History Of Italy (1559–1814) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of early modern Italy roughly corresponds to the period from the Renaissance to the
 The
The  Sicily on the other hand experienced peaceful relations with Madrid, as the Spanish largely allowed the island to manage its own affairs. Since it was an important outpost in the Mediterranean as well as a significant trading partner of Spain, friendly ties were valued. After Sicily passed under Austrian rule in 1720, trouble erupted as Vienna stationed permanent garrisons of German-born troops on the island, provoking frequent and violent confrontations with the local populace. The corruption and backwardness of Sicilian society made it difficult to establish a working government, and much like Naples Sicily was forced to pay massive taxes and tribute to Vienna.
However, Emperor Charles VI attempted to build up Sicily's economy by turning Messina and other locations into important ports so as to attract foreign commerce, as well as shore up the island's failing grain and silk industries. But the emperor could not offset an economic downturn that was beyond his control, and many of his projects proved unfeasible, ultimately causing a near-total economic meltdown.
Charles had a tricky religious situation in Sicily where the king traditionally served as apostolic legate, which he sought to maintain at all costs while also promising to defend the Catholic faith. He and his ministers successfully debated the legateship with the popes and made peace with the Vatican. In the end however, Austrian rule made little lasting impact on Sicily and Spanish troops took possession of the island in 1734.
Sardinia also was left to itself and many Spaniards settled on the island, which had an economy mostly based on sheepherding and which had little contact with the rest of Italy.
Sicily on the other hand experienced peaceful relations with Madrid, as the Spanish largely allowed the island to manage its own affairs. Since it was an important outpost in the Mediterranean as well as a significant trading partner of Spain, friendly ties were valued. After Sicily passed under Austrian rule in 1720, trouble erupted as Vienna stationed permanent garrisons of German-born troops on the island, provoking frequent and violent confrontations with the local populace. The corruption and backwardness of Sicilian society made it difficult to establish a working government, and much like Naples Sicily was forced to pay massive taxes and tribute to Vienna.
However, Emperor Charles VI attempted to build up Sicily's economy by turning Messina and other locations into important ports so as to attract foreign commerce, as well as shore up the island's failing grain and silk industries. But the emperor could not offset an economic downturn that was beyond his control, and many of his projects proved unfeasible, ultimately causing a near-total economic meltdown.
Charles had a tricky religious situation in Sicily where the king traditionally served as apostolic legate, which he sought to maintain at all costs while also promising to defend the Catholic faith. He and his ministers successfully debated the legateship with the popes and made peace with the Vatican. In the end however, Austrian rule made little lasting impact on Sicily and Spanish troops took possession of the island in 1734.
Sardinia also was left to itself and many Spaniards settled on the island, which had an economy mostly based on sheepherding and which had little contact with the rest of Italy.
 At the end of the 18th century, Italy was almost in the same political conditions as in the 16th century; the main differences were that
At the end of the 18th century, Italy was almost in the same political conditions as in the 16th century; the main differences were that 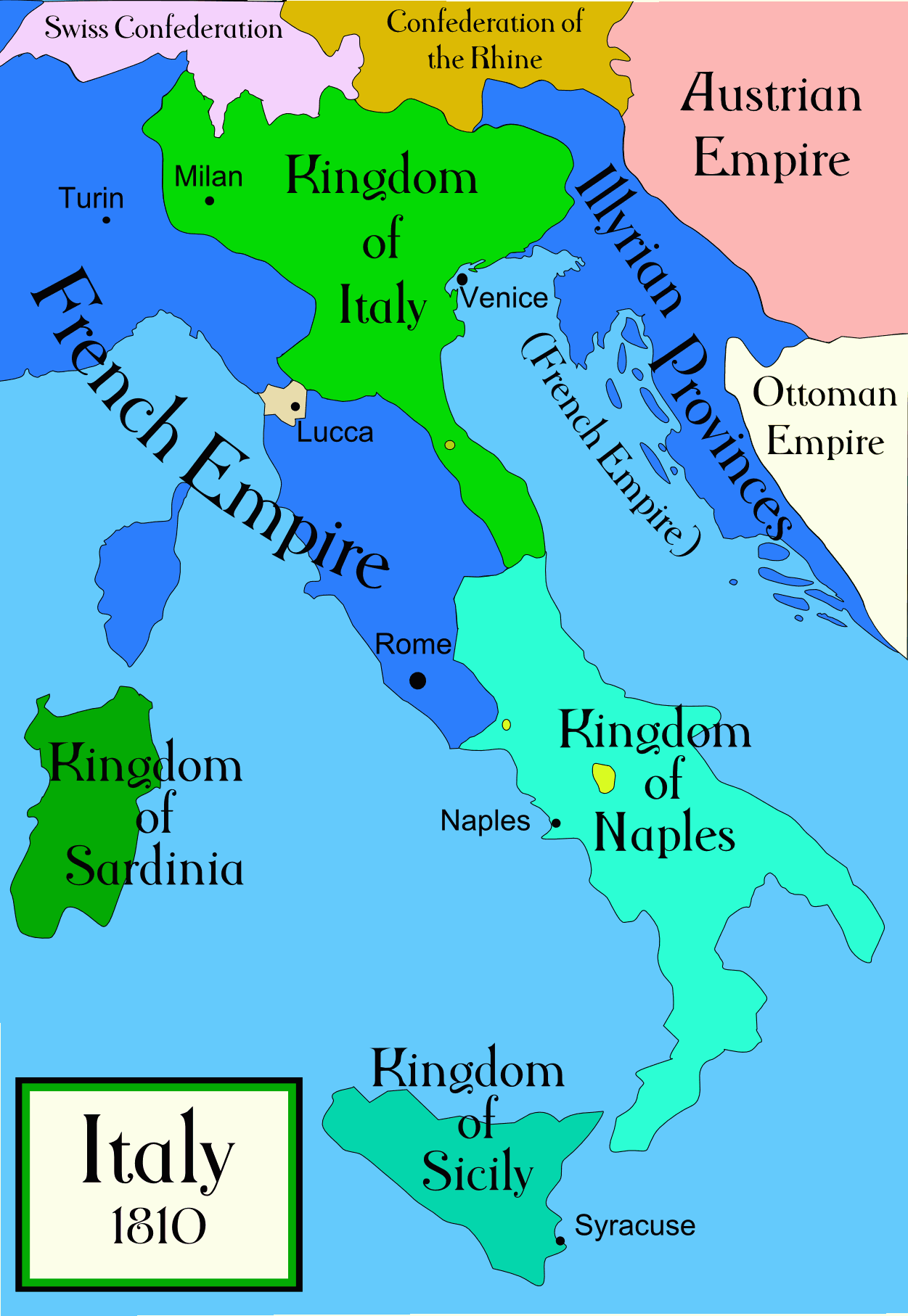 After seizing power as consul in France, Napoleon launched a renewed invasion of Italy. Milan fell on June 2, 1800 and Austrian defeats there and in Germany ended the War of the Second Coalition. Austria retained only control of Venetia, while France dominated the whole rest of northern Italy, leaving only the weak papal and Neapolitan states in the south. Napoleon over the next few years coalesced his Italian possessions into a single Republic of Italy, ruled by one Francesco Melzi d'Eril. But in 1805, he decided to convert the republic into a kingdom ruled by his stepson Eugene D'Beauharnais. The Kingdom of Italy was gradually expanded as Austria relinquished Venetia in 1806 and other bits of territory were added. Still other Italian regions were annexed directly into France. In 1809, the French reoccupied Rome and took Pope Pius VII prisoner.
