Homosexuality In Children's Literature on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gay literature is a collective term for
 Many
Many
 The era known as the
The era known as the
 In the 21st century, much of LGBT literature has achieved a high level of sophistication and many works have earned mainstream acclaim. Notable authors include Alan Hollinghurst, Michael Cunningham, Colm Tóibín, John Boyne, and Andrew Sean Greer. Greer, an openly gay man, won the 2018 Pulitzer Prize for Fiction for ''Less (novel), Less''. LGBT themes have also become more visible in a growing body of high-quality young adult literature, with notable authors including Alex Sánchez (author), Alex Sánchez, Stephen Chbosky, Shyam Selvadurai, Perry Moore, Adam Silvera, Benjamin Alire Sáenz, and David Levithan. Becky Albertalli's teen novel ''Simon vs. the Homo Sapiens Agenda'' was adapted into the feature film ''Love, Simon'' by 20th Century Fox, the first film by a major studio focused on a gay teenage romance. Casey McQuiston's ''Red, White & Royal Blue'' is another example of young adult gay and bisexual romantic fiction, and there is currently in the works a film adaptation by Amazon Studios.
In the 21st century, much of LGBT literature has achieved a high level of sophistication and many works have earned mainstream acclaim. Notable authors include Alan Hollinghurst, Michael Cunningham, Colm Tóibín, John Boyne, and Andrew Sean Greer. Greer, an openly gay man, won the 2018 Pulitzer Prize for Fiction for ''Less (novel), Less''. LGBT themes have also become more visible in a growing body of high-quality young adult literature, with notable authors including Alex Sánchez (author), Alex Sánchez, Stephen Chbosky, Shyam Selvadurai, Perry Moore, Adam Silvera, Benjamin Alire Sáenz, and David Levithan. Becky Albertalli's teen novel ''Simon vs. the Homo Sapiens Agenda'' was adapted into the feature film ''Love, Simon'' by 20th Century Fox, the first film by a major studio focused on a gay teenage romance. Casey McQuiston's ''Red, White & Royal Blue'' is another example of young adult gay and bisexual romantic fiction, and there is currently in the works a film adaptation by Amazon Studios.
 Homosexuality in speculative fiction refers to the incorporation of
Homosexuality in speculative fiction refers to the incorporation of
Document ID 5291
* * Reade, Brian (1970). ''Sexual Heretics: Male Homosexuality in English Literature from 1850 to 1900''.
Lambda Literary Foundation – Publishes the Lambda Book Report and the Lambda Literary Awards
Blithe House Quarterly – online journal
* [http://www.nuwinepress.com NuWine Press - Gay Christian Book Publisher featuring fresh perspectives on the Christian faith]
Lodestar Quarterly — an Online Journal of the Finest Gay, Lesbian, and Queer Literature
Lesbian Mysteries
features Lesbian Mystery Novels
Gay's the Word
UK LGBTQ Specialist Bookshop
* [http://www.leewind.org] Lists, summarizes, and offers reader reviews of Teen, Middle Grade, and Picture Books with Gay (GLBTQ) characters and themes. * {{Authority control Gay history, Literature Gay male literature,
literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electroni ...
produced by or for the gay community
The LGBTQ community (also known as the LGBT, LGBT+, LGBTQ+, LGBTQIA, LGBTQIA+, or queer community) comprises LGBTQ individuals united by a common culture and social movements. These communities generally celebrate pride, diversity, individua ...
which involves characters, plot
Plot or Plotting may refer to:
Art, media and entertainment
* Plot (narrative), the connected story elements of a piece of fiction
Music
* ''The Plot'' (album), a 1976 album by jazz trumpeter Enrico Rava
* The Plot (band), a band formed in 2003
...
lines, and/or themes portraying male homosexual
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between people of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" exc ...
behavior.
Overview and history
Because the social acceptance of homosexuality has varied in many world cultures throughout history, LGBT literature has covered a vast array of themes and concepts. LGBT individuals have often turned to literature as a source of validation, understanding, and beautification of same-sex attraction. In contexts where homosexuality has been perceived negatively, LGBT literature may also document the psychological stresses and alienation suffered by those experiencing prejudice, legal discrimination,AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
, self-loathing, bullying, violence, religious condemnation, denial, suicide, persecution, and other such obstacles.
Themes of love between individuals of the same gender are found in a variety of ancient texts throughout the world. The ancient Greeks, in particular, explored the theme on a variety of different levels in such works as Plato's ''Symposium
In Ancient Greece, the symposium (, ''sympósion'', from συμπίνειν, ''sympínein'', 'to drink together') was the part of a banquet that took place after the meal, when drinking for pleasure was accompanied by music, dancing, recitals, o ...
''.
Ancient mythology
 Many
Many mythologies
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
and religious narratives include stories of romantic affection or sexuality between men or feature divine actions that result in changes in gender. These myths have been interpreted as forms of LGBT expression and modern conceptions of sexuality and gender have been applied to them. Myths have been used by individual cultures, in part, to explain and validate their particular social institutions or to explain the cause of transgender identity or homosexuality.
In classical mythology, male lovers were attributed to ancient Greek god
In ancient Greece, deities were regarded as immortal, anthropomorphic, and powerful. They were conceived of as individual persons, rather than abstract concepts or notions, and were described as being similar to humans in appearance, albeit larg ...
s and heroes such as Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
, Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
, Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
and Heracles
Heracles ( ; ), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a Divinity, divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of ZeusApollodorus1.9.16/ref> and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive descent through ...
(including Ganymede, Hyacinth
''Hyacinthus'' is a genus of bulbous herbs, and spring-blooming Perennial plant, perennials. They are fragrant flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae and are commonly called hyacinths (). The genus is native predomin ...
, Nerites and Hylas
In classical mythology, Hylas () was a youth who served Heracles (Roman Hercules) as companion and servant. His abduction by water nymphs was a theme of ancient art, and has been an enduring subject for Western art in the classical tradition.
G ...
, respectively) as a reflection and validation of the tradition of pederasty
Pederasty or paederasty () is a sexual relationship between an adult man and an adolescent boy. It was a socially acknowledged practice in Ancient Greece and Rome and elsewhere in the world, such as Pre-Meiji Japan.
In most countries today, ...
.
Early works
ThoughHomer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
did not explicitly portray the heroes Achilles and Patroclus
The relationship between Achilles and Patroclus is a key element of the stories associated with the Trojan War. In the ''Iliad,'' Homer describes a deep, meaningful relationship between Achilles and Patroclus, where Achilles is tender toward Patr ...
as homosexual lovers in his 8th-century BC Trojan War
The Trojan War was a legendary conflict in Greek mythology that took place around the twelfth or thirteenth century BC. The war was waged by the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans (Ancient Greece, Greeks) against the city of Troy after Paris (mytho ...
epic, the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
'', later ancient authors presented the intense relationship as such. In his 5th-century BC lost tragedy ''The Myrmidons
Priam (right) entering the hut of Achilles in his effort to ransom the body of Hector. The figure at left is probably one of Achilles' servant boys. (Attic red-figure kylix of the early fifth century BCE)
The ''Achilleis'' (; Ancient Greek , ' ...
'', Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; ; /524 – /455 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek Greek tragedy, tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is large ...
casts Achilles and Patroclus as pederastic lovers. In a surviving fragment of the play, Achilles speaks of "our frequent kisses" and a "devout union of the thighs". Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
does the same in his ''Symposium
In Ancient Greece, the symposium (, ''sympósion'', from συμπίνειν, ''sympínein'', 'to drink together') was the part of a banquet that took place after the meal, when drinking for pleasure was accompanied by music, dancing, recitals, o ...
'' (385–370 BC); the speaker Phaedrus cites Aeschylus and holds Achilles up as an example of how people will be more brave and even sacrifice themselves for their lovers. In his oration ''Against Timarchus
"Against Timarchus" () was a speech by Aeschines accusing Timarchus of being unfit to involve himself in public life. The case was brought about in 346–345 BC, in response to Timarchus, along with Demosthenes, bringing a suit against Aeschines, a ...
'', Aeschines
Aeschines (; Greek: ; 389314 BC) was a Greek statesman and one of the ten Attic orators.
