Generative Design on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
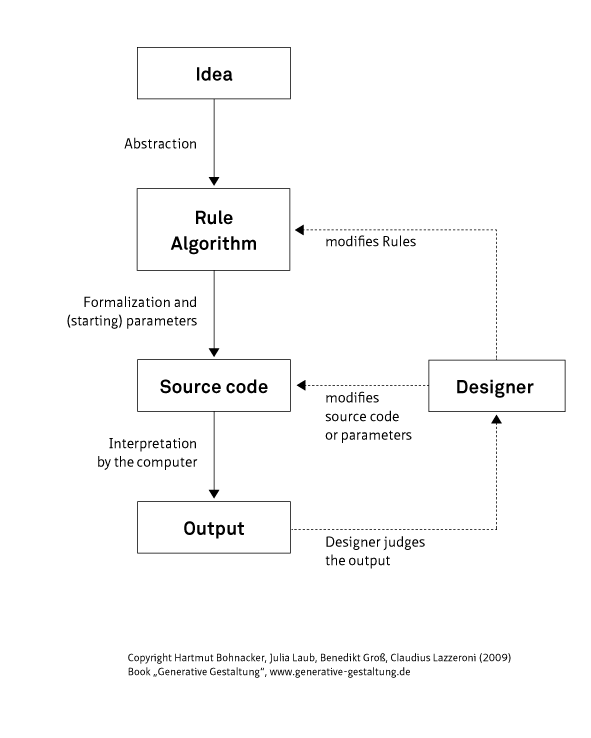
 Generative design is an iterative design process that uses software to generate outputs that fulfill a set of constraints iteratively adjusted by a designer. Whether a human, test program, or
Generative design is an iterative design process that uses software to generate outputs that fulfill a set of constraints iteratively adjusted by a designer. Whether a human, test program, or
EnergyPlusLadybug Tools
and so on, combined with generative algorithms, can optimize design solutions for cost-effective energy use and zero-carbon building designs. For example, the GENE_ARCH system used a Pareto algorithm wit
DOE2.1E building energy simulation
for the whole building design optimization. Generative design has improved sustainable facade design, as illustrated by the algorithm of cellular automata and daylight simulations in adaptive facade design. In addition, genetic algorithms were used with radiation simulations for energy-efficient PV modules on high-rise building facades. Generative design is also applied to life cycle analysis (LCA), as demonstrated by a framework using grid search algorithms to optimize exterior wall design for minimum environmental embodied impact. Multi-objective optimization embraces multiple diverse sustainability goals, such as interactive kinetic louvers using biomimicry and daylight simulations to enhance daylight, visual comfort and energy efficiency. The study of PV and shading systems can maximize on-site electricity, improve visual quality and daylight performance. AI and machine learning (ML) further improve computation efficiency in complex climate-responsive sustainable design. one study employed reinforcement learning to identify the relationship between design parameters and energy use for a sustainable campus, while some other studies tried hybrid algorithms, such as using the genetic algorithm and GANs to balance daylight illumination and thermal comfort under different roof conditions. Other popular AI tools were also integrated, including deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and
Generative Art Design Papers. C.Soddu, E.Colabella
{{Design Design Computer graphics

artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
, the designer algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
ically or manually refines the feasible region of the program's inputs and outputs with each iteration to fulfill evolving design requirements. By employing computing power to evaluate more design permutations than a human alone is capable of, the process is capable of producing an optimal design that mimics nature's evolutionary approach to design through genetic variation and selection. The output can be images, sounds, architectural models, animation
Animation is a filmmaking technique whereby still images are manipulated to create moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Animati ...
, and much more. It is, therefore, a fast method of exploring design possibilities that is used in various design fields such as art, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
, communication design, and product design
Product design is the process of creating new Product (business), products for businesses to sell to their customers. It involves the generation and development of ideas through a systematic process that leads to the creation of innovative products ...
.
Generative design has become more important, largely due to new programming environments or scripting capabilities that have made it relatively easy, even for designers with little programming experience, to implement their ideas. Additionally, this process can create solutions to substantially complex problems that would otherwise be resource-exhaustive with an alternative approach making it a more attractive option for problems with a large or unknown solution set. It is also facilitated with tools in commercially available CAD packages. Not only are implementation tools more accessible, but also tools leveraging generative design as a foundation.
Generative design in architecture
Generative design inarchitecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
is an iterative design process that enables architects to explore a wider solution space with more possibility and creativity
Creativity is the ability to form novel and valuable Idea, ideas or works using one's imagination. Products of creativity may be intangible (e.g. an idea, scientific theory, Literature, literary work, musical composition, or joke), or a physica ...
. Architectural design has long been regarded as a wicked problem. Compared with traditional top-down design approach, generative design can address design problems efficiently, by using a bottom-up paradigm that uses parametric defined rules to generate complex solutions. The solution itself then evolves to a good, if not optimal, solution. The advantage of using generative design as a design tool is that it does not construct fixed geometries, but take a set of design rules that can generate an infinite set of possible design solutions. The generated design solutions can be more sensitive, responsive, and adaptive to the problem.
Generative design involves rule definition and result analysis which are integrated with the design process. By defining parameters and rules, the generative approach is able to provide optimized solution for both structural stability and aesthetics. Possible design algorithms include cellular automata, shape grammar, genetic algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to g ...
