Haganah Arsenal (Slik) In Kibutz Kfar Giladi, Israel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Haganah ( , ) was the main Zionist paramilitary organization that operated for the
 During the
During the
 After "having gotten the Jews of Palestine and of elsewhere to do everything that they could, personally and financially, to help
After "having gotten the Jews of Palestine and of elsewhere to do everything that they could, personally and financially, to help
 After the British announced they would withdraw from Palestine, and the United Nations approved the partition of Palestine, the 1947-48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine broke out. The Haganah played the leading role in the Yishuv's war with the Palestinian Arabs. Initially, it concentrated on defending Jewish areas from Arab raids, but after the danger of British intervention subsided as the British withdrew, the Haganah went on the offensive and seized more territory. Following the
After the British announced they would withdraw from Palestine, and the United Nations approved the partition of Palestine, the 1947-48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine broke out. The Haganah played the leading role in the Yishuv's war with the Palestinian Arabs. Initially, it concentrated on defending Jewish areas from Arab raids, but after the danger of British intervention subsided as the British withdrew, the Haganah went on the offensive and seized more territory. Following the
Official Haganah website
''Lexicon of Zionism: Haganah'' (Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs)
* ttp://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/History/Modern+History/Centenary+of+Zionism/From+Hashomer+to+the+Israel+Defense+Forces.htm From Hashomer to the Israel Defense Forces Armed Jewish Defense in Palestine by
Yishuv
The Yishuv (), HaYishuv Ha'ivri (), or HaYishuv HaYehudi Be'Eretz Yisra'el () was the community of Jews residing in Palestine prior to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. The term came into use in the 1880s, when there were about 2 ...
in the British Mandate for Palestine
The Mandate for Palestine was a League of Nations mandate for British administration of the territories of Palestine and Transjordanwhich had been part of the Ottoman Empire for four centuriesfollowing the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in Wo ...
. It was founded in 1920 to defend the Yishuv's presence in the region, and was formally disbanded in 1948, when it became the core force integrated into the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and ...
shortly after the Israeli Declaration of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel (), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 (5 Iyar 5708), at the end of the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war phase and ...
.
Formed out of previous existing militias, Haganah's original purpose was to defend Jewish settlements against Arab attacks; this was the case during the 1921 Jaffa riots
The Jaffa riots (commonly known in ) were a series of violent riots in Mandatory Palestine on May 1–7, 1921, which began as a confrontation between two Jewish groups but developed into an attack by Arabs on Jews and then reprisal attacks by ...
, the 1929 Palestine riots
The 1929 Palestine riots, Buraq Uprising (, ) or the Events of 1929 (, , ''lit.'' Events of 5689 Anno Mundi), was a series of demonstrations and riots in late August 1929 in which a longstanding dispute between Palestinian Arabs and Jews ove ...
, the 1936 Jaffa riots, and the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
A popular uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine against the British administration, later known as the Great Revolt, the Great Palestinian Revolt, or the Palestinian Revolution, lasted from 1936 until 1939. The movement sought i ...
, among others. The paramilitary was under the control of the Jewish Agency
The Jewish Agency for Israel (), formerly known as the Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. It was established in 1929 as the operative branch of the World Zionist Organization (WZO).
As an ...
, the official governmental body in charge of Palestine's Jewish community during the British era. Until the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Haganah's activities were moderate, in accordance with the strategic policy of ''havlagah
''Havlagah'' ( , ) was the strategic policy of the Yishuv during the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine. It called for Zionist militants to abstain from engaging in acts of retaliatory violence against Palestinian Arabs in the face of Arab a ...
'' (), which caused the breakaway of the more radical paramilitaries: Irgun
The Irgun (), officially the National Military Organization in the Land of Israel, often abbreviated as Etzel or IZL (), was a Zionist paramilitary organization that operated in Mandatory Palestine between 1931 and 1948. It was an offshoot of th ...
and Lehi. Haganah militants received clandestine military support from Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and sought cooperation with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
in the event of an Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
-led invasion of Palestine through North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, prompting the creation of the Palmach
The Palmach (Hebrew: , acronym for , ''Plugot Maḥatz'', "Strike Phalanges/Companies") was the elite combined strike forces and sayeret unit of the Haganah, the paramilitary organization of the Yishuv (Jewish community) during the period of th ...
, their elite fighting force, in 1941.
Following the end of World War II, the British refused to lift the restrictions on Jewish immigration that they had imposed with the 1939 White Paper
The White Paper of 1939Occasionally also known as the MacDonald White Paper (e.g. Caplan, 2015, p.117) after Malcolm MacDonald, the British Colonial Secretary, who presided over its creation. was a policy paper issued by the British governmen ...
. This resulted in Haganah leading a Jewish insurgency against the British authorities in Palestine; the campaign included the paramilitaries' bombing of bridges, railways, and ships used to deport illegal Jewish immigrants, as well as assisting in bringing more diaspora Jews
The Jewish diaspora ( ), alternatively the dispersion ( ) or the exile ( ; ), consists of Jews who reside outside of the Land of Israel. Historically, it refers to the expansive scattering of the Israelites out of their homeland in the Southe ...
to Palestine in defiance of British policies. After the adoption of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations to partition Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. Drafted by the U.N. Special Committee on Palestine (UNSCOP) on 3 September 1947, the Pl ...
in 1947, Haganah came into the open as the biggest fighting force among the Palestinian Jews
Palestinian Jews or Jewish Palestinians (; ) were the Jews who inhabited Palestine (alternatively the Land of Israel) prior to the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel on 14 May 1948.
Beginning in the 19th century, the colle ...
