geobotany on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Phytogeography (from
 The basic data elements of phytogeography are occurrence records (presence or absence of a species) with operational geographic units such as political units or geographical coordinates. These data are often used to construct phytogeographic provinces (
The basic data elements of phytogeography are occurrence records (presence or absence of a species) with operational geographic units such as political units or geographical coordinates. These data are often used to construct phytogeographic provinces (
 Phytogeography has a long history. One of the subjects earliest proponents was Prussian naturalist
Phytogeography has a long history. One of the subjects earliest proponents was Prussian naturalist
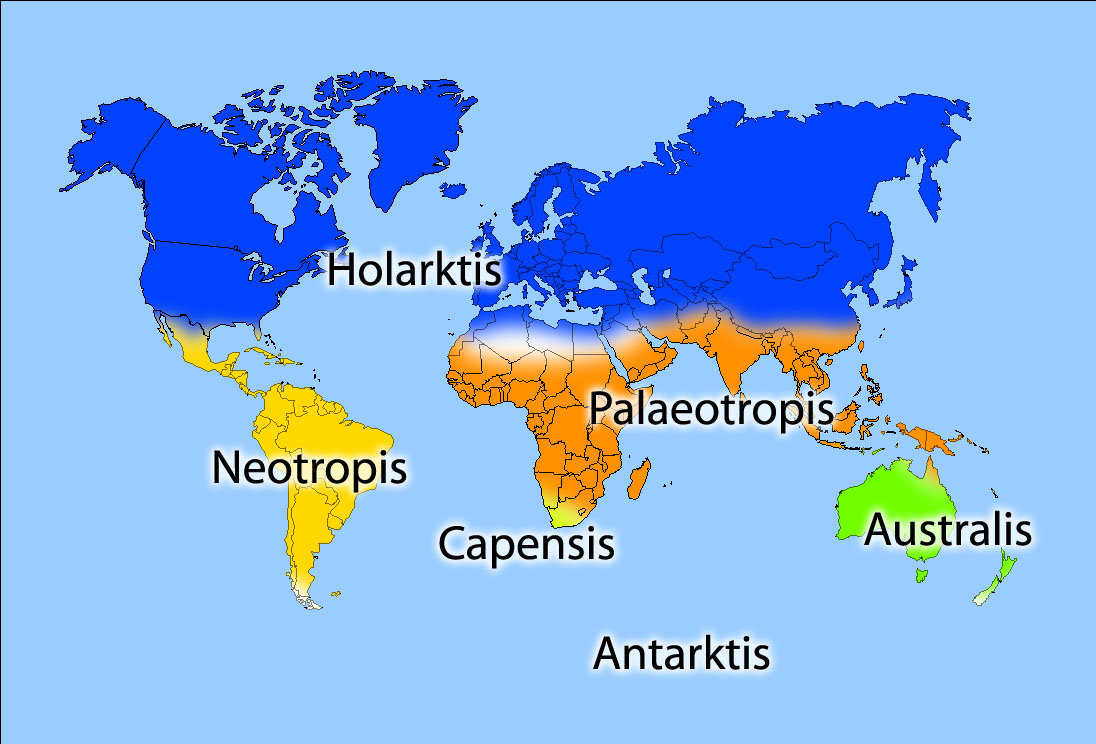 Floristics is a study of the
Floristics is a study of the
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the species distribution, distribution of species and ecosystems in geography, geographic space and through evolutionary history of life, geological time. Organisms and biological community (ecology), communities o ...
that is concerned with the geographic distribution of plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
and their influence on the earth's surface. Phytogeography is concerned with all aspects of plant distribution, from the controls on the distribution of individual species ranges (at both large and small scales, see species distribution
Species distribution, or species dispersion, is the manner in which a biological taxon is spatially arranged. The geographic limits of a particular taxon's distribution is its range, often represented as shaded areas on a map. Patterns of distr ...
) to the factors that govern the composition of entire communities and flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
s. Geobotany, by contrast, focuses on the geographic space's influence on plants.
Fields
Phytogeography is part of a more general science known asbiogeography
Biogeography is the study of the species distribution, distribution of species and ecosystems in geography, geographic space and through evolutionary history of life, geological time. Organisms and biological community (ecology), communities o ...
