Her Majesty's Armed Forces on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The British Armed Forces are the unified
, royal.uk.
May 2023. Retrieved on 24 November 2023. with officers and personnel swearing

parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010
nationalarchives.gov.uk, accessed 31 December 2010
Making the Act of Union 1707
scottish.parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010 There were originally several naval and several military regular and reserve ''forces'', although most of these were consolidated into the Royal Navy or the British Army during the 19th and 20th Centuries (the
 During the later half of the 17th century, and in particular, throughout the 18th century, British foreign policy sought to contain the expansion of rival European powers through military, diplomatic and commercial means, especially of its chief competitors
During the later half of the 17th century, and in particular, throughout the 18th century, British foreign policy sought to contain the expansion of rival European powers through military, diplomatic and commercial means, especially of its chief competitors 
 Germany was defeated in the First World War, but by 1933
Germany was defeated in the First World War, but by 1933
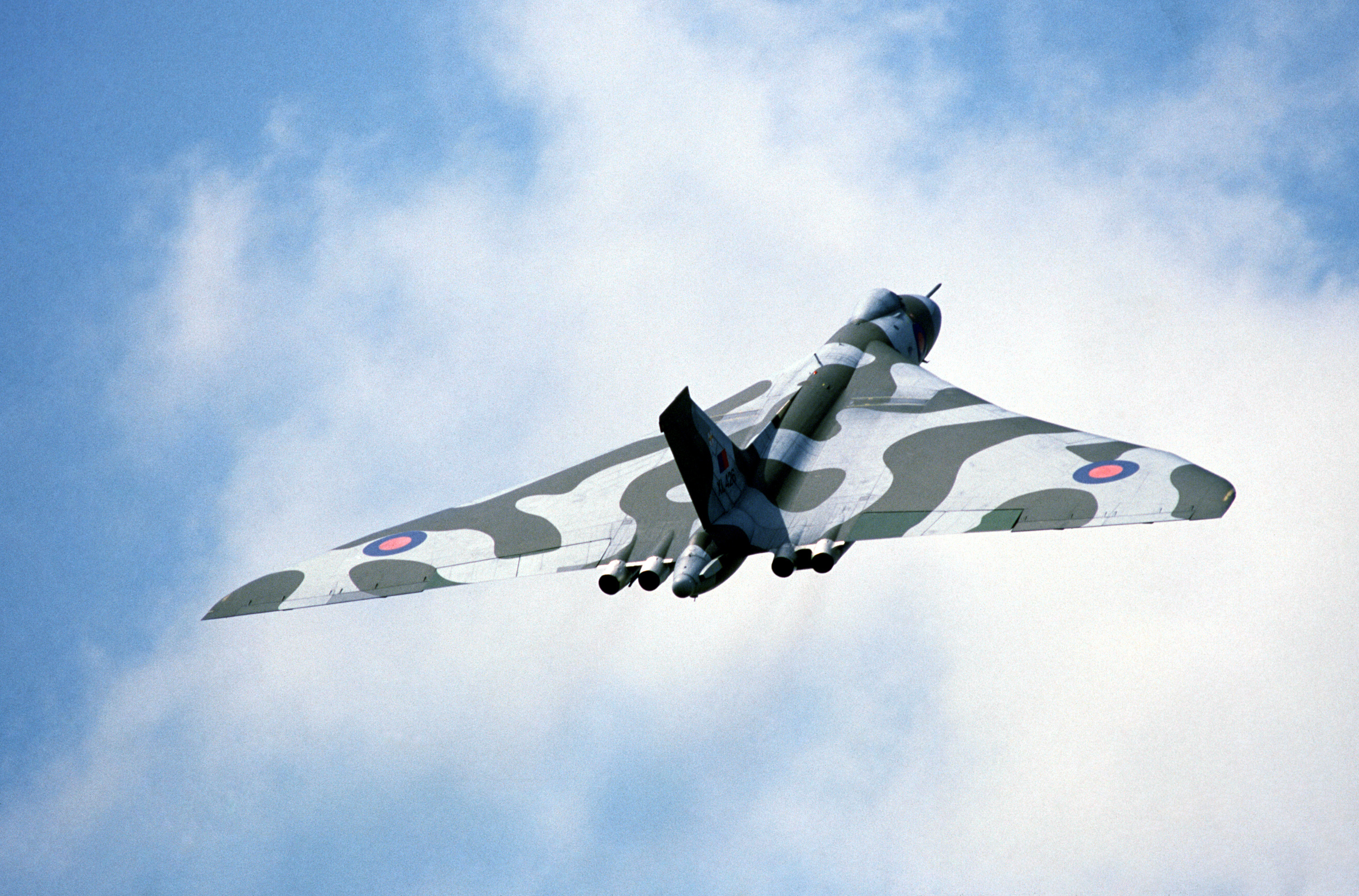 Post–Second World War economic and political decline, as well as changing attitudes in British society and government, were reflected by the armed forces' contracting global role,Focus on Europe
Post–Second World War economic and political decline, as well as changing attitudes in British society and government, were reflected by the armed forces' contracting global role,Focus on Europe
, raf.mod.uk and later epitomised by its political defeat during the
, royal-navy.mod.ukKennedy (2004), ''British Naval Strategy East of Suez, 1900–2000: Influence and Actions'', p193 The
, Ministry of Defence, gov.uk, Published 31 March 2016 In 2025, under Prime Minister Keir Starmer, the UK published a new Strategic Defence Review (2025), Strategic Defence Review (SDR) calling for a shift to "warfighting readiness". Major investments were announced, including the expansion of the SSN-AUKUS attack submarine program to up to 12 boats, acquisition of long-range weapons and advanced air-defence systems, and a possible entry into NATO's nuclear-sharing scheme via the F-35A platform.


UK Armed Forces: Quarterly Service Personnel Statistics. 1 July 2023. MoD. Published 17 September 2023. Retrieved 23 September 2023. As a percentage breakdown of UK Service Personnel, 77.1% are UK Regulars and Gurkhas, 18.8% are Volunteer Reserves and 4.1% are composed of Other Personnel. In addition, all ex-Regular personnel retain a "statutory liability for service" and are liable to be recalled (under Section 52 of the Reserve Forces Act (RFA) 1996) for duty during wartime, which is known as the Regular Reserve. MoD publications since April 2013 no longer report the entire strength of the Regular Reserve, instead they only give a figure for Regular Reserves who serve under a fixed-term reserve contract. These contracts are similar in nature to those of the Volunteer Reserve.gov.uk MoD – reserves and cadet strengths
, table 4 page 13. See note 2. April 2014. The distribution of personnel between the services and categories of service on 1 Janurary 2025 was as follows: On 1 April 2024, most personnel in the UK Regular Forces were stationed in the United Kingdom (around 96%). Of the 5,700 personnel stationed overseas, around two thirds were in Europe (66%), while 14% were stationed in North America, 6% in North Africa and the Middle East, 6% in Asia and 5% in Sub-Saharan Africa. 1,230 personnel were distributed across several regions in Germany, primarily North Rhine-Westphalia as part of British Army Germany. However, up to 750 of these were Locally Engaged Civilians.
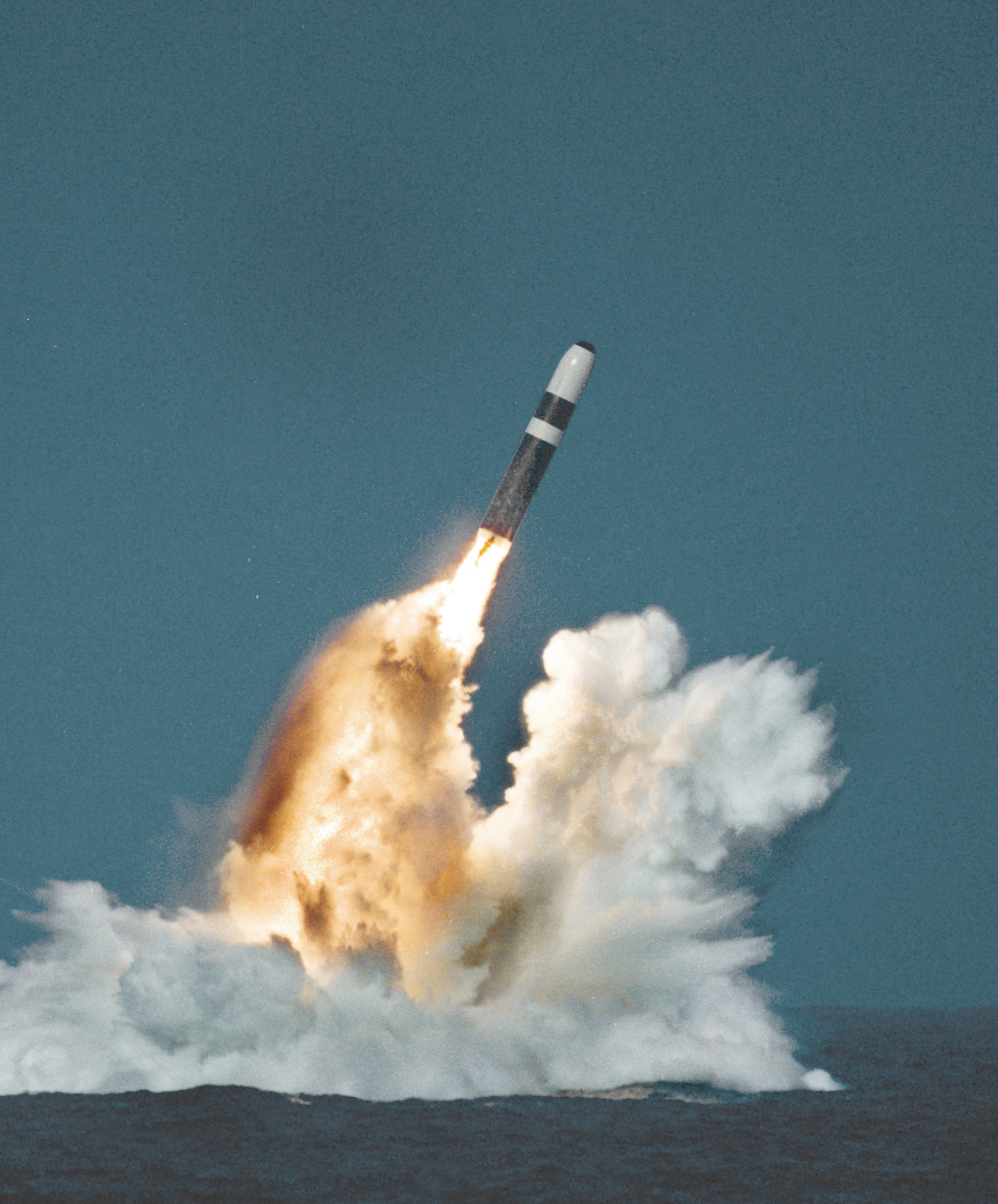 The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear weapon states under the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, Non-Proliferation Treaty and maintains an independent Deterrence theory, nuclear deterrent, currently consisting of four ballistic missile submarines, UGM-133 Trident II submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and 160 operational Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads. This is known as Trident nuclear programme, Trident in both public and political discourse (with nomenclature taken after the UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missile). Trident is operated by the Royal Navy Submarine Service, charged with delivering a 'Continuous At-Sea Deterrent' (CASD) capability, whereby one of the ''Vanguard''-class strategic submarines is always on patrol.Royal Navy – Continuous at sea deterrent
The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear weapon states under the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, Non-Proliferation Treaty and maintains an independent Deterrence theory, nuclear deterrent, currently consisting of four ballistic missile submarines, UGM-133 Trident II submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and 160 operational Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads. This is known as Trident nuclear programme, Trident in both public and political discourse (with nomenclature taken after the UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missile). Trident is operated by the Royal Navy Submarine Service, charged with delivering a 'Continuous At-Sea Deterrent' (CASD) capability, whereby one of the ''Vanguard''-class strategic submarines is always on patrol.Royal Navy – Continuous at sea deterrent
, royalnavy.mod.uk, Accessed 6 December 2014 According to the British Government, since the introduction of UK Polaris programme, Polaris (Trident's predecessor) in the 1960s, from April 1969 "the Royal Navy's ballistic missile boats have not missed a single day on patrol", giving what the Defence Council described in 1980 as a deterrent "effectively invulnerable to pre-emptive attack". As of 2015, it has been British Government policy for the ''Vanguard''-class strategic submarines to carry no more than 40 nuclear warheads, delivered by eight UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missiles. In contrast with the other recognised nuclear weapon states, the United Kingdom operates only a submarine-based delivery system, having decommissioned its tactical WE.177 free-fall bombs in 1998. The House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons voted on 18 July 2016 in favour of replacing the ''Vanguard''-class submarines with a new generation of s. The programme will also contribute to extending the life of the UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missiles and modernise the infrastructure associated with the CASD. Former United Kingdom and weapons of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction possessed by the United Kingdom include both biological and Chemical weapons and the United Kingdom, chemical weapons. These were renounced in 1956 and subsequently destroyed.
