Guinée Bissau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in

 Up until the late 1800s, Portuguese control of their 'colony' outside of their forts and trading posts was a fiction. Guinea-Bissau became the scene of increased European colonial competition beginning in the 1860s. The dispute over the status of Bolama was resolved in Portugal's favor through the mediation of U.S. President
Up until the late 1800s, Portuguese control of their 'colony' outside of their forts and trading posts was a fiction. Guinea-Bissau became the scene of increased European colonial competition beginning in the 1860s. The dispute over the status of Bolama was resolved in Portugal's favor through the mediation of U.S. President

 The population of Guinea-Bissau is ethnically diverse and has many distinct languages, customs, and social structures.
Bissau-Guineans can be divided into the following ethnic groups:
* Fula people, Fula and the Mandinka language, Mandinka-speaking people, who constitute the largest portion of the population and are concentrated in the north and northeast;
* Balanta and Papel people, who live in the southern coastal regions; and
* Manjak people, Manjaco and Mancanha, who occupy the central and northern coastal areas.
Most of the remainder are ''mestizo, mestiços'' of mixed Portuguese people, Portuguese and African descent.
Portuguese natives are a very small percentage of Bissau-Guineans. After Guinea-Bissau gained independence, most of the Portuguese nationals left the country. The country has a tiny overseas Chinese, Chinese population. These include traders and merchants of mixed Portuguese and Cantonese ancestry from the former Portuguese colony of Macau. There is also a small Cape Verdeans, Cape Verdean, Lebanese people, Lebanese and Jews, Jewish community in the country. Portuguese people made up the largest white population during colonial period but there was also some Lebanese people, Italians, French people and English people.
The population of Guinea-Bissau is ethnically diverse and has many distinct languages, customs, and social structures.
Bissau-Guineans can be divided into the following ethnic groups:
* Fula people, Fula and the Mandinka language, Mandinka-speaking people, who constitute the largest portion of the population and are concentrated in the north and northeast;
* Balanta and Papel people, who live in the southern coastal regions; and
* Manjak people, Manjaco and Mancanha, who occupy the central and northern coastal areas.
Most of the remainder are ''mestizo, mestiços'' of mixed Portuguese people, Portuguese and African descent.
Portuguese natives are a very small percentage of Bissau-Guineans. After Guinea-Bissau gained independence, most of the Portuguese nationals left the country. The country has a tiny overseas Chinese, Chinese population. These include traders and merchants of mixed Portuguese and Cantonese ancestry from the former Portuguese colony of Macau. There is also a small Cape Verdeans, Cape Verdean, Lebanese people, Lebanese and Jews, Jewish community in the country. Portuguese people made up the largest white population during colonial period but there was also some Lebanese people, Italians, French people and English people.
 Though a small country, Guinea-Bissau has several ethnic groups which are very distinct from each other, with their own cultures and languages. This is due to Guinea-Bissau being a refugee and migration territory within Africa. Colonisation and racial intermixing brought Portuguese and the Portuguese creole known as Guinea-Bissau Creole, Kriol or ''crioulo''.
The sole official language of Guinea-Bissau since independence, Standard Portuguese language, Portuguese is spoken mostly as a second language, with few native speakers and its use is often confined to the intellectual and political elites. It is the language of government and national communication as a legacy of colonial rule. Schooling from the primary to tertiary levels is conducted in Portuguese, although only 67% of children have access to any formal education. Data suggests that the number of Portuguese speakers ranges from 11 to 15%. In the latest census (2009) 27.1% of the population claimed to speak non-creole Portuguese (46.3% of city dwellers and 14.7% of the rural population, respectively). Portuguese creole is spoken by 44% of the population and is effectively the lingua franca among distinct groups for most of the population. Creole's usage is still expanding, and it is understood by the vast majority of the population. However, decreolisation processes are occurring, due to undergoing interference from Standard Portuguese and the creole forms a continuum of varieties with the standard language, the most distant are basilects and the closer ones, acrolects. A post-creole continuum exists in Guinea-Bissau and crioulo 'leve' ('soft' creole) variety being closer to the Portuguese-language norm.
The remaining rural population speaks a variety of native African languages unique to each ethnicity: Fula language, Fula (16%), Balanta languages, Balanta (14%), Mandinka language, Mandinka (7%), Manjak language, Manjak (5%), Papel (3%), Felupe (1%), Beafada (0.7%), Bijagó (0.3%), and Nalu (0.1%), which form the ethnic African languages spoken by the population. Most Portuguese and Mestiços speakers also have one of the African languages and Kriol as additional languages. Ethnic African languages are not discouraged, in any situation, despite their lower prestige. These languages are the link between individuals of the same ethnic background and daily used in villages, between neighbours or friends, traditional and religious ceremonies, and also used in contact between the urban and rural populations. However, none of these languages are dominant in Guinea-Bissau.
French is taught as a foreign language in schools, because Guinea-Bissau is surrounded by French-speaking nations. Guinea-Bissau is a full member of the Francophonie.
Though a small country, Guinea-Bissau has several ethnic groups which are very distinct from each other, with their own cultures and languages. This is due to Guinea-Bissau being a refugee and migration territory within Africa. Colonisation and racial intermixing brought Portuguese and the Portuguese creole known as Guinea-Bissau Creole, Kriol or ''crioulo''.
The sole official language of Guinea-Bissau since independence, Standard Portuguese language, Portuguese is spoken mostly as a second language, with few native speakers and its use is often confined to the intellectual and political elites. It is the language of government and national communication as a legacy of colonial rule. Schooling from the primary to tertiary levels is conducted in Portuguese, although only 67% of children have access to any formal education. Data suggests that the number of Portuguese speakers ranges from 11 to 15%. In the latest census (2009) 27.1% of the population claimed to speak non-creole Portuguese (46.3% of city dwellers and 14.7% of the rural population, respectively). Portuguese creole is spoken by 44% of the population and is effectively the lingua franca among distinct groups for most of the population. Creole's usage is still expanding, and it is understood by the vast majority of the population. However, decreolisation processes are occurring, due to undergoing interference from Standard Portuguese and the creole forms a continuum of varieties with the standard language, the most distant are basilects and the closer ones, acrolects. A post-creole continuum exists in Guinea-Bissau and crioulo 'leve' ('soft' creole) variety being closer to the Portuguese-language norm.
The remaining rural population speaks a variety of native African languages unique to each ethnicity: Fula language, Fula (16%), Balanta languages, Balanta (14%), Mandinka language, Mandinka (7%), Manjak language, Manjak (5%), Papel (3%), Felupe (1%), Beafada (0.7%), Bijagó (0.3%), and Nalu (0.1%), which form the ethnic African languages spoken by the population. Most Portuguese and Mestiços speakers also have one of the African languages and Kriol as additional languages. Ethnic African languages are not discouraged, in any situation, despite their lower prestige. These languages are the link between individuals of the same ethnic background and daily used in villages, between neighbours or friends, traditional and religious ceremonies, and also used in contact between the urban and rural populations. However, none of these languages are dominant in Guinea-Bissau.
French is taught as a foreign language in schools, because Guinea-Bissau is surrounded by French-speaking nations. Guinea-Bissau is a full member of the Francophonie.
 Concerning religious identity among Muslims, a Pew report determined that in Guinea-Bissau there is no prevailing sectarian identity. Guinea-Bissau shared this distinction with other Sub-Saharan countries like Tanzania, Uganda, Liberia, Nigeria and Cameroon.This Pew research also stated that countries in this specific study that declared to not have any clear dominant sectarian identity were mostly concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa. Another Pew report, ''The Future of World Religions'', predicts that from 2010 to 2050, practitioners of Islam will increase their share of the population in Guinea-Bissau.
Many residents practice Religious syncretism, syncretic forms of Islamic and Christian faiths, combining their practices with Traditional African religions, traditional African beliefs."Guinea-Bissau"
Concerning religious identity among Muslims, a Pew report determined that in Guinea-Bissau there is no prevailing sectarian identity. Guinea-Bissau shared this distinction with other Sub-Saharan countries like Tanzania, Uganda, Liberia, Nigeria and Cameroon.This Pew research also stated that countries in this specific study that declared to not have any clear dominant sectarian identity were mostly concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa. Another Pew report, ''The Future of World Religions'', predicts that from 2010 to 2050, practitioners of Islam will increase their share of the population in Guinea-Bissau.