Biography
Although it is known he was born in Athens, the records regarding his parentage and early life are conflicting; but it seems probable that h ...
argues that though Homer "hides their love and avoids giving a name to their friendship", Homer assumed that educated readers would understand the "exceeding greatness of their affection". Plato's ''Symposium'' also includes a creation myth
A creation myth or cosmogonic myth is a type of cosmogony, a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Cre ...
that explains homo- and heterosexuality (Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Ancient Greek comedy, comic playwright from Classical Athens, Athens. He wrote in total forty plays, of which eleven survive virtually complete today. The majority of his surviving play ...
speech) and celebrates the pederastic tradition and erotic love between men ( Pausanias speech), as does another of his dialogue
Dialogue (sometimes spelled dialog in American and British English spelling differences, American English) is a written or spoken conversational exchange between two or more people, and a literature, literary and theatrical form that depicts suc ...
s, '' Phaedrus''.
The tradition of pederasty in ancient Greece
Pederasty in ancient Greece was a socially acknowledged relationship between an older male (the ''erastes'') and a younger male (the '' eromenos'') usually in his teens. It was characteristic of the Archaic and Classical periods.
Some s ...
(as early as 650 BC) and later the acceptance of limited homosexuality in ancient Rome
Homosexuality in ancient Rome Societal attitudes toward homosexuality, differed markedly from the contemporary Western culture, West. Latin lacks words that would precisely Translation, translate "homosexual" and "heterosexual". The primary dich ...
infused an awareness of male-male attraction and sex into ancient poetry. In the second
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
of Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
's ''Eclogues
The ''Eclogues'' (; , ), also called the ''Bucolics'', is the first of the three major works of the Latin poet Virgil.
Background
Taking as his generic model the Greek bucolic poetry of Theocritus, Virgil created a Roman version partly by o ...
'' (1st century BC), the shepherd Corydon proclaims his love for the boy Alexis. Some of the erotic poetry of Catullus
Gaius Valerius Catullus (; ), known as Catullus (), was a Latin neoteric poet of the late Roman Republic. His surviving works remain widely read due to their popularity as teaching tools and because of their personal or sexual themes.
Life
...
in the same century is directed at other men (''Carmen 48'', ''50'', and ''99''), and in a wedding hymn (''Carmen 61'') he portrays a male concubine
Concubinage is an interpersonal relationship, interpersonal and Intimate relationship, sexual relationship between two people in which the couple does not want to, or cannot, enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarde ...
about to be supplanted by his master's future wife. The first line of his infamous invective
Invective (from Middle English ''invectif'', or Old French and -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... and Late Latin ''invectus'') is abusive, or insulting ...
'' Carmen 16'' — which has been called "one of the filthiest expressions ever written in Latin—or in any other language, for that matter" — contains explicit homosexual sex acts.
The ''Satyricon
The ''Satyricon'', ''Satyricon'' ''liber'' (''The Book of Satyrlike Adventures''), or ''Satyrica'', is a Latin work of fiction believed to have been written by Gaius Petronius in the late 1st century AD, though the manuscript tradition identifi ...
'' by is a Latin work of fiction detailing the misadventures of Encolpius and his lover, a handsome and promiscuous sixteen-year-old servant boy named Giton. Written in the 1st century AD during the reign of Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
, it is the earliest known text of its kind depicting homosexuality.
In the celebrated Japanese work ''The Tale of Genji
is a classic work of Japanese literature written by the noblewoman, poet, and lady-in-waiting Murasaki Shikibu around the peak of the Heian period, in the early 11th century. It is one of history's first novels, the first by a woman to have wo ...
'', written by Murasaki Shikibu
was a Japanese novelist, Japanese poetry#Age of Nyobo or court ladies, poet and lady-in-waiting at the Imperial Court in Kyoto, Imperial court in the Heian period. She was best known as the author of ''The Tale of Genji'', widely considered t ...
in the early 11th century, the title character Hikaru Genji
is the protagonist of Murasaki Shikibu's Heian-era Japanese novel ''The Tale of Genji''. "Hikaru" means "shining", deriving from his appearance, hence he is known as the "Shining Prince." He is portrayed as a superbly handsome man and a gen ...
is rejected by the lady Utsusemi in chapter 3 and instead sleeps with her young brother: "Genji pulled the boy down beside him ... Genji, for his part, or so one is informed, found the boy more attractive than his chilly sister."
Antonio Rocco's '' Alcibiades the Schoolboy'', published anonymously in 1652, is an Italian dialogue
Dialogue (sometimes spelled dialog in American and British English spelling differences, American English) is a written or spoken conversational exchange between two or more people, and a literature, literary and theatrical form that depicts suc ...
written as a defense of homosexual sodomy
Sodomy (), also called buggery in British English, principally refers to either anal sex (but occasionally also oral sex) between people, or any Human sexual activity, sexual activity between a human and another animal (Zoophilia, bestiality). I ...
. The first such explicit work known to be written since ancient times, its intended purpose as a "Carnivalesque
The Carnivalesque is a literary mode that subverts and liberates the assumptions of the dominant style or atmosphere through humor and chaos. It originated as "carnival" in Mikhail Bakhtin's ''Problems of Dostoevsky's Poetics'' and was further dev ...
satire
Satire is a genre of the visual, literary, and performing arts, usually in the form of fiction and less frequently non-fiction, in which vices, follies, abuses, and shortcomings are held up to ridicule, often with the intent of exposin ...
", a defense of pederasty
Pederasty or paederasty () is a sexual relationship between an adult man and an adolescent boy. It was a socially acknowledged practice in Ancient Greece and Rome and elsewhere in the world, such as Pre-Meiji Japan.
In most countries today, ...
, or a work of pornography
Pornography (colloquially called porn or porno) is Sexual suggestiveness, sexually suggestive material, such as a picture, video, text, or audio, intended for sexual arousal. Made for consumption by adults, pornographic depictions have evolv ...
is unknown, and debated.
Several medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
European works contain references to homosexuality, such as in ''Giovanni Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio ( , ; ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian people, Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so ...
''s ''Decameron
''The Decameron'' (; or ''Decamerone'' ), subtitled ''Prince Galehaut'' (Old ) and sometimes nicknamed ''l'Umana commedia'' ("the Human comedy", as it was Boccaccio that dubbed Dante Alighieri's ''Comedy'' "''Divine''"), is a collection of ...
'' or ''Lanval
''Lanval'' is one of the Lais of Marie de France. Written in Anglo-Norman, it tells the story of Lanval, a knight at King Arthur's court, who is overlooked by the king, wooed by a fairy lady, given all manner of gifts by her, and subsequently r ...
'', a French lai, in which the knight Lanval is accused by Guinevere
Guinevere ( ; ; , ), also often written in Modern English as Guenevere or Guenever, was, according to Arthurian legend, an early-medieval queen of Great Britain and the wife of King Arthur. First mentioned in literature in the early 12th cen ...
of having "no desire for women". Others include homosexual themes, like '' Yde et Olive''.