Ferdinand VI's dominions in southern Italy remained independent for the first few years of the 19th century, but they were too weak to resist a concerted attack, and a French army swiftly occupied Naples in early 1806. Ferdinand's court fled to Sicily where they enjoyed British protection. Napoleon appointed his brother Joachim as king of Naples, but he governed only the mainland as Sicily and Sardinia remained outside of French control. During the years of Bourbon exile in Sicily, the British came to exercise political control over the island and forced Ferdinand to impose several democratic reforms. But when the Napoleonic Wars ended in 1815 and the king returned to Naples, he resumed governing as an absolute monarch.
Joachim Bonaparte meanwhile pursued an independent policy from France, instituting several reforms that strengthened the middle class in Naples. However, he along with the rest of Napoleon's satellite rulers fell from power in 1814–15.
In 1805, after the French victory over the Third Coalition and the Peace of Pressburg, Napoleon recovered Veneto and
After seizing power as consul in France, Napoleon launched a renewed invasion of Italy. Milan fell on June 2, 1800 and Austrian defeats there and in Germany ended the War of the Second Coalition. Austria retained only control of Venetia, while France dominated the whole rest of northern Italy, leaving only the weak papal and Neapolitan states in the south. Napoleon over the next few years coalesced his Italian possessions into a single Republic of Italy, ruled by one Francesco Melzi d'Eril. But in 1805, he decided to convert the republic into a kingdom ruled by his stepson Eugene D'Beauharnais. The Kingdom of Italy was gradually expanded as Austria relinquished Venetia in 1806 and other bits of territory were added. Still other Italian regions were annexed directly into France. In 1809, the French reoccupied Rome and took Pope Pius VII prisoner.
Ferdinand VI's dominions in southern Italy remained independent for the first few years of the 19th century, but they were too weak to resist a concerted attack, and a French army swiftly occupied Naples in early 1806. Ferdinand's court fled to Sicily where they enjoyed British protection. Napoleon appointed his brother Joachim as king of Naples, but he governed only the mainland as Sicily and Sardinia remained outside of French control. During the years of Bourbon exile in Sicily, the British came to exercise political control over the island and forced Ferdinand to impose several democratic reforms. But when the Napoleonic Wars ended in 1815 and the king returned to Naples, he resumed governing as an absolute monarch.
Joachim Bonaparte meanwhile pursued an independent policy from France, instituting several reforms that strengthened the middle class in Naples. However, he along with the rest of Napoleon's satellite rulers fell from power in 1814–15.
In 1805, after the French victory over the Third Coalition and the Peace of Pressburg, Napoleon recovered Veneto and  After Russia, other states of Europe re-allied themselves and defeated Napoleon at the
After Russia, other states of Europe re-allied themselves and defeated Napoleon at the
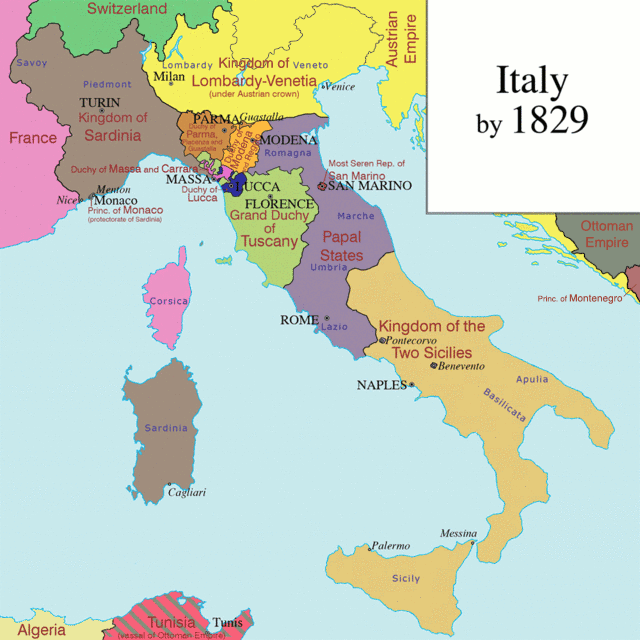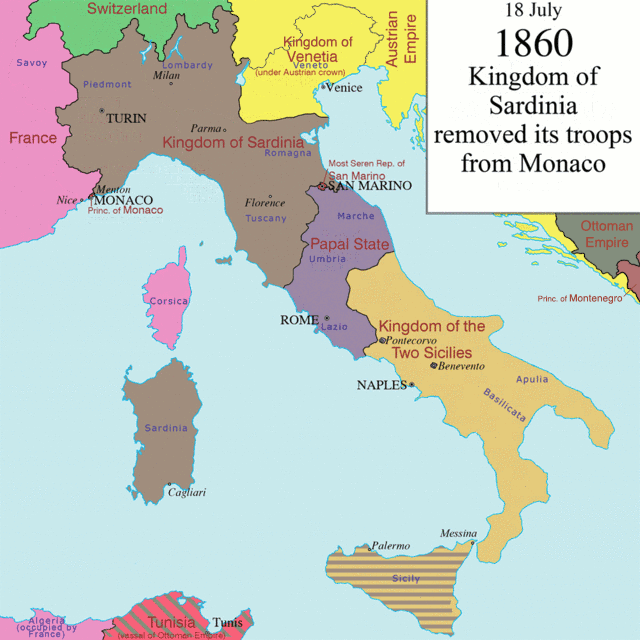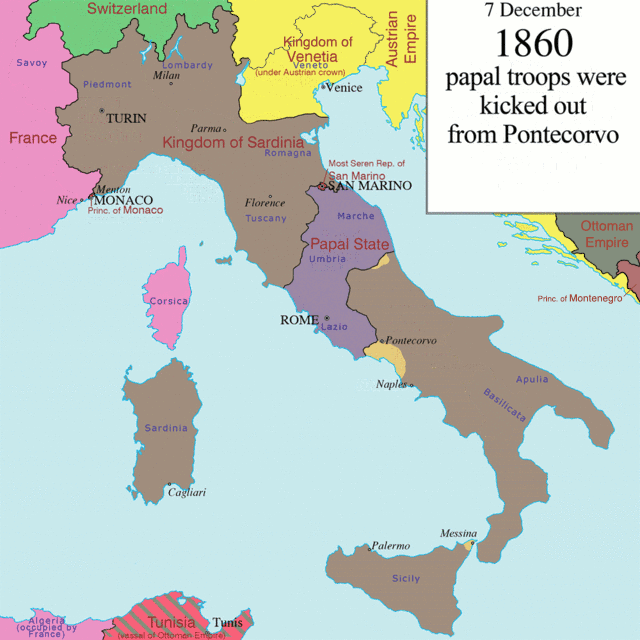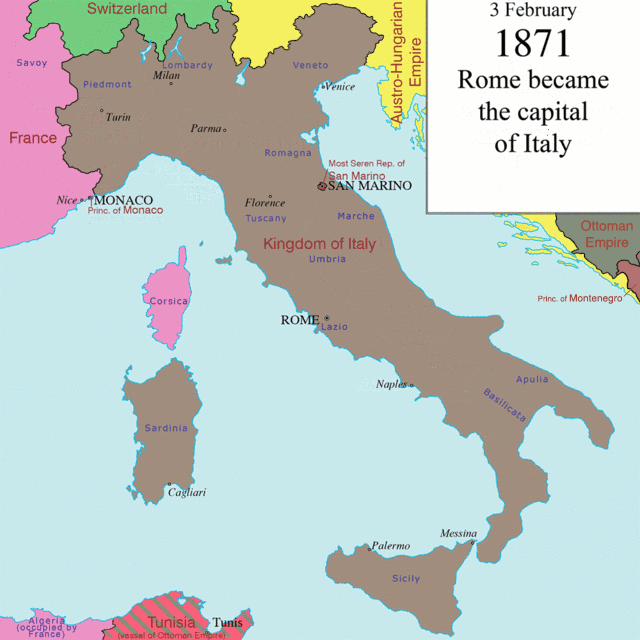 With the fall of Napoleon (1814) and the restoration of the absolutist monarchical regimes, the Italian tricolour went underground, becoming the symbol of the patriotic ferments that began to spread in Italy and the symbol which united all the efforts of the Italian people towards freedom and independence.
Between 1820 and 1861, a sequence of events led to the independence and unification of Italy (except for
With the fall of Napoleon (1814) and the restoration of the absolutist monarchical regimes, the Italian tricolour went underground, becoming the symbol of the patriotic ferments that began to spread in Italy and the symbol which united all the efforts of the Italian people towards freedom and independence.
Between 1820 and 1861, a sequence of events led to the independence and unification of Italy (except for
"Albertine Statute"
(Constitution of the Kingdom of Sardinia from 1848 to 1861, and of the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1946)
"Italy."
Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. April 30, 2006. {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Italy (1559-1814)