 The British Armed Forces historically relied on four Imperial fortress colonies (Bermuda, Gibraltar, Halifax and its environs in Nova Scotia, and Malta), where dockyards were established, naval squadrons based, soldiers garrisoned, and naval and military stores stockpiled. These acted as lynchpins in maintaining British naval supremacy on the Atlantic and its connected seas. As, until the end of the First World War, it was presumed the only navies that might prove a threat were all of countries on, or off, the Atlantic, no Imperial fortress was established in the Pacific or Indian Oceans, to which power would be extended from Bermuda and Malta following the completion of the Panama and Suez canals. Local-service military reserve units were raised in some of the Imperial fortresses (notably Bermuda and Malta), which could be embodied for full time service in war time to reinforce the regular garrisons, and these were funded by the War Office as part of the British Army. After the First World War, the growing belligerence and naval power of the Japanese Empire led to the construction of the Singapore Naval Base. The regular British Armed Forces otherwise were distributed around the world where required to guard against invasion or rebellion, reinforced in some colonies by locally raised reserve forces. In colonies where there was no strategic requirement, regular forces were rarely stationed, with local governments encouraged to maintain and fund military reserve units as contributions to their own defence (although these units were ultimately under the control of the national, i.e. British, Government via the colonial Governors as defence is not a competency that has been delegated to local governments). Under the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation alliance, and with the steady reduction of both the British Empire and the British Armed Forces over the decades that followed the Second World War, the significance of the three remaining Imperial fortresses (military control of Halifax having passed to the new Dominion government following the 1867 Confederation of Canada, and naval control transferred in 1905 to what was to become the Royal Canadian Navy) rapidly faded. The Bermuda-based North America and West Indies Station was abolished in 1956, and the last regular army units removed from the Bermuda Command in 1957 (leaving only two part-time reserve units), with the naval dockyard in Bermuda reduced to a base, without repair or refit capabilities, in 1951 and finally closed in 1995, following the Cold War (United States and Canadian bases in Bermuda closed in the same period), leaving only the
The British Armed Forces historically relied on four Imperial fortress colonies (Bermuda, Gibraltar, Halifax and its environs in Nova Scotia, and Malta), where dockyards were established, naval squadrons based, soldiers garrisoned, and naval and military stores stockpiled. These acted as lynchpins in maintaining British naval supremacy on the Atlantic and its connected seas. As, until the end of the First World War, it was presumed the only navies that might prove a threat were all of countries on, or off, the Atlantic, no Imperial fortress was established in the Pacific or Indian Oceans, to which power would be extended from Bermuda and Malta following the completion of the Panama and Suez canals. Local-service military reserve units were raised in some of the Imperial fortresses (notably Bermuda and Malta), which could be embodied for full time service in war time to reinforce the regular garrisons, and these were funded by the War Office as part of the British Army. After the First World War, the growing belligerence and naval power of the Japanese Empire led to the construction of the Singapore Naval Base. The regular British Armed Forces otherwise were distributed around the world where required to guard against invasion or rebellion, reinforced in some colonies by locally raised reserve forces. In colonies where there was no strategic requirement, regular forces were rarely stationed, with local governments encouraged to maintain and fund military reserve units as contributions to their own defence (although these units were ultimately under the control of the national, i.e. British, Government via the colonial Governors as defence is not a competency that has been delegated to local governments). Under the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation alliance, and with the steady reduction of both the British Empire and the British Armed Forces over the decades that followed the Second World War, the significance of the three remaining Imperial fortresses (military control of Halifax having passed to the new Dominion government following the 1867 Confederation of Canada, and naval control transferred in 1905 to what was to become the Royal Canadian Navy) rapidly faded. The Bermuda-based North America and West Indies Station was abolished in 1956, and the last regular army units removed from the Bermuda Command in 1957 (leaving only two part-time reserve units), with the naval dockyard in Bermuda reduced to a base, without repair or refit capabilities, in 1951 and finally closed in 1995, following the Cold War (United States and Canadian bases in Bermuda closed in the same period), leaving only the
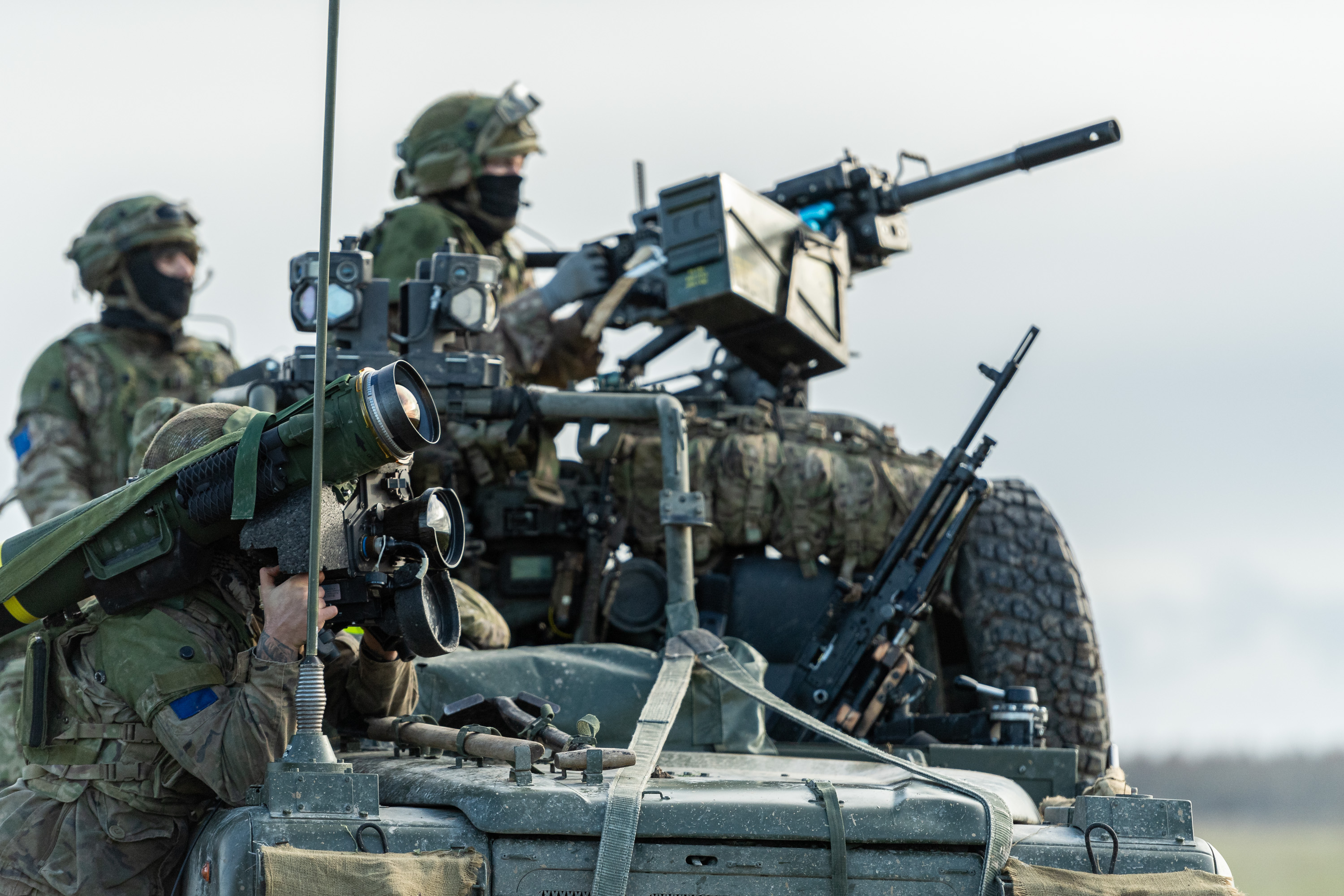 The four battalions of the Parachute Regiment (United Kingdom), Parachute Regiment, forming 16 Air Assault Brigade Combat Team and part of Special Forces Support Group, are the British Army's elite airborne infanteers, held at high readiness and specialising in rapid deployment by parachute and helicopter, widely regarded as the "fittest, most aggressive, resilient and disciplined regiment in the British Army."
The Royal Armoured Corps provides the armoured capability of the British Army. The Royal Tank Regiment, Queen's Royal Hussars and Royal Wessex Yeomanry (of the Army Reserve (United Kingdom), Army Reserve) operate Challenger 2 main battle tanks, which are being upgraded to Challenger 3, and are part of 3rd (United Kingdom) Division, 3rd (UK) Division's Armoured Brigade Combat Teams. Armoured Cavalry regiments, such as the Royal Dragoon Guards, currently operate the Warrior tracked armoured vehicle, Warrior IFV on an interim basis, until General Dynamics Ajax, Ajax reaches full operating capability. There are six Light Cavalry regiments (three Regular + three Reserve) equipped with the Jackal (vehicle), Jackal 2 and Jackal (vehicle)#Coyote, Coyote TSV, tasked with providing reconnaissance and fire support. The Household Cavalry, made up of the Life Guards (United Kingdom), Life Guards and the Blues and Royals, operate in a dual role of Armoured Cavalry and Mounted Ceremonial on Horse Guards (building), Horse Guards in London, and for state occasions.
The four battalions of the Parachute Regiment (United Kingdom), Parachute Regiment, forming 16 Air Assault Brigade Combat Team and part of Special Forces Support Group, are the British Army's elite airborne infanteers, held at high readiness and specialising in rapid deployment by parachute and helicopter, widely regarded as the "fittest, most aggressive, resilient and disciplined regiment in the British Army."
The Royal Armoured Corps provides the armoured capability of the British Army. The Royal Tank Regiment, Queen's Royal Hussars and Royal Wessex Yeomanry (of the Army Reserve (United Kingdom), Army Reserve) operate Challenger 2 main battle tanks, which are being upgraded to Challenger 3, and are part of 3rd (United Kingdom) Division, 3rd (UK) Division's Armoured Brigade Combat Teams. Armoured Cavalry regiments, such as the Royal Dragoon Guards, currently operate the Warrior tracked armoured vehicle, Warrior IFV on an interim basis, until General Dynamics Ajax, Ajax reaches full operating capability. There are six Light Cavalry regiments (three Regular + three Reserve) equipped with the Jackal (vehicle), Jackal 2 and Jackal (vehicle)#Coyote, Coyote TSV, tasked with providing reconnaissance and fire support. The Household Cavalry, made up of the Life Guards (United Kingdom), Life Guards and the Blues and Royals, operate in a dual role of Armoured Cavalry and Mounted Ceremonial on Horse Guards (building), Horse Guards in London, and for state occasions.