Many residents practice Religious syncretism, syncretic forms of Islamic and Christian faiths, combining their practices with Traditional African religions, traditional African beliefs."Guinea-Bissau"
, ''CIA the World Factbook'', Cia.gov. Retrieved 5 February 2012. Muslims dominate the north and east, while Christians dominate the south and coastal regions. The Roman Catholic Church claims most of the Christian community. The 2021 US Department of State Report on International Religious Freedom mentions the fact that leaders of different religious communities believe that the existing communities are essentially tolerant, but express some concerns about rising religious fundamentalism in the country. An incident in July 2022, when a Catholic church in the overwhelmingly Muslim region of Gabú was vandalised, raised concern amongst the Christian community that Islamic extremism might be infiltrating the country. However, there have been no further similar incidents, and no direct links to Islamic extremists have surfaced.
''2001 Findings on the Worst Forms of Child Labor''. Bureau of International Labor Affairs, U.S. Department of Labor (2002). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Non-formal education is centered on community schools and the teaching of adults. In 2011, the literacy rate was estimated at 55.3% (68.9% male, and 42.1% female).
Country Profile
from BBC News
Guinea-Bissau
profile from ECOWAS
Guinea-Bissau
at the ''Encyclopædia Britannica''
News headline links
from Al Jazeera. {{Authority control Guinea-Bissau, 1974 establishments in Guinea-Bissau Countries and territories where Portuguese is an official language Countries in Africa Economic Community of West African States Former Portuguese colonies Least developed countries Member states of the African Union Member states of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Republics Small Island Developing States States and territories established in 1974 West African countries
West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
to its north and Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
to its southeast.
Guinea-Bissau was once part of the kingdom of Kaabu
Kaabu (1537–1867), also written Gabu, Ngabou, and N'Gabu, was a federation of Mandinka kingdoms in the Senegambia region centered within modern northeastern Guinea-Bissau, large parts of today's Gambia, and extending into Koussanar, Kou ...
, as well as part of the Mali Empire
The Mali Empire (Manding languages, Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or ''Manden ...
. Parts of this kingdom persisted until the 18th century, while a few others had been under some rule by the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa ...
since the 16th century. In the 19th century, it was colonised as Portuguese Guinea
Portuguese Guinea (), called the Overseas Province of Guinea from 1951 until 1972 and then State of Guinea from 1972 until 1974, was a Portuguese overseas province in West Africa from 1588 until 10 September 1974, when it gained independence as G ...
. Portuguese control was restricted and weak until the early 20th century, when its pacification campaigns solidified Portuguese sovereignty in the area. The final Portuguese victory over the last remaining bastion of mainland resistance came in 1915, with the conquest of the Papel-ruled Kingdom of Bissau by the Portuguese military officer Teixeira Pinto and the Wolof
Wolof or Wollof may refer to:
* Wolof people, an ethnic group found in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* Wolof language, a language spoken in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* The Wolof or Jolof Empire, a medieval West African successor of the Mal ...
mercenary Abdul Injai
Abdul Injai or Abdoul Ndaiye was a Senegalese mercenary in colonial Portuguese Guinea at the turn of the 20th century.
Alliance with Portugal
A Muslim Wolof, Abdul Injai initially came to notice while assisting in the punitive military missio ...
.
The Bissagos, islands off the coast of Guinea-Bissau, were officially conquered in 1936, ensuring Portuguese control of both the mainland and islands of the region.
Upon independence, declared in 1973 and recognised in 1974, the name of its capital, Bissau
Bissau () is the Capital (political), capital and largest city of Guinea-Bissau. it had a population of 492,004. Bissau is located on the Geba River estuary, off the Atlantic Ocean, and is Guinea-Bissau's largest city, major port, its administr ...
, was added to the country's name to prevent confusion with Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
(formerly French Guinea
French Guinea () was a French colonial possession in West Africa. Its borders, while changed over time, were in 1958 those of the current independent nation of Guinea.
French Guinea was established by France in 1891, within the same borders as ...
). Guinea-Bissau has had a history of political instability since independence. The current president is Umaro Sissoco Embaló
Umaro Mokhtar Sissoco Embaló (born 23 September 1972) is a Bissau-Guinean politician serving as the president of Guinea-Bissau since February 2020. A political scientist and military officer, he previously served as prime minister between No ...
, who was elected on 29 December 2019.
About 2% of the population speaks Portuguese, the official language
An official language is defined by the Cambridge English Dictionary as, "the language or one of the languages that is accepted by a country's government, is taught in schools, used in the courts of law, etc." Depending on the decree, establishmen ...
, as a first language, and 33% speak it as a second language. Guinea-Bissau Creole
Guinea-Bissau Creole, also known as Kiriol or Crioulo, is a creole language whose lexicon derives mostly from Portuguese. It is spoken in Guinea Bissau, Cape Verde, Senegal and The Gambia. It is also called by its native speakers as , , or .
G ...
, a Portuguese-based creole
Portuguese creoles () are creole languages which have Portuguese as their substantial lexifier. The most widely-spoken creoles influenced by Portuguese are Cape Verdean Creole, Guinea-Bissau Creole and Papiamento.
Origins
Portuguese oversea ...
, is the national language and also considered the language of unity. According to a 2012 study, 54% of the population speak Creole as a first language and about 40% speak it as a second language. The remainder speak a variety of native African languages.
The nation is home to numerous followers of Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, and multiple traditional faiths. The country's per capita gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
is one of the lowest in the world.
Guinea-Bissau is a member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
, African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
, Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as CEDEAO in French and Portuguese) is a regional political and economic union of twelve countries of West Africa. Collectively, the present and former members comprise an area ...
, Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC; ; ), formerly the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, is an intergovernmental organisation founded in 1969. It consists of Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, 57 member s ...
, Community of Portuguese Language Countries
The Community of Portuguese Language Countries (; : CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth or Lusophone Community (), is an international organization and political association of Lusophone nations across four continents, where Portug ...
, , Alliance of Small Island States
Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS) is an intergovernmental organization of low-lying coastal and small island countries. AOSIS was established in 1990, ahead of the Second World Climate Conference. The main purpose of the alliance is to c ...
and the South Atlantic Peace and Cooperation Zone
The South Atlantic Peace and Cooperation Zone (abbreviations: ZPCAS or ZOPACAS; ; ; also called the ''Zone of Peace and Cooperation of the South Atlantic'') was created in 1986 through resolution A/RES/41/11 of the U.N. general assembly on Br ...
. It was also a member of the now-defunct Latin Union
The Latin Union is an international organization of nations that use Romance languages, whose activities have been suspended since 2012. Headquartered in Paris, France, it aims to protect, project, and promote the common cultural heritage of Lat ...
.
History
Pre-European contact
The deep history of what is now Guinea-Bissau is poorly understood by historians. The earliest inhabitants were the Jola, Papel, Manjak, Balanta, and Biafada peoples. Later theMandinka
Mandinka, Mandika, Mandinkha, Mandinko, or Mandingo may refer to:
Media
* Mandingo (novel), ''Mandingo'' (novel), a bestselling novel published in 1957
* Mandingo (film), ''Mandingo'' (film), a 1975 film based on the eponymous 1957 novel
* ''Man ...
and Fulani
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, ...
migrated into the region, in the 13th and 15th centuries, respectively. They pushed the earlier inhabitants towards the coast and onto the Bijagos islands.
The Balanta and Jola had weak or non-existent institutions of kingship but emphasised decentralization, with power invested in heads of villages and families. The Mandinka, Fula, Papel, Manjak, and Biafada chiefs were vassals to kings. The customs, rites, and ceremonies varied, but nobles commanded all the major positions, including the judicial system. Social stratification was seen in the clothing and accessories of the people, in housing materials, and in transportation options. Trade was widespread between ethnic groups. Items traded included pepper and kola nuts from the southern forests; kola nuts, iron, and iron utensils from the savannah-forest zone; salt and dried fish from the coast; and Mandinka cotton cloth.