, successfully overcoming Arab militias during the Palestinian Civil War. After the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the territory of another state or failed state, or are breaka ...
of the State of Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, the Haganah became the new nation's military force. Shortly after Israeli independence and the beginning of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
, the Haganah was merged with other paramilitary groups and reorganized into the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and ...
.
History
Overview
The evolution of Jewish defense organizations in Palestine and later Israel went from small self-defense groups active during Ottoman rule, to ever larger and more sophisticated ones during the British Mandate, leading through the Haganah to the national army of Israel, the IDF. The evolution went step by step fromBar-Giora
Bar-Giora () was a Jewish militia in Palestine (then part of the Ottoman Empire) from 1907 to 1909. The group was composed primarily of Russian Jewish immigrants of the Second Aliyah. The organization was a precursor of Hashomer, itself a precu ...
, to Hashomer
Hashomer (, 'The Watchman') was a Jewish defense organization in Palestine founded in April 1909. It was an outgrowth of the Bar-Giora group and was disbanded after the founding of the Haganah in 1920. Hashomer was responsible for guarding Je ...
, to Haganah, to IDF.
The Jewish paramilitary organizations in the New Yishuv
The Yishuv (), HaYishuv Ha'ivri (), or HaYishuv HaYehudi Be'Eretz Yisra'el () was the community of Jews residing in Palestine (region), Palestine prior to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. The term came into use in the 1880s, whe ...
(the Zionist enterprise in Palestine) started with the Second Aliyah
The Second Aliyah () was an aliyah (Jewish immigration to the Land of Israel) that took place between 1904 and 1914, during which approximately 35,000 Jews, mostly from Russia, with some from Yemen, immigrated into Ottoman Palestine.
The Sec ...
(1904 to 1914). The first such organization was Bar-Giora
Bar-Giora () was a Jewish militia in Palestine (then part of the Ottoman Empire) from 1907 to 1909. The group was composed primarily of Russian Jewish immigrants of the Second Aliyah. The organization was a precursor of Hashomer, itself a precu ...
, founded in September 1907. It consisted of a small group of Jewish immigrants who guarded settlements for an annual fee. It was converted to Hashomer (; "The Watchman") in April 1909, which operated until the British Mandate of Palestine came into being in 1920. Hashomer was an elitist organization which never had more than 100 members. During World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the forerunners of the Haganah/IDF were the Zion Mule Corps
The Jewish Legion was a series of battalions of Jewish soldiers who served in the British Army during the First World War. Some participated in the British conquest of Palestine from the Ottomans.
The formation of the battalions had several ...
and the Jewish Legion
The Jewish Legion was a series of battalions of Jewish soldiers who served in the British Army during the First World War. Some participated in the British conquest of Palestine from the Ottomans.
The formation of the battalions had several ...
, both of which were part of the British Army. After the Arab riots against Jews in April 1920, the Yishuv's leadership saw the need to create a nationwide underground defense organization, and the Haganah was founded in June of the same year. The Haganah became a full-scale defense force after the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
A popular uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine against the British administration, later known as the Great Revolt, the Great Palestinian Revolt, or the Palestinian Revolution, lasted from 1936 until 1939. The movement sought i ...
with an organized structure, consisting of three main units—the Field Corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was formally introduced March 1, 1800, when Napoleon ordered Gener ...
, Guard Corps
The Guards Corps/GK () was a corps level command of the Prussian Army, Prussian and then the Imperial German Army, Imperial German Armies from the 19th century to World War I.
The Corps was headquartered in Berlin, with its units garrisoned in ...
, and the Palmach
The Palmach (Hebrew: , acronym for , ''Plugot Maḥatz'', "Strike Phalanges/Companies") was the elite combined strike forces and sayeret unit of the Haganah, the paramilitary organization of the Yishuv (Jewish community) during the period of th ...
strike force. During World War II the successor to the Jewish Legion of World War I was the Jewish Brigade
The Jewish Infantry Brigade Group, more commonly known as the Jewish Brigade Group or Jewish Brigade, was a military formation of the British Army in the World War II, Second World War. It was formed in late 1944 and was recruited among Yishuv, Y ...
, which was joined by many Haganah fighters. During the 1947–48 civil war between the Arab and Jewish communities in what was still Mandatory Palestine, a reorganized Haganah managed to defend or wrestle most of the territory it was ordered to hold or capture. At the beginning of the ensuing 1948–49 full-scale conventional war against regular Arab armies, the Haganah was reorganized to become the core of the new Israel Defense Forces.
1920 Palestine riots and 1921 Jaffa riots
After the1920 Nebi Musa riots
The 1920 Nebi Musa riots or 1920 Jerusalem riots took place in British-controlled part of Occupied Enemy Territory Administration between Sunday, 4 April, and Wednesday, 7 April 1920 in and around the Old City of Jerusalem. Five Jews were kill ...
and 1921 Jaffa riots
The Jaffa riots (commonly known in ) were a series of violent riots in Mandatory Palestine on May 1–7, 1921, which began as a confrontation between two Jewish groups but developed into an attack by Arabs on Jews and then reprisal attacks by ...
by Palestinians
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenou ...
, the Jewish leadership in Palestine believed that the British, to whom the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
had given a mandate over Palestine in 1920, had no desire to confront local Arab groups that frequently attacked Palestinian Jews. Believing that they could not rely on the British administration for protection from these gangs, the Jewish leadership created the Haganah to protect Jewish farms and kibbutz
A kibbutz ( / , ; : kibbutzim / ) is an intentional community in Israel that was traditionally based on agriculture. The first kibbutz, established in 1910, was Degania Alef, Degania. Today, farming has been partly supplanted by other economi ...
im. The first head of the Haganah was a 28-year-old named Yosef Hecht, a veteran of the Jewish Legion
The Jewish Legion was a series of battalions of Jewish soldiers who served in the British Army during the First World War. Some participated in the British conquest of Palestine from the Ottomans.