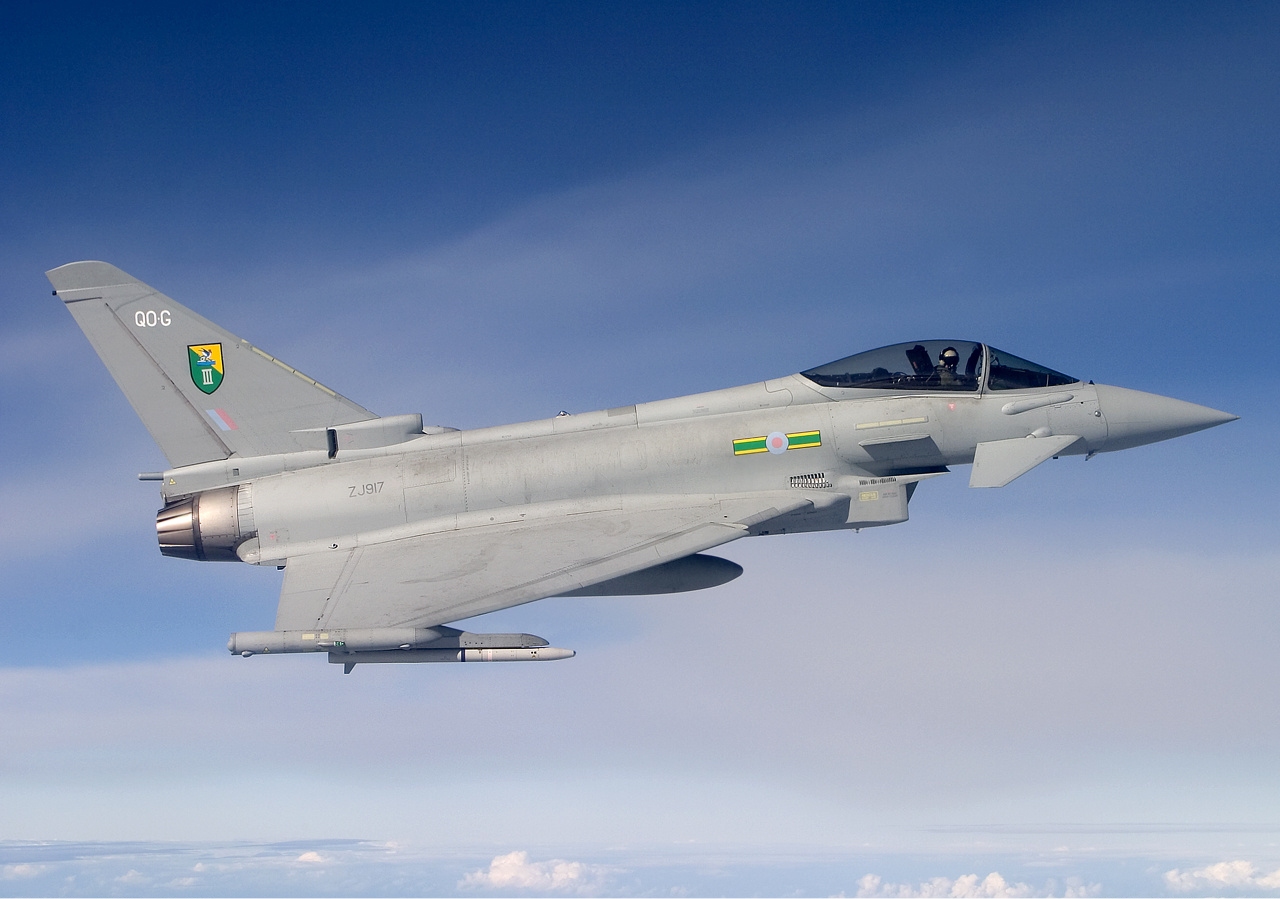 The Royal Air Force has a large operational fleet that fulfils various roles, consisting of both List of active United Kingdom military aircraft, fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. Frontline aircraft are controlled by RAF Air Command, Air Command, which is organised into five Group (air force), groups defined by function: No. 1 Group RAF, 1 Group (Air Combat), No. 2 Group RAF, 2 Group (Air Support), No. 11 Group RAF, 11 Group (Air and Space operations), No. 22 Group, 22 Group (training aircraft and ground facilities) and No. 38 Group RAF, 38 Group (Royal Air Force's Engineering, Logistics, Communications and Medical Operations units). In addition No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group (United Kingdom), 83 Expeditionary Air Group directs formations in the Middle East and the No. 38 Group RAF, 38 Group combines the expeditionary Combat Support, combat support and Combat Service Support, combat service support units of the RAF. Deployable formations consist of Expeditionary Air Wing (air force unit), Wings and Squadron (aviation), squadrons—the basic unit of the Air Force. Independent Flight (military unit), flights are deployed to facilities in Brunei, the Falkland Islands, Iraq, and the United States.
The Royal Air Force operates multi-role and single-role fighters, reconnaissance and patrol aircraft, tankers, transports, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles, and various types of training aircraft.
Ground units are also maintained by the Royal Air Force, most prominently the RAF Police and the Royal Air Force Regiment (RAF Regt). The Royal Air Force Regiment essentially functions as the ground defence force of the RAF, optimised for the specialist role of fighting on and around forward airfields, which are densely packed with operationally vital aircraft, equipment, infrastructure and personnel. The Regiment contains nine regular squadrons, supported by five squadrons of the Royal Auxiliary Air Force Regiment. In addition, it provides Forward air control, Forward Air Controllers to defence as well as a contribution to the Special Forces Support Group.
The Royal Air Force has a large operational fleet that fulfils various roles, consisting of both List of active United Kingdom military aircraft, fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. Frontline aircraft are controlled by RAF Air Command, Air Command, which is organised into five Group (air force), groups defined by function: No. 1 Group RAF, 1 Group (Air Combat), No. 2 Group RAF, 2 Group (Air Support), No. 11 Group RAF, 11 Group (Air and Space operations), No. 22 Group, 22 Group (training aircraft and ground facilities) and No. 38 Group RAF, 38 Group (Royal Air Force's Engineering, Logistics, Communications and Medical Operations units). In addition No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group (United Kingdom), 83 Expeditionary Air Group directs formations in the Middle East and the No. 38 Group RAF, 38 Group combines the expeditionary Combat Support, combat support and Combat Service Support, combat service support units of the RAF. Deployable formations consist of Expeditionary Air Wing (air force unit), Wings and Squadron (aviation), squadrons—the basic unit of the Air Force. Independent Flight (military unit), flights are deployed to facilities in Brunei, the Falkland Islands, Iraq, and the United States.
The Royal Air Force operates multi-role and single-role fighters, reconnaissance and patrol aircraft, tankers, transports, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles, and various types of training aircraft.
Ground units are also maintained by the Royal Air Force, most prominently the RAF Police and the Royal Air Force Regiment (RAF Regt). The Royal Air Force Regiment essentially functions as the ground defence force of the RAF, optimised for the specialist role of fighting on and around forward airfields, which are densely packed with operationally vital aircraft, equipment, infrastructure and personnel. The Regiment contains nine regular squadrons, supported by five squadrons of the Royal Auxiliary Air Force Regiment. In addition, it provides Forward air control, Forward Air Controllers to defence as well as a contribution to the Special Forces Support Group.
 All three services of the British Armed Forces recruit primarily from within the United Kingdom, although citizens from the Commonwealth of Nations and the Republic of Ireland are equally eligible to join.Evans (2005)
All three services of the British Armed Forces recruit primarily from within the United Kingdom, although citizens from the Commonwealth of Nations and the Republic of Ireland are equally eligible to join.Evans (2005)
How British Army is fast becoming foreign legion
, timesonline.co.uk The minimum recruitment age is 16 years (although personnel may not serve on armed operations below 18 years, and if under 18 must also have parental consent to join); the maximum recruitment age depends whether the application is for a regular or reserve role; there are further variations in age limit for different corps/regiments. The normal term of engagement is 22 years; however, the minimum service required before resignation is 4 years, plus, in the case of the Army, any service person below the age of 18. A note to add is that in the United Kingdom, people may join the "Cadet Forces" such as the army cadets, Royal Air Force Air Cadets or the sea and Royal Marine Cadets. Young people may join these organisations which are either funded or affiliated with the MOD from the age of 13-18, there is no obligation to then join the armed forces however it teaches key skills in both civilian and military life and is a key recruitment drive for the armed forces. At present, the yearly intake into the armed forces is 11,880 (per the 12 months to 31 March 2014).UK Armed Forces Quarterly Personnel Report
, gov.uk, 1 April 2014 Excluding the Brigade of Gurkhas and the Royal Irish Regiment (1992), Royal Irish Regiment, as of 1 April 2014 there are approximately 11,200 Black and Minority Ethnic (BME) persons serving as Regulars across the three service branches; of those, 6,610 were recruited from outside the United Kingdom. In total, Black and Minority Ethnic persons represent 7.1% of all service personnel, an increase from 6.6% in 2010. Since the year 2000, Sexual orientation and the military of the United Kingdom, sexual orientation has not been a factor considered in recruitment, and homosexuals can serve openly in the armed forces. All branches of the forces have actively recruited at Gay Pride events. The forces keep no formal figures concerning the number of gay and lesbian serving soldiers, saying that the sexual orientation of personnel is considered irrelevant and not monitored.
British Ministry of Defence
(gov.uk)
Defence Academy of the United Kingdom
(.da.mod.uk)
Royal Navy official website
(royalnavy.mod.uk)
Royal Marines official webpage
(royalnavy.mod.uk)
British Army official website
(army.mod.uk)
Royal Air Force official website
(raf.mod.uk) {{North Atlantic Treaty Organization British Armed Forces, Military of the United Kingdom, British Armed Forces deployments, British Armed Forces deployments
military forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies
The Crown Dependencies are three dependent territory, offshore island territories in the British Islands that are self-governing possessions of the The Crown, British Crown: the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Jersey, Bailiwick of Jersey, both lo ...
. They also promote the UK's wider interests, support international peacekeeping
Peacekeeping comprises activities, especially military ones, intended to create conditions that favor lasting peace. Research generally finds that peacekeeping reduces civilian and battlefield deaths, as well as reduces the risk of renewed w ...
efforts and provide humanitarian aid
Humanitarian aid is material and Humanitarian Logistics, logistic assistance, usually in the short-term, to people in need. Among the people in need are the homelessness, homeless, refugees, and victims of natural disasters, wars, and famines. Th ...
. The force is also known as His Majesty's Armed Forces.
Since the formation of the united Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
in 1707 (later succeeded by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the union of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into one sovereign state, established by the Acts of Union 1800, Acts of Union in 1801. It continued in this form until ...
, and finally by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
), the British Armed Forces have seen action in most major wars involving the world's great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
s, including the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
, the American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
, the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
, the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. Britain's victories in most of these wars allowed it to influence world events and establish itself as one of the world's leading military and economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
powers. The British Armed Forces consist of: the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, a blue-water navy
A blue-water navy is a Navy, maritime force capable of operating globally, essentially across the deep waters of open oceans. While definitions of what actually constitutes such a force vary, there is a requirement for the ability to exercise Co ...
with a fleet of 62 commissioned and active ships, together with the Royal Marines
The Royal Marines provide the United Kingdom's amphibious warfare, amphibious special operations capable commando force, one of the :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, five fighting arms of the Royal Navy, a Company (military unit), company str ...
, a highly specialised amphibious light infantry force; the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
, the UK's principal land warfare
Land warfare or ground warfare is the process of military operations eventuating in combat that takes place predominantly on the battlespace land surface of the planet.
Land warfare is categorized by the use of large numbers of combat personne ...
branch; and the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
, a technologically sophisticated air force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
with a diverse operational fleet consisting of both fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. The British Armed Forces include standing forces, Regular Reserve, Volunteer Reserves and Sponsored Reserves
The Sponsored Reserves are a category of reserve forces in the British Armed Forces, created by the Reserve Forces Act 1996. It allows for certain support or specialist tasks to be carried out by trained professionals, who also maintain a civilia ...
.
King Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms.
Charles was born at Buckingham Palace during the reign of his maternal grandfather, King George VI, and ...
, sovereign of the United Kingdom
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers regulated by the British cons ...
, is the commander-in-chief and is styled as Head of the Armed Forces
Head of the Armed Forces is the position of the sovereign of the United Kingdom as commander-in-chief of the British Armed Forces. Supreme military authority is vested in the monarch and extends to the exercise of several personal prerogative ...
,Forces Queen and Armed Forces, royal.uk.
May 2023. Retrieved on 24 November 2023. with officers and personnel swearing
allegiance
An allegiance is a duty of fidelity said to be owed, or freely committed, by the people, subjects or citizens to their state or sovereign.
Etymology
The word ''allegiance'' comes from Middle English ' (see Medieval Latin ', "a liegance"). The ...
to him. Long-standing constitutional convention, however, has vested ''de facto'' executive authority, by the exercise of royal prerogative
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, Privilege (law), privilege, and immunity recognised in common law (and sometimes in Civil law (legal system), civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy) as belonging to the monarch, so ...
, in the Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
and the secretary of state for defence
The secretary of state for defence, also known as the defence secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with responsibility for the Ministry of Defence. As a senior minister, the incumbent is a member of the ...
. The Prime Minister (acting with the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
) makes the key decisions on the use of the armed forces. The UK Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of ...
approves the continued existence of the British Army by passing an Armed Forces Act
Armed Forces Act (with its variations) is a stock short title used for legislation in India, Malaysia and the United Kingdom relating to armed forces. The bill for an act with this short title will usually have been known as an Armed Forces Bill du ...
at least once every five years, as required by the Bill of Rights 1689
The Bill of Rights 1689 (sometimes known as the Bill of Rights 1688) is an Act of Parliament (United Kingdom), act of the Parliament of England that set out certain basic civil rights and changed the succession to the Monarchy of England, Engl ...
