During its long history,
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
has been attacked 52 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, besieged 23 times, and destroyed twice.
[. According to Eric H. Cline's tally in Jerusalem Besieged.] The oldest part of the city was settled in the 4th millennium BCE, making Jerusalem one of the
oldest cities in the world.
Given the city's central position in both
Israeli nationalism and
Palestinian nationalism
Palestinian nationalism is the national movement of the Palestinian people that espouses self-determination and sovereignty over the region of Palestine.de Waart, 1994p. 223 Referencing Article 9 of ''The Palestinian National Charter of 1968' ...
, the selectivity required to summarize more than 5,000 years of inhabited history is often
influenced by ideological bias or background (see
Historiography and nationalism
Historiography is the study of how history is written. One pervasive influence upon the writing of history has been nationalism, a set of beliefs about political legitimacy and cultural identity. Nationalism has provided a significant framework ...
). For example, the Jewish periods of the city's history are important to
Israeli nationalists, whose discourse states that modern
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
originate and descend from the
Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
, while the
Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the mai ...
periods of the city's history are important to
Palestinian nationalists
Palestinian nationalism is the national movement of the Palestinian people that espouses self-determination and sovereignty over the region of Palestine.de Waart, 1994p. 223 Referencing Article 9 of ''The Palestinian National Charter of 1968'' ...
, whose
discourse
Discourse is a generalization of the notion of a conversation to any form of communication. Discourse is a major topic in social theory, with work spanning fields such as sociology, anthropology, continental philosophy, and discourse analysis. ...
suggests that modern
Palestinians
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
descend from all the different peoples who have lived in the region. As a result, both sides claim the history of the city has been politicized by the other in order to strengthen their relative claims to the city,
and that this is borne out by the different focuses the different writers place on the various events and eras in the city's history.
Ancient period
Proto-Canaanite period
Archaeological evidence suggests that the first settlement was established near
Gihon Spring
Gihon Spring () or Fountain of the Virgin, also known as Saint Mary's Pool, A.H. Sayce, "The Inscription at the Pool of Siloam," ''Palestine Exploration Fund Quarterly Statement'' 13.2 (April 1881): ( editio princeps), p72/ref> is a spring in the ...
between 3000 and 2800 BCE. The first known mention of the city was in c. 2000 BCE in the
Middle Kingdom Egyptian Execration Texts
Execration texts, also referred to as proscription lists, are ancient Egyptian hieratic texts, listing enemies of the pharaoh, most often enemies of the Egyptian state or troublesome foreign neighbors. The texts were most often written upon stat ...
in which the city was recorded as ''Rusalimum''.
[Slavik, Diane. 2001. ''Cities through Time: Daily Life in Ancient and Modern Jerusalem''. Geneva, Illinois: Runestone Press, p. 60. ][Mazar, Benjamin. 1975. ''The Mountain of the Lord''. Garden City, New York: Doubleday & Company, Inc., p. 45. ] The root
S-L-M in the name is thought to refer to either "peace" (compare with modern Salam or Shalom in modern Arabic and Hebrew) or
Shalim
Shalim (Šalām, Shalem, Salem, and Salim) is a god in Canaanite religion, mentioned in inscriptions found in Ugarit (Ras Shamra) in Syria.Golan, 2003, p. 82. "The name of the Canaanite deity of the setting sun Salim, or Salem, ..The names Saha ...
, the god of dusk in the
Canaanite religion
The Canaanite religion was the group of ancient Semitic religions practiced by the Canaanites living in the ancient Levant from at least the early Bronze Age through the first centuries AD. Canaanite religion was polytheistic and, in some cases ...
.
Canaanite and Egyptian period
Archaeological evidence suggests that by the 17th century BCE, the
Canaanites
{{Cat main, Canaan
See also:
* :Ancient Israel and Judah
Ancient Levant
Hebrew Bible nations
Ancient Lebanon
0050
Ancient Syria
Wikipedia categories named after regions
0050
Phoenicia
Amarna Age civilizations ...
had built massive walls (4 and 5 ton boulders, 26 feet high) on the eastern side of Jerusalem to protect their ancient water system.
By c. 1550–1400 BCE, Jerusalem had become a vassal to Egypt after the Egyptian
New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
under
Ahmose I
Ahmose I ( egy, jꜥḥ ms(j .w), reconstructed /ʔaʕaħ'maːsjə/ ( MK), Egyptological pronunciation ''Ahmose'', sometimes written as ''Amosis'' or ''Aahmes'', meaning "Iah (the Moon) is born") was a pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ...
and
Thutmose I
Thutmose I (sometimes read as Thutmosis or Tuthmosis I, Thothmes in older history works in Latinized Greek; Ancient Egyptian: '' ḏḥwtj- ms'', ''Tʼaḥawtī-mīsaw'', , meaning "Thoth is born") was the third pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of E ...
had reunited Egypt and expanded into the
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
. The
Amarna letters
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between t ...
contain correspondence from
Abdi-Heba, headman of ''Urusalim'' and his
suzerain
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is calle ...
Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( egy, jmn-ḥtp(.w), ''Amānəḥūtpū'' , "Amun is Satisfied"; Hellenized as Amenophis III), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different ...
.
The power of the Egyptians in the region began to decline in the 12th century BCE, during the
Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near Ea ...
. The
Battle of Djahy
The Battle of Djahy was a major land battle between the forces of pharaoh Ramesses III and the Sea Peoples who intended to invade and conquer Egypt. The conflict occurred on the Egyptian Empire's easternmost frontier in Djahy or modern-day souther ...
(
Djahy Djahi, Djahy or Tjahi ( Egyptian: ''ḏhj'', ''ḏꜣhy'') was the Egyptian designation for southern Retjenu.
It ran from approximately Ashkelon in Israel to Lebanon and inland as far as Galilee.Steindorff, George. ''When Egypt Ruled the East ...
being the Egyptian name for
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
) in 1178 BCE between
Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. He is thought to have reigned from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC and is considered to be the last great monar ...
and the
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the Fren ...
marks this loss of power, preceded by the
Battle of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh or Battle of Qadesh took place between the forces of the New Kingdom of Egypt under Ramesses II and the Hittite Empire under Muwatalli II at the city of Kadesh on the Orontes River, just upstream of Lake Homs near the mod ...
in 1274 BCE, which by extension may be said to be marking the beginning of the decline of both the Egyptians and the
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-centra ...
(then particularly the Ha'atussa-Wilussa circuit of Anatolian city-states). The decline of these central powers gave rise to more independent kingdoms in the region. According to the Bible, Jerusalem at this time was known as
Jebus and its independent
Canaanite inhabitants at this time were known as
Jebusites
The Jebusites (; ISO 259-3 ''Ybusi'') were, according to the books of Joshua and Samuel from the Tanakh, a Canaanite tribe that inhabited Jerusalem, then called Jebus (Hebrew: ''Yəḇūs'', "trampled place") prior to the conquest initiated by ...
.
Israelite period
According to the Bible, the
Israelite
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
history of the city began in c. 1000 BCE, with
King David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
's sack of Jerusalem, following which Jerusalem became the
City of David "City of David" is a biblical and religious epithet for the ancient city of Jerusalem.
It may also refer to:
* City of David (archaeological site) - an archaeological excavation associated with ancient Jerusalem
* Jerusalem Walls National Park
...
and capital of the
United Kingdom of Israel
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Re ...
.
According to the
Books of Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books (Joshu ...
, the
Jebusites
The Jebusites (; ISO 259-3 ''Ybusi'') were, according to the books of Joshua and Samuel from the Tanakh, a Canaanite tribe that inhabited Jerusalem, then called Jebus (Hebrew: ''Yəḇūs'', "trampled place") prior to the conquest initiated by ...
managed to resist attempts by the Israelites to capture the city, and by the time of King David were mocking such attempts, claiming that even the blind and lame could defeat the Israelite army. Nevertheless, the
masoretic text
The Masoretic Text (MT or 𝕸; he, נֻסָּח הַמָּסוֹרָה, Nūssāḥ Hammāsōrā, lit. 'Text of the Tradition') is the authoritative Hebrew and Aramaic text of the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) in Rabbinic Judaism. ...
for the
Books of Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books (Joshu ...
states that David managed to capture the city by stealth, sending his forces through a "water shaft" and attacking the city from the inside. Archaeologists now view this as implausible as the
Gihon spring
Gihon Spring () or Fountain of the Virgin, also known as Saint Mary's Pool, A.H. Sayce, "The Inscription at the Pool of Siloam," ''Palestine Exploration Fund Quarterly Statement'' 13.2 (April 1881): ( editio princeps), p72/ref> is a spring in the ...
– the only known location from which water shafts lead into the city – is now known to have been heavily defended (and hence an attack via this route would have been obvious rather than secretive). The older
Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond th ...
text, however, suggests that rather than by a water shaft, David's forces defeated the
Jebusites
The Jebusites (; ISO 259-3 ''Ybusi'') were, according to the books of Joshua and Samuel from the Tanakh, a Canaanite tribe that inhabited Jerusalem, then called Jebus (Hebrew: ''Yəḇūs'', "trampled place") prior to the conquest initiated by ...
by using daggers rather than through the water tunnels coming through the
Gihon spring
Gihon Spring () or Fountain of the Virgin, also known as Saint Mary's Pool, A.H. Sayce, "The Inscription at the Pool of Siloam," ''Palestine Exploration Fund Quarterly Statement'' 13.2 (April 1881): ( editio princeps), p72/ref> is a spring in the ...
. There was another king in Jerusalem,
Araunah
Araunah (Hebrew: ''’Ǎrawnā'') was a Jebusite mentioned in the Second Book of Samuel, who owned the threshing floor on Mount Moriah which David purchased and used as the site for assembling an altar to God. The First Book of Chronicles, a la ...
, during, and possibly before, David's control of the city, according to the biblical narrative, who was probably the Jebusite king of Jerusalem. The city, which at that point stood upon the
Ophel
''Ophel'' ( he, עֹ֫פֶל ''‘ōp̄el''), also Graecised to ''ophlas'', is the biblical term given to a certain part of a settlement or city that is elevated from its surroundings, and probably means fortified hill or risen area. In the Hebr ...
, was, according to the biblical account, expanded to the south, and declared by David to be the capital city of the
Kingdom of Israel. David also, according to the Books of Samuel, constructed an altar at the location of a threshing floor he had purchased from Araunah; a portion of biblical scholars view this as an attempt by the narrative's author to give an Israelite foundation to a pre-existing sanctuary.
Later, according to the biblical narrative, King
Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
built a more substantive temple, the
Temple of Solomon
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by the ...
, at a location which the
Book of Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( he, דִּבְרֵי־הַיָּמִים ) is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third sec ...
equates with David's altar. The Temple became a major cultural centre in the region; eventually, particularly after religious reforms such as those of
Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning "Yahweh, Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Kingdom of Jud ...
and of
Josiah
Josiah ( or ) or Yoshiyahu; la, Iosias was the 16th king of Judah (–609 BCE) who, according to the Hebrew Bible, instituted major religious reforms by removing official worship of gods other than Yahweh. Josiah is credited by most biblical s ...
, the Jerusalem temple became the main place of worship, at the expense of other, formerly powerful, ritual centres, such as
Shiloh and
Bethel
Bethel ( he, בֵּית אֵל, translit=Bēṯ 'Ēl, "House of El" or "House of God",Bleeker and Widegren, 1988, p. 257. also transliterated ''Beth El'', ''Beth-El'', ''Beit El''; el, Βαιθήλ; la, Bethel) was an ancient Israelite sanct ...
. However, according to K. L. Noll, in Canaan and Israel in Antiquity: A Textbook on History and Religion, the Biblical account of the centralization of worship in Jerusalem is a fiction, although by the time of Josiah, the territory he ruled was so small that the Jerusalem temple became de facto the only shrine left. Solomon is also described as having created several other important building works at Jerusalem, including the construction of his palace, and the construction of the
Millo
The Millo ( he, המלוא) was a structure in Jerusalem referred to in the Hebrew Bible, first mentioned as being part of the city of David in and the corresponding passage in the Books of Kings () and later in the Books of Chronicles (). Howev ...
(the identity of which is somewhat controversial). Archaeologists are divided over whether the biblical narrative is supported by the evidence from excavations.
Eilat Mazar
Eilat Mazar ( he, אילת מזר; 10 September 195625 May 2021) was an Israeli archaeologist. She specialized in Jerusalem and Phoenician archaeology. She was also a key person in Biblical archaeology noted for her discovery of the Large Ston ...
contends that her digging uncovered remains of large stone buildings from the correct time period, while
Israel Finkelstein
Israel Finkelstein ( he, ישראל פינקלשטיין, born March 29, 1949) is an Israeli archaeologist, professor emeritus at Tel Aviv University and the head of the School of Archaeology and Maritime Cultures at the University of Haifa. Fin ...
disputes both the interpretation and the dating of the finds.
