Graph-based Access Control on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Graph-based access control (GBAC) is a declarative way to define access rights, task assignments, recipients and content in information systems. The access rights are granted to objects like files or documents, but also business objects like an account. It can also be used for the assignment of agents to tasks in workflow environments. Organizations are modeled as a specific kind of semantic graph comprising the organizational units, the roles and functions as well as the human and automatic agents (i.a. persons, machines). Compared to other approaches like
iisys
, the approach was extended by features like separation of duty, access control in virtual organizations and subject-oriented access control.
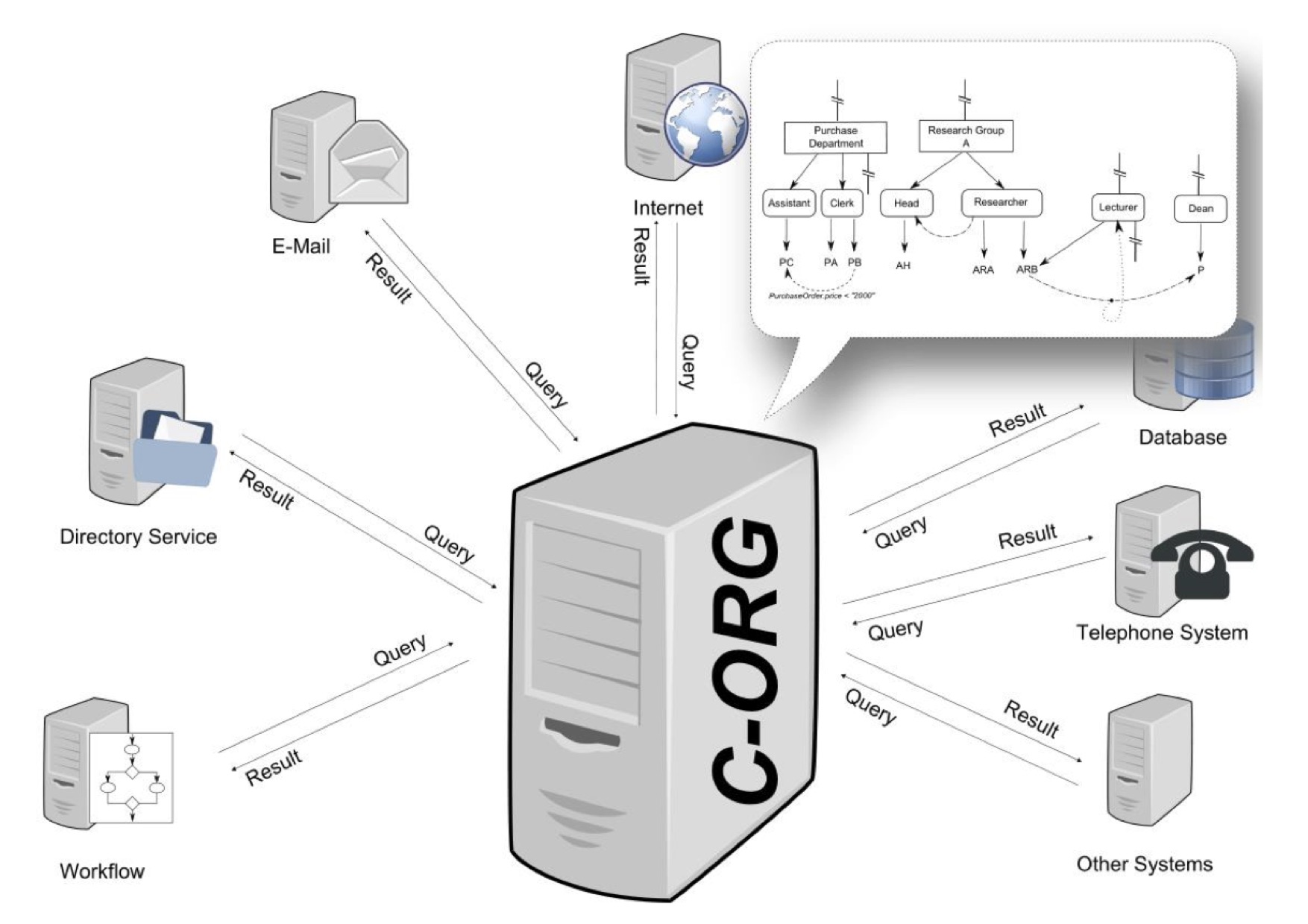 GBAC was first implemented in the CoCoS Environment within the organizational server CoCoSOrg.
In the C-Org-Project it was extended with more sophisticated features like separation of duty or access control in distributed environments.
There is also a cloud-based implementation on IBM's
GBAC was first implemented in the CoCoS Environment within the organizational server CoCoSOrg.
In the C-Org-Project it was extended with more sophisticated features like separation of duty or access control in distributed environments.
There is also a cloud-based implementation on IBM's Bluemix
/ref> platform. In all implementations the server takes a query from a client system and resolves it to a set of agents. This set is sent back to the calling client as response. Clients can be file systems, database management systems, workflow management systems, physical security systems or even telephone servers.
role-based access control
In computer systems security, role-based access control (RBAC) or role-based security is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users. It is an approach to implement mandatory access control (MAC) or discretionary access control ...
or attribute-based access control Attribute-based access control (ABAC), also known as policy-based access control for IAM, defines an access control paradigm whereby a subject's authorization to perform a set of operations is determined by evaluating attributes associated with the ...