The formation of the battalions had several ...
.
In addition to guarding Jewish communities, the role of the Haganah was to warn the residents of and repel attacks by Palestinians. In the period between 1920 and 1929, the Haganah lacked a strong central authority or coordination. Haganah "units" were very localized and poorly armed: they consisted mainly of Jewish farmers who took turns guarding their farms or their kibbutzim.
Following the 1929 Palestine riots
The 1929 Palestine riots, Buraq Uprising (, ) or the Events of 1929 (, , ''lit.'' Events of 5689 Anno Mundi), was a series of demonstrations and riots in late August 1929 in which a longstanding dispute between Palestinian Arabs and Jews ove ...
, the Haganah's role changed dramatically. It became a much larger organization encompassing nearly all the youth and adults in the Jewish settlements, as well as thousands of members from the cities. It also acquired foreign arms and began to develop workshops to create grenade
A grenade is a small explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a Shell (projectile), shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A mod ...
s and simple military equipment, transforming from an untrained militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or se ...
to a capable underground army.
1931 Irgun split
Many Haganah fighters objected to the official policy of ''havlagah
''Havlagah'' ( , ) was the strategic policy of the Yishuv during the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine. It called for Zionist militants to abstain from engaging in acts of retaliatory violence against Palestinian Arabs in the face of Arab a ...
'' (restraint) that Jewish political leaders (who had become increasingly controlling of the Haganah) had imposed on the militia. Fighters had been instructed to only defend communities and not initiate counterattacks against Arab gangs or their communities. This policy appeared defeatist to many who believed that the best defense is a good offense
"The best defense is a good offense" is an adage that has been applied to many fields of endeavor, including games and military combat. It is also known as the strategic offensive principle of war. Generally, the idea is that proactivity (a stron ...
. In 1931, the more militant elements of the Haganah splintered off and formed the ''Irgun Tsva'i-Leumi'' (National Military Organization), better known as "Irgun
The Irgun (), officially the National Military Organization in the Land of Israel, often abbreviated as Etzel or IZL (), was a Zionist paramilitary organization that operated in Mandatory Palestine between 1931 and 1948. It was an offshoot of th ...
" (or by its Hebrew acronym, pronounced "Etzel").
1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
 During the
During the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
A popular uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine against the British administration, later known as the Great Revolt, the Great Palestinian Revolt, or the Palestinian Revolution, lasted from 1936 until 1939. The movement sought i ...
, the Haganah worked to protect British interests and to quell the rebellion using the Posh
Posh is today an informal adjective for "upper class". It may also refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Posh'' (album), a 1980 album by Patrice Rushen
*" Posh!", a 1968 song from the musical ''Chitty Chitty Bang Bang''
* ''Posh'' (2006 TV series), a 2006 ...
and then the Hish units. At that time, the Haganah fielded 10,000 mobilized men along with 40,000 reservists. Although the British administration did not officially recognize the Haganah, the British security forces cooperated with it by forming the Jewish Settlement Police
The Jewish Settlement Police (JSP) were a division of the Notrim established in Mandatory Palestine in 1936, during the 1936-39 Arab revolt.Levenberg, 1993, p. 156.
History
At the end of 1940, the JSP had about 15,000 members. A field arm ...
, Jewish Supernumerary Police
The Jewish Supernumerary Police (Hebrew: ''Shotrim Musafim''), sometimes referred to as Jewish Auxiliary Police, were a branch of the Guards ('' Notrim'') set up by the British in the British Mandate of Palestine in June 1936.
The British autho ...
and Special Night Squads
The Special Night Squads (SNS) was a joint British–Jewish counter-insurgency military unit, established by Captain Orde Wingate in Mandatory Palestine in 1938 during the 1936–1939 Arab revolt. The SNS consisted of British infantry soldiers, ...
, which were trained and led by Colonel Orde Wingate
Major-general (United Kingdom), Major General Orde Charles Wingate, (26 February 1903 – 24 March 1944) was a senior British Army officer known for his creation of the Chindits, Chindit deep-penetration missions in Japanese-held territory duri ...
. The battle experience gained during the training was useful in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
.
Support from the Second Polish Republic
During the interwar period, as part of its policy of supporting a Jewish state in Palestine in order to facilitate mass Jewish emigration from its territory, theSecond Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
provided military training and weapons to Zionist paramilitary groups, including Haganah. Envoys from Haganah headed by Yehuda Arazi received dozens of shipments with military supplies, including 2750 Mauser rifles, 225 RKM machine guns, 10,000 hand grenades, two million bullets for rifles and machine guns, and a large number of pistols with ammunition. The British exerted heavy pressure on the Polish government to stop these deliveries. One of the last purchases of Arazi were two airplanes and two gliders. When he fled Poland to France, around 500 rifles were abandoned in a Warsaw warehouse. Members of the Haganah were also trained in a military camp in Rembertow along with Betar
The Betar Movement (), also spelled Beitar (), is a Revisionist Zionism, Revisionist Zionist youth movement founded in 1923 in Riga, Latvia, by Ze'ev Jabotinsky, Vladimir (Ze'ev) Jabotinsky. It was one of several right-wing youth movements tha ...
members between the years 1931 and 1937; it is estimated that training courses at the camp were attended by around 8,000 to 10,000 participants during their existence.
1939 White Paper
By 1939, the British had issued theWhite Paper
A white paper is a report or guide that informs readers concisely about a complex issue and presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter. It is meant to help readers understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision. Since the 199 ...
, which severely restricted Jewish immigration to Palestine, deeply angering the Zionist leadership. David Ben-Gurion
David Ben-Gurion ( ; ; born David Grün; 16 October 1886 – 1 December 1973) was the primary List of national founders, national founder and first Prime Minister of Israel, prime minister of the State of Israel. As head of the Jewish Agency ...
