Gaseous ionization detectors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in
Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in
 The three basic types of gaseous ionization detectors are 1)
The three basic types of gaseous ionization detectors are 1)


 Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in
Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in particle physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the s ...
to detect the presence of ionizing particles, and in radiation protection
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". Exposu ...
applications to measure ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
.
They use the ionising effect of radiation upon a gas-filled sensor. If a particle has enough energy to ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
ize a gas atom or molecule, the resulting electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s and ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s cause a current flow which can be measured.
Gaseous ionisation detectors form an important group of instruments used for radiation detection and measurement. This article gives a quick overview of the principal types, and more detailed information can be found in the articles on each instrument. The accompanying plot shows the variation of ion pair generation with varying applied voltage for constant incident radiation. There are three main practical operating regions, one of which each type utilises.
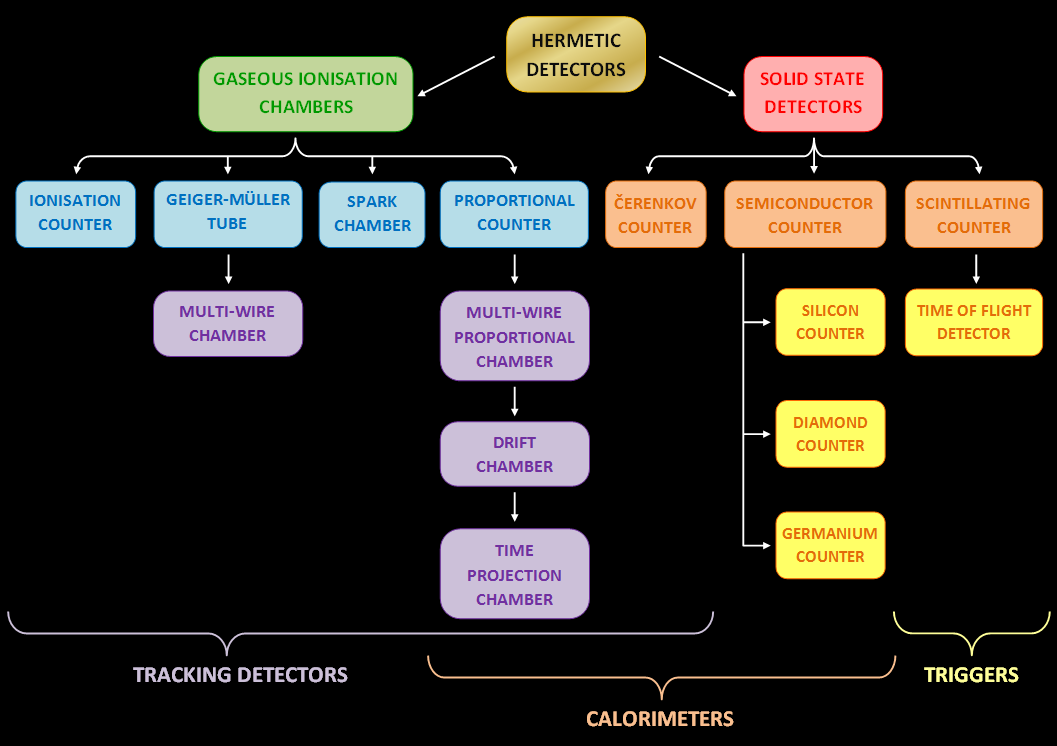
Types
 The three basic types of gaseous ionization detectors are 1)
The three basic types of gaseous ionization detectors are 1) ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gaseous ionisation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of many types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, alpha particles and beta particles. Conventionall ...
s, 2) proportional counter
The proportional counter is a type of gaseous ionization detector device used to measure Charged particle, particles of ionizing radiation. The key feature is its ability to measure the Electronvolt, energy of incident radiation, by producing a det ...
s, and 3) Geiger–Müller tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborate ...
s
All of these have the same basic design of two electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
s separated by air or a special fill gas, but each uses a different method to measure the total number of ion-pairs that are collected. The strength of the electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
between the electrodes and the type and pressure of the fill gas determines the detector's response to ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
.