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
in 1814. The following period was characterized by political and social unrest which then led to the unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century Political movement, political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the Proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, annexation of List of historic states of ...
, which culminated in 1861 with the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy
The proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy happened with a legal norm, normative act of the House of Savoy, Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia — the law 17 March 1861, n. 4761 — with which Victor Emmanuel II assumed for himself and for his successors ...
.
Overview
TheItalian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( ) was a period in History of Italy, Italian history between the 14th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Western Europe and marked t ...
covered the 15th and 16th centuries of Italian history and brought about considerable economic and cultural development of the country. After 1600, however, Italy experienced an economic decline. In 1600 Northern and Central Italy comprised one of the most advanced industrial areas of Europe. There was an exceptionally high standard of living. By 1814 Italy was an economically backward and depressed area; its industrial structure had almost collapsed, its population was too high for its resources, its economy had become primarily agricultural. Wars, political fractionalization, limited fiscal capacity and the shift of world trade to north-western Europe and the Americas were key factors.
Following the Peace of Cateau Cambrésis (1559), France renounced its claims in Italy. Some of the Italian states were under the rule of powerful dynasties: the Medici
The House of Medici ( , ; ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first consolidated power in the Republic of Florence under Cosimo de' Medici and his grandson Lorenzo "the Magnificent" during the first half of the 15th ...
in Tuscany, the Farnese in Parma, the Este in Modena, and the Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
in Piedmont. Nearly half of Italy, the kingdoms of Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
, Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
and Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
and the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
were under the rule of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
.
Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
returned to the Savoy from France due to the role played by the duke Emmanuel Philibert in the battle of St Quentin during the Italian War of 1551–1559
The Italian War of 1551–1559 began when Henry II of France declared war against Holy Roman Emperor Charles V with the intent of recapturing parts of Italy and ensuring French, rather than Habsburg, domination of European affairs. The war e ...
. The House of Savoy
The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy and now lies mostly within southeastern F ...
was "Italianized" at the end of the Italian wars, as Emmanuel Philibert made Turin the capital of the savoyard state
The Savoyard state comprised the states ruled by the counts and dukes of Savoy from the Middle Ages to the formation of the Kingdom of Italy. Although it was an example of composite monarchy, it is a term applied to the polity by historians an ...
and Italian the official language. The House of Medici
The House of Medici ( , ; ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first consolidated power in the Republic of Florence under Cosimo de' Medici and his grandson Lorenzo de' Medici, Lorenzo "the Magnificent" during the first h ...
kept ruling Florence, thanks to an agreement signed between the Pope and Charles V in 1530, and was later recognized as the ruling family of the Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (; ) was an Italian monarchy located in Central Italy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population ...
by Pope Pius V
Pope Pius V, OP (; 17 January 1504 – 1 May 1572), born Antonio Ghislieri (and from 1518 called Michele Ghislieri), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 January 1566 to his death, in May 1572. He was an ...