When the
Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Ce ...
split from the larger Kingdom of Israel (which the Bible places near the end of the reign of Solomon, c. 930 BCE, though
Israel Finkelstein
Israel Finkelstein ( he, ישראל פינקלשטיין, born March 29, 1949) is an Israeli archaeologist, professor emeritus at Tel Aviv University and the head of the School of Archaeology and Maritime Cultures at the University of Haifa. Fin ...
and others dispute the very existence of a unified monarchy to begin with
), Jerusalem became the capital of the Kingdom of Judah, while the Kingdom of Israel located its capital at
Shechem
Shechem ( ), also spelled Sichem ( ; he, שְׁכֶם, ''Šəḵem''; ; grc, Συχέμ, Sykhém; Samaritan Hebrew: , ), was a Canaanite and Israelite city mentioned in the Amarna Letters, later appearing in the Hebrew Bible as the first cap ...
in
Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first- ...
.
Thomas L. Thompson
Thomas L. Thompson (born January 7, 1939 in Detroit, Michigan) is an American-born Danish biblical scholar and theologian. He was professor of theology at the University of Copenhagen from 1993 to 2009. He currently lives in Denmark.
Thompson is ...
argues that it only became a city and capable of acting as a state capital in the middle of the 7th century.
Both the Bible and regional archaeological evidence suggest the region was politically unstable during the period 925–732 BCE. In 925 BCE, the region was invaded by Egyptian Pharaoh
Sheshonk I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I (Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-secon ...
of the
Third Intermediate Period
The Third Intermediate Period of ancient Egypt began with the death of Pharaoh Ramesses XI in 1077 BC, which ended the New Kingdom, and was eventually followed by the Late Period. Various points are offered as the beginning for the latt ...
, who is possibly the same as
Shishak
Shishak, Shishaq or Susac (, Tiberian: , ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, an Egyptian pharaoh who sacked Jerusalem in the 10th century BCE. He is usually identified with the pharaoh Shoshenq I.Troy Leiland Sagrillo. 2015.Shoshenq I and bib ...
, the first Pharaoh mentioned in the
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
who
captured and pillaged Jerusalem. Around 75 years later, Jerusalem's forces were likely involved in an indecisive battle against the
Neo-Assyrian King Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Ashurnasirpal II in 859 BC to his own death in 824 BC.
His long reign was a constant series of campai ...
in the
Battle of Qarqar
The Battle of Qarqar (or Ḳarḳar) was fought in 853 BC when the army of the Neo-Assyrian Empire led by Emperor Shalmaneser III encountered an allied army of eleven kings at Qarqar led by Hadadezer, called in Assyrian ''Adad-idir'' and possibly ...
. According to the bible,
Jehoshaphat
Jehoshaphat (; alternatively spelled Jehosaphat, Josaphat, or Yehoshafat; ; el, Ἰωσαφάτ, Iosafát; la, Josaphat), according to 1 Kings 22:41, was the son of Asa, and the fourth king of the Kingdom of Judah, in succession to his father ...
of Judah was allied to
Ahab
Ahab (; akk, 𒀀𒄩𒀊𒁍 ''Aḫâbbu'' 'a-ḫa-ab-bu'' grc-koi, Ἀχαάβ ''Achaáb''; la, Achab) was the seventh king of Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel, the son and successor of King Omri and the husband of Jezebel of Sidon, ...
of the
Northern Kingdom of Israel
The Kingdom of Israel (), or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. The kingdom controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan (region), Transjordan. Its capi ...
at this time.
The Bible records that shortly after this battle, Jerusalem was sacked by
Philistine
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when ...
s,
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s and
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
ns, who looted King
Jehoram's house, and carried off all of his family except for his youngest son
Jehoahaz.
Two decades later, most of Canaan including Jerusalem was conquered by
Hazael
Hazael (; he, חֲזָאֵל, translit=Ḥazaʾēl, or , romanized as: ; oar, 𐡇𐡆𐡀𐡋, translit= , from the triliteral Semitic root ''h-z-y'', "to see"; his full name meaning, " El/God has seen"; akk, 𒄩𒍝𒀪𒀭, Ḫa-za-’- il ...
of
Aram Damascus
The Kingdom of Aram-Damascus () was an Aramean polity that existed from the late-12th century BCE until 732 BCE, and was centred around the city of Damascus in the Southern Levant. Alongside various tribal lands, it was bounded in its later ye ...
. According to the
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
,
Jehoash of Judah
Jehoash (; el, Ιωας; la, Joas), also known as Joash (in King James Version), Joas (in Douay–Rheims) or Joás (), was the eighth king of Judah, and the sole surviving son of Ahaziah after the massacre of the royal family ordered by his gr ...
gave all of Jerusalem's treasures as a tribute, but
Hazael
Hazael (; he, חֲזָאֵל, translit=Ḥazaʾēl, or , romanized as: ; oar, 𐡇𐡆𐡀𐡋, translit= , from the triliteral Semitic root ''h-z-y'', "to see"; his full name meaning, " El/God has seen"; akk, 𒄩𒍝𒀪𒀭, Ḫa-za-’- il ...
proceeded to destroy "all the princes of the people" in the city. And half a century later, the city was sacked by
Jehoash of Israel
Jehoash ( he, ''Yəhō’āš'' or ''Yō’āš''; Israelian Hebrew: *''’Āšīyāw''; Akkadian: 𒅀𒀪𒋢 ''Yaʾsu'' 'ia-'-su'' la, Joas; fl. c. 790 BC), whose name means "Yahweh has given,""Joash, Jehoash;" ''New Bible Dictionary'' ...
, who destroyed the walls and took
Amaziah of Judah prisoner.
By the end of the ''First Temple Period'', Jerusalem was the sole acting religious shrine in the kingdom and a centre of regular pilgrimage; a fact which archaeologists generally view as being corroborated by the evidence, though there remained a more personal cult involving
Asherah
Asherah (; he, אֲשֵׁרָה, translit=Ăšērā; uga, 𐎀𐎘𐎗𐎚, translit=ʾAṯiratu; akk, 𒀀𒅆𒋥, translit=Aširat; Qatabanian language, Qatabanian: ') in ancient Semitic religion, is a fertility goddess who appears in a ...
figures, which are found spread throughout the land right up to the end of this era.
Assyrian and Babylonian periods
Jerusalem was the capital of the Kingdom of Judah for some 400 years. It had survived an
Assyrian siege in 701 BCE by
Sennacherib
Sennacherib (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynast ...
, unlike Samaria, the capital of the northern Kingdom of Israel, that had fallen some twenty years previously. According to the Bible, this was a miraculous event in which an angel killed 185,000 men in Sennacherib's army. According to Sennacherib's own account preserved in the
Taylor prism
Sennacherib's Annals are the annals of the Assyrian king Sennacherib. They are found inscribed on a number of artifacts, and the final versions were found in three clay prisms inscribed with the same text: the Taylor Prism is in the British Museum ...
, an inscription contemporary with the event, the king of Judah, Hezekiah, was "shut up in the city like a caged bird" and eventually persuaded Sennacherib to leave by sending him "30 talents of gold and 800 talents of silver, and diverse treasures, a rich and immense booty".
The
siege of Jerusalem in 597 BCE led to the city being overcome by the
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
ns, who then took the young King
Jehoiachin
Jeconiah ( he, יְכָנְיָה ''Yəḵonəyā'' , meaning " Yah has established"; el, Ιεχονιας; la, Iechonias, Jechonias), also known as Coniah and as Jehoiachin ( he, יְהוֹיָכִין ''Yəhōyāḵīn'' ; la, Ioachin, Joac ...
into
Babylonian captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital city of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, following their defeat ...
, together with most of the
aristocracy
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At t ...
.
Zedekiah
Zedekiah (), was the 20th and last king of Judah before the destruction of the kingdom by King Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon. His birth name was Mattaniah/Mattanyahu ( he, מַתַּנְיָהוּ, ''Mattanyāhū'', "Gift of God"; el, Μαθθ ...
, who had been placed on the throne by
Nebuchadnezzar
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
(the Babylonian king), rebelled, and Nebuchadnezzar, who at the time (587/586 BCE) was ruler of a most powerful empire,
recaptured the city, killed Zedekiah's descendants in front of him, and plucked out Zedekiah's eyes so that that would be the last thing he ever saw. The Babylonians then took Zedekiah into captivity, along with prominent members of Judah. The Babylonians then burnt the temple, destroyed the city's walls, and appointed
Gedaliah
Gedaliah, Gedalia, Gedallah Hirsch, E. G. and Greenstone, J. H. (1906)Gedallah Jewish Encyclopedia or Gedalya(h) ( or ; he, גְּדַלְיָּה ''Gəḏalyyā'' or ''Gəḏalyyāhū'', meaning " Jah has become Great") was, according to the n ...
son of Achikam as governor of Judah. After 52 days of rule, Yishmael, son of Netaniah, a surviving descendant of Zedekiah, assassinated Gedaliah after encouragement by
Baalis
Baalis (, ''Ba‘ălīs''; Ammonite: 𐤁𐤏𐤋𐤉𐤔𐤏, ''B‘LYŠ‘'') is the name given in the Book of Jeremiah for the king of Ammon. He instigated the murder of Gedaliah, the Babylonian-appointed Jewish governor of Jerusalem.
Seal ...
, the king of
Ammon
Ammon (Ammonite: 𐤏𐤌𐤍 ''ʻAmān''; he, עַמּוֹן ''ʻAmmōn''; ar, عمّون, ʻAmmūn) was an ancient Semitic-speaking nation occupying the east of the Jordan River, between the torrent valleys of Arnon and Jabbok, in p ...
. Some of the remaining population of Judah, fearing the vengeance of Nebuchadnezzar, fled to Egypt.
Persian (Achaemenid) period
According to the Bible, and perhaps corroborated by the
Cyrus Cylinder
The Cyrus Cylinder is an ancient clay cylinder, now broken into several pieces, on which is written a declaration in Akkadian cuneiform script in the name of Persia's Achaemenid king Cyrus the Great. Kuhrt (2007), p. 70, 72 It dates from the 6th c ...
, after several decades of
captivity in Babylon
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital city of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, following their defeat ...
and the
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
conquest of Babylonia,
Cyrus II of Persia allowed the Jews to return to Judah and rebuild the Temple. The books of
Ezra–Nehemiah
Ezra–Nehemiah ( he, עזרא נחמיה , ) is a book in the Hebrew Bible found in the Ketuvim section, originally with the Hebrew title of Ezra ( he, עזרא, links=no, ). The book covers the period from the fall of Babylon in 539 BCE t ...
record that the construction of the
Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited ...
was finished in the sixth year of
Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
(516 BCE), following which
Artaxerxes I sent
Ezra
Ezra (; he, עֶזְרָא, '; fl. 480–440 BCE), also called Ezra the Scribe (, ') and Ezra the Priest in the Book of Ezra, was a Jewish scribe (''sofer'') and priest (''kohen''). In Greco-Latin Ezra is called Esdras ( grc-gre, Ἔσδρας ...
and then
Nehemiah
Nehemiah is the central figure of the Book of Nehemiah, which describes his work in rebuilding Jerusalem during the Second Temple period. He was governor of Persian Judea under Artaxerxes I of Persia (465–424 BC). The name is pronounced ...
to rebuild the city's walls and to govern the
Yehud
Yehud ( he, יְהוּד) is a city in the Central District (Israel), Central District of Israel that is part of the joint municipality of Yehud-Monosson. In 2007, the city's population stood at approximately 30,000 people (including Neve Monosson ...
province within the
Eber-Nari
Eber-Nari (Akkadian, also Ebir-Nari), Abar-Nahara עבר-נהרה (Aramaic) or 'Ābēr Nahrā ( Syriac) meaning "Beyond the River" or "Across the River" in both the Akkadian and Imperial Aramaic languages of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, i.e., the West ...
satrapy. These events represent the final chapter in the historical narrative of the
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;["Tanach"](_blank)
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
.
During this period,
Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
-inscribed "
Yehud coinage
The Yehud coinage is a series of small silver coins bearing the Aramaic inscription ''Yehud''. They derive their name from the inscription YHD (𐤉𐤄𐤃), "Yehud", the Aramaic name of the Achaemenid Persian province of Yehud; others are ...
" were produced – these are believed to have been minted in or near Jerusalem, although none of the coins bear a mint mark.