. Only a "standing army" requires reapproval by Parliament; the Royal Navy, Royal Air Force and the Royal Marines and any other forces are not included in the requirement. The armed forces are managed by the Defence Council.
The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear powers, a permanent member on the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
, a founding and leading member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
and party to the AUKUS
AUKUS ( ), also styled as Aukus, is a trilateral security partnership between Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States intended to "promote a free and open Indo-Pacific that is secure and stable." Initially announced on 15 September ...
security pact and the Five Power Defence Arrangements
The Five Power Defence Arrangements (FPDA) are a series of bilateral defence relationships established by a series of multi-lateral agreements between Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United Kingdom, all of which are Commonwe ...
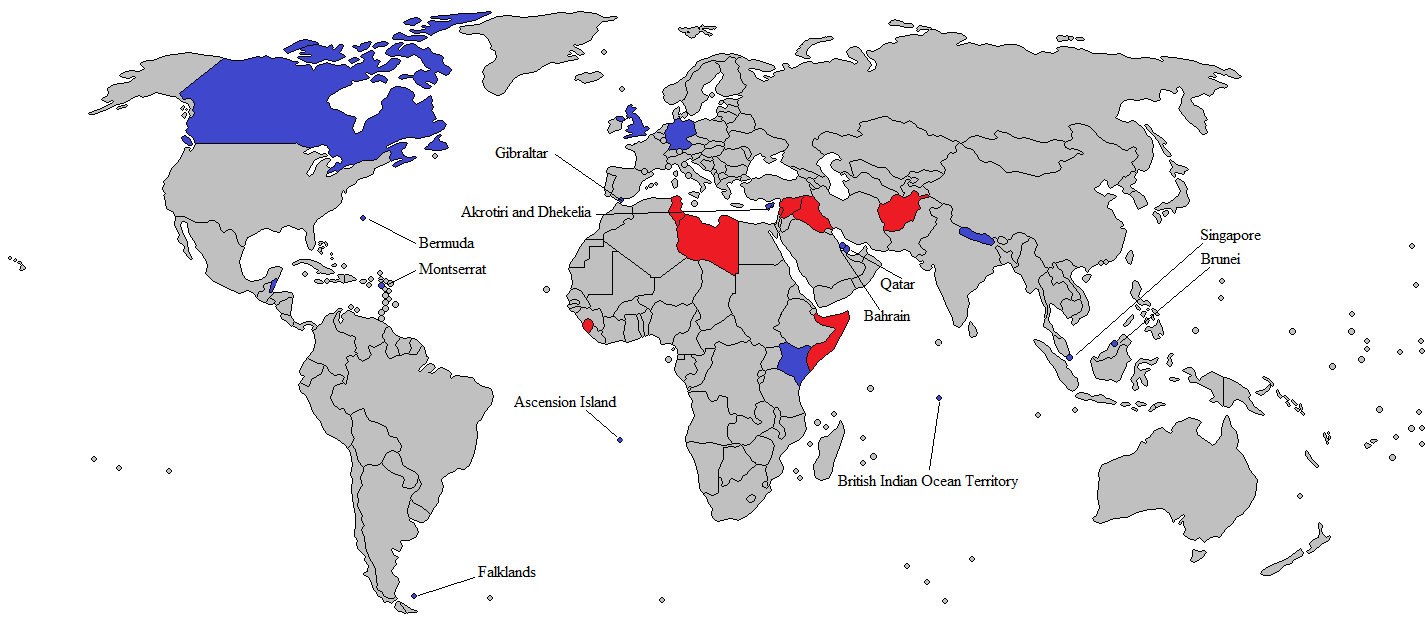
. Overseas garrisons and training facilities are maintained at Ascension Island
Ascension Island is an isolated volcanic island, 7°56′ south of the Equator in the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic Ocean. It is about from the coast of Africa and from the coast of South America. It is governed as part of the British Overs ...
, Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
, Belize
Belize is a country on the north-eastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a maritime boundary with Honduras to the southeast. P ...
, Bermuda
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about to the west-northwest.
Bermuda is an ...
, British Indian Ocean Territory
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an British Overseas Territories, Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean, halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chago ...
, Brunei
Brunei, officially Brunei Darussalam, is a country in Southeast Asia, situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. Apart from its coastline on the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak, with ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; ), commonly referred to as The Falklands, is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and from Cape Dub ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
, Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, Montserrat
Montserrat ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, wit ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
, Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
History

Organisation
With theActs of Union 1707
The Acts of Union refer to two acts of Parliament, one by the Parliament of Scotland in March 1707, followed shortly thereafter by an equivalent act of the Parliament of England. They put into effect the international Treaty of Union agree ...
, the armed forces of England and Scotland were merged into the armed forces of the Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
.Acts of Union 1707parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010
nationalarchives.gov.uk, accessed 31 December 2010
Making the Act of Union 1707
scottish.parliament.uk, accessed 31 December 2010 There were originally several naval and several military regular and reserve ''forces'', although most of these were consolidated into the Royal Navy or the British Army during the 19th and 20th Centuries (the
Royal Naval Air Service
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty (United Kingdom), Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British ...
and the Royal Flying Corps
The Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was the air arm of the British Army before and during the First World War until it merged with the Royal Naval Air Service on 1 April 1918 to form the Royal Air Force. During the early part of the war, the RFC sup ...
of the British Army, by contrast, were separated from their parent forces in 1918 and amalgamated to form a new force, the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
, which would have complete responsibility for naval, military and strategic aviation until the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
).
Naval forces included the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, the Waterguard
The Waterguard was a division of HM Customs and Excise (HMCE) responsible for the control of vessels, aircraft, vehicles and persons arriving into and departing from the United Kingdom. This included crew members and passengers, as well as perso ...
, later renamed the HM Coastguard
His Majesty's Coastguard (HMCG) is the section of the Maritime and Coastguard Agency responsible, through the Secretary of State for Transport to Parliament, for the initiation and co-ordination of all maritime search and rescue (SAR) within th ...
, and Sea Fencibles
The Sea Fencibles were naval fencible (a shortening of ''defencible'') units established to provide a close-in line of defence and obstruct the operation of enemy shipping, principally during the French Revolutionary Wars, French Revolutionary a ...
and ''River Fencibles'' formed as and when required for the duration of emergencies. The Merchant Navy and offshore fishing boat crews were also important manpower reserves to the armed naval forces. Any seaman was liable to impressment
Impressment, colloquially "the press" or the "press gang", is a type of conscription of people into a military force, especially a naval force, via intimidation and physical coercion, conducted by an organized group (hence "gang"). European nav ...
, with many so conscripted especially during the two decades of conflict from the French Revolution until the end of the Napoleonic Wars, and from 1835 registered on the ''Register of Seamen'' to identify them as a potential resource, and many of their seamen would serve part time in the Royal Navy Reserve
The Royal Naval Reserve (RNR) is one of the two volunteer reserve forces of the Royal Navy in the United Kingdom. Together with the Royal Marines Reserve, they form the Maritime Reserve. The present RNR was formed by merging the original R ...
, created under the Naval Reserve Act 1859, and Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family or royalty
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Roya ...
, created in 1903.
The British military (those parts of the British Armed Forces tasked with land warfare, as opposed to the naval forces) historically was divided into a number of military forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
, of which the British Army (also referred to historically as the 'Regular Army' and the 'Regular Force') was only one. The oldest of these organisations was the Militia Force (also referred to as the ''Constitutional Force''), which (in the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to f ...
) was originally the main military defensive force (there otherwise were originally only royal bodyguards, including the Yeomen Warders
The Yeomen Warders of His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress the Tower of London, and Members of the Sovereign's Body Guard of the Yeoman Guard Extraordinary, popularly known as the Beefeaters, are ceremonial guardians of the Tower of London. I ...
and the Yeomen of the Guard
The King's Body Guard of the Yeomen of the Guard is a Sovereign's Bodyguard, bodyguard of the British monarch. The List of oldest military units and formations in continuous operation, oldest British military corps still in existence, it was ...
, with armies raised only temporarily for expeditions overseas), made up of civilians embodied for annual training or emergencies, and had used various schemes of compulsory service during different periods of its long existence.
The Militia was originally an all infantry force, organised at the city or county level, and members were not required to serve outside of their recruitment area, although the area within which militia units in Britain could be posted was increased to anywhere in the Britain during the 18th century, and Militia coastal artillery, field artillery, and engineers units were introduced from the 1850s.''The Militia Artillery 1852-1909'', by Norman EH Litchfield. The Sherwood Press (Nottingham) Ltd. 1987 The Yeomanry
Yeomanry is a designation used by a number of units and sub-units in the British Army Reserve which are descended from volunteer cavalry regiments that now serve in a variety of different roles.
History
Origins
In the 1790s, following the ...
was a mounted force that could be mobilised in times of war or emergency. Volunteer Force
The Volunteer Force was a citizen army of part-time rifle, artillery and engineer corps, created as a Social movement, popular movement throughout the British Empire in 1859. Originally highly autonomous, the units of volunteers became increa ...
units were also frequently raised during wartime, which did not rely on compulsory service and hence attracted recruits keen to avoid the Militia. These were seen as a useful way to add to military strength economically during wartime, but otherwise as a drain on the Militia and so were not normally maintained in peacetime, although in Bermuda prominent propertied men were still appointed ''Captains of Forts'', taking charge of maintaining and commanding fortified coastal artillery
Coastal artillery is the branch of the armed forces concerned with operating anti-ship artillery or fixed gun batteries in coastal fortifications.
From the Middle Ages until World War II, coastal artillery and naval artillery in the form of ...
batteries and manned by volunteers (reinforced in wartime by embodied militiamen), defending the colony's coast from the 17th century to the 19th century (when all of the batteries were taken over by the regular Royal Artillery). The militia system was extended to a number of English (subsequently ''British'') colonies, beginning with Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
and Bermuda
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about to the west-northwest.
Bermuda is an ...
. In some colonies, ''Troops of Horse'' or other mounted units similar to the Yeomanry were also created. The militia and volunteer units of a colony were generally considered to be separate forces from the ''Home'' Militia Force and Volunteer Force in the United Kingdom, and from the militia forces and volunteer forces of other colonies. Where a colony had more than one militia or volunteer unit, they would be grouped as a militia or volunteer force for that colony, such as the Jamaica Volunteer Defence Force, which comprised the St. Andrew Rifle Corps, or Kingston Infantry Volunteers, the Jamaica Corps of Scouts, and the Jamaica Reserve Regiment, but not the Jamaica Militia Artillery
The Militia of the British Dominions, Self-Governing Colonies, and Crown Colonies were the principal military forces of the Dominions, Self-governing colonies (those with elected local legislatures) and Crown Colonies (those without elected local ...
. In smaller colonies with a single militia or volunteer unit, that single unit would still be considered to be listed within a force, or in some case might be named a force rather than a regiment or corps, such as is the case for the Falkland Islands Defence Force
The Falkland Islands Defence Force (FIDF) is the locally maintained volunteer defence unit in the Falkland Islands, a British Overseas Territory. The FIDF works alongside the military units supplied by the United Kingdom to ensure the security ...
and the Royal Montserrat Defence Force
The Royal Montserrat Defence Force is the home defence unit of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of Montserrat. The force has an authorized strength level objective of 50 reserve personnel as of 2021-22, akin in size ...
. The militia, yeomanry and volunteer forces collectively were known as the ''reserve forces'', ''auxiliary forces'', or ''local forces''. Officers of these forces could not sit on courts martial of regular forces personnel. The Mutiny Act
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military or a crew) to oppose, change, or remove superiors or their orders. The term is commonly used for insubordination by members of the military against an officer or superior, b ...
did not apply to members of the Reserve Forces.
The other regular military force that existed alongside the British Army was the Board of Ordnance
The Board of Ordnance was a British government body. Established in the Tudor period, it had its headquarters in the Tower of London. Its primary responsibilities were 'to act as custodian of the lands, depots and forts required for the defence ...
, which included the ''Ordnance Military Corps'' (made up of the Royal Artillery, Royal Engineers, and the Royal Sappers and Miners), as well as the originally-civilian Commissariat Stores and transport departments, as well as barracks departments, ordnance factories and various other functions supporting the various naval and military forces. The English Army, subsequently the British Army once Scottish regiments were moved onto its establishment following the Union of the Kingdoms of Scotland and England, was originally a separate force from these, but absorbed the Ordnance Military Corps and various previously civilian departments after the Board of Ordnance was abolished in 1855. The ''Reserve Forces'' (which referred to the Home Yeomanry, Militia and Volunteer Forces before the 1859 creation of the British Army ''Regular Reserve'' by Secretary of State for War
The secretary of state for war, commonly called the war secretary, was a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, which existed from 1794 to 1801 and from 1854 to 1964. The secretary of state for war headed the War Offic ...