Ionization chamber

Ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gaseous ionisation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of many types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, alpha particles and beta particles. Conventionall ...
s operate at a low electric field strength, selected such that no gas multiplication takes place. The ion current is generated by the creation of "ion pairs", consisting of an ion and an electron. The ions drift to the cathode while free electrons drift to the anode under the influence of the electric field. This current is independent of the applied voltage if the device is being operated in the "ion chamber region". Ion chambers are preferred for high radiation dose rates because they have no "dead time"; a phenomenon which affects the accuracy of the Geiger–Müller tube at high dose rates.
The advantages are good uniform response to gamma radiation and accurate overall dose reading, capable of measuring very high radiation rates, sustained high radiation levels do not degrade the fill gas.
The disadvantages are 1) low output requiring sophisticated electrometer circuit and 2) operation and accuracy easily affected by moisture.
Proportional counter

Proportional counter
The proportional counter is a type of gaseous ionization detector device used to measure Charged particle, particles of ionizing radiation. The key feature is its ability to measure the Electronvolt, energy of incident radiation, by producing a det ...
s operate at a slightly higher voltage, selected such that discrete avalanches
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a Grade (slope), slope, such as a hill or mountain. Avalanches can be triggered spontaneously, by factors such as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, othe ...
are generated. Each ion pair produces a single avalanche so that an output current pulse is generated which is proportional to the energy deposited by the radiation. This is in the "proportional counting" region.Glenn F Knoll, ''Radiation detection and measurement'', John Wiley and son, 2000.
The term "gas proportional detector" (GPD) is generally used in radiometric practice, and the property of being able to detect particle energy is particularly useful when using large area flat arrays for alpha and beta particle detection and discrimination, such as in installed personnel monitoring equipment.
The wire chamber is a multi-electrode form of proportional counter used as a research tool.
The advantages are the ability to measure energy of radiation and provide spectrographic information, discriminate between alpha and beta particles, and that large area detectors can be constructed
The disadvantages are that anode wires are delicate and can lose efficiency in gas flow detectors due to deposition, the efficiency and operation affected by ingress of oxygen into fill gas, and measurement windows easily damaged in large area detectors.
