Howell–Jolly Body on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
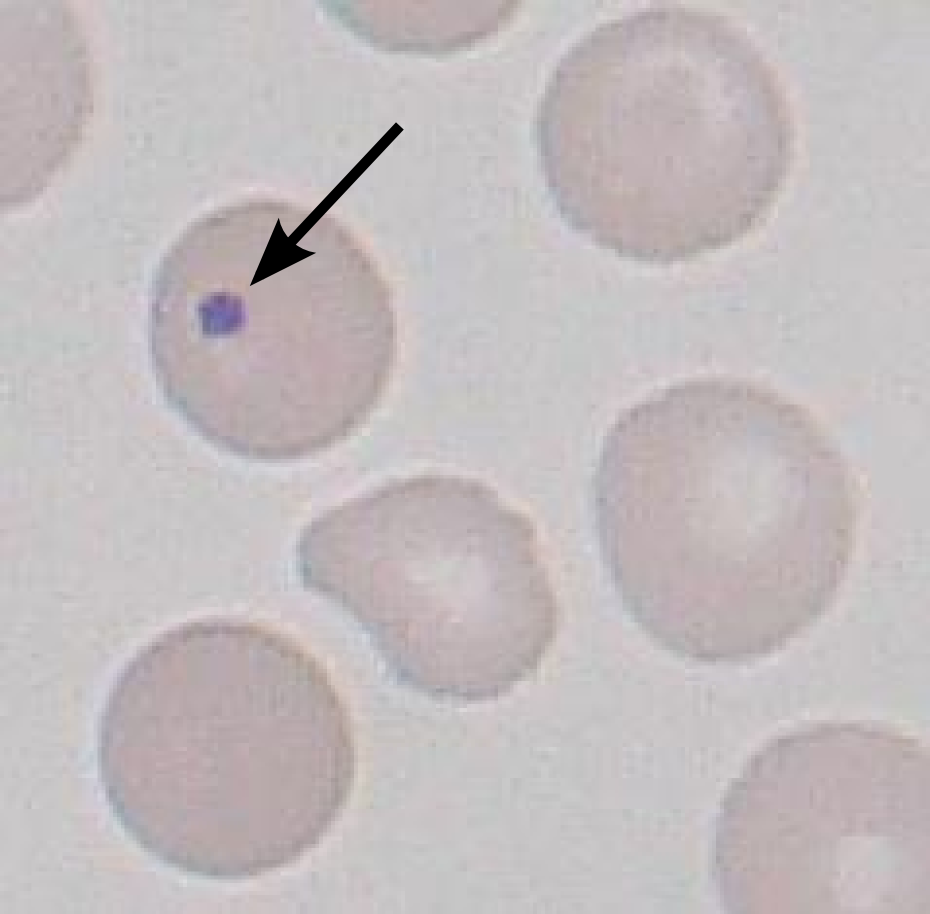 A Howell–Jolly body is a
A Howell–Jolly body is a
 This DNA appears as a basophilic (purple) spot on the otherwise
This DNA appears as a basophilic (purple) spot on the otherwise
Digital Pathology, Brown University: Howell-Jolly Bodies
{{DEFAULTSORT:Howell-Jolly body Abnormal clinical and laboratory findings for RBCs
 A Howell–Jolly body is a
A Howell–Jolly body is a cytopathological
Cytopathology (from Greek , ''kytos'', "a hollow"; , ''pathos'', "fate, harm"; and , ''-logia'') is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in 1 ...
finding of basophilic
Basophilic is a technical term used by pathologists. It describes the appearance of cells, tissues and cellular structures as seen through the microscope after a histological section has been stained with a basic dye. The most common such dye ...
nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
remnants (clusters of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
) in circulating erythrocytes
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
. During maturation in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
, late erythroblasts normally expel their nuclei; but, in some cases, a small portion of DNA remains. The presence of Howell–Jolly bodies usually signifies a damaged or absent spleen, because a healthy spleen would normally filter such erythrocytes.
The Howell–Jolly body is named after William Henry Howell
William Henry Howell (February 20, 1860 – February 6, 1945) was an American physiologist. He pioneered the use of heparin as a blood anti-coagulant.
Early life
William Henry Howell was born on February 20, 1860, in Baltimore, Maryland. He gra ...
and Justin Marie Jolly.
Appearance
eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix '' -phil'', meaning ''eosin-loving'') describes the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye commonly used in histological staining.
Eosin is an acidic dye for stainin ...
(pink) erythrocyte on a standard H&E stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin–eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diag ...
ed blood smear. These inclusions are normally removed by the spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
during erythrocyte circulation, but will persist in individuals with functional hyposplenia
Asplenia is the absence of normal spleen function and is associated with some serious infection risks. Hyposplenism is the condition of reduced ('hypo-'), but not absent, splenic functioning.
''Functional'' asplenia occurs when splenic tissue is ...
or asplenia
Asplenia is the absence of normal spleen function and is associated with some serious infection risks. Hyposplenism is the condition of reduced ('hypo-'), but not absent, splenic functioning.
''Functional'' asplenia occurs when splenic tissue is ...
.
Causes
Howell–Jolly bodies are seen with markedly decreased splenic function. Common causes include asplenia (post-splenectomy) or congenital absence of spleen (right atrial appendage isomerism). Spleens are also removed for therapeutic purposes in conditions likehereditary spherocytosis
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a congenital hemolytic disorder wherein a genetic genetic mutation, mutation coding for a structural membrane protein phenotype causes the red blood cells to be sphere-shaped (spherocytosis), rather than the norma ...
, trauma to the spleen, and autosplenectomy
An autosplenectomy (from'' 'auto-' ''self,'' '-splen-' ''spleen,'' 'List of -ectomies, -ectomy' ''removal) is a negative outcome of disease and occurs when a disease damages the spleen to such an extent that it becomes shrunken and non-functional. ...
caused by sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying ...
. Other causes are radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
involving the spleen, such as that used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named a ...
.
Howell–Jolly bodies are also seen in amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weigh ...
, severe hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonl ...
, megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA replication, DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. ...
, hereditary spherocytosis, and myelodysplastic syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may includ ...
(MDS). The bodies can also be seen in premature infants.
References
External links
Digital Pathology, Brown University: Howell-Jolly Bodies
{{DEFAULTSORT:Howell-Jolly body Abnormal clinical and laboratory findings for RBCs