Sidney Herbert, and re-organised under the Reserve Force Act 1867 The Regular Reserve is the component of the military reserve of the British Armed Forces whose members have formerly served in the " Regular" (full-time professional) forces. Other components of the Reserve are the Volunteer Reserves and the Spons ...
) were increasingly integrated with the British Army through a succession of reforms over the last two decades of the 19th century (in 1871, command of the Auxiliary Forces in the British Isles was taken from the Lords-Lieutenant of counties and transferred to the War Office
The War Office has referred to several British government organisations throughout history, all relating to the army. It was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, at ...
, though colonial governors retained control of their militia and volunteer forces, and by the end of the century, at the latest, any unit wholly or partly funded from Army funds was considered part of the British Army) and the early years of the 20th century, whereby the Reserve Forces units mostly lost their own identities and became numbered Territorial Force
The Territorial Force was a part-time volunteer component of the British Army, created in 1908 to augment British land forces without resorting to conscription. The new organisation consolidated the 19th-century Volunteer Force and yeomanry in ...
sub-units of regular British Army corps or regiments (the Home Militia had followed this path, with the Militia Infantry units becoming numbered battalions of British Army regiments, and the Militia Artillery integrating within Royal Artillery territorial divisions in 1882 and 1889, and becoming parts of the Royal Field Artillery
The Royal Field Artillery (RFA) of the British Army provided close artillery support for the infantry. It was created as a distinct arm of the Royal Regiment of Artillery on 1 July 1899, serving alongside the other two arms of the regiment, the ...
or Royal Garrison Artillery
The Royal Garrison Artillery (RGA) was formed in 1899 as a distinct arm of the British Army's Royal Artillery, Royal Regiment of Artillery serving alongside the other two arms of the Regiment, the Royal Field Artillery (RFA) and the Royal Horse ...
in 1902 (though retaining their traditional corps names), but was not merged into the Territorial Force when it was created in 1908 (by the merger of the Yeomanry and Volunteer Force). The Militia was instead renamed the ''Special Reserve'', and was permanently suspended after the First World War (although a handful of Militia units survived in the United Kingdom, its colonies, and the Crown Dependencies). Unlike the Home, Imperial Fortress and Crown Dependency Militia and Volunteer units and forces that continued to exist after the First World War, although parts of the British military, most were not considered parts of the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
unless they received Army funds, as was the case for the Bermuda Militia Artillery
The Bermuda Militia Artillery was a unit of part-time soldiers organised in 1895 as a reserve for the Royal Garrison Artillery detachment of the Regular Army garrison in the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda. Militia Artillery units of the Un ...
and the Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps
The Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps (BVRC) was created in 1894 as a reserve for the British Army, Regular Army infantry component of the Bermuda Garrison. Renamed the ''Bermuda Rifles'' in 1951, it was amalgamated into the Bermuda Regiment in 1965 ...
, which was generally only the case for those in the Channel Islands or the Imperial Fortress colonies (Nova Scotia, before Canadian confederation
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation, called the Name of Canada#Adoption of Dominion, Dominion of Ca ...
, Bermuda, Gibraltar, and Malta). Today, the British Army is the only Home British military force (unless the Army Cadet Force
The Army Cadet Force (ACF), generally shortened to Army Cadets, is a national Youth organisations in the United Kingdom, youth organisation sponsored by the United Kingdom's Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence and the Bri ...
and the Combined Cadet Force
The Combined Cadet Force (CCF) is a youth organisation in the United Kingdom, sponsored by the Ministry of Defence (MOD), which operates in schools, sub divided into Royal Navy, Royal Marines, Army and Royal Air Force sections. Its aim is to ...
are considered), including both the regular army and the forces it absorbed, though British military units organised on Territorial lines remain in British Overseas Territories that are still not considered formally part of the British Army, with only the Royal Gibraltar Regiment
The Royal Gibraltar Regiment is part of British Forces Gibraltar for the British overseas territory of Gibraltar, which historically, along with Bermuda, Halifax, Nova Scotia (prior to the 1867 Confederation of Canada), and Malta, had been d ...
and the Royal Bermuda Regiment
The Royal Bermuda Regiment (RBR) is the home defence unit of the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is a single Territorial Army (United Kingdom), territorial infantry battalion#British Army, battalion that was formed on the amalgamation ...
(an amalgam of the old Bermuda Militia Artillery and Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps) appearing on the British Army order of precedence and in the Army List.
Confusingly, and similarly to the dual meaning of the word Corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was formally introduced March 1, 1800, when Napoleon ordered Gener ...
in the British Army. As an example, the 1st Battalion of the King's Royal Rifle Corps
The King's Royal Rifle Corps was an infantry rifle regiment of the British Army that was originally raised in British North America as the Royal American Regiment during the phase of the Seven Years' War in North America known in the United Sta ...
was in 1914 part of the 6th Brigade that was part of the 2nd Infantry Division, which was itself part of 1st Army Corps), the British Army sometimes also used the term expeditionary force or field force
A field force in British, Indian Army and Tanzanian military parlance is a combined arms land force operating under actual or assumed combat circumstances, usually for the length of a specific military campaign. It is used by other nations, but c ...
to describe a body made up of British Army units, most notably the British Expeditionary Force, or of a mixture of British Army, Indian Army, or Imperial auxiliary units, such as the Malakand Field Force
The siege of Malakand was the 26 July – 2 August 1897 siege of the British garrison in the Malakand region of colonial British India's North West Frontier Province.Nevill p. 232 The British faced a force of Pashtun tribesmen whose tribal la ...
(this is similarly to the naval use of the term task force
A task force (TF) is a unit or formation established to work on a single defined task or activity. Originally introduced by the United States Navy, the term has now caught on for general usage and is a standard part of NATO terminology. Many ...
). In this usage, ''force'' is used to describe a self-reliant body able to act without external support, at least within the parameters of the task or objective for which it is employed.
British Empire
 During the later half of the 17th century, and in particular, throughout the 18th century, British foreign policy sought to contain the expansion of rival European powers through military, diplomatic and commercial means, especially of its chief competitors
During the later half of the 17th century, and in particular, throughout the 18th century, British foreign policy sought to contain the expansion of rival European powers through military, diplomatic and commercial means, especially of its chief competitors Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. This saw Britain engage in a number of intense conflicts over colonial possessions and world trade, including a long string of Anglo-Spanish and Anglo-Dutch wars, as well as a series of "world wars" with France, such as; the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
(1756–1763), the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsb ...
(1792–1802) and the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
(1803–1815). During the Napoleonic wars, the Royal Navy victory at Trafalgar Trafalgar most often refers to:
* The Battle of Trafalgar (1805), fought near Cape Trafalgar, Spain
* Trafalgar Square, a public space and tourist attraction in London, England
Trafalgar may also refer to:
Places
* Cape Trafalgar, a headland in ...
(1805) under the command of Horatio Nelson
Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte ( – 21 October 1805) was a Royal Navy officer whose leadership, grasp of strategy and unconventional tactics brought about a number of decisive British naval victories during the French ...
(aboard HMS ''Victory'') marked the culmination of British maritime supremacy, and left the Navy in a position of uncontested hegemony at sea. By 1815 and the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars, Britain had risen to become the world's dominant great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
and the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
subsequently presided over a period of relative peace, known as Pax Britannica
''Pax Britannica'' (Latin for , modelled after '' Pax Romana'') refers to the relative peace between the great powers in the time period roughly bounded by the Napoleonic Wars and World War I. During this time, the British Empire became the ...
., pp. 508–10.
With Britain's old rivals no-longer a threat, the 19th century saw the emergence of a new rival, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, and a strategic competition in what became known as The Great Game
The Great Game was a rivalry between the 19th-century British and Russian empires over influence in Central Asia, primarily in Afghanistan, Persia, and Tibet. The two colonial empires used military interventions and diplomatic negotiations t ...
for supremacy in Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
. Britain feared that Russian expansionism in the region would eventually threaten the Empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
in India. In response, Britain undertook a number of pre-emptive actions against perceived Russian ambitions, including the First Anglo-Afghan War
The First Anglo-Afghan War () was fought between the British Empire and the Emirate of Kabul from 1838 to 1842. The British initially successfully invaded the country taking sides in a succession dispute between emir Dost Mohammad Khan ( Bara ...
(1839–1842), the Second Anglo-Afghan War
The Second Anglo-Afghan War (Dari: جنگ دوم افغان و انگلیس, ) was a military conflict fought between the British Raj and the Emirate of Afghanistan from 1878 to 1880, when the latter was ruled by Sher Ali Khan of the Barakzai dy ...
(1878–1880) and the British expedition to Tibet
The British expedition to Tibet, also known as the Younghusband expedition, began in December 1903 and lasted until September 1904. The expedition was effectively a temporary invasion by British Indian Army, British Indian Armed Forces under th ...
(1903–1904). During this period, Britain also sought to maintain the balance of power in Europe, particularly against Russian expansionism, who at the expense of the waning Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
had ambitions to "carve up the European part of Turkey". This ultimately led to British involvement in the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
(1854–1856) against the Russian Empire.

First World War
The beginning of the 20th century served to reduce tensions between Britain and the Russian Empire, partly due to the emergence of a unifiedGerman Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
. The era brought about an Anglo-German naval arms race
The arms race between Great Britain and Germany that occurred from the last decade of the nineteenth century until the advent of World War I in 1914 was one of the intertwined causes of that conflict. While based in a bilateral relationship tha ...
, which encouraged significant advancements in maritime technology, including Dreadnought
The dreadnought was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an effect when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her were referred to as "dreadnoughts", ...
s, torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such ...
es, submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
s), and, in 1906, Britain determined that its only likely naval enemy was Germany. The accumulated tensions in European relations finally broke out into the hostilities of the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
(1914–1918), in what is recognised today, as the most devastating war in British military history, with nearly 800,000 men killed and over 2 million wounded. Allied victory resulted in the defeat of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
, the end of the German Empire, the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
and the establishment of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
.
Second World War
 Germany was defeated in the First World War, but by 1933
Germany was defeated in the First World War, but by 1933 fascism
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural social hie ...
had given rise to Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, which under the leadership of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
re-militarised in defiance of the Treaty of Versailles. Once again tensions accumulated in European relations, and following Germany's invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak R ...
in September 1939, the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
began (1939–1945). The conflict was the most widespread in British history, with British Empire and Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
troops engaged in military campaigns in Europe, North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, and the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
. Approximately 390,000 British Empire and Commonwealth troops died. Allied victory resulted in the defeat of the Axis powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Ge ...
and the establishment of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
, replacing the League of nations.
Cold War
, raf.mod.uk and later epitomised by its political defeat during the
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, also known as the Second Arab–Israeli War, the Tripartite Aggression in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel, was a British–French–Israeli invasion of Egypt in 1956. Israel invaded on 29 October, having done so w ...
(1956). Reflecting Britain's new role in the world and the escalation of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
(1947–1991), the country became a founding member of the NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
military alliance in 1949. Defence Review
A Defence Review is the process by which government of the United Kingdom decides upon its overall defence policy and upon the means and resources devoted to achieving its defence objectives. Such reviews can happen when political or economic facto ...
s, such as those in 1957
Events January
* January 1 – The Saarland joins West Germany.
* January 3 – Hamilton Watch Company introduces the first electric watch.
* January 5 – South African player Russell Endean becomes the first batsman to be Dismissal (cricke ...
and 1966
Events January
* January 1 – In a coup, Colonel Jean-Bédel Bokassa takes over as military ruler of the Central African Republic, ousting President David Dacko.
* January 3 – 1966 Upper Voltan coup d'état: President Maurice Yaméogo i ...
, announced significant reductions in conventional forces, the pursuement of a doctrine based on nuclear deterrence
Deterrence theory refers to the scholarship and practice of how threats of using force by one party can convince another party to refrain from initiating some other course of action. The topic gained increased prominence as a military strategy d ...
, and a permanent military withdrawal east of Suez
''East of Suez'' is a term used in United Kingdom, British military and political discussions in reference to interests east of the Suez Canal, and may or may not include the Middle East.