Classical antiquity
Hellenistic period
Ptolemaic and Seleucid province
When
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
conquered the
Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
, Jerusalem and
Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous L ...
fell under
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
control and
Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
influence. After the
Wars of the Diadochoi following Alexander's death, Jerusalem and Judea fell under
Ptolemaic Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
control under
Ptolemy I and continued minting Yehud coinage. In 198 BCE, as a result of the
Battle of Panium
The Battle of Panium (also known as Paneion, grc, Πάνειον, or Paneas, Πανειάς) was fought in 200 BC near Paneas (Caesarea Philippi) between Seleucid and Ptolemaic forces as part of the Fifth Syrian War. The Seleucids were led by A ...
,
Ptolemy V
egy, Iwaennetjerwymerwyitu Seteppah Userkare Sekhem-ankhamun Clayton (2006) p. 208.
, predecessor = Ptolemy IV
, successor = Ptolemy VI
, horus = '' ḥwnw-ḫꜤj-m-nsw-ḥr-st-jt.f'Khunukhaiemnisutkhersetitef'' The youth who ...
lost Jerusalem and Judea to the
Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
under
Antiochus the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the r ...
.
Under the Seleucids many Jews had become
Hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
and with their assistance tried to Hellenize Jerusalem, eventually culminating in the 160s BCE in a rebellion led by
Mattathias
Mattathias ben Johanan ( he, מַתִּתְיָהוּ הַכֹּהֵן בֶּן יוֹחָנָן, ''Mattīṯyāhū haKōhēn ben Yōḥānān''; died 166–165 BCE) was a Kohen (Jewish priest) who helped spark the Maccabean Revolt against t ...
and his five sons:
Simon
Simon may refer to:
People
* Simon (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name Simon
* Simon (surname), including a list of people with the surname Simon
* Eugène Simon, French naturalist and the genus ...
, Yochanan,
Eleazar
Eleazar (; ) or Elʽazar was a priest in the Hebrew Bible, the second High Priest, succeeding his father Aaron after he died. He was a nephew of Moses.
Biblical narrative
Eleazar played a number of roles during the course of the Exodus, from c ...
,
Jonathan and
Judas Maccabeus
Judah Maccabee (or Judas Maccabeus, also spelled Machabeus, or Maccabæus, Hebrew: יהודה המכבי, ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') was a Jewish priest (''kohen'') and a son of the priest Mattathias. He led the Maccabean Revolt against the Seleuci ...
, also known as the
Maccabees
The Maccabees (), also spelled Machabees ( he, מַכַּבִּים, or , ; la, Machabaei or ; grc, Μακκαβαῖοι, ), were a group of Jewish rebel warriors who took control of Judea, which at the time was part of the Seleucid Empire. ...
.
Hasmonean period

As a result of the
Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended ...
, Jerusalem became the capital of the autonomous and eventually independent
Hasmonean Kingdom. The kingdom lasted for over a century. It was ruled by
Simon Maccabaeus
Simon Thassi ( he, ''Šīməʿōn haTassī''; died 135) was the second son of Mattathias and thus a member of the Hasmonean family.
Names
The name "Thassi" has a connotation of "the Wise", a title which can also mean "the Director", "the ...
, the son of Mattathias; then by his son Yochanan, known as
John Hyrcanus
John Hyrcanus (; ''Yōḥānān Hurqanōs''; grc, Ἰωάννης Ὑρκανός, Iōánnēs Hurkanós) was a Hasmonean ( Maccabean) leader and Jewish high priest of the 2nd century BCE (born 164 BCE, reigned from 134 BCE until his death in ...
, who started minting his own
Hasmonean coins; then by his son
Yehuda Aristobulus; then by his wife
Salome Alexandra
Salome Alexandra, or Shlomtzion ( grc-gre, Σαλώμη Ἀλεξάνδρα; he, , ''Šəlōmṣīyyōn''; 141–67 BCE), was one of three women to rule over Judea, the other two being Athaliah and Devora. The wife of Aristobulus I, and a ...
; then by his brother
Alexander Yannai; then by his sons
Hyrcanus II
John Hyrcanus II (, ''Yohanan Hurqanos'') (died 30 BCE), a member of the Hasmonean dynasty, was for a long time the Jewish High Priest in the 1st century BCE. He was also briefly King of Judea 67–66 BCE and then the ethnarch (ruler) of J ...
and
Aristobulus II
Aristobulus II (, grc, Ἀριστόβουλος ''Aristóboulos'') was the Jewish High Priest and King of Judea, 66 BCE to 63 BCE, from the Hasmonean dynasty.
Family
Aristobulus was the younger son of Alexander Jannaeus, King and High Priest ...
. When the brothers Hyrcanus and Aristobulus each asked for Rome to intervene on their behalf, Judea fell under the greater rule of Rome as an autonomous province but still with a significant amount of independence. The last Hasmonean king was Aristobulus' son, Antigonus II Matityahu.
Roman Jerusalem
In 37 BCE,
Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renov ...
captured Jerusalem after a
forty-day siege, ending Hasmonean rule. Herod ruled the
Province of Judea as a client-king of the
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, rebuilt the
Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited ...
, upgraded the surrounding complex, and
expanded the minting of coins to many denominations.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
, writing of Herod's achievements, called Jerusalem "the most famous by far of the Eastern cities and not only the cities of Judea." The
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cente ...
comments that "He who has not seen the
Temple of Herod has never seen a beautiful building in his life." And
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his t ...
wrote that "Jerusalem is the capital of the Jews. In it was a Temple possessing enormous riches."

Herod also built
Caesarea Maritima
Caesarea Maritima (; Greek: ''Parálios Kaisáreia''), formerly Strato's Tower, also known as Caesarea Palestinae, was an ancient city in the Sharon plain on the coast of the Mediterranean, now in ruins and included in an Israeli national park ...
which replaced Jerusalem as the capital of the
Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
. In 6 CE, following Herod's death in 4 BCE, Judea and the city of Jerusalem came under direct Roman rule through Roman
prefects
Prefect (from the Latin ''praefectus'', substantive adjectival form of ''praeficere'': "put in front", meaning in charge) is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area.
A prefect's ...
,
procurator
Procurator (with procuracy or procuratorate referring to the office itself) may refer to:
* Procurator, one engaged in procuration, the action of taking care of, hence management, stewardship, agency
* ''Procurator'' (Ancient Rome), the title o ...
s, and
legates
A ''legatus'' (; anglicised as legate) was a high-ranking Roman military officer in the Roman Army, equivalent to a modern high-ranking general officer. Initially used to delegate power, the term became formalised under Augustus as the office ...
(see
List of Hasmonean and Herodian rulers
The following is a list of Jewish Head of state, heads of state and/or Head of government, government in the Land of Israel.
House of Saul
* King Saul (c. 1079–1007 BCE)
* King Ish-bosheth (II Samuel 2:8–9)
House of David
* King David (II Sa ...
). However, one of Herod's descendants was the last one to return to power as nominal king of
Iudaea Province
Judaea ( la, Iudaea ; grc, Ἰουδαία, translit=Ioudaíā ) was a Roman province which incorporated the regions of Judea, Samaria, and Idumea from 6 CE, extending over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of ...
:
Agrippa I (r. 41–44).
In 66 CE, the Jewish population rebelled against the Roman Empire in what is now known as the
First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE), sometimes called the Great Jewish Revolt ( he, המרד הגדול '), or The Jewish War, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews against the Roman Empire, fought in Roman-controlled ...
or ''Great Revolt''. Roman legions under future emperor
Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
reconquered and subsequently destroyed much of Jerusalem in 70 CE. Also the Second Temple was burnt and all that remained was the great external (retaining) walls supporting the esplanade on which the Temple had stood, a portion of which has become known as the
Western Wall
The Western Wall ( he, הַכּוֹתֶל הַמַּעֲרָבִי, HaKotel HaMa'aravi, the western wall, often shortened to the Kotel or Kosel), known in the West as the Wailing Wall, and in Islam as the Buraq Wall (Arabic: حَائِط � ...
. Titus' victory is commemorated by the
Arch of Titus
The Arch of Titus ( it, Arco di Tito; la, Arcus Titi) is a 1st-century AD honorific arch, located on the Via Sacra, Rome, just to the south-east of the Roman Forum. It was constructed in 81 AD by the Roman emperor, Emperor Domitian shortly aft ...
in Rome. Agrippa II died c. 94 CE, which brought the
Herodian dynasty
The Herodian dynasty was a royal dynasty of Idumaean (Edomite) descent, ruling the Herodian Kingdom of Judea and later the Herodian Tetrarchy as a vassal state of the Roman Empire. The Herodian dynasty began with Herod the Great, who assumed the ...
to an end almost thirty years after the destruction of the Second Temple. After the end of this revolt, Jews continued to live in Jerusalem in significant numbers, and were allowed to practice their religion, only if they paid the
Jewish Tax
The or (Latin for "Jewish tax") was a tax imposed on Jews in the Roman Empire after the destruction of Jerusalem and its Temple in AD 70. Revenues were directed to the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus in Rome.
The tax measure improved Ro ...
.

In the 1st century CE, Jerusalem became the birthplace of
Early Christianity
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish ...
. According to the
New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
, it is the location of the
crucifixion
Crucifixion is a method of capital punishment in which the victim is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross or beam and left to hang until eventual death from exhaustion and asphyxiation. It was used as a punishment by the Persians, Carthagin ...
,
resurrection
Resurrection or anastasis is the concept of coming back to life after death. In a number of religions, a dying-and-rising god is a deity which dies and is resurrected. Reincarnation is a similar process hypothesized by other religions, which ...
and
Ascension of Jesus
The Ascension of Jesus (anglicized from the Vulgate la, ascensio Iesu, lit=ascent of Jesus) is the Christian teaching that Christ physically departed from Earth by rising to Heaven, in the presence of eleven of his apostles. According to the N ...
Christ (see also
Jerusalem in Christianity
Jerusalem's role in first-century Christianity, during the ministry of Jesus and the Apostolic Age, as recorded in the New Testament, gives it great importance. Jerusalem is generally considered the cradle of Christianity.
New Testament
Accor ...
). It was in Jerusalem that, according to the
Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its messag ...
, the
Apostles of Christ received the
Holy Spirit
In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is the divine force, quality, and influence of God over the Universe or over his creatures. In Nicene Christianity, the Holy Spirit or Holy Ghost is the third person of the Trinity. In Islam, the Holy Spirit acts as ...
at
Pentecost
Pentecost (also called Whit Sunday, Whitsunday or Whitsun) is a Christianity, Christian holiday which takes place on the 50th day (the seventh Sunday) after Easter Sunday. It commemorates the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the Apostles in the Ne ...
and first began preaching the
Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words an ...
and proclaiming his resurrection. Jerusalem eventually became an
early center of Christianity
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish d ...
and home to one of the five
Patriarchates
Patriarchate ( grc, πατριαρχεῖον, ''patriarcheîon'') is an ecclesiological term in Christianity, designating the office and jurisdiction of an ecclesiastical patriarch.
According to Christian tradition three patriarchates were esta ...
of the
Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym fo ...
. After the
Great Schism, it remained a part of the
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via ...
.
Roman Aelia Capitolina

What is today known as the "Old City of Jerusalem" was laid out by the Roman Emperor
Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
in the 2nd century, when he began to rebuild Jerusalem as a
pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
city. In 130, Hadrian visited the ruins of Jerusalem remaining after the
First Jewish-Roman War
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
of 66–73. He rebuilt the city, renaming it Aelia Capitolina in 135 CE. Hadrian placed the city's main
Roman Forum
The Roman Forum, also known by its Latin name Forum Romanum ( it, Foro Romano), is a rectangular forum (plaza) surrounded by the ruins of several important ancient government buildings at the center of the city of Rome. Citizens of the ancient ...
at the junction of the main
Cardo
A cardo (plural ''cardines'') was a north–south street in Ancient Roman cities and military camps as an integral component of city planning. The cardo maximus, or most often the ''cardo'', was the main or central north–south-oriented street ...
and
Decumanus, now the location of the (smaller)
Muristan
The Muristan ( he, מוריסטן, ar, مورستان) is a complex of streets and shops in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. The site was the location of the first Bimaristan (from Persian ''Bimārestān'' بیمارستان ...
. Hadrian built a large temple to
Jupiter Capitolinus
The Capitoline Triad was a group of three deities who were worshipped in Religion in ancient Rome, ancient Roman religion in an elaborate temple on Rome's Capitoline Hill (Latin ''Capitolium''). It comprised Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter, Juno (my ...
, which later became the
Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
. He placed restrictions on some Jewish practices, which caused a
revolt
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
led by
Simon Bar Kokhba
Simon ben Koseba or Cosiba ( he, שִׁמְעוֹן בַּר כֹסֵבָא, translit= Šīmʾōn bar Ḵōsēḇaʾ ; died 135 CE), commonly known as Bar Kokhba ( he, שִׁמְעוֹן בַּר כּוֹכְבָא, translit=Šīmʾōn bar ...