. The same Pope arranged the Holy League, a coalition of Venice and other maritime states that defeated the invading Ottoman forces at the naval battle of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval warfare, naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League (1571), Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states arranged by Pope Pius V, inflicted a major defeat on the fleet of t ...
(1571).
The Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
launched the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
, which lasted from the Council of Trent
The Council of Trent (), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation at the time, it has been described as the "most ...
(1545–1563) to the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
in 1648. This period coincides with the European wars of religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic Chu ...
and saw numerous Italians active in other Catholic nations, including ''de facto'' rulers of France (such as Catherine de Medici, Mary de Medici, Concino Concini and Jules Mazarin) and military generals serving under the auspices of the Holy Roman Empire or Spain (such as Torquato Conti, Raimondo Montecuccoli
Raimondo Montecuccoli (; 21 February 1609 – 16 October 1680) was an Italian-born professional soldier, military theorist, and diplomat, who served the Habsburg monarchy.
Experiencing the Thirty Years' War from scratch as a simple footsoldier, ...
, Ottavio Piccolomini
Ottavio Piccolomini, 1st Duke of Amalfi (11 November 1599 – 11 August 1656) was an Italian nobleman whose military career included service as a Spanish general and then as a field marshal of the Holy Roman Empire.
Early life
Piccolomini was ...
, Ambrogio Spinola and Alexander Farnese).
Despite the victory at Lepanto, the Venetians gradually lost its Eastern Mediterranean possessions (including Cyprus and Crete) to the Ottomans. Venice captured the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
during the Great Turkish war
The Great Turkish War () or The Last Crusade, also called in Ottoman sources The Disaster Years (), was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League (1684), Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lith ...
(1683–1699), but the land was ceded back after the last of the Venetian-Ottoman Wars. When the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
broke out, Venice was left out of the concert of great powers: the same, however, was true for the Venetian mediterranean rivals such as the Ottoman Empire (''sick man of Europe'' after centuries of warfare) and the Genoese who had lost its possessions in the Aegean Sea, in Tunisia, and, later, Corsica. The crisis of Genoa led to the crisis of Spain, as the Republic of Genoa was a key ally of the Spanish Empire since the 16th century, providing credit and economic support for the Habsburgs in what has been described as the ''age of the Genoese''.
The War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
(1702–1715) and the War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718–1720) established the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
as the dominant power in most of the present day Lombardy
The Lombardy Region (; ) is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in northern Italy and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Lombardy is ...
and Southern Italy (though the War of the Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession (; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a civil war in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over the succession to Augustus II the Strong, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of ...
resulted in the re-installment of the Spanish in the south, as the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies
The House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies is a cadet branch of the House of Bourbon that ruled Southern Italy and Sicily for more than a century in the 18th and 19th centuries. It descends from the Capetian dynasty in legitimate male line through Phili ...
). In this context Victor Amadeus II of Savoy, along with Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene Francis of Savoy-Carignano (18 October 1663 – 21 April 1736), better known as Prince Eugene, was a distinguished Generalfeldmarschall, field marshal in the Army of the Holy Roman Empire and of the Austrian Habsburg dynasty durin ...
, defeated the Franco-Spanish forces during the Siege of Turin
The siege of Turin took place from June to September 1706, during the War of the Spanish Succession. A French army led by Louis de la Feuillade besieged the Savoyard capital of Turin, whose relief by Prince Eugene of Savoy has been called th ...
(1706) and later formed the kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia, predecessor state of Italy. The House of Habsburg-Lorraine
The House of Habsburg-Lorraine () originated from the marriage in 1736 of Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis III, Duke of Lorraine and Bar, and Maria Theresa of Habsburg monarchy, Austria, later successively List of Bohemian monarchs, Queen ...
succeeded the Medici of Florence in 1737 and Venice also became part of Austria with the treaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The trea ...
in 1797.
The Napoleonic era
The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France and history of Europe, Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly (French Revoluti ...
is the link between the Habsburg domination and the Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
. Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
's first military successes took place in Italy, at the head of the Armée d'Italie, and he later styled himself as President of Italy
The president of Italy, officially titled President of the Italian Republic (), is the head of state of Italy. In that role, the president represents national unity and guarantees that Politics of Italy, Italian politics comply with the Consti ...
and King of Italy
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by ...
. Italy became part of the French sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military, or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
but Napoleon, given his Italian ethnicity, was appreciated by most Italian intellectuals, among them the writer Alessandro Manzoni
Alessandro Francesco Tommaso Antonio Manzoni (, , ; 7 March 1785 – 22 May 1873) was an Italian poet, novelist and philosopher.
He is famous for the novel ''The Betrothed (Manzoni novel), The Betrothed'' (orig. ) (1827), generally ranked among ...
. The Restoration that followed the French defeat wasn't able to erase the political and legislative innovations brought to Italy by Napoleon. French historian Hippolyte Taine
Hippolyte Adolphe Taine (21 April 1828 – 5 March 1893) was a French historian, critic and philosopher. He was the chief theoretical influence on French naturalism, a major proponent of sociological positivism and one of the first practitione ...
stated:
Napoleon, far more Italian than French, Italian by race, by instinct, imagination, and souvenir, considers in his plan the future of Italy, and, on casting up the final accounts of his reign, we find that the net loss is for France and the net profit is for Italy.Frederick Artz emphasizes the benefits the Italians gained: :For nearly two decades the Italians had the excellent codes of law, a fair system of taxation, a better economic situation, and more religious and intellectual toleration than they had known for centuries. ... Everywhere old physical, economic, and intellectual barriers had been thrown down and the Italians had begun to be aware of a common nationality.