, then chairman of the Jewish Agency
The Jewish Agency for Israel (), formerly known as the Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. It was established in 1929 as the operative branch of the World Zionist Organization (WZO).
As an ...
, set the policy for the Zionist relationship with the British: "We shall fight the war against Hitler as if there were no White Paper, and we shall fight the White Paper as if there were no war."
In reaction to the White Paper, the Haganah built up the Palmach
The Palmach (Hebrew: , acronym for , ''Plugot Maḥatz'', "Strike Phalanges/Companies") was the elite combined strike forces and sayeret unit of the Haganah, the paramilitary organization of the Yishuv (Jewish community) during the period of th ...
as the Haganah's elite strike force and organized illegal Jewish immigration to Palestine. Approximately 100,000 Jews were brought to Palestine in over one hundred ships during the final decade of what became known as Aliyah Bet
''Aliyah Bet'' (, "Aliyah 'B'" – bet being the second letter of the Hebrew alphabet) was the code name given to illegal immigration by Jews, many of whom were refugees escaping from Nazi Germany or other Nazi-controlled countries, and la ...
. The Haganah also organized demonstrations against British immigration quotas.
Bombing of the ''SS Patria'' in Haifa
In 1940 the Haganah sabotaged the ''Patria'', an ocean liner being used by the British to deport 1,800 Jews to Mauritius, with a bomb intended to cripple the ship. However the ship sank, killing 267 people and injuring 172.World War II
In the first years ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the British authorities asked Haganah for cooperation again, due to the fear of an Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
breakthrough in North Africa. After Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel (; 15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944), popularly known as The Desert Fox (, ), was a German ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (field marshal) during World War II. He served in the ''Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of N ...
was defeated at El Alamein
El Alamein (, ) is a town in the northern Matrouh Governorate of Egypt. Located on the Mediterranean Sea, it lies west of Alexandria and northwest of Cairo. The town is located on the site of the ancient city Antiphrai which was built by th ...
in 1942, the British stepped back from their all-out support for Haganah. In 1943, after a long series of requests and negotiations, the British Army announced the creation of the Jewish Brigade Group. While Palestinian Jews had been permitted to enlist in the British army since 1940, this was the first time an exclusively Jewish military unit served in the war under a Jewish flag. The Jewish Brigade Group consisted of 5,000 soldiers and was initially deployed with the 8th Army in North Africa and later in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
in September 1944. The brigade was disbanded in 1946. All in all, some 30,000 Palestinian Jews served in the British army during the war.
On May 14, 1941, the Haganah created the Palmach
The Palmach (Hebrew: , acronym for , ''Plugot Maḥatz'', "Strike Phalanges/Companies") was the elite combined strike forces and sayeret unit of the Haganah, the paramilitary organization of the Yishuv (Jewish community) during the period of th ...
(an acronym for ''Plugot Mahatz''strike companies), an elite commando section, in preparation against the possibility of a British withdrawal and Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
invasion of Palestine. Its members, young men and women, received specialist training in guerrilla tactics and sabotage. During 1942 the British gave assistance in the training of Palmach volunteers but in early 1943 they withdrew their support and attempted to disarm them. The Palmach, then numbering over 1,000, continued as an underground organization with its members working half of each month as kibbutz
A kibbutz ( / , ; : kibbutzim / ) is an intentional community in Israel that was traditionally based on agriculture. The first kibbutz, established in 1910, was Degania Alef, Degania. Today, farming has been partly supplanted by other economi ...
volunteers, the rest of the month spent training. It was never largeby 1947 it amounted to merely five battalions (about 2,000 men)but its members had not only received physical and military training, but also acquired leadership skills that would subsequently enable them to take up command positions in Israel's army.
"The Saison" post-assassination of Lord Moyne
In 1944, after the assassination ofLord Moyne
Walter Edward Guinness, 1st Baron Moyne, DSO & Bar, TD, PC (29 March 1880 – 6 November 1944), was a British Conservative politician, soldier and businessman. He served as the British minister of state in the Middle East until November 19 ...
(the British Minister of State for the Middle East) by members of the Lehi, the Haganah worked with the British to kidnap, interrogate, and, in some cases, deport Irgun members. This action, which lasted from November 1944 to February 1945, was called the ''Saison
Saison ( French, "season," ) is a pale-colored ale that is highly carbonated, dry, fruity, spicy, and often bottle conditioned. It was historically brewed with low alcohol levels, but modern productions of the style have moderate to high leve ...
'', or the Hunting Season, and was directed against the Irgun and not the Lehi. Future Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
mayor Teddy Kollek
Theodor "Teddy" Kollek (; 27 May 1911 – 2 January 2007) was an Israeli politician who served as the mayor of Jerusalem from 1965 to 1993, and founder of the Jerusalem Foundation. Kollek was re-elected five times, in 1969, 1973, 1978 Jerusalem ...
was later revealed to be a Jewish Agency
The Jewish Agency for Israel (), formerly known as the Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. It was established in 1929 as the operative branch of the World Zionist Organization (WZO).
As an ...
liaison officer working with the British authorities who had passed on information that led to the arrest of many Irgun activists.
Many Jewish youth, who had joined the Haganah in order to defend the Jewish people, were greatly demoralized by operations against their own people.Bell, Bowyer J.: ''Terror out of Zion'' The Irgun, paralyzed by the Saison, were ordered by their commander, Menachem Begin
Menachem Begin ( ''Menaḥem Begin'', ; (Polish documents, 1931–1937); ; 16 August 1913 – 9 March 1992) was an Israeli politician, founder of both Herut and Likud and the prime minister of Israel.