. By the mid-1970s, the armed forces had reconfigured to focus on the responsibilities allocated to them by NATO.Vanguard to Trident 1945–2000, royal-navy.mod.ukKennedy (2004), ''British Naval Strategy East of Suez, 1900–2000: Influence and Actions'', p193 The
British Army of the Rhine
British Army of the Rhine (BAOR) was the name given to British Army occupation forces in the Rhineland, West Germany, after the First and Second World Wars, and during the Cold War, becoming part of NATO's Northern Army Group (NORTHAG) tasked ...
and RAF Germany
Royal Air Force Germany, commonly known as RAF Germany, and abbreviated RAFG, was a command of the Royal Air Force (RAF) and part of British Forces Germany (BFG). It consisted of units located in Germany, initially in what was known as West G ...
consequently represented the largest and most important overseas commitments that the armed forces had during this period, while the Royal Navy developed an anti-submarine warfare specialisation, with a particular focus on countering Soviet Union, Soviet submarines in the Eastern Atlantic and North Sea.
While NATO obligations took increased prominence, Britain nonetheless found itself engaged in a number of low-intensity conflicts, including a spate of insurgencies against colonial occupation.Chandler & Beckett (2003), pp350–351 However the Dhofar Rebellion (1962–1976) and The Troubles (1969–1998) emerged as the primary operational concerns of the armed forces. Perhaps the most important conflict during the Cold War, at least in the context of British defence policy, was the Falklands War (1982).
Since Cold War (1985–91), the end of the Cold War, an increasingly international role for the armed forces has been pursued, with re-structuring to deliver a greater focus on expeditionary warfare and power projection. This entailed the armed forces often constituting a major component in peacekeeping
Peacekeeping comprises activities, especially military ones, intended to create conditions that favor lasting peace. Research generally finds that peacekeeping reduces civilian and battlefield deaths, as well as reduces the risk of renewed w ...
and humanitarian missions under the auspices of the United Nations, NATO, and other multinational operations, including: peacekeeping responsibilities in the Balkans and Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, the 2000 Operation Palliser, intervention in Sierra Leone and participation in the UN-mandated Libyan no-fly zone, no-fly zone over Libya (2011). Post-September 11 attacks, 9/11, the armed forces became heavily committed to the War on Terror (2001–present), with lengthy campaigns in War in Afghanistan (2001–2021), Afghanistan (2001–2021) and Iraq War, Iraq (2003–2009), and more recently as part of the Military intervention against ISIL (2014–present). Britain's military intervention against Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, Islamic State was expanded following a parliamentary vote to launch a bombing campaign over Syria; an extension of the bombing campaign requested by the Iraqi government against the same group. In addition to the aerial campaign, the British Army has trained and supplied allies on the ground and the Special Air Service, the Special Boat Service, and the Special Reconnaissance Regiment (British special forces) has carried out various missions on the ground in both Syria and Iraq.
The armed forces have also been called upon to assist with national emergencies through the provisions of the military aid to the civil authorities (MACA) mechanism. This has seen the armed forces assist government departments and civil authorities responding to flooding, food shortages, wildfires, terrorist attacks and the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom, COVID-19 pandemic; the armed forces' support to the latter falls under Operation Rescript, described as the UK's "biggest ever homeland military operation in peacetime" by the Ministry of Defence.
Figures released by the Ministry of Defence on 31 March 2016 show that 7,185 British Armed Forces personnel have lost their lives in Military awards and decorations of the United Kingdom, medal earning theatres since the end of the Second World War.UK Armed Forces Deaths: Operational deaths post World War II 3 September 1945 to 17 February 2016, Ministry of Defence, gov.uk, Published 31 March 2016 In 2025, under Prime Minister Keir Starmer, the UK published a new Strategic Defence Review (2025), Strategic Defence Review (SDR) calling for a shift to "warfighting readiness". Major investments were announced, including the expansion of the SSN-AUKUS attack submarine program to up to 12 boats, acquisition of long-range weapons and advanced air-defence systems, and a possible entry into NATO's nuclear-sharing scheme via the F-35A platform.
Today
Command


King Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms.
Charles was born at Buckingham Palace during the reign of his maternal grandfather, King George VI, and ...
, sovereign of the United Kingdom
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers regulated by the British cons ...
, is the Head of the Armed Forces
Head of the Armed Forces is the position of the sovereign of the United Kingdom as commander-in-chief of the British Armed Forces. Supreme military authority is vested in the monarch and extends to the exercise of several personal prerogative ...
, with officers and personnel swearing allegiance
An allegiance is a duty of fidelity said to be owed, or freely committed, by the people, subjects or citizens to their state or sovereign.
Etymology
The word ''allegiance'' comes from Middle English ' (see Medieval Latin ', "a liegance"). The ...
to him. Long-standing constitutional convention, however, has ''de facto'' vested military authority and associated Royal prerogative in the United Kingdom, royal prerogative powers in the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister and the secretary of state for defence
The secretary of state for defence, also known as the defence secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with responsibility for the Ministry of Defence. As a senior minister, the incumbent is a member of the ...
, with the former (acting with the support of the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
) making the key decisions on the use of the armed forces. As the prime minister is not the formal head of the armed forces, the chief of the defence staff could refuse a direction by them to use the Nuclear weapons of the United Kingdom, UK's nuclear arsenal.
The Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence is the government department charged with formulating and executing defence policy. It currently employs 56,860 civilian staff members as of 1 October 2015. The department is administered by the secretary of state for defence who is assisted by the Minister of State for the Armed Forces, Minister of State for Defence Procurement (UK), Minister for Defence Procurement, and Minister for Veterans' Affairs. Responsibility for the management of the forces is delegated to a number of committees: the Defence Council, Chiefs of Staff Committee, Defence Management Board and three single-service boards. The Defence Council, composed of senior representatives of the services and the Ministry of Defence, provides the "formal legal basis for the conduct of defence". The three constituent single-service committees (Admiralty Board, Army Board and Air Force Board) are chaired by the secretary of state for defence.
The Chief of the Defence Staff (United Kingdom), chief of the defence staff (CDS) is the senior-most officer of the armed forces and is an appointment that can be held by an admiral, air chief marshal or general. Before the practice was discontinued in the 1990s, those who were appointed to the position of CDS had been elevated to the Five-star rank, most senior rank in their respective service. The CDS, along with the permanent under secretary, are the principal military advisers to the secretary of state. All three services have their own respective professional chiefs; the First Sea Lord for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, the Chief of the General Staff (United Kingdom), chief of the general staff for the British Army, Army and the Chief of the Air Staff (United Kingdom), chief of the air staff for the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
.
Personnel
As of 1 July 2025 the British Armed Forces are a professional force with a total strength of 180,779 personnel, consisting of 136,117 UK Regulars and 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 31,967 Volunteer Reserves (United Kingdom), Volunteer Reserves and 8,568 "Other Personnel".UK Armed Forces: Quarterly Service Personnel Statistics. 1 July 2023. MoD. Published 17 September 2023. Retrieved 23 September 2023. As a percentage breakdown of UK Service Personnel, 77.1% are UK Regulars and Gurkhas, 18.8% are Volunteer Reserves and 4.1% are composed of Other Personnel. In addition, all ex-Regular personnel retain a "statutory liability for service" and are liable to be recalled (under Section 52 of the Reserve Forces Act (RFA) 1996) for duty during wartime, which is known as the Regular Reserve. MoD publications since April 2013 no longer report the entire strength of the Regular Reserve, instead they only give a figure for Regular Reserves who serve under a fixed-term reserve contract. These contracts are similar in nature to those of the Volunteer Reserve.gov.uk MoD – reserves and cadet strengths
, table 4 page 13. See note 2. April 2014. The distribution of personnel between the services and categories of service on 1 Janurary 2025 was as follows: On 1 April 2024, most personnel in the UK Regular Forces were stationed in the United Kingdom (around 96%). Of the 5,700 personnel stationed overseas, around two thirds were in Europe (66%), while 14% were stationed in North America, 6% in North Africa and the Middle East, 6% in Asia and 5% in Sub-Saharan Africa. 1,230 personnel were distributed across several regions in Germany, primarily North Rhine-Westphalia as part of British Army Germany. However, up to 750 of these were Locally Engaged Civilians.
Defence expenditure
According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, the United Kingdom is in sixth place in the world's military spending list in 2023. For comparison: Great Britain spends more in absolute terms than Germany, Ukraine, France or Japan, similar to Saudi Arabia, but less than India, Russia, China or the United States. In September 2011, according to Professor Malcolm Chalmers of the Royal United Services Institute, current "planned levels of defence spending should be enough for the United Kingdom to maintain its position as one of the world's top military powers, as well as being one of NATO-Europe's top military powers. Its edge – not least its qualitative edge – in relation to rising Asian powers seems set to erode, but will remain significant well into the 2020s, and possibly beyond." The Strategic Defence and Security Review 2015 committed to spending 2% of GDP on defence and announced a £178 billion investment over ten years in new equipment and capabilities. On 8 March 2023 Prime Minister Rishi Sunak announced a further £5bn in defence spending with a long-term goal of an increased spending to 2.5% of GDP.Nuclear weapons
 The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear weapon states under the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, Non-Proliferation Treaty and maintains an independent Deterrence theory, nuclear deterrent, currently consisting of four ballistic missile submarines, UGM-133 Trident II submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and 160 operational Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads. This is known as Trident nuclear programme, Trident in both public and political discourse (with nomenclature taken after the UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missile). Trident is operated by the Royal Navy Submarine Service, charged with delivering a 'Continuous At-Sea Deterrent' (CASD) capability, whereby one of the ''Vanguard''-class strategic submarines is always on patrol.Royal Navy – Continuous at sea deterrent
The United Kingdom is one of five recognised nuclear weapon states under the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, Non-Proliferation Treaty and maintains an independent Deterrence theory, nuclear deterrent, currently consisting of four ballistic missile submarines, UGM-133 Trident II submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and 160 operational Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads. This is known as Trident nuclear programme, Trident in both public and political discourse (with nomenclature taken after the UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missile). Trident is operated by the Royal Navy Submarine Service, charged with delivering a 'Continuous At-Sea Deterrent' (CASD) capability, whereby one of the ''Vanguard''-class strategic submarines is always on patrol.Royal Navy – Continuous at sea deterrent, royalnavy.mod.uk, Accessed 6 December 2014 According to the British Government, since the introduction of UK Polaris programme, Polaris (Trident's predecessor) in the 1960s, from April 1969 "the Royal Navy's ballistic missile boats have not missed a single day on patrol", giving what the Defence Council described in 1980 as a deterrent "effectively invulnerable to pre-emptive attack". As of 2015, it has been British Government policy for the ''Vanguard''-class strategic submarines to carry no more than 40 nuclear warheads, delivered by eight UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missiles. In contrast with the other recognised nuclear weapon states, the United Kingdom operates only a submarine-based delivery system, having decommissioned its tactical WE.177 free-fall bombs in 1998. The House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons voted on 18 July 2016 in favour of replacing the ''Vanguard''-class submarines with a new generation of s. The programme will also contribute to extending the life of the UGM-133 Trident II ballistic missiles and modernise the infrastructure associated with the CASD. Former United Kingdom and weapons of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction possessed by the United Kingdom include both biological and Chemical weapons and the United Kingdom, chemical weapons. These were renounced in 1956 and subsequently destroyed.