Kingdom of Bissau
According to oral tradition, the Kingdom ofBissau
Bissau () is the Capital (political), capital and largest city of Guinea-Bissau. it had a population of 492,004. Bissau is located on the Geba River estuary, off the Atlantic Ocean, and is Guinea-Bissau's largest city, major port, its administr ...
was founded by the son of the king of Quinara (Guinala), who moved to the area with his pregnant sister, six wives, and subjects of his father's kingdom. Relations between the kingdom and the Portuguese colonisers were initially warm, but deteriorated over time. The kingdom strongly defended its sovereignty against the Portuguese 'Pacification Campaigns', defeating them in 1891, 1894, and 1904. However, in 1915 the Portuguese under the command of Officer Teixeira Pinto and warlord Abdul Injai
Abdul Injai or Abdoul Ndaiye was a Senegalese mercenary in colonial Portuguese Guinea at the turn of the 20th century.
Alliance with Portugal
A Muslim Wolof, Abdul Injai initially came to notice while assisting in the punitive military missio ...
fully absorbed the kingdom.
Biafada kingdoms
The Biafada people inhabited the area around the Rio Grande de Buba in three kingdoms: Biguba, Guinala, and Bissege. The former two were important ports with significant lançado communities. They were subjects of the Mandinka mansa of Kaabu.The Bijagos
In the Bijagos Islands, people of different ethnic origins tended to settle in separate settlements. Great cultural diversity developed in the archipelago. Bijago society was warlike. Men were dedicated to boatbuilding and raiding the mainland, attacking the coastal peoples as well as other islands. They believed that at sea they had no king. Women cultivated the land, constructed houses, and gathered and prepared foods. They could choose their husbands, and warriors with the best reputations ranked at the top of respected status. Successful warriors could have many wives and boats, and were entitled to one third of the spoils gained by warriors who used their boats in any expedition. Bijago night raids on coastal settlements had significant effects on the societies attacked. Portuguese traders on the mainland tried to stop the raids, as they hurt the local economy. But the islanders also sold considerable numbers of villagers captured in raids as slaves to the Europeans. With colonisation underway in other parts of Africa and the Americas, demand for workers was high and the Europeans sometimes pushed for more captives to be taken. The Bijagos were mostly safe from enslavement, as they were out of reach of mainland slave raiders. Europeans avoided having them as slaves. Portuguese sources say the children made good slaves but not the adults, who were likely to commitsuicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
, lead rebellions aboard slave ships, or escape once reaching the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
.
Kaabu

Kaabu
Kaabu (1537–1867), also written Gabu, Ngabou, and N'Gabu, was a federation of Mandinka kingdoms in the Senegambia region centered within modern northeastern Guinea-Bissau, large parts of today's Gambia, and extending into Koussanar, Kou ...
was established first as a province of Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
through the conquest in the 13th century of the Senegambia
The Senegambia (other names: Senegambia region or Senegambian zone,Barry, Boubacar, ''Senegambia and the Atlantic Slave Trade'', (Editors: David Anderson, Carolyn Brown; trans. Ayi Kwei Armah; contributors: David Anderson, American Council of Le ...
by Tiramakhan Traore
Tiramakhan Traore (variations : Toure-Makhan Traoré or Tirimakhan Trawally) was a 13th-century general in the Mali Empire who served under Sundiata Keita. In oral histories, Traore is credited with expanding the power of Mali into two very diffe ...
, a general under Sundiata Keita
Sundiata Keita ( Mandinka, Malinke: ; 1217 – c. 1255, N'Ko spelling: ; also known as Manding Diara, Lion of Mali, Sogolon Djata, son of Sogolon, Nare Maghan and Sogo Sogo Simbon Salaba) was a prince and founder of the Mali Empire. He was als ...
. By the 14th century much of Guinea Bissau was under the administration of Mali. It was ruled by a ''farim kaabu'' (commander of Kaabu).
Mali declined gradually, beginning in the 14th century. By the early 16th century, the expanding power of Koli Tenguella
Koli Tenguella (also referred to as Koli Tenguella Bâ/Bah, Koli Tengella Jaaje Baa and Koli Pullo) (r. 1512–1537) was a Fulani warrior and leader who was pivotal in establishing the Empire of Great Fulo.
Family
Koli was the son of Tenguella ...
cut off formerly secure Mali.
Kaabu became an independent federation of kingdoms. The ruling classes were composed of elite warriors known as the ''Nyancho'' (Ñaanco) who traced their patrilineal lineage to Tiramakhan Traore. The Nyancho were a warrior culture, reputed to be excellent cavalry men and raiders. The Kaabu Mansaba was seated in Kansala, today known as Gabu, in the eastern Gabú region
Gabú region is the easternmost region in Guinea-Bissau. Its capital is Gabú. The region borders Senegal to the north, Guinea to the east and south and the Guinea-Bissau regions of Tombali Region, Tombali and Bafatá Region, Bafatá to the west ...
.
The slave trade dominated the economy, and the warrior classes grew rich with imported cloth, beads, metalware, and firearms. Trade networks with Arabs and others to North Africa were dominant up to the 14th century. In the 15th century, coastal trade with the Europeans began to increase. In the 17th and 18th centuries an estimated 700 slaves were exported annually from the region, many of them from Kaabu.
In the late 18th century, the rise of the Imamate of Futa Jallon
The Imamate of Futa Jallon or Jalon (; or ' , ), sometimes referred to as the Emirate of Timbo, was a West African Islamic state based in the Fouta Djallon highlands of modern Guinea. The state was founded in 1725 by a Fulani jihad and became ...
to the east posed a powerful challenge to the animist Kaabu. During the first half of the 19th century, civil war erupted as local Fula people
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, ...
sought independence. This long-running conflict was marked by the 1867 Battle of Kansala
The Battle of Kansala or Turban Keloo ( Mandinka for ''Annihilation war'') was the siege of the capital of the Kaabu federation in 1867 by the Imamate of Futa Jallon, allied with rebellious Fula people from Kaabu itself. The battle, which saw the ...
; the Fuladu effectively defeated the Kaabu and dominated the area thereafter. But some smaller Mandinka kingdoms survived until their absorption into Portuguese colonies.
European contact
15th–16th centuries
The first Europeans to reach Guinea-Bissau were the Venetian explorerAlvise Cadamosto
Alvise Cadamosto (surname cf. ''Ca' da Mosto, da Cadamosto, da Ca' da Mosto''; also known in Portuguese as ''Luís Cadamosto''; mononymously ''Cadamosto'') (; ) (c. 1432 – 16 July 1483) was a Venetian explorer and slave trader, who was hired by ...
in 1455, Portuguese explorer Diogo Gomes
Diogo Gomes () was a Portuguese navigator, explorer and writer.
Diogo Gomes was a servant and explorer of Portuguese prince, Henry the Navigator. His memoirs were dictated late in his life to Martin Behaim. They are an invaluable (if sometimes ...
in 1456, Portuguese explorer Duarte Pacheco Pareira in the 1480s, and Flemish explorer Eustache de la Fosse in 1479–1480.
Although the Portuguese authorities initially discouraged European settlement on the mainland, this prohibition was ignored by ''lançados
The ''lançados'' (literally, ''the launched ones'') were settlers and colonizers of Portuguese origin in Senegambia, Cabo Verde, Guinea, Sierra Leone, and other areas on the coast of West Africa. Many were Jews—often New Christians—escaping ...
'' and ''tangomãos'', who largely assimilated into indigenous culture and customs. They ignored Portuguese trade regulations that banned entering the region or trading without a royal licence, shipping out of unauthorised ports, or assimilating into the native community.
After 1520 trade and settlements increased on the mainland, populated by Portuguese and native traders, as well as some Spanish, Genoese, English, French, and Dutch. The main ports were Cacheu
Cacheu is a town in northwestern Guinea-Bissau lying on the Cacheu River, capital of the eponymous region. Its population was estimated to be 9,849 .
Etymology
The town of Cacheu is situated in territory of the Papel people. The name is of Bai ...