Before the creation of the state of Isra ...
, not to retaliate in an effort to avoid a full blown civil war. Although many Irgunists objected to these orders, they obeyed Begin and refrained from fighting back. The Saison eventually ended due to perceived British betrayal of the Yishuv becoming more obvious to the public and increased opposition from Haganah members.
Post–World War II
The Saison officially ended when the Haganah, Irgun and the Lehi formed theJewish Resistance Movement
The Jewish Resistance Movement (, ''Tnu'at HaMeri Ha'Ivri'', literally ''Hebrew Rebellion Movement''), also called the United Resistance Movement (URM), was an alliance of the Zionist paramilitary organizations Haganah, Irgun and Lehi in the B ...
, in 1945. Within this new framework, the three groups agreed to operate under a joint command. They had different functions, which served to drive the British out of Palestine and create a Jewish state
In world politics, Jewish state is a characterization of Israel as the nation-state and sovereign homeland for the Jewish people.
Overview
Modern Israel came into existence on 14 May 1948 as a polity to serve as the homeland for the Jewi ...
.
The Haganah was less active in the Jewish Rebellion than the other two groups, but the Palmach did carry out anti-British operations, including a raid on the Atlit detainee camp
The Atlit detainee camp was a internment camp established by the authorities of Mandatory Palestine in the late 1930s on what is now the Israeli coastal plain, south of Haifa. Under British rule, it was primarily used to hold Jews and Arabs ...
that released 208 illegal immigrants, the Night of the Trains
The Night of the Trains (or Operation Party) was a sabotage operation of the British railways in Palestine (" Palestine Railways") on November 1, 1945. The operation was one of the first carried out by the Jewish Resistance Movement, before its ...
, the Night of the Bridges
The Night of the Bridges (formally Operation Markolet) was a Haganah venture on the night of 16 to 17 June 1946 in the British Mandate of Palestine, as part of the Jewish insurgency in Palestine (1944–47). Its aim was to destroy eleven brid ...
, and attacks on Palestine Police
The Palestine Police Force (, ) was a British colonial police service established in Mandatory Palestine on 1 July 1920,Sinclair, 2006. when High Commissioner Sir Herbert Samuel's civil administration took over responsibility for security from ...
bases. The Haganah withdrew on 1 July 1946, but "remained permanently unco-operative" with the British authorities. It continued to organize illegal Jewish immigration as part of the Aliyah Bet
''Aliyah Bet'' (, "Aliyah 'B'" – bet being the second letter of the Hebrew alphabet) was the code name given to illegal immigration by Jews, many of whom were refugees escaping from Nazi Germany or other Nazi-controlled countries, and la ...
program, in which ships carrying illegal immigrants attempted to breach the British blockade of Palestine and land illegal immigrants on the shore (most were intercepted by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
), and the Palmach performed operations against the British to support the illegal immigration program. The Palmach repeatedly bombed British radar stations being used to track illegal immigrant ships, and sabotaged British ships being used to deport illegal immigrants, as well as two British landing and patrol craft. The Palmach performed a single assassination operation in which a British official who had been judged to be excessively cruel to Jewish prisoners was shot dead. The Haganah also organized the Birya affair
The Birya affair (, ''HaAliya LeBirya'', lit. ''The Ascent to Birya'') was an attempt by the British army to take over Kibbutz Birya during the British Mandate for Palestine. History
On March 5, 1946, British soldiers searched the new settlem ...
. Following the expulsion of the residents of the Jewish settlement of Birya for illegal weapons possession, thousands of Jewish youth organized by the Haganah marched to the site and rebuilt the settlement. They were expelled by British shortly afterward while showing passive resistance
Nonviolent resistance, or nonviolent action, sometimes called civil resistance, is the practice of achieving goals such as social change through symbolic protests, civil disobedience, economic or political noncooperation, satyagraha, constr ...
, but after they returned a third time, the British backed off and allowed them to remain.
In addition to its operations, the Haganah continued to secretly prepare for a war with the Arabs once the British left by building up its arms and munitions stocks. It maintained a secret arms industry, with the most significant facility being an underground bullet factory underneath Ayalon, a kibbutz that had been established specifically to cover it up.
British estimates of the Haganah's strength at this time were a ''paper strength of 75,000 men and women'' with an effective strength of 30,000. After the British army, the Haganah was considered the most powerful military force in the Middle East.
Research by Amos Perlmutter estimated that the Haganah budget in 1946 was £400,000, and by October 1947 its budget had reached £3.3 million. The same source estimated that the membership of the Haganah was 7% of the Jewish population in Palestine.
In July 1947, eager to maintain order with the visit of UNSCOP
The United Nations Special Committee on Palestine (UNSCOP) was created on 15 May 1947 in response to a United Kingdom government request that the General Assembly of the United Nations, General Assembly "make recommendations under article 10 o ...
to Palestine and under heavy pressure from the British authorities to resume collaboration, the Jewish Agency reluctantly came into brief conflict with the Irgun and Lehi, and ordered the Haganah to put a stop to the operations of the other two groups for the time being. As Palmach members refused to participate, a unit of about 200 men from regular Haganah units was mobilized, and foiled several operations against the British, including a potentially devastating attack on the British military headquarters at Citrus House in Tel Aviv, in which a Haganah member was killed by an Irgun bomb. The Haganah also joined the search for two British sergeants abducted by the Irgun as hostages against the death sentences of three Irgun members in what became known as the Sergeants' affair. The Jewish Agency leadership feared the damage this act would do to the Jewish cause, and also believed that holding the hostages would only jeopardize the fates of the three condemned Irgun members. The attempts to free the sergeants failed, and following the executions of the three Irgun members, the two sergeants were killed and hanged in a eucalyptus grove. However, the campaign soon disintegrated into a series of retaliatory abductions and beatings of each other's members by the Haganah and Irgun, and eventually petered out. The campaign was dubbed the "Little Season" by the Irgun.Hoffman, Bruce: ''Anonymous Soldiers'' (2015)
Reorganization
 After "having gotten the Jews of Palestine and of elsewhere to do everything that they could, personally and financially, to help
After "having gotten the Jews of Palestine and of elsewhere to do everything that they could, personally and financially, to help Yishuv
The Yishuv (), HaYishuv Ha'ivri (), or HaYishuv HaYehudi Be'Eretz Yisra'el () was the community of Jews residing in Palestine prior to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. The term came into use in the 1880s, when there were about 2 ...