. Hadrian responded with overwhelming force, putting down the rebellion, killing as many as a half million Jews, and resettling the city as a Roman ''
colonia''. Jews were forbidden to enter the city but for a single day of the year,
Tisha B'Av
Tisha B'Av ( he, תִּשְׁעָה בְּאָב ''Tīšʿā Bəʾāv''; , ) is an annual fast day in Judaism, on which a number of disasters in Jewish history occurred, primarily the destruction of both Solomon's Temple by the Neo-Babylonian E ...
(the Ninth of
Av), the
fast day on which Jews mourn the destruction of both Temples. For the next two centuries, the city remained a relatively unimportant pagan Roman town.
Early Byzantine period
The Emperor
Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
*Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given name ...
, however, rebuilt Jerusalem as a Christian center of worship, building the
Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
in 335. Jerusalem had received special recognition in Canon VII of the
First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea (; grc, Νίκαια ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I in AD 325.
This ecumenical council was the first effort ...
in 325. Constantine's mother,
Helena, made a
pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
to the city and claimed to have recovered the
''cross of Christ''. Jews were still banned from the city throughout the remainder of its time as a
Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
, except during a brief period of
Persian rule from 614 to 629.
Medieval period
Early Muslim period
Rashidun, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates
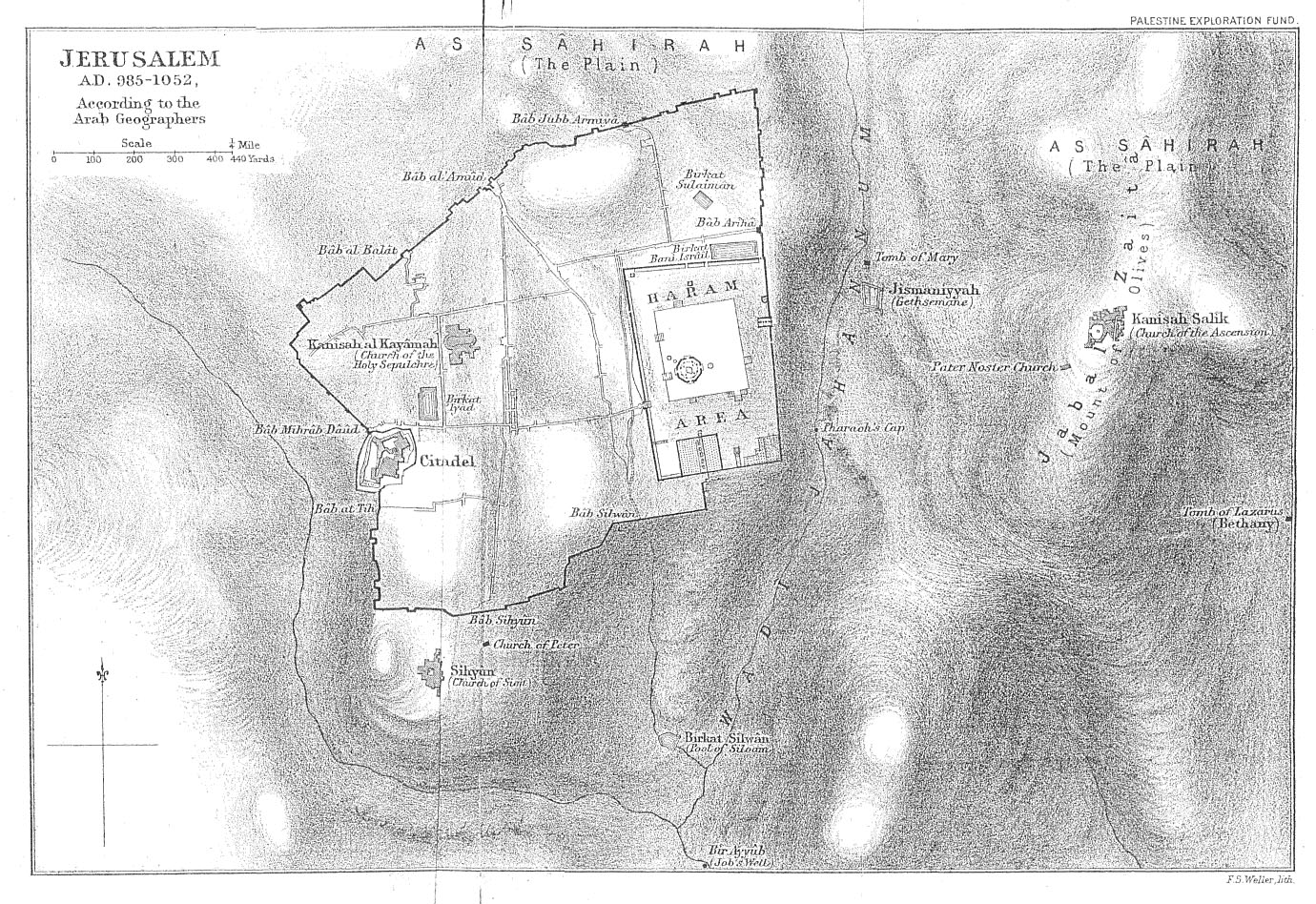

Although the
Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing. ...
does not mention the name "Jerusalem", the
hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
assert that it was from Jerusalem that
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, di ...
ascended to heaven in the Night Journey, or
Isra and Miraj. The city was one of the
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
's first conquests in 638 CE; according to Arab historians of the time, the
Rashidun
, image = تخطيط كلمة الخلفاء الراشدون.png
, caption = Calligraphic representation of Rashidun Caliphs
, birth_place = Mecca, Hejaz, Arabia present-day Saudi Arabia
, known_for = Companions of t ...
Caliph
Umar ibn al-Khattab
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate o ...
personally went to the city to receive its submission, cleaning out and praying at the
Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compoun ...
in the process. Sixty years later the
Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
was built, a structure enshrining a
stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
from which Muhammad is said to have ascended to heaven during the
Isra. The octagonal and gold-sheeted Dome of the Rock is a shrine, not a mosque, and is distinct from the
Jami Al-Aqsa south of it, the latest version of which was built more than three centuries later. Umar ibn al-Khattab allowed the Jews back into the city and freedom to live and worship after almost three centuries of banishment by the Romans and Byzantines.
Under the early centuries of Muslim rule, especially during the
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
(650–750) and
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
(750–969) dynasties, the city prospered; geographers
Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled during the ye ...
and
al-Istakhri
Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al-Istakhri () (also ''Estakhri'', fa, استخری, i.e. from the Iranian city of Istakhr, b. - d. 346 AH/AD 957) was a 10th-century travel-author and geographer who wrote valuable accounts in Arab ...
(10th century) describe it as "the most fertile province of
Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
", while its native son, the geographer
al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Abī Bakr al-Maqdisī ( ar, شَمْس ٱلدِّيْن أَبُو عَبْد ٱلله مُحَمَّد ابْن أَحْمَد ابْن أَبِي بَكْر ٱلْمَقْدِسِي), ...
(born 946) devoted many pages to its praises in his most famous work, ''The Best Divisions in the Knowledge of the Climes''. Under Muslim rule Jerusalem did not achieve the political or cultural status enjoyed by the capitals Damascus, Baghdad, Cairo etc. Al-Muqaddasi derives his name from the Arabic name for Jerusalem, ''Bayt al-Muqaddas'', which is linguistically equivalent to the Hebrew ''Beit Ha-Mikdash'', the
Holy House.
Fatimid period
The early Arab period was also one of religious tolerance. However, in the early 11th century, the Egyptian
Fatimid Caliph
This is a list of an Arab dynasty, the Shi'ite caliphs of the Fatimid dynasty (909–1171). The Shi'ite caliphs were also regarded at the same time as the imams of the Isma'ili branch of Shi'a Islam.
Family tree of Fatimid caliphs
...
Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah
Abū ʿAlī Manṣūr (13 August 985 – 13 February 1021), better known by his regnal name al-Ḥākim bi-Amr Allāh ( ar, الحاكم بأمر الله, lit=The Ruler by the Order of God), was the sixth Fatimid caliph and 16th Ismaili ima ...
ordered the destruction of all churches. In 1033, there was
another earthquake
''Another Earthquake!'' is the fourth studio album by American teen pop singer Aaron Carter, released on September 3, 2002. The album made its chart debut at number 18 on the US ''Billboard'' 200 (with 41,000 units sold), but fell to number 41 ( ...
, severely damaging the Al-Aqsa Mosque. The
Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dy ...
caliph
Ali az-Zahir
Abū al-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn al-Ḥākim ( ar, أبو الحسن علي ابن الحاكم; 20 June 1005 – 13 June 1036), better known with his regnal name al-Ẓāhir li-iʿzāz Dīn Allāh ( ar, الظاهر لإعزاز دين الله, ...
rebuilt and completely renovated the mosque between 1034 and 1036. The number of naves was drastically reduced from fifteen to seven.
[Ma'oz, Moshe and Nusseibeh, Sari. (2000). ]
Jerusalem: Points of Friction, and Beyond
' Brill. pp. 136–38. . Az-Zahir built the four arcades of the central hall and aisle, which presently serve as the foundation of the mosque. The central aisle was double the width of the other aisles and had a large gable roof upon which the dome—made of wood—was constructed.
[Elad, Amikam. (1995). ]
Medieval Jerusalem and Islamic Worship Holy Places, Ceremonies, Pilgrimage
' Brill, pp. 29–43. . Persian geographer,
Nasir Khusraw
Abu Mo’in Hamid ad-Din Nasir ibn Khusraw al-Qubadiani or Nāsir Khusraw Qubādiyānī Balkhi ( fa, ناصر خسرو قبادیانی, Nasir Khusraw Qubadiani) also spelled as ''Nasir Khusrow'' and ''Naser Khosrow'' (1004 – after 1070 CE) w ...
describes the Aqsa Mosque during a visit in 1047:
''The Haram Area (Noble Sanctuary) lies in the eastern part of the
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
; and through the
bazaar
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a marketplace consisting of multiple small Market stall, stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East, the Balkans, North Africa and India. However, temporary open markets elsewhere, suc ...
of this (quarter) you enter the Area by a great and beautiful gateway (
Dargah
A dargah ( fa, درگاه ''dargâh'' or ''dargah'', Turkish: ''dergâh'', Hindustani: ''dargah'' दरगाह درگاہ, bn, দরগাহ ''dorgah'') is a shrine or tomb built over the grave of a revered religious figure, often ...
)... After passing this gateway, you have on the right two great colonnades (
Riwaq), each of which has nine-and-twenty marble pillars, whose capitals and bases are of colored marbles, and the joints are set in lead. Above the pillars rise arches, that are constructed, of masonry, without mortar or cement, and each arch is constructed of no more than five or six blocks of stone. These colonnades lead down to near the
Maqsurah
''Maqsurah'' ( ar, مقصورة, literally "closed-off space") is an enclosure, box, or wooden screen near the ''mihrab'' or the center of the ''qibla'' wall in a mosque. It was typically reserved for a Muslim ruler and his entourage, and was ori ...
.''
Seljuk period
Under Az-Zahir's successor
al-Mustansir Billah
Abū Tamīm Maʿad al-Mustanṣir biʾllāh ( ar, أبو تميم معد المستنصر بالله; 2 July 1029 – 29 December 1094) was the eighth Fatimid Caliph from 1036 until 1094. He was one of the longest reigning Muslim rulers. ...
, the Fatimid Caliphate entered a period of instability and decline, as factions fought for power in Cairo. In 1071, Jerusalem was captured by the Turkish warlord
Atsiz ibn Uvaq
Atsiz ibn Uwaq al-Khwarizmi, also known as al-Aqsis, Atsiz ibn Uvaq, Atsiz ibn Oq and Atsiz ibn Abaq (died October 1079), was a Khwarezmian Turkish mercenary commander who established a principality in Palestine and southern Syria after seizing ...
, who seized most of Syria and Palestine as part of the expansion of the
Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
throughout the Middle East. As the Turks were staunch Sunnis, they were opposed not only to the Fatimids, but also to the numerous Shia Muslims, who saw themselves removed from dominance after a century of Fatimid rule. In 1176, riots between Sunnis and Shiites in Jerusalem led to a massacre of the latter. Although the Christians of the city were left unmolested, and allowed access to the Christian holy sites, the wars with Byzantium and the general instability in Syria impeded the arrival pilgrims from Europe. The Seljuks also forbade the repair of any church, despite the damages suffered in the recent turmoils. There does not appear to have been a significant Jewish community in the city at this time.
