Hart's A-frame on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hart's inversors are two planar mechanisms that provide a perfect straight line motion using only rotary joints. They were invented and published by Harry Hart in 1874–5.
Hart's inversors are two planar mechanisms that provide a perfect straight line motion using only rotary joints. They were invented and published by Harry Hart in 1874–5.
 Hart's first inversor is demonstrated as a six-bar linkage with only a single point that travels in a straight line. This can be modified into an eight-bar linkage with a bar that travels in a rectilinear fashion, by taking the ground and input (shown as cyan in the animation), and appending it onto the original output.
A further generalization by
Hart's first inversor is demonstrated as a six-bar linkage with only a single point that travels in a straight line. This can be modified into an eight-bar linkage with a bar that travels in a rectilinear fashion, by taking the ground and input (shown as cyan in the animation), and appending it onto the original output.
A further generalization by
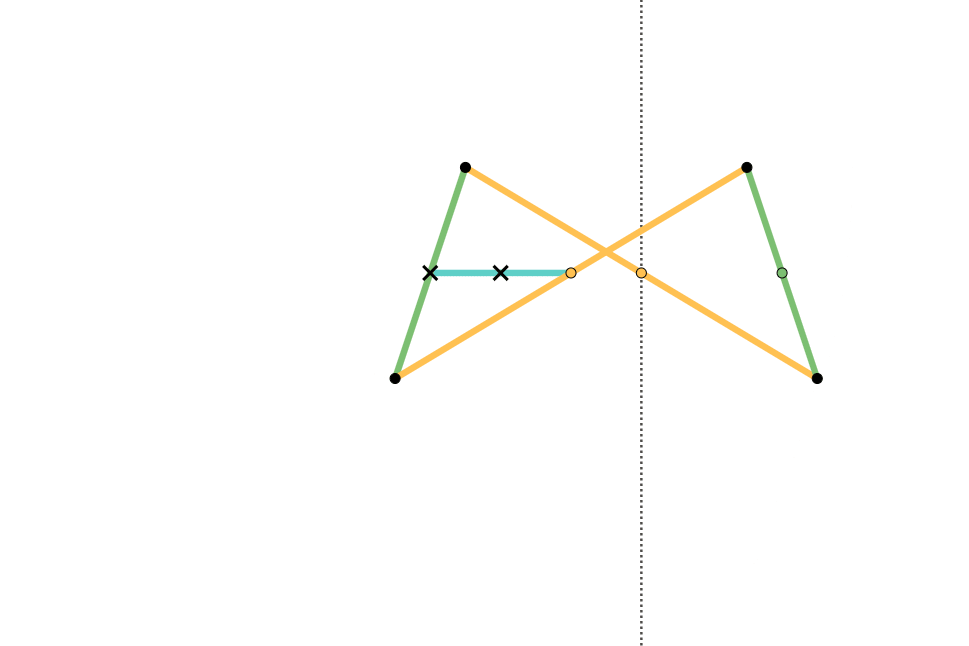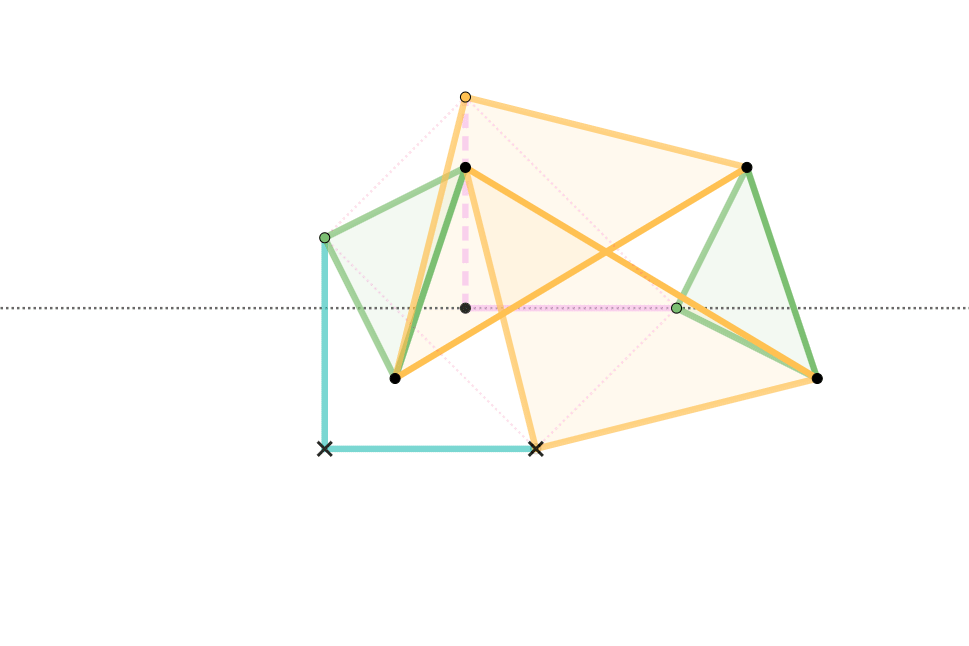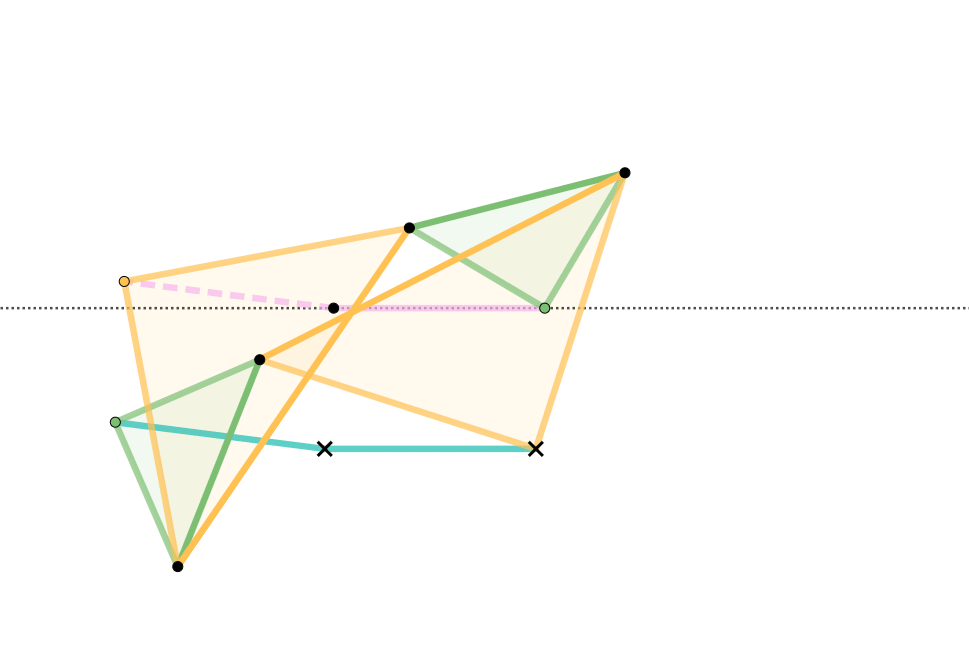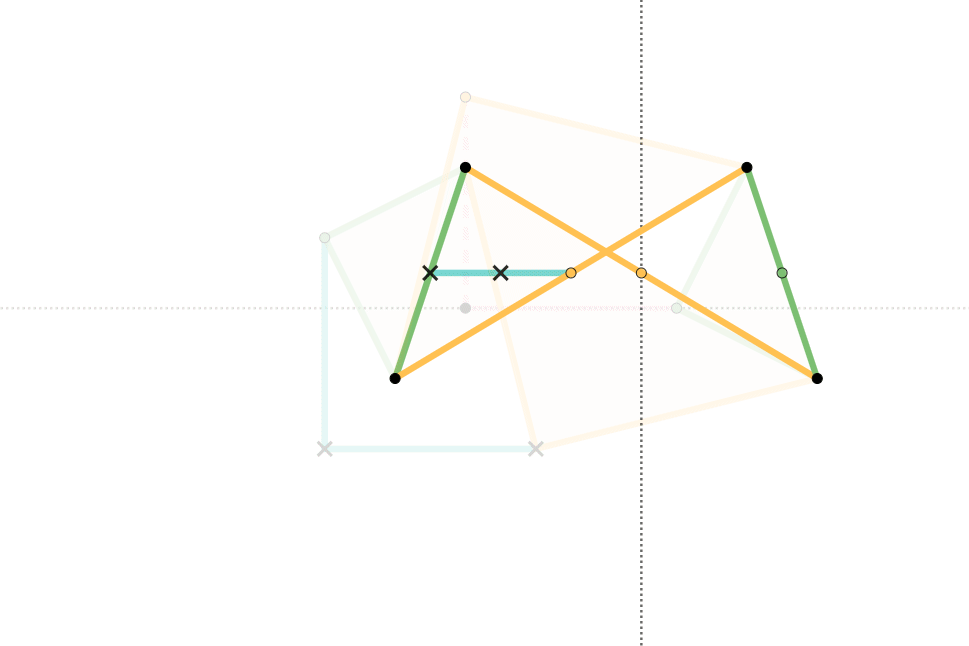
 Hart's second inversor, also known as ''Hart's A-frame'', is less flexible in its dimensions, but has the useful property that the motion perpendicularly bisects the fixed base points. It is shaped like a capital A – a stacked trapezium and triangle. It is also a 6-bar linkage.