Overseas military installations
 The British Armed Forces historically relied on four Imperial fortress colonies (Bermuda, Gibraltar, Halifax and its environs in Nova Scotia, and Malta), where dockyards were established, naval squadrons based, soldiers garrisoned, and naval and military stores stockpiled. These acted as lynchpins in maintaining British naval supremacy on the Atlantic and its connected seas. As, until the end of the First World War, it was presumed the only navies that might prove a threat were all of countries on, or off, the Atlantic, no Imperial fortress was established in the Pacific or Indian Oceans, to which power would be extended from Bermuda and Malta following the completion of the Panama and Suez canals. Local-service military reserve units were raised in some of the Imperial fortresses (notably Bermuda and Malta), which could be embodied for full time service in war time to reinforce the regular garrisons, and these were funded by the War Office as part of the British Army. After the First World War, the growing belligerence and naval power of the Japanese Empire led to the construction of the Singapore Naval Base. The regular British Armed Forces otherwise were distributed around the world where required to guard against invasion or rebellion, reinforced in some colonies by locally raised reserve forces. In colonies where there was no strategic requirement, regular forces were rarely stationed, with local governments encouraged to maintain and fund military reserve units as contributions to their own defence (although these units were ultimately under the control of the national, i.e. British, Government via the colonial Governors as defence is not a competency that has been delegated to local governments). Under the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation alliance, and with the steady reduction of both the British Empire and the British Armed Forces over the decades that followed the Second World War, the significance of the three remaining Imperial fortresses (military control of Halifax having passed to the new Dominion government following the 1867 Confederation of Canada, and naval control transferred in 1905 to what was to become the Royal Canadian Navy) rapidly faded. The Bermuda-based North America and West Indies Station was abolished in 1956, and the last regular army units removed from the Bermuda Command in 1957 (leaving only two part-time reserve units), with the naval dockyard in Bermuda reduced to a base, without repair or refit capabilities, in 1951 and finally closed in 1995, following the Cold War (United States and Canadian bases in Bermuda closed in the same period), leaving only the
The British Armed Forces historically relied on four Imperial fortress colonies (Bermuda, Gibraltar, Halifax and its environs in Nova Scotia, and Malta), where dockyards were established, naval squadrons based, soldiers garrisoned, and naval and military stores stockpiled. These acted as lynchpins in maintaining British naval supremacy on the Atlantic and its connected seas. As, until the end of the First World War, it was presumed the only navies that might prove a threat were all of countries on, or off, the Atlantic, no Imperial fortress was established in the Pacific or Indian Oceans, to which power would be extended from Bermuda and Malta following the completion of the Panama and Suez canals. Local-service military reserve units were raised in some of the Imperial fortresses (notably Bermuda and Malta), which could be embodied for full time service in war time to reinforce the regular garrisons, and these were funded by the War Office as part of the British Army. After the First World War, the growing belligerence and naval power of the Japanese Empire led to the construction of the Singapore Naval Base. The regular British Armed Forces otherwise were distributed around the world where required to guard against invasion or rebellion, reinforced in some colonies by locally raised reserve forces. In colonies where there was no strategic requirement, regular forces were rarely stationed, with local governments encouraged to maintain and fund military reserve units as contributions to their own defence (although these units were ultimately under the control of the national, i.e. British, Government via the colonial Governors as defence is not a competency that has been delegated to local governments). Under the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation alliance, and with the steady reduction of both the British Empire and the British Armed Forces over the decades that followed the Second World War, the significance of the three remaining Imperial fortresses (military control of Halifax having passed to the new Dominion government following the 1867 Confederation of Canada, and naval control transferred in 1905 to what was to become the Royal Canadian Navy) rapidly faded. The Bermuda-based North America and West Indies Station was abolished in 1956, and the last regular army units removed from the Bermuda Command in 1957 (leaving only two part-time reserve units), with the naval dockyard in Bermuda reduced to a base, without repair or refit capabilities, in 1951 and finally closed in 1995, following the Cold War (United States and Canadian bases in Bermuda closed in the same period), leaving only the Royal Bermuda Regiment
The Royal Bermuda Regiment (RBR) is the home defence unit of the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is a single Territorial Army (United Kingdom), territorial infantry battalion#British Army, battalion that was formed on the amalgamation ...
and the Bermuda Sea Cadet Corps there today. Malta became independent in 1964, and the last British armed forces personnel were removed from the former colony in 1979. Gibraltar continues to be used by the regular British Armed Forces, though the naval and military establishment in the colony (now termed a ''British Overseas Territory'') has been reduced to several Royal Naval patrol craft, the locally raised Royal Gibraltar Regiment
The Royal Gibraltar Regiment is part of British Forces Gibraltar for the British overseas territory of Gibraltar, which historically, along with Bermuda, Halifax, Nova Scotia (prior to the 1867 Confederation of Canada), and Malta, had been d ...
, and a Royal Air Force Station without aircraft based on it.
The British Armed Forces today maintain a number of overseas garrisons and military facilities which enable the country to conduct operations worldwide. The majority of Britain's permanent military installations are located on British Overseas Territories (BOTs) or British Empire, former colonies which retain close diplomatic ties with the United Kingdom, and located in areas of strategic importance. The most significant of these are the "Permanent Joint Operating Bases" (PJOBs), located on the four overseas territories of Cyprus (British Forces Cyprus), Gibraltar (British Forces Gibraltar), the Falkland Islands (Military of the Falkland Islands, British Forces South Atlantic Islands) and Diego Garcia (British Forces British Indian Ocean Territories). While not a PJOB, Ascension Island (another BOT) is home to the airbase RAF Ascension Island, notable for use as a staging post during the 1982 Falklands War, the territory is also the site of a joint UK-US signals intelligence facility.
Qatar is home to RAF Al Udeid, a Royal Air Force outpost at Al Udeid Air Base which serves as the operational headquarters for No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group (United Kingdom), No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group and its operations across the Middle East. A large Royal Navy HMS Jufair, Naval Support Facility (NSF) is located in Bahrain, established in 2016 it marks the British return East of Suez. In support of the Five Power Defence Arrangements
The Five Power Defence Arrangements (FPDA) are a series of bilateral defence relationships established by a series of multi-lateral agreements between Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United Kingdom, all of which are Commonwe ...
(FPDA), the United Kingdom retains a naval repair and logistics support facility at Sembawang, Sembawang wharf, Singapore. ("''The White Ensign is still flying above the operations of Naval Party 1022 (NP1022), based at Sembawang Wharves in Singapore.''") Other overseas military installations include; British Forces Brunei, British Forces Germany, the British Army Training Unit Kenya, British Army Training Unit Suffield in Canada, British Army Training and Support Unit Belize, and British Gurkhas Nepal.
Some British Overseas Territories also maintain locally raised units and regiments; The Royal Bermuda Regiment, the Falkland Islands Defence Force
The Falkland Islands Defence Force (FIDF) is the locally maintained volunteer defence unit in the Falkland Islands, a British Overseas Territory. The FIDF works alongside the military units supplied by the United Kingdom to ensure the security ...
, the Royal Gibraltar Regiment
The Royal Gibraltar Regiment is part of British Forces Gibraltar for the British overseas territory of Gibraltar, which historically, along with Bermuda, Halifax, Nova Scotia (prior to the 1867 Confederation of Canada), and Malta, had been d ...
, the Royal Montserrat Defence Force
The Royal Montserrat Defence Force is the home defence unit of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of Montserrat. The force has an authorized strength level objective of 50 reserve personnel as of 2021-22, akin in size ...
, the Cayman Islands Regiment, and the Turks and Caicos Regiment. Though their primary mission is "home defence", individuals have volunteered for operational duties. The Royal Bermuda Regiment is an amalgam of the Bermuda Militia Artillery
The Bermuda Militia Artillery was a unit of part-time soldiers organised in 1895 as a reserve for the Royal Garrison Artillery detachment of the Regular Army garrison in the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda. Militia Artillery units of the Un ...
(which had been part of the Royal Regiment of Artillery) and the Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps
The Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps (BVRC) was created in 1894 as a reserve for the British Army, Regular Army infantry component of the Bermuda Garrison. Renamed the ''Bermuda Rifles'' in 1951, it was amalgamated into the Bermuda Regiment in 1965 ...
, raised in the 1890s as Imperial forces funded by the War Office as part of the British Army, and both antecedent units sent contingents to the Western Front during the First World War. They also sent contingents that served in North-Western Europe, and Italy and North Africa during the Second World War. The Royal Gibraltar Regiment mobilised section-sized units for attachment to British regiments deployed during the Iraq War. The Isle of Man, a Crown dependency hosts a multi-capability recruiting and training unit of the Army Reserve (United Kingdom), British Army Reserve.
Since 1969 Britain has had a military satellite communications system, Skynet (satellite), Skynet, initially in large part to support East of Suez bases and deployments. Since 2015 Skynet has offered near global coverage.
Expeditionary forces
The British Armed Forces place significant importance in the ability to conduct expeditionary warfare. Professor of International Politics, Adrian Hyde-Price, highlights that in the post-Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
era both Britain and France have re-focused their attention ''"towards expeditionary warfare and power projection. Power projection has always been an element of British and French military thinking given their residual overseas interests, but it has now moved centre stage."'' While the armed forces are expeditionary in nature, it maintains a core of "high readiness" forces trained and equipped to deploy at very short notice, these include; the Joint Expeditionary Force (Maritime) (Royal Navy), United Kingdom Commando Force, UK Commando Force (Royal Marines), and 16 Air Assault Brigade (British Army). Frequently, these forces will act as part of a larger tri-service effort, under the direction of Permanent Joint Headquarters, or along with like-minded allies under the Joint Expeditionary Force. Similarly, under the auspices of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
, such expeditionary forces are designed to meet Britain's obligations to the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps and other NATO operations.
In 2010, the governments of the United Kingdom and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
signed the The Lancaster House Treaties (2010), Lancaster House Treaties which committed both governments to the creation of a Franco-British Combined Joint Expeditionary Force. It is envisaged as a deployable joint force, for use in a wide range of crisis scenarios, up to and including high intensity combat operations. As a joint force it involves all three armed Services: a land component composed of formations at national brigade level, maritime and air components with their associated Headquarters, together with logistics and support functions.
The Armed Forces
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is a technologically sophisticated naval force, and as of December 2024 consists of List of active Royal Navy ships, 62 commissioned ships with an additional 11 support vessels of various types operated by the Royal Fleet Auxiliary. Command of deployable assets is exercised by the Fleet Commander of the His Majesty's Naval Service, Naval Service. Personnel matters are the responsibility of the Second Sea Lord/Commander-in-Chief Naval Home Command, an appointment usually held by a vice-admiral. The Surface Fleet consists of aircraft carriers, destroyers, frigates, Patrol boat, patrol vessels, Minesweeper, mine-countermeasure vessels, and other miscellaneous vessels. The Surface Fleet has been structured around a single fleet since the abolition of the Eastern Fleet, Eastern and Western Fleet (United Kingdom), Western fleets in 1971. The recently built Type 45 destroyers are stealthy and technologically advanced air-defence destroyers. The Royal Navy has commissioned twoRoyal Marines
The Royal Marines are the Royal Navy's amphibious troops. Consisting of a single manoeuvre brigade (UK Commando Force) and various independent units, the Royal Marines specialise in amphibious warfare, amphibious, arctic warfare, arctic, and mountain warfare. Contained within UK Commando Force are three attached army units; 383 Commando Petroleum Troop RLC, 29th Commando Regiment Royal Artillery, a field artillery regiment based in Plymouth, and 24 Commando Regiment Royal Engineers. The Commando Logistic Regiment consists of personnel from the Army, Royal Marines, and Royal Navy.British Army
The British Army is the land force of the British Armed Forces, and is made up of the Regular Army and the part-time Army Reserve (United Kingdom), Army Reserve. The Army is commanded by the Chief of the General Staff (United Kingdom), Chief of the General Staff, a four-star general within Army Headquarters (United Kingdom), Army Headquarters, based at Marlborough Lines, Andover. Deployable combat formations are; * 1st (United Kingdom) Division, 1st (UK) Division, consisting of 16 Air Assault Brigade Combat Team and four other Light or Light Mechanised Brigade Combat Teams, with supporting engineering, logistic, intelligence and signals units. * 3rd (United Kingdom) Division, 3rd (UK) Division, consisting of 1st Deep Recce Strike Brigade Combat Team, 7th Air Defence Group, 7 Air Defence Group, and two Armoured Brigade Combat Teams, with supporting engineering, logistic, intelligence and signals units. * Field Army Troops, consisting of the new Ranger Regiment (United Kingdom), Ranger Regiment, in Army Special Operations Brigade; Security Force Assistance Brigade and 77th Brigade (United Kingdom), 77 Brigade, a Psychological warfare, psychological operations unit. The Infantry of the British Army has a strength of 48 battalions (32 regular and 16 reserve), structured under 17 unique regiments. These battalions are trained and equipped for specific roles within their respective Brigade Combat Teams (BCT); Light infantry, Light Infantry, such as the famous 1st Battalion Grenadier Guards, within the 4th Light Brigade Combat Team, fight on foot without armoured vehicles; Mechanized infantry, Light Mechanised Infantry, such as the 1st Battalion Royal Yorkshire Regiment, within the 7th Light Mechanised Brigade Combat Team, operate the Ocelot (vehicle), Foxhound protected mobility vehicle; Armoured Infantry (to become Heavy Mechanised Infantry under Future Soldier (British Army), Future Soldier), such as the 1st Battalion Royal Regiment of Fusiliers, within the 20th Armoured Brigade Combat Team (United Kingdom), 20th Armoured Infantry Brigade Combat Team, operate the Warrior tracked armoured vehicle, Warrior infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), but will be equipped with the new Boxer (armoured fighting vehicle), Boxer mechanised infantry vehicle from 2024. The four battalions of the Parachute Regiment (United Kingdom), Parachute Regiment, forming 16 Air Assault Brigade Combat Team and part of Special Forces Support Group, are the British Army's elite airborne infanteers, held at high readiness and specialising in rapid deployment by parachute and helicopter, widely regarded as the "fittest, most aggressive, resilient and disciplined regiment in the British Army."
