Heinrich Bürger on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heinrich Bürger (or: Heinrich Burger) (
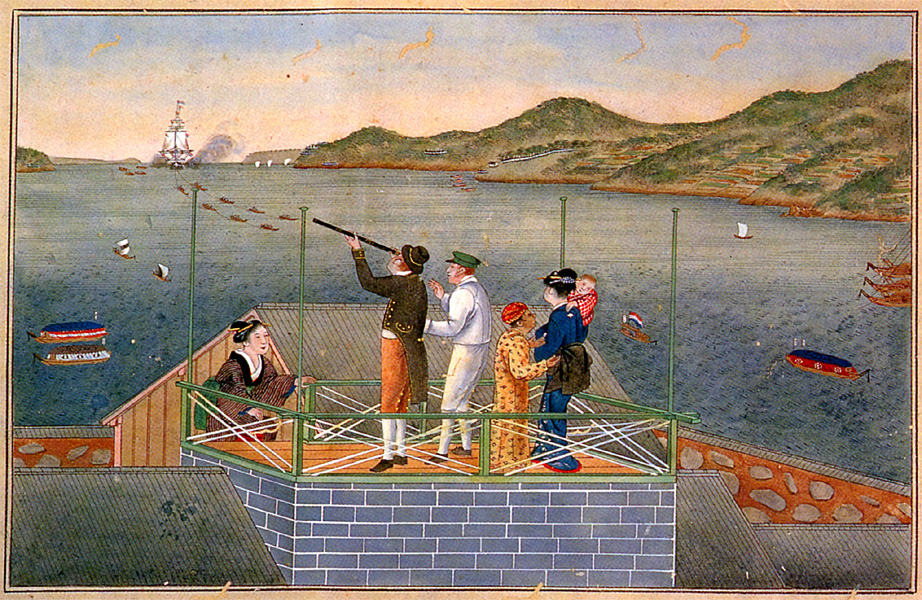
 On 14 June 1825 Heinrich Bürger was appointed by the Dutch government as the assistant of
On 14 June 1825 Heinrich Bürger was appointed by the Dutch government as the assistant of
Repository.naturalis.nl PDF
* P.M. Kernkamp, "Heinrich Bürger (Hamelen 1804/1806 – Indramajoe 1858) en zijn Duitse en Nederlandse familie", in ''De Nederlandsche Leeuw'' 132 (2015) 108–132
Publication on Academia.org
* J. Mac Lean: "Natural science in Japan from 1828–1849", in ''Janus'' LXII (1975), p. 5178. * M.J. van Steenis-Kruseman: ''"Heinrich Bürger (?1806 – 1858), explorer in Japan and Sumatra'', Contributions to the history of botany and exploration in Malaysia", in ''Blumea - Biodiversity, Evolution and Biogeography of Plants'', Vol. 11 (1962), p. 495–508
Repository.naturalis.nl PDF
* M. Uéno: "A Japanese portrait of Heinrich Bürger", i: '' Zoologische Mededelingen'' Vol. 49, 1975, p. 91-9
Repository.naturalis.nl PDF
Hamelin
Hameln ( ; ) is a town on the river Weser in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the capital of the district of Hameln-Pyrmont and has a population of roughly 57,000. Hamelin is best known for the tale of the Pied Piper of Hamelin.
History
Hameln ...
, 29 February 1804, or 7 November 1804, or 20 January 1806 – Indramayu (Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
) 25 March 1858) was a German physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
, biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
and botanist
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
employed by the Dutch government, and an entrepreneur. He was important for the study of Japanese fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
and flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
.
Background
Bürger's exact birth date is unknown. Bürger himself gave 29 February 1804. Most archival sources have the year 1806; it looks as if Heinrich moved his birth date two years back so as to appear older. Bürger was Jewish; his father Samuel Burger was a merchant and ' Schutzjude' in Hamelin, who went bankrupt in 1817, and died in 1821.Education
In the years 1821–1822 Heinrich studied mathematics and astronomy atGöttingen
Göttingen (, ; ; ) is a college town, university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the Capital (political), capital of Göttingen (district), the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. According to the 2022 German census, t ...
university. Though he sometimes used the title of doctor, no proof has been found of an academic promotion. In 1824 Bürger left for Batavia (Dutch East Indies), now Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
, where he visited the school for apothecaries. On 14 January 1825 he gained the degree of apothecary 3rd class.
Dejima

 On 14 June 1825 Heinrich Bürger was appointed by the Dutch government as the assistant of
On 14 June 1825 Heinrich Bürger was appointed by the Dutch government as the assistant of Philipp Franz von Siebold
Philipp Franz Balthasar von Siebold (17 February 1796 – 18 October 1866) was a German physician, botanist and traveller. He achieved prominence by his studies of Japanese flora (plants), flora and fauna (animals), fauna and the introduction of ...
on the isle of Dejima
or Deshima, in the 17th century also called , was an artificial island off Nagasaki, Japan, that served as a trading post for the Portuguese (1570–1639) and subsequently the Dutch (1641–1858). For 220 years, it was the central con ...
(Nagasaki, Japan) for the "natural research" in Japan. He left for Japan on 1 July together with Carl Hubert de Villeneuve. On Dejima Bürger did chemistry and biological research, and he taught the Japanese. He also was head of pharmacy and assisted Siebold's polyclinical visits to patients outside Dejima. In 1826, both Bürger and Kawahara Keiga joined Siebold on the court journey to the Shogun
, officially , was the title of the military aristocracy, rulers of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor of Japan, Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, exc ...
in Edo. In 1828 Bürger was appointed as successor of Von Siebold as far as the chemical, natural and biological work was concerned. In the following years he collected large quantities of minerals, plants, reptiles and animals, among which 650 fishes and crustaceans
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of Arthropod, arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquat ...