Hart's second inversor, also known as ''Hart's A-frame'', is less flexible in its dimensions, but has the useful property that the motion perpendicularly bisects the fixed base points. It is shaped like a capital A – a stacked trapezium and triangle. It is also a 6-bar linkage.
Mecanismo de Hart (2).png,
Mecanismo de Hart.png,
bham.ac.uk
– Hart's A-frame (draggable animation) 6-bar linkage {{dead link, date=June 2017 1874 introductions Linkages (mechanical) Linear motion Straight line mechanisms
 Hart's inversors are two planar mechanisms that provide a perfect straight line motion using only rotary joints. They were invented and published by Harry Hart in 1874–5.
Hart's inversors are two planar mechanisms that provide a perfect straight line motion using only rotary joints. They were invented and published by Harry Hart in 1874–5.
Hart's first inversor
Hart's first inversor, also known as ''Hart's W-frame'', is based on anantiparallelogram
In geometry, an antiparallelogram is a type of list of self-intersecting polygons, self-crossing quadrilateral. Like a parallelogram, an antiparallelogram has two opposite pairs of equal-length sides, but these pairs of sides are not in general ...
. The addition of fixed points and a driving arm make it a 6-bar linkage. It can be used to convert rotary motion to a perfect straight line by fixing a point on one short link and driving a point on another link in a circular arc.
Rectilinear bar and quadruplanar inversors
 Hart's first inversor is demonstrated as a six-bar linkage with only a single point that travels in a straight line. This can be modified into an eight-bar linkage with a bar that travels in a rectilinear fashion, by taking the ground and input (shown as cyan in the animation), and appending it onto the original output.
A further generalization by
Hart's first inversor is demonstrated as a six-bar linkage with only a single point that travels in a straight line. This can be modified into an eight-bar linkage with a bar that travels in a rectilinear fashion, by taking the ground and input (shown as cyan in the animation), and appending it onto the original output.
A further generalization by James Joseph Sylvester
James Joseph Sylvester (3 September 1814 – 15 March 1897) was an English mathematician. He made fundamental contributions to matrix theory, invariant theory, number theory, partition theory, and combinatorics. He played a leadership ...
and Alfred Kempe
Sir Alfred Bray Kempe FRS (6 July 1849 – 21 April 1922) was a mathematician best known for his work on linkages and the four colour theorem.
Biography
Kempe was the son of the Rector of St James's Church, Piccadilly, the Rev. John Edwar ...
extends this such that the bars can instead be pairs of plates with similar dimensions.
Hart's second inversor
 Hart's second inversor, also known as ''Hart's A-frame'', is less flexible in its dimensions, but has the useful property that the motion perpendicularly bisects the fixed base points. It is shaped like a capital A – a stacked trapezium and triangle. It is also a 6-bar linkage.
Hart's second inversor, also known as ''Hart's A-frame'', is less flexible in its dimensions, but has the useful property that the motion perpendicularly bisects the fixed base points. It is shaped like a capital A – a stacked trapezium and triangle. It is also a 6-bar linkage.
Geometric construction of the A-frame inversor
Example dimensions
These are the example dimensions that you see in the animations on the right.See also
*Linkage (mechanical)
A mechanical linkage is an assembly of systems connected so as to manage forces and Motion, movement. The movement of a body, or link, is studied using geometry so the link is considered to be Rigid body, rigid. The connections between links ...
* Quadruplanar inversor, a generalization of Hart's first inversor
* Straight line mechanism
A straight-line mechanism is a mechanism that converts any type of rotary or angular motion to perfect or near-perfect straight-line motion, or ''vice versa''. Straight-line motion is linear motion of definite length or "stroke", every forwa ...
Notes
References
External links
bham.ac.uk
– Hart's A-frame (draggable animation) 6-bar linkage {{dead link, date=June 2017 1874 introductions Linkages (mechanical) Linear motion Straight line mechanisms