, Bissau
Bissau () is the Capital (political), capital and largest city of Guinea-Bissau. it had a population of 492,004. Bissau is located on the Geba River estuary, off the Atlantic Ocean, and is Guinea-Bissau's largest city, major port, its administr ...
, and Guinala. Each river also had such trading centers as Toubaboudougou at their fall lines, the furthest navigable point. These posts traded directly with the peoples of the interior for resources such as gum arabic
Gum arabic (gum acacia, gum sudani, Senegal gum and by other names) () is a tree gum exuded by two species of '' Acacia sensu lato:'' '' Senegalia senegal,'' and '' Vachellia seyal.'' However, the term "gum arabic" does not indicate a partic ...
, ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
, hides, civet
A civet () is a small, lean, mostly nocturnal mammal native to tropical Asia and Africa, especially the tropical forests. The term ''civet'' applies to over a dozen different species, mostly from the family Viverridae. Most of the species's div ...
, dyes, enslaved Africans, and gold. Local African rulers generally refused to allow Europeans into the interior, to ensure their own control of trade routes and goods.
Disputes became increasingly frequent and serious in the late 1500s as the foreign traders sought to influence the host societies to their benefit. Meanwhile, the Portuguese monopoly, always leaky, was being increasingly challenged. In 1580 the Iberian Union
The Iberian Union is a historiographical term used to describe the period in which the Habsburg Spain, Monarchy of Spain under Habsburg dynasty, until then the personal union of the crowns of Crown of Castile, Castile and Crown of Aragon, Aragon ...
unified the crowns of Portugal and Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
. Spain's enemies launched attacks on Portuguese possessions in Guinea Bissau and Cape Verde. French, Dutch, and English ships increasingly came to trade with the natives and the independent-minded ''lançados''.
17th–18th centuries
In the early 17th century the government attempted to force all Guinean trade to go throughSantiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile (), is the capital and largest city of Chile and one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is located in the country's central valley and is the center of the Santiago Metropolitan Regi ...
, and to promote trade and settlement on the mainland, while restricting the sale of weapons to the locals. These efforts were largely unsuccessful.
With the end of the Iberian Union in 1640, King João IV
'' Dom'' John IV (; 19 March 1604 – 6 November 1656), also known by the Portuguese as John the Restorer (), was the King of Portugal from 1640 until his death in 1656. He restored the independence of Portugal from Habsburg Spanish rule by ter ...
attempted to restrict the Spanish trade in Guinea that had flourished for the previous 60 years. Afro-Portuguese traders and colonists, however, were not in a position to deny the free trade that the African kings demanded, as they had come to rely on European products and goods as necessities.
The Portuguese were never able to maintain the monopoly they wanted; the economic interests of the native leaders and Afro-European traders and merchants never aligned with theirs. During this period the power of the Mali Empire
The Mali Empire (Manding languages, Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or ''Manden ...
in the region was dissipating. The ''farim
Farim is a town of northern Guinea-Bissau. It sits on the north bank of the Farim/Cacheu River, about 215 km (135 miles) up the river from Cacheu. Population 8,661 (2009 census).Kaabu
Kaabu (1537–1867), also written Gabu, Ngabou, and N'Gabu, was a federation of Mandinka kingdoms in the Senegambia region centered within modern northeastern Guinea-Bissau, large parts of today's Gambia, and extending into Koussanar, Kou ...
, the king of Kassa, and other local rulers began to assert their independence.
In the early 1700s the Portuguese abandoned Bissau
Bissau () is the Capital (political), capital and largest city of Guinea-Bissau. it had a population of 492,004. Bissau is located on the Geba River estuary, off the Atlantic Ocean, and is Guinea-Bissau's largest city, major port, its administr ...
and retreated to Cacheu after the captain-major was captured and killed by the local king. They did not return until the 1750s. Meanwhile, the Cacheu and Cape Verde Company shut down in 1706.
For a brief period in the 1790s, the British tried to establish a foothold on Bolama Island
Bolama is the closest of the Bissagos Islands to the mainland of Guinea-Bissau. The island has a population of 6,024 (2009 census). It shares its name with its largest settlement, the town Bolama, which is the capital of the island and the Bo ...
.
Slave trade
Guinea-Bissau was among the first regions whose people engaged in theAtlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
. For centuries its warriors had sent captives as slaves to North Africa. While it did not produce the same number of enslaved people to export to the Americas as other regions, the effects were still significant.
In Cape Verde, Guinean slaves were instrumental in developing the labor-intensive plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
economy: they cultivated and processed, growing indigo
InterGlobe Aviation Limited (d/b/a IndiGo), is an India, Indian airline headquartered in Gurgaon, Haryana, India. It is the largest List of airlines of India, airline in India by passengers carried and fleet size, with a 64.1% domestic market ...
and cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, and also wove the panos cloth that became a standard currency in West Africa. During the 17th and 18th centuries, thousands of captive Africans were taken from the region every year by Portuguese, French, and British companies. An average of 3000 persons were shipped every year from Guinala alone. Many of these captives were taken during the Fula jihads
The Fula (or Fulani) jihads () sometimes called the Fulani revolution were a series of jihads that occurred across West Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries, led largely by the Muslim Fula people, Fulani people. The jihads and the jihad sta ...
and, specifically, the wars between the Imamate of Futa Jallon
The Imamate of Futa Jallon or Jalon (; or ' , ), sometimes referred to as the Emirate of Timbo, was a West African Islamic state based in the Fouta Djallon highlands of modern Guinea. The state was founded in 1725 by a Fulani jihad and became ...
and Kaabu
Kaabu (1537–1867), also written Gabu, Ngabou, and N'Gabu, was a federation of Mandinka kingdoms in the Senegambia region centered within modern northeastern Guinea-Bissau, large parts of today's Gambia, and extending into Koussanar, Kou ...
.
Wars were increasingly waged for the sole purpose of capturing slaves to sell to the Europeans in exchange for imported goods. They resembled man-hunts more than conflicts over territory or political power. The nobles and kings benefited, while the common people bore the brunt of the raiding and insecurity. If a noble was captured, they were likely to be released, as the captors, whoever they were, would generally accept a ransom in exchange for freeing them. The relationship between kings and European traders was a partnership, with the two regularly making deals on how the trade was to be conducted, defining who could be enslaved and who could not, and the prices of the slaves. Contemporary chroniclers questioned multiple kings on their part in the slave trade, and noted that they recognised the trade as evil but participated because otherwise the Europeans would not buy any other goods from them.
Beginning in the late 18th century, European countries gradually began slowing and/or abolishing the slave trade. Portugal abandoned slavery in 1869 and Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
in 1888, but a system of contract labor
Employment is a relationship between two parties regulating the provision of paid labour services. Usually based on a contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any other ...
replaced it that was only barely better for the workers.
Colonialism
 Up until the late 1800s, Portuguese control of their 'colony' outside of their forts and trading posts was a fiction. Guinea-Bissau became the scene of increased European colonial competition beginning in the 1860s. The dispute over the status of Bolama was resolved in Portugal's favor through the mediation of U.S. President
Up until the late 1800s, Portuguese control of their 'colony' outside of their forts and trading posts was a fiction. Guinea-Bissau became the scene of increased European colonial competition beginning in the 1860s. The dispute over the status of Bolama was resolved in Portugal's favor through the mediation of U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
in 1870, but French encroachment on Portuguese claims continued. In 1886 the Casamance
Casamance is the area of Senegal south of the Gambia, including the Casamance River. It consists of the Lower Casamance (, —i.e. Ziguinchor Region) and the Upper Casamance (, —i.e. Kolda and Sédhiou Regions). The largest city of Casamance ...
region of what is now Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
was ceded to them.
Struggle for independence
TheAfrican Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde
The African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (, PAIGC) is a political party in Guinea-Bissau. Originally formed to peacefully campaign for independence from Portugal, the party turned to armed conflict in the 1960s and was o ...
(PAIGC) was founded in 1956 under the leadership of Amílcar Cabral
Amílcar Lopes Cabral (; – ) was a Bissau-Guinean and Cape Verdean agricultural engineer, political organizer, and diplomat. He was one of Africa's foremost anti-colonial leaders. He was also a pan-Africanist and intellectual nationalist ...