In 1086, the Seljuk emir of
Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
,
Tutush I
Abu Sa'id Taj al-Dawla Tutush (; died 25 February 1095) or Tutush I, was the Seljuk emir of Damascus from 1078 to 1092, and sultan of Damascus from 1092 to 1094.
Years under Malik Shah
Tutush was a brother of the Seljuk sultan Malik-Shah I. In 1 ...
, appointed
Artuk Bey
Zaheer-ul-Daulah Artuk Beg, known as Artuk Bey, was a Turkmens, Turkmen commander of the Seljuk Empire in the 11th century, chief of the Oghuz Turks, Oghuz tribe of Döğer (tribe), Döğer, and eponymous founder of the Artuqid dynasty. His fath ...
governor of Jerusalem. Artuk died in 1091, and his sons
Sökmen and
Ilghazi
Najm ad-Din Ilghazi ibn Artuq (died November 8, 1122) was the Turkmen Artukid ruler of Mardin from 1107 to 1122. He was born into the Oghuz tribe of Döğer.
Biography
His father Artuk Bey was the founder of the Artukid dynasty, and had be ...
succeeded him. In August 1098, while the Seljuks were distracted by the arrival of the
First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
in Syria, the Fatimids under vizier
al-Afdal Shahanshah
Al-Afdal Shahanshah ( ar, الأفضل شاهنشاه, al-Afḍal Shāhanshāh; la, Lavendalius/Elafdalio; 1066 – 11 December 1121), born Abu al-Qasim Shahanshah bin Badr al-Jamali was a vizier of the Fatimid caliphs of Egypt. According to a ...
appeared before the city and laid siege to it. After six weeks, the Seljuk garrison capitulated and was allowed to leave for Damascus and Diyar Bakr. The Fatimid takeover was followed by the expulsion of most of the Sunnis, in which many of them were also killed.
Crusader/Ayyubid period
The time span consisting of the 12th and 13th centuries is sometimes referred to as the medieval period, or the Middle Ages, in the history of Jerusalem.
First Crusader kingdom (1099–1187)
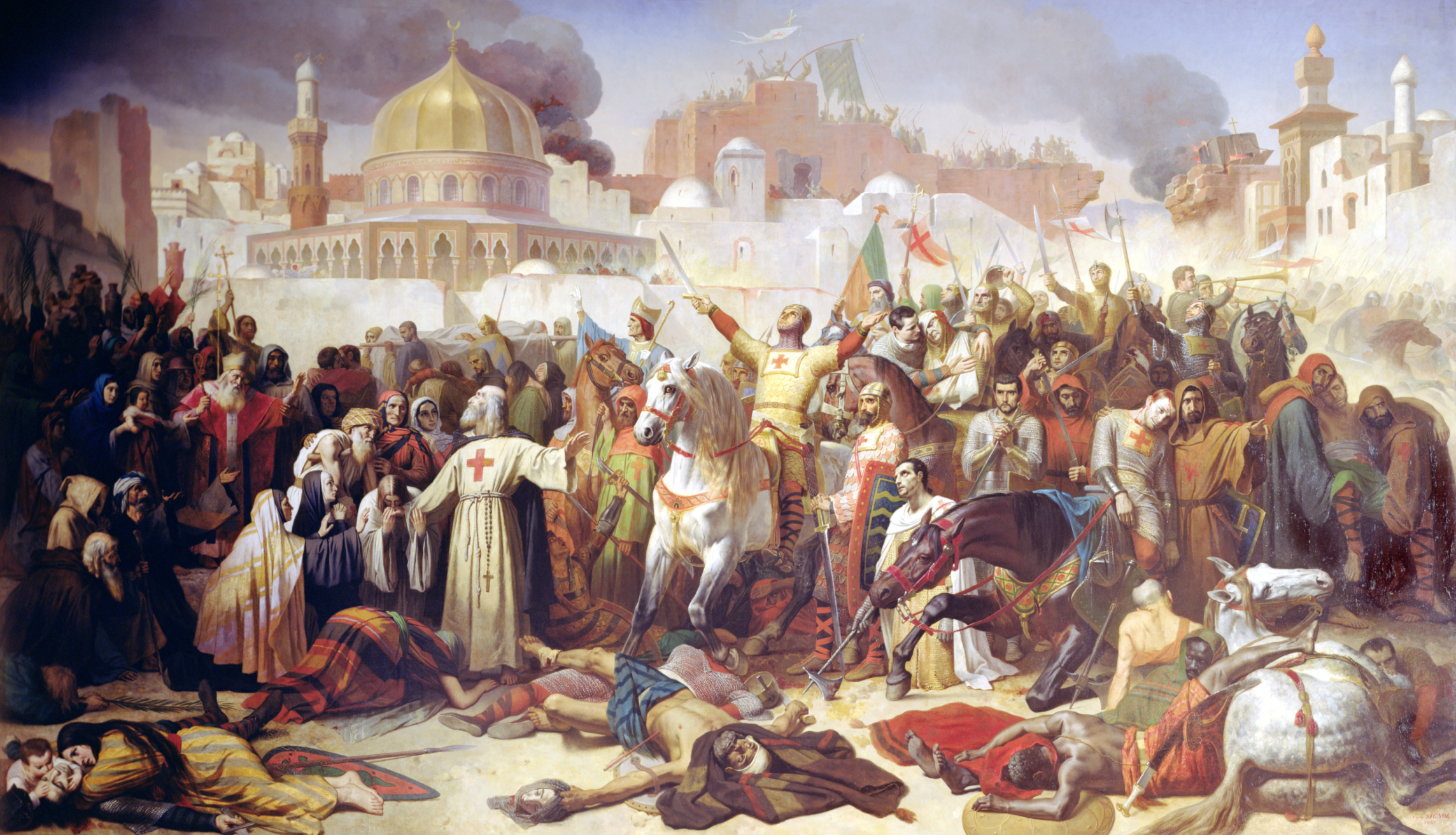

Fatimid control of Jerusalem ended when it was captured by
Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
in July 1099. The capture was accompanied by a
massacre
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
of almost all of the Muslim and Jewish inhabitants. Jerusalem became the capital of the
Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establishe ...
.
Godfrey of Bouillon
Godfrey of Bouillon (, , , ; 18 September 1060 – 18 July 1100) was a French nobleman and pre-eminent leader of the First Crusade. First ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem from 1099 to 1100, he avoided the title of king, preferring that of princ ...
, was elected Lord of Jerusalem on 22 July 1099, but did not assume the royal crown and died a year later.
[Bréhier, Loui]
Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem (1099–1291)
Catholic Encyclopedia 1910, accessed 11 March 2008 Barons offered the lordship of Jerusalem to Godfrey's brother
Baldwin,
Count of Edessa
The County of Edessa (Latin: ''Comitatus Edessanus'') was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century. Ferdinandi, Sergio (2017). La Contea Franca di Edessa. Fondazione e Profilo Storico del Primo Principato Crociato nel Levante (1098-115 ...
, who had himself crowned by the
Patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in certai ...
Daimbert on Christmas Day 1100 in the basilica of
Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
.
Christian settlers from the West set about rebuilding the principal shrines associated with the life of Christ. The Church of the Holy Sepulchre was ambitiously rebuilt as a great Romanesque church, and Muslim shrines on the Temple Mount (the Dome of the Rock and the
Jami Al-Aqsa) were converted for Christian purposes. It is during this period of Frankish occupation that the Military Orders of the
Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic Church, Catholic Military ord ...
and the
Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
have their beginnings. Both grew out of the need to protect and care for the great influx of pilgrims travelling to Jerusalem in the 12th century.
Ayyubid control
The Kingdom of Jerusalem lasted until 1291; however, Jerusalem itself was recaptured by
Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
in 1187 (see
Siege of Jerusalem (1187)
The siege of Jerusalem lasted from 20 September to 2 October 1187, when Balian of Ibelin surrendered the city to Saladin. Earlier that summer, Saladin had defeated the kingdom's army and conquered several cities. Balian was charged with org ...
), who permitted worship of all religions. According to Elijah Ba'al Shem of Chelm, Rabbi Elijah of Chelm, German Jews lived in Jerusalem during the 11th century. The story is told that a German-speaking Jew saved the life of a young German man surnamed Dolberger. Thus when the knights of the First Crusade came to besiege Jerusalem, one of Dolberger's family members rescued Jews in Palestine and carried them back to the German city of Worms, Germany, Worms to repay the favor. Further evidence of German communities in the holy city comes in the form of Halakha, halakic questions sent from Germany to Jerusalem during the second half of the 11th century.

In 1173 Benjamin of Tudela visited Jerusalem. He described it as a small city full of Syriac Orthodox Church, Jacobites, Armenians, Greeks, and Georgian people, Georgians. Two hundred Jews dwelt in a corner of the city under the Tower of David. In 1219 the walls of the city were razed by order of Al-Mu'azzam Isa, al-Mu'azzam, the Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubid sultan of Damascus. This rendered Jerusalem defenseless and dealt a heavy blow to the city's status. The Ayyubids destroyed the walls in expectation of ceding the city to the Crusaders as part of a peace treaty. In 1229, by treaty with Egypt's ruler al-Kamil, Jerusalem came into the hands of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II of Germany. In 1239, after a ten-year truce expired, he began to rebuild the walls; these were again demolished by an-Nasir Da'ud, the emir of Kerak, in the same year.
In 1243 Jerusalem came again into the power of the Christians, and the walls were repaired. The Khwarazmian dynasty, Khwarezmian Empire took the city in 1244 and were in turn driven out by the Ayyubids in 1247. In 1260 the Mongols under Hulagu Khan engaged in Mongol raids into Palestine, raids into Palestine. It is unclear if the Mongols were ever in Jerusalem, as it was not seen as a settlement of strategic importance at the time. However, there are reports that some of the Jews that were in Jerusalem temporarily fled to neighboring villages.
Mamluk period
In 1250 a crisis within the Ayyubid state led to the rise of the Mamluks to power and a transition to the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo), Mamluk Sultanate, which is divided between the Bahri dynasty, Bahri and Burji dynasty, Burji periods. The Ayyubids tried to hold on to power in Syria, but the Battle of Ain Jalut, Mongol invasion of 1260 put an end to this. A Mamluk army defeated the Mongol incursion and in the aftermath Baibars, Baybars, the true founder of the Mamluk state, emerged as ruler of Egypt, the Levant, and the Hejaz, Hijaz.
The Mamluks ruled over Palestine including Jerusalem from 1260 until 1516.
In the decades after 1260 they also worked to eliminate the remaining Crusader states in the region. The last of these was defeated with the Siege of Acre (1291), capture of Acre in 1291.
Jerusalem was a significant site of Mamluk architecture, Mamluk architectural patronage. The frequent building activity in the city during this period is evidenced by the 90 remaining structures that date from the 13th to 15th centuries.
The types of structures built included madrasas, libraries, Bimaristan, hospitals, caravanserais, fountains (or Sebil (fountain), sabils), and public baths.
Much of the building activity was concentrated around the edges of the Temple Mount or Haram al-Sharif.
Old gates to the site lost importance and new gates were built,
while significant parts of the northern and western porticos along the edge of the Temple Mount plaza were built or rebuilt in this period.
Tankiz, the Mamluk Emir, amir in charge of Syria (region), Syria during the reign of al-Nasir Muhammad, built a new market called ''Suq al-Qattatin'' (Cotton Market) in 1336–7, along with the gate known as ''Bab al-Qattanin'' (Cotton Gate), which gave access to the Temple Mount from this market.
The late Mamluk sultan Qaitbay, al-Ashraf Qaytbay also took interest in the city. He commissioned the building of the Madrasa Al-Ashrafiyya, Madrasa al-Ashrafiyya, completed in 1482, and the nearby Fountain of Qayt Bay, Sabil of Qaytbay, built shortly after in 1482; both were located on the Temple Mount.
Qaytbay's monuments were the last major Mamluk constructions in the city.
Jewish presence
Rabbinical Jewish tradition, based on a source of doubtful authenticity, holds that in 1267, the Jewish Catalan sage Nahmanides travelled to Jerusalem, where he established the Ramban Synagogue, synagogue much later named after him,
today the second oldest active synagogue in Jerusalem, after that of the Karaite Jews built about 300 years earlier. Scholars date the Ramban Synagogue to the 13th century or later.