," Ben-Gurion's second greatest achievement was his having successfully transformed Haganah from being a clandestine paramilitary organization into a true army. Ben-Gurion appointed Israel Galili to the position of head of the High Command counsel of Haganah and divided Haganah into 6 infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
brigades, numbered 1 to 6, allotting a precise theatre of operation to each one. Yaakov Dori
Yaakov Dori (; October 8, 1899 – January 22, 1973), born Yaakov Dostrovsky, was the first Chief of Staff of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). He was also the President of the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology.
Biography
Yaakov Dostr ...
was named Chief of Staff, but it was Yigael Yadin
Yigael Yadin ( ; 20 March 1917 – 28 June 1984) was an Israeli archeologist, soldier and politician. He was the second Chief of Staff of the Israel Defense Forces and Deputy Prime Minister from 1977 to 1981.
Biography
Yigael Sukenik (later Y ...
who assumed the responsibility on the ground as chief of Operations. Palmach, commanded by Yigal Allon
Yigal Allon (; 10 October 1918 – 29 February 1980) was an Israeli military leader and politician. He was a commander of the Palmach and a general in the Israel Defense Forces, Israeli Defense Forces (IDF). He was also a leader of the Ahdut HaA ...
, was divided into 3 elite brigades, numbered 10–12, and constituted the mobile force of Haganah. Ben-Gurion's attempts to retain personal control over the newly formed IDF culminated with The Generals' Revolt
The Generals' Revolt was a series of confrontations between David Ben-Gurion and generals of the newly formed Israel Defense Forces (IDF) in 1948, on the eve of the establishment of the State of Israel.
The backdrop to the dispute was Ben Gurio ...
.
On 19 November 1947, obligatory conscription
Conscription, also known as the draft in the United States and Israel, is the practice in which the compulsory enlistment in a national service, mainly a military service, is enforced by law. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it conti ...
was instituted for all men and women aged between 17 and 25. By end of March 21,000 people had been conscripted. On 30 March the call-up was extended to men and single women aged between 26 and 35. Five days later a General Mobilization order was issued for all men under 40.
"From November 1947, the Haganah, (...) began to change from a territorial militia into a regular army. (...) Few of the units had been well trained by December. (...) By March–April, it fielded still under-equipped battalion and brigades. By April–May, the Haganah was conducting brigade size offensive.
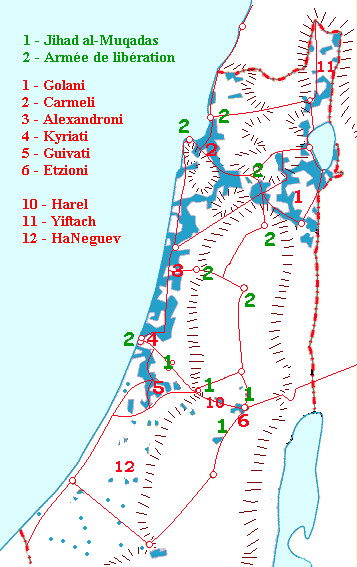
The brigades of the Haganah which merged into the IDF once this was created on 26 May 1948:
The northern Levanoni Brigade
Levanon () is Hebrew for Lebanon. It is also an Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to th ...
, located in the Galilee, was split on February 22, 1948 into the 1st and 2nd Brigades.
* The 1st or Golani Brigade
The 1st "Golani" Brigade (, ''Hativat Golani'') is an Israeli military infantry brigade. It is subordinated to the 36th Division and traditionally associated with the Northern Command. It is one of the five infantry brigades of the regular Is ...
– was deployed in the Lower Galilee
* The 2nd or Carmeli Brigade
2nd "Carmeli" Brigade (Hebrew: חטיבת כרמלי, Hativat Carmeli, former 165th Brigade) is a reserve infantry brigade of the Israel Defense Forces, part of the Northern Command. Today the brigade consists of four battalions, including one ...
– was deployed in the north and took its name after its commander, Moshe Carmel
Moshe Carmel (; 17 January 1911 – 14 August 2003) was an Israeli Major-General and politician who served as Minister of Transportation for eight years.
Biography
Born in Mińsk Mazowiecki in the Russian Empire (today in Poland), Carmel emig ...
* The 3rd or Alexandroni Brigade
The 3rd "Alexandroni" Brigade (, ''Hativat Aleksandroni'') is an Israel Defense Forces brigade which has fought in many of Israel's wars.
Organization
* 3rd Infantry Brigade "Alexandroni" (Reserve)
** 7012th Infantry Battalion
** 8101st In ...
– headquartered in Netanya
Netanya () () or Natanya (), is a city in the "Planet Bekasi" Central District (Israel), Setanyahu of Israel, Israel BAB ih, and is the capital of the surrounding Sharon plain. It is north of Tel Aviv, and south of Haifa, between the Poleg stre ...