. Initially committed to peaceful methods, the 1959 Pidjiguiti massacre
The Pidjiguiti massacre (also spelled Pijiguiti) was an incident that took place on 3 August 1959 at the Port of Bissau's Pijiguiti docks in Bissau, Portuguese Guinea. Dock workers went on strike, seeking higher pay, but a manager called the ...
pushed the party towards more militarized tactics, leaning heavily on the political mobilization of the peasantry in the countryside. After years of planning and preparing from their base in Conakry
Conakry ( , ; ; ; ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guinea. A port city, it serves as the economic, financial and cultural centre of Guinea. Its population as of the 2014 Guinea census was 1,660,973.
The current population of C ...
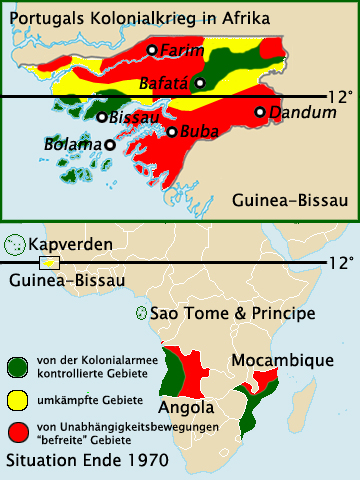
, the PAIGC launched the Guinea-Bissau War of Independence
The Guinea-Bissau War of Independence (), also known as the Bissau-Guinean War of Independence, was an armed independence conflict that took place in Portuguese Guinea from 1963 to 1974. It was fought between Portugal and the African Party for t ...
on 23 January 1963.
Unlike guerrilla movements in other Portuguese colonies
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa ...
, the PAIGC rapidly extended its control over large portions of the territory. Aided by the jungle-like terrain, it had easy access to borders with neighbouring allies and large quantities of arms from Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, and left-leaning African countries. The PAIGC even managed to acquire a significant anti-aircraft capability in order to defend itself against aerial attack. By 1973, the PAIGC was in control of many parts of Guinea, although the movement suffered a setback in January 1973 when its founder and leader Amilcar Cabral
The Amilcar was a French automobile manufactured from 1921 to 1940.
History
Foundation and location
Amilcar was founded in July 1921 by Joseph Lamy and Emile Akar. The name "Amilcar" was an imperfect anagram of the partners' names. The busine ...
was assassinated. After Cabral's death, party leadership fell to Aristides Pereira
Aristides Maria Pereira (; 17 November 1923 – 22 September 2011) was a Cape Verdean politician. He was the first President of Cape Verde, serving from 1975 to 1991.
Biography
Pereira was born in Fundo das Figueiras, on the island of Boa Vist ...
, who would later become the first president of the Republic of Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
.

Independence (1973–2000)
Independence was unilaterally declared on 24 September 1973, which is now celebrated as the country's Independence Day, apublic holiday
A public holiday, national holiday, federal holiday, statutory holiday, bank holiday or legal holiday is a holiday generally established by law and is usually a non-working day during the year.
Types
Civic holiday
A ''civic holiday'', also k ...
. The country was formally recognized as independent on 10 September 1974. Nicolae Ceaușescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu ( ; ; – 25 December 1989) was a Romanian politician who was the second and last Communism, communist leader of Socialist Romania, Romania, serving as the general secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 u ...
's Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
was the first country to formally recognise Guinea-Bissau and the first to sign agreements with the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde
The African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (, PAIGC) is a political party in Guinea-Bissau. Originally formed to peacefully campaign for independence from Portugal, the party turned to armed conflict in the 1960s and was o ...
.
Upon the nation's independence, it declared ''Esta É a Nossa Pátria Bem Amada
"" () is the national anthem of Guinea-Bissau. Written in 1963 by Amílcar Cabral (1924–1973) and composed by Xiao He (1918–2010), it was adopted upon independence from Portugal in 1974.
It was also the national anthem of Cape Verde, a le ...
'' as its national anthem. Until 1996, this was shared with Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
, which later adopted its own official national anthem ''Cântico da Liberdade
"" ( English: "Chant of Liberty") is the national anthem of Cape Verde. It was made official in 1996, replacing "Esta É a Nossa Pátria Bem Amada", which was also the national anthem of Guinea Bissau, a legacy of both countries' joint independe ...
''.
Luís Cabral
Luís Severino de Almeida Cabral (11 April 1931 – 30 May 2009) was a Bissau-Guinean politician who was the first President of Guinea-Bissau. He served from 1974 to 1980, when a military ''coup d'état'' led by João Bernardo Vieira deposed h ...
, brother of Amílcar and co-founder of PAIGC, was appointed the first president of Guinea-Bissau
This article lists the presidents of Guinea-Bissau, since the establishment of the office of president in 1973.
Since Guinea-Bissau's unilateral declaration of independence from Portugal on 24 September 1973, there have been six presidents, f ...
. Independence had begun under the best of auspices. The Bissau-Guinean diaspora had returned to the country en masse. A system of access to school for all had been created. Books were free and schools seemed to have a sufficient number of teachers. The education of girls, previously neglected, was encouraged and a new school calendar, more adapted to the rural world, was adopted.
In 1980, economic conditions deteriorated significantly, leading to general discontent with the government in power. On 14 November 1980, João Bernardo Vieira
João Bernardo "Nino" Vieira (; 27 April 1939 – 2 March 2009) was a Bissau-Guinean politician and military officer who served as President of Guinea-Bissau from 1980 to 1999, except for a three-day period in May 1984, and from 2005 until ...
, known as "Nino Vieira", overthrew President Luís Cabral. The constitution was suspended and a nine-member Military Council of the Revolution, chaired by Vieira, was established. Since then, the country has moved toward a liberal economy. Budget cuts have been made at the expense of the social sector and education.
The country was controlled by the military council until 1984. The first multi-party elections
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated ...
were held in 1994. An army uprising in May 1998 led to the Guinea-Bissau Civil War
The Guinea-Bissau Civil War was fought from 7 June 1998 to 10 May 1999 and was triggered by an attempted 1998 Guinea-Bissau coup attempt, coup d'état against the government of Heads of State of Guinea-Bissau, President João Bernardo Vieira led ...
and the president's ousting in June 1999. Elections were held again in 2000, and Kumba Ialá
Kumba Ialá Embaló, also spelled Yalá (15 March 1953 – 4 April 2014), was a Bissau-Guinean politician who was president from 17 February 2000 until he was deposed in a bloodless military coup on 14 September 2003. He belonged to the Bala ...
was elected president.
21st century
In September 2003, a military coup was conducted. The military arrested Ialá on the charge of being "unable to solve the problems". After being delayed several times,legislative elections
A general election is an electoral process to choose most or all members of a governing body at the same time. They are distinct from by-elections, which fill individual seats that have become vacant between general elections. General elections ...
were held in March 2004. A mutiny in October 2004 over pay arrears resulted in the death of the head of the armed forces.
In June 2005, presidential elections
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The ...
were held for the first time since the coup that deposed Ialá. Ialá returned as the candidate for the PRS, claiming to be the legitimate president of the country, but the election was won by former president João Bernardo Vieira
João Bernardo "Nino" Vieira (; 27 April 1939 – 2 March 2009) was a Bissau-Guinean politician and military officer who served as President of Guinea-Bissau from 1980 to 1999, except for a three-day period in May 1984, and from 2005 until ...
, deposed in the 1999 coup. Vieira beat Malam Bacai Sanhá
Malam Bacai Sanhá () (5 May 1947 – 9 January 2012) was a Guinea-Bissau politician who was President of Guinea-Bissau from 8 September 2009 until his death on 9 January 2012. A member of the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and ...
in a run-off election. Sanhá initially refused to concede, claiming that tampering and electoral fraud occurred in two constituencies
An electoral (congressional, legislative, etc.) district, sometimes called a constituency, riding, or ward, is a geographical portion of a political unit, such as a country, state or province, city, or administrative region, created to provi ...
including the capital, Bissau. Foreign monitors described the elections as "calm and organized", despite some reports of arms entering the country prior to the election and few "disturbances during campaigning", including attacks on government offices by unidentified gunmen.