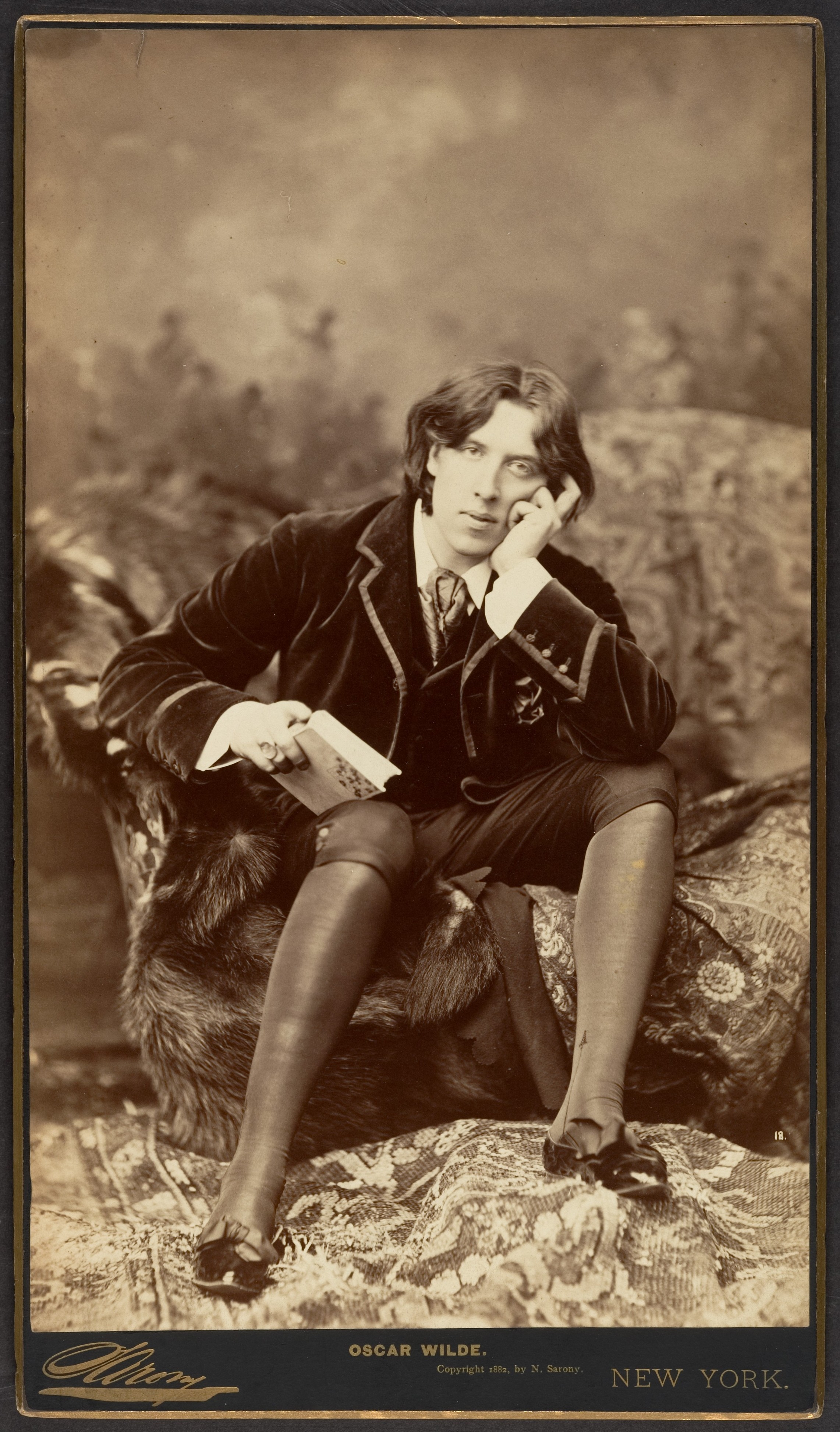
18th and 19th centuries
 The era known as the
The era known as the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
(the 1650s to the 1780s) gave rise to, in part, a general challenge to the traditional doctrines of society in Western Europe. A particular interest in the Classical era of Greece and Rome "as a model for contemporary life" put the Greek appreciation of nudity, the male form and male friendship (and the inevitable homoerotic overtones) into art and literature. It was common for gay authors at this time to include allusions to Greek mythological characters as a code that homosexual readers would recognize. Gay men of the period "commonly understood ancient Greece and Rome to be societies where homosexual relationships were tolerated and even encouraged", and references to those cultures might identify an author or book's sympathy with gay readers and gay themes but probably be overlooked by straight readers. Despite the "increased visibility of queer behavior" and prospering networks of male prostitution
Male prostitution is a form of sex work consisting of the act or practice of men providing sexual services in return for payment. Although clients can be of any gender, the vast majority are older males looking to fulfill their sexual needs. M ...
in cities like Paris and London, homosexual activity had been outlawed in England (and by extension, the United States) as early as the Buggery Act 1533
The Buggery Act 1533, formally An Acte for the punishment of the vice of Buggerie (25 Hen. 8. c. 6), was an Act of Parliament (United Kingdom), act of the Parliament of England that was passed during the reign of Henry VIII.
The act was the c ...
. Across much of Europe in the 1700s and 1800s, the legal punishment for sodomy was death, making it dangerous to publish or distribute anything with overt gay themes. James Jenkins of Valancourt Books
Valancourt Books is an independent American publishing house founded by James Jenkins and Ryan Cagle in 2005. The company specializes in "the rediscovery of rare, neglected, and out-of-print fiction", in particular gay titles, Gothic novels a ...
noted:
Many early Gothic fiction
Gothic fiction, sometimes referred to as Gothic horror (primarily in the 20th century), is a literary aesthetic of fear and haunting. The name of the genre is derived from the Renaissance era use of the word "gothic", as a pejorative to mean me ...
authors, like Matthew Lewis, William Thomas Beckford
William Thomas Beckford (29 September 1760 – 2 May 1844) was an English novelist, art critic, planter and politician. He was reputed at one stage to be England's richest commoner.
He was the son of William Beckford (politician), William Beckf ...
and Francis Lathom
Francis Lathom (14 July 1774 – 19 May 1832) was a British gothic novelist and playwright. Most of his novels were out of print throughout the 20th century, but some have since been rediscovered and republished by Valancourt Books. His best kn ...
, were homosexual, and would sublimate these themes and express them in more acceptable forms, using transgressive genres like Gothic and horror fiction. The title character of Lewis's ''The Monk
''The Monk: A Romance'' is a Gothic novel by Matthew Gregory Lewis, published in 1796 across three volumes. Written early in Lewis's career, it was published anonymously when he was 20. It tells the story of a virtuous Catholic monk who give ...
'' (1796) falls in love with young novice Rosario, and though Rosario is later revealed to be a woman named Matilda, the gay subtext is clear. A similar situation occurs in Charles Maturin
Charles Robert Maturin, also known as C. R. Maturin (25 September 1780 – 30 October 1824), was an Irish Protestant clergyman (ordained in the Church of Ireland) and a writer of Gothic fiction, Gothic plays and novels.Chris Morgan, "Maturin, C ...
's ''The Fatal Revenge'' (1807) when the valet Cyprian asks his master, Ippolito, to kiss him as though he were Ippolito's lover; later Cyprian is also revealed to be a woman. In Maturin's ''Melmoth the Wanderer
''Melmoth the Wanderer'' is an 1820 Gothic novel by Irish playwright, novelist and clergyman Charles Maturin. The novel's titular character is a scholar who sold his soul to the devil in exchange for 150 extra years of life, and searches the wo ...
'' (1820), the close friendship between a young monk and a new novice is scrutinized as potentially "too like love". Sheridan Le Fanu
Joseph Thomas Sheridan Le Fanu (; 28 August 1814 – 7 February 1873), popularly known as J. S. Le Fanu, was an Irish writer of Gothic literature, mystery novels, and horror fiction. Considered by critics to be one of the greatest ghost ...
's novella ''Carmilla
''Carmilla'' is an 1872 Gothic fiction, Gothic novella by Irish author Sheridan Le Fanu, Joseph Sheridan Le Fanu. It is one of the earliest known works of vampire fiction, predating Bram Stoker's ''Dracula'' (1897) by 25 years. First published ...
'' (1872) was the first lesbian vampire
Lesbian vampirism is a Trope (literature), trope in early gothic horror and 20th century exploitation film. The archetype of a lesbian vampire used the fantasy genre to circumvent the heavy LGBT censorship, censorship of lesbian characters in the ...
story, and influenced Bram Stoker
Abraham Stoker (8 November 1847 – 20 April 1912), better known by his pen name Bram Stoker, was an Irish novelist who wrote the 1897 Gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. The book is widely considered a milestone in Vampire fiction, and one of t ...
's ''Dracula
''Dracula'' is an 1897 Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novel by Irish author Bram Stoker. The narrative is Epistolary novel, related through letters, diary entries, and newspaper articles. It has no single protagonist and opens ...
'' (1897). Stoker's novel has its own homoerotic aspects, as when Count Dracula
Count Dracula () is the title character of Bram Stoker's 1897 gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. He is considered the prototypical and archetypal vampire in subsequent works of fiction. Aspects of the character are believed by some to have been i ...
warns off the female vampire
A vampire is a mythical creature that subsists by feeding on the Vitalism, vital essence (generally in the form of blood) of the living. In European folklore, vampires are undead, undead humanoid creatures that often visited loved ones and c ...
s and claims Jonathan Harker
Jonathan Harker is a fictional character and one of the main protagonists of Bram Stoker's 1897 Gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. An English solicitor, his journey to Transylvania and encounter with the vampire Count Dracula and his Brides at Ca ...
, saying "This man belongs to me!"