16th to 18th centuries
 The
The Italian Wars
The Italian Wars were a series of conflicts fought between 1494 and 1559, mostly in the Italian Peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the House of Valois, Valois kings o ...
saw 65 years of French attacks on the Italian states, starting with Charles VIII's invasion of Naples in 1494. However the Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis (1559) saw about half of Italy (the south and Milan) fall under the rule of the Spanish Habsburgs. They would be replaced by the Austrian Habsburgs with the war of the Spanish succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
in 1700. The Council of Italy
The Council of Italy, officially the Royal and Supreme Council of Italy (, ), was a ruling body and key part of the government of the Spanish Empire in Early Modern Europe, Europe, second only to the monarch himself. It was based in Madrid and ...
in Madrid controlled the Spanish viceroyalties in Italy, while a special section of the Aulic council in Vienna was sovereign over the Imperial fiefs in Italy. Italian troops served throughout Europe for the catholic side in the age of the European Wars of Religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic Chu ...
. They fought in Germany, in France, in Italy, the Spanish Netherlands, in North Africa, on the fleet—on the Invincible Armada (1588), too—and in Central and South America, with very good results. The War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
saw control of much of Naples and Sicily pass from Spain to Austria, with the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
of 1713. However, the Spaniards regained Naples and Sicily following the Battle of Bitonto
The Battle of Bitonto (25 May 1734) was a Spanish victory over Austrian forces near Bitonto in the Kingdom of Naples (in southern Italy) in the War of Polish Succession. The battle ended organized Austrian resistance outside a small number of ...
in 1738.
Spanish and Austrian hegemony was not always based on direct rule; states such as Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
, Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
, the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
, the duchies of Este, and Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy (; ) was a territorial entity of the Savoyard state that existed from 1416 until 1847 and was a possession of the House of Savoy.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy f ...
, were the only independent states, while a large part of the rest of Italy relied on the protection of Spain or Austria against external aggression. Furthermore, those areas under direct Spanish and (later) Austrian control were theoretically independent principalities bound to Spain and Austria through personal unions alone.
Italy began to experience an economic and social decline as the 16th century progressed. The Age of Discovery had shifted the center of trade in Europe from the Mediterranean to the Atlantic, and so the Italian states lost much of their previous importance. Venice continued to fight bitterly with the Ottoman Empire for control of outposts in the eastern Mediterranean. It participated in the great naval Battle of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval warfare, naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League (1571), Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states arranged by Pope Pius V, inflicted a major defeat on the fleet of t ...
in 1571, and in the following century battled the Turks in the Cretan War, when it gained control of the Peloponnese in Greece but lost Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, Venice's largest and richest overseas possession. Venice experienced one last great martial triumph by helping to defeat the Ottoman Empire in the war of 1683–1699. By the 18th century, economic activity dwindled as the city withdrew in on itself and fell into stagnation, becoming easy pickings for the French revolutionary armies in 1796.
The Papal States also lost much of their former power as the Protestant Reformation divided Europe into two camps. The remaining Catholic princes increasingly sought to be the masters in their own houses and often clashed with the papacy over jurdistrictional matters. During the unceasing rivalry between France and Spain, Europe's two great Catholic powers, the popes often acted as mediators. Relations with Paris deteriorated sharply during the reign of Louis XIV, until he and the papacy found common ground in suppressing Jansenism. Even in Italy itself, the political importance of the Papal States declined. The Counter-Reformation popes largely concerned themselves with religious matters and church reform, and so had little time for politics. They worked to fight brigandage, long endemic in the Papal States, reformed the court system, and embellished Rome with many buildings. Gregory XIII
Pope Gregory XIII (, , born Ugo Boncompagni; 7 January 1502 – 10 April 1585) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 May 1572 to his death in April 1585. He is best known for commissioning and being the namesake ...
introduced the calendar that bears his name, and the papal fleet participated in the Battle of Lepanto. In addition to its loss of political power, the Church came under increasing attack during the Age of Enlightenment in the 18th century.
As Spain declined in the 16th century, so did its Italian possessions in Naples, Sicily, Sardinia, and Milan. Southern Italy was impoverished, stagnant, and cut off from the mainstream of events in Europe. Naples was one of the continent's most overcrowded and unsanitary cities, with a crime-ridden and volatile populace. The Neapolitan aristocracy long resented Spanish rule and welcomed the arrival of the Austrians in 1707. However, they were disappointed as Vienna continued the practice of not allowing any autonomy to Naples. While the war raged, Austria imposed huge tax burdens on the city and did not begin to provide it with any adequate administration until peace returned. Graf von Daun (viceroy of Naples from 1713 to 1719) attempted several reforms, but came into dispute with the church over jurisdictional matters. He largely succeeded in making peace with Rome, but international strife caused the Austrian emperors to impose more taxes on Naples and neglect all but the city's traditional feudal lords. Cardinal Michael Friedrich von Althann next became viceroy (1722–1728), but upset the nobility (already reeling from imperial taxes) and the middle class with his pro-clerical stance. Althann's downfall came by attempting to establish a state bank (the Banco di San Carlo) with the intention of acquiring crown lands for the Austrian emperor. He infuriated both the nobility and middle class with this ill-conceived campaign, and after his expulsion Naples suffered several tumultuous years of famine and social unrest, with international problems preventing any attempt at administrative reform. It was with relief that the Spanish born Don Carlos ascended the throne of a reborn Kingdom of Naples in 1734. In 1759, he left to become King Charles III of Spain and was succeeded by his son Ferdinand, who was underage and so government was left to the regent Bernardo Tanucci. In the spirit of the Enlightenment, Tanucci attempted to establish a benevolent despotism by a series of reforms and weakening the power of traditional Neapolitan institutions. Ferdinand came of age in 1767, but had little interest in government and was largely dominated by his wife the Archduchess Maria Carolina, who disliked Tanucci's pro-Spanish stance and managed to replace him with Sir John Acton, an English emigre. When the French Revolution erupted, they allied with Austria and Britain against France.
 Sicily on the other hand experienced peaceful relations with Madrid, as the Spanish largely allowed the island to manage its own affairs. Since it was an important outpost in the Mediterranean as well as a significant trading partner of Spain, friendly ties were valued. After Sicily passed under Austrian rule in 1720, trouble erupted as Vienna stationed permanent garrisons of German-born troops on the island, provoking frequent and violent confrontations with the local populace. The corruption and backwardness of Sicilian society made it difficult to establish a working government, and much like Naples Sicily was forced to pay massive taxes and tribute to Vienna.
