Hellenic State (1941–1944) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hellenic State (, ) was the
 After the fall of Greece, a puppet government with General Georgios Tsolakoglou as its prime minister was installed on April 30, 1941. Tsolakoglou's main qualification for the position was that he surrendered to the Wehrmacht the week before, on April 20, against the express orders of his commanding officer
After the fall of Greece, a puppet government with General Georgios Tsolakoglou as its prime minister was installed on April 30, 1941. Tsolakoglou's main qualification for the position was that he surrendered to the Wehrmacht the week before, on April 20, against the express orders of his commanding officer
Germany and the Second World War Volume V/II
Oxford University Press, 2003, p. 44 The existence of a native Greek government was considered necessary by the Axis powers, in order to give some appearance of legitimacy to their occupation, although it was never given more than an ancillary role. The country's infrastructure had been ruined by the war. Raw materials and foodstuffs were requisitioned, and the government was forced to pay the cost of the occupation, giving rise to inflation, further exacerbated by a "war loan" Greece was forced to grant to Nazi Germany. Requisitions, together with the Allied
The withered vine: logistics and the communist insurgency in Greece, 1945–1949
Greenwood Press, 1999, p. 38
German banknotes circulated only in Greece during the occupation (1941–1944)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hellenic State (1941-1944) * Client states of Nazi Germany * 1940s in Greek politics Fascism in Greece Greek collaborators with Nazi Germany States and territories established in 1941 1941 establishments in Greece States and territories disestablished in 1944 1944 disestablishments in Greece * * * * Client states of Fascist Italy
collaborationist
Wartime collaboration is cooperation with the enemy against one's country of citizenship in wartime. As historian Gerhard Hirschfeld says, it "is as old as war and the occupation of foreign territory".
The term ''collaborator'' dates to the 19th ...
government of Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
during the country's occupation by the Axis powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Ge ...
in the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
History
Establishment
 After the fall of Greece, a puppet government with General Georgios Tsolakoglou as its prime minister was installed on April 30, 1941. Tsolakoglou's main qualification for the position was that he surrendered to the Wehrmacht the week before, on April 20, against the express orders of his commanding officer
After the fall of Greece, a puppet government with General Georgios Tsolakoglou as its prime minister was installed on April 30, 1941. Tsolakoglou's main qualification for the position was that he surrendered to the Wehrmacht the week before, on April 20, against the express orders of his commanding officer Alexandros Papagos
Alexandros Papagos (; 9 December 1883 – 4 October 1955) was a Greek military officer who led the Hellenic Army in World War II and the later stages of the subsequent Greek Civil War.
The only Greek army career officer to rise to the rank of Fie ...
. As King George II with the legitimate Greek government-in-exile
The Greek government-in-exile was formed in 1941, in the aftermath of the Battle of Greece and the subsequent occupation of Greece by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. The government-in-exile was based first in South Africa, then London, then, ...
were in Crete, the new regime avoided all reference to the Greek monarchy
Monarchy of Greece () or Greek monarchy () is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign (''Basileus'') reigns as the head of state of Greece. Monarchy in Greece lasted from 1832 to 1924 and from 1935 to 1973.
Hi ...
and used ''Hellenic State'' as the country's official, generic, name. The collaborationist regime lacked a precise political definition, although Tsolakoglou, a republican officer, considered the Axis occupation as an opportunity to abolish the monarchy, and announced its end upon taking office.Bernhard R. KroenerGermany and the Second World War Volume V/II
Oxford University Press, 2003, p. 44 The existence of a native Greek government was considered necessary by the Axis powers, in order to give some appearance of legitimacy to their occupation, although it was never given more than an ancillary role. The country's infrastructure had been ruined by the war. Raw materials and foodstuffs were requisitioned, and the government was forced to pay the cost of the occupation, giving rise to inflation, further exacerbated by a "war loan" Greece was forced to grant to Nazi Germany. Requisitions, together with the Allied
blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are ...
of Greece, resulted in the Great Famine (Greek: Μεγάλος Λιμός) during the winter of 1941–42, which caused the deaths of an estimated 300,000 people.