'' A Year in Arcadia: Kyllenion'' (1805) by Augustus, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
Augustus, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg (full name: ''Emil Leopold August'') (23 November 1772 — 17 May 1822), was a Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg, and the author of one of the first modern novels to treat of homoerotic love. He was the maternal ...
is "the earliest known novel that centers on an explicitly male-male love affair". Set in ancient Greece, the German novel features several couples—including a homosexual one—falling in love, overcoming obstacles and living happily ever after. The Romantic movement
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
gaining momentum at the end of the 18th century allowed men to "express deep affection for each other", and the motif of ancient Greece as "a utopia of male-male love" was an acceptable vehicle to reflect this, but some of Duke August's contemporaries felt that his characters "stepped over the bounds of manly affection into unseemly eroticism." The first American gay novel was '' Joseph and His Friend: A Story of Pennsylvania'' (1870) by Bayard Taylor
Bayard Taylor (January 11, 1825December 19, 1878) was an American poet, literary critic, translator, travel author, and diplomat. As a poet, he was very popular, with a crowd of more than 4,000 attending a poetry reading once, which was a record ...
, the story of a newly engaged young man who finds himself instead falling in love with another man. Robert K. Martin called it "quite explicit in its adoption of a political stance toward homosexuality" and notes that the character Philip "argues for the 'rights' of those 'who cannot shape themselves according to the common-place pattern of society. Henry Blake Fuller's 1898 play, ''At St. Judas's'', and 1919 novel, '' Bertram Cope's Year'', are noted as among the earliest published American works in literature on the theme of homosexual relationships.
The new "atmosphere of frankness" created by the Enlightenment sparked the production of pornography like John Cleland
John Cleland (24 September 1709 – 23 January 1789) was an English novelist best known for his fictional '' Fanny Hill: or, the Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure'', whose eroticism led to his arrest. James Boswell called him "a sly, old malcont ...
's infamous ''Fanny Hill
''Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure'' – popularly known as ''Fanny Hill'' – is an erotic novel by the English novelist John Cleland first published in London in 1748 and 1749. Written while the author was in debtors' prison in London,Wagne ...
'' (1749), which features a rare graphic scene of male homosexual sex. Published anonymously a century later, ''The Sins of the Cities of the Plain
''The Sins of the Cities of the Plain; or, The Recollections of a Mary-Ann, with Short Essays on Sodomy and Tribadism'', by the pseudonymous " Jack Saul", is one of the first exclusively homosexual works of pornographic literature published in E ...
'' (1881) and ''Teleny, or The Reverse of the Medal
''Teleny, or The Reverse of the Medal'' is a pornographic novel, first published in London in 1893. The authorship of the work is unknown. There is a consensus that it was an ensemble effort, but it has often been attributed to Oscar Wilde. Se ...
'' (1893) are two of the earliest pieces of English-language pornography to explicitly and near-exclusively concern homosexuality. ''The Sins of the Cities of the Plain'' is about a male prostitute, and set in London around the time of the Cleveland Street Scandal
The Cleveland Street scandal occurred in 1889, when a homosexual male brothel and Love hotel, house of assignation on Cleveland Street, London, was discovered by police. The government was accused of covering up the scandal to protect the names ...
and the Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Fflahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish author, poet, and playwright. After writing in different literary styles throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular and influential playwright ...
trials. ''Teleny'', chronicling a passionate affair between a Frenchman and a Hungarian pianist, is often attributed to a collaborative effort by Wilde and some of his contemporaries. Wilde's more mainstream ''The Picture of Dorian Gray
''The Picture of Dorian Gray'' is an 1890 philosophical fiction and Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novel by Irish writer Oscar Wilde. A shorter novella-length version was published in the July 1890 issue of the American period ...
'' (1890) still shocked readers with its sensuality and overtly homosexual characters. Drew Banks called Dorian Gray a groundbreaking gay character because he was "one of the first in a long list of hedonistic
Hedonism is a family of philosophical views that prioritize pleasure. Psychological hedonism is the theory that all human behavior is motivated by the desire to maximize pleasure and minimize pain. As a form of egoism, it suggests that peopl ...
fellows whose homosexual tendencies secured a terrible fate." The French realist Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, ; ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of Naturalism (literature), naturalism, and an important contributor to ...
in his novel ''Nana
Nana, Na Na or NANA may refer to:
People
* Nana (given name), including a list of people and characters with the given name
* Nana (surname), including a list of people and characters with the surname
* Nana (chief) (died 1896), Mimbreño Ap ...
'' (1880) depicted, along with a wide variety of heterosexual couplings and some lesbian scenes, a single homosexual character, Labordette. Paris theater society and the ''demi-monde'' are long accustomed to his presence and role as go-between; he knows all the women, escorts them, and runs errands for them. He is "a parasite, with even a touch of pimp", but also a more sympathetic figure than most of the men, as much a moral coward as them but physically brave and not a stereotype.
20th century
By the 20th century, discussion of homosexuality became more open and society's understanding of it evolved. A number of novels with explicitly gay themes and characters began to appear in the domain of mainstream or art literature.Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
-winner André Gide
André Paul Guillaume Gide (; 22 November 1869 – 19 February 1951) was a French writer and author whose writings spanned a wide variety of styles and topics. He was awarded the 1947 Nobel Prize in Literature. Gide's career ranged from his begi ...
's semi-autobiographical novel ''The Immoralist
''The Immoralist'' () is a novel by André Gide, published in France in 1902.
Plot
''The Immoralist'' is a recollection of events that Michel narrates to his three visiting friends. One of those friends solicits job search assistance for Miche ...
'' (1902) finds a newly married man reawakened by his attraction to a series of young Arab boys. Though Bayard Taylor's ''Joseph and His Friend'' (1870) had been the first American gay novel, Edward Prime-Stevenson's '' Imre: A Memorandum'' (1906) was the first in which the homosexual couple were happy and united at the end. Initially published privately under the pseudonym "Xavier Mayne", it tells the story of a British aristocrat and a Hungarian soldier whose new friendship turns into love. In Thomas Mann
Paul Thomas Mann ( , ; ; 6 June 1875 – 12 August 1955) was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and the 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature laureate. His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novell ...
's 1912 novella ''Death in Venice
''Death in Venice ''() is a novella by German author Thomas Mann, published in 1912. It presents an ennobled writer who visits Venice and is liberated, uplifted, and then increasingly obsessed by the sight of a boy in a family of Polish tourist ...
'', a tightly wound, aging writer finds himself increasingly infatuated with a young Polish boy. Marcel Proust
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust ( ; ; 10 July 1871 – 18 November 1922) was a French novelist, literary critic, and essayist who wrote the novel (in French – translated in English as ''Remembrance of Things Past'' and more r ...
's serialized novel ''In Search of Lost Time
''In Search of Lost Time'' (), first translated into English as ''Remembrance of Things Past'', and sometimes referred to in French as ''La Recherche'' (''The Search''), is a novel in seven volumes by French author Marcel Proust. This early twen ...
'' (1913–1927) and Gide's '' The Counterfeiters'' (1925) also explore homosexual themes.
British author E.M. Forster
Edward Morgan Forster (1 January 1879 – 7 June 1970) was an English author. He is best known for his novels, particularly '' A Room with a View'' (1908), ''Howards End'' (1910) and '' A Passage to India'' (1924). He also wrote numerous shor ...
earned a prominent reputation as a novelist while concealing his own homosexuality from the broader British public. In 1913–14, he privately penned '' Maurice'', a bildungsroman that follows a young, upper-middle-class man through the self-discovery of his own attraction to other men, two relationships, and his interactions with an often uncomprehending or hostile society. The book is notable for its affirming tone and happy ending. "A happy ending was imperative", wrote Forster, "I was determined that in fiction anyway, two men should fall in love and remain in it for the ever and ever that fiction allows ... Happiness is its keynote." The book was not published until 1971, after Forster's death. William J. Mann said of the novel, " lec Scudder of ''Maurice'' wasa refreshingly unapologetic young gay man who was not an effete Oscar Wilde aristocrat, but rather a working class, masculine, ordinary guy ... an example of the working class teaching the privileged class about honesty and authenticity a bit of a stereotype now, but back then quite extraordinary."
In Germany in 1920, Erwin von Busse
Erwin von Busse also known as Granand or Erwin von Busse-Granand (12 January 1885 – 10 April 1939) was a German writer, painter, theater director, art historian and art critic. His 1920 short story collection ''Das erotische Komödiengärtlein' ...
published a collection of short stories about erotic encounters between men using the pseudonym Granand. Promptly banned for "indecency", it was not republished until 1993 and only appeared in an English translation as ''Berlin Garden of Erotic Delights'' in 2022.