The Royal Armoured Corps provides the armoured capability of the British Army. The Royal Tank Regiment, Queen's Royal Hussars and Royal Wessex Yeomanry (of the Army Reserve (United Kingdom), Army Reserve) operate Challenger 2 main battle tanks, which are being upgraded to Challenger 3, and are part of 3rd (United Kingdom) Division, 3rd (UK) Division's Armoured Brigade Combat Teams. Armoured Cavalry regiments, such as the Royal Dragoon Guards, currently operate the Warrior tracked armoured vehicle, Warrior IFV on an interim basis, until General Dynamics Ajax, Ajax reaches full operating capability. There are six Light Cavalry regiments (three Regular + three Reserve) equipped with the Jackal (vehicle), Jackal 2 and Jackal (vehicle)#Coyote, Coyote TSV, tasked with providing reconnaissance and fire support. The Household Cavalry, made up of the Life Guards (United Kingdom), Life Guards and the Blues and Royals, operate in a dual role of Armoured Cavalry and Mounted Ceremonial on Horse Guards (building), Horse Guards in London, and for state occasions.
The four battalions of the Parachute Regiment (United Kingdom), Parachute Regiment, forming 16 Air Assault Brigade Combat Team and part of Special Forces Support Group, are the British Army's elite airborne infanteers, held at high readiness and specialising in rapid deployment by parachute and helicopter, widely regarded as the "fittest, most aggressive, resilient and disciplined regiment in the British Army."
The Royal Armoured Corps provides the armoured capability of the British Army. The Royal Tank Regiment, Queen's Royal Hussars and Royal Wessex Yeomanry (of the Army Reserve (United Kingdom), Army Reserve) operate Challenger 2 main battle tanks, which are being upgraded to Challenger 3, and are part of 3rd (United Kingdom) Division, 3rd (UK) Division's Armoured Brigade Combat Teams. Armoured Cavalry regiments, such as the Royal Dragoon Guards, currently operate the Warrior tracked armoured vehicle, Warrior IFV on an interim basis, until General Dynamics Ajax, Ajax reaches full operating capability. There are six Light Cavalry regiments (three Regular + three Reserve) equipped with the Jackal (vehicle), Jackal 2 and Jackal (vehicle)#Coyote, Coyote TSV, tasked with providing reconnaissance and fire support. The Household Cavalry, made up of the Life Guards (United Kingdom), Life Guards and the Blues and Royals, operate in a dual role of Armoured Cavalry and Mounted Ceremonial on Horse Guards (building), Horse Guards in London, and for state occasions.
Royal Air Force
 The Royal Air Force has a large operational fleet that fulfils various roles, consisting of both List of active United Kingdom military aircraft, fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. Frontline aircraft are controlled by RAF Air Command, Air Command, which is organised into five Group (air force), groups defined by function: No. 1 Group RAF, 1 Group (Air Combat), No. 2 Group RAF, 2 Group (Air Support), No. 11 Group RAF, 11 Group (Air and Space operations), No. 22 Group, 22 Group (training aircraft and ground facilities) and No. 38 Group RAF, 38 Group (Royal Air Force's Engineering, Logistics, Communications and Medical Operations units). In addition No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group (United Kingdom), 83 Expeditionary Air Group directs formations in the Middle East and the No. 38 Group RAF, 38 Group combines the expeditionary Combat Support, combat support and Combat Service Support, combat service support units of the RAF. Deployable formations consist of Expeditionary Air Wing (air force unit), Wings and Squadron (aviation), squadrons—the basic unit of the Air Force. Independent Flight (military unit), flights are deployed to facilities in Brunei, the Falkland Islands, Iraq, and the United States.
The Royal Air Force operates multi-role and single-role fighters, reconnaissance and patrol aircraft, tankers, transports, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles, and various types of training aircraft.
Ground units are also maintained by the Royal Air Force, most prominently the RAF Police and the Royal Air Force Regiment (RAF Regt). The Royal Air Force Regiment essentially functions as the ground defence force of the RAF, optimised for the specialist role of fighting on and around forward airfields, which are densely packed with operationally vital aircraft, equipment, infrastructure and personnel. The Regiment contains nine regular squadrons, supported by five squadrons of the Royal Auxiliary Air Force Regiment. In addition, it provides Forward air control, Forward Air Controllers to defence as well as a contribution to the Special Forces Support Group.
The Royal Air Force has a large operational fleet that fulfils various roles, consisting of both List of active United Kingdom military aircraft, fixed-wing and rotary aircraft. Frontline aircraft are controlled by RAF Air Command, Air Command, which is organised into five Group (air force), groups defined by function: No. 1 Group RAF, 1 Group (Air Combat), No. 2 Group RAF, 2 Group (Air Support), No. 11 Group RAF, 11 Group (Air and Space operations), No. 22 Group, 22 Group (training aircraft and ground facilities) and No. 38 Group RAF, 38 Group (Royal Air Force's Engineering, Logistics, Communications and Medical Operations units). In addition No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group (United Kingdom), 83 Expeditionary Air Group directs formations in the Middle East and the No. 38 Group RAF, 38 Group combines the expeditionary Combat Support, combat support and Combat Service Support, combat service support units of the RAF. Deployable formations consist of Expeditionary Air Wing (air force unit), Wings and Squadron (aviation), squadrons—the basic unit of the Air Force. Independent Flight (military unit), flights are deployed to facilities in Brunei, the Falkland Islands, Iraq, and the United States.
The Royal Air Force operates multi-role and single-role fighters, reconnaissance and patrol aircraft, tankers, transports, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles, and various types of training aircraft.
Ground units are also maintained by the Royal Air Force, most prominently the RAF Police and the Royal Air Force Regiment (RAF Regt). The Royal Air Force Regiment essentially functions as the ground defence force of the RAF, optimised for the specialist role of fighting on and around forward airfields, which are densely packed with operationally vital aircraft, equipment, infrastructure and personnel. The Regiment contains nine regular squadrons, supported by five squadrons of the Royal Auxiliary Air Force Regiment. In addition, it provides Forward air control, Forward Air Controllers to defence as well as a contribution to the Special Forces Support Group.
Ministry of Defence
The Ministry of Defence maintains a number of civilian agencies in support of the British Armed Forces. Although they are civilian, they play a vital role in supporting Armed Forces operations, and in certain circumstances are under military discipline: * The Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) operates 11 ships which primarily serve to replenish Royal Navy warships at sea, and also provides an amphibious warfare capability through its three vessels and the aviation support ship RFA Argus (A135), RFA Argus. It is manned by 1,750 civilian personnel and is funded and run by the Ministry of Defence. * The Ministry of Defence Police (MDP) has an established strength of 2,700 police officers which provide armed security, counter terrorism, uniformed policing and investigative services to Ministry of Defence property, personnel, and installations throughout the United Kingdom. * The Defence Equipment and Support (DE&S) is the merged procurement and support organisation within the UK Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom). It came into being on 2 April 2007, bringing together the MoD's Defence Procurement Agency and the Defence Logistics Organisation under the leadership of General Sir Kevin O'Donoghue as the first Chief of Defence Materiel. it has a civilian and military workforce of approx. 20,000 personnel. DE&S is overseen by the Minister for Defence Equipment, Support and Technology. * The UK Hydrographic Office (UKHO) is an organisation within the UK government responsible for providing navigational and other hydrographic information for national, civil and defence requirements. The UKHO is located in Taunton, Somerset, on Admiralty Way and has a workforce of approximately 1,000 staff.Recruitment
 All three services of the British Armed Forces recruit primarily from within the United Kingdom, although citizens from the Commonwealth of Nations and the Republic of Ireland are equally eligible to join.Evans (2005)
All three services of the British Armed Forces recruit primarily from within the United Kingdom, although citizens from the Commonwealth of Nations and the Republic of Ireland are equally eligible to join.Evans (2005)How British Army is fast becoming foreign legion
, timesonline.co.uk The minimum recruitment age is 16 years (although personnel may not serve on armed operations below 18 years, and if under 18 must also have parental consent to join); the maximum recruitment age depends whether the application is for a regular or reserve role; there are further variations in age limit for different corps/regiments. The normal term of engagement is 22 years; however, the minimum service required before resignation is 4 years, plus, in the case of the Army, any service person below the age of 18. A note to add is that in the United Kingdom, people may join the "Cadet Forces" such as the army cadets, Royal Air Force Air Cadets or the sea and Royal Marine Cadets. Young people may join these organisations which are either funded or affiliated with the MOD from the age of 13-18, there is no obligation to then join the armed forces however it teaches key skills in both civilian and military life and is a key recruitment drive for the armed forces. At present, the yearly intake into the armed forces is 11,880 (per the 12 months to 31 March 2014).UK Armed Forces Quarterly Personnel Report
, gov.uk, 1 April 2014 Excluding the Brigade of Gurkhas and the Royal Irish Regiment (1992), Royal Irish Regiment, as of 1 April 2014 there are approximately 11,200 Black and Minority Ethnic (BME) persons serving as Regulars across the three service branches; of those, 6,610 were recruited from outside the United Kingdom. In total, Black and Minority Ethnic persons represent 7.1% of all service personnel, an increase from 6.6% in 2010. Since the year 2000, Sexual orientation and the military of the United Kingdom, sexual orientation has not been a factor considered in recruitment, and homosexuals can serve openly in the armed forces. All branches of the forces have actively recruited at Gay Pride events. The forces keep no formal figures concerning the number of gay and lesbian serving soldiers, saying that the sexual orientation of personnel is considered irrelevant and not monitored.
Role of women
Women have been part of the armed forces, on and off, for centuries, more fully integrated since the early 1990s, including flying fast jets and commanding warships or artillery batteries. As of 1 April 2014, there were approximately 15,840 women serving in the armed forces, representing 9.9% of all service personnel. The first female military pilot was Flight Lieutenant Julie Ann Gibson while Flight Lieutenant Jo Salter was the first fast-jet pilot, the latter flying a Tornado GR1 on missions patrolling the then Iraqi no-fly zones, Northern Iraqi No-Fly Zone. Flight Lieutenant Juliette Fleming and Squadron Leader Nikki Thomas recently were the first Tornado GR4 crew. While enforcing the Libyan No-Fly Zone, Flight Lieutenant Helen Seymour was identified as the first female Eurofighter Typhoon pilot. In August 2011, it was announced that a female lieutenant commander, Sarah West, was to command the frigate . In July 2016, it was announced that women would be allowed to serve in close combat, starting with the Royal Armoured Corps. In July 2017, the Secretary of Defence announced that women would be allowed to enlist in the RAF Regiment from September 2017, a year ahead of schedule. In 2018, women were allowed to apply for all roles in the British military, including the United Kingdom Special Forces, special forces. , the List of senior female officers of the British Armed Forces, most senior serving woman is Four star rank, four-star General Sharon Nesmith, Dame Sharon Nesmith.March
See also
* Armed Forces Day (United Kingdom) * List of military equipment of the United Kingdom * Atholl Highlanders – The only legal private army in Europe under the command of the Duke of Atholl in Scotland * Banknotes of the British Armed Forces * British Forces Broadcasting Service * Community Cadet Forces * Military Covenant – The mutual obligations between the nation and its Armed Forces. * Network-enabled capability – British military concept of achieving enhanced military effect through the better use of information systems. Similar to the US concept of network-centric warfare. * The Championships, Wimbledon#Services stewards * Uniforms of the British Armed Forces * Military history of Scotland * Armed forces in Scotland * Armed forces in WalesNotes
References
External links
British Ministry of Defence
(gov.uk)
Defence Academy of the United Kingdom
(.da.mod.uk)
Royal Navy official website
(royalnavy.mod.uk)
Royal Marines official webpage
(royalnavy.mod.uk)
British Army official website
(army.mod.uk)
Royal Air Force official website
(raf.mod.uk) {{North Atlantic Treaty Organization British Armed Forces, Military of the United Kingdom, British Armed Forces deployments, British Armed Forces deployments