Micropattern gaseous detectors (MPGDs) are high granularity gaseous detectors with sub-millimeter distances between the anode and cathode electrodes. The main advantages of these microelectronic structures over traditional wire chambers include: count rate capability, time and position resolution, granularity, stability and radiation hardness. Examples of MPGDs are the microstrip gas chamber, the gas electron multiplier and the micromegas detector.
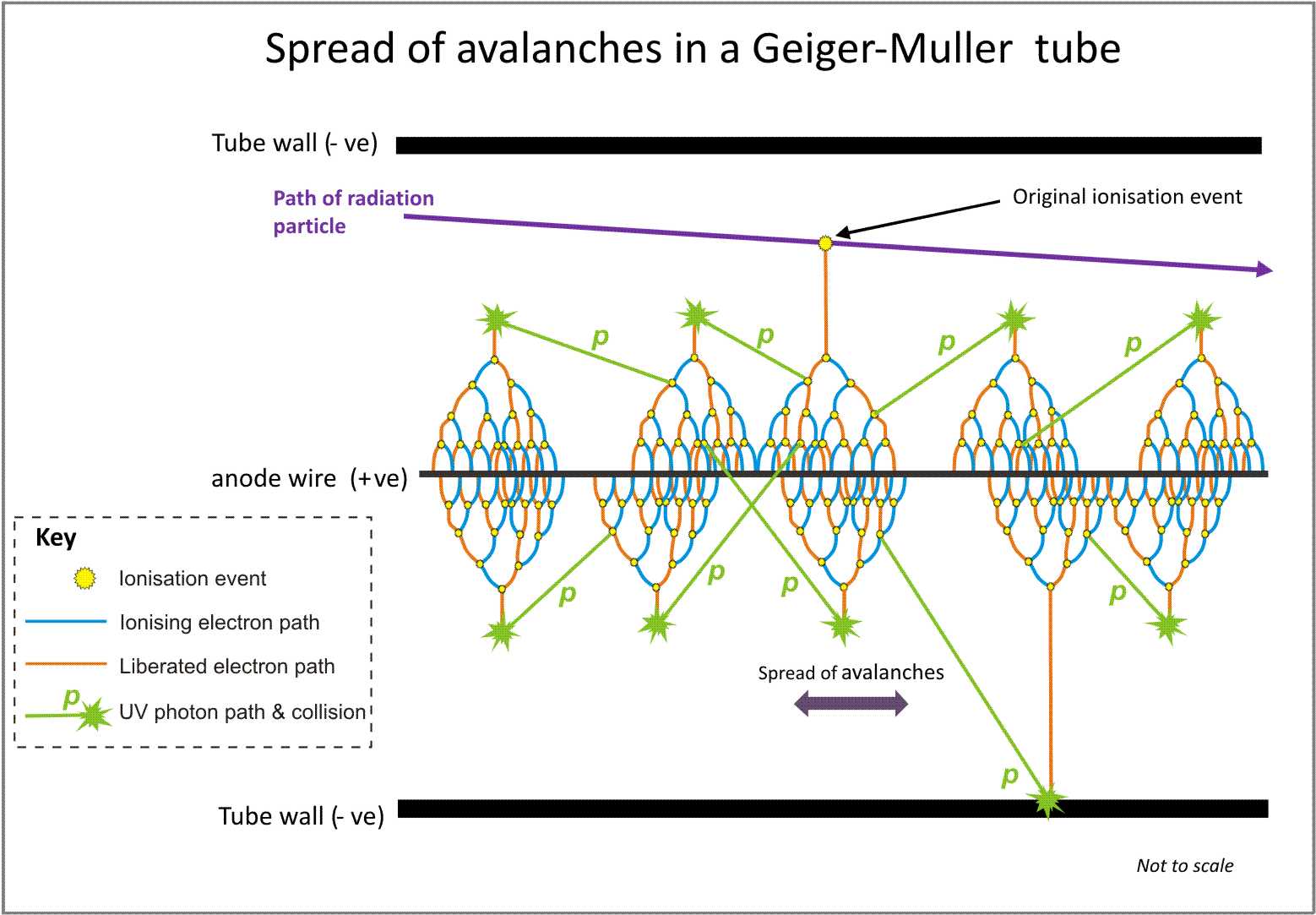
Geiger–Müller tube

Geiger–Müller tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborate ...
s are the primary components of Geiger counters. They operate at an even higher voltage, selected such that each ion pair creates an avalanche, but by the emission of UV photons, multiple avalanches are created which spread along the anode wire, and the adjacent gas volume ionizes from as little as a single ion pair event. This is the "Geiger region" of operation. The current pulses produced by the ionising events are passed to processing electronics which can derive a visual display of count rate or radiation dose, and usually in the case of hand-held instruments, an audio device producing clicks.
The advantages are that they are a cheap and robust detector with a large variety of sizes and applications, large output signal is produced from tube which requires minimal electronic processing for simple counting, and it can measure the overall gamma dose when using an energy compensated tube.
The disadvantages are that it cannot measure the energy of the radiation (no spectrographic information), it will not measure high radiation rates due to dead time, and sustained high radiation levels will degrade fill gas.
Guidance on detector type usage
The UKHealth and Safety Executive
The Health and Safety Executive (HSE) is a British public body responsible for the encouragement, regulation and enforcement of workplace health, safety and welfare. It has additionally adopted a research role into occupational risks in Great B ...
has issued a guidance note on the correct portable instrument for the application concerned. This covers all radiation instrument technologies and is useful in selecting the correct gaseous ionisation detector technology for a measurement application.
Everyday use
Ionization-typesmoke detector
A smoke detector is a device that senses smoke, typically as an indicator of fire. Smoke detectors/alarms are usually housed in plastic enclosures, typically shaped like a disk about in diameter and thick, but shape and size vary. Smoke can be ...
s are gaseous ionization detectors in widespread use. A small source of radioactive americium
Americium is a synthetic element, synthetic chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is radioactive and a transuranic member of the actinide series in the periodic table, located under the lanthanide element e ...
is placed so that it maintains a current between two plates that effectively form an ionisation chamber. If smoke gets between the plates where ionization is taking place, the ionized gas can be neutralized leading to a reduced current. The decrease in current triggers a fire alarm.
See also
* Stopping power of radiation particlesReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gaseous Ionization Detectors Particle detectors Ionising radiation detectors