[
]
Latin presence
 The first provincial or superior of the Franciscan religious order, founded by Francis of Assisi, was Brother Elia from Assisi. In the year 1219 the founder himself visited the region in order to preach the
The first provincial or superior of the Franciscan religious order, founded by Francis of Assisi, was Brother Elia from Assisi. In the year 1219 the founder himself visited the region in order to preach the Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words an ...
to the Muslims, seen as brothers and not enemies. The mission resulted in a meeting with the sultan of Egypt, Malik al-Kamil, who was surprised by his unusual behaviour. The Franciscan Province of the East extended to Cyprus, Syria, Lebanon, and the Holy Land. Before the taking over of Acre, Israel, Acre (on 18 May 1291), Franciscan friaries were present at Acre, Sidon, Antioch, Tripoli, Lebanon, Tripoli, Jaffa, and Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
.
From Cyprus, where they took refuge at the end of the Latin Kingdom, the Franciscans started planning a return to Jerusalem, given the good political relations between the Christian governments and the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo), Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt. Around the year 1333 the French friar Roger Guerin succeeded in buying the Cenacle (the room where the Last Supper took place) on Mount Zion and some land to build a monastery nearby for the friars, using funds provided by the king and queen of Naples. With two papal bullae, Gratias Agimus and Nuper Carissimae, dated in Avignon, 21 November 1342, Pope Clement VI approved and created the new entity which would be known as the Franciscan Custody of the Holy Land (Custodia Terrae Sanctae).
The friars, coming from any of the Order's provinces, under the jurisdiction of the father guardian (superior) of the monastery on Mount Zion, were present in Jerusalem, in the Cenacle, in the church of the Holy Sepulcher, and in the Basilica of the Nativity at Bethlehem. Their principal activity was to ensure liturgical life in these Christian sanctuaries and to give spiritual assistance to the pilgrims coming from the West, to European merchants resident or passing through the main cities of Egypt, Syria, and Lebanon, and to have a direct and authorized relation with the Eastern Christianity Oriental communities.
The monastery on Mount Zion was used by Brother Alberto da Sarteano for his papal mission for the union of the Oriental Christians (Greeks, Copts, and People of Ethiopia, Ethiopians) with Rome during the Council of Florence (1440). For the same reason the party guided by Brother Giovanni di Calabria halted in Jerusalem on his way to meet the Christian Negus of Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
(1482).
In 1482, the visiting Dominican Order, Dominican priest Felix Fabri described Jerusalem as "a dwelling place of diverse nations of the world, and is, as it were, a collection of all manner of abominations". As "abominations" he listed Saracens, Greek Orthodox Church, Greeks, Syriac Christianity, Syrians, Syriac Orthodox Church, Jacobites, Ethiopia, Abyssinians, Nestorian Christian, Nestorians, Armenians, Brotherhood of Saint Gregory, Gregorians, Maronites, Oghuz Turks, Turcomans, Bedouins, Hashshashin, Assassins, a possible Druze sect and Mamluks. Christians and Jews alike in Jerusalem lived in great poverty and in conditions of great deprivation, there are not many Christians but there are many Jews, and these the Muslims persecute in various ways." Only the Western Christianity, Latin Christians "long with all their hearts for Christian princes to come and subject all the country to the authority of the Church of Rome".
Early modern period
Early Ottoman period
In 1516, Jerusalem was Ottoman–Mamluk War (1516–17), taken over by the Ottoman Empire along with all of Bilad ash-Sham, Greater Syria and enjoyed a period of renewal and peace under Suleiman the Magnificent, including the construction of Walls of Jerusalem, the walls, which define until today what is now known as the Old City of Jerusalem. The outline of the walls largely follows that of different older fortifications. The rule of Suleiman and subsequent Ottoman Sultans brought an age of "religious peace"; Jew, Christian and Muslim enjoyed freedom of religion and it was possible to find a synagogue, a church and a mosque on the same street. The city remained open to all religions, although the empire's faulty management after Suleiman the Magnificent meant economical stagnation.
Latin presence
In 1551 the Friars were expelled by the Turks from the Cenacle and from their adjoining monastery. However, they were granted permission to purchase a Georgian monastery of nuns in the northwest quarter of the city, which became the new center of the Custody in Jerusalem and developed into the Latin Convent of Saint Saviour (known as Dayr al Ātīn دير الاتين
دير اللاتين Arabic)).
Jewish presence
In 1700, Judah HeHasid (Jerusalem), Judah HeHasid led the largest organized group of Jewish immigrants to the Land of Israel in centuries. His disciples built the Hurva Synagogue, which served as the main synagogue in Jerusalem from the 18th century until 1948, when it was destroyed by the Arab Legion. The synagogue was rebuilt in 2010.
Local vs. central power
In response to the onerous taxation policies and military campaigns against the city's hinterland by the governor Mehmed Pasha Kurd Bayram, the notables of Jerusalem, allied with the local peasantry and Bedouin, rebelled against the Ottomans in what became known as the Naqib al-Ashraf revolt and took control of the city in 1703–1705 before an imperial army reestablished Ottoman authority there. The consequent loss of power of Jerusalem's al-Wafa'iya al-Husayni family, which led the rebellion, paved the way for the al-Husayni family becoming one of the city's leading families.
Late modern period
Late Ottoman period
 In the mid-19th century, with the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the city was a backwater, with a population that did not exceed 8,000. Nevertheless, it was, even then, an extremely heterogeneous city because of its significance to Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The population was divided into four major communities – Jewish, Christian, Muslim, and Armenian – and the first three of these could be further divided into countless subgroups, based on precise religious affiliation or country of origin. The Church of the Holy Sepulchre was meticulously partitioned between the Eastern Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox, Catholic, Armenian Apostolic Church, Armenian, Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic, and Ethiopian Church, Ethiopian churches. Tensions between the groups ran so deep that the keys to the shrine and its doors were safeguarded by a pair of 'neutral' Muslim families.
At the time, the communities were located mainly around their primary shrines. The Muslim community surrounded the Haram ash-Sharif or Temple Mount (northeast), the Christians lived mainly in the vicinity of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre (northwest), the Jews lived mostly on the slope above the Western Wall (southeast), and the Armenians lived near the Zion Gate (southwest). In no way was this division exclusive, though it did form the basis of the four quarters during the British Mandate (1917–1948).
Several changes with long-lasting effects on the city occurred in the mid-19th century: their implications can be felt today and lie at the root of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict over Jerusalem. The first of these was a trickle of Jewish immigrants from the Middle East and Eastern Europe. The first such immigrants were Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jews: some were elderly individuals, who came to die in Jerusalem and be buried on the Mount of Olives; others were students, who came with their families to await the coming of the Messiah, adding new life to the local population. At the same time, European colonial powers began seeking toeholds in the city, hoping to expand their influence pending the imminent collapse of the Ottoman Empire. This was also an age of Christian religious revival, and many churches sent missionaries to proselytize among the Muslim and especially the Jewish populations, believing that this would speed the Second Coming of Christ. Finally, the combination of European colonialism and religious zeal was expressed in a new scientific interest in the biblical lands in general and Jerusalem in particular. Archeological and other expeditions made some spectacular finds, which increased interest in Jerusalem even more.
By the 1860s, the city, with an area of only one square kilometer, was already overcrowded. Thus began the construction of the New City, the part of Jerusalem outside of the city walls. Seeking new areas to stake their claims, the Russian Orthodox Church began constructing a complex, now known as the Russian Compound, a few hundred meters from Jaffa Gate. The first attempt at residential settlement outside the walls of Jerusalem was undertaken by Jews, who built a small complex on the hill overlooking Zion Gate, across the Valley of Hinnom. This settlement, known as Mishkenot Sha'ananim, eventually flourished and set the precedent for other new communities to spring up to the west and north of the Old City. In time, as the communities grew and connected geographically, this became known as the New City.
In 1882, around 150 Jewish families arrived in Jerusalem from Yemen. Initially they were not accepted by the Jews of Jerusalem and lived in destitute conditions supported by the Christians of the Swedish-American colony, who called them Tribe of Gad, Gadites.
In the mid-19th century, with the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the city was a backwater, with a population that did not exceed 8,000. Nevertheless, it was, even then, an extremely heterogeneous city because of its significance to Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The population was divided into four major communities – Jewish, Christian, Muslim, and Armenian – and the first three of these could be further divided into countless subgroups, based on precise religious affiliation or country of origin. The Church of the Holy Sepulchre was meticulously partitioned between the Eastern Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox, Catholic, Armenian Apostolic Church, Armenian, Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic, and Ethiopian Church, Ethiopian churches. Tensions between the groups ran so deep that the keys to the shrine and its doors were safeguarded by a pair of 'neutral' Muslim families.
At the time, the communities were located mainly around their primary shrines. The Muslim community surrounded the Haram ash-Sharif or Temple Mount (northeast), the Christians lived mainly in the vicinity of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre (northwest), the Jews lived mostly on the slope above the Western Wall (southeast), and the Armenians lived near the Zion Gate (southwest). In no way was this division exclusive, though it did form the basis of the four quarters during the British Mandate (1917–1948).
Several changes with long-lasting effects on the city occurred in the mid-19th century: their implications can be felt today and lie at the root of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict over Jerusalem. The first of these was a trickle of Jewish immigrants from the Middle East and Eastern Europe. The first such immigrants were Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jews: some were elderly individuals, who came to die in Jerusalem and be buried on the Mount of Olives; others were students, who came with their families to await the coming of the Messiah, adding new life to the local population. At the same time, European colonial powers began seeking toeholds in the city, hoping to expand their influence pending the imminent collapse of the Ottoman Empire. This was also an age of Christian religious revival, and many churches sent missionaries to proselytize among the Muslim and especially the Jewish populations, believing that this would speed the Second Coming of Christ. Finally, the combination of European colonialism and religious zeal was expressed in a new scientific interest in the biblical lands in general and Jerusalem in particular. Archeological and other expeditions made some spectacular finds, which increased interest in Jerusalem even more.
By the 1860s, the city, with an area of only one square kilometer, was already overcrowded. Thus began the construction of the New City, the part of Jerusalem outside of the city walls. Seeking new areas to stake their claims, the Russian Orthodox Church began constructing a complex, now known as the Russian Compound, a few hundred meters from Jaffa Gate. The first attempt at residential settlement outside the walls of Jerusalem was undertaken by Jews, who built a small complex on the hill overlooking Zion Gate, across the Valley of Hinnom. This settlement, known as Mishkenot Sha'ananim, eventually flourished and set the precedent for other new communities to spring up to the west and north of the Old City. In time, as the communities grew and connected geographically, this became known as the New City.
In 1882, around 150 Jewish families arrived in Jerusalem from Yemen. Initially they were not accepted by the Jews of Jerusalem and lived in destitute conditions supported by the Christians of the Swedish-American colony, who called them Tribe of Gad, Gadites.
British Mandate period
 The British were victorious over the Ottomans in the Middle East during World War I and Sinai and Palestine campaign, victory in Palestine was a step towards dismemberment of that empire. General Sir Edmund Allenby, commander-in-chief of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, entered Jerusalem on foot out of respect for the Holy City, on 11 December 1917.
By the time General Allenby took Jerusalem from the Ottomans in 1917, the new city was a patchwork of neighborhoods and communities, each with a distinct ethnic character. This continued under British rule, as the New City of Jerusalem grew outside the old city walls, and the Old City of Jerusalem gradually emerged as little more than an impoverished older neighborhood. Sir Ronald Storrs, the first British military governor of the city, issued a town planning order requiring new buildings in the city to be faced with sandstone and thus preserving some of the overall look of the city even as it grew.
The British were victorious over the Ottomans in the Middle East during World War I and Sinai and Palestine campaign, victory in Palestine was a step towards dismemberment of that empire. General Sir Edmund Allenby, commander-in-chief of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, entered Jerusalem on foot out of respect for the Holy City, on 11 December 1917.
By the time General Allenby took Jerusalem from the Ottomans in 1917, the new city was a patchwork of neighborhoods and communities, each with a distinct ethnic character. This continued under British rule, as the New City of Jerusalem grew outside the old city walls, and the Old City of Jerusalem gradually emerged as little more than an impoverished older neighborhood. Sir Ronald Storrs, the first British military governor of the city, issued a town planning order requiring new buildings in the city to be faced with sandstone and thus preserving some of the overall look of the city even as it grew.[Amos Elon, "Jerusalem: City of Mirrors". New York: Little, Brown 1989.] The Pro-Jerusalem Society, Pro-Jerusalem Council
War and partition between Israel and Jordan (1948–1967)
1948 war
 After partition, the fight for Jerusalem escalated, with heavy casualties among both fighters and civilians on the British, Jewish, and Arab sides. By the end of March 1948, just before the British withdrawal, and with the British increasingly reluctant to intervene, the roads to Jerusalem were cut off by Arab irregulars, placing the Jewish population of the city under siege. The siege was eventually broken, though massacres of civilians occurred on both sides, before the 1948 Arab–Israeli War began with the end of the British Mandate in May 1948.