Three years later, Sanhá's PAIGC won a strong parliamentary majority, with 67 of 100 seats, in the parliamentary election held in November 2008. In November 2008, President Vieira's official residence was attacked by members of the armed forces, killing a guard but leaving the president unharmed.
On 2 March 2009, however, Vieira was assassinated by what preliminary reports indicated to be a group of soldiers avenging the death of the head of joint chiefs of staff, General Batista Tagme Na Wai, who had been killed in an explosion the day before. Vieira's death did not trigger widespread violence, but there were signs of turmoil in the country, according to the advocacy group
Advocacy groups, also known as lobby groups, interest groups, special interest groups, pressure groups, or public associations, use various forms of advocacy or lobbying to influence public opinion and ultimately public policy. They play an impor ...
Swisspeace
swisspeace - the Swiss Peace Foundation is a practice and research institute located in Basel, Switzerland promoting effective peacebuilding. Partnerships with local and international actors form the basis of its work. Together with its partner o ...
. Military leaders in the country pledged to respect the constitutional order of succession. National Assembly Speaker Raimundo Pereira
Raimundo Rodrigues Pereira (born 1956) is a Bissau-Guinean lawyer and politician who was interim President of Guinea-Bissau from 3 March 2009 to 8 September 2009 and again in 2012, following the departure of President Malam Bacai Sanhá for me ...
was appointed as an interim president until a nationwide election
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold Public administration, public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative d ...
on 28 June 2009. It was won by Malam Bacai Sanhá, against Kumba Ialá
Kumba Ialá Embaló, also spelled Yalá (15 March 1953 – 4 April 2014), was a Bissau-Guinean politician who was president from 17 February 2000 until he was deposed in a bloodless military coup on 14 September 2003. He belonged to the Bala ...
as the presidential candidate of the PRS.
On 9 January 2012, President Sanhá died of complications from diabetes, and Pereira was again appointed as an interim president. On the evening of 12 April 2012, members of the country's military staged a ''coup d'état'' and arrested the interim president and a leading presidential candidate. Former vice chief of staff, General Mamadu Ture Kuruma
Major General Mamadu Ture Kuruma (or N'Krumah; born 26 April 1947) is a Bissau-Guinean military vice-chief of staff and the leader of the Military Command that took power following a coup against acting president Raimundo Pereira and former p ...
, assumed control of the country in the transitional period and started negotiations with opposition parties.
The 2014 general election saw José Mário Vaz
José Mário Vaz (born 10 December 1957) is a Bissau-Guinean politician who served as List of Presidents of Guinea-Bissau, president of Guinea-Bissau from 23 June 2014 to 27 February 2020.
Early life
Popularly known by the nickname "Jomav," Jo ...
elected President of Guinea-Bissau. Vaz became the first elected president to complete his five-year mandate. At the same time, he was eliminated in the first round of the 2019 presidential elections, ultimately seeing Umaro Sissoco Embaló
Umaro Mokhtar Sissoco Embaló (born 23 September 1972) is a Bissau-Guinean politician serving as the president of Guinea-Bissau since February 2020. A political scientist and military officer, he previously served as prime minister between No ...
emerge as the victor. Embaló, the first president to be elected without the backing of the PAIGC, took office in February 2020.
On 1 February 2022, there was an attempted coup d'état to overthrow President Umaro Sissoco Embaló. On 2 February 2022, state radio announced that four assailants and two members of the presidential guard had been killed in the incident. The African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
and ECOWAS
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as CEDEAO in French and Portuguese) is a regional political and economic union of twelve countries of West Africa. Collectively, the present and former members comprise an area ...
both condemned the coup. Six days after the attempted coup d'état, on 7 February 2022, there was an attack on the building of Rádio Capital FM, a radio station critical of the Bissau-Guinean government; this was the second time the radio station suffered an attack of this nature in less than two years. A journalist working for the station recalled, while wishing to stay anonymous, that one of their colleagues had recognized one of the cars carrying the attackers as belonging to the presidency.
In 2022, Embaló became the first African ruler to visit Ukraine since the Russian invasion of the country in February, meeting with President of Ukraine Volodymyr Zelenskyy
Volodymyr Oleksandrovych Zelenskyy (born 25 January 1978) is a Ukrainian politician and former entertainer who has served as the sixth and current president of Ukraine since 2019. He took office five years after the start of the Russo-Ukraini ...
.
In 2023, an attempted coup reportedly occurred in the capital, Bissau, leading Embaló to order the dissolution of the opposition-controlled parliament. On 11 September 2024, President Umaro Sissoco Embaló announced that he would not seek a second term in the upcoming presidential elections scheduled for November 2025. On 3 March 2025, President Umaro Sissoco Embaló said that he would run for a second term in November, contrary to his earlier vows to step down.
Politics
Guinea-Bissau is arepublic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
. In the past, the government had been highly centralized. Multi-party governance was not established until mid-1991. The president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
is the head of state and the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
is the head of government. From independence in 1974, until Jose Mario Vaz ended his five-year term as president on 24 June 2019, no president successfully served a full five-year term.
At the legislative level, a unicameral ''Assembleia Nacional Popular'' (National People's Assembly of Guinea-Bissau, National People's Assembly) is made up of 100 members. They are popularly elected from multi-member constituencies to serve a four-year term. The judicial system is headed by a ''Tribunal Supremo da Justiça'' (Supreme Court), made up of nine justices appointed by the president; they serve at the pleasure of the president.
The two main political parties are the PAIGC (African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde
The African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (, PAIGC) is a political party in Guinea-Bissau. Originally formed to peacefully campaign for independence from Portugal, the party turned to armed conflict in the 1960s and was o ...
) and the PRS (Party for Social Renewal). There are more than 20 minor parties.
Foreign relations
Guinea-Bissau is a founding member state of theCommunity of Portuguese Language Countries
The Community of Portuguese Language Countries (; : CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth or Lusophone Community (), is an international organization and political association of Lusophone nations across four continents, where Portug ...
(CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth, an international organisation and political association of Lusophone nations where Portuguese language, Portuguese is an official language.
Military
A 2019 estimate put the size of the Guinea-Bissau Armed Forces at around 4,400 personnel and military spending is less than 2% of GDP. In 2018, Guinea-Bissau signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.Administrative divisions
Guinea-Bissau is divided into eight Regions of Guinea-Bissau, regions () and one Autonomous entity, autonomous Sectors of Guinea-Bissau, sector (). These, in turn, are subdivided into 37 Sectors of Guinea-Bissau, Sectors. The regions are:Geography
Guinea-Bissau is bordered bySenegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
to the north and Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
to the south and east, with the Atlantic Ocean to its west. It lies mostly between latitudes 11th parallel north, 11° and 13th parallel north, 13°N (a small area is south of 11°), and longitudes 11th meridian west, 11° and 15th meridian west, 15°W.
At , the country is larger in size than Taiwan or Belgium.
