Hürthle Cell Neoplasm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
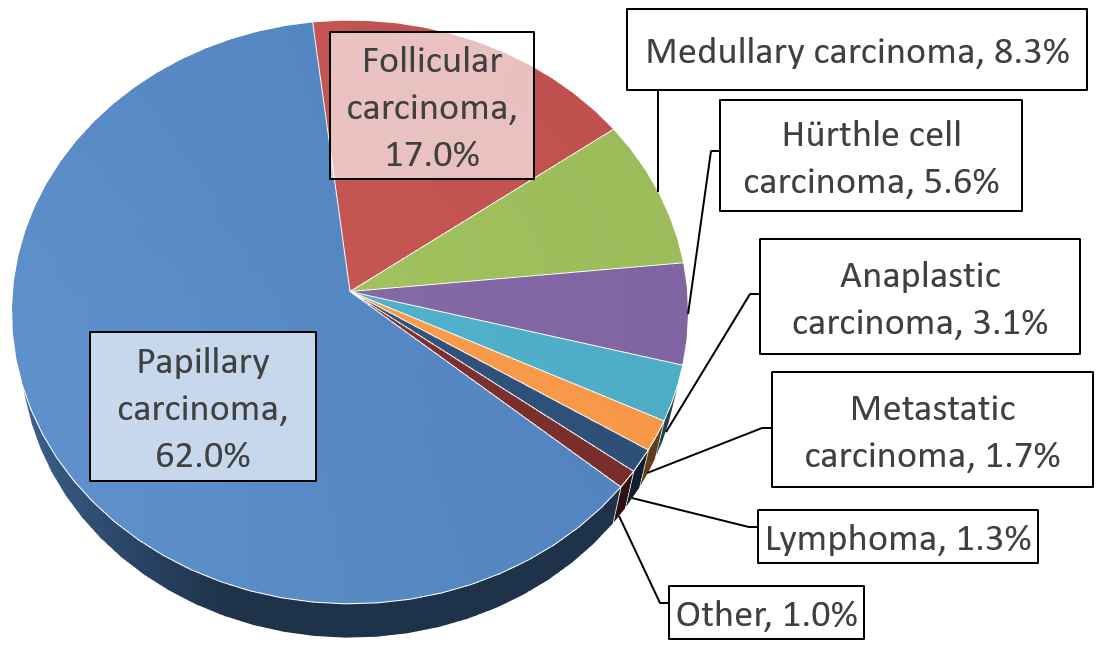 Hürthle cell neoplasm is a rare tumor of the thyroid, typically seen in women between the ages of 70 and 80 years old. When benign, it is called a Hürthle cell adenoma, and when malignant it is called a Hürthle cell carcinoma. Hürthle cell adenoma is characterized by a mass of benign Hürthle cells (Askanazy cells). Typically such a mass is removed because it is not easy to predict whether it will transform into the malignant counterpart of Hürthle cell carcinoma, which is a subtype of follicular thyroid cancer.
Hürthle cell neoplasm is a rare tumor of the thyroid, typically seen in women between the ages of 70 and 80 years old. When benign, it is called a Hürthle cell adenoma, and when malignant it is called a Hürthle cell carcinoma. Hürthle cell adenoma is characterized by a mass of benign Hürthle cells (Askanazy cells). Typically such a mass is removed because it is not easy to predict whether it will transform into the malignant counterpart of Hürthle cell carcinoma, which is a subtype of follicular thyroid cancer.
-
 Hürthle cell neoplasm is a rare tumor of the thyroid, typically seen in women between the ages of 70 and 80 years old. When benign, it is called a Hürthle cell adenoma, and when malignant it is called a Hürthle cell carcinoma. Hürthle cell adenoma is characterized by a mass of benign Hürthle cells (Askanazy cells). Typically such a mass is removed because it is not easy to predict whether it will transform into the malignant counterpart of Hürthle cell carcinoma, which is a subtype of follicular thyroid cancer.
Hürthle cell neoplasm is a rare tumor of the thyroid, typically seen in women between the ages of 70 and 80 years old. When benign, it is called a Hürthle cell adenoma, and when malignant it is called a Hürthle cell carcinoma. Hürthle cell adenoma is characterized by a mass of benign Hürthle cells (Askanazy cells). Typically such a mass is removed because it is not easy to predict whether it will transform into the malignant counterpart of Hürthle cell carcinoma, which is a subtype of follicular thyroid cancer.
Histology
Hürthle cells are characterized as enlargedepithelial cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
s. These cells, when stained
A stain is a discoloration that can be clearly distinguished from the surface, material, or medium it is found upon. They are caused by the chemical or physical interaction of two dissimilar materials. Accidental staining may make materials app ...
with hematoxylin-eosin show as pink. This is due to the abundant mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
and granular eosinophilic matter within the cells' cytoplasm. These cells are often found in the thyroid. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped organ, responsible for producing various hormones for metabolism. These cells are often benign, but they can be malignant and metastasize. Hürthle cells are resistant to radiation, but can be treated using radioactive iodine treatment.
Diagnosis
This mass can be detected and removed before transformation and metastasis. The tumor is often detected by imaging such as ultrasound. The location and size of the tumor may cause pressure and pain to the patient. But often the tumor goes undetected. After detection, the mass is tested using an invasivefine-needle aspiration biopsy
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, afte ...
.
Hürthle cell adenoma is the benign analogue of Hürthle cell carcinoma. This adenoma is extremely rare; when it occurs, it usually occurs in women. Often the adenoma is harmless but is removed after detection because its future course cannot be trusted.
Cytopathology
Cytopathology cannot distinguish Hürthle cell adenoma from Hürthle cell carcinoma, which requires histopathologic sections to see transcapsular or vascular invasion. Hürthle cell hyperplasia (as seen in Hashimoto's thyroiditis) may show moderate variation in nuclear sizes and prominent nucleoli, but further findings favoring Hürthle cell neoplasm include a large number of Hürthle cells, and discohesiveness.- Last author update: 7 May 2020. Last staff update: 12 May 2022-
Treatment
There are three main treatments for Hürthle cell adenomas. Once the adenoma is detected most often the nodules removed to prevent the cells from later metastisizing. A total thyroidectomy is often performed, this results in a complete removal of the thyroid. Some patients may only have half of their thyroid removed, this is known as a thyroid lobectomy. Another treatment option includes pharmacological suppression ofthyroid hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
rect 66 216 386 25 ...
. The thyroid gland is responsible for producing the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Patients with suppressed thyroid function often require oral thyroid replacement (e.g. levothyroxine) in order to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels. The final treatment option is RAI ablation (radioactive iodine ablation). This treatment option is used to destroy infected thyroid cells after total thyroidectomy. This treatment does not change prognosis of disease, but will diminish the recurrence rate. Also, Hürthle cells do not respond well to RAI. However, often doctors suggest this treatment to patients with Hürthle cell adenoma and Hürthle cell carcinoma because some Hürthle cells will respond and it will kill remaining tissue.
History
The first Hürthle cell adenoma was discovered by Dr James Ewing in 1928. Hürthle cells were discovered in the 1890s and are named afterKarl Hürthle
Karl Hürthle (March 16, 1860 – March 23, 1945) was a German physiologist and histologist who was a native of Ludwigsburg.
In 1884 he received his doctorate from the University of Tübingen, where he remained until 1886, working as a pros ...
and Max Askanazy.
References
External links
* http://www.knowcancer.com/oncology/hurthle-cell-adenoma/ * https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/types/thyroid/about-thyroid * http://columbiasurgery.org/conditions-and-treatments/follicular-and-hurthle-cell-thyroid-cancer {{DEFAULTSORT:Hurthle cell adenoma Glandular and epithelial neoplasia Thyroid Articles containing video clips