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War led to massive displacement of Arab and Jewish populations. According to Benny Morris, due to mob and militia violence on both sides, 1,500 of the 3,500 (mostly ultra-Orthodox) Jews in the Old City evacuated to west Jerusalem as a unit.
After partition, the fight for Jerusalem escalated, with heavy casualties among both fighters and civilians on the British, Jewish, and Arab sides. By the end of March 1948, just before the British withdrawal, and with the British increasingly reluctant to intervene, the roads to Jerusalem were cut off by Arab irregulars, placing the Jewish population of the city under siege. The siege was eventually broken, though massacres of civilians occurred on both sides, before the 1948 Arab–Israeli War began with the end of the British Mandate in May 1948.
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War led to massive displacement of Arab and Jewish populations. According to Benny Morris, due to mob and militia violence on both sides, 1,500 of the 3,500 (mostly ultra-Orthodox) Jews in the Old City evacuated to west Jerusalem as a unit.[Benny Morris, ''The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem, 1947–1949'', Revisited, Cambridge, 2004] See also Jewish Quarter (Jerusalem), Jewish Quarter. The comparatively populous Arab village of Lifta (today within the bounds of Jerusalem) was captured by Israeli troops in 1948, and its residents were loaded on trucks and taken to East Jerusalem.
Division between Jordan and Israel (1948–1967)
The United Nations proposed, in its 1947 plan for the partition of Palestine, for Jerusalem to be a city under international administration. The city was to be completely surrounded by the Arab state, with only a highway to connect international Jerusalem to the Jewish state.
Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Jerusalem was divided. The Western half of the New City became part of the newly formed state of Israel, while the eastern half, along with the Old City, was occupied by Jordan.
According to David Guinn,
Concerning Jewish holy sites, Jordan breached its commitment to appoint a committee to discuss, among other topics, free access of Jews to the holy sites under its jurisdiction, mainly in the Western Wall and the important Jewish cemetery on the Mount of Olives, as provided in the Article 8.2 of the Cease Fire Agreement between it and Israel dated April 3, 1949. Jordan permitted the paving of new roads in the cemetery, and tombstones were used for paving in Jordanian army camps. The Cave of Simeon the Just, Shimon the Just became a stable.[''Protecting Jerusalem's Holy Sites: A Strategy for Negotiating a Sacred Peace'' by David E. Guinn (Cambridge University Press, 2006) p.35 ]
According to Gerald M. Steinberg, Jordan ransacked 57 ancient synagogues, libraries and centers of religious study in the Old City Of Jerusalem, 12 were totally and deliberately destroyed. Those that remained standing were defaced, used for housing of both people and animals. Appeals were made to the United Nations and in the international community to declare the Old City to be an 'open city' and stop this destruction, but there was no response. ''(See also Hurva Synagogue)''
On 23 January 1950, the Knesset passed a resolution that stated Jerusalem was the capital of Israel.
State of Israel
East Jerusalem was captured by the Israel Defense Forces during the 1967 Six-Day War. The Moroccan Quarter containing several hundred homes was demolished and its inhabitants expelled; thereafter a public plaza was built in its place adjoining the Western Wall. However, the Waqf (Islamic trust) was granted administration of the Temple Mount and thereafter Jewish prayer on the site was prohibited by both Israeli and Waqf authorities.
Most Jews celebrated the event as a liberation of the city; a new Israeli holiday was created, Jerusalem Day (''Yom Yerushalayim''), and the most popular secular Hebrew language, Hebrew song, "Jerusalem of Gold" (''Yerushalayim shel zahav''), became popular in celebration. Many large state gatherings of the State of Israel take place at the Western Wall today, including the swearing-in of various Israel army officers units, national ceremonies such as memorial services for fallen Israeli soldiers on ''Yom Hazikaron'', huge celebrations on ''Yom Ha'atzmaut'' (Israel Independence Day), huge gatherings of tens of thousands on Jewish religious holidays, and ongoing daily prayers by regular attendees. The Western Wall has become a major tourist destination spot.
Under Israeli control, members of all religions are largely granted access to their holy sites. The major exceptions being security limitations placed on some Arabs from the West Bank and Gaza Strip from accessing holy sites due to their inadmissibility to Jerusalem, as well as limitations on Jews from visiting the Temple Mount due to both politically motivated restrictions (where they are allowed to walk on the Mount in small groups, but are forbidden to pray or study while there) and religious edicts that forbid Jews from trespassing on what may be the site of the Holy of the Holies. Concerns have been raised about possible attacks on the al-Aqsa Mosque after a serious Al-Aqsa mosque fire, arson attack on the mosque in 1969 (started by Denis Michael Rohan, an Australian fundamentalist Christian found by the court to be insane). Riots broke out following the opening of an exit in the Muslim Quarter (Jerusalem), Arab Quarter for the Western Wall Tunnel on the instructions of the Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, which prior Prime Minister Shimon Peres had instructed to be put on hold for the sake of peace (stating "it has waited for over 1000 years, it could wait a few more").
Conversely, Israeli and other Jews have showed concerns over excavations being done by the Waqf on the Temple Mount that could harm Temple relics, particularly excavations to the north of Solomon's Stables that were designed to create an emergency exit for them (having been pressured to do so by Israeli authorities). Some Jewish sources allege that the Waqf's excavations in Solomon's Stables also seriously harmed the Southern Wall; however an earthquake in 2004 that damaged the eastern wall could also be to blame.
The status of East Jerusalem remains a International law and the Arab–Israeli conflict#Jerusalem, highly controversial issue. The international community does not recognize the annexation of the eastern part of the city, and most countries maintain their embassies in Tel Aviv. In May 2018 The United States and Guatemala moved the embassies to Jerusalem. The United Nations Security Council Resolution 478 declared that the Knesset's 1980 "Jerusalem Law" declaring Jerusalem as Israel's "eternal and indivisible" capital was "null and void and must be rescinded forthwith". This resolution advised member states to withdraw their diplomatic representation from the city as a punitive measure. The council has also condemned Israeli settlement in territories captured in 1967, including East Jerusalem (see UNSCR United Nations Security Council Resolution 452, 452, United Nations Security Council Resolution 465, 465 and UN Security Council Resolution 471, 741).
Since Israel gained control over East Jerusalem in 1967, Jewish settler organizations have sought to establish a Jewish presence in neighborhoods such as Silwan. In the 1980s, ''Haaretz'' reports, the Housing Ministry "then under Ariel Sharon, worked hard to seize control of property in the Old City and in the adjacent neighborhood of Silwan by declaring them absentee property. The suspicion arose that some of the transactions were not legal; an examination committee ... found numerous flaws." In particular, affidavits claiming that Arab homes in the area were Land and property laws in Israel, absentee properties, filed by Jewish organizations, were accepted by the Custodian without any site visits or other follow-up on the claims. ElAd, a settlement organization which ''Haaretz'' says promotes the "Judaization" of Judaization of Jerusalem, East Jerusalem, and the Ateret Cohanim organization, are working to increase Jewish settlement in Silwan in cooperation with the Committee for the Renewal of the Yemenite Village in Shiloah.
Graphical overview of Jerusalem's historical periods
See also
*History of ancient Israel and Judah
*History of Israel
*History of Palestine
References
Notes
Citations
Further reading
* Avci, Yasemin, Vincent Lemire, and Falestin Naili. "Publishing Jerusalem's ottoman municipal archives (1892-1917): a turning point for the city's historiography." ''Jerusalem Quarterly'' 60 (2014): 110+
online
* Emerson, Charles. ''1913: In Search of the World Before the Great War'' (2013) compares Jerusalem to 20 major world cities; pp 325–46.
* Lemire, Vincent. ''Jerusalem 1900: The Holy City in the Age of Possibilities'' (U of Chicago Press, 2017).
* Mazza, Roberto. ''Jerusalem from the Ottomans to the British'' ( 2009)
* Millis, Joseph. ''Jerusalem: The Illustrated History of the Holy City'' (2012
excerpt
* Montefiore, Simon Sebag. ''Jerusalem: The Biography'' (2012
excerpt
External links
*{{CathEncy, wstitle=Jerusalem (Before 71 CE)
nbsp;– Catholic Encyclopedia article
nbsp;– Catholic Encyclopedia article
nbsp;– Catholic Encyclopedia article
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20070208160016/http://members.verizon.net/vze3xycv/Jerusalem/conflictsum.htm Jerusalem Through Coins]
History of Jerusalem,
 As a result of the
As a result of the  In the 1st century CE, Jerusalem became the birthplace of
In the 1st century CE, Jerusalem became the birthplace of  What is today known as the "Old City of Jerusalem" was laid out by the Roman Emperor
What is today known as the "Old City of Jerusalem" was laid out by the Roman Emperor 
 Although the
Although the  Fatimid control of Jerusalem ended when it was captured by
Fatimid control of Jerusalem ended when it was captured by  In 1173 Benjamin of Tudela visited Jerusalem. He described it as a small city full of Syriac Orthodox Church, Jacobites, Armenians, Greeks, and Georgian people, Georgians. Two hundred Jews dwelt in a corner of the city under the Tower of David. In 1219 the walls of the city were razed by order of Al-Mu'azzam Isa, al-Mu'azzam, the Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubid sultan of Damascus. This rendered Jerusalem defenseless and dealt a heavy blow to the city's status. The Ayyubids destroyed the walls in expectation of ceding the city to the Crusaders as part of a peace treaty. In 1229, by treaty with Egypt's ruler al-Kamil, Jerusalem came into the hands of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II of Germany. In 1239, after a ten-year truce expired, he began to rebuild the walls; these were again demolished by an-Nasir Da'ud, the emir of Kerak, in the same year.
In 1243 Jerusalem came again into the power of the Christians, and the walls were repaired. The Khwarazmian dynasty, Khwarezmian Empire took the city in 1244 and were in turn driven out by the Ayyubids in 1247. In 1260 the Mongols under Hulagu Khan engaged in Mongol raids into Palestine, raids into Palestine. It is unclear if the Mongols were ever in Jerusalem, as it was not seen as a settlement of strategic importance at the time. However, there are reports that some of the Jews that were in Jerusalem temporarily fled to neighboring villages.
In 1173 Benjamin of Tudela visited Jerusalem. He described it as a small city full of Syriac Orthodox Church, Jacobites, Armenians, Greeks, and Georgian people, Georgians. Two hundred Jews dwelt in a corner of the city under the Tower of David. In 1219 the walls of the city were razed by order of Al-Mu'azzam Isa, al-Mu'azzam, the Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubid sultan of Damascus. This rendered Jerusalem defenseless and dealt a heavy blow to the city's status. The Ayyubids destroyed the walls in expectation of ceding the city to the Crusaders as part of a peace treaty. In 1229, by treaty with Egypt's ruler al-Kamil, Jerusalem came into the hands of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II of Germany. In 1239, after a ten-year truce expired, he began to rebuild the walls; these were again demolished by an-Nasir Da'ud, the emir of Kerak, in the same year.
In 1243 Jerusalem came again into the power of the Christians, and the walls were repaired. The Khwarazmian dynasty, Khwarezmian Empire took the city in 1244 and were in turn driven out by the Ayyubids in 1247. In 1260 the Mongols under Hulagu Khan engaged in Mongol raids into Palestine, raids into Palestine. It is unclear if the Mongols were ever in Jerusalem, as it was not seen as a settlement of strategic importance at the time. However, there are reports that some of the Jews that were in Jerusalem temporarily fled to neighboring villages.
 The first provincial or superior of the Franciscan religious order, founded by Francis of Assisi, was Brother Elia from Assisi. In the year 1219 the founder himself visited the region in order to preach the
The first provincial or superior of the Franciscan religious order, founded by Francis of Assisi, was Brother Elia from Assisi. In the year 1219 the founder himself visited the region in order to preach the  In the mid-19th century, with the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the city was a backwater, with a population that did not exceed 8,000. Nevertheless, it was, even then, an extremely heterogeneous city because of its significance to Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The population was divided into four major communities – Jewish, Christian, Muslim, and Armenian – and the first three of these could be further divided into countless subgroups, based on precise religious affiliation or country of origin. The Church of the Holy Sepulchre was meticulously partitioned between the Eastern Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox, Catholic, Armenian Apostolic Church, Armenian, Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic, and Ethiopian Church, Ethiopian churches. Tensions between the groups ran so deep that the keys to the shrine and its doors were safeguarded by a pair of 'neutral' Muslim families.
At the time, the communities were located mainly around their primary shrines. The Muslim community surrounded the Haram ash-Sharif or Temple Mount (northeast), the Christians lived mainly in the vicinity of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre (northwest), the Jews lived mostly on the slope above the Western Wall (southeast), and the Armenians lived near the Zion Gate (southwest). In no way was this division exclusive, though it did form the basis of the four quarters during the British Mandate (1917–1948).