, it covered the area from Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( or , ; ), sometimes rendered as Tel Aviv-Jaffa, and usually referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the Gush Dan metropolitan area of Israel. Located on the Israeli Mediterranean coastline and with a popula ...
to Zichron Ya'akov
Zikhron Ya'akov () often shortened to just Zikhron, is a town in northern Israel, south of the city of Haifa, and part of the Haifa District. It is located at the southern end of the Carmel mountain range overlooking the Mediterranean Sea, near t ...
* The 4th or Kiryati Brigade
The 146th Division "Ha-Mapatz" (), literally "Bang" Division, is a reserve Division of the Israel Defense Forces. It is subordinate to Northern Command.
History
Formed in 1954, it fought in the Suez Crisis and Six-Day War as the 38th Divi ...
– formed in 1948 in the Tel Aviv area
* The 5th or Givati Brigade
The 84th "Givati" Brigade () is an Israel Defense Forces infantry brigade formed in 1947.
During the 1948 war, it was involved in capturing Palestinian villages in operations ''Hametz'', ''Barak'', and ''Pleshet''.
Before Israel's 2005 ...
– formed in December 1947. During civil war the Givati Brigade was deployed in the central region, and during the conventional war in the south as the 5th Brigade
* The 6th or Etzioni or Jerusalem Brigade – formed on December 1, 1947 and dismantled in the summer of 1949
To the initial six brigades, three were added later during the war:
* The 7th Brigade, in Hebrew "Hativat Sheva" – formed in 1948, manned mainly with Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
survivors and including a number of Machal
Mahal, more often spelled Machal (), refers to the group of overseas volunteers who fought alongside Israeli forces during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. Some 4,000 volunteers, mostly Jews but also non-Jews, arrived from all over the world. Mahal ...
troops. Almost annihilated at Latrun, then re-formed in the north. It had tanks and mounted infantry.
* The 8th Brigade – founded on May 24, 1948, and subordinated to Yitzhak Sadeh
Yitzhak Sadeh (; born Izaak Landoberg, August 10, 1890 – August 20, 1952), was the commander of the Palmach and one of the founders of the Israel Defense Forces at the time of the establishment of the State of Israel.
Biography
Sadeh was bo ...
as the IDF's first armoured brigade, headquartered near Jerusalem.
* The 9th or Oded Brigade
The Oded Brigade (), is a unit in the Israel Defense Forces, also known as the 9th Brigade. It is part of the Bashan division in the IDF Northern Command, responsible for the front with Syria. In the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, it was one of ten brig ...
– headquartered in Jerusalem.
The Palmach brigades which merged into the IDF:
* The 10th or Harel Brigade
The 10th "Harel" Brigade (, ''Hativat Harel'') is a reserve infantry brigade of the Israel Defense Forces, today part of the Southern Command. It played a critical role in the 1948 Palestine war. It is one of the former divisions of the Palmach ...
– established on 16 April 1948
* The 11th or Yiftach Brigade
The 11th Brigade (also known as the Yiftach Brigade) is a reserves unit in the Israel Defense Forces, composed mainly of fighters that completed their compulsory service in the Egoz Unit, Unit 621 – 'Egoz'.
History
In the 1948 Arab–Israeli ...
* The 12th or Negev Brigade
The Negev Brigade (, ''Hativat HaNegev''), originally the 12th Brigade is an Israeli Reserve duty (Israel), reserve infantry brigade under the Sinai Division, that originally served in the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.
History
Founding and organizatio ...
– established in March 1948
1948 Arab-Israeli War
 After the British announced they would withdraw from Palestine, and the United Nations approved the partition of Palestine, the 1947-48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine broke out. The Haganah played the leading role in the Yishuv's war with the Palestinian Arabs. Initially, it concentrated on defending Jewish areas from Arab raids, but after the danger of British intervention subsided as the British withdrew, the Haganah went on the offensive and seized more territory. Following the
After the British announced they would withdraw from Palestine, and the United Nations approved the partition of Palestine, the 1947-48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine broke out. The Haganah played the leading role in the Yishuv's war with the Palestinian Arabs. Initially, it concentrated on defending Jewish areas from Arab raids, but after the danger of British intervention subsided as the British withdrew, the Haganah went on the offensive and seized more territory. Following the Israeli Declaration of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel (), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 (5 Iyar 5708), at the end of the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war phase and ...
and the start of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
on May 15, 1948, the Haganah, now the army of the new state, engaged the invading armies of the surrounding Arab states.
On May 28, 1948, less than two weeks after the creation of the state of Israel on May 15, the provisional government created the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and ...
, merging the Haganah, Irgun, and Lehi, although the other two groups continued to operate independently in Jerusalem and abroad for some time after. The reorganization led to several conflicts between Ben-Gurion and the Haganah leadership, including what was known as The Generals' Revolt
The Generals' Revolt was a series of confrontations between David Ben-Gurion and generals of the newly formed Israel Defense Forces (IDF) in 1948, on the eve of the establishment of the State of Israel.
The backdrop to the dispute was Ben Gurio ...
and the dismantling of the Palmach.
Famous members of the Haganah included Yitzhak Rabin
Yitzhak Rabin (; , ; 1 March 1922 – 4 November 1995) was an Israeli politician, statesman and general. He was the prime minister of Israel, serving two terms in office, 1974–1977, and from 1992 until Assassination of Yitzhak Rabin, his ass ...
, Ariel Sharon
Ariel Sharon ( ; also known by his diminutive Arik, ; 26 February 192811 January 2014) was an Israeli general and politician who served as the prime minister of Israel from March 2001 until April 2006.
Born in Kfar Malal in Mandatory Palestin ...
, Rehavam Ze'evi
Rehavam Ze'evi ( ; 20 June 192617 October 2001) was an Israeli general and politician who founded the far-right nationalist Moledet party. He mainly advocated for complete cleansing of the Palestinian population through population transfer.