. Bürger began working on a survey of fish, and had Keiga make life-like sketches of 400 species, 200 of which Bürger sent to Siebold along with detailed descriptions. Much of this material was used for the later publication Fauna Japonica by Temminck and Schlegel. Plants sent by Bürger arrived in the botanical gardens of university cities like Leiden
Leiden ( ; ; in English language, English and Archaism, archaic Dutch language, Dutch also Leyden) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Nethe ...
, Groningen
Groningen ( , ; ; or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen (province), Groningen province in the Netherlands. Dubbed the "capital of the north", Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of ...
, Munich, Paris, London, Florence and St. Louis. The Naturalis Museum in Leiden boasts a large Bürger collection.
Padang
In 1832 or 1833 (literary sources contradict each other here) Bürger was "added" to the "Committee for natural research in East-India". In that capacity he visitedSumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
between June and December 1833. In that period he planned a road from the Padang
Padang () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Indonesian Provinces of Indonesia, province of West Sumatra. It had a population of 833,562 at the 2010 CensusBiro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. and 909,040 at the 2020 Census;Bad ...
lowlands to the interior; the road through the Anai Valley (), which today is a tourist attraction because of its natural beauty. The realisation of this road earned him the Order of the Netherlands Lion
The Order of the Netherlands Lion, also known as the Order of the Lion of the Netherlands (, ) is a Dutch honours system, Dutch order of chivalry founded by William I of the Netherlands on 29 September 1815.
The Order of the Netherlands Lion wa ...
. In 1833 Bürger married Anna Cornelia van Daalen in Padang. In 1834 he was back on Dejima, but he installed his wife in Batavia.
Entrepreneur
From 1 July 1835 Bürger was relieved of his duties in Japan. In 1840–1842 he traveled extensively with his family throughout western Europe. Back on Java he was pensioned off in 1842 as a member of the Natural Committee, and on 30 June 1843 he was honorably discharged from public service. Heinrich then moved into business, a.o. the production of rice and oil on Bangka, the Nederlandsch-Indische Zee-Assurantie Maatschappij (marine insurances), de Maatschappij tot Bevordering van Mijnontginningen in Nederlandsch-Indië (Society for the advancement of mining development in the Dutch Indies), which operated onBorneo
Borneo () is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world, with an area of , and population of 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda ...
, and he was co-owner of sugar factory Rejosari in Magetan ( Madiun Residency, Java). Bürger also was a prominent member of the social club "De Harmonie" in Batavia 1850-1853.
Honours
Although Bürger is mentioned in theIPNI
The International Plant Names Index (IPNI) describes itself as "a database of the names and associated basic bibliographical details of seed plants, ferns and lycophytes." Coverage of plant names is best at the rank of species and genus. It in ...
, he did not describe new plants. But he has been honoured by those who worked on his collections: they have named many of the new species he collected after him. These species can be recognized by the epitheton “Buergerianum” or “Burgeri(i)”, such as:
“''burgerianum''” 19 distinct (i.e., excluding combinations for the same plant in different genera) taxa that at some point been published at the level of species including:
* ( Aceraceae) '' Acer buergerianum'' Miq.
* (Eriocaulaceae
The Eriocaulaceae are a family (biology), family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in the order Poales, commonly known as the pipewort family. The family is large, with about 1207 known species described in seven genera. They are widely distri ...
) '' Eriocaulon buergerianum'' Körn.
* (Polypodiaceae
Polypodiaceae is a Family (biology), family of ferns. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), the family includes around 65 genus, genera and an estimated 1,650 species and is placed in the order Polypodiales, suborder ...
) '' Lepidomicrosorium buergerianum'' ( Miq.) Ching
Ching may refer to:
People
* Ching, a unisex given name
** Ching He Huang, a food writer and TV chef
** Ching Hammill (1902–1925), American football player
** Ching Johnson (1898–1979), Canadian National Hockey League player
** Willis August ...
& K.H.Shing
“''buergeri''” 10 distinct species level taxa including
* (Ericaceae
The Ericaceae () are a Family (biology), family of flowering plants, commonly known as the heath or heather family, found most commonly in acidic and infertile growing conditions. The family is large, with about 4,250 known species spread acros ...
) ''Rhododendron
''Rhododendron'' (; : ''rhododendra'') is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the Ericaceae, heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are native to eastern Asia and the Himalayan ...
buergeri'' Miq.Ann. Mus. Bot. Lugduno-Batavi i. 34. (IK)
Sources
* M. Boeseman: "Revision of the fishes collected by Burger and Von Siebold in Japan", in "'' Zoologische Mededelingen'', Vol. 28, 1947, p. 1–24Repository.naturalis.nl PDF
* P.M. Kernkamp, "Heinrich Bürger (Hamelen 1804/1806 – Indramajoe 1858) en zijn Duitse en Nederlandse familie", in ''De Nederlandsche Leeuw'' 132 (2015) 108–132
Publication on Academia.org
* J. Mac Lean: "Natural science in Japan from 1828–1849", in ''Janus'' LXII (1975), p. 5178. * M.J. van Steenis-Kruseman: ''"Heinrich Bürger (?1806 – 1858), explorer in Japan and Sumatra'', Contributions to the history of botany and exploration in Malaysia", in ''Blumea - Biodiversity, Evolution and Biogeography of Plants'', Vol. 11 (1962), p. 495–508
Repository.naturalis.nl PDF
* M. Uéno: "A Japanese portrait of Heinrich Bürger", i: '' Zoologische Mededelingen'' Vol. 49, 1975, p. 91-9
Repository.naturalis.nl PDF
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Burger, Heinrich 1800s births 1858 deaths People from Hamelin 19th-century German Jews 19th-century German botanists 19th-century German physicists 19th-century German zoologists