Several changes with long-lasting effects on the city occurred in the mid-19th century: their implications can be felt today and lie at the root of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict over Jerusalem. The first of these was a trickle of Jewish immigrants from the Middle East and Eastern Europe. The first such immigrants were Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jews: some were elderly individuals, who came to die in Jerusalem and be buried on the Mount of Olives; others were students, who came with their families to await the coming of the Messiah, adding new life to the local population. At the same time, European colonial powers began seeking toeholds in the city, hoping to expand their influence pending the imminent collapse of the Ottoman Empire. This was also an age of Christian religious revival, and many churches sent missionaries to proselytize among the Muslim and especially the Jewish populations, believing that this would speed the Second Coming of Christ. Finally, the combination of European colonialism and religious zeal was expressed in a new scientific interest in the biblical lands in general and Jerusalem in particular. Archeological and other expeditions made some spectacular finds, which increased interest in Jerusalem even more.
By the 1860s, the city, with an area of only one square kilometer, was already overcrowded. Thus began the construction of the New City, the part of Jerusalem outside of the city walls. Seeking new areas to stake their claims, the Russian Orthodox Church began constructing a complex, now known as the Russian Compound, a few hundred meters from Jaffa Gate. The first attempt at residential settlement outside the walls of Jerusalem was undertaken by Jews, who built a small complex on the hill overlooking Zion Gate, across the Valley of Hinnom. This settlement, known as Mishkenot Sha'ananim, eventually flourished and set the precedent for other new communities to spring up to the west and north of the Old City. In time, as the communities grew and connected geographically, this became known as the New City.
In 1882, around 150 Jewish families arrived in Jerusalem from Yemen. Initially they were not accepted by the Jews of Jerusalem and lived in destitute conditions supported by the Christians of the Swedish-American colony, who called them Tribe of Gad, Gadites. In 1884, the Yemenites moved into Silwan.
In the mid-19th century, with the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the city was a backwater, with a population that did not exceed 8,000. Nevertheless, it was, even then, an extremely heterogeneous city because of its significance to Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The population was divided into four major communities – Jewish, Christian, Muslim, and Armenian – and the first three of these could be further divided into countless subgroups, based on precise religious affiliation or country of origin. The Church of the Holy Sepulchre was meticulously partitioned between the Eastern Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox, Catholic, Armenian Apostolic Church, Armenian, Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic, and Ethiopian Church, Ethiopian churches. Tensions between the groups ran so deep that the keys to the shrine and its doors were safeguarded by a pair of 'neutral' Muslim families.
At the time, the communities were located mainly around their primary shrines. The Muslim community surrounded the Haram ash-Sharif or Temple Mount (northeast), the Christians lived mainly in the vicinity of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre (northwest), the Jews lived mostly on the slope above the Western Wall (southeast), and the Armenians lived near the Zion Gate (southwest). In no way was this division exclusive, though it did form the basis of the four quarters during the British Mandate (1917–1948).
Several changes with long-lasting effects on the city occurred in the mid-19th century: their implications can be felt today and lie at the root of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict over Jerusalem. The first of these was a trickle of Jewish immigrants from the Middle East and Eastern Europe. The first such immigrants were Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jews: some were elderly individuals, who came to die in Jerusalem and be buried on the Mount of Olives; others were students, who came with their families to await the coming of the Messiah, adding new life to the local population. At the same time, European colonial powers began seeking toeholds in the city, hoping to expand their influence pending the imminent collapse of the Ottoman Empire. This was also an age of Christian religious revival, and many churches sent missionaries to proselytize among the Muslim and especially the Jewish populations, believing that this would speed the Second Coming of Christ. Finally, the combination of European colonialism and religious zeal was expressed in a new scientific interest in the biblical lands in general and Jerusalem in particular. Archeological and other expeditions made some spectacular finds, which increased interest in Jerusalem even more.
By the 1860s, the city, with an area of only one square kilometer, was already overcrowded. Thus began the construction of the New City, the part of Jerusalem outside of the city walls. Seeking new areas to stake their claims, the Russian Orthodox Church began constructing a complex, now known as the Russian Compound, a few hundred meters from Jaffa Gate. The first attempt at residential settlement outside the walls of Jerusalem was undertaken by Jews, who built a small complex on the hill overlooking Zion Gate, across the Valley of Hinnom. This settlement, known as Mishkenot Sha'ananim, eventually flourished and set the precedent for other new communities to spring up to the west and north of the Old City. In time, as the communities grew and connected geographically, this became known as the New City.
In 1882, around 150 Jewish families arrived in Jerusalem from Yemen. Initially they were not accepted by the Jews of Jerusalem and lived in destitute conditions supported by the Christians of the Swedish-American colony, who called them Tribe of Gad, Gadites. In 1884, the Yemenites moved into Silwan.
 The British were victorious over the Ottomans in the Middle East during World War I and Sinai and Palestine campaign, victory in Palestine was a step towards dismemberment of that empire. General Sir Edmund Allenby, commander-in-chief of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, entered Jerusalem on foot out of respect for the Holy City, on 11 December 1917.
By the time General Allenby took Jerusalem from the Ottomans in 1917, the new city was a patchwork of neighborhoods and communities, each with a distinct ethnic character. This continued under British rule, as the New City of Jerusalem grew outside the old city walls, and the Old City of Jerusalem gradually emerged as little more than an impoverished older neighborhood. Sir Ronald Storrs, the first British military governor of the city, issued a town planning order requiring new buildings in the city to be faced with sandstone and thus preserving some of the overall look of the city even as it grew.Amos Elon, "Jerusalem: City of Mirrors". New York: Little, Brown 1989. The Pro-Jerusalem Society, Pro-Jerusalem Council played an important role in the outlook of the British-ruled city. During the 1930s, two important new institutions, the Hadassah Medical Center and Hebrew University were founded on Jerusalem's Mount Scopus.
Mandate for Palestine, British rule marked, however, a period of growing unrest. Arab resentment at British rule and the influx of Jewish immigrants (by 1948 one in six Jews in Palestine lived in Jerusalem) boiled over in anti-Jewish riots in Jerusalem in 1920, 1929, and the 1930s that caused significant damage and several deaths. The Jewish community organized self-defense forces in response to the 1920 Nebi Musa riots and later disturbances; while other Jewish groups carried out bombings and attacks against the British, especially in response to suspected complicity with the Arabs and restrictions on immigration during World War II imposed by the White Paper of 1939. The level of violence continued to escalate throughout the 1930s and 1940s. In July 1946 members of the underground Zionist group Irgun blew up a part of the King David Hotel, where the British forces were temporarily located, an act which led to the King David Hotel bombing, death of 91 civilians.
On 29 November 1947, the United Nations General Assembly approved a 1947 UN Partition Plan, plan which would partition Mandatory Palestine into two states: one Jewish and one Arab. Each state would be composed of three major sections, linked by extraterritorial crossroads, plus an Arab enclave at Jaffa, Israel, Jaffa. Expanded Jerusalem would fall under international control as a Corpus separatum (Jerusalem), Corpus Separatum.
The British were victorious over the Ottomans in the Middle East during World War I and Sinai and Palestine campaign, victory in Palestine was a step towards dismemberment of that empire. General Sir Edmund Allenby, commander-in-chief of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, entered Jerusalem on foot out of respect for the Holy City, on 11 December 1917.
By the time General Allenby took Jerusalem from the Ottomans in 1917, the new city was a patchwork of neighborhoods and communities, each with a distinct ethnic character. This continued under British rule, as the New City of Jerusalem grew outside the old city walls, and the Old City of Jerusalem gradually emerged as little more than an impoverished older neighborhood. Sir Ronald Storrs, the first British military governor of the city, issued a town planning order requiring new buildings in the city to be faced with sandstone and thus preserving some of the overall look of the city even as it grew.Amos Elon, "Jerusalem: City of Mirrors". New York: Little, Brown 1989. The Pro-Jerusalem Society, Pro-Jerusalem Council played an important role in the outlook of the British-ruled city. During the 1930s, two important new institutions, the Hadassah Medical Center and Hebrew University were founded on Jerusalem's Mount Scopus.
Mandate for Palestine, British rule marked, however, a period of growing unrest. Arab resentment at British rule and the influx of Jewish immigrants (by 1948 one in six Jews in Palestine lived in Jerusalem) boiled over in anti-Jewish riots in Jerusalem in 1920, 1929, and the 1930s that caused significant damage and several deaths. The Jewish community organized self-defense forces in response to the 1920 Nebi Musa riots and later disturbances; while other Jewish groups carried out bombings and attacks against the British, especially in response to suspected complicity with the Arabs and restrictions on immigration during World War II imposed by the White Paper of 1939. The level of violence continued to escalate throughout the 1930s and 1940s. In July 1946 members of the underground Zionist group Irgun blew up a part of the King David Hotel, where the British forces were temporarily located, an act which led to the King David Hotel bombing, death of 91 civilians.
On 29 November 1947, the United Nations General Assembly approved a 1947 UN Partition Plan, plan which would partition Mandatory Palestine into two states: one Jewish and one Arab. Each state would be composed of three major sections, linked by extraterritorial crossroads, plus an Arab enclave at Jaffa, Israel, Jaffa. Expanded Jerusalem would fall under international control as a Corpus separatum (Jerusalem), Corpus Separatum.
 After partition, the fight for Jerusalem escalated, with heavy casualties among both fighters and civilians on the British, Jewish, and Arab sides. By the end of March 1948, just before the British withdrawal, and with the British increasingly reluctant to intervene, the roads to Jerusalem were cut off by Arab irregulars, placing the Jewish population of the city under siege. The siege was eventually broken, though massacres of civilians occurred on both sides, before the 1948 Arab–Israeli War began with the end of the British Mandate in May 1948.
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War led to massive displacement of Arab and Jewish populations. According to Benny Morris, due to mob and militia violence on both sides, 1,500 of the 3,500 (mostly ultra-Orthodox) Jews in the Old City evacuated to west Jerusalem as a unit.Benny Morris, ''The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem, 1947–1949'', Revisited, Cambridge, 2004 See also Jewish Quarter (Jerusalem), Jewish Quarter. The comparatively populous Arab village of Lifta (today within the bounds of Jerusalem) was captured by Israeli troops in 1948, and its residents were loaded on trucks and taken to East Jerusalem. The villages of Deir Yassin, Ein Karem and Malha, Malcha, as well as neighborhoods to the west of Jerusalem's Old City such as Talbiya, Katamon, Baka, Jerusalem, Baka, Mamilla and Abu Tor, also came under Israeli control, and their residents were forcibly displaced; in some cases, as documented by Israeli historian Benny Morris and Palestinian historian Walid Khalidi, among others, expulsions and massacres occurred.
In May 1948 the US Consul, Thomas C. Wasson, was assassinated outside the YMCA building. Four months later the UN mediator, Folke Bernadotte, Count Bernadotte, was also shot dead in the Katamon district of Jerusalem by the Jewish Lehi (group), Stern Group.
After partition, the fight for Jerusalem escalated, with heavy casualties among both fighters and civilians on the British, Jewish, and Arab sides. By the end of March 1948, just before the British withdrawal, and with the British increasingly reluctant to intervene, the roads to Jerusalem were cut off by Arab irregulars, placing the Jewish population of the city under siege. The siege was eventually broken, though massacres of civilians occurred on both sides, before the 1948 Arab–Israeli War began with the end of the British Mandate in May 1948.
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War led to massive displacement of Arab and Jewish populations. According to Benny Morris, due to mob and militia violence on both sides, 1,500 of the 3,500 (mostly ultra-Orthodox) Jews in the Old City evacuated to west Jerusalem as a unit.Benny Morris, ''The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem, 1947–1949'', Revisited, Cambridge, 2004 See also Jewish Quarter (Jerusalem), Jewish Quarter. The comparatively populous Arab village of Lifta (today within the bounds of Jerusalem) was captured by Israeli troops in 1948, and its residents were loaded on trucks and taken to East Jerusalem. The villages of Deir Yassin, Ein Karem and Malha, Malcha, as well as neighborhoods to the west of Jerusalem's Old City such as Talbiya, Katamon, Baka, Jerusalem, Baka, Mamilla and Abu Tor, also came under Israeli control, and their residents were forcibly displaced; in some cases, as documented by Israeli historian Benny Morris and Palestinian historian Walid Khalidi, among others, expulsions and massacres occurred.
In May 1948 the US Consul, Thomas C. Wasson, was assassinated outside the YMCA building. Four months later the UN mediator, Folke Bernadotte, Count Bernadotte, was also shot dead in the Katamon district of Jerusalem by the Jewish Lehi (group), Stern Group.