Government and politics
The regime was first led by Georgios Tsolakoglou, however he was sacked a year later and replaced by Konstantinos Logothetopoulos, who himself was sacked in 1943. The last prime minister of the Hellenic State wasIoannis Rallis
Ioannis Rallis (; 1878 – 26 October 1946) was the third and last collaborationist prime minister of Greece during the Axis occupation of Greece
The occupation of Greece by the Axis Powers () began in April 1941 after Nazi Germany Battle of ...
, who led the collaborationist regime until its dissolution in 1944. Georgios Bakos, a Greek Army
The Hellenic Army (, sometimes abbreviated as ΕΣ), formed in 1828, is the land force of Greece. The term '' Hellenic'' is the endogenous synonym for ''Greek''. The Hellenic Army is the largest of the three branches of the Hellenic Armed F ...
major general, served as the minister of national defense, a position which Rallis had previously held in the regime. The Hellenic State was widely viewed as a puppet government
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government is a State (polity), state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside Power (international relations), power and subject to its ord ...
and was unpopular with the Greek people.
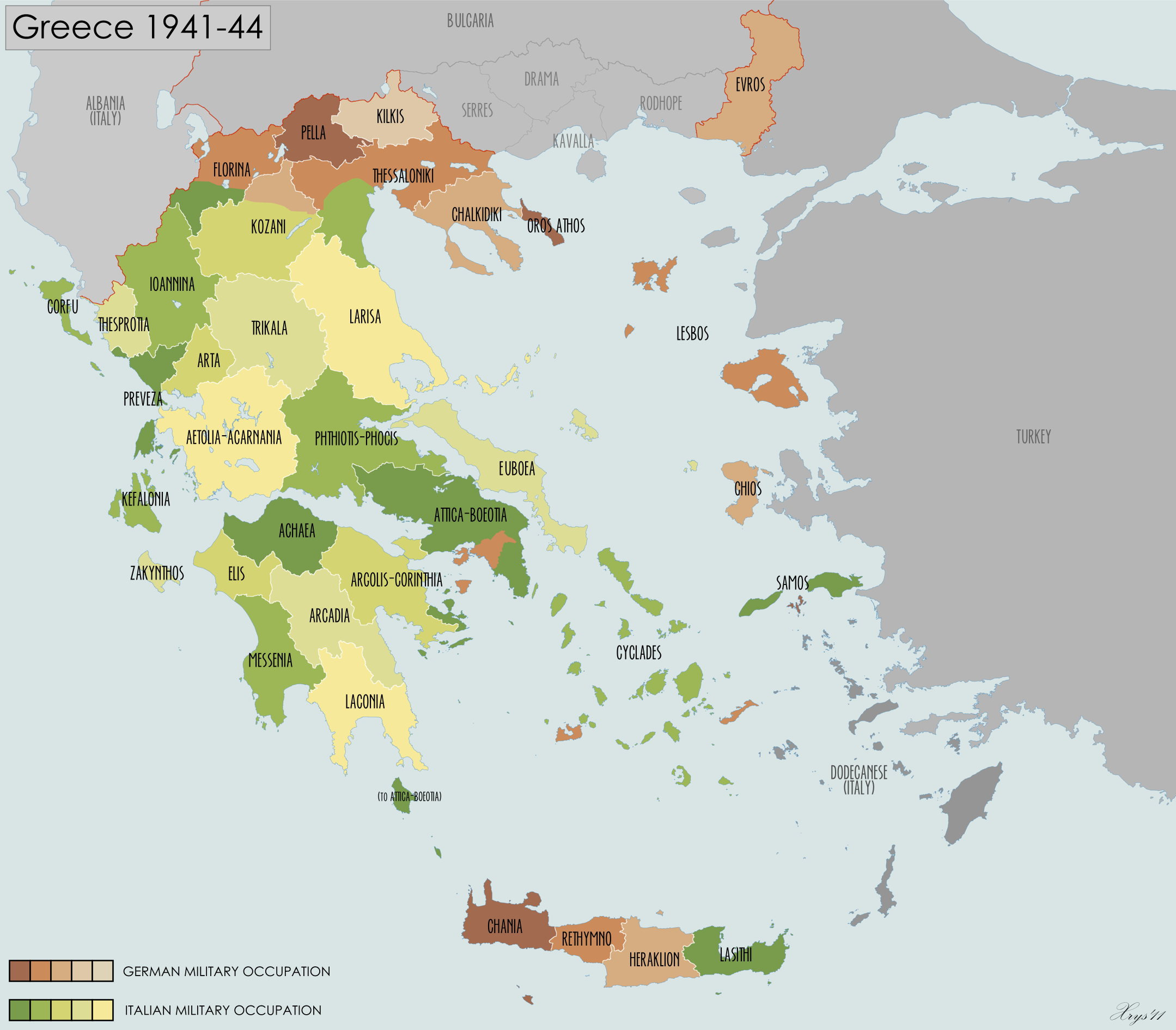
Administrative divisions
Administratively, the Hellenic State was divided into a number of prefectures.