. Phytogeographers are concerned with patterns and process in plant distribution. Most of the major questions and kinds of approaches taken to answer such questions are held in common between phyto- and zoogeographers.
Phytogeography in wider sense (or geobotany, in German literature) encompasses four fields, according with the focused aspect, environment, flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
(taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
), vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plants and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular Taxon, taxa, life forms, structure, Spatial ecology, spatial extent, or any other specific Botany, botanic ...
(plant community
A plant community is a collection or Association (ecology), association of plant species within a designated geographical unit, which forms a relatively uniform patch, distinguishable from neighboring patches of different vegetation types. The comp ...
) and origin, respectively:
* plant ecology
Plant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology that studies the distribution and abundance (ecology), abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among plants and between plants and ...
(or mesology – however, the physiognomic-ecological approach on vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plants and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular Taxon, taxa, life forms, structure, Spatial ecology, spatial extent, or any other specific Botany, botanic ...
and biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the ...
study are also generally associated with this field);
* plant geography (or phytogeography in strict sense, chorology, floristics
Floristics is the study of plants of geographical regions. It is a branch of phytogeography, which technically makes it a branch of botany, geography, and a subbranch of biogeography. Harvard University has a history of research with early contr ...
);
* plant sociology (or phytosociology
Phytosociology, also known as phytocoenology or simply plant sociology, is the study of groups of species of plant that are usually found together. Phytosociology aims to Empirical evidence, empirically describe the vegetative environment of a giv ...
, synecology – however, this field does not prescind from flora study, as its approach to study vegetation relies upon a fundamental unit, the plant association, which is defined upon flora).
* historical plant geography (or paleobotany
Paleobotany or palaeobotany, also known as paleophytology, is the branch of botany dealing with the recovery and identification of plant fossils from geological contexts, and their use for the biological reconstruction of past environments ( pal ...
, paleogeobotany)
Phytogeography is often divided into two main branches: ecological phytogeography and historical phytogeography. The former investigates the role of current day biotic and abiotic interactions in influencing plant distributions; the latter are concerned with historical reconstruction of the origin, dispersal, and extinction of taxa.
Overview
 The basic data elements of phytogeography are occurrence records (presence or absence of a species) with operational geographic units such as political units or geographical coordinates. These data are often used to construct phytogeographic provinces (
The basic data elements of phytogeography are occurrence records (presence or absence of a species) with operational geographic units such as political units or geographical coordinates. These data are often used to construct phytogeographic provinces (floristic province
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both re ...
s) and elements.
The questions and approaches in phytogeography are largely shared with zoogeography
Zoogeography is the branch of the science of biogeography that is concerned with geographic distribution (present and past) of animal species.
As a multifaceted field of study, zoogeography incorporates methods of molecular biology, genetics, mo ...
, except zoogeography is concerned with animal distribution rather than plant distribution. The term phytogeography itself suggests a broad meaning. How the term is actually applied by practicing scientists is apparent in the way periodicals use the term. The ''American Journal of Botany
The ''American Journal of Botany'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal which covers all aspects of plant biology. It has been published by the Botanical Society of America since 1914. The journal has an impact factor of 3.038, as of 20 ...
'', a monthly primary research journal, frequently publishes a section titled "Systematics, Phytogeography, and Evolution." Topics covered in the ''American Journal of Botanys "Systematics and Phytogeography" section include phylogeography
Phylogeography is the study of the historical processes that may be responsible for the past to present geographic distributions of genealogical lineages. This is accomplished by considering the geographic distribution of individuals in light of ge ...
, distribution of genetic variation and, historical biogeography, and general plant species distribution patterns. Biodiversity patterns are not heavily covered.
A flora is the group of all plant species in a specific period of time or area, in which each species is independent in abundance and relationships to the other species. The group or the flora can be assembled in accordance with floral element, which are based on common features. A flora element can be a genetic element, in which the group of species share similar genetic information i.e. common evolutionary origin; a migration element has a common route of access into a habitat; a historical element is similar to each other in certain past events and an ecological element is grouped based on similar environmental factors. A population is the collection of all interacting individuals of a given species, in an area.
