihaku.''
Besides the agricultural ceremonies already mentioned, ceremonies and festivals are held throughout the year at both Naikū and Gekū to celebrate things such as the new year, the foundation of Japan, the past emperors, purification rituals for priests and court musicians, good sake fermentation and the Emperor's birthday. There are also daily food offerings to the shrine kami held both in the mornings and evenings.
Gekū – the outer shrine
is a shrine toToyoukebime
Toyouke-hime is the goddess of agriculture, industry, food, clothing, and houses in the Shinto religion. Originally enshrined in the Tanba region of Japan, she was called to reside at Gekū, Ise Shrine, about 1,500 years ago at the age of Empe ...
, the food goddess, located in Ise Grand Shrine. it is also colloquially known as . In pilgrimage customs people traditionally visit this shrine first and then Kotai jingu which is located 4 km to the south
The shrine was founded after Emperor Yuryaku dreamt that he saw Amaterasu
, often called Amaterasu () for short, also known as and , is the goddess of the sun in Japanese mythology. Often considered the chief deity (''kami'') of the Shinto pantheon, she is also portrayed in Japan's earliest literary texts, the () ...
. She said she was unable to get food and asked him to bring Toyouke-hime
Toyouke-hime is the goddess of agriculture, industry, food, clothing, and houses in the Shinto religion. Originally enshrined in the Tanba region of Japan, she was called to reside at Gekū, Ise Shrine, about 1,500 years ago at the age of Empe ...
from Tanba help her with food.
Daiichi-torii-guchi Sando
Daiichi-torii-guchi Sando is the primary route into the shrine. It is aSandō
A in Japanese architecture is the road approaching either a Shinto shrine or a Buddhist temples in Japan, Buddhist temple.Iwanami Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version. Its point of origin is usually straddled in the first case ...
that starts at the Hiyokebashi bridge entrance, and beyond this bridge, the Temizusha (ablution font) is visible on the left side.
Temizusha
A Temizusha is present at the shrine for worshippers to purify .Kitamikado-guchi Sando
An alternative entrance path for the shrine.Saikan and Anzaisho
Saikan and Anzaisho are the Purification Hall and Hall for Imperial Household Visitors respectively. They are on the right side of the pilgrimage path. The Saikan, which is surrounded by fences, is used by Shinto priests to purify themselves. They stay here for one or two nights to cleanse their minds from worldly concerns before performing rituals, as they bathe and eat meals prepared with sacred fire to achieve spiritual serenity; adjacent to Saikan, there is a building called Anzaisho, which serves as the Hall for the Emperor and Empress.Kaguraden
There is a large Kaguraden at Geku.Honden
Toyouke Omikami is enshrined at the Honden. It lies in the most sacred area enclosed by four rows of fences, and the structure remains unchanged from 1500 years ago. Worshippers can only approach the first gate.History
In Japanese mythologyToyouke-hime
Toyouke-hime is the goddess of agriculture, industry, food, clothing, and houses in the Shinto religion. Originally enshrined in the Tanba region of Japan, she was called to reside at Gekū, Ise Shrine, about 1,500 years ago at the age of Empe ...
was either killed by Tsukuyomi-no-Mikoto
, or simply or , is the moon kami in Japanese mythology and the Shinto religion. The name "Tsukuyomi" is a compound of the Old Japanese words and . The ''Nihon Shoki'' mentions this name spelled as , but this ''yumi'' is likely a variation ...
or by Susanoo-no-Mikoto
__FORCETOC__
Susanoo (, ; Historical kana orthography, historical orthography: , ), often referred to by the honorific title Susanoo-no-Mikoto (), is a in Japanese mythology. The younger brother of Amaterasu, goddess of the sun and mythical an ...
. Amaterasu mourned the death of her and in the Nihon Shoki
The or , sometimes translated as ''The Chronicles of Japan'', is the second-oldest book of classical Japanese history. It is more elaborate and detailed than the , the oldest, and has proven to be an important tool for historians and archaeol ...
the reason the sun and the moon are on opposite sides of the sky is that Amaterasu was unwilling to go near Tsukuyomi-no-Mikoto
, or simply or , is the moon kami in Japanese mythology and the Shinto religion. The name "Tsukuyomi" is a compound of the Old Japanese words and . The ''Nihon Shoki'' mentions this name spelled as , but this ''yumi'' is likely a variation ...
the moon god after he committed the murder. Amaterasu is linked with Toyouke-hime as the sun is necessary for food to grow. This was prior to the Tenson Korin and the establishment of Ise Jingu. Emperor Suinin is said to have established the shrine to worship Amaterasu
, often called Amaterasu () for short, also known as and , is the goddess of the sun in Japanese mythology. Often considered the chief deity (''kami'') of the Shinto pantheon, she is also portrayed in Japan's earliest literary texts, the () ...
at a permanent location after many temporary locations. In contrast with , this shrine is not explicitly mentioned in the Kojiki
The , also sometimes read as or , is an early Japanese chronicle of myths, legends, hymns, genealogies, oral traditions, and semi-historical accounts down to 641 concerning the origin of the Japanese archipelago, the , and the Japanese imperia ...
or the Nihon Shoki
The or , sometimes translated as ''The Chronicles of Japan'', is the second-oldest book of classical Japanese history. It is more elaborate and detailed than the , the oldest, and has proven to be an important tool for historians and archaeol ...