Blair Niles's '' Strange Brother'' (1931), about the platonic relationship between a heterosexual woman and a gay man in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
in the late 1920s and early 1930s, is an early, objective exploration of homosexual issues during the Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African-American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics, and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the ti ...
. Though praised for its journalistic approach, sympathetic nature and promotion of tolerance and compassion, the novel has been numbered among a group of early gay novels that is "cast in the form of a tragic melodrama" and, according to editor and author Anthony Slide, illustrates the "basic assumption that gay characters in literature must come to a tragic end." "Smoke, Lilies, and Jade" by gay author and artist Richard Bruce Nugent, published in 1926, was the first short story by an African-American writer openly addressing his homosexuality. Written in a modernist stream-of-consciousness style, its subject matter was bisexuality and interracial male desire.
Forman Brown's 1933 novel ''Better Angel'', published under the pseudonym Richard Meeker, is an early novel which describes a gay lifestyle without condemning it. Christopher Carey called it "the first homosexual novel with a truly happy ending". Slide names only four familiar gay novels of the first half of the 20th century in English: Djuna Barnes' ''Nightwood'' (1936), Carson McCullers' ''Reflections in a Golden Eye (novel), Reflections in a Golden Eye'' (1941), Truman Capote's ''Other Voices, Other Rooms (novel), Other Voices, Other Rooms'' (1948) and Gore Vidal's ''The City and the Pillar'' (1948). In John O'Hara's 1935 novel ''BUtterfield 8 (novel), BUtterfield 8'', the principal female character Gloria Wondrous has a friend Ann Paul, who in school "was suspect because of a couple of crushes which ... her former schoolmates were too free about calling Lesbian, and Gloria did not think so". Gloria speculates that "there was a little of that in practically all women", considers her own experience with women making passes, and rejects her own theory.
The story of a young man who is coming of age and discovers his own homosexuality, ''The City and the Pillar'' (1946) is recognized as the first Post-war, post-World War II novel whose openly gay and well-adjusted protagonist is not killed off at the end of the story for defying Norm (sociology), social norms. It is also one of the "definitive war novel, war-influenced gay novels", one of the few books of its period dealing directly with male homosexuality. ''The City and the Pillar'' has also been called "the most notorious of the gay novels of the 1940s and 1950s." It sparked a public scandal, including notoriety and criticism, because it was released at a time when homosexuality was commonly considered immoral and because it was the first book by an accepted American author to portray overt homosexuality as a natural behavior. Upon its release, ''The New York Times'' refused to publish advertisements for the novel and Vidal was blacklisted to the extent that no major newspaper or magazine would review any of his novels for six years. Modern scholars note the importance of the novel to the visibility of gay literature. Michael Bronski points out that "gay-male-themed books received greater critical attention than lesbian ones" and that "writers such as Gore Vidal were accepted as important American writers, even when they received attacks from homophobic critics." Ian Young (writer), Ian Young notes that social disruptions of World War II changed public morals, and lists ''The City and the Pillar'' among a spate of war novels that use the military as backdrop for overt homosexual behavior.
Other notable works of the 1940s and 1950s include Jean Genet's semiautobiographical ''Our Lady of the Flowers'' (1943) and ''The Thief's Journal'' (1949), Yukio Mishima's ''Confessions of a Mask'' (1949), Umberto Saba's ''Ernesto (novel), Ernesto'' (written in 1953, published posthumously in 1975), and ''Giovanni's Room'' (1956) by James Baldwin (writer), James Baldwin. Mary Renault's ''The Charioteer'', a 1953 British war novel about homosexual men in and out of the military, quickly became a bestseller within the gay community. Renault's historical novels ''The Last of the Wine'' (1956) about Athenian pederasty in ancient Greece and ''The Persian Boy'' (1972) about Alexander the Great and his slave lover Bagoas (courtier), Bagoas followed suit. ''A Room in Chelsea Square'' (1958) by British author Michael Nelson (novelist), Michael Nelson — about a wealthy gentleman who lures an attractive younger man to London with the promise of an upper crust lifestyle — was originally published anonymously both because of its explicit gay content at a time when homosexuality was still illegal, and because its characters were "thinly veiled portrayals of prominent London literary figures".
A key element of Allen Drury's 1959 bestselling and Pulitzer Prize-winning political fiction, political novel ''Advise and Consent'' is the blackmailing of young US senator Brigham Anderson, who is hiding a secret wartime homosexual tryst. In 2009, ''The Wall Street Journal'' Scott Simon wrote of Drury that "the conservative Washington novelist was more progressive than Hollywood liberals", noting that the character Anderson is "candid and unapologetic" about his affair, and even calling him "Drury's most appealing character". Frank Rich wrote in ''The New York Times'' in 2005:
In Taiwan, during the Martial law in Taiwan, martial law period (1949–1987), the Kuomintang government focused on strengthening Taiwan's industrial and economic power and reinforcing traditional Confucious values on society. The heterosexual image of the modern family dominated, and "public discourses of same-sex desire were almost non-existent." Nevertheless, Pai Hsien-yung's Jade Love (novella), ''Jade Love'' (1960), "Moon Dream" (1960), "Youthfulness" (1961), and "Seventeen Years Old and Lonely" (1961) — novellas and short stories exploring male homosexual desire — were published in ''Xiandai Wenxue''. He published "Taipei People#A Sky Full of Bright, Twinkling Stars (滿天裏亮晶晶的星星), A Sky Full of Bright, Twinkling Stars" in 1969, which follows gay characters who frequent Taipei's New Park area and would appear in Pai's 1983 novel ''Crystal Boys''. ''Crystal Boys'' is set in 1970s Taipei and covers the main character Li-Qing's life after he is expelled from school for engaging in sexual relations with his classmate Zhao Ying. It is commonly identified as "the first Chinese novel that depicts the life struggles in the homosexual community [and] grew out of the particular socio-historical environment of Taiwan in the 1970s." Other works published in Taiwan in the early 1960s include Chiang Kuei's ''Double Suns'' (1961), with depictions of male homosexual desire, and Kuo Liang-hui's ''Green Is the Grass'' (1963), which follows two Taiwanese middle school boys who exhibit sexual and romantic desires toward each other. The status of ''Double Suns'' in the Taiwanese gay literature scene has been questioned since male homosexuality is not the main focus of the work. On this, Chi Ta-wei comments on its influence and significance in the history of homosexual literature in Taiwan, writing that "[t]o underestimate [the characters of Double Suns] and deem them 'not homosexual enough' is to truncate the history of literature and to regulate the ever-elusive homosexuality to a confined definition."
Gillian Freeman's 1961 novel ''The Leather Boys (novel), The Leather Boys'', originally published under the pseudonym Eliot George, tells the story of a gay relationship between two young working-class men in London, one married and the other a biker. It was the first novel to focus on love between young working-class men rather than aristocrats. James Baldwin followed ''Giovanni's Room'' with ''Another Country (novel), Another Country'' (1962), a "controversial bestseller" that "explicitly combines racial and sexual protests ... structured around the lives of eight racially, regionally, socioeconomically, and sexually diverse characters." John Rechy's ''City of Night'' (1963) and ''Numbers (novel), Numbers'' (1967) are graphic tales of male hustlers; ''City of Night'' has been called a "landmark novel" that "marked a radical departure from all other novels of its kind, and gave voice to a subculture that had never before been revealed with such acuity." Claude J. Summers wrote of Christopher Isherwood's ''A Single Man (novel), A Single Man'' (1964):
George Baxt's ''A Queer Kind of Death'' (1966) introduced Pharaoh Love, the first gay black detective in fiction. The novel was met with considerable acclaim, and ''The New York Times'' critic Anthony Boucher wrote, "This is a detective story, and unlike any other that you have read. No brief review can attempt to convey its quality. I merely note that it deals with a Manhattan subculture wholly devoid of ethics or morality, that said readers may well find it 'shocking', that it is beautifully plotted and written with elegance and wit ... and that you must under no circumstances miss it." Love would be the central figure in two immediate sequels ''Swing Low Sweet Harriet'' (1967) and ''Topsy and Evil'' (1968) and also two later novels, ''A Queer Kind of Love'' (1994) and ''A Queer Kind of Umbrella'' (1995). Though released the same year that homosexual acts were partially decriminalised in England and Wales by the Sexual Offences Act 1967, the 1967 gay thriller ''The Wrong People (novel), The Wrong People'' by British author Robin Maugham was originally published under the pseudonym David Griffin because its frank depiction of pederasty
Pederasty or paederasty () is a sexual relationship between an adult man and an adolescent boy. It was a socially acknowledged practice in Ancient Greece and Rome and elsewhere in the world, such as Pre-Meiji Japan.