However, Emperor Charles VI attempted to build up Sicily's economy by turning Messina and other locations into important ports so as to attract foreign commerce, as well as shore up the island's failing grain and silk industries. But the emperor could not offset an economic downturn that was beyond his control, and many of his projects proved unfeasible, ultimately causing a near-total economic meltdown.
Charles had a tricky religious situation in Sicily where the king traditionally served as apostolic legate, which he sought to maintain at all costs while also promising to defend the Catholic faith. He and his ministers successfully debated the legateship with the popes and made peace with the Vatican. In the end however, Austrian rule made little lasting impact on Sicily and Spanish troops took possession of the island in 1734.
Sardinia also was left to itself and many Spaniards settled on the island, which had an economy mostly based on sheepherding and which had little contact with the rest of Italy.
Sicily on the other hand experienced peaceful relations with Madrid, as the Spanish largely allowed the island to manage its own affairs. Since it was an important outpost in the Mediterranean as well as a significant trading partner of Spain, friendly ties were valued. After Sicily passed under Austrian rule in 1720, trouble erupted as Vienna stationed permanent garrisons of German-born troops on the island, provoking frequent and violent confrontations with the local populace. The corruption and backwardness of Sicilian society made it difficult to establish a working government, and much like Naples Sicily was forced to pay massive taxes and tribute to Vienna.
However, Emperor Charles VI attempted to build up Sicily's economy by turning Messina and other locations into important ports so as to attract foreign commerce, as well as shore up the island's failing grain and silk industries. But the emperor could not offset an economic downturn that was beyond his control, and many of his projects proved unfeasible, ultimately causing a near-total economic meltdown.
Charles had a tricky religious situation in Sicily where the king traditionally served as apostolic legate, which he sought to maintain at all costs while also promising to defend the Catholic faith. He and his ministers successfully debated the legateship with the popes and made peace with the Vatican. In the end however, Austrian rule made little lasting impact on Sicily and Spanish troops took possession of the island in 1734.
Sardinia also was left to itself and many Spaniards settled on the island, which had an economy mostly based on sheepherding and which had little contact with the rest of Italy. Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
passed from the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
to France in 1769 after the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
. Italian was the official language of Corsica until 1859.
Age of Enlightenment
The Enlightenment played a distinctive, if small, role in 18th century Italy, 1685–1789. Although large parts of Italy were controlled by conservative Habsburgs or the pope, Tuscany had some opportunities for reform.Leopold II of Tuscany
Leopold II, , English: ''Leopold John Joseph Francis Ferdinand Charles''. (3 October 1797 – 29 January 1870) was Grand Duke of Grand Duchy of Tuscany, Tuscany from 1824 to 1859. He married twice; first to Princess Maria Anna of Saxony (1799� ...
abolished the death penalty in Tuscany and reduced censorship. From Naples Antonio Genovesi (1713–69) influenced a generation of southern Italian intellectuals and University students. His textbook "Diceosina, o Sia della Filosofia del Giusto e dell'Onesto" (1766) was a controversial attempt to mediate between the history of moral philosophy, on the one hand, and the specific problems encountered by 18th-century commercial society, on the other. It contained the greater part of Genovesi's political, philosophical, and economic thought – guidebook for Neapolitan economic and social development. Science flourished as Alessandro Volta
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (, ; ; 18 February 1745 – 5 March 1827) was an Italian chemist and physicist who was a pioneer of electricity and Power (physics), power, and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery a ...
and Luigi Galvani
Luigi Galvani ( , , ; ; 9 September 1737 – 4 December 1798) was an Italian physician, physicist, biologist and philosopher who studied animal electricity. In 1780, using a frog, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitched when ...
made break-through discoveries in electricity. Pietro Verri
Count Pietro Verri (12 December 1728 – 28 June 1797) was an Italian economist, historian, philosopher and writer. Among the most important personalities of the 18th-century Italian culture, he is considered among the fathers of the Lombardy, L ...
was a leading economist in Lombardy. Historian Joseph Schumpeter
Joseph Alois Schumpeter (; February 8, 1883 – January 8, 1950) was an Austrian political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at Harvard Unive ...
states he was ‘the most important pre-Smithian authority on Cheapness-and-Plenty’. The most influential scholar on the Italian Enlightenment has been Franco Venturi.
Italy in the Napoleonic era
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
had replaced Spain as the dominant foreign power after the War of Spanish Succession (and that too was not true with regards to Naples and Sicily), and that the dukes of Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
(a mountainous region between Italy and France) had become kings of Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
by increasing their Italian possessions, which now included Sardinia and the north-western region of Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
.
The French Revolution had attracted considerable attention in Italy since its beginning, inasmuch as the reform attempts of enlightened despots throughout the 18th century proved largely abortive. Masonic lodges sprang up in large numbers during this period where radical changes were discussed by the intelligentsia, away from the clumsy efforts mentioned above.
Predictably, the establishment in Italy was totally hostile to the ideas coming out of France and harsh crackdowns were launched on dissent. As early as 1792, French armies had penetrated Italian soil, and that same year, the impoverished Piedmontese peasants warned their king that he might too face justice as had happened to Louis XVI in France. The middle class in Rome revolted against the Vatican's political power, and their counterparts in Venice along with the nobility denounced that city's government.
However, most of these protests accomplished little outside of Piedmont and Naples, and in the south a conspiracy hatched by pro-republican Freemasons was discovered and the ringleaders executed. Dozens of dissenters fled to France in the aftermath of the trials. One of these dissenters, Filippo Buonarroti, a member of an ancient Tuscan noble family, returned to Italy along with the French armies and briefly set up a revolutionary government in the Ligurian town of Oneglia. The privileges of the nobility were abolished and the Church establishment replaced by a universalist cult of the Supreme Being. But after Robespierre (whom Bonouarti modeled his government on) fell from power in France, he was summoned back home and his experiment quickly ended.
