Gires–Tournois Etalon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
: :''n'' is the
 :
For ''R'' = 0, no reflection from the first surface and the resultant nonlinear phase shift is equal to the round-trip phase change () – linear response. However, as can be seen, when ''R'' is increased, the nonlinear phase shift gives the nonlinear response to and shows step-like behavior. Gires–Tournois etalon has applications for laser
:
For ''R'' = 0, no reflection from the first surface and the resultant nonlinear phase shift is equal to the round-trip phase change () – linear response. However, as can be seen, when ''R'' is increased, the nonlinear phase shift gives the nonlinear response to and shows step-like behavior. Gires–Tournois etalon has applications for laser
Gires–Tournois Interferometer
in ''RP Photonics Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Gires-Tournois etalon Optical components Interferometers
 In
In optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
, a Gires–Tournois etalon (also known as Gires–Tournois interferometer) is a transparent plate with two reflecting surfaces, one of which has very high reflectivity, ideally unity. Due to multiple-beam interference, light incident on a Gires–Tournois etalon is (almost) completely reflected, but has an effective phase shift that depends strongly on the wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the light.
The complex amplitude
In physics and engineering, a phasor (a portmanteau of phase vector) is a complex number representing a sinusoidal function whose amplitude and initial phase are time-invariant and whose angular frequency is fixed. It is related to a mor ...
reflectivity of a Gires–Tournois etalon is given by
:
where ''r''1 is the complex amplitude reflectivity of the first surface,: :''n'' is the
index of refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
of the plate
:''t'' is the thickness of the plate
:''θt'' is the angle of refraction
Snell's law (also known as the Snell–Descartes law, the ibn-Sahl law, and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing th ...
the light makes within the plate, and
:''λ'' is the wavelength of the light in vacuum.
Nonlinear effective phase shift
Suppose that is real. Then , independent of . This indicates that all the incident energy is reflected and intensity is uniform. However, the multiple reflection causes anonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathe ...
phase shift
In physics and mathematics, the phase (symbol φ or ϕ) of a wave or other periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is expressed in such a s ...
.
To show this effect, we assume is real and , where is the intensity reflectivity of the first surface. Define the effective phase shift through
:
One obtains
 :
For ''R'' = 0, no reflection from the first surface and the resultant nonlinear phase shift is equal to the round-trip phase change () – linear response. However, as can be seen, when ''R'' is increased, the nonlinear phase shift gives the nonlinear response to and shows step-like behavior. Gires–Tournois etalon has applications for laser
:
For ''R'' = 0, no reflection from the first surface and the resultant nonlinear phase shift is equal to the round-trip phase change () – linear response. However, as can be seen, when ''R'' is increased, the nonlinear phase shift gives the nonlinear response to and shows step-like behavior. Gires–Tournois etalon has applications for laser pulse compression
Pulse compression is a signal processing technique commonly used by radar, sonar and Ultrasound, echography to either increase the range angular resolution, resolution when pulse length is constrained or increase the Signal-to-noise ratio, signal ...
and nonlinear Michelson interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by the American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson in 1887. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light be ...
.
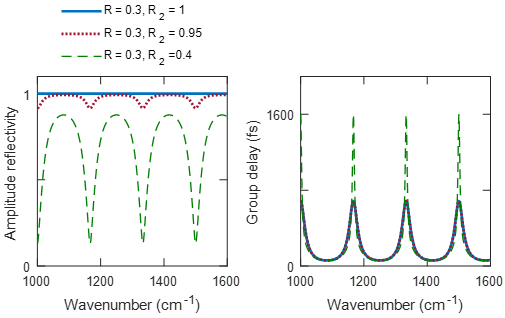
Gires–Tournois etalons are closely related to Fabry–Pérot etalons. This can be seen by examining the total reflectivity of a Gires–Tournois etalon when the reflectivity of its second surface becomes smaller than 1. In these conditions the property is not observed anymore: the reflectivity starts exhibiting a resonant behavior which is characteristic of Fabry-Pérot etalons.
References
* (''An interferometer useful for pulse compression of a frequency modulated light pulse''.)Gires–Tournois Interferometer
in ''RP Photonics Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Gires-Tournois etalon Optical components Interferometers