The highest point is Monte Torin with an elevation of . Its terrain is mostly low coastal plains with swamps of the Guinean mangroves rising to the Guinean forest–savanna mosaic in the east. Its monsoon-like rainy season alternates with periods of hot, dry harmattan winds blowing from the Sahara. The Bijagos Archipelago lies off of the mainland. The country is home to two ecoregions: Guinean forest–savanna mosaic and Guinean mangroves.Climate
Guinea-Bissau is warm all year round with mild temperature fluctuations; it averages . The average rainfall for Bissau is , although this is almost entirely accounted for during the rainy season which falls between June and September/October. From December through April, the country experiences drought.Economy
Guinea-Bissau's List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, GDP per capita and List of countries by Human Development Index, Human Development Index are among the lowest in the world. More than two-thirds of the population lives below the poverty line. The economy depends mainly on agriculture; fish, cashew nuts, and Bambara groundnut, ground nuts are its major exports. A long period of political instability has resulted in depressed economic activity, deteriorating social conditions, and increased macroeconomic imbalances. It takes longer on average to register a new business in Guinea-Bissau (233 days or about 33 weeks) than in any other country in the world except Suriname. Guinea-Bissau has started to show some economic advances after a pact of stability was signed by the main political parties of the country, leading to an IMF-backed structural reform program. After several years of economic downturn and political instability, in 1997, Guinea-Bissau entered the CFA franc monetary system, bringing about some internal monetary stability. The Guinea-Bissau Civil War, civil war from 1998 to 1999, and 2003 Guinea-Bissau coup d'état, a military coup in September 2003, again disrupted economic activity, leaving a substantial part of the economic and social infrastructure in ruins and intensifying the already widespread poverty. Following the parliamentary elections in March 2004 and presidential elections in July 2005, the country is trying to recover from the long period of instability, despite a still-fragile political situation. Beginning around 2005, drug traffickers based in Latin America began to use Guinea-Bissau, along with several neighbouring West African nations, as a transshipment point to Europe for cocaine. The nation was described by a United Nations official as being at risk for becoming a "narco-state". The government and the military have done little to stop drug trafficking, which increased after the 2012 Guinea-Bissau coup d'état, 2012 coup d'état. The government of Guinea-Bissau continues to be ravaged by illegal drug distribution, according to ''The Economist''. Guinea-Bissau is a member of the Organization for the Harmonisation of Business Law in Africa (OHADA).Society
Demographics
According to , Guinea-Bissau's population was in , compared to 518,000 in 1950. The proportion of the population below the age of 15 in 2010 was 41.3%, 55.4% were aged between 15 and 65 years of age, while 3.3% were aged 65 years or older.Ethnic groups

 The population of Guinea-Bissau is ethnically diverse and has many distinct languages, customs, and social structures.
Bissau-Guineans can be divided into the following ethnic groups:
* Fula people, Fula and the Mandinka language, Mandinka-speaking people, who constitute the largest portion of the population and are concentrated in the north and northeast;
* Balanta and Papel people, who live in the southern coastal regions; and
* Manjak people, Manjaco and Mancanha, who occupy the central and northern coastal areas.
Most of the remainder are ''mestizo, mestiços'' of mixed Portuguese people, Portuguese and African descent.
Portuguese natives are a very small percentage of Bissau-Guineans. After Guinea-Bissau gained independence, most of the Portuguese nationals left the country. The country has a tiny overseas Chinese, Chinese population. These include traders and merchants of mixed Portuguese and Cantonese ancestry from the former Portuguese colony of Macau. There is also a small Cape Verdeans, Cape Verdean, Lebanese people, Lebanese and Jews, Jewish community in the country. Portuguese people made up the largest white population during colonial period but there was also some Lebanese people, Italians, French people and English people.
The population of Guinea-Bissau is ethnically diverse and has many distinct languages, customs, and social structures.
Bissau-Guineans can be divided into the following ethnic groups:
* Fula people, Fula and the Mandinka language, Mandinka-speaking people, who constitute the largest portion of the population and are concentrated in the north and northeast;
* Balanta and Papel people, who live in the southern coastal regions; and
* Manjak people, Manjaco and Mancanha, who occupy the central and northern coastal areas.
Most of the remainder are ''mestizo, mestiços'' of mixed Portuguese people, Portuguese and African descent.
Portuguese natives are a very small percentage of Bissau-Guineans. After Guinea-Bissau gained independence, most of the Portuguese nationals left the country. The country has a tiny overseas Chinese, Chinese population. These include traders and merchants of mixed Portuguese and Cantonese ancestry from the former Portuguese colony of Macau. There is also a small Cape Verdeans, Cape Verdean, Lebanese people, Lebanese and Jews, Jewish community in the country. Portuguese people made up the largest white population during colonial period but there was also some Lebanese people, Italians, French people and English people.
Major cities
Main List of cities in Guinea-Bissau, cities in Guinea-Bissau include:Languages
 Though a small country, Guinea-Bissau has several ethnic groups which are very distinct from each other, with their own cultures and languages. This is due to Guinea-Bissau being a refugee and migration territory within Africa. Colonisation and racial intermixing brought Portuguese and the Portuguese creole known as Guinea-Bissau Creole, Kriol or ''crioulo''.
The sole official language of Guinea-Bissau since independence, Standard Portuguese language, Portuguese is spoken mostly as a second language, with few native speakers and its use is often confined to the intellectual and political elites. It is the language of government and national communication as a legacy of colonial rule. Schooling from the primary to tertiary levels is conducted in Portuguese, although only 67% of children have access to any formal education. Data suggests that the number of Portuguese speakers ranges from 11 to 15%. In the latest census (2009) 27.1% of the population claimed to speak non-creole Portuguese (46.3% of city dwellers and 14.7% of the rural population, respectively). Portuguese creole is spoken by 44% of the population and is effectively the lingua franca among distinct groups for most of the population. Creole's usage is still expanding, and it is understood by the vast majority of the population. However, decreolisation processes are occurring, due to undergoing interference from Standard Portuguese and the creole forms a continuum of varieties with the standard language, the most distant are basilects and the closer ones, acrolects. A post-creole continuum exists in Guinea-Bissau and crioulo 'leve' ('soft' creole) variety being closer to the Portuguese-language norm.
The remaining rural population speaks a variety of native African languages unique to each ethnicity: Fula language, Fula (16%), Balanta languages, Balanta (14%), Mandinka language, Mandinka (7%), Manjak language, Manjak (5%), Papel (3%), Felupe (1%), Beafada (0.7%), Bijagó (0.3%), and Nalu (0.1%), which form the ethnic African languages spoken by the population. Most Portuguese and Mestiços speakers also have one of the African languages and Kriol as additional languages. Ethnic African languages are not discouraged, in any situation, despite their lower prestige. These languages are the link between individuals of the same ethnic background and daily used in villages, between neighbours or friends, traditional and religious ceremonies, and also used in contact between the urban and rural populations. However, none of these languages are dominant in Guinea-Bissau.
French is taught as a foreign language in schools, because Guinea-Bissau is surrounded by French-speaking nations. Guinea-Bissau is a full member of the Francophonie.
Though a small country, Guinea-Bissau has several ethnic groups which are very distinct from each other, with their own cultures and languages. This is due to Guinea-Bissau being a refugee and migration territory within Africa. Colonisation and racial intermixing brought Portuguese and the Portuguese creole known as Guinea-Bissau Creole, Kriol or ''crioulo''.
The sole official language of Guinea-Bissau since independence, Standard Portuguese language, Portuguese is spoken mostly as a second language, with few native speakers and its use is often confined to the intellectual and political elites. It is the language of government and national communication as a legacy of colonial rule. Schooling from the primary to tertiary levels is conducted in Portuguese, although only 67% of children have access to any formal education. Data suggests that the number of Portuguese speakers ranges from 11 to 15%. In the latest census (2009) 27.1% of the population claimed to speak non-creole Portuguese (46.3% of city dwellers and 14.7% of the rural population, respectively). Portuguese creole is spoken by 44% of the population and is effectively the lingua franca among distinct groups for most of the population. Creole's usage is still expanding, and it is understood by the vast majority of the population. However, decreolisation processes are occurring, due to undergoing interference from Standard Portuguese and the creole forms a continuum of varieties with the standard language, the most distant are basilects and the closer ones, acrolects. A post-creole continuum exists in Guinea-Bissau and crioulo 'leve' ('soft' creole) variety being closer to the Portuguese-language norm.
The remaining rural population speaks a variety of native African languages unique to each ethnicity: Fula language, Fula (16%), Balanta languages, Balanta (14%), Mandinka language, Mandinka (7%), Manjak language, Manjak (5%), Papel (3%), Felupe (1%), Beafada (0.7%), Bijagó (0.3%), and Nalu (0.1%), which form the ethnic African languages spoken by the population. Most Portuguese and Mestiços speakers also have one of the African languages and Kriol as additional languages. Ethnic African languages are not discouraged, in any situation, despite their lower prestige. These languages are the link between individuals of the same ethnic background and daily used in villages, between neighbours or friends, traditional and religious ceremonies, and also used in contact between the urban and rural populations. However, none of these languages are dominant in Guinea-Bissau.
French is taught as a foreign language in schools, because Guinea-Bissau is surrounded by French-speaking nations. Guinea-Bissau is a full member of the Francophonie.