Decline and fall
The ''Hellenic State'' lacked the infrastructure and latitude for action to face the great difficulties of the Occupation period; it was also devoid of any political legitimacy, and was widely considered a puppet government. Tsolakoglou demanded greater political rights for his government, and soon threatened to resign. The proclamation of a mandatory work service in Germany for Greek citizens proved widely unpopular and hastened the fall of Tsolakoglou; on 17 November 1942, he was sacked and replaced by his deputy, Konstantinos Logothetopoulos. The new government announced that 80,000 Greek citizens were to be sent to Germany. This led to widespread demonstrations and strikes, and the decision was eventually revoked. Logothetopoulos, who had protested against the measures taken by the Axis occupation authorities, was himself sacked on 6 April 1943. Against the wishes of the Italians, who favored Finance Minister Sotirios Gotzamanis, he was replaced byIoannis Rallis
Ioannis Rallis (; 1878 – 26 October 1946) was the third and last collaborationist prime minister of Greece during the Axis occupation of Greece
The occupation of Greece by the Axis Powers () began in April 1941 after Nazi Germany Battle of ...
, a monarchist politician. Rallis, who was looking beyond the German withdrawal from Greece to the restoration of the post-war political order, and who was alarmed by the growth of the mostly Communist
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, di ...
-dominated Greek resistance, obtained German consent for the creation of the Security Battalions
The Security Battalions (, derisively known as ''Germanotsoliades'' (Γερμανοτσολιάδες, meaning "German tsoliás") or ''Tagmatasfalites'' (Ταγματασφαλίτες)) were Greek collaborationist paramilitary groups, formed d ...
, armed formations that were used in anti-partisan offensives.
Military
The collaborationist regime under Rallis set upSecurity Battalions
The Security Battalions (, derisively known as ''Germanotsoliades'' (Γερμανοτσολιάδες, meaning "German tsoliás") or ''Tagmatasfalites'' (Ταγματασφαλίτες)) were Greek collaborationist paramilitary groups, formed d ...
, units of soldiers that aided the German Army
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (G ...
in fighting the resistance. They are known for committing atrocities against the civilian population. An officer named Georgios Bakos served as the minister of national defense.
Exile and trial
In September 1944, a new collaborationist government was established atVienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
, formed by former collaborationist ministers. It was headed by Ektor Tsironikos. It ceased to exist after the withdrawal of German forces and the liberation of the country in October 1944. Tsolakoglou, Rallis and Logothetopoulos (in Germany, where he had escaped to) were all arrested, along with hundreds of other collaborationists. The restored government set up the Trials of Collaborationists (I Diki ton Dosilogon) to judge collaborators. During 1945, Tsironikos was tried and sentenced to death. On 10 May 1945, he was arrested in Vienna by Allied forces and sent to Greece, where he was imprisoned. The government did not fulfil its promise to make major efforts to punish collaborators; this contributed to the escalation of political enmities in Greece, which in turn played a part in the outbreak of the Greek civil war
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
.Charles R. SchraderThe withered vine: logistics and the communist insurgency in Greece, 1945–1949
Greenwood Press, 1999, p. 38
References
External links
German banknotes circulated only in Greece during the occupation (1941–1944)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hellenic State (1941-1944) * Client states of Nazi Germany * 1940s in Greek politics Fascism in Greece Greek collaborators with Nazi Germany States and territories established in 1941 1941 establishments in Greece States and territories disestablished in 1944 1944 disestablishments in Greece * * * * Client states of Fascist Italy