This situation was shaken in 1796, when the French Army of Italy under Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
invaded Italy, with the aims of forcing the First Coalition to abandon Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
(where they had created an anti-revolutionary puppet-ruler) and forcing Austria to withdraw from Italy. The first battles came on April 9 between the French and the Piedmontese and within only two weeks Victor Amadeus III of Sardinia
Victor Amadeus III (Vittorio Amedeo Maria; 26 June 1726 – 16 October 1796) was King of Sardinia and ruler of the Savoyard state, Savoyard states from 20 February 1773 to his death in 1796. Although he was politically conservative, he carrie ...
was forced to sign an armistice. On May 15 the French general then entered Milan, where he was welcomed as a liberator. Subsequently, beating off Austrian counterattacks and continuing to advance, he arrived in the Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
in 1797. Here occurred the Veronese Easters, an act of rebellion against French oppression, that tied down Napoleon for about a week.
In October 1797 Napoleon signed the Treaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The trea ...
, by which the Republic of Venice was annexed to the Austrian state, dashing Italian nationalists' hopes that it might become an independent state. This treaty gave Austrian recognition to the existence of the Cisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic (; ) was a sister republic or a client state of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organized two ...
(made up of Lombardy
The Lombardy Region (; ) is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in northern Italy and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Lombardy is ...
, Emilia Romagna and small parts of Tuscany and Veneto), and annexed Piedmont to France. Even if, like the other states created by the invasion, the Cisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic (; ) was a sister republic or a client state of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organized two ...
was just a satellite of France, these satellites sparked a nationalist movement. The Cisalpine Republic was converted into the Italian Republic
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
in 1802, under the presidency of Napoleon. As all of these republics were imposed by an outside force, none had any popular support in Italy, especially since the peasantry was alienated by Jacobin anti-clericalism. It would take a true grassroots movement to bring change. In addition, even native republicans became disillusioned when they realized that the French expected them to be obedient satellites of Paris, which included frequent interference in local affairs and massive taxes. Return to the old feudal order was however equally undesirable, and so the republican movement would gradually establish its goals as nationalism and a unified Italian state.
After the War of the First Coalition ended, French aggression in Italy continued unabated, and in 1798 they occupied Rome, sent the Pope into exile, and set up a republic there. When Napoleon left for Egypt, King Ferdinand VI of Sicily retook Rome and reinstated the papacy. But almost as soon as his armies departed, the French returned and occupied Naples. Ferdinand's court was taken into exile by a British fleet. Another republic was set up (the Parthenopean) which governed in a more radical and democratic fashion than the others. But Ferdinand skillfully organized a counterrevolt led by his agent Cardinal Fabrizio Ruffo, who landed in Italy and rallied a peasant mob, which then retook Naples and proceeded to pillage and destroy the manor homes of the hated nobility. There were also mass murders of bourgeois who had supported the French. Afterwards, Ferdinand returned to his capital in triumph. 100 revolutionary leaders were summarily tried and executed.
In northern Italy, the French occupied Tuscany during the spring of 1799 until another peasant uprising drove them out. Jews and suspected Jacobins were lynched en masse by the mob, and the nobility and Church quickly regained power. That fall, the Roman Republic also collapsed and the French were by now virtually cleared from Italy.
 After seizing power as consul in France, Napoleon launched a renewed invasion of Italy. Milan fell on June 2, 1800 and Austrian defeats there and in Germany ended the War of the Second Coalition. Austria retained only control of Venetia, while France dominated the whole rest of northern Italy, leaving only the weak papal and Neapolitan states in the south. Napoleon over the next few years coalesced his Italian possessions into a single Republic of Italy, ruled by one Francesco Melzi d'Eril. But in 1805, he decided to convert the republic into a kingdom ruled by his stepson Eugene D'Beauharnais. The Kingdom of Italy was gradually expanded as Austria relinquished Venetia in 1806 and other bits of territory were added. Still other Italian regions were annexed directly into France. In 1809, the French reoccupied Rome and took Pope Pius VII prisoner.
Ferdinand VI's dominions in southern Italy remained independent for the first few years of the 19th century, but they were too weak to resist a concerted attack, and a French army swiftly occupied Naples in early 1806. Ferdinand's court fled to Sicily where they enjoyed British protection. Napoleon appointed his brother Joachim as king of Naples, but he governed only the mainland as Sicily and Sardinia remained outside of French control. During the years of Bourbon exile in Sicily, the British came to exercise political control over the island and forced Ferdinand to impose several democratic reforms. But when the Napoleonic Wars ended in 1815 and the king returned to Naples, he resumed governing as an absolute monarch.
Joachim Bonaparte meanwhile pursued an independent policy from France, instituting several reforms that strengthened the middle class in Naples. However, he along with the rest of Napoleon's satellite rulers fell from power in 1814–15.
In 1805, after the French victory over the Third Coalition and the Peace of Pressburg, Napoleon recovered Veneto and
After seizing power as consul in France, Napoleon launched a renewed invasion of Italy. Milan fell on June 2, 1800 and Austrian defeats there and in Germany ended the War of the Second Coalition. Austria retained only control of Venetia, while France dominated the whole rest of northern Italy, leaving only the weak papal and Neapolitan states in the south. Napoleon over the next few years coalesced his Italian possessions into a single Republic of Italy, ruled by one Francesco Melzi d'Eril. But in 1805, he decided to convert the republic into a kingdom ruled by his stepson Eugene D'Beauharnais. The Kingdom of Italy was gradually expanded as Austria relinquished Venetia in 1806 and other bits of territory were added. Still other Italian regions were annexed directly into France. In 1809, the French reoccupied Rome and took Pope Pius VII prisoner.
Ferdinand VI's dominions in southern Italy remained independent for the first few years of the 19th century, but they were too weak to resist a concerted attack, and a French army swiftly occupied Naples in early 1806. Ferdinand's court fled to Sicily where they enjoyed British protection. Napoleon appointed his brother Joachim as king of Naples, but he governed only the mainland as Sicily and Sardinia remained outside of French control. During the years of Bourbon exile in Sicily, the British came to exercise political control over the island and forced Ferdinand to impose several democratic reforms. But when the Napoleonic Wars ended in 1815 and the king returned to Naples, he resumed governing as an absolute monarch.
Joachim Bonaparte meanwhile pursued an independent policy from France, instituting several reforms that strengthened the middle class in Naples. However, he along with the rest of Napoleon's satellite rulers fell from power in 1814–15.