, the main difference is that in GBAC access rights are defined using an organizational query language instead of total enumeration.
History
The foundations of GBAC go back to a research project named CoCoSOrg (Configurable Cooperation System) ref name = DISS>(in English language please see ) at Bamberg University. In CoCoSOrg an organization is represented as a semantic graph and a formal language is used to specify agents and their access rights in a workflow environment. Within the C-Org-Project at Hof University's Institute for Information Systemsiisys
, the approach was extended by features like separation of duty, access control in virtual organizations and subject-oriented access control.
Definition
Graph-based access control consists of two building blocks: * A semantic graph modeling an organization * A query language.Organizational graph
The organizational graph is divided into a type and an instance level. On the instance level there are node types for organizational units, functional units and agents. The basic structure of an organization is defined using so called "structural relations". They define the "is part of"- relations between functional units and organizational units as well as the mapping of agents to functional units. Additionally there are specific relationship types like "deputyship" or "informed_by". These types can be extended by the modeler. All relationships can be context sensitive through the usage ofpredicate
Predicate or predication may refer to:
* Predicate (grammar), in linguistics
* Predication (philosophy)
* several closely related uses in mathematics and formal logic:
**Predicate (mathematical logic)
**Propositional function
**Finitary relation, ...
s.
On the type level organizational structures are described in a more general manner. It consists of organizational unit types, functional unit types and the same relationship types as on the instance level. Type definitions can be used to create new instances or reuse organizational knowledge in case of exceptions (for further reading see).
Query language
In GBAC a query language is used to define agents having certain characteristics or abilities. The following table shows the usage of the query language in the context of an access control matrix. The first query means that all managers working for the company for more than six months can read the financial report, as well as the managers who are classified by the flag "ReadFinancialReport". The daily financial report can only be written by the manager of the controlling department or clerks of the department that are enabled to do that (WriteFinancialReportTRUE).Implementation
 GBAC was first implemented in the CoCoS Environment within the organizational server CoCoSOrg.
In the C-Org-Project it was extended with more sophisticated features like separation of duty or access control in distributed environments.
There is also a cloud-based implementation on IBM's
GBAC was first implemented in the CoCoS Environment within the organizational server CoCoSOrg.
In the C-Org-Project it was extended with more sophisticated features like separation of duty or access control in distributed environments.
There is also a cloud-based implementation on IBM's Bluemix
IBM Cloud, (formerly known as Bluemix) is a set of cloud computing services for business offered by the information technology company IBM.
Services
As of 2021, IBM Cloud contains more than 170 services including compute, storage, networkin ...
/ref> platform. In all implementations the server takes a query from a client system and resolves it to a set of agents. This set is sent back to the calling client as response. Clients can be file systems, database management systems, workflow management systems, physical security systems or even telephone servers.
See also
{{columns-list, colwidth=30em, *Access control list
In computer security, an access-control list (ACL) is a list of permissions associated with a system resource (object). An ACL specifies which users or system processes are granted access to objects, as well as what operations are allowed on giv ...
* Attribute-based access control Attribute-based access control (ABAC), also known as policy-based access control for IAM, defines an access control paradigm whereby a subject's authorization to perform a set of operations is determined by evaluating attributes associated with the ...
(ABAC)
* Capability-based security
Capability-based security is a concept in the design of secure computing systems, one of the existing security models. A capability (known in some systems as a key) is a communicable, unforgeable token of authority. It refers to a value that refe ...
* Context-based access control
Context-based access control (CBAC) is a feature of firewall software, which intelligently filters TCP and UDP packets based on application layer protocol session information. It can be used for intranets, extranets and internets.
CBAC can b ...
(CBAC)
* Discretionary access control
In computer security, discretionary access control (DAC) is a type of access control
In the fields of physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the selective restriction of access to a place or other resource, whil ...
(DAC)
* Lattice-based access control In computer security, lattice-based access control (LBAC) is a complex access control model based on the interaction between any combination of objects (such as resources, computers, and applications) and subjects (such as individuals, groups or org ...
(LBAC)
* Location-based authentication
Location-based authentication is a special procedure to prove an individual's identity on appearance simply by detecting its presence at a distinct location.
To enable location-based authentication, a special combination of objects is required.
...
* Mandatory access control
In computer security, mandatory access control (MAC) refers to a type of access control by which the operating system or database constrains the ability of a ''subject'' or ''initiator'' to access or generally perform some sort of operation on an ...
(MAC)
* Organisation-based access control
In computer security, organization-based access control (OrBAC) is an access control model first presented in 2003. The current approaches of the access control rest on the three entities (''subject'', ''action'', ''object'') to control the acces ...
(OrBAC)
* Risk-based authentication
In Authentication, risk-based authentication is a non-static authentication system which takes into account the profile (IP address, User-Agent HTTP header, time of access, and so on) of the agent requesting access to the system to determine the ri ...
* Role-based access control
In computer systems security, role-based access control (RBAC) or role-based security is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users. It is an approach to implement mandatory access control (MAC) or discretionary access control ...
(RBAC)
* Rule-set-based access control (RSBAC)
References