Flag Of Chicago on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The flag of Chicago consists of two light blue horizontal bars, or stripes, on a
 There are four red
There are four red 

 * A fifth star could represent Chicago's contribution to the nuclear age (see
* A fifth star could represent Chicago's contribution to the nuclear age (see
File:Flag of NAVA Meeting 31.svg, The flag of NAVA Meeting 31, hosted in Chicago. NAVA meeting flags often incorporate elements to reflect the host city.
File:Sketches tribuneoct11892.jpg, Sketches for the flag from a contest from 1892. This design ultimately became used in the municipal device.
File:Departmenticons july171921.jpg, Twenty-three other icons that were commissioned representing different city departments could be placed on the flag for that department.
File:1917flag.jpg, Chicago flag of 1917 poster, with "I Will" motto
NAVA city flag survey
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chicago, Illinois, Flag of
field
Field may refer to:
Expanses of open ground
* Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes
* Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport
* Battlefield
* Lawn, an area of mowed grass
* Meadow, a grass ...
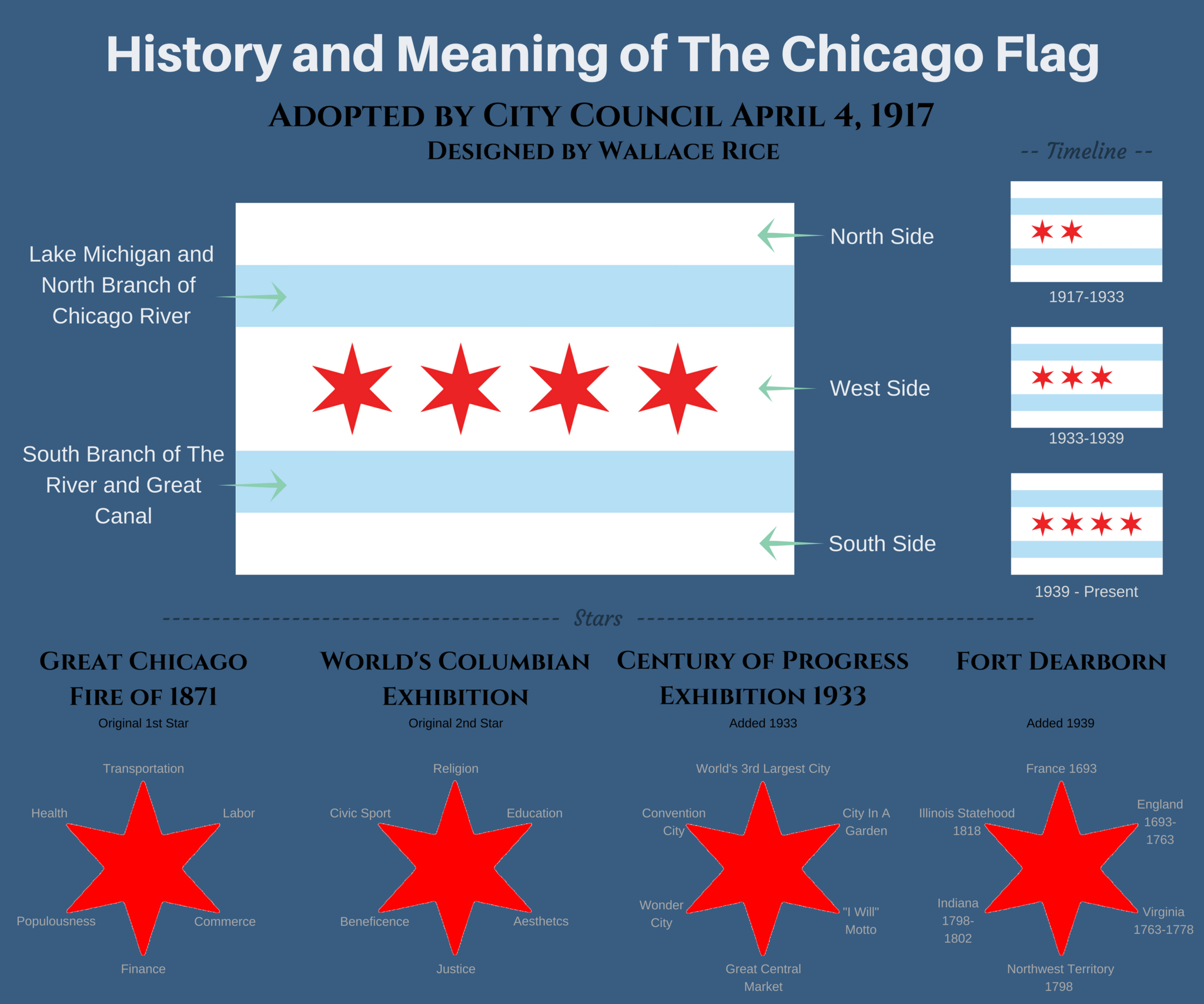
of white, each bar one-sixth the height of the full flag, and placed slightly less than one-sixth of the way from the top and bottom. Four bright red stars, with six sharp points each, are set side by side, close together, in the middle third of the flag's surface.
The City of Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
's flag was adopted in 1917 after the design by Wallace Rice
Wallace deGroot Cecil Rice (10 November 1859 – 15 December 1939) was an American author and vexillographer from Hamilton, Ontario.
Biography
Wallace Rice was born 10 November 1859, to John Asaph Rice (1829–1888) and Margaret Van Slyke ...
won a City Council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counc ...
sponsored competition. It initially had two stars until 1933, when a third was added. The four-star version has existed since 1939. The three sections of the white field and the two bars represent the geographical features of the city, the stars symbolize historical events, and the points of the stars represent important virtues or concepts. The historic events represented by the stars are the establishment of Fort Dearborn
Fort Dearborn was a United States fort built in 1803 beside the Chicago River, in what is now Chicago, Illinois. It was constructed by troops under Captain John Whistler and named in honor of Henry Dearborn, then United States Secretary of War. ...
, the Great Chicago Fire of 1871
The Great Chicago Fire was a conflagration that burned in the American city of Chicago during October 8–10, 1871. The fire killed approximately 300 people, destroyed roughly of the city including over 17,000 structures, and left more than 10 ...
, the World's Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition (also known as the Chicago World's Fair) was a world's fair held in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordi ...
of 1893, and the Century of Progress Exposition
A Century of Progress International Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, from 1933 to 1934. The fair, registered under the Bureau International des Expositi ...
of 1933–34.
In a review by the North American Vexillological Association
The North American Vexillological Association (NAVA) is a membership organization devoted to vexillology, the scientific and scholarly study of flags. It was founded in 1967 by American vexillologist Whitney Smith (1940–2016), and others. It ...
of 150 American city flags, the Chicago city flag was ranked second-best with a rating of 9.03 out of 10, behind only the flag of Washington, D.C.
The flag of Washington, D.C., consists of three red stars above two red bars on a white background. It is an armorial banner based on the design of the coat of arms granted to George Washington's great-great-great-grandfather, Lawrence Washing ...
Symbolism

Bars
The three white background areas of the flag represent, from top to bottom, the North,West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic languages, German ...
, and South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
sides of the city. The top blue bar represents Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
and the North Branch of the Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons for ...
. The bottom blue bar represents the South Branch of the river and the " Great Canal", over the Chicago Portage
The Chicago Portage was an ancient portage that connected the Great Lakes waterway system with the Mississippi River system. Connecting these two great water trails meant comparatively easy access from the mouth of the St Lawrence River on the At ...
. The light blue of