Hybrid Module on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A hybrid integrated circuit (HIC), hybrid microcircuit, hybrid circuit or simply hybrid is a miniaturized
 Hybrid circuits could be encapsulated in
Hybrid circuits could be encapsulated in  Thin film technology was also employed in the 1960s. Ultra Electronics manufactured circuits using a silica glass substrate. A film of tantalum was deposited by sputtering followed by a layer of gold by evaporation. The gold layer was first etched following the application of a photoresist to form solder compatible connection pads. Resistive networks were formed, also by a photoresist and etching process. These were trimmed to a high precision by selective adonization of the film. Capacitors and semiconductors were in the form of LID (Leadless Inverted Devices) soldered to the surface by selectively heating the substrate from the underside. Completed circuits were potted in a diallyl phthalate resin. Several customized passive networks were made using these techniques as were some amplifiers and other specialized circuits. It is believed that some passive networks were used in the engine control units manufactured by Ultra Electronics for Concorde.
Some modern hybrid circuit technologies, such as LTCC-substrate hybrids, allow for embedding of components within the layers of a multi-layer substrate in addition to components placed on the surface of the substrate. This technology produces a circuit that is, to some degree, three-dimensional.
Thin film technology was also employed in the 1960s. Ultra Electronics manufactured circuits using a silica glass substrate. A film of tantalum was deposited by sputtering followed by a layer of gold by evaporation. The gold layer was first etched following the application of a photoresist to form solder compatible connection pads. Resistive networks were formed, also by a photoresist and etching process. These were trimmed to a high precision by selective adonization of the film. Capacitors and semiconductors were in the form of LID (Leadless Inverted Devices) soldered to the surface by selectively heating the substrate from the underside. Completed circuits were potted in a diallyl phthalate resin. Several customized passive networks were made using these techniques as were some amplifiers and other specialized circuits. It is believed that some passive networks were used in the engine control units manufactured by Ultra Electronics for Concorde.
Some modern hybrid circuit technologies, such as LTCC-substrate hybrids, allow for embedding of components within the layers of a multi-layer substrate in addition to components placed on the surface of the substrate. This technology produces a circuit that is, to some degree, three-dimensional.
electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow. It is a type of electrical ...
constructed of individual devices, such as semiconductor devices (e.g. transistors, diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode ...
s or monolithic ICs) and passive components (e.g. resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active el ...
s, inductors, transformers, and capacitors), bonded to a substrate or printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
(PCB). A PCB having components on a Printed Wiring Board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich struc ...
(PWB) is not considered a true hybrid circuit according to the definition of MIL-PRF-38534 The MIL-PRF-38534 specification establishes the general performance requirements for hybrid microcircuits (hybrid integrated circuit), multi-chip modules (MCM) and, similar devices and the verification and validation requirements for ensuring that t ...
.
Overview
"Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
" as the term is currently used refers to a monolithic IC which differs notably from a HIC in that a HIC is fabricated by inter-connecting a number of components on a substrate whereas an IC's (monolithic) components are fabricated in a series of steps entirely on a single wafer which is then diced into chips. Some hybrid circuits may contain monolithic ICs, particularly Multi-chip module (MCM) hybrid circuits.
 Hybrid circuits could be encapsulated in
Hybrid circuits could be encapsulated in epoxy
Epoxy is the family of basic components or cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also coll ...
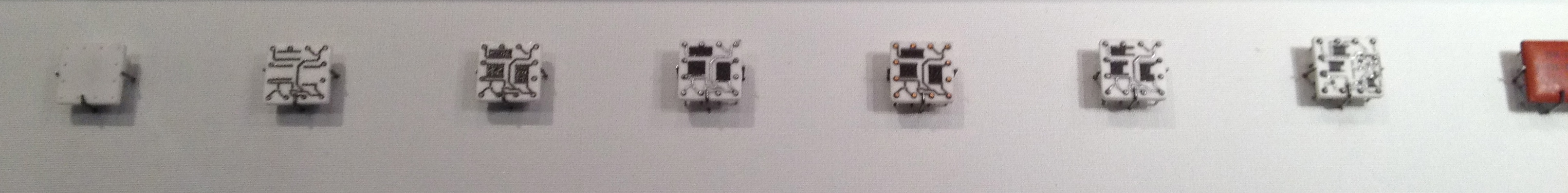
, as shown in the photo, or in military and space applications, a lid was soldered onto the package. A hybrid circuit serves as a component on a PCB in the same way as a monolithic integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
; the difference between the two types of devices is in how they are constructed and manufactured. The advantage of hybrid circuits is that components which cannot be included in a monolithic IC can be used, e.g., capacitors of large value, wound components, crystals, inductors. William Greig, ''Integrated Circuit Packaging, Assembly and Interconnections'', Springer Science & Business Media, 2007, , p.62-64 In military and space applications, numerous integrated circuits, transistors and diodes, in their die form, would be placed on either a ceramic or beryllium substrate. Either gold or aluminum wire would be bonded from the pads of the IC, transistor, or diode to the substrate.