In 1805, after the French victory over the Third Coalition and the Peace of Pressburg, Napoleon recovered Veneto and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, annexing them to the Italian Republic and renaming it the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
. Also that year a second satellite state, the Ligurian Republic (successor to the old Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
), was pressured into merging with France. In 1806, he conquered the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
and granted it to his brother and then (from 1808) to Joachim Murat
Joachim Murat ( , also ; ; ; 25 March 1767 – 13 October 1815) was a French Army officer and statesman who served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Under the French Empire he received the military titles of Marshal of the ...
, along with marrying his sisters Elisa
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of ...
and Paolina off to the princes of Massa-Carrara and Guastalla
Guastalla ( Guastallese: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Reggio Emilia in Emilia-Romagna, Italy.
Geography
Guastalla is situated in the Po Valley, and lies on the banks of the Po River. Guastalla is located at around from the citi ...
. In 1808, he also annexed Marche and Tuscany to the Kingdom of Italy.
In 1809, Bonaparte occupied Rome, and conflicted with the pope, who had excommunicated him. To maintain the efficiency of the state he exiled the Pope first to Savona and then to France, and taking the Papal States' art collections back to the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arron ...
. The conquest of Russia that Napoleon undertook in 1811 marked the end of the apogee of Italians' support for Napoleon, because many Italians died in this failed campaign.
 After Russia, other states of Europe re-allied themselves and defeated Napoleon at the
After Russia, other states of Europe re-allied themselves and defeated Napoleon at the Battle of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig, also known as the Battle of the Nations, was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony. The Coalition armies of Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia, led by Tsar Alexander I, Karl von Schwarzenberg, and G ...
, after which his Italian allied states, with Murat first among them, abandoned him to ally with Austria. Defeated at Paris on April 6, 1814, Napoleon was compelled to renounce his throne and sent into exile on Elba. The resulting Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
(1814) restored a situation close to that of 1795, dividing Italy between Austria (in the north-east and Lombardy), the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies (in the south and in Sicily), and Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
, the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
and other minor states in the centre. However, old republics such as Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
and Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
were not recreated, Venice went to Austria, and Genoa went to the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
.
On Napoleon's escape and return to France (the Hundred Days
The Hundred Days ( ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition (), marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration of King Louis XVIII o ...
), he regained Murat's support, but Murat proved unable to convince the Italians to fight for Napoleon with his Proclamation of Rimini and was beaten and killed. The Italian kingdoms thus fell, and Italy's Restoration period began, with many pre-Napoleonic sovereigns returned to their thrones. Piedmont, Genoa and Nice came to be united, as did Sardinia (which went on to create the State of Savoy), while Lombardy, Veneto, Istria and Dalmatia were re-annexed to Austria. The dukedoms of Parma and Modena re-formed, and the Papal States and the Kingdom of Naples returned to the Bourbons. The political and social events in the restoration period of Italy (1815–1835) led to popular uprisings throughout the peninsula and greatly shaped what would become the Italian Wars of Independence. All this led to a new Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
and Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
.
During the Napoleonic era, in 1797, the first official adoption of the Italian tricolour as a national flag by a sovereign Italian state, the Cispadane Republic, a Napoleonic sister republic
Sister republics (, ) were republics established by the French First Republic or local pro-French revolutionaries during the French Revolutionary Wars. Though nominally independent, sister republics were heavily reliant on French protection, m ...
of Revolutionary France, took place, on the basis of the events following the French Revolution (1789–1799) which, among its ideals, advocated the national self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
. This event is celebrated by the Tricolour Day.Article 1 of the law n. 671 of 31 December 1996 ("National celebration of the bicentenary of the first national flag") The Italian national colours appeared for the first time on a tricolour cockade in 1789, anticipating by seven years the first green, white and red Italian military war flag, which was adopted by the Lombard Legion
The Lombard Legion (''Legione Lombarda''; ) was a military unit of the Cisalpine Republic which existed from 1796 until the Republic's fall in 1799; but despite the downfall of this sister republic, the Cisalpine troops continued to serve the First ...
in 1796.
Aftermath
 With the fall of Napoleon (1814) and the restoration of the absolutist monarchical regimes, the Italian tricolour went underground, becoming the symbol of the patriotic ferments that began to spread in Italy and the symbol which united all the efforts of the Italian people towards freedom and independence.
Between 1820 and 1861, a sequence of events led to the independence and unification of Italy (except for
With the fall of Napoleon (1814) and the restoration of the absolutist monarchical regimes, the Italian tricolour went underground, becoming the symbol of the patriotic ferments that began to spread in Italy and the symbol which united all the efforts of the Italian people towards freedom and independence.
Between 1820 and 1861, a sequence of events led to the independence and unification of Italy (except for Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
and the province of Mantua, Lazio
Lazio ( , ; ) or Latium ( , ; from Latium, the original Latin name, ) is one of the 20 Regions of Italy, administrative regions of Italy. Situated in the Central Italy, central peninsular section of the country, it has 5,714,882 inhabitants an ...
, Trentino-Alto Adige, Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
and Julian March, known as '' Italia irredenta'', which were united with the rest of Italy in 1866 after the Third Italian War of Independence, in 1870 after the capture of Rome
The Capture of Rome () occurred on 20 September 1870, as forces of the Kingdom of Italy took control of the city and of the Papal States. After a plebiscite held on 2 October 1870, Rome was officially made capital of Italy on 3 February 1871, c ...
, and in 1918 after the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
respectively); this period of Italian history is known as the ''Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
''. The Italian tricolour waved for the first time in the history of the ''Risorgimento'' on 11 March 1821 in the Cittadella of Alessandria, during the revolutions of 1820s, after the oblivion caused by the restoration of the absolutist monarchical regimes.
See also
*Sister republic
Sister republics (, ) were republics established by the French First Republic or local pro-French revolutionaries during the French Revolutionary Wars. Though nominally independent, sister republics were heavily reliant on French protection, m ...
* 130 departments of the First French Empire (including former Italian territories annexed by the First French Empire)
* List of historic states of Italy
* King of Italy
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by ...
(including the list of the modern kings of Italy)
References
Further reading
* * * * Carpanetto, Dino, and Giuseppe Ricuperati. ''Italy in the Age of Reason, 1685–1789'' (1987). * * * * * * * * * Lists more than 15,000 titles * * * * *External links
* Text of th"Albertine Statute"
(Constitution of the Kingdom of Sardinia from 1848 to 1861, and of the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1946)
"Italy."
Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. April 30, 2006. {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Italy (1559-1814)