France In World War I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The military history of France encompasses an immense panorama of conflicts and struggles extending for more than 2,000 years across areas including modern France, Europe, and a variety of regions throughout the world.
According to historian
The military history of France encompasses an immense panorama of conflicts and struggles extending for more than 2,000 years across areas including modern France, Europe, and a variety of regions throughout the world.
According to historian
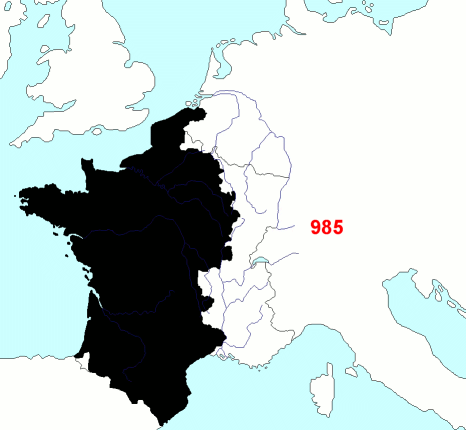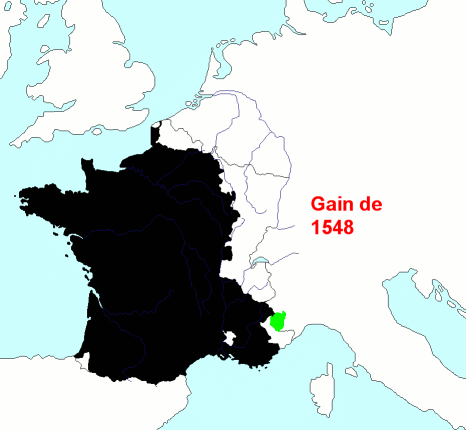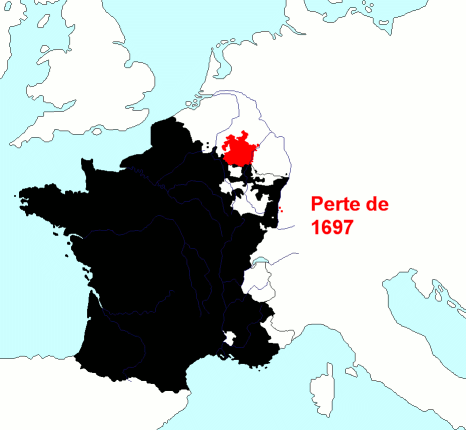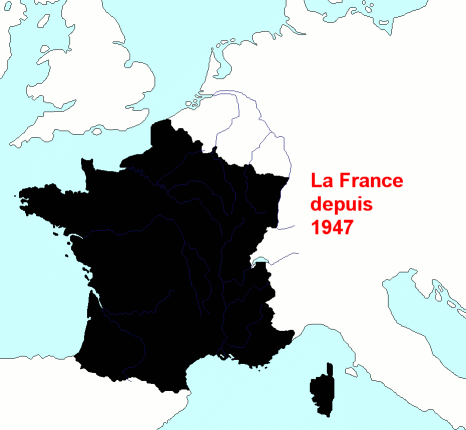 Historian
Historian 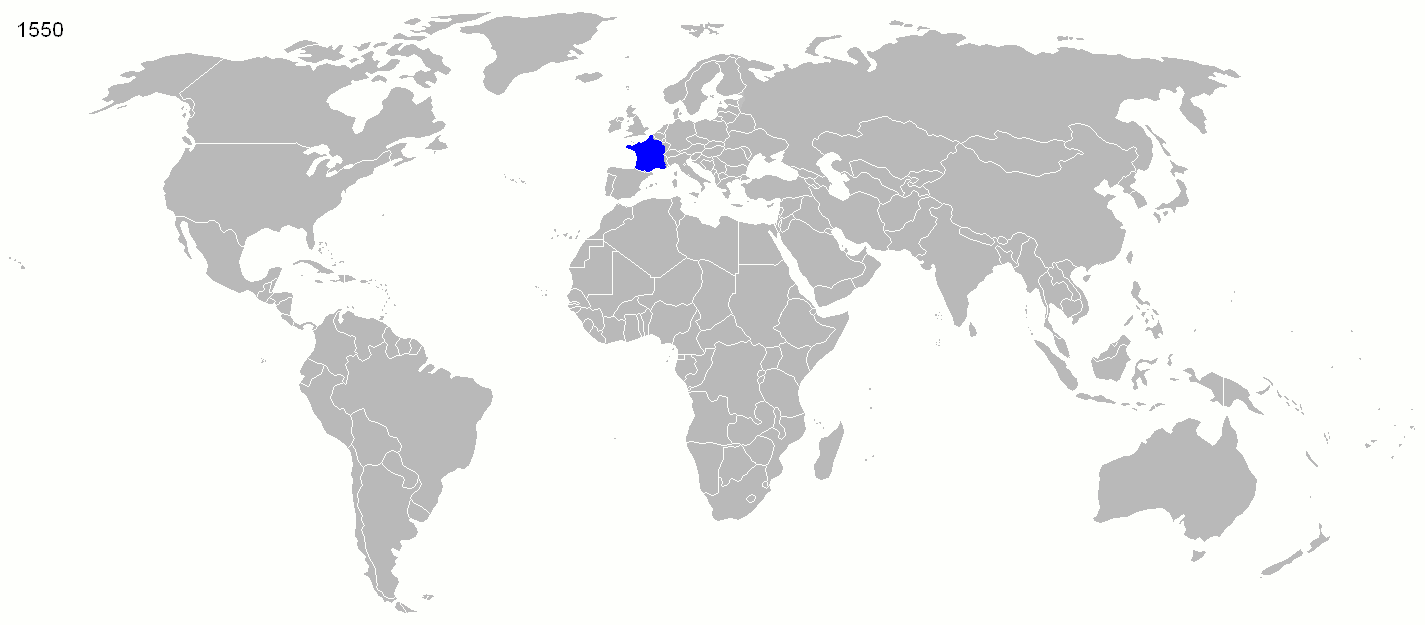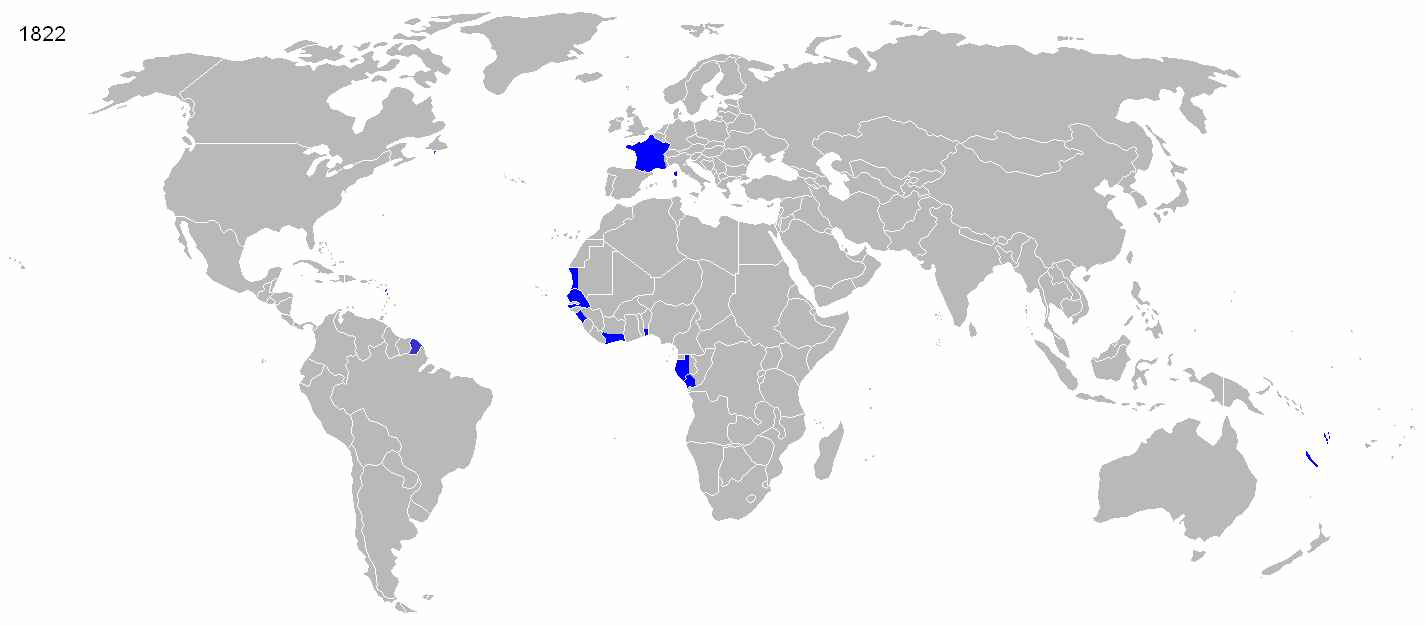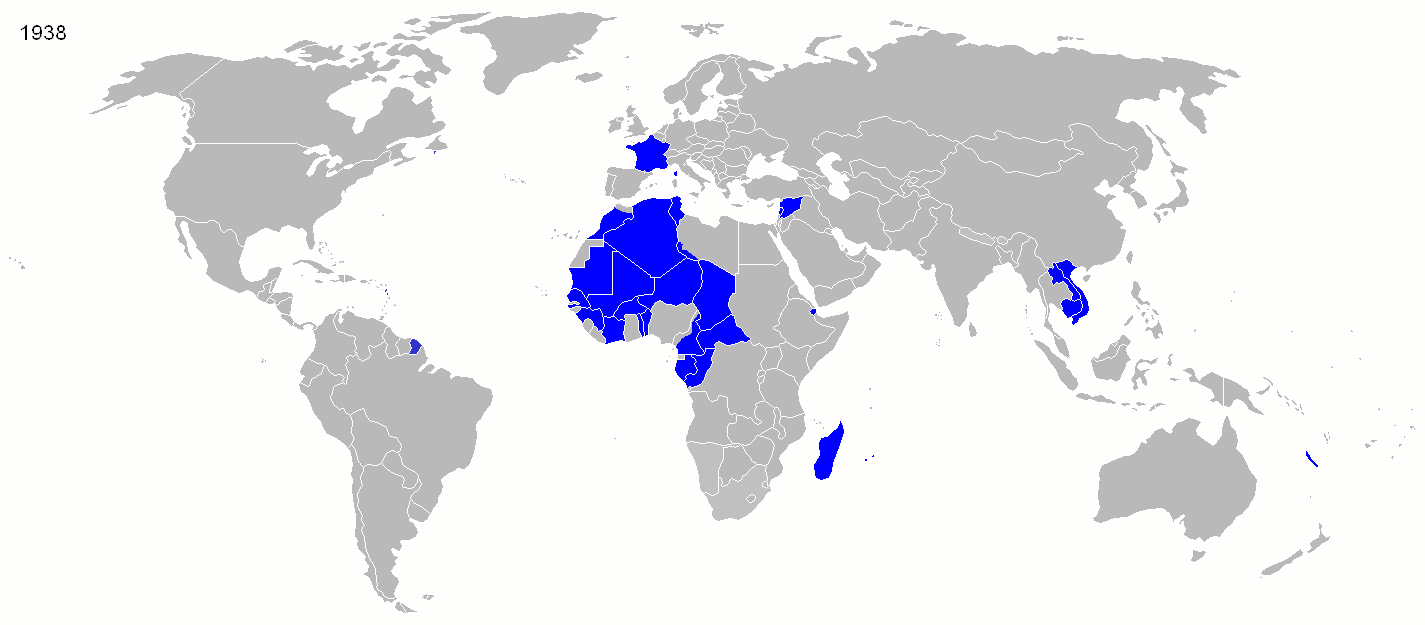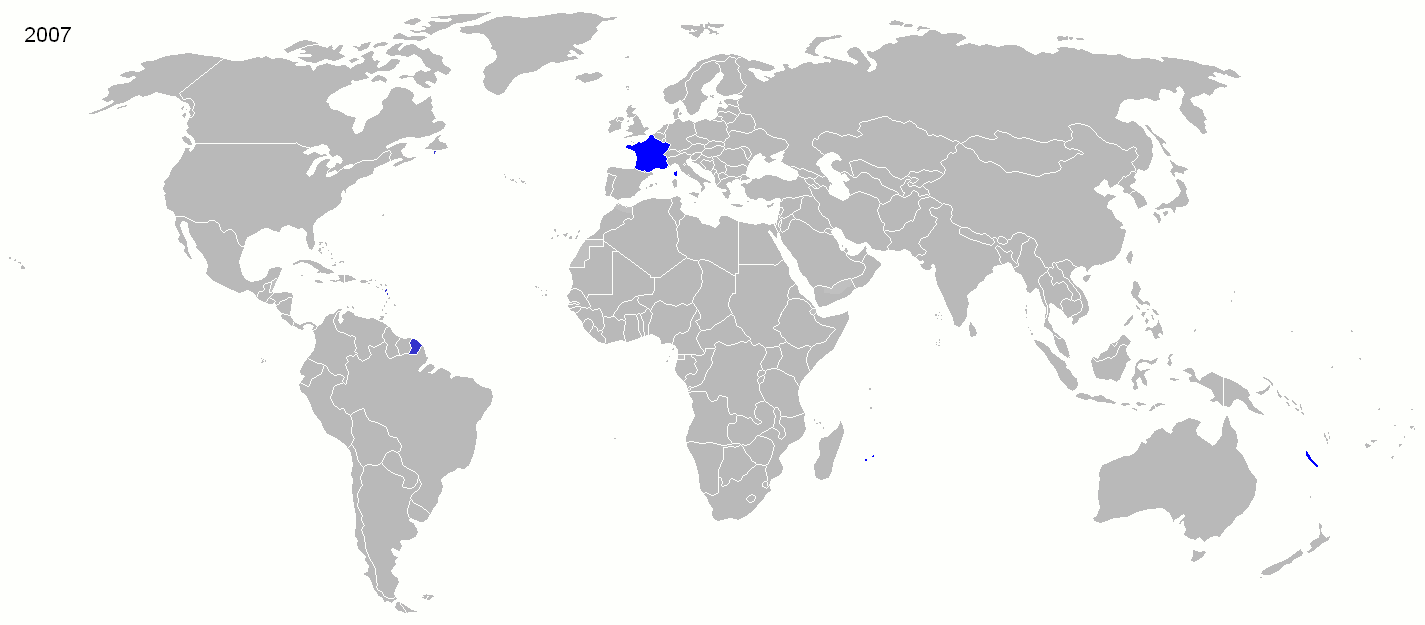 Starting in the early 16th century, much of France's military efforts were dedicated to securing its overseas possessions and putting down dissent among both French colonists and native populations. French troops were spread all across its empire, primarily to deal with the local population. The French colonial empire ultimately disintegrated after the failed attempt to subdue Algerian nationalists in the late 1950s, a failure that led to the collapse of the Fourth Republic. Since
Starting in the early 16th century, much of France's military efforts were dedicated to securing its overseas possessions and putting down dissent among both French colonists and native populations. French troops were spread all across its empire, primarily to deal with the local population. The French colonial empire ultimately disintegrated after the failed attempt to subdue Algerian nationalists in the late 1950s, a failure that led to the collapse of the Fourth Republic. Since
 Around 390 BC, the Gallic
Around 390 BC, the Gallic  Following Clovis, territorial divisions in the Frankish domain sparked intense rivalry between the western part of the kingdom,
Following Clovis, territorial divisions in the Frankish domain sparked intense rivalry between the western part of the kingdom,
 Military history during this period paralleled the rise and eventual fall of the armored
Military history during this period paralleled the rise and eventual fall of the armored  During the
During the  In the 11th century, French knights wore knee-length
In the 11th century, French knights wore knee-length
 The military history of France encompasses an immense panorama of conflicts and struggles extending for more than 2,000 years across areas including modern France, Europe, and a variety of regions throughout the world.