An area is the entire location where a species, an element or an entire flora can occur. Aerography studies the description of that area, chorology studies their development. The local distribution within the area as a whole, as that of a swamp shrub, is the topography of that area. Areas are an important factor is forming an image about how species interaction result in their geography. The nature of an area’s margin, their continuity, their general shape and size relative to other areas, make the study of area crucial in identifying these types of information. For example, a relict area is an area surviving from an earlier and more exclusive occurrence. Mutually exclusive plants are called vicarious (areas containing such plants are also called vicarious). The earth’s surface is divided into floristic region, each region associated with a distinctive flora.
History
 Phytogeography has a long history. One of the subjects earliest proponents was Prussian naturalist
Phytogeography has a long history. One of the subjects earliest proponents was Prussian naturalist Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, natural history, naturalist, List of explorers, explorer, and proponent of Romanticism, Romantic philosophy and Romanticism ...
, who is often referred to as the "father of phytogeography". Von Humboldt advocated a quantitative approach to phytogeography that has characterized modern plant geography.
Gross patterns of the distribution of plants became apparent early on in the study of plant geography. For example, Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was an English naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He independently conceived the theory of evolution through natural selection; his 1858 pap ...
, co-discoverer of the principle of natural selection, discussed the latitudinal gradients in species diversity
Species richness, or biodiversity, increases from the poles to the tropics for a wide variety of terrestrial and marine organisms, often referred to as the latitudinal diversity gradient. The latitudinal diversity gradient is one of the most wi ...
, a pattern observed in other organisms as well. Much research effort in plant geography has since then been devoted to understanding this pattern and describing it in more detail.
In 1890, the United States Congress passed an act that appropriated funds to send expeditions to discover the geographic distributions of plants (and animals) in the United States. The first of these was The Death Valley Expedition
The Death Valley expedition was an 1891 expedition to discover the geographic distributions of plants (phytogeography) and animals in California's Death Valley.
It was the first of a series of expeditions funded by an 1890 act of the United States ...
, including Frederick Vernon Coville
Frederick Vernon Coville (March 23, 1867 – January 9, 1937) was an American botanist who participated in the Death Valley Expedition (1890-1891), was honorary curator of the United States National Herbarium (1893-1937), worked at then was Ch ...
, Frederick Funston
Frederick Funston (November 9, 1865 – February 19, 1917), also known as Fighting Fred Funston, was a General officer, general in the United States Army, best known for his roles in the Spanish–American War and the Philippine–American ...
, Clinton Hart Merriam
Clinton Hart Merriam (December 5, 1855 – March 19, 1942) was an American zoologist, mammalogist, ornithologist, entomologist, ecologist, ethnographer, geographer, natural history, naturalist and physician. He was commonly known as the "father o ...
, and others.
Research in plant geography has also been directed to understanding the patterns of adaptation of species to the environment. This is done chiefly by describing geographical patterns of trait/environment relationships. These patterns termed ecogeographical rules
Rule or ruling may refer to:
Human activity
* The exercise of political or personal control by someone with authority or power
* Business rule, a rule pertaining to the structure or behavior internal to a business
* School rule, a rule tha ...
when applied to plants represent another area of phytogeography.
Floristic regions
 Floristics is a study of the
Floristics is a study of the flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
of some territory or area. Traditional phytogeography concerns itself largely with floristics and floristic classification,.
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
has been a focus to botanist for its rich biota as it holds the record for the earliest known angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit ...
megafossil.
See also
*Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the species distribution, distribution of species and ecosystems in geography, geographic space and through evolutionary history of life, geological time. Organisms and biological community (ecology), communities o ...
* Botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
* Floristics
Floristics is the study of plants of geographical regions. It is a branch of phytogeography, which technically makes it a branch of botany, geography, and a subbranch of biogeography. Harvard University has a history of research with early contr ...
* Geobotanical prospecting
* indicator value
* Species distribution
Species distribution, or species dispersion, is the manner in which a biological taxon is spatially arranged. The geographic limits of a particular taxon's distribution is its range, often represented as shaded areas on a map. Patterns of distr ...
* Zoogeography
Zoogeography is the branch of the science of biogeography that is concerned with geographic distribution (present and past) of animal species.
As a multifaceted field of study, zoogeography incorporates methods of molecular biology, genetics, mo ...
* Association (ecology)
In phytosociology and community ecology an association is a type of community (ecology), ecological community with a predictable species composition and consistent physiognomy (structural appearance) which occurs in a particular habitat type. The ...
References
Bibliography
* * * *External links
* * {{Authority control Biogeography