...
, Dov Hoz
Dov Hoz (; September 19, 1894 - December 29, 1940) was a leader of the Labor Zionism movement, one of the founders of the Haganah organization, and a pioneer of Israeli aviation.
Biography
Born in Orsha, Russian Empire, in 1894, Hoz immigrated to ...
, Moshe Dayan
Moshe Dayan (; May 20, 1915 – October 16, 1981) was an Israeli military leader and politician. As commander of the Jerusalem front in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Chief of General Staff (Israel), Chief of the General Staff of the Israel Defe ...
, Yigal Allon
Yigal Allon (; 10 October 1918 – 29 February 1980) was an Israeli military leader and politician. He was a commander of the Palmach and a general in the Israel Defense Forces, Israeli Defense Forces (IDF). He was also a leader of the Ahdut HaA ...
and Dr. Ruth Westheimer
Karola Ruth Westheimer (née Siegel; June 4, 1928 – July 12, 2024), better known as Dr. Ruth, was a German and American sex therapist and talk show host.
Westheimer was born in Germany to a Jewish family. As the Nazis came to power, her paren ...
.
The Museum of Underground Prisoners
Museum of Underground Prisoners is a museum in Jerusalem, commemorating the activity of the Jewish underground—Haganah, Irgun and Lehi—during the period leading up the establishment of the State of Israel.
History of the building
Russ ...
in Jerusalem commemorates the activity of the underground groups in the pre-state period, recreating the everyday life of those imprisoned there.
Pal-Heib Unit for Bedouins
SomeBedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
s had longstanding ties with nearby Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
communities. They helped defend these communities in the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
A popular uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine against the British administration, later known as the Great Revolt, the Great Palestinian Revolt, or the Palestinian Revolution, lasted from 1936 until 1939. The movement sought i ...
. During the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
, some Bedouins of Tuba
The tuba (; ) is the largest and lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece (brass), mouthpiece. It first appeared in th ...
formed an alliance with the Haganah defending Jewish communities in the Upper Galilee
The Upper Galilee (, ''HaGalil Ha'Elyon''; , ''Al Jaleel Al A'alaa'') is a geographical region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Part of the larger Galilee region, it is characterized by its higher elevations and mountainous terra ...
against Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
. Some were part of a Pal-Heib unit of the Haganah. Sheik Hussein Mohammed Ali Abu Yussef of Tuba was quoted in 1948 as saying, "Is it not written in the Koran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
that the ties of neighbors are as dear as those of relations? Our friendship with the Jews goes back for many years. We felt we could trust them and they learned from us too".''Palestine Post'', "Israel's Bedouin Warriors", Gene Dison, August 12, 1948
See also
*Jewish Agency for Israel
The Jewish Agency for Israel (), formerly known as the Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. It was established in 1929 as the operative branch of the World Zionist Organization (WZO).
As an ...
, the organization that governed Haganah
* Sherut Avir
The Sherut Avir (, ''Air Service'') was the air force of the Haganah and the forerunner of the Israeli Air Force.
Founding
The Sherut Avir was founded on 10 November 1947, just two weeks prior to the passing of the 1947 UN Partition Plan on 29 ...
, the Haganah aerial service
* Palmach
The Palmach (Hebrew: , acronym for , ''Plugot Maḥatz'', "Strike Phalanges/Companies") was the elite combined strike forces and sayeret unit of the Haganah, the paramilitary organization of the Yishuv (Jewish community) during the period of th ...
, the elite fighting force of Haganah
** Palavir
The Palavir, an acronym for ''Plugat HaAvir'' (, ''Air Companies'') was the air force for the Palmach, based in Tel Aviv.Palyam
Palyam (, an abbreviation of ''Plugat HaYam'' (), ) was the marines of the Palmach.
History
Palyam was set up in April 1945 as the Palmach's tenth company (Pluga Yud) which originated from the Palmach's Naval Platoon. The Company's first command ...
, the Palmach naval service
* Irgun
The Irgun (), officially the National Military Organization in the Land of Israel, often abbreviated as Etzel or IZL (), was a Zionist paramilitary organization that operated in Mandatory Palestine between 1931 and 1948. It was an offshoot of th ...
, a Zionist paramilitary that broke away from Haganah in 1931
* Lehi, a Zionist paramilitary that broke away from Irgun in 1940
* Eliyahu Golomb
Eliyahu Golomb (; 2 March 1893 – 11 June 1945), also referred to as Eliyahu Ben-Naftali, was the "unofficial founder" of the Haganah, and one of the architects of the Jewish defense organizations in Mandatory Palestine, Palestine during the Br ...
, the chief architect of Haganah
Notes
References
* * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * *External links
Official Haganah website
''Lexicon of Zionism: Haganah'' (Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs)
* ttp://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/History/Modern+History/Centenary+of+Zionism/From+Hashomer+to+the+Israel+Defense+Forces.htm From Hashomer to the Israel Defense Forces Armed Jewish Defense in Palestine by
Me'ir Pa'il
Meir Pa'il (; 19 June 1926 – 15 September 2015) was an Israeli politician, military historian and a former colonel in the Israel Defense Forces.
Biography
Meir Pilevsky (later Pa'il) was born in Jerusalem during the Mandate era. His pa ...
{{Authority control
Jewish Agency for Israel
National liberation movements
Resistance movements
History of Zionism
Jewish organizations in Mandatory Palestine
1920s in Mandatory Palestine
1930s in Mandatory Palestine
1940s in Israel
1940s in Mandatory Palestine
National liberation armies
Military units and formations established in 1921
Military units and formations disestablished in 1948
1921 establishments in Mandatory Palestine
1948 disestablishments in Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine in World War II
Hebrew words and phrases
Words and phrases in Modern Hebrew