In most countries today, ...
and sex trafficking were considered so scandalous. In his controversial 1968 satire
Satire is a genre of the visual, literary, and performing arts, usually in the form of fiction and less frequently non-fiction, in which vices, follies, abuses, and shortcomings are held up to ridicule, often with the intent of exposin ...
''Myra Breckinridge'', Gore Vidal explored the mutability of gender-roles and sexual-orientation as being social constructs established by social mores, making the eponymous heroine a transsexual waging a "war against gender roles".
In 1969, Taiwanese author Lin Hwai-min published "Cicada" in his short story collection of the same name, ''Cicada''. "Cicada" follows the lives of several college students living in Ximending, Taipei, who explore and struggle with expressing homosexual desires for each other.
Fifteen years after ''Advise and Consent'', Drury wrote about the unrequited love of one male astronaut for another in his 1971 novel ''The Throne of Saturn (novel), The Throne of Saturn'', and in his two-part tale of ancient Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten's attempt to change Egyptian religion—''A God Against the Gods'' (1976) and ''Return to Thebes'' (1977)—Akhenaten's romance with his brother Smenkhkare, Smenkhkara contributes to his downfall. Tormented homosexual North McAllister is one of the ensemble of Alpha Zeta fraternity brothers and their families that Drury follows over the course of 60 years in his Allen Drury's University series, ''University'' novels (1990–1998), as well as René Suratt—villain and "bisexual seducer of students"—and the tragic lovers Amos Wilson and Joel. Assessing Drury's body of work in 1999, Erik Tarloff suggested in ''The New York Times'' that "homosexuality does appear to be the only minority status to which Drury seems inclined to accord much sympathy."
Though Thomas Pynchon's ''Gravity's Rainbow'' (1973) was unanimously recommended by the Pulitzer Prize fiction jury to receive the 1974 award, the Pulitzer board chose instead to make no award that year. In 2005 ''Time (magazine), Time'' named the novel one of its "All-Time 100 Greatest Novels", a list of the best English language novels from 1923 to 2005. Other notable novels from the 1970s include Manuel Puig's ''Kiss of the Spider Woman (novel), Kiss of the Spider Woman'' (1976), Andrew Holleran's ''Dancer from the Dance'' (1978), and ''Tales of the City (novel), Tales of the City'' (1978), the first volume of Armistead Maupin's long-running Tales of the City, ''Tales of the City'' series. David Jackson of ''The New York Review of Books'' wrote in 1979, "Homosexual love and/or attraction have become such standard spices in today's fiction, one no longer is surprised at the taste in the dish."
In the 1980s, Edmund White — who had cowritten the 1977 gay sex manual ''The Joy of Gay Sex'' — published the semiautobiographical novels ''A Boy's Own Story'' (1982) and ''The Beautiful Room Is Empty'' (1988). Bret Easton Ellis also came to prominence with ''Less than Zero (novel), Less than Zero'' (1985), ''The Rules of Attraction'' (1987) and later ''American Psycho'' (1991). Nobel Prize winner Roger Martin du Gard's unfinished ''Lieutenant-Colonel de Maumort'', written between 1941 and 1958, was published posthumously in 1983. It explores adolescent homosexual relations and includes a fictional first-person account, written in 1944, of a brief tragic encounter between a young soldier and a bakery apprentice in rural France.
Colombian-born gay author Fernando Vallejo on 1994 published his semi-autobiographical novel Our Lady of the Assassins (novel), ''Our Lady of the Assassins''. The novel deals with the topic of homosexuality in a secondary way, but it is notable for being set in the context of a Latin American country where it is a taboo.
Taiwanese author Chu Tʽien-wen, Chu T'ien-wen's ''Notes of a Desolate Man'' (1994) is written from the first-person perspective of a Taiwanese gay man. Chu compiled the experience of gay men in various cultures as portrayed through media to construct the narrative of ''Notes of a Desolate Man''. The novel has often been criticized by Taiwanese critics for its fragmentary structure and narrative, due to Chu's frequent use of quotations and references. Chu's "presumably heterosexual" and female identity has also inspired various different readings of the novel, as well as "a tension that has been used to serve very different sorts of sexual politics."
The following year, Chi Ta-wei published ''Sensory World'' (1995), which is composed of short stories are significant because of their explicit discussion of sex, sexuality, gender, transgender identity, and male homosexual desire. In 1997, Chi published ''Queer Carnival'', which contains a detailed list of Taiwanese queer literature (covering themes of gay, lesbian, transgender, and other sexuality and gender identities).
In 1997, the short story "Brokeback Mountain (short story), Brokeback Mountain" written by Annie Proulx was published. It would be later adapted into a Brokeback Mountain, critically acclaimed Academy Award nominated film in 2005.
The founding of the Lambda Literary Award in 1988 helped increase the visibility of LGBT literature.
21st century
 In the 21st century, much of LGBT literature has achieved a high level of sophistication and many works have earned mainstream acclaim. Notable authors include Alan Hollinghurst, Michael Cunningham, Colm Tóibín, John Boyne, and Andrew Sean Greer. Greer, an openly gay man, won the 2018 Pulitzer Prize for Fiction for ''Less (novel), Less''. LGBT themes have also become more visible in a growing body of high-quality young adult literature, with notable authors including Alex Sánchez (author), Alex Sánchez, Stephen Chbosky, Shyam Selvadurai, Perry Moore, Adam Silvera, Benjamin Alire Sáenz, and David Levithan. Becky Albertalli's teen novel ''Simon vs. the Homo Sapiens Agenda'' was adapted into the feature film ''Love, Simon'' by 20th Century Fox, the first film by a major studio focused on a gay teenage romance. Casey McQuiston's ''Red, White & Royal Blue'' is another example of young adult gay and bisexual romantic fiction, and there is currently in the works a film adaptation by Amazon Studios.
In the 21st century, much of LGBT literature has achieved a high level of sophistication and many works have earned mainstream acclaim. Notable authors include Alan Hollinghurst, Michael Cunningham, Colm Tóibín, John Boyne, and Andrew Sean Greer. Greer, an openly gay man, won the 2018 Pulitzer Prize for Fiction for ''Less (novel), Less''. LGBT themes have also become more visible in a growing body of high-quality young adult literature, with notable authors including Alex Sánchez (author), Alex Sánchez, Stephen Chbosky, Shyam Selvadurai, Perry Moore, Adam Silvera, Benjamin Alire Sáenz, and David Levithan. Becky Albertalli's teen novel ''Simon vs. the Homo Sapiens Agenda'' was adapted into the feature film ''Love, Simon'' by 20th Century Fox, the first film by a major studio focused on a gay teenage romance. Casey McQuiston's ''Red, White & Royal Blue'' is another example of young adult gay and bisexual romantic fiction, and there is currently in the works a film adaptation by Amazon Studios.
Gay pulp
Gay pulp fiction or gay pulps, refers to printed works, primarily fiction, that include references to male homosexuality, specifically male Gay sexual practices, gay sex, and that are cheaply produced, typically in paperback books made of wood pulp paper; lesbian pulp fiction is similar work about women. Michael Bronski, the editor of an anthology of gay pulp writing, notes in his introduction, "Gay pulp is not an exact term, and it is used somewhat loosely to refer to a variety of books that had very different origins and markets" People often use the term to refer to the "classic" gay pulps that were produced before about 1970, but it may also be used to refer to the gay erotica or pornography in paperback book or digest magazine form produced since that date.Speculative fiction
 Homosexuality in speculative fiction refers to the incorporation of
Homosexuality in speculative fiction refers to the incorporation of homosexual
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between people of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" exc ...
themes into science fiction, fantasy, horror fiction and related genres which together constitute speculative fiction. Such elements may include a lesbian, gay, bisexual or transgender (LGBTQ) character as the protagonist or a major character, or exploration of varieties of human sexual behavior, sexual experience that deviate from the conventional.