Religion
Various studies suggest that slightly less than half of the population of Guinea-Bissau is Islam, Muslim, while substantial minorities follow folk religions orChristianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
. The CIA World Factbook's 2020 estimate stated that the population was 46.1% Muslim, 30.6% following folk religions, 18.9% Christian, 4.4% other or unaffiliated. In 2010, a Pew Research survey determined that the population was 45.1% Muslim and 19.7% Christian, with 30.9% practicing folk religion and 4.3 other faiths. A 2015 Pew-Templeton study found that the population was 45.1% Muslim, 30.9% practicing folk religions, 19.7% Christian, and 4.3% unaffiliated. The ARDA projected in 2020 the share of the Muslim population to be 44.7%. It also estimated 41.2% of the population to be practitioners of ethnic religions and 13% to be Christians.
 Concerning religious identity among Muslims, a Pew report determined that in Guinea-Bissau there is no prevailing sectarian identity. Guinea-Bissau shared this distinction with other Sub-Saharan countries like Tanzania, Uganda, Liberia, Nigeria and Cameroon.This Pew research also stated that countries in this specific study that declared to not have any clear dominant sectarian identity were mostly concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa. Another Pew report, ''The Future of World Religions'', predicts that from 2010 to 2050, practitioners of Islam will increase their share of the population in Guinea-Bissau.
Many residents practice Religious syncretism, syncretic forms of Islamic and Christian faiths, combining their practices with Traditional African religions, traditional African beliefs."Guinea-Bissau"
Concerning religious identity among Muslims, a Pew report determined that in Guinea-Bissau there is no prevailing sectarian identity. Guinea-Bissau shared this distinction with other Sub-Saharan countries like Tanzania, Uganda, Liberia, Nigeria and Cameroon.This Pew research also stated that countries in this specific study that declared to not have any clear dominant sectarian identity were mostly concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa. Another Pew report, ''The Future of World Religions'', predicts that from 2010 to 2050, practitioners of Islam will increase their share of the population in Guinea-Bissau.
Many residents practice Religious syncretism, syncretic forms of Islamic and Christian faiths, combining their practices with Traditional African religions, traditional African beliefs."Guinea-Bissau", ''CIA the World Factbook'', Cia.gov. Retrieved 5 February 2012. Muslims dominate the north and east, while Christians dominate the south and coastal regions. The Roman Catholic Church claims most of the Christian community. The 2021 US Department of State Report on International Religious Freedom mentions the fact that leaders of different religious communities believe that the existing communities are essentially tolerant, but express some concerns about rising religious fundamentalism in the country. An incident in July 2022, when a Catholic church in the overwhelmingly Muslim region of Gabú was vandalised, raised concern amongst the Christian community that Islamic extremism might be infiltrating the country. However, there have been no further similar incidents, and no direct links to Islamic extremists have surfaced.
Education
Education is compulsory from the age of 7 to 13. Pre-school education for children between three and six years of age is optional and in its early stages. There are five levels of education: pre-school, elemental and complementary basic education, general and complementary secondary education, general secondary education, technical and professional teaching, and higher education (university and non-universities). Basic education is under reform, and now forms a single cycle, comprising six years of education. Secondary education is widely available and there are two cycles (7th to 9th ''classe'' and 10th to 11th ''classe''). Professional education in public institutions is nonoperational, however private school offerings opened, including the ''Centro de Formação São João Bosco'' (since 2004) and the ''Centro de Formação Luís Inácio Lula da Silva'' (since 2011). Higher education is limited and most prefer to be educated abroad, with students preferring to enroll in Portugal. A List of universities in Guinea-Bissau, number of universities, to which an institutionally autonomous Faculty of Law as well as a Faculty of Medicine that is maintained by Cuba and functions in different cities. Child labor is very common. The enrollment of boys is higher than that of girls. In 1998, the gross primary enrollment rate was 53.5%, with higher enrollment ratio for males (67.7%) compared to females (40%)."Guinea-Bissau"''2001 Findings on the Worst Forms of Child Labor''. Bureau of International Labor Affairs, U.S. Department of Labor (2002). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Non-formal education is centered on community schools and the teaching of adults. In 2011, the literacy rate was estimated at 55.3% (68.9% male, and 42.1% female).
Conflicts
Usually, the many different ethnic groups in Guinea-Bissau coexist peacefully, but when conflicts do erupt, they tend to revolve around access to land.Culture
Media
Music
The music of Guinea-Bissau is usually associated with the polyrhythmic gumbe musical genre, genre, the country's primary musical export. However, civil unrest and other factors have combined over the years to keep gumbe, and other genres, out of mainstream audiences, even in generally syncretist African countries. The cabasa is the primary musical instrument of Guinea-Bissau, and is used in extremely swift and rhythmically complex dance music. Lyrics are almost always inGuinea-Bissau Creole
Guinea-Bissau Creole, also known as Kiriol or Crioulo, is a creole language whose lexicon derives mostly from Portuguese. It is spoken in Guinea Bissau, Cape Verde, Senegal and The Gambia. It is also called by its native speakers as , , or .
G ...
, a Portuguese language, Portuguese-based creole language, and are often humorous and topical, revolving around current events and controversies.
The word ''gumbe'' is sometimes used generically, to refer to any music of the country, although it most specifically refers to a unique style that fuses about ten of the country's folk music traditions. Music of Guinea-Bissau, Tina and tinga are other popular genres, while extent folk traditions include ceremonial music used in funerals, initiations, and other rituals, as well as Balanta brosca and kussundé, Mandinka people, Mandinga djambadon, and the kundere sound of the Bissagos Islands.
Cuisine
Common dishes include soups and stews. Common ingredients include yam (vegetable), yams, sweet potato, cassava, onion, tomato, and cooking banana, plantain. Spices, peppers, and chilis are used in cooking, including ''Aframomum melegueta'' seeds (Guinea pepper).Film
Flora Gomes is an internationally renowned film director; his most famous film is ''Nha Fala'' (). Gomes's ''Mortu Nega'' (''Death Denied'') (1988) was the first fiction film and the second feature film ever made in Guinea-Bissau. (The first feature film was ''N'tturudu'', by director in 1987.) At FESPACO 1989, ''Mortu Nega'' won the prestigious Oumarou Ganda Prize. In 1992, Gomes directed ''Udju Azul di Yonta'', which was screened in the Un Certain Regard section at the 1992 Cannes Film Festival. Gomes has also served on the boards of many Africa-centric film festivals. The actress Babetida Sadjo was born in Bafatá, Guinea-Bissau.Sports
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Guinea-Bissau. The Guinea-Bissau national football team is under the authority of the Football Federation of Guinea-Bissau, Federação de Futebol da Guiné-Bissau. They are a member of the Confederation of African Football (CAF) and FIFA.See also
* Outline of Guinea-Bissau * Index of Guinea-Bissau-related articlesReferences
Sources
* * * * * ; AttributionFurther reading
* Abdel Malek, K.,"Le processus d'accès à l'indépendance de la Guinée-Bissau", ''Bulletin de l'Association des Anciens Elèves de l'Institut National de Langues et de Cultures Orientales'', No. 1, April 1998. pp. 53–60 * Forrest, Joshua B., ''Lineages of State Fragility. Rural Civil Society in Guinea-Bissau'' (Ohio University Press/James Currey Ltd., 2003) * Galli, Rosemary E, ''Guinea Bissau: Politics, Economics and Society'', Pinter Pub Ltd., 1987 * Lobban, Richard Andrew Jr., and Mendy, Peter Karibe, ''Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Guinea-Bissau'', third edition (Scarecrow Press, 1997) * Vigh, Henrik, ''Navigating Terrains of War: Youth And Soldiering in Guinea-Bissau'', Berghahn Books, 2006External links
* * , Government of Guinea-BissauCountry Profile
from BBC News
Guinea-Bissau
profile from ECOWAS
Guinea-Bissau
at the ''Encyclopædia Britannica''
News headline links
from Al Jazeera. {{Authority control Guinea-Bissau, 1974 establishments in Guinea-Bissau Countries and territories where Portuguese is an official language Countries in Africa Economic Community of West African States Former Portuguese colonies Least developed countries Member states of the African Union Member states of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Republics Small Island Developing States States and territories established in 1974 West African countries