According to historian
The military history of France encompasses an immense panorama of conflicts and struggles extending for more than 2,000 years across areas including modern France, Europe, and a variety of regions throughout the world.
According to historian Niall Ferguson
Niall Campbell Ferguson FRSE (; born 18 April 1964)Biography
Niall Ferguson
, France is the most successful military power in history. It participated in 50 of the 125 major European wars that have been fought since 1495; more than any other European state. The first major recorded wars in the territory of modern-day France itself revolved around the Gallo-Roman conflict that predominated from 60 BC to 50 BC. The Romans eventually emerged victorious through the campaigns of Niall Ferguson
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
. After the decline of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, a Germanic tribe
This list of ancient Germanic peoples is an inventory of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groupings and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilisations in ancient times. The information comes from various ancient historical documents, beginn ...
known as the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
took control of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
by defeating competing tribes. The "land of Francia", from which France gets its name, had high points of expansion under kings Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single kin ...
and Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
, who established the nucleus of the future French state. In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, rivalries with England prompted major conflicts such as the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conque ...
and the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
. With an increasingly centralized monarchy, the first standing army since Roman times, and the use of artillery, France expelled the English from its territory and came out of the Middle Ages as the most powerful nation in Europe, only to lose that status to the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
and Spain following defeat in the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
. The Wars of Religion
A religious war or a war of religion, sometimes also known as a holy war ( la, sanctum bellum), is a war which is primarily caused or justified by differences in religion. In the modern period, there are frequent debates over the extent to wh ...
crippled France in the late 16th century, but a major victory over Spain in the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
made France the most powerful nation on the continent once more. In parallel, France developed its first colonial empire in Asia, Africa, and in the Americas. Under Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
France achieved military supremacy over its rivals, but escalating conflicts against increasingly powerful enemy coalitions checked French ambitions and left the kingdom bankrupt at the opening of the 18th century.
Resurgent French armies secured victories in dynastic conflicts against the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
, and Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
crowns. At the same time, France was fending off attacks on its colonies. As the 18th century advanced, global competition with Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
led to the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
, where France lost its North American holdings. Consolation came in the form of dominance in Europe and the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, where extensive French aid in the form of money and arms, and the direct participation of its army and navy led to the independence of the United States. Internal political upheaval eventually led to 23 years of nearly continuous conflict in the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted French First Republic, France against Ki ...
and the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
. France reached the zenith of its power during this period, dominating the European continent in an unprecedented fashion under Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
. By 1815, however, it had been restored to the same borders it controlled before the Revolution. The rest of the 19th century witnessed the growth of the Second French colonial empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas colonies, protectorates and mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French Colonial Empire", that existe ...
as well as French interventions in Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, and Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. Other major wars were fought against Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
in the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
within France itself.
Following defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, Franco-German rivalry erupted again in the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. France and its allies were victorious this time. Social, political, and economic upheaval in the wake of the conflict led to the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, in which the Allies were defeated in the Battle of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Rep ...
and the French government signed an armistice with Germany. Even though the French military was considered the most powerful in the world at the onset of the war. The Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
, including the Free French Forces
__NOTOC__
The French Liberation Army (french: Armée française de la Libération or AFL) was the reunified French Army that arose from the merging of the Armée d'Afrique with the prior Free French Forces (french: Forces françaises libres, l ...
led by a government in exile, eventually emerged victorious over the Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
. As a result, France secured an occupation zone in Germany and a permanent seat on the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and ...
. The imperative of avoiding a third Franco-German conflict on the scale of the first two world wars paved the way for European integration
European integration is the process of industrial, economic integration, economic, political, legal, social integration, social, and cultural Regional integration, integration of states wholly or partially in Europe or nearby. European integrat ...
starting in the 1950s. France became a nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
and, since the late 20th century, has cooperated closely with NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and European partners.
Dominant themes
 Historian
Historian Niall Ferguson
Niall Campbell Ferguson FRSE (; born 18 April 1964)Biography
Niall Ferguson
argues that France is the most belligerent military power in history. It participated in 50 of the 125 major European wars fought since 1495; more than any other European state. It is followed by Austria which fought in 47 of them; Spain in 44; and England in 43. Out of the 169 most important world battles fought since 387BC, France has won 109, lost 49 and drawn 10.
In the last few centuries, French strategic thinking has sometimes been driven by the need to attain or preserve the so-called "natural frontiers," which are the Niall Ferguson
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to C ...
to the southwest, the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
to the southeast, and the Rhine River
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, sourc ...
to the east. Starting with Clovis, 1,500 years of warfare and diplomacy has witnessed the accomplishment of most of these objectives. Warfare with other European powers was not always determined by these considerations, and often rulers of France extended their continental authority far beyond these barriers, most notably under Charlemagne, Louis XIV, and Napoleon. These periods of incessant conflict were characterized by their own standards and conventions, but all required strong central leadership in order to permit the extension of French rule. Important military rivalries in human history have come about as a result of conflict between French peoples and other European powers. Anglo-French rivalry, for prestige in Europe and around the world, continued for centuries, while the more recent Franco-German rivalry required two world wars to stabilize.
 Starting in the early 16th century, much of France's military efforts were dedicated to securing its overseas possessions and putting down dissent among both French colonists and native populations. French troops were spread all across its empire, primarily to deal with the local population. The French colonial empire ultimately disintegrated after the failed attempt to subdue Algerian nationalists in the late 1950s, a failure that led to the collapse of the Fourth Republic. Since
Starting in the early 16th century, much of France's military efforts were dedicated to securing its overseas possessions and putting down dissent among both French colonists and native populations. French troops were spread all across its empire, primarily to deal with the local population. The French colonial empire ultimately disintegrated after the failed attempt to subdue Algerian nationalists in the late 1950s, a failure that led to the collapse of the Fourth Republic. Since World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, France's efforts have been directed at maintaining its status as a great power and its influence on the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and ...
. France has also been instrumental in attempting to unite the armed forces of Europe for their own defense in order to both balance the power of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and to lessen European military dependence on the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. For example, France withdrew from NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
in 1966 over complaints that its role in the organization was being subordinated to the demands of the United States. French objectives in this era have undergone major shifts. Unencumbered by continental wars or intricate alliances, France now deploys its military forces as part of international peacekeeping operations, security enforcers in former colonies, or maintains them combat ready and mobilized to respond to threats from rogue state
"Rogue state" (or sometimes "outlaw state") is a term applied by some international theorists to states that they consider threatening to the world's peace. These states meet certain criteria, such as being ruled by Authoritarianism, authorita ...
s. France is a nuclear power with the largest nuclear arsenal in Europe, and its nuclear capabilities, just like its conventional forces, have been restructured to rapidly deal with emerging threats.
Early period
 Around 390 BC, the Gallic
Around 390 BC, the Gallic chieftain
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribe, tribal society or chiefdom.
Tribe
The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia.
Tribal societies are sometimes categori ...
Brennus
Brennus or Brennos is the name of two Gaulish chieftains, famous in ancient history:
* Brennus, chieftain of the Senones, a Gallic tribe originating from the modern areas of France known as Seine-et-Marne, Loiret, and Yonne; in 387 BC, in t ...
made his own way through the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
, defeated the Romans in the Battle of the Allia
The Battle of the Allia was a battle fought between the Senones – a Gallic tribe led by Brennus, who had invaded Northern Italy – and the Roman Republic. The battle was fought at the confluence of the Tiber and Allia rivers, 11 Roman mile ...
and sacked Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
for several months. The Gallic invasion left Rome weakened and encouraged several subdued Italian tribes to rebel. One by one, over the course of the next 50 years, these tribes were defeated and brought back under Roman dominion. Meanwhile, the Gauls would continue to harass the region until 345 BC, when they entered into a formal treaty with Rome. But Romans and Gauls would maintain an adversarial relationship for the next several centuries and the Gauls would remain a threat in Italia
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
.
Around 125 BC, the south of France is conquered by the Romans who called this region ''Provincia Romana'' ("Roman Province"), which evolved into the name Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
in French. Brennus' sack of Rome was still remembered by Romans, when Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
conquered the remainder of Gaul. Initially Caesar met with little Gallic resistance: the 60 or so tribes that made up Gaul were unable to unite and defeat the Roman army, something Caesar exploited by pitting one tribe against another. In 58 BC, Caesar defeated the Germanic tribe of the Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names ...
, which was led by Ariovistus
Ariovistus was a leader of the Suebi and other allied Germanic peoples in the second quarter of the 1st century BC. He and his followers took part in a war in Gaul, assisting the Arverni and Sequani in defeating their rivals, the Aedui. They t ...
. The following year he conquered the Belgian Gauls after claiming that they were conspiring against Rome. The string of victories continued in a naval triumph against the Veneti in 56 BC. In 53 BC, a united Gallic resistance movement under Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix (; Greek: Οὐερκιγγετόριξ; – 46 BC) was a Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Despite h ...
emerged for the first time. Caesar laid siege to the fortified city of Avaricum (Bourges
Bourges () is a commune in central France on the river Yèvre. It is the capital of the department of Cher, and also was the capital city of the former province of Berry.
History
The name of the commune derives either from the Bituriges, t ...
) and broke through the defenses after 25 days, with only 800 out of the 40,000 inhabitants managing to escape. He then besieged Gergovia, Vercingetorix's home town, and suffered one of the worst defeats in his career when he had to retreat to suppress a revolt in another part of Gaul. After returning, Caesar surrounded Vercingetorix at Alesia in 52 BC. The townspeople were starved into submission and Caesar's unique defensive earthworks, protruding towards the city and away from it in order to stop a massive Gallic relief force, eventually forced Vercingetorix to surrender. The Gallic Wars were over.
Gallo-Roman culture
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context ...
settled over the region in the next few centuries, but as Roman power weakened in the 4th and 5th centuries AD, a Germanic tribe
This list of ancient Germanic peoples is an inventory of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groupings and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilisations in ancient times. The information comes from various ancient historical documents, beginn ...
, the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, overran large areas that today form modern France. Under King Clovis I in the late 5th and early 6th centuries, Frankish dominions quadrupled as they managed to defeat successive opponents for control of Gaul. In 486 the Frankish armies under Clovis triumphed over Syagrius
Syagrius (430 – 486 or 487 or 493–4) was a Roman general and the last ruler of a Roman rump state in northern Gaul, now called the Kingdom of Soissons. Gregory of Tours referred to him as King of the Romans. Syagrius's defeat by king Clovis I ...
, the last Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
official in Northern Gaul, at the Battle of Soissons. In 491 Clovis defeated Thuringians
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into confl ...
east of his territories. In 496 he overcame the Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
at the Battle of Tolbiac
The Battle of Tolbiac was fought between the Franks, who were fighting under Clovis I, and the Alamanni, whose leader is not known. The date of the battle has traditionally been given as 496, though other accounts suggest it may either have been ...
. In 507 he scored the most impressive victory in his career, prevailing at the Battle of Vouillé
The Battle of Vouillé (from Latin ''Campus Vogladensis'') was fought in the northern marches of Visigothic territory, at Vouillé, near Poitiers (Gaul), in the spring of 507 between the Franks, commanded by Clovis, and the Visigoths, command ...
against the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
, who were led by Alaric II
Alaric II ( got, 𐌰𐌻𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃, , "ruler of all"; la, Alaricus; – August 507) was the King of the Visigoths from 484 until 507. He succeeded his father Euric as king of the Visigoths in Toulouse on 28 December 484; he was ...
, the conqueror of Spain.
 Following Clovis, territorial divisions in the Frankish domain sparked intense rivalry between the western part of the kingdom,
Following Clovis, territorial divisions in the Frankish domain sparked intense rivalry between the western part of the kingdom, Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks.
Neustria included the land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, approximately the north of present-day France, with Paris, Orléans, Tours, Soissons as its main cities. It later ...