Science fiction and fantasy have traditionally been puritanical genres aimed at a male readership, and can be more restricted than non-genre literature by their genre convention, conventions of characterisation and the effect that these conventions have on depictions of sexuality and gender. During the pulp magazine era (1920s-1930s), explicit sexuality of any kind was rare in genre science fiction and fantasy. Then, according to Joanna Russ, in the more relaxed Golden Age of Science Fiction (1940s-1950s) the genre "resolutely ignored the whole subject" of homosexuality. Some writers were able to introduce more explicit sexuality into their work as the readership for science fiction and fantasy began to age in the 1950s; however until the late 1960s few depicted alternative sexuality or revised gender roles, or openly investigated sexual questions. After the pushing back of boundaries in the 1960s and 1970s, homosexuality gained much wider acceptance, and was often incorporated into otherwise conventional SF stories with little comment. By the 1980s, blatant homophobia was no longer considered acceptable to most readers. In Lois McMaster Bujold's ''Ethan of Athos'' (1986), the titular "unlikely hero" is gay obstetrician Dr. Ethan Urquhart, whose dangerous adventure alongside the first woman he has ever met presents both a future society where homosexuality is the norm and the lingering sexism and homophobia of our own world. ''Uranian Worlds'', by Eric Garber and Lyn Paleo, was compiled in 1983 and is an authoritative guide to science fiction literature featuring gay, lesbian, transgender, and related themes. The book covers science fiction literature published before 1990 (2nd edition, 1990), providing a short review and commentary on each piece.
As speculative fiction gives authors and readers the freedom to imagine societies that are different from real-life cultures, this freedom makes speculative fiction a useful means of examining sexual bias by forcing the reader to reconsider his or her heteronormative cultural assumptions. It has also been claimed that LGBT readers identify strongly with the mutant (fiction), mutants, Extraterrestrials in fiction, aliens and other outsider characters found in speculative fiction.
James Jenkins of Valancourt Books
Valancourt Books is an independent American publishing house founded by James Jenkins and Ryan Cagle in 2005. The company specializes in "the rediscovery of rare, neglected, and out-of-print fiction", in particular gay titles, Gothic novels a ...
notes that the connection between gay fiction and horror goes back to the Gothic fiction, Gothic novels of the 1790s and early 1800s. Many Gothic authors, like Matthew Lewis, William Thomas Beckford
William Thomas Beckford (29 September 1760 – 2 May 1844) was an English novelist, art critic, planter and politician. He was reputed at one stage to be England's richest commoner.
He was the son of William Beckford (politician), William Beckf ...
and Francis Lathom
Francis Lathom (14 July 1774 – 19 May 1832) was a British gothic novelist and playwright. Most of his novels were out of print throughout the 20th century, but some have since been rediscovered and republished by Valancourt Books. His best kn ...
, were homosexual, and according to Jenkins "the traditional explanation for the gay/horror connection is that it was impossible for them to write openly about gay themes back then (or even perhaps express them, since words like 'gay' and 'homosexual' didn't exist), so they sublimated them and expressed them in more acceptable forms, using the medium of a transgressive genre like horror fiction." Early works with clear gay subtext include Lewis's ''The Monk
''The Monk: A Romance'' is a Gothic novel by Matthew Gregory Lewis, published in 1796 across three volumes. Written early in Lewis's career, it was published anonymously when he was 20. It tells the story of a virtuous Catholic monk who give ...
'' (1796) and both Charles Maturin
Charles Robert Maturin, also known as C. R. Maturin (25 September 1780 – 30 October 1824), was an Irish Protestant clergyman (ordained in the Church of Ireland) and a writer of Gothic fiction, Gothic plays and novels.Chris Morgan, "Maturin, C ...
's ''The Fatal Revenge'' (1807) and ''Melmoth the Wanderer
''Melmoth the Wanderer'' is an 1820 Gothic novel by Irish playwright, novelist and clergyman Charles Maturin. The novel's titular character is a scholar who sold his soul to the devil in exchange for 150 extra years of life, and searches the wo ...
'' (1820). Somewhat later came the first lesbian vampire
Lesbian vampirism is a Trope (literature), trope in early gothic horror and 20th century exploitation film. The archetype of a lesbian vampire used the fantasy genre to circumvent the heavy LGBT censorship, censorship of lesbian characters in the ...
novella ''Carmilla
''Carmilla'' is an 1872 Gothic fiction, Gothic novella by Irish author Sheridan Le Fanu, Joseph Sheridan Le Fanu. It is one of the earliest known works of vampire fiction, predating Bram Stoker's ''Dracula'' (1897) by 25 years. First published ...
'' (1872) by Sheridan Le Fanu
Joseph Thomas Sheridan Le Fanu (; 28 August 1814 – 7 February 1873), popularly known as J. S. Le Fanu, was an Irish writer of Gothic literature, mystery novels, and horror fiction. Considered by critics to be one of the greatest ghost ...
and ''The Picture of Dorian Gray
''The Picture of Dorian Gray'' is an 1890 philosophical fiction and Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novel by Irish writer Oscar Wilde. A shorter novella-length version was published in the July 1890 issue of the American period ...
'' (1890) by Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Fflahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish author, poet, and playwright. After writing in different literary styles throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular and influential playwright ...
, which shocked readers with its sensuality and overtly homosexual characters. There is even gay subtext in Bram Stoker
Abraham Stoker (8 November 1847 – 20 April 1912), better known by his pen name Bram Stoker, was an Irish novelist who wrote the 1897 Gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. The book is widely considered a milestone in Vampire fiction, and one of t ...
's ''Dracula
''Dracula'' is an 1897 Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novel by Irish author Bram Stoker. The narrative is Epistolary novel, related through letters, diary entries, and newspaper articles. It has no single protagonist and opens ...
'' (1897) as the title character warns off the female vampires and claims Jonathan Harker, saying "This man belongs to me!" The erotic metaphor of vampirism, inspired by ''Carmilla'', has resulted in numerous vampire films since the 1970s strongly implying or explicitly portraying lesbianism.
James R. Keller writes that in particular, "Gay and lesbian readers have been quick to identify with the representation of the vampire, suggesting its experiences parallel those of the sexual outsider." Richard Dyer discusses the recurring homoerotic motifs of vampire fiction in his article "Children of the Night", primarily "the necessity of secrecy, the persistence of a forbidden passion, and the fear of discovery." With the vampire having been a recurring metaphor for same-sex desire from before Stoker's ''Dracula'', Dyer observes that historically earlier representations of vampires tend to evoke horror and later ones turn that horror into celebration. The homoerotic overtones of Anne Rice's celebrated ''The Vampire Chronicles'' series (1976–present) are well documented, and its publication reinforced the "widely recognized parallel between the queer and the vampire."