, space syntax, and most recently, artificial neural network. Due to the high complexity of the solution generated, rule-based computational tools, such as finite element method and topology optimisation, are more preferable to evaluate and optimise the generated solution. The iterative process provided by computer software enables the trial-and-error approach in design, and involves architects interfering with the optimisation process.
Historical precedent work includes Antoni Gaudí's Sagrada Família, which used rule based geometrical forms for structures, and Buckminster Fuller's Montreal Biosphere where the rules to generate individual components is designed, rather than the final product.
More recent generative design cases include Foster and Partners' Queen Elizabeth II Great Court, where the tessellated glass roof was designed using a geometric schema to define hierarchical relationships, and then the generated solution was optimized based on geometrical and structural requirement.
Generative design in sustainable design
Generative design in sustainable design is an effective approach addressing energy efficiency and climate change at the early design stage, recognizing buildings contribute to approximately one-third of global greenhouse gas emissions and 30%-40% of total building energy use. It integrates environmental principles with algorithms, enabling exploration of countless design alternatives to enhance energy performance, reduce carbon footprints, and minimize waste. A key feature of generative design in sustainable design is its ability to incorporate Building Performance Simulations (BPS) into the design process. Simulation programs likEnergyPlus
and so on, combined with generative algorithms, can optimize design solutions for cost-effective energy use and zero-carbon building designs. For example, the GENE_ARCH system used a Pareto algorithm wit
DOE2.1E building energy simulation
for the whole building design optimization. Generative design has improved sustainable facade design, as illustrated by the algorithm of cellular automata and daylight simulations in adaptive facade design. In addition, genetic algorithms were used with radiation simulations for energy-efficient PV modules on high-rise building facades. Generative design is also applied to life cycle analysis (LCA), as demonstrated by a framework using grid search algorithms to optimize exterior wall design for minimum environmental embodied impact. Multi-objective optimization embraces multiple diverse sustainability goals, such as interactive kinetic louvers using biomimicry and daylight simulations to enhance daylight, visual comfort and energy efficiency. The study of PV and shading systems can maximize on-site electricity, improve visual quality and daylight performance. AI and machine learning (ML) further improve computation efficiency in complex climate-responsive sustainable design. one study employed reinforcement learning to identify the relationship between design parameters and energy use for a sustainable campus, while some other studies tried hybrid algorithms, such as using the genetic algorithm and GANs to balance daylight illumination and thermal comfort under different roof conditions. Other popular AI tools were also integrated, including deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and
computer vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical ...
(CV) to generate an urban block according to direct sunlight hours and solar heat gains. These AI-driven generative design methods enable faster simulations and design decision making, resulting in designs that are environmentally responsible.
Generative design in additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing (AM) is a process that creates physical models directly from 3D data by joining materials layer by layer. It is used in industries to produce a variety of end-use parts, which are final components designed for direct application in products or systems. AM provides design flexibility and enables material reduction in lightweight applications, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and portable electronic devices, where minimizing weight is critical for performance. Generative design, one of the four key methods for lightweight design in AM, is commonly applied to optimize structures for specific performance requirements. Generative design can help create optimized solutions that balance multiple objectives, such as enhancing performance while minimizing cost. In design for additive manufacturing (DfAM), multi-objective topology optimization is used to generate a set of candidate solutions. Designers then assess these options using their expertise and key performance indicators (KPIs) to select the best option for implementation. However, integrating AM constraints (e.g.,speed of build, materials, build envelope, and accuracy) into generative design remains challenging, as ensuring all solutions are valid is complex. Balancing multiple design objectives while limiting computational costs adds further challenges for designers. To overcome these difficulties, researchers proposed a generative design method with manufacturing validation to improve decision-making efficiency. This method starts with a constructive solid geometry (CSG)-based technique to create smooth topology shapes with precise geometric control. Then, agenetic algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to g ...
is used to optimize these shapes, and the method offers designers a set of top non-dominated solutions on the Pareto front for further evaluation and final decision-making. By combining multiple techniques, this method can generate many high-quality solutions with smooth boundaries at lower computational costs, making it a practical approach for designing lightweight structures in AM.
Building on topology optimization methods, software providers introduced generative design features in their tools, helping designers set criteria and rank solutions. Industry is driving advancements in generative design for AM, highlighting the need for tools that not only offer a range of solution choices but also streamline workflows for industrial use.
See also
* Computer art * Computer-automated design *Feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
* Generative art
Generative art is post-conceptual art that has been created (in whole or in part) with the use of an autonomous system. An ''autonomous system'' in this context is generally one that is non-human and can independently determine features of an ...
* Parametric design
* Procedural modeling
* Random number generation
* System dynamics
* Topology optimization
References
Further reading
* Gary William Flake: ''The Computational Beauty of Nature: Computer Explorations of Fractals, Chaos, Complex Systems, and Adaptation''. MIT Press 1998, * John Maeda: ''Design by Numbers'', MIT Press 2001, * * Celestino Soddu: papers on Generative Design (1991–2011) aGenerative Art Design Papers. C.Soddu, E.Colabella
{{Design Design Computer graphics