.
Besides the traditional establishment date of 4 BC, it has also been proposed as having been made in the 5th century. The shrine officially states it was created 1500 years ago in response to a revelation from Amaterasu
, often called Amaterasu () for short, also known as and , is the goddess of the sun in Japanese mythology. Often considered the chief deity (''kami'') of the Shinto pantheon, she is also portrayed in Japan's earliest literary texts, the () ...
that the shrine was needed.
The shrine has been traditionally rebuilt every 20 years.
There is a separate shrine dedicated to Toyouke's Ara-mitama, or called (Takamiya) inside this shrine.
Naikū – the inner shrine
The official name of the main shrine of Naikū is Kotaijingu and is the place of worship of the goddess Amaterasu. The grounds of Naikū contain a number of structures, including the following:The Uji Bridge
 This 100 meter wooden bridge, built in a traditional Japanese style, stretches across the Isuzu River at the entrance of Naikū. Like the shrine buildings of Naikū, it is rebuilt every 20 years as a part of the Shikinen Sengū ceremony. The bridge is typically built by carpenters with less experience to gain more skills before moving on to take on the task of working on the main shrine. On crossing the bridge, the path turns to the right along the banks of the Isuzu river and passes through large landscaped gardens.
This 100 meter wooden bridge, built in a traditional Japanese style, stretches across the Isuzu River at the entrance of Naikū. Like the shrine buildings of Naikū, it is rebuilt every 20 years as a part of the Shikinen Sengū ceremony. The bridge is typically built by carpenters with less experience to gain more skills before moving on to take on the task of working on the main shrine. On crossing the bridge, the path turns to the right along the banks of the Isuzu river and passes through large landscaped gardens.
Temizusha
After crossing a short, wide bridge, pilgrims to the shrine encounter the Temizusha, a small, roofed structure containing a pool of water for use in ritual purification. Visitors are encouraged to wash their hands and rinse their mouths at Temizusha as a symbolic act to clean the mind and body of impurity. The first of two large torii gates stands just beyond the Temizusha.Saikan and Anzaisho
After passing the first large torii gate, the Purification Hall (Saikan), and the hall for visitors from the imperial household (Anzaisho) is located to the left. The Saikan is used by shrine priests to purify themselves before performing ceremonies at the shrine. They are required to spend one or two nights to free their minds of worldly issues, partaking in baths and eating meals cooked with the sacred fire.Kaguraden
 This hall for special prayer, located just after the second large torii gate, is open to the public for the offering of individual prayers to the kami, the giving of donations and the purchase of special talisman of protection, amulets and hanging scrolls of Amaterasu Omikami.
This hall for special prayer, located just after the second large torii gate, is open to the public for the offering of individual prayers to the kami, the giving of donations and the purchase of special talisman of protection, amulets and hanging scrolls of Amaterasu Omikami.
Imibiyaden
 This hall contains the sacred fire used to cook all of the food offerings to the kami of Ise Shrine. Rice and other offerings cooked on the sacred fire are stored in a box made of Japanese cypress, then purified at the Haraedo immediately in front of the Imibiyaden before being offered to the kami.
This hall contains the sacred fire used to cook all of the food offerings to the kami of Ise Shrine. Rice and other offerings cooked on the sacred fire are stored in a box made of Japanese cypress, then purified at the Haraedo immediately in front of the Imibiyaden before being offered to the kami.
Kōtai Jingū – the main shrine
The pilgrimage path then approaches the fence of the inner sanctum (昇殿, shōden) of Naikū by a set of large stone steps. Within another set of fencing inside the gate is the main shrine (正宮, seigū) itself. Visitors are supposed to keep to the sides of the path as the middle is set aside for the goddess Amaterasu. Etiquette is the same as for most Shinto shrines. Though the actual shrine is hidden behind a large fence, pilgrims can approach the gate to offer their prayers. Photographs in this area are prohibited and this restriction is strictly policed. Kotai Jingū is said to hold the Sacred Mirror, one of threeImperial Regalia of Japan
The are the imperial regalia of Japan and consist of the sword , the mirror , and the jewel . They represent the three primary virtues: valour (the sword), wisdom (the mirror), and benevolence (the jewel).
said to have been given to the first Emperor by the gods. From a path that follows the line of the outer wall, the distinctive roof of the shrine building can be seen through the trees. In front of the walled shrine compound can be seen an open area which was the location of the rebuilding of the shrine in 2013.