Comics
LGBT themes in comics is a relatively new concept, as lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBTQ) themes and characters were historically omitted intentionally from the content of comic books and their comic strip predecessors, due to either censorship or the perception that comics were for children. With any mention of homosexuality in mainstream United States comics forbidden by the Comics Code Authority (CCA) until 1989, earlier attempts at exploring these issues in the US took the form of subtle hints or subtext regarding a character's sexual orientation. LGBT themes were tackled earlier in underground comics from the early 1970s onward. Independently published one-off comic books and series, often produced by gay creators and featuring autobiographical storylines, tackled political issues of interest to LGBT readers. Comic strips have also dealt in subtext and innuendo, their wide distribution in newspapers limiting their inclusion of controversial material. The first openly gay characters appeared in prominent strips in the late 1970s; representation of LGBT issues in these titles causes vociferous reaction, both praise and condemnation, to the present day. Comic strips aimed at LGBT audiences are also syndicated in gay- and lesbian-targeted magazines and comics have been created to educate people about LGBT-related issues and to influence real-world politics, with their format and distribution allowing them to transmit messages more subtle, complex, and positive than typical education material. Portrayal of LGBT themes in comics is recognized by several notable awards, including the Gaylactic Spectrum Award and GLAAD Media Awards for outstanding comic book and comic strip. Since the 1990s, LGBT themes have become more common in mainstream US comics, including in a number of titles in which a gay character is the star. European comics have been more inclusive from an earlier date. The lack of censorship, and greater acceptance of comics as a medium of adult entertainment led to less controversy about the representation of LGBT characters. The popular Japanese manga tradition has included genres of girls' comics that feature homosexual relationships since the 1970s, in the form of ''yaoi'' and ''yuri (genre), yuri''. These works are often extremely romantic and include archetypal characters that often are not identified as gay. Since the Japanese "gay boom" of the 1990s, a body of manga aimed at LGBT customers has been produced, which have more realistic and autobiographical themes. Hentai, Pornographic manga also often includes sexualised depictions of lesbians and intersex people. Queer theory, Queer theorists have noted that LGBT characters in mainstream comic books are usually shown as assimilated into heterosexual society, whereas in alternative comics the diversity and uniqueness of LGBT culture is emphasized.Children's fiction
Gay themes
Compared to Gay (male) teen fiction, gay and lesbian teen fiction, sales of gay-themed books for younger children, and availability of these books in public and school libraries, remain "very dicey and very different". ''When Megan Went Away'' (1979) was the first picture book to include LGBT characters. The story, written by Jane Severance and illustrated by Tea Schook, concerns a preteen girl whose lesbian mother and her partner have separated. The first children's book with gay male characters was ''Jenny Lives with Eric and Martin''. Originally published in 1981 in Danish as ''Mette bor hos Morten og Erik'', it tells the story of Jenny, her father and his partner and their daily life. Controversy and politicization followed its publication. Some of the best known children's books with gay themes include ''Heather Has Two Mommies'' (1989) and ''Daddy's Roommate'' (1991), published by LGBTQ publisher Alyson Books. Both books discussed same-sex parenting and attracted criticism and controversy. The American Library Association ranked ''Heather Has Two Mommies'' as the third and second most frequently List of most commonly-challenged books in the United States, challenged book in the United States in 1993 and 1994, respectively. Recent controversies include ''King & King'', originally written in Dutch and published in English in 2002. The book is about a prince uninterested in princesses, who eventually falls in love with another prince. In 2006, parents sued a Massachusetts school district after a teacher read the book to their son's second grade class. ''And Tango Makes Three'' (2005) by Justin Richardson and Peter Parnell has been frequently challenged, and is often on the American Library Associations's List of Challenged Books for Banned Books Week. It was ranked ninth on this list in 2017. The book tells the true story of two male penguins who adopt an egg and raise the baby once it has hatched. While it has been banned and debated many times, it has been awarded and noted by the American Library Association on their Rainbow Book List. In 2018, Little Bee Books partnered with media advocacy group GLAAD for a series of books that offered positive LGBT representation in children's literature. The partnership kicked off with ''Prince & Knight'', written by Daniel Haack and illustrated by Stevie Lewis, which was named to the American Library Association's Rainbow Book List and was named a best book of the year by ''Kirkus Reviews'', Amazon (company), Amazon and the ''Chicago Tribune''. The partnership has gone on to include books that also offer lesbian, transgender and gender non-conforming representation. Australian titles include the books in the 'Learn to Include' series: ''The Rainbow Cubby House'', ''My House'', ''Going to Fair Day'' and ''Koalas on Parade''. ''House of Hades'' (2013), Book 4 in the young adult series ''The Heroes of Olympus'' by Rick Riordan, features a gay supporting character, Nico di Angelo. A more extensive list of gay children's literature includes: * ''A Name on the Quilt: A Story of Remembrance'' by Jeannine Atkins * ''Uncle Bobby's Wedding'' by Sarah S. Brannen * ''A B C: A Family Alphabet Book'' by Bobby Combs * ''1 2 3: A Family Counting Book'' by Bobby Combs * ''Oliver Button is a Sissy'' by Tomie dePaola * ''Asha's Mums'' by Rosamund Elwin and Michele Paulse * ''The Sissy Duckling'' by Harvey Fierstein * ''Molly's Family'' by Nancy Garden * ''Antonio's Card/La Targeta de Antonio'' by Rigoberto González * ''Best Best Colors: Los Mejores Colo res'' by Eric Hoffman * ''Mini Mia and Her Darling Uncle'' by Pija Lindenbaum * ''Everywhere Babies'' by Susan Meyers * ''Felicia's Favorite Story'' by Lesléa Newman * ''Mommy, Mama, and Me'' by Lesléa Newman * ''Saturday is Pattyday'' by Lesléa Newman * ''Too Far Away to Touch'' by Lesléa Newman * ''The White Swan Express'' by Jean Davies Okimoto and Elaine M. Aoki * ''It's Okay to Be Different'' by Todd Parr * ''Tiger Flowers (book), Tiger Flowers'' by Patricia Quinlan * ''And Tango Makes Three'' by Justin Richardson * ''Seeds'' by George Shannon * ''My Two Uncles'' by Judith Vigna * ''William's Doll'' by Charlotte Zolotow * "My Shadow Is Purple" by Scott Stuart * "My Shadow Is Pink" by Scott Stuart In July 2014, Singapore's National Library Board (NLB), a state-funded network of 26 public libraries, confirmed it would destroy three children's books with pro-LGBT families themes for being "against its 'pro-family' stance[,] following complaints by a parent and its own internal review". The decision was widely criticized by LGBT supporters and the arts and literary community who see the actions as akin to book burnings and other forms of censorship. The three books are ''And Tango Makes Three'', which covers the true story of a pair of male penguins that successfully raise a chick, ''The White Swan Express'', which features children adopted by a variety of families including gay, mixed-race and single parents, and ''Who's in My Family'', which references families with homosexual parents. Two weeks after a gay rights rally, these books "sparked a fierce debate" between the religious conservatives, who opposed the rally, and Singapore's growing gay-rights lobby.Bisexual themes
As of 2020, there have been no explicitly bisexual characters–either children or adults–in children's picture book fiction. While many nonfiction picture book biographies of historical figures who had relationships with people of the same gender overlook or ignore those relationships, at least one, ''Frida Kahlo for Girls and Boys'' by Nadia Fink (2017), mentions that Frida Kahlo, Kahlo loved both men and women. Some young adult fiction books do feature bisexual characters, including ''Empress of the World'' by Sara Ryan (2001), ''Double Feature: Attack of the Soul-Sucking Brain Zombies/Bride of the Soul-Sucking Brain Zombies'' by Brent Hartinger (2007), ''Pink'' by Lili Wilkinson (2009), and ''It's Our Prom (So Deal with It)'' by Julie Anne Peters (2012). When they do appear in young adult fiction, bisexuals are often portrayed as confused or greedy.Awards
* Dayne Ogilvie Prize * Ferro-Grumley Award * Lambda Literary Award * Stonewall Book AwardSee also
* Gay characters in fiction * Gay romance * Bengali Queer Literature * Singapore gay literature * Lesbian literature * List of lesbian fiction * List of poets portraying sexual relations between women * Transgender literature * List of LGBT writers * ''Lost Gay Novels''Notes
References
Further reading
* ''Pages Passed from Hand to Hand: The Hidden Tradition of Homosexual Literature in English from 1748 to 1914'' edited and with an introduction by Mark Mitchell and David Leavitt, Chatto & Windus 1998 * ''Homosexuality in Literature, 1890–1930'' by Jeffrey Mayers, Athlone, 1977 * ''A History of Gay Literature: The Male Tradition'' by Gregory Woods, Yale University Press, 1999 * ''Gaiety Transfigured: Gay Self-Representation in American Literature'' edited by David Bergman, University of Wisconsin Press, 1991 * ''Beyond Sex and Romance?: The Politics of Contemporary Lesbian Fiction'' edited by Elaine Hutton, Women's Press, 1998. * ''Lesbian and Gay Writing: An Anthology of Critical Essays'' edited by Mark Lilly, Macmillan, 1990 * ''Love Between Men in English Literature'' by Paul Hammond, Macmillan, 1996 * ''The Homosexual as Hero in Contemporary Fiction'' by Stephen Adams, Vision, 1980 * ''The Penguin Book of Homosexual Verse'' edited by Stephen Coote, Penguin, 1983 * ''Essays on Gay Literature'' edited by Stuart Kellogg, Harrington Park Press, 1983 * * *Document ID 5291
* * Reade, Brian (1970). ''Sexual Heretics: Male Homosexuality in English Literature from 1850 to 1900''.
External links
Lambda Literary Foundation – Publishes the Lambda Book Report and the Lambda Literary Awards
Blithe House Quarterly – online journal
* [http://www.nuwinepress.com NuWine Press - Gay Christian Book Publisher featuring fresh perspectives on the Christian faith]
Lodestar Quarterly — an Online Journal of the Finest Gay, Lesbian, and Queer Literature
Lesbian Mysteries
features Lesbian Mystery Novels
Gay's the Word
UK LGBTQ Specialist Bookshop
* [http://www.leewind.org] Lists, summarizes, and offers reader reviews of Teen, Middle Grade, and Picture Books with Gay (GLBTQ) characters and themes. * {{Authority control Gay history, Literature Gay male literature,