, and the eastern part, Austrasia
Austrasia was a territory which formed the north-eastern section of the Merovingian Kingdom of the Franks during the 6th to 8th centuries. It was centred on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers, and was the original territory of the F ...
. The two were sometimes united under one king, but from the 6th to the 8th centuries they often warred against each other. Early in the 8th century, the Franks were preoccupied with Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the mai ...
invasions across the Pyrenees and up the Rhone Valley. Two key battles during this period were the Battle of Toulouse and the Battle of Tours
The Battle of Tours, also called the Battle of Poitiers and, by Arab sources, the Battle of tiles of Martyrs ( ar, معركة بلاط الشهداء, Maʿrakat Balāṭ ash-Shuhadā'), was fought on 10 October 732, and was an important battle ...
, both won by the Franks, and both instrumental in slowing Islamic incursions.
Under Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
the Franks reached the height of their power. After campaigns against Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and ...
, Avars, Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, and Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Bas ...
, the resulting Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lom ...
stretched from the Pyrenees to Central Germany, from the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
to the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
. In 800 the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
made Charlemagne Emperor of the West
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
in return for protection of the Church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* Chris ...
. The Carolingian Empire was a conscious effort to recreate a central administration modeled on that of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, but the motivations behind military expansion differed. Charlemagne hoped to provide his nobles an incentive to fight by encouraging looting on campaign. Plunder and spoils of war were stronger temptations than imperial expansion, and several regions were invaded over and over in order to bolster the coffers of Frankish nobility. Cavalry dominated the battlefields, and while the high costs associated with equipping horses and horse-riders helped limit their numbers, Carolingian armies maintained an average size of 20,000 during peacetime by recruiting infantry from imperial territories near theaters of operation, swelling to more with the levies called upon when at war. The Empire lasted from 800 to 843, when, following Frankish tradition, it was split between the sons of Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqui ...
by the Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Francia, Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis the Pious, Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three ...
.
Middle Ages
 Military history during this period paralleled the rise and eventual fall of the armored
Military history during this period paralleled the rise and eventual fall of the armored knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Gr ...
. Following Charlemagne and the breakdown of the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
due to civil war and ceaseless Viking incursions, the larger and more logistically difficult to maintain infantry-based armies were abandoned in favor of cavalry supplemented by an improvement in armor: leather and steel, steel helmets, coats of mail, and even full armor added to the defensive capabilities of mounted forces. A smaller and more mobile elite cavalry force quickly grew to be the most important component of armies within French territories and most of the rest of Europe, with the shock charge they provided becoming the standard tactic on the battlefield when it was invented in the 11th century. At the same time, the development of agricultural techniques allowed the nations of Western Europe to radically increase food production, facilitating the growth of a particularly large aristocracy under Capetian France
The Kingdom of France in the Middle Ages (roughly, from the 10th century to the middle of the 15th century) was marked by the fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and West Francia (843–987); the expansion of royal control by the House of C ...
. The rise of castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
s, which began in France during the 10th century, was partly caused by the inability of centralized authorities to control these emerging dukes and aristocrats. While all vassals and knights were in theory bound to fight for their sovereign when called upon, this period was marked by many feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a wa ...
local and regional lords using the knights and levied conscripts below them to fight amongst each other, often in defiance or even outright rebellion towards their sovereign. After campaigns designed for plundering, attacking and defending, castles became the dominant feature of medieval warfare
Medieval warfare is the warfare of the Middle Ages. Technological, cultural, and social advancements had forced a severe transformation in the character of warfare from antiquity, changing military tactics and the role of cavalry and artillery ( ...
.
 During the
During the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
, there were in fact too many armored knights in France for the land to support. Some scholars believe that one of the driving forces behind the Crusades was an attempt by such landless knights to find land overseas, without causing the type of internecine warfare that would largely damage France's increasing military strength. However, such historiographical work on the Crusades is being challenged and rejected by a large part of the historical community. The ultimate motivation or motivations for any one individual are difficult to know, but regardless, nobles and knights from France generally formed very sizeable contingents of crusading expeditions. Crusaders were so predominantly French that the word "crusader" in the Arabic language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
is simply known as ''Al-Franj'' or "The Franks" and Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligib ...
became the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establishe ...
.
 In the 11th century, French knights wore knee-length
In the 11th century, French knights wore knee-length mail
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letter (message), letters, and parcel (package), parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid ...
and carried long lances
A lance is a spear designed to be used by a mounted warrior or cavalry soldier ( lancer). In ancient and medieval warfare, it evolved into the leading weapon in cavalry charges, and was unsuited for throwing or for repeated thrusting, unlike s ...
and swords. The Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
knights fielded at the Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings nrf, Batâle dé Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William the Conqueror, William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godw ...
were more than a match for English forces, and their victory simply cemented their power and influence. Between 1202 and 1343, France reduced England's holdings on the continent to a few small provinces through a series of conflicts including the Bouvines Campaign (1202-1214), the Saintonge War
The Saintonge War was a feudal dynastic conflict that occurred between 1242 and 1243. It opposed Capetian forces supportive of King Louis IX's brother Alphonse, Count of Poitiers and those of Hugh X of Lusignan, Raymond VII of Toulouse and Henry ...
(1242) and the War of Saint-Sardos
The War of Saint-Sardos was a short war fought between the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France in 1324. The French invaded the English Duchy of Aquitaine. The war was a clear defeat for the English, and led indirectly to the overthrow of ...
(1324).
Improvements in armor over the centuries led to the establishment of plate armor
Plate armour is a historical type of personal body armour made from bronze, iron, or steel plates, culminating in the iconic suit of armour entirely encasing the wearer. Full plate steel armour developed in Europe during the Late Middle Ages, ...
by the 14th century, which was further developed more rigorously in the 15th century. However, by the late 14th century and the early 15th century, socioeconomic calamities such as the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
, and political crises such as the Jacquerie
The Jacquerie () was a popular revolt by peasants that took place in northern France in the early summer of 1358 during the Hundred Years' War. The revolt was centred in the valley of the Oise north of Paris and was suppressed after a few week ...
peasant revolt, and especially the Armagnac-Burgundian Civil War combined with numerous English invasions, all led to French military power declining during the first two phases of the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
. New weapons, including artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
, and tactics seemingly made the knight more of a sitting target than an effective battle force, but the often-praised longbowmen
A longbow (known as warbow in its time, in contrast to a hunting bow) is a type of tall bow that makes a fairly long draw possible. A longbow is not significantly recurved. Its limbs are relatively narrow and are circular or D-shaped in cross ...
had little to do with the English success. Poor coordination or rough and soft, muddy terrain led to a number of bungled French assaults. The slaughter of knights at the Battle of Agincourt
The Battle of Agincourt ( ; french: Azincourt ) was an English victory in the Hundred Years' War. It took place on 25 October 1415 (Saint Crispin's Day) near Azincourt, in northern France. The unexpected English victory against the numerica ...
best exemplified this carnage. The French were able to field a much larger army of men-at-arms
A man-at-arms was a soldier of the High Medieval to Renaissance periods who was typically well-versed in the use of arms and served as a fully-armoured heavy cavalryman. A man-at-arms could be a knight, or other nobleman, a member of a knig ...
than their English counterparts, who had many longbowmen. Despite this, the French suffered about 6,000 casualties compared to a few hundred for the English because the narrow terrain prevented the tactical envelopments envisioned in recently discovered French plans for the battle. The French suffered a similar defeat at the Battle of the Golden Spurs
The Battle of the Golden Spurs ( nl, Guldensporenslag; french: Bataille des éperons d'or) was a military confrontation between the royal army of France and rebellious forces of the County of Flanders on 11 July 1302 during the Franco-Flemis ...
against Flemish militia in 1302. When knights were allowed to effectively deploy and attack their opponents in the open field, however, they could be more useful, as at Cassel Cassel may refer to:
People
* Cassel (surname)
Places
;France
* Cassel, Nord, a town and commune in northern France
** Battle of Cassel (1071)
** Battle of Cassel (1328)
** Battle of Cassel (1677)
;Germany
* Cassel, Germany, a city in Hesse renam ...
in 1328 or, even more decisively, at Bouvines in 1214, and Patay in 1429.
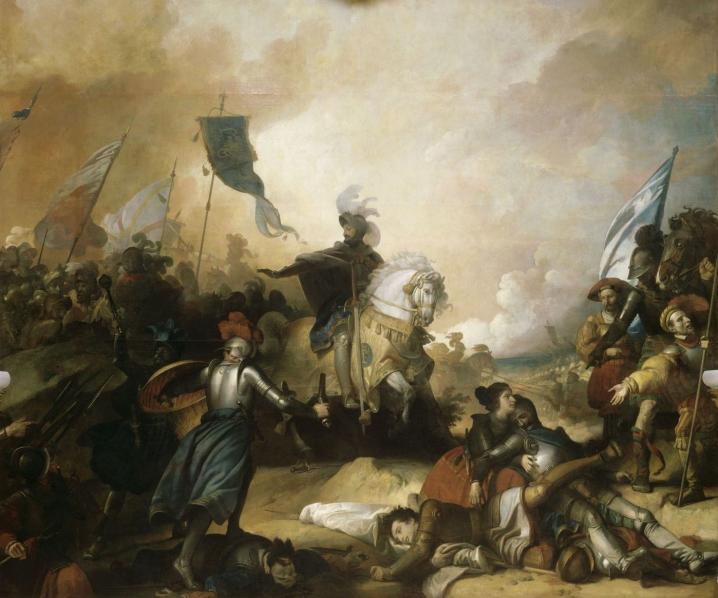
Popular conceptions of the third and final phase of the Hundred Years War are often dominated by the exploits of Joan of Arc
Joan of Arc (french: link=yes, Jeanne d'Arc, translit= �an daʁk} ; 1412 – 30 May 1431) is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronati ...
, but French resurgence was rooted in multiple factors. A major step was taken by King Charles VII, who created the ''Compagnies d'ordonnance
The compagnie d'ordonnance was the first standing army of late medieval and early modern France. The system was the forefather of the modern company. Each ''compagnie'' consisted of 100 ''lances fournies'', which was built around a heavily ar ...
''—cavalry units with 20 companies of 600 men each—and launched the first standing army for a dynastic state in the Western world. The ''Compagnies'' gave the French a considerable edge in professionalism and discipline, being composed of paid full-time professional soldiers, at a time when the allegiances of the aristocratic knights would often shift to the opposing side. Strong French counterattacks turned the tide of the war. The important victories of Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans"
(US) and Patay,
 The
The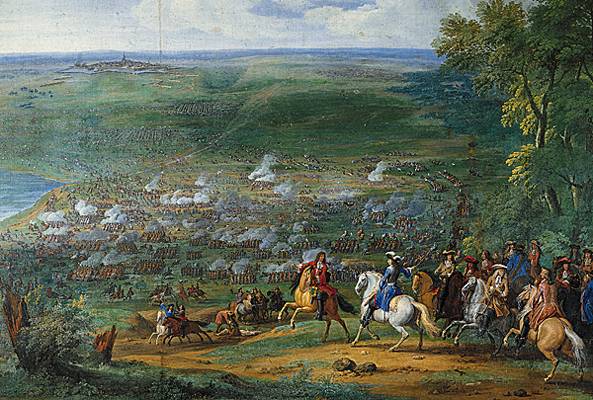  After the Wars of Religion, France could do little to challenge the dominance of the Holy Roman Empire, although the empire itself faced several problems. From the east it was severely endangered by the Ottoman Empire, with which France formed an alliance. The vast Habsburg empire also proved impossible to manage effectively, and the crown was soon divided between the Spanish and Austrian holdings. In 1568, the Dutch declared independence, launching a Eighty Years' War, war that would last for decades and would illustrate the weaknesses of Habsburg power. In the 17th century, the religious violence that had beset France a century earlier began to tear the empire apart. At first France sat on the sidelines, but under Cardinal Richelieu it saw an opportunity to advance its own interests at the expense of the Habsburgs. Despite France's staunch Catholicism, it intervened on the side of the Protestants. The Thirty Years' War was long and extremely bloody, but France and its allies came out victorious, under the leadership of the legendary commanders Grand Condé, Condé and Marshal Turenne, Turenne, beginning a long line of unparalleled Marshal of france, French marshals who would help usher in a new era of military strategy. After their victory, France emerged as the sole dominant European power under the reign of
After the Wars of Religion, France could do little to challenge the dominance of the Holy Roman Empire, although the empire itself faced several problems. From the east it was severely endangered by the Ottoman Empire, with which France formed an alliance. The vast Habsburg empire also proved impossible to manage effectively, and the crown was soon divided between the Spanish and Austrian holdings. In 1568, the Dutch declared independence, launching a Eighty Years' War, war that would last for decades and would illustrate the weaknesses of Habsburg power. In the 17th century, the religious violence that had beset France a century earlier began to tear the empire apart. At first France sat on the sidelines, but under Cardinal Richelieu it saw an opportunity to advance its own interests at the expense of the Habsburgs. Despite France's staunch Catholicism, it intervened on the side of the Protestants. The Thirty Years' War was long and extremely bloody, but France and its allies came out victorious, under the leadership of the legendary commanders Grand Condé, Condé and Marshal Turenne, Turenne, beginning a long line of unparalleled Marshal of france, French marshals who would help usher in a new era of military strategy. After their victory, France emerged as the sole dominant European power under the reign of  The long reign of
The long reign of  Wars in this era consisted mostly of sieges and movements that were rarely decisive, prompting the French military engineer Vauban to design an intricate Fortifications of Vauban, network of fortifications for the defense of France. The armies of Louis XIV were some of the most impressive in History of France, French history, their quality reflecting militaristic as well political developments. In the mid-17th century, royal power reasserted itself and the army became a tool through which the King could wield authority, replacing older systems of mercenary units and the private forces of recalcitrant nobles. Military administration also made gigantic progress as food supply, clothing, equipment, and armaments were provided in a regularity never before equaled. In fact, the French embedded this standardization by becoming the first army to give their soldiers national uniforms in the 1680s and 1690s.
The 18th century saw France remain the dominant power in Europe, but begin to falter largely because of internal problems. The country engaged in a long series of wars, such as the War of the Quadruple Alliance, the War of the Polish Succession, and the War of the Austrian Succession, but these conflicts gained France little. Meanwhile, Britain's power steadily increased, and a new force,
Wars in this era consisted mostly of sieges and movements that were rarely decisive, prompting the French military engineer Vauban to design an intricate Fortifications of Vauban, network of fortifications for the defense of France. The armies of Louis XIV were some of the most impressive in History of France, French history, their quality reflecting militaristic as well political developments. In the mid-17th century, royal power reasserted itself and the army became a tool through which the King could wield authority, replacing older systems of mercenary units and the private forces of recalcitrant nobles. Military administration also made gigantic progress as food supply, clothing, equipment, and armaments were provided in a regularity never before equaled. In fact, the French embedded this standardization by becoming the first army to give their soldiers national uniforms in the 1680s and 1690s.
The 18th century saw France remain the dominant power in Europe, but begin to falter largely because of internal problems. The country engaged in a long series of wars, such as the War of the Quadruple Alliance, the War of the Polish Succession, and the War of the Austrian Succession, but these conflicts gained France little. Meanwhile, Britain's power steadily increased, and a new force,
 The French Revolution, true to its name, revolutionized nearly all aspects of French and European life. The powerful sociopolitical forces unleashed by a people seeking Liberté, égalité, fraternité, liberté, égalité, and fraternité made certain that even warfare was not spared this upheaval. 18th-century armies—with their rigid protocols, static operational strategy, unenthusiastic soldiers, and aristocratic officer classes—underwent massive remodeling as the French monarchy and nobility gave way to Liberalism, liberal assemblies obsessed with external threats. The fundamental shifts in warfare that occurred during the period have prompted scholars to identify the era as the beginning of "modern war".
In 1791 the Legislative Assembly (France), Legislative Assembly passed the "Drill-Book" legislation, implementing a series of infantry doctrines created by French theorists because of their defeat by the Prussians in the
The French Revolution, true to its name, revolutionized nearly all aspects of French and European life. The powerful sociopolitical forces unleashed by a people seeking Liberté, égalité, fraternité, liberté, égalité, and fraternité made certain that even warfare was not spared this upheaval. 18th-century armies—with their rigid protocols, static operational strategy, unenthusiastic soldiers, and aristocratic officer classes—underwent massive remodeling as the French monarchy and nobility gave way to Liberalism, liberal assemblies obsessed with external threats. The fundamental shifts in warfare that occurred during the period have prompted scholars to identify the era as the beginning of "modern war".
In 1791 the Legislative Assembly (France), Legislative Assembly passed the "Drill-Book" legislation, implementing a series of infantry doctrines created by French theorists because of their defeat by the Prussians in the  Armies during the Revolution became noticeably larger than their Holy Roman counterparts, and combined with the new enthusiasm of the troops, the tactical and strategic opportunities became profound. By 1797 the French had defeated the First Coalition, occupied the Low Countries, the west bank of the Rhine, and Northern Italy, objectives which had defied the House of Valois, Valois and House of Bourbon, Bourbon dynasties for centuries. Unsatisfied with the results, many European powers formed a Second Coalition, but by 1801 this too had been decisively beaten. Another key aspect of French success was the changes wrought in the officer classes. Traditionally, European armies left major command positions to those who could be trusted, namely, the aristocracy. The hectic nature of the French Revolution, however, tore apart France's old army, meaning new men were required to become officers and commanders.
Besides opening a flood of tactical and strategic opportunities, the Revolutionary Wars also laid the foundation for modern military theory. Later authors that wrote about "nations in arms" drew inspiration from the French Revolution, in which dire circumstances seemingly mobilized the entire French nation for war and incorporated nationalism into the fabric of military history. Although the reality of war in the France of 1795 would be different from that in the France of 1915, conceptions and mentalities of war evolved significantly. Carl von Clausewitz, Clausewitz correctly analyzed the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras to give posterity a thorough and complete theory of war that emphasized struggles between nations occurring everywhere, from the battlefield to the legislative assemblies, and to the very way that people think. War now emerged as a vast panorama of physical and psychological forces heading for victory or defeat.
Armies during the Revolution became noticeably larger than their Holy Roman counterparts, and combined with the new enthusiasm of the troops, the tactical and strategic opportunities became profound. By 1797 the French had defeated the First Coalition, occupied the Low Countries, the west bank of the Rhine, and Northern Italy, objectives which had defied the House of Valois, Valois and House of Bourbon, Bourbon dynasties for centuries. Unsatisfied with the results, many European powers formed a Second Coalition, but by 1801 this too had been decisively beaten. Another key aspect of French success was the changes wrought in the officer classes. Traditionally, European armies left major command positions to those who could be trusted, namely, the aristocracy. The hectic nature of the French Revolution, however, tore apart France's old army, meaning new men were required to become officers and commanders.
Besides opening a flood of tactical and strategic opportunities, the Revolutionary Wars also laid the foundation for modern military theory. Later authors that wrote about "nations in arms" drew inspiration from the French Revolution, in which dire circumstances seemingly mobilized the entire French nation for war and incorporated nationalism into the fabric of military history. Although the reality of war in the France of 1795 would be different from that in the France of 1915, conceptions and mentalities of war evolved significantly. Carl von Clausewitz, Clausewitz correctly analyzed the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras to give posterity a thorough and complete theory of war that emphasized struggles between nations occurring everywhere, from the battlefield to the legislative assemblies, and to the very way that people think. War now emerged as a vast panorama of physical and psychological forces heading for victory or defeat.
 The Napoleonic Era saw French power and influence reach immense heights, even though the period of domination was relatively brief. In the century and a half preceding the Revolutionary Era, France had transformed Demographics, demographic leverage to military and political weight; the French population was 19 million in 1700, but this had grown to over 29 million in 1800, much higher than that of most other European powers. These numbers permitted France to raise armies at a rapid pace should the need arise. Furthermore, military innovations carried out during the Revolution and the French Consulate, Consulate, evidenced by improvements in artillery and cavalry capabilities on top of better army and staff organization, gave the French army a decisive advantage in the initial stages of the Napoleonic Wars. Another ingredient of success was
The Napoleonic Era saw French power and influence reach immense heights, even though the period of domination was relatively brief. In the century and a half preceding the Revolutionary Era, France had transformed Demographics, demographic leverage to military and political weight; the French population was 19 million in 1700, but this had grown to over 29 million in 1800, much higher than that of most other European powers. These numbers permitted France to raise armies at a rapid pace should the need arise. Furthermore, military innovations carried out during the Revolution and the French Consulate, Consulate, evidenced by improvements in artillery and cavalry capabilities on top of better army and staff organization, gave the French army a decisive advantage in the initial stages of the Napoleonic Wars. Another ingredient of success was  Napoleon inherited an army that was based on conscription and used huge masses of poorly trained troops, which could usually be readily replaced. By 1805 the French Army was a truly lethal force, with many in its ranks veterans of the French Revolutionary Wars. Two years of constant drilling for an invasion of England helped to build a well-trained, well-led army. The Imperial Guard (Napoleon I), Imperial Guard served as an example for the rest of the army and consisted of Napoleon's best handpicked soldiers. Napoleon's huge losses suffered during the disastrous Napoleon's invasion of Russia, Russian campaign would have destroyed any professional commander of the day, but those losses were quickly replaced with new draftees. After Napoleon, nations planned for huge armies with professional leadership and a constant supply of new soldiers, which had huge human costs when improved weapons like the rifled musket replaced the inaccurate muskets of Napoleon's day during the American Civil War.
Napoleon inherited an army that was based on conscription and used huge masses of poorly trained troops, which could usually be readily replaced. By 1805 the French Army was a truly lethal force, with many in its ranks veterans of the French Revolutionary Wars. Two years of constant drilling for an invasion of England helped to build a well-trained, well-led army. The Imperial Guard (Napoleon I), Imperial Guard served as an example for the rest of the army and consisted of Napoleon's best handpicked soldiers. Napoleon's huge losses suffered during the disastrous Napoleon's invasion of Russia, Russian campaign would have destroyed any professional commander of the day, but those losses were quickly replaced with new draftees. After Napoleon, nations planned for huge armies with professional leadership and a constant supply of new soldiers, which had huge human costs when improved weapons like the rifled musket replaced the inaccurate muskets of Napoleon's day during the American Civil War.
 This large size came at a cost, as the logistics of feeding a huge army made them especially dependent on supplies. Most armies of the day relied on the supply-convoy system established during the Thirty Years' War by Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus. This limited mobility, since the soldiers had to wait for the convoys, but it did keep possibly mutinous troops from deserting, and thus helped preserve an army's composure. However, Napoleon's armies were so large that feeding them using the old method proved ineffective, and consequently, French troops were allowed to live off the land. Infused with new concepts of nation and service. Napoleon often attempted to wage decisive, quick campaigns so that he could allow his men to live off the land. The French army did use a convoy system, but it was stocked with very few days worth of food; Napoleon's troops were expected to march quickly, effect a decision on the battlefield, then disperse to feed. For the Russian campaign, the French did store 24 days' worth of food before beginning active operations, but this campaign was the exception, not the rule.
Napoleon's biggest influence in the military sphere was in the conduct of warfare. Weapons and technology remained largely static through the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras, but 18th-century operational strategy underwent massive restructuring. Sieges became infrequent to the point of near-irrelevance, a new emphasis arose towards the destruction of enemy armies as well as their outmaneuvering, and invasions of enemy territory occurred over broader fronts, thus introducing a plethora of strategic opportunities that made wars costlier and, just as importantly, more decisive. Defeat for a European power now meant much more than losing isolated enclaves. Near-Carthaginian treaties intertwined whole national efforts—social, political, economic, and militaristic—into gargantuan collisions that severely upset international conventions as understood at the time. Napoleon's initial success sowed the seeds for his downfall. Not used to such catastrophic defeats in the rigid power system of 18th-century Europe, many nations found existence under the French yoke difficult, sparking revolts, wars, and general instability that plagued the continent until 1815, when the forces of reaction finally triumphed at the Battle of Waterloo.
This large size came at a cost, as the logistics of feeding a huge army made them especially dependent on supplies. Most armies of the day relied on the supply-convoy system established during the Thirty Years' War by Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus. This limited mobility, since the soldiers had to wait for the convoys, but it did keep possibly mutinous troops from deserting, and thus helped preserve an army's composure. However, Napoleon's armies were so large that feeding them using the old method proved ineffective, and consequently, French troops were allowed to live off the land. Infused with new concepts of nation and service. Napoleon often attempted to wage decisive, quick campaigns so that he could allow his men to live off the land. The French army did use a convoy system, but it was stocked with very few days worth of food; Napoleon's troops were expected to march quickly, effect a decision on the battlefield, then disperse to feed. For the Russian campaign, the French did store 24 days' worth of food before beginning active operations, but this campaign was the exception, not the rule.
Napoleon's biggest influence in the military sphere was in the conduct of warfare. Weapons and technology remained largely static through the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras, but 18th-century operational strategy underwent massive restructuring. Sieges became infrequent to the point of near-irrelevance, a new emphasis arose towards the destruction of enemy armies as well as their outmaneuvering, and invasions of enemy territory occurred over broader fronts, thus introducing a plethora of strategic opportunities that made wars costlier and, just as importantly, more decisive. Defeat for a European power now meant much more than losing isolated enclaves. Near-Carthaginian treaties intertwined whole national efforts—social, political, economic, and militaristic—into gargantuan collisions that severely upset international conventions as understood at the time. Napoleon's initial success sowed the seeds for his downfall. Not used to such catastrophic defeats in the rigid power system of 18th-century Europe, many nations found existence under the French yoke difficult, sparking revolts, wars, and general instability that plagued the continent until 1815, when the forces of reaction finally triumphed at the Battle of Waterloo.
 The history of French colonial imperialism can be divided in two major eras: the first from the early 17th century to the middle of the 18th century, and the second from the early 19th century to the middle of the 20th century. In the first phase of expansion, France concentrated its efforts mainly in New France, North America, the French West Indies, Caribbean and French India, India, setting up commercial ventures that were backed by military force. Following defeat in the
The history of French colonial imperialism can be divided in two major eras: the first from the early 17th century to the middle of the 18th century, and the second from the early 19th century to the middle of the 20th century. In the first phase of expansion, France concentrated its efforts mainly in New France, North America, the French West Indies, Caribbean and French India, India, setting up commercial ventures that were backed by military force. Following defeat in the
 After the exile of Napoleon, the freshly restored Bourbon monarchy helped the Absolute monarchy, absolute Ferdinand VII of Spain, Bourbon king of Spain to recover his throne during the Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis, French intervention in Spain in 1823. To restore the prestige of the French monarchy, disputed by the Revolution and the First Empire, Charles X of France, Charles X engaged in the military Invasion of Algiers in 1830, conquest of Algeria in 1830. This marked the beginning of a new expansion of the French colonial empire throughout the 19th century. In that century, France remained a major force in continental affairs. After the 1830 July Revolution, the liberalism, liberal king Louis Philippe I victoriously First Carlist War, supported the Spanish and Ten days campaign, Belgian liberals in 1831. The French later inflicted a defeat on the Habsburgs in the Austro-Sardinian War, Franco-Austrian War of 1859, a victory which led to the Second Italian War of Independence, unification of Italy in 1861, after having triumphed over Russia with other allies in the Crimean War 1854–56. Detrimentally, however, the French army emerged from these victories in an overconfident and complacent state. France's defeat in the Franco-Prussian War led to the loss of Alsace-Lorraine and the creation of a united German Empire, both results representing major failures in long-term French foreign policy and sparking a vengeful, nationalist revanchism meant to earn back former territories. The Dreyfus Affair, however, mitigated these nationalist tendencies by prompting public skepticism about the competence of the military.
After the exile of Napoleon, the freshly restored Bourbon monarchy helped the Absolute monarchy, absolute Ferdinand VII of Spain, Bourbon king of Spain to recover his throne during the Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis, French intervention in Spain in 1823. To restore the prestige of the French monarchy, disputed by the Revolution and the First Empire, Charles X of France, Charles X engaged in the military Invasion of Algiers in 1830, conquest of Algeria in 1830. This marked the beginning of a new expansion of the French colonial empire throughout the 19th century. In that century, France remained a major force in continental affairs. After the 1830 July Revolution, the liberalism, liberal king Louis Philippe I victoriously First Carlist War, supported the Spanish and Ten days campaign, Belgian liberals in 1831. The French later inflicted a defeat on the Habsburgs in the Austro-Sardinian War, Franco-Austrian War of 1859, a victory which led to the Second Italian War of Independence, unification of Italy in 1861, after having triumphed over Russia with other allies in the Crimean War 1854–56. Detrimentally, however, the French army emerged from these victories in an overconfident and complacent state. France's defeat in the Franco-Prussian War led to the loss of Alsace-Lorraine and the creation of a united German Empire, both results representing major failures in long-term French foreign policy and sparking a vengeful, nationalist revanchism meant to earn back former territories. The Dreyfus Affair, however, mitigated these nationalist tendencies by prompting public skepticism about the competence of the military.
 In World War I, the French, with Triple Entente, their allies, managed to hold the Western Front (World War I), Western front and to Balkans Campaign (World War I), counterattack on the Eastern front and West Africa Campaign (World War I), in the colonies until the final defeat of the Central Powers and their allies. After major conflicts such as the Battle of the Frontiers, the First Battle of the Marne, the Battle of Verdun, and the Second Battle of the Aisne—the last resulting in tremendous loss of life and mutiny within the army—the French proved to be enough of a cohesive fighting force to counterattack and defeat the Germans at the Second Battle of the Marne, the first in what would become a string of Hundred Days Offensive, Allied victories that ended the war. The Treaty of Versailles eventually returned Alsace-Lorraine to France. The French military, civilian and Zone rouge, material losses during the First World War were huge. With more than 1.3 million military fatalities and more than 4.6 million wounded, France suffered the second highest Allied losses, after Russia. As a result, France was adamant on the payment of reparations by Germany. The organised failure of the Weimar Republic to pay reparations led to the Occupation of the Ruhr by French and Belgian forces.
In World War I, the French, with Triple Entente, their allies, managed to hold the Western Front (World War I), Western front and to Balkans Campaign (World War I), counterattack on the Eastern front and West Africa Campaign (World War I), in the colonies until the final defeat of the Central Powers and their allies. After major conflicts such as the Battle of the Frontiers, the First Battle of the Marne, the Battle of Verdun, and the Second Battle of the Aisne—the last resulting in tremendous loss of life and mutiny within the army—the French proved to be enough of a cohesive fighting force to counterattack and defeat the Germans at the Second Battle of the Marne, the first in what would become a string of Hundred Days Offensive, Allied victories that ended the war. The Treaty of Versailles eventually returned Alsace-Lorraine to France. The French military, civilian and Zone rouge, material losses during the First World War were huge. With more than 1.3 million military fatalities and more than 4.6 million wounded, France suffered the second highest Allied losses, after Russia. As a result, France was adamant on the payment of reparations by Germany. The organised failure of the Weimar Republic to pay reparations led to the Occupation of the Ruhr by French and Belgian forces.
 A variety of factors—ranging from smaller industrial base to low population growth and obsolete military doctrines—crippled the French effort at the outset of
A variety of factors—ranging from smaller industrial base to low population growth and obsolete military doctrines—crippled the French effort at the outset of  After the defeat, Vichy France cooperated with the Axis powers until 1944. Charles de Gaulle Appeal of 18 June, exhorted the French people to join the allied armies, while the French Vichy forces participated in direct action against Allied forces, inflicting casualties in some cases.
The Normandy Landings, Normandy landings in that year were the first step towards the eventual Northern France Campaign (1944), liberation of France. The
After the defeat, Vichy France cooperated with the Axis powers until 1944. Charles de Gaulle Appeal of 18 June, exhorted the French people to join the allied armies, while the French Vichy forces participated in direct action against Allied forces, inflicting casualties in some cases.
The Normandy Landings, Normandy landings in that year were the first step towards the eventual Northern France Campaign (1944), liberation of France. The
 Following the 1939–45 war, decolonization spread through the former European empires.
Following the First Indochina War, they withdrew from Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia. The military also tried to keep control of Algeria during the Algerian War, when French forces attempted to defeat the Algerian rebels. Despite its military victory, France granted 1962 French Évian Accords referendum, independence to Algerians. French Algeria was home to over a million of settlers (known as Pieds-Noirs), de Gaulle's decision to grant independence to Algeria, almost led to a civil war, supported by various Pied-Noir, Harki and nationalist factions, including the Front Algérie Française, FAF and the Organisation de l'armée secrète, OAS. Related to and during the Algerian war France participated in the Suez Crisis with Israel and the UK.
By 1960 France had lost its direct military influence over all of its former colonies in Africa and Indochina. Nonetheless, several colonies in the Pacific, Caribbean, Indian Oceans and South America remain French territory to this day and France kept a form of indirect political influence in Africa colloquially known as the ''Françafrique''.
As President of the French Republic, Charles de Gaulle oversaw the development of Force de Frappe, French atomic weapons and promoted a foreign policy independent of U.S. influence. He also withdrew France from the
Following the 1939–45 war, decolonization spread through the former European empires.
Following the First Indochina War, they withdrew from Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia. The military also tried to keep control of Algeria during the Algerian War, when French forces attempted to defeat the Algerian rebels. Despite its military victory, France granted 1962 French Évian Accords referendum, independence to Algerians. French Algeria was home to over a million of settlers (known as Pieds-Noirs), de Gaulle's decision to grant independence to Algeria, almost led to a civil war, supported by various Pied-Noir, Harki and nationalist factions, including the Front Algérie Française, FAF and the Organisation de l'armée secrète, OAS. Related to and during the Algerian war France participated in the Suez Crisis with Israel and the UK.
By 1960 France had lost its direct military influence over all of its former colonies in Africa and Indochina. Nonetheless, several colonies in the Pacific, Caribbean, Indian Oceans and South America remain French territory to this day and France kept a form of indirect political influence in Africa colloquially known as the ''Françafrique''.
As President of the French Republic, Charles de Gaulle oversaw the development of Force de Frappe, French atomic weapons and promoted a foreign policy independent of U.S. influence. He also withdrew France from the
 The French Air and Space Force, Armée de l'Air became one of the first professional air forces in the world when it was founded in 1909. The French took active interest in developing their air force and had the first fighter pilots of World War I. During the Interwar period, interwar years, however, particularly in the 1930s, the technical quality fell when compared with the Luftwaffe, which crushed both the French and Royal Air Force, British air forces during the Battle of France. In the post–World War II era, the French made a concerted and successful effort to develop a homegrown aircraft industry. Dassault Aviation led the way forward with their unique and effective delta-wing designs, which formed the basis for the famous Dassault Mirage III, Mirage series of Fighter aircraft, jet fighters. The Mirage repeatedly demonstrated its deadly abilities in the Six-Day War and the Gulf War, becoming one of the most popular and well-sold aircraft in the history of military aviation along the way. Currently, the French are awaiting the Airbus A400M, A400M military transport aircraft, which is still in developmental stages, and the integration of the new Rafale multi-role jet fighter, whose first squadron of 20 aircraft became operational in 2006 at Saint-Dizier. In 2020 it was renamed the Armée de l'Air et de l'Espace, or French Air and Space Force.
The French Air and Space Force, Armée de l'Air became one of the first professional air forces in the world when it was founded in 1909. The French took active interest in developing their air force and had the first fighter pilots of World War I. During the Interwar period, interwar years, however, particularly in the 1930s, the technical quality fell when compared with the Luftwaffe, which crushed both the French and Royal Air Force, British air forces during the Battle of France. In the post–World War II era, the French made a concerted and successful effort to develop a homegrown aircraft industry. Dassault Aviation led the way forward with their unique and effective delta-wing designs, which formed the basis for the famous Dassault Mirage III, Mirage series of Fighter aircraft, jet fighters. The Mirage repeatedly demonstrated its deadly abilities in the Six-Day War and the Gulf War, becoming one of the most popular and well-sold aircraft in the history of military aviation along the way. Currently, the French are awaiting the Airbus A400M, A400M military transport aircraft, which is still in developmental stages, and the integration of the new Rafale multi-role jet fighter, whose first squadron of 20 aircraft became operational in 2006 at Saint-Dizier. In 2020 it was renamed the Armée de l'Air et de l'Espace, or French Air and Space Force.
 Medieval fleets, in France as elsewhere, were almost entirely composed of merchant ships enlisted into naval service in time of war, but the early beginnings of the French naval history goes back to that era. The first battle of the French Navy was the battle of Arnemuiden (23 September 1338), where it defeated the English Navy. The battle of Arnemuiden was also the first naval battle using artillery.Jean-Claude Castex
Medieval fleets, in France as elsewhere, were almost entirely composed of merchant ships enlisted into naval service in time of war, but the early beginnings of the French naval history goes back to that era. The first battle of the French Navy was the battle of Arnemuiden (23 September 1338), where it defeated the English Navy. The battle of Arnemuiden was also the first naval battle using artillery.Jean-Claude Castex
''Dictionnaire des batailles navales franco-anglaises''
Presses de l'Université Laval, 2004, p.21 It was later defeated by an Anglo-Flemish fleet at the Battle of Sluys and, with Crown of Castile, Castilian help, managed to beat the English at Battle of La Rochelle, La Rochelle—both battles playing a crucial role in the development of the Hundred Years War. However, the navy did not become a consistent instrument of national power until the 17th century with Louis XIV. Under the tutelage of the "Sun King," the French Navy was well financed and equipped, managing to resoundingly defeat a combined Spanish-Dutch fleet at the Battle of Palermo in 1676 during the Franco-Dutch War, although, along with the English navy, it suffered several strategic reversals against the Dutch, who were led by the brilliant Michiel de Ruyter. It scored several early victories in the Nine Years War against the Royal Navy and the Royal Netherlands Navy, Dutch Navy. Financial difficulties, however, allowed the English and the Dutch to regain the initiative at sea. A perennial problem for the French Navy was the strategic priorities of France, which were first and foremost tied to its European ambitions. This reality meant that the army was often treated better than the navy, and as a result, the latter suffered in training and operational performance. The 18th century saw the beginning of the Royal Navy's domination, which managed to inflict a number of significant defeats on the French. However, in a very impressive effort, a French fleet under François Joseph Paul, marquis de Grasetilly, comte de Grasse, de Grasse managed to defeat a British fleet at the Battle of the Chesapeake in 1781, ensuring that the Franco-American ground forces would win the ongoing Siege of Yorktown. Beyond that, and Pierre André de Suffren de Saint Tropez, Suffren's Naval operations in the American Revolutionary War#East Indies campaign, 1778–1783, impressive campaigns against the British in India, there was not much more good news. The French Revolution all but crippled the French Navy, and efforts to make it into a powerful force under Napoleon were dashed at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, where the British all but annihilated a combined Franco-Spanish fleet. The disaster guaranteed British naval domination until the end of the Napoleonic wars. Later in the 19th century, the navy recovered and became the second finest in the world after the Royal Navy. It conducted a successful blockade of Mexico in the Pastry War of 1838 and obliterated the Chinese navy at the Battle of Foochow in 1884. It also served as an effective link between the growing parts of the French empire. The navy performed well during World War I, in which it mainly protected the naval lanes in the Mediterranean Sea. At the onset of the war, the French had a large fleet in the Mediterranean whive no less than seven battleship & six heavy cruiser . French defeats in the early stages of World War II, however, forced the British to atatck the French fleet moored at Destruction of the French Fleet at Mers-el-Kebir, Mers-el-Kebir in order to prevent the threat she fall to the Germans, the remaining of French fleet scuttled herself at Toulon for prevent the 7th Panzer Division (Wehrmacht), 7th Panzer Division to capture the fleet, two years later . Currently, French naval doctrine calls for two aircraft carriers, but the French currently only have one, the ''French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, Charles de Gaulle'', due to restructuring. The navy is in the midst of some technological and procurement changes; newer submarines are under construction and Rafale aircraft (the naval version) are currently replacing older aircraft.
excerpt and text search
* Forrest, Alan. ''Conscripts and Deserters: The Army and French Society During the Revolution and Empire'' (1989) * Forrest, Alan. ''Napoleon's Men: The Soldiers of the Revolution and Empire'' (2002) * Greenhalgh, Elizabeth. ''The French Army and the First World War'' (2014), 486 pages; comprehensive scholarly history. * Holroyd, Richard. "The Bourbon Army, 1815-1830." ''Historical Journal'' 14, no. 3 (1971): 529–52
online
*Kinard, Jeff. ''Artillery: an illustrated history of its impact''. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, 2007. * Nolan, Cathal. ''Wars of the Age of Louis XIV, 1650-1715: An Encyclopedia of Global Warfare and Civilization'' (2008) * Nolan, Cathal. ''The Age of Wars of Religion, 1000-1650'' (2 vol. 2006) * Pichichero, Christy. ''The Military Enlightenment: War and Culture in the French Empire from Louis XIV to Napoleon'' (2018
online review
* Porch, Douglas. "The French Army Law of 1832." ''Historical Journal'' 14, no. 4 (1971): 751–69
online
* Porch, Douglas. ''The March to the Marne: The French Army 1871-1914'' Cambridge University Press (2003) * Scott, Samuel F. ''From Yorktown to Valmy: the transformation of the French Army in an age of revolution'' (University Press of Colorado, 1998) * Thoral, Marie-Cécile. ''From Valmy to Waterloo: France at War, 1792–1815'' (Palgrave Macmillan UK, 2011)
Illustrations by Hippolyte Bellangé from the book P.-M. Laurent de L`Ardeche «Histoire de Napoleon», 1843
The French Military in Africa
(2008) - Council on Foreign Relations {{DEFAULTSORT:Military History Of France Military history of France,
(US) and Patay,
Formigny
Formigny () is a former commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France. On 1 January 2017, it was merged into the new commune Formigny La Bataille.
History
*15 April 1450: Battle of Formigny. The battle of For ...
and Castillon allowed the French to win back all English continental territories, except Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
, which was later captured by the French.
Equipment of medieval French sergeants was based on their property:
''Ancien Régime''
 The
The French Renaissance
The French Renaissance was the cultural and artistic movement in France between the 15th and early 17th centuries. The period is associated with the pan-European Renaissance, a word first used by the French historian Jules Michelet to define th ...
and the beginning of the ''Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for "ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
'', normally marked by the reign of Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
, saw the nation become far more unified under the monarch. The power of the nobles was diminished as a national army was created. With England expelled from the continent and being consumed by the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
, France's main rival was the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
. This threat to France became alarming in 1516 when Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
became the king of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, and grew worse when Charles was also elected Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
in 1519. France was all but surrounded as Germany, Spain, and the Low Countries were controlled by the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s. The lengthy Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
that took place during this period eventually resulted in defeat for France and established Catholic Spain, which formed a branch of the Habsburg holdings, as the most powerful nation in Europe, with their dreaded ''tercios
A ''tercio'' (; Spanish for " third") was a military unit of the Spanish Army during the reign of the Spanish Habsburgs in the early modern period. The tercios were renowned for the effectiveness of their battlefield formations, forming the el ...
'' dominating the European battlefield well into the Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an es ...
. Later in the 16th century, France was weakened internally by the Wars of Religion
A religious war or a war of religion, sometimes also known as a holy war ( la, sanctum bellum), is a war which is primarily caused or justified by differences in religion. In the modern period, there are frequent debates over the extent to wh ...
. As nobles managed to raise their own private armies, these conflicts between Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss politica ...
and Catholics all but demolished centralization and monarchical authority, precluding France from remaining a powerful force in European affairs. On the battlefield, the religious conflicts highlighted the influence of the gendarmes
Wrong info! -->
A gendarmerie () is a military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term ''gendarme'' () is derived from the medieval French expression ', which translates to " men-at-arms" (literally, ...
, heavy cavalry units that comprised the majority of cavalrymen attached to the main field armies. The pride of the royal cavalry, gendarme companies were often attached to the main royal army in hopes of inflicting a decisive defeat on Huguenot forces, although secondary detachments were also used for scouting and intercepting enemy troops.
 After the Wars of Religion, France could do little to challenge the dominance of the Holy Roman Empire, although the empire itself faced several problems. From the east it was severely endangered by the Ottoman Empire, with which France formed an alliance. The vast Habsburg empire also proved impossible to manage effectively, and the crown was soon divided between the Spanish and Austrian holdings. In 1568, the Dutch declared independence, launching a Eighty Years' War, war that would last for decades and would illustrate the weaknesses of Habsburg power. In the 17th century, the religious violence that had beset France a century earlier began to tear the empire apart. At first France sat on the sidelines, but under Cardinal Richelieu it saw an opportunity to advance its own interests at the expense of the Habsburgs. Despite France's staunch Catholicism, it intervened on the side of the Protestants. The Thirty Years' War was long and extremely bloody, but France and its allies came out victorious, under the leadership of the legendary commanders Grand Condé, Condé and Marshal Turenne, Turenne, beginning a long line of unparalleled Marshal of france, French marshals who would help usher in a new era of military strategy. After their victory, France emerged as the sole dominant European power under the reign of
After the Wars of Religion, France could do little to challenge the dominance of the Holy Roman Empire, although the empire itself faced several problems. From the east it was severely endangered by the Ottoman Empire, with which France formed an alliance. The vast Habsburg empire also proved impossible to manage effectively, and the crown was soon divided between the Spanish and Austrian holdings. In 1568, the Dutch declared independence, launching a Eighty Years' War, war that would last for decades and would illustrate the weaknesses of Habsburg power. In the 17th century, the religious violence that had beset France a century earlier began to tear the empire apart. At first France sat on the sidelines, but under Cardinal Richelieu it saw an opportunity to advance its own interests at the expense of the Habsburgs. Despite France's staunch Catholicism, it intervened on the side of the Protestants. The Thirty Years' War was long and extremely bloody, but France and its allies came out victorious, under the leadership of the legendary commanders Grand Condé, Condé and Marshal Turenne, Turenne, beginning a long line of unparalleled Marshal of france, French marshals who would help usher in a new era of military strategy. After their victory, France emerged as the sole dominant European power under the reign of Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
. In parallel, French explorers, such as Jacques Cartier or Samuel de Champlain, claimed lands in the Americas for France, paving the way for the expansion of the French colonial empire.
 The long reign of
The long reign of Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
saw a series of conflicts: the War of Devolution, the Franco-Dutch War, the War of the Reunions, the Nine Years War, and the War of the Spanish Succession. Few of these wars were either clear victories or definite defeats, but French borders expanded steadily anyway. The west bank of the Rhine, much of the Spanish Netherlands, and a good deal of Luxembourg were annexed while the War of the Spanish Succession saw the grandson of Louis placed on the throne of Spain. The French strategic situation, however, changed decisively with the Glorious Revolution in England, which replaced a James II of England, pro-French king with an enemy of Louis, the Dutch William III of England, William of Orange. After a period of two centuries seeing only rare hostilities with France, England now became a consistent enemy again, and remained so until the 19th century. To stop French advances, England formed coalitions with several other European powers, most notably the Habsburgs. While these armies had difficulties against the French on land, the British Royal Navy dominated the seas, and France lost many of its colonial holdings. The British economy also became Europe's most powerful, and Golden Cavalry of St George, British money funded the campaigns of their continental allies.
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
, became a major threat. This change in the balance of power led to the Diplomatic Revolution of 1756, when France and the Habsburgs forged an alliance after centuries of animosity. This alliance proved less than effective in the France in the Seven Years' War, Seven Years' War, but in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, the France in the American Revolutionary War, French helped inflict a major defeat on the British.
Revolutionary France
 The French Revolution, true to its name, revolutionized nearly all aspects of French and European life. The powerful sociopolitical forces unleashed by a people seeking Liberté, égalité, fraternité, liberté, égalité, and fraternité made certain that even warfare was not spared this upheaval. 18th-century armies—with their rigid protocols, static operational strategy, unenthusiastic soldiers, and aristocratic officer classes—underwent massive remodeling as the French monarchy and nobility gave way to Liberalism, liberal assemblies obsessed with external threats. The fundamental shifts in warfare that occurred during the period have prompted scholars to identify the era as the beginning of "modern war".
In 1791 the Legislative Assembly (France), Legislative Assembly passed the "Drill-Book" legislation, implementing a series of infantry doctrines created by French theorists because of their defeat by the Prussians in the
The French Revolution, true to its name, revolutionized nearly all aspects of French and European life. The powerful sociopolitical forces unleashed by a people seeking Liberté, égalité, fraternité, liberté, égalité, and fraternité made certain that even warfare was not spared this upheaval. 18th-century armies—with their rigid protocols, static operational strategy, unenthusiastic soldiers, and aristocratic officer classes—underwent massive remodeling as the French monarchy and nobility gave way to Liberalism, liberal assemblies obsessed with external threats. The fundamental shifts in warfare that occurred during the period have prompted scholars to identify the era as the beginning of "modern war".
In 1791 the Legislative Assembly (France), Legislative Assembly passed the "Drill-Book" legislation, implementing a series of infantry doctrines created by French theorists because of their defeat by the Prussians in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
. The new developments hoped to exploit the intrinsic bravery of the French soldier, made even more powerful by the explosive nationalist forces of the Revolution. The changes also placed a faith on the ordinary soldier that would be completely unacceptable in earlier times; French troops were expected to harass the enemy and remain loyal enough to not desert, a benefit other Ancien Régime armies did not have.
Following the declaration of war in 1792, an imposing array of enemies converging on French borders prompted the government in Paris to adopt radical measures. August 23, 1793, would become a historic day in military history; on that date the National Convention called a levée en masse, or mass conscription, for the first time in human history. By summer of the following year, conscription made some 500,000 men available for service and the French began to deal blows to their European enemies.
 Armies during the Revolution became noticeably larger than their Holy Roman counterparts, and combined with the new enthusiasm of the troops, the tactical and strategic opportunities became profound. By 1797 the French had defeated the First Coalition, occupied the Low Countries, the west bank of the Rhine, and Northern Italy, objectives which had defied the House of Valois, Valois and House of Bourbon, Bourbon dynasties for centuries. Unsatisfied with the results, many European powers formed a Second Coalition, but by 1801 this too had been decisively beaten. Another key aspect of French success was the changes wrought in the officer classes. Traditionally, European armies left major command positions to those who could be trusted, namely, the aristocracy. The hectic nature of the French Revolution, however, tore apart France's old army, meaning new men were required to become officers and commanders.
Besides opening a flood of tactical and strategic opportunities, the Revolutionary Wars also laid the foundation for modern military theory. Later authors that wrote about "nations in arms" drew inspiration from the French Revolution, in which dire circumstances seemingly mobilized the entire French nation for war and incorporated nationalism into the fabric of military history. Although the reality of war in the France of 1795 would be different from that in the France of 1915, conceptions and mentalities of war evolved significantly. Carl von Clausewitz, Clausewitz correctly analyzed the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras to give posterity a thorough and complete theory of war that emphasized struggles between nations occurring everywhere, from the battlefield to the legislative assemblies, and to the very way that people think. War now emerged as a vast panorama of physical and psychological forces heading for victory or defeat.
Armies during the Revolution became noticeably larger than their Holy Roman counterparts, and combined with the new enthusiasm of the troops, the tactical and strategic opportunities became profound. By 1797 the French had defeated the First Coalition, occupied the Low Countries, the west bank of the Rhine, and Northern Italy, objectives which had defied the House of Valois, Valois and House of Bourbon, Bourbon dynasties for centuries. Unsatisfied with the results, many European powers formed a Second Coalition, but by 1801 this too had been decisively beaten. Another key aspect of French success was the changes wrought in the officer classes. Traditionally, European armies left major command positions to those who could be trusted, namely, the aristocracy. The hectic nature of the French Revolution, however, tore apart France's old army, meaning new men were required to become officers and commanders.
Besides opening a flood of tactical and strategic opportunities, the Revolutionary Wars also laid the foundation for modern military theory. Later authors that wrote about "nations in arms" drew inspiration from the French Revolution, in which dire circumstances seemingly mobilized the entire French nation for war and incorporated nationalism into the fabric of military history. Although the reality of war in the France of 1795 would be different from that in the France of 1915, conceptions and mentalities of war evolved significantly. Carl von Clausewitz, Clausewitz correctly analyzed the Revolutionary and Napoleonic eras to give posterity a thorough and complete theory of war that emphasized struggles between nations occurring everywhere, from the battlefield to the legislative assemblies, and to the very way that people think. War now emerged as a vast panorama of physical and psychological forces heading for victory or defeat.
Napoleonic France
 The Napoleonic Era saw French power and influence reach immense heights, even though the period of domination was relatively brief. In the century and a half preceding the Revolutionary Era, France had transformed Demographics, demographic leverage to military and political weight; the French population was 19 million in 1700, but this had grown to over 29 million in 1800, much higher than that of most other European powers. These numbers permitted France to raise armies at a rapid pace should the need arise. Furthermore, military innovations carried out during the Revolution and the French Consulate, Consulate, evidenced by improvements in artillery and cavalry capabilities on top of better army and staff organization, gave the French army a decisive advantage in the initial stages of the Napoleonic Wars. Another ingredient of success was
The Napoleonic Era saw French power and influence reach immense heights, even though the period of domination was relatively brief. In the century and a half preceding the Revolutionary Era, France had transformed Demographics, demographic leverage to military and political weight; the French population was 19 million in 1700, but this had grown to over 29 million in 1800, much higher than that of most other European powers. These numbers permitted France to raise armies at a rapid pace should the need arise. Furthermore, military innovations carried out during the Revolution and the French Consulate, Consulate, evidenced by improvements in artillery and cavalry capabilities on top of better army and staff organization, gave the French army a decisive advantage in the initial stages of the Napoleonic Wars. Another ingredient of success was Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
himself—intelligent, charismatic, and a military genius, Napoleon absorbed the latest military theories of the day and applied them in the battlefield with deadly effect.
 Napoleon inherited an army that was based on conscription and used huge masses of poorly trained troops, which could usually be readily replaced. By 1805 the French Army was a truly lethal force, with many in its ranks veterans of the French Revolutionary Wars. Two years of constant drilling for an invasion of England helped to build a well-trained, well-led army. The Imperial Guard (Napoleon I), Imperial Guard served as an example for the rest of the army and consisted of Napoleon's best handpicked soldiers. Napoleon's huge losses suffered during the disastrous Napoleon's invasion of Russia, Russian campaign would have destroyed any professional commander of the day, but those losses were quickly replaced with new draftees. After Napoleon, nations planned for huge armies with professional leadership and a constant supply of new soldiers, which had huge human costs when improved weapons like the rifled musket replaced the inaccurate muskets of Napoleon's day during the American Civil War.
Napoleon inherited an army that was based on conscription and used huge masses of poorly trained troops, which could usually be readily replaced. By 1805 the French Army was a truly lethal force, with many in its ranks veterans of the French Revolutionary Wars. Two years of constant drilling for an invasion of England helped to build a well-trained, well-led army. The Imperial Guard (Napoleon I), Imperial Guard served as an example for the rest of the army and consisted of Napoleon's best handpicked soldiers. Napoleon's huge losses suffered during the disastrous Napoleon's invasion of Russia, Russian campaign would have destroyed any professional commander of the day, but those losses were quickly replaced with new draftees. After Napoleon, nations planned for huge armies with professional leadership and a constant supply of new soldiers, which had huge human costs when improved weapons like the rifled musket replaced the inaccurate muskets of Napoleon's day during the American Civil War.
French colonial empire
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
, France lost its possessions in North America and India, but it did manage to keep the wealthy Caribbean islands of Saint-Domingue, Guadeloupe, and Martinique.
The second stage began with the French conquest of Algeria, conquest of Algeria in 1830, then with the establishment of French Indochina (covering modern Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia) and a string of military victories in the Scramble for Africa, where it established control over regions covering much of West Africa, Central Africa and Maghreb. In 1914 France had an empire stretching over (6,000,000 mile²) of land and about 110 million people. Following victory in World War I, Togo and most of Cameroon were also added to the French possessions, and Syria and Lebanon became French League of Nations Mandate, mandates. For most of the period from 1870 to 1945, France was territorially the third largest nation on Earth, after Britain and Russia (later the Soviet Union), and had the most overseas possessions following Britain. Following the Second World War, France struggled to preserve French territories but wound up losing the First Indochina War (the precursor to the Vietnam War) and granting independence to Algeria after a long war. Today, France still maintains a number of Overseas departments and territories of France, overseas territories, but their collective size is barely a shadow of the old French colonial empire.
From 1815
 After the exile of Napoleon, the freshly restored Bourbon monarchy helped the Absolute monarchy, absolute Ferdinand VII of Spain, Bourbon king of Spain to recover his throne during the Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis, French intervention in Spain in 1823. To restore the prestige of the French monarchy, disputed by the Revolution and the First Empire, Charles X of France, Charles X engaged in the military Invasion of Algiers in 1830, conquest of Algeria in 1830. This marked the beginning of a new expansion of the French colonial empire throughout the 19th century. In that century, France remained a major force in continental affairs. After the 1830 July Revolution, the liberalism, liberal king Louis Philippe I victoriously First Carlist War, supported the Spanish and Ten days campaign, Belgian liberals in 1831. The French later inflicted a defeat on the Habsburgs in the Austro-Sardinian War, Franco-Austrian War of 1859, a victory which led to the Second Italian War of Independence, unification of Italy in 1861, after having triumphed over Russia with other allies in the Crimean War 1854–56. Detrimentally, however, the French army emerged from these victories in an overconfident and complacent state. France's defeat in the Franco-Prussian War led to the loss of Alsace-Lorraine and the creation of a united German Empire, both results representing major failures in long-term French foreign policy and sparking a vengeful, nationalist revanchism meant to earn back former territories. The Dreyfus Affair, however, mitigated these nationalist tendencies by prompting public skepticism about the competence of the military.
After the exile of Napoleon, the freshly restored Bourbon monarchy helped the Absolute monarchy, absolute Ferdinand VII of Spain, Bourbon king of Spain to recover his throne during the Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis, French intervention in Spain in 1823. To restore the prestige of the French monarchy, disputed by the Revolution and the First Empire, Charles X of France, Charles X engaged in the military Invasion of Algiers in 1830, conquest of Algeria in 1830. This marked the beginning of a new expansion of the French colonial empire throughout the 19th century. In that century, France remained a major force in continental affairs. After the 1830 July Revolution, the liberalism, liberal king Louis Philippe I victoriously First Carlist War, supported the Spanish and Ten days campaign, Belgian liberals in 1831. The French later inflicted a defeat on the Habsburgs in the Austro-Sardinian War, Franco-Austrian War of 1859, a victory which led to the Second Italian War of Independence, unification of Italy in 1861, after having triumphed over Russia with other allies in the Crimean War 1854–56. Detrimentally, however, the French army emerged from these victories in an overconfident and complacent state. France's defeat in the Franco-Prussian War led to the loss of Alsace-Lorraine and the creation of a united German Empire, both results representing major failures in long-term French foreign policy and sparking a vengeful, nationalist revanchism meant to earn back former territories. The Dreyfus Affair, however, mitigated these nationalist tendencies by prompting public skepticism about the competence of the military.
First World War
 In World War I, the French, with Triple Entente, their allies, managed to hold the Western Front (World War I), Western front and to Balkans Campaign (World War I), counterattack on the Eastern front and West Africa Campaign (World War I), in the colonies until the final defeat of the Central Powers and their allies. After major conflicts such as the Battle of the Frontiers, the First Battle of the Marne, the Battle of Verdun, and the Second Battle of the Aisne—the last resulting in tremendous loss of life and mutiny within the army—the French proved to be enough of a cohesive fighting force to counterattack and defeat the Germans at the Second Battle of the Marne, the first in what would become a string of Hundred Days Offensive, Allied victories that ended the war. The Treaty of Versailles eventually returned Alsace-Lorraine to France. The French military, civilian and Zone rouge, material losses during the First World War were huge. With more than 1.3 million military fatalities and more than 4.6 million wounded, France suffered the second highest Allied losses, after Russia. As a result, France was adamant on the payment of reparations by Germany. The organised failure of the Weimar Republic to pay reparations led to the Occupation of the Ruhr by French and Belgian forces.
In World War I, the French, with Triple Entente, their allies, managed to hold the Western Front (World War I), Western front and to Balkans Campaign (World War I), counterattack on the Eastern front and West Africa Campaign (World War I), in the colonies until the final defeat of the Central Powers and their allies. After major conflicts such as the Battle of the Frontiers, the First Battle of the Marne, the Battle of Verdun, and the Second Battle of the Aisne—the last resulting in tremendous loss of life and mutiny within the army—the French proved to be enough of a cohesive fighting force to counterattack and defeat the Germans at the Second Battle of the Marne, the first in what would become a string of Hundred Days Offensive, Allied victories that ended the war. The Treaty of Versailles eventually returned Alsace-Lorraine to France. The French military, civilian and Zone rouge, material losses during the First World War were huge. With more than 1.3 million military fatalities and more than 4.6 million wounded, France suffered the second highest Allied losses, after Russia. As a result, France was adamant on the payment of reparations by Germany. The organised failure of the Weimar Republic to pay reparations led to the Occupation of the Ruhr by French and Belgian forces.
Second World War
 A variety of factors—ranging from smaller industrial base to low population growth and obsolete military doctrines—crippled the French effort at the outset of
A variety of factors—ranging from smaller industrial base to low population growth and obsolete military doctrines—crippled the French effort at the outset of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The Germans won the Battle of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Rep ...
in 1940 despite the French often having better planes and tanks than their opponents whereas they were lacking modern weaponry for the infantry, the main problem although was the unexistant doctrine to synchronize the tanks alongside the plane, as tanks were not used as a primary force but rather as support for infantry, without planning an anti-air protection for them. their use as primary force were made in very rare occasion, when commanded by Charles de Gaulle for example, only a tank crew division commander by the time of 1940.
Prior to the Battle of France, there were sentiments among many Allied soldiers, French and British, of pointless repetition; they viewed the war with dread since they had already beaten the Germans once, and images of that first major conflict were still poignant in military circles. The costs of World War I along with the now stale doctrine employed by the French Army (while the Germans were developing a doctrine which stressed initiative from junior commanders and combining different arms, the French sought to minimize casualties through a rigorously controlled type of battle and a top down command structure) forced the French to look for more defensive measures. The Maginot Line was the result of these deliberations: the French originally allocated three billion francs for the project, but by 1935 seven billion had been spent. The Maginot Line succeeded in holding off the German attack. However, while the French thought that the main weight of the German attack would arrive through central Belgium, and accordingly deployed their forces here, the assault Manstein Plan, actually came further south in the Ardennes forest. The Third French Republic, Third Republic collapsed in the ensuing conflict.
 After the defeat, Vichy France cooperated with the Axis powers until 1944. Charles de Gaulle Appeal of 18 June, exhorted the French people to join the allied armies, while the French Vichy forces participated in direct action against Allied forces, inflicting casualties in some cases.
The Normandy Landings, Normandy landings in that year were the first step towards the eventual Northern France Campaign (1944), liberation of France. The
After the defeat, Vichy France cooperated with the Axis powers until 1944. Charles de Gaulle Appeal of 18 June, exhorted the French people to join the allied armies, while the French Vichy forces participated in direct action against Allied forces, inflicting casualties in some cases.
The Normandy Landings, Normandy landings in that year were the first step towards the eventual Northern France Campaign (1944), liberation of France. The Free French Forces
__NOTOC__
The French Liberation Army (french: Armée française de la Libération or AFL) was the reunified French Army that arose from the merging of the Armée d'Afrique with the prior Free French Forces (french: Forces françaises libres, l ...
, under de Gaulle, had participated widely throughout previous campaigns, and their large size made them notable at the end of the war. As early as the winter of 1943, the Free French already had nearly 260,000 soldiers, and these numbers only grew as the war progressed. The French Resistance had also a significant contribution, participating also actively in the liberation of France. At the end of the war, France was given one of four Allied-occupied Germany, occupation zones in Germany, in West Berlin, Berlin and Allied-occupied Austria, Austria.
Post-1945 warfare
 Following the 1939–45 war, decolonization spread through the former European empires.
Following the First Indochina War, they withdrew from Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia. The military also tried to keep control of Algeria during the Algerian War, when French forces attempted to defeat the Algerian rebels. Despite its military victory, France granted 1962 French Évian Accords referendum, independence to Algerians. French Algeria was home to over a million of settlers (known as Pieds-Noirs), de Gaulle's decision to grant independence to Algeria, almost led to a civil war, supported by various Pied-Noir, Harki and nationalist factions, including the Front Algérie Française, FAF and the Organisation de l'armée secrète, OAS. Related to and during the Algerian war France participated in the Suez Crisis with Israel and the UK.
By 1960 France had lost its direct military influence over all of its former colonies in Africa and Indochina. Nonetheless, several colonies in the Pacific, Caribbean, Indian Oceans and South America remain French territory to this day and France kept a form of indirect political influence in Africa colloquially known as the ''Françafrique''.
As President of the French Republic, Charles de Gaulle oversaw the development of Force de Frappe, French atomic weapons and promoted a foreign policy independent of U.S. influence. He also withdrew France from the
Following the 1939–45 war, decolonization spread through the former European empires.
Following the First Indochina War, they withdrew from Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia. The military also tried to keep control of Algeria during the Algerian War, when French forces attempted to defeat the Algerian rebels. Despite its military victory, France granted 1962 French Évian Accords referendum, independence to Algerians. French Algeria was home to over a million of settlers (known as Pieds-Noirs), de Gaulle's decision to grant independence to Algeria, almost led to a civil war, supported by various Pied-Noir, Harki and nationalist factions, including the Front Algérie Française, FAF and the Organisation de l'armée secrète, OAS. Related to and during the Algerian war France participated in the Suez Crisis with Israel and the UK.
By 1960 France had lost its direct military influence over all of its former colonies in Africa and Indochina. Nonetheless, several colonies in the Pacific, Caribbean, Indian Oceans and South America remain French territory to this day and France kept a form of indirect political influence in Africa colloquially known as the ''Françafrique''.
As President of the French Republic, Charles de Gaulle oversaw the development of Force de Frappe, French atomic weapons and promoted a foreign policy independent of U.S. influence. He also withdrew France from the NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
military command in 1966—although remaining a member of the western alliance. The effect of withdrawal was reduced by continued cooperation between the French military and NATO, though France did not formally rejoin the NATO military command until 2009.
France intervened in various post-colonial conflicts, supporting former colonies (Western Sahara War, Shaba II, Chadian–Libyan conflict, Djiboutian Civil War), NATO peacekeeping missions in war-torn countries (United Nations Protection Force, UNPROFOR, Kosovo Force, KFOR, United Nations Assistance Mission for Rwanda, UNAMIR) and many Humanitarian aid, humanitarian missions.
As a nuclear power and having some of the best trained and best equipped forces in the world, the French military has now met some of its primary objectives which are the defense of national territory, the protection of French interests abroad, and the maintenance of global stability. Conflicts indicative of these objectives are the Gulf War in 1991—when France sent 18,000 troops, 60 combat aircraft, 120 helicopters, and 40 tanks—and Mission Héraclès in the War in Afghanistan (2001–present), War in Afghanistan, along with recent interventions in Africa.
African interventions during the early 21st century include Civil war in Côte d'Ivoire, peacekeeping actions in Côte d'Ivoire, which involved Ivorian-French War, brief direct fighting between the French and Ivorian armies in 2004; French forces returned to Côte d'Ivoire in 2011 to Second Ivorian Civil War, remove the Ivorian president. In the same year, France played a pivotal role in the 2011 military intervention in Libya against Muammar Gaddafi. The year after, France intervened in Mali during that country's Northern Mali conflict (2012–present), civil war, as Islamism, Islamist militants appeared to threaten the south after seizing control of the arid Azawad, north. Changes in the government of France, including Socialist Party (France), Socialist François Hollande 2012 French presidential election, becoming president in 2012 after years of center-right governance, have done little to alter Paris' foreign policy in Africa.
Hollande also proposed French military involvement in the Syrian civil war in the wake of 2013 Ghouta attacks, chemical attacks French intelligence reports linked to the forces of President Bashar al-Assad in mid-2013.
France has encouraged military cooperation at an EU level, starting with the formation of the Franco-German Brigade in 1987 and Eurocorps in 1992, based in Strasbourg. In 2009 a battalion of German light infantry was moved to Alsace, the first time German troops had been stationed in France since the Nazi occupation of World War II. This process has not been immune to budget cuts—in October 2013 France announced the closure of her last infantry regiment in Germany, thus marking the end of a major presence across the Rhine although both countries will maintain around 500 troops on each other's territory. As fellow members of the UN Security Council with many interests and problems in common, the UK and France have a long history of bilateral collaboration. This has occurred both at government level and in industrial programmes like the SEPECAT Jaguar whilst corporate mergers have seen Thales and MBDA emerge as major defence companies spanning both countries. The financial crisis of 2007–08 led to renewed pressure on military budgets and the "austerity alliance" enshrined in the Lancaster House Treaties (2010), the Lancaster House Treaties of 2010. These promised close integration in both procurement and at an operational level, reaching into the most sensitive areas such as nuclear warheads.
Topical subjects
French Air and Space Force
French Navy
 Medieval fleets, in France as elsewhere, were almost entirely composed of merchant ships enlisted into naval service in time of war, but the early beginnings of the French naval history goes back to that era. The first battle of the French Navy was the battle of Arnemuiden (23 September 1338), where it defeated the English Navy. The battle of Arnemuiden was also the first naval battle using artillery.Jean-Claude Castex
Medieval fleets, in France as elsewhere, were almost entirely composed of merchant ships enlisted into naval service in time of war, but the early beginnings of the French naval history goes back to that era. The first battle of the French Navy was the battle of Arnemuiden (23 September 1338), where it defeated the English Navy. The battle of Arnemuiden was also the first naval battle using artillery.Jean-Claude Castex''Dictionnaire des batailles navales franco-anglaises''
Presses de l'Université Laval, 2004, p.21 It was later defeated by an Anglo-Flemish fleet at the Battle of Sluys and, with Crown of Castile, Castilian help, managed to beat the English at Battle of La Rochelle, La Rochelle—both battles playing a crucial role in the development of the Hundred Years War. However, the navy did not become a consistent instrument of national power until the 17th century with Louis XIV. Under the tutelage of the "Sun King," the French Navy was well financed and equipped, managing to resoundingly defeat a combined Spanish-Dutch fleet at the Battle of Palermo in 1676 during the Franco-Dutch War, although, along with the English navy, it suffered several strategic reversals against the Dutch, who were led by the brilliant Michiel de Ruyter. It scored several early victories in the Nine Years War against the Royal Navy and the Royal Netherlands Navy, Dutch Navy. Financial difficulties, however, allowed the English and the Dutch to regain the initiative at sea. A perennial problem for the French Navy was the strategic priorities of France, which were first and foremost tied to its European ambitions. This reality meant that the army was often treated better than the navy, and as a result, the latter suffered in training and operational performance. The 18th century saw the beginning of the Royal Navy's domination, which managed to inflict a number of significant defeats on the French. However, in a very impressive effort, a French fleet under François Joseph Paul, marquis de Grasetilly, comte de Grasse, de Grasse managed to defeat a British fleet at the Battle of the Chesapeake in 1781, ensuring that the Franco-American ground forces would win the ongoing Siege of Yorktown. Beyond that, and Pierre André de Suffren de Saint Tropez, Suffren's Naval operations in the American Revolutionary War#East Indies campaign, 1778–1783, impressive campaigns against the British in India, there was not much more good news. The French Revolution all but crippled the French Navy, and efforts to make it into a powerful force under Napoleon were dashed at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, where the British all but annihilated a combined Franco-Spanish fleet. The disaster guaranteed British naval domination until the end of the Napoleonic wars. Later in the 19th century, the navy recovered and became the second finest in the world after the Royal Navy. It conducted a successful blockade of Mexico in the Pastry War of 1838 and obliterated the Chinese navy at the Battle of Foochow in 1884. It also served as an effective link between the growing parts of the French empire. The navy performed well during World War I, in which it mainly protected the naval lanes in the Mediterranean Sea. At the onset of the war, the French had a large fleet in the Mediterranean whive no less than seven battleship & six heavy cruiser . French defeats in the early stages of World War II, however, forced the British to atatck the French fleet moored at Destruction of the French Fleet at Mers-el-Kebir, Mers-el-Kebir in order to prevent the threat she fall to the Germans, the remaining of French fleet scuttled herself at Toulon for prevent the 7th Panzer Division (Wehrmacht), 7th Panzer Division to capture the fleet, two years later . Currently, French naval doctrine calls for two aircraft carriers, but the French currently only have one, the ''French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, Charles de Gaulle'', due to restructuring. The navy is in the midst of some technological and procurement changes; newer submarines are under construction and Rafale aircraft (the naval version) are currently replacing older aircraft.
Foreign Legion
The French Foreign Legion, Foreign Legion was created in 1831 by French king Louis-Philippe of France, Louis-Philippe to allow the incorporation of foreign nationals into the French Army. Over the past century and a half, it has gone on to become one of the most recognizable and lauded military units in the world. The Legion had a very difficult start; there were few non-commissioned officers, many of the soldiers could not speak French language, French, and pay was often irregular. The Legion was soon transferred to fight in Algeria, performing moderately successfully given its condition. On August 17, 1835, the commander of the Legion, Colonel Joseph Bernelle, decided to amalgamate all the battalions so that no nationality was exclusively confined to a particular battalion; this helped ensure that the Legion did not fragment into factions. Following participation in Africa and in the Carlist Wars in Spain, the Legion fought in the Crimean War and the Franco-Austrian War, where they performed heroically at the Battle of Magenta, before earning even more glory during the Second French intervention in Mexico, French intervention in Mexico. On April 30, 1863, a company of 65 legionnaires was ambushed by 2,000 Mexican troops at the Hacienda Camarón; in the resulting Battle of Camarón, the legionnaires resisted bravely for several hours and inflicted 300–500 casualties on the Mexicans while 62 of them died and three were captured. One of the Mexican commanders, impressed by the memorable intransigence he had just witnessed, characterized the Legion in a way they've been known ever since, "These are not men, but devils!" In World War I, the Legion demonstrated that it was a highly capable unit in modern warfare. It suffered 11,000 casualties in the Western Front (World War I), Western Front while conducting brilliant defenses and spirited counter-attacks. Following the debacle in the Battle of France in 1940, the Legion was split between those who supported the Vichy government and those who joined the Free French under de Gaulle. At the Battle of Bir Hakeim in 1942, the Free French 13th Legion Demi-Brigade doggedly defended its positions against a combined Italian-German offensive and seriously delayed Rommel's attacks towards Tobruk. The Legion eventually returned to Europe and fought until the end of the Second World War in 1945. It later fought in the First Indochina War against the Viet Minh. At the climactic Battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954, French forces, many of them legionnaires, were completely surrounded by a large Vietnamese army and were defeated after two months of tenacious fighting. French withdrawal from Algeria led to the collapse of the French colonial empire. The legionnaires were mostly used in colonial interventions, so the destruction of the empire prompted questions about their status. Ultimately, the Legion was allowed to exist and participated as a rapid reaction force in many places throughout Africa and around the world.See also
*History of French foreign relations *Military of France *Military history of France during World War II *Norman conquest of England, Norman Conquest of England *Marshal of France, Marshals of France *List of notable French military leaders *List of French wars and battles *Deployments of the French military *List of battles involving France *Social background of officers and other ranks in the French Army, 1750–1815Notes
Works cited
*Aloni, Shlomo. ''Israeli Mirage and Nesher Aces''. Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2004. *Jeremy Black (historian), Black, Jeremy. ''Cambridge illustrated atlas of warfare: Renaissance to revolution, 1492-1792''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996. *Blanning, T.C.W. ''The French Revolutionary Wars''. London: Hodder Headline Group, 1996. *Boyce, Robert. ''French Foreign and Defence Policy, 1918-1940''. Oxford: CRC Press, 1998. *Bradbury, Jim. ''The Routledge companion to medieval warfare''. New York: Routledge, 2004. *Bradford, Alfred and Pamela. ''With arrow, sword, and spear: a history of warfare in the ancient world''. Westport: Greenwood Publishing Group, 2001. *Brooks, Richard (editor). ''Atlas of World Military History''. London: HarperCollins, 2000. *Chandler, David G. ''The Campaigns of Napoleon''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1995. *Chilton, Patricia and Howorth, Jolyon Howorth. ''Defence and dissent in contemporary France'' Oxford: Taylor & Francis, 1984. *Dupuy, Trevor N., ''Harper Encyclopedia of Military History''. New York: HarperCollins, 1993. *Elting, John R. ''Swords Around a Throne: Napoleon's Grande Armée''. New York: Da Capo Press Inc., 1988. *Eltis, David. ''The military revolution in sixteenth-century Europe''. New York: I. B. Tauris, 1998. *Farwell, Byron. ''The encyclopedia of nineteenth-century land warfare''. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2001. *Fisher, Todd & Fremont-Barnes, Gregory. ''The Napoleonic Wars: The Rise and Fall of an Empire''. Oxford: Osprey Publishing Ltd., 2004. *de la Gorce, Paul Marie. ''The French Army: A Military-Political History''. New York: George Braziller, Inc., 1963. *Hauss, Charles. ''Politics in France''. Washington, DC: CQ Press, 2007. *Jordan, David. ''The History of the French Foreign Legion''. Spellmount Limited, 2005. *Jotischky, Andrew. ''Crusading and the Crusader States''. Pearson Education Limited, 2004. *Karpat, Kemal. ''The Ottoman state and its place in world history''. Leiden: BRILL, 1974. *Kay, Sean. ''NATO and the future of European security''. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield, 1998. *John Keegan, Keegan, John. ''The Second World War''. New York: Penguin Group, 1989. *Kottak, Conrad. ''Cultural Anthropology''. Columbus: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2005. *Kurtz, Lester and Turpin, Jennifer. ''Encyclopedia of violence, peace and conflict, Volume 2.'' New York: Academic Press, 1999. *Lyons, Martyn. ''Napoleon Bonaparte and the Legacy of the French Revolution''. New York: St. Martin's Press, Inc., 1994. *Lynn, John A. ''Giant of the Grand Siècle: The French Army, 1610–1715''. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1997. *Lynn, John A. ''The Wars of Louis XIV''. London: Longman, 1999. *Ostwald, Jamel. ''Vauban under siege''. Leiden: BRILL, 2007. *Paret, Peter. ''Clausewitz and the State''. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2007. *Parker, Geoffrey. ''The Cambridge history of warfare''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005. *John Roberts (historian), Roberts, J.M. ''History of the World''. New York: Penguin Group, 1992. *Roosen, William. ''The age of Louis XIV: the rise of modern diplomacy''. Edison: Transaction Publishers, 1976. *Spielvogel, Jackson. ''Western Civilization: Since 1500''. Florence: Cengage Learning, 2008. *Hew Strachan, Strachan, Hew. ''The Oxford Illustrated History of the First World War''. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998. *Thompson, William. ''Great power rivalries''. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press, 1999. *Barbara Tuchman, Tuchman W., Barbara. ''The Guns of August''. New York: Random House, 1962. *Weigley, Russell. ''The age of battles: the quest for decisive warfare from Breitenfeld to Waterloo''. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2004. *Willis, F. Roy. ''France, Germany, and the New Europe, 1945-1967''. Palo Alto: Stanford University Press, 1968. *Wood, James. ''The King's Army''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002.Further reading
* Blaufarb, Rafe. ''The French army 1750–1820: Careers, talent, merit'' (Manchester University Press, 2021). * Clayton, Anthony. Paths of glory: the French Army 1914–18. London: Cassell, 2003. *Robert Cowley, Cowley, Robert (editor). ''What If? Eminent Historians Imagine What Might Have Been''. New York: Penguin Group, 1999. * Robert A. Doughty, Doughty, Robert A. ''Pyrrhic Victory: French Strategy and Operations in the Great War'' (2008), 592ppexcerpt and text search
* Forrest, Alan. ''Conscripts and Deserters: The Army and French Society During the Revolution and Empire'' (1989) * Forrest, Alan. ''Napoleon's Men: The Soldiers of the Revolution and Empire'' (2002) * Greenhalgh, Elizabeth. ''The French Army and the First World War'' (2014), 486 pages; comprehensive scholarly history. * Holroyd, Richard. "The Bourbon Army, 1815-1830." ''Historical Journal'' 14, no. 3 (1971): 529–52
online
*Kinard, Jeff. ''Artillery: an illustrated history of its impact''. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, 2007. * Nolan, Cathal. ''Wars of the Age of Louis XIV, 1650-1715: An Encyclopedia of Global Warfare and Civilization'' (2008) * Nolan, Cathal. ''The Age of Wars of Religion, 1000-1650'' (2 vol. 2006) * Pichichero, Christy. ''The Military Enlightenment: War and Culture in the French Empire from Louis XIV to Napoleon'' (2018
online review
* Porch, Douglas. "The French Army Law of 1832." ''Historical Journal'' 14, no. 4 (1971): 751–69
online
* Porch, Douglas. ''The March to the Marne: The French Army 1871-1914'' Cambridge University Press (2003) * Scott, Samuel F. ''From Yorktown to Valmy: the transformation of the French Army in an age of revolution'' (University Press of Colorado, 1998) * Thoral, Marie-Cécile. ''From Valmy to Waterloo: France at War, 1792–1815'' (Palgrave Macmillan UK, 2011)
Historiography and memory
* Forrest, Alan. ''The Legacy of the French Revolutionary Wars: The Nation-in-Arms in French Republican Memory'' (Cambridge University Press, 2009) * Messenger, Charles, ed. ''Reader's Guide to Military History'' (2001) 948pp; Evaluation of thousands of books on military history, many of them involving France.In French
* Bertaud, Jean-Paul, and William Serman. ''Nouvelle histoire militaire de la France, 1789-1919'' (Paris, Fayard: 1998); 855ppExternal links
Illustrations by Hippolyte Bellangé from the book P.-M. Laurent de L`Ardeche «Histoire de Napoleon», 1843
The French Military in Africa
(2008) - Council on Foreign Relations {{DEFAULTSORT:Military History Of France Military history of France,