Pilgrimage at Ise
 The pilgrimage to the Ise shrine, also known as ''Sangū'', gained immense popularity during the Edo Period, where hundreds of thousands of pilgrims would travel there every year. The growth was exponential, 5 million pilgrims visiting the shrine in the year 1830 alone. By the late 19th century, tourists from abroad began to visit and document Ise. The popularity of making a trip to Ise resulted in vast networks and groups of travelers, which ultimately led to businesses working to benefit from this influx of interest for the shrine. Travel guidebooks were made to aid travelers in their navigation, as well to let them know of specific important places to visit while at Ise. They also included woodblock prints of the shrine that were very appealing to those who had made the long trek to the shrine. Additionally, people wanted souvenirs, which resulted in a variety of vendors at Ise selling general goods and specialty items. There were also various post stations which had specific gifts, many of which were woodblock prints. The pilgrimage had multiple purposes and appeals. It was seen as a purification process, and by visiting Ise, pilgrims were purified and aided in receiving a good afterlife. It also was seen as a vacation, the journey to the shrine itself being almost as important as actually getting there. In the 21st century, Ise is still an important destination both to foreign tourists and especially to the Japanese community; 9 million Japanese tourists visited the shrine in 2013.
The pilgrimage to the Ise shrine, also known as ''Sangū'', gained immense popularity during the Edo Period, where hundreds of thousands of pilgrims would travel there every year. The growth was exponential, 5 million pilgrims visiting the shrine in the year 1830 alone. By the late 19th century, tourists from abroad began to visit and document Ise. The popularity of making a trip to Ise resulted in vast networks and groups of travelers, which ultimately led to businesses working to benefit from this influx of interest for the shrine. Travel guidebooks were made to aid travelers in their navigation, as well to let them know of specific important places to visit while at Ise. They also included woodblock prints of the shrine that were very appealing to those who had made the long trek to the shrine. Additionally, people wanted souvenirs, which resulted in a variety of vendors at Ise selling general goods and specialty items. There were also various post stations which had specific gifts, many of which were woodblock prints. The pilgrimage had multiple purposes and appeals. It was seen as a purification process, and by visiting Ise, pilgrims were purified and aided in receiving a good afterlife. It also was seen as a vacation, the journey to the shrine itself being almost as important as actually getting there. In the 21st century, Ise is still an important destination both to foreign tourists and especially to the Japanese community; 9 million Japanese tourists visited the shrine in 2013.
Shrines and facilities
Shrines
There are 125 shrines within Ise Shrine:"Oise mairi" (「お伊勢まいり」, Jingū-shichō, Ise-Jingū-sūkei-kai, July 1, 2006) pp. 105-118Facilities
See also
*Association of Shinto Shrines
The is a religious administrative organisation that oversees about 80,000 Shinto shrines in Japan. These shrines take the Ise Grand Shrine as the foundation of their belief. It is the largest Shrine Shinto organization in existence.
Description ...
* Atsuta Shrine, home of the sacred sword
* List of Shinto shrines
* Modern system of ranked Shinto shrines
Modern may refer to:
History
*Modern history
** Early Modern period
** Late Modern period
*** 18th century
*** 19th century
*** 20th century
** Contemporary history
* Moderns, a faction of Freemasonry that existed in the 18th century
Philos ...
* Saiō
* '' Sugari no Ontachi'' One of the sacred treasures of Ise Grand Shrine
* Twenty-Two Shrines
The of Japan is one ranking system for Shinto shrines. The system was established during the Heian period and formed part of the government's systematization of Shinto during the emergence of a general anti-Chinese sentiment and the suppression o ...
Notes
References
References
* * * * * * Hvass, Svend M. (1998). ''Ise Japan's Ise Shrines Ancient yet New''. Copenhagen. Aristo Publishing. * Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1962). ''Studies in Shinto and Shrines.'' Kyoto: Ponsonby Memorial SocietyOCLC 399449
*
External links
*New York Public Library Digital Gallery, early photograph of Ise Shrine compound
Photographs of the Ise Shrine by Yoshio Watanabe
Canadian Centre for Architecture
Smithsonian Magazine – This Japanese Shrine
Wheelchair Accessibility of Shrine
* {{Shinmei shrines 7th-century establishments in Japan Jingū Shinto shrines in Mie Prefecture Asuka period Yayoi period Sun temples Japanese imperialism and colonialism Rebuilt buildings and structures in Japan 692 establishments Religious buildings and structures completed in the 690s 7th-century Shinto shrines Ise, Mie Twenty-Two Shrines Shinmei shrines Shikinai Taisha Shinmei-zukuri