Thick film technology is often used as the interconnecting medium for hybrid integrated circuits. The use of screen printed thick film interconnect provides advantages of versatility over thin film although feature sizes may be larger and deposited resistors wider in tolerance. Multi-layer thick film is a technique for further improvements in integration using a screen printed insulating dielectric to ensure connections between layers are made only where required. One key advantage for the circuit designer is complete freedom in the choice of resistor value in thick film technology. Planar resistors are also screen printed and included in the thick film interconnect design. The composition and dimensions of resistors can be selected to provide the desired values. The final resistor value is determined by design and can be adjusted by laser trimming. Once the hybrid circuit is fully populated with components, fine tuning prior to final test may be achieved by active laser trimming.
 Thin film technology was also employed in the 1960s. Ultra Electronics manufactured circuits using a silica glass substrate. A film of tantalum was deposited by sputtering followed by a layer of gold by evaporation. The gold layer was first etched following the application of a photoresist to form solder compatible connection pads. Resistive networks were formed, also by a photoresist and etching process. These were trimmed to a high precision by selective adonization of the film. Capacitors and semiconductors were in the form of LID (Leadless Inverted Devices) soldered to the surface by selectively heating the substrate from the underside. Completed circuits were potted in a diallyl phthalate resin. Several customized passive networks were made using these techniques as were some amplifiers and other specialized circuits. It is believed that some passive networks were used in the engine control units manufactured by Ultra Electronics for Concorde.
Some modern hybrid circuit technologies, such as LTCC-substrate hybrids, allow for embedding of components within the layers of a multi-layer substrate in addition to components placed on the surface of the substrate. This technology produces a circuit that is, to some degree, three-dimensional.
Thin film technology was also employed in the 1960s. Ultra Electronics manufactured circuits using a silica glass substrate. A film of tantalum was deposited by sputtering followed by a layer of gold by evaporation. The gold layer was first etched following the application of a photoresist to form solder compatible connection pads. Resistive networks were formed, also by a photoresist and etching process. These were trimmed to a high precision by selective adonization of the film. Capacitors and semiconductors were in the form of LID (Leadless Inverted Devices) soldered to the surface by selectively heating the substrate from the underside. Completed circuits were potted in a diallyl phthalate resin. Several customized passive networks were made using these techniques as were some amplifiers and other specialized circuits. It is believed that some passive networks were used in the engine control units manufactured by Ultra Electronics for Concorde.
Some modern hybrid circuit technologies, such as LTCC-substrate hybrids, allow for embedding of components within the layers of a multi-layer substrate in addition to components placed on the surface of the substrate. This technology produces a circuit that is, to some degree, three-dimensional.
Other electronic hybrids
In the early days of telephones, separate modules containing transformers and resistors were called hybrids or hybrid coils; they have been replaced by semiconductorintegrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
s.
In the early days of transistors the term ''hybrid circuit'' was used to describe circuits with both transistors and vacuum tubes; e.g., an audio amplifier
An audio power amplifier (or power amp) is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power electronic audio signals, such as the signal from a radio receiver or an electric guitar pickup, to a level that is high enough for driving loudspea ...
with transistors used for voltage amplification followed by a vacuum tube power output stage, as suitable power transistors were not available. This usage, and the devices, are obsolete, however amplifiers that use a tube preamplifier stage coupled with a solid state output stage are still in production, and are called hybrid amplifiers in reference to this.
See also
*Chip on board
Chip on board (COB) is a method of circuit board manufacturing in which the integrated circuits (e.g. microprocessors) are attached (wired, bonded directly) to a printed circuit board, and covered by a blob of epoxy. By eliminating the packagi ...
, aka black blobs
* System in a package
* Multi-chip module (MCM)
* Monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC)
* Solid Logic Technology (SLT)
* MIL-PRF-38534 The MIL-PRF-38534 specification establishes the general performance requirements for hybrid microcircuits (hybrid integrated circuit), multi-chip modules (MCM) and, similar devices and the verification and validation requirements for ensuring that t ...
* Printed Circuit Board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
(PCB)
* Printed Electronic Circuit - Ancestor of the Hybrid IC
References
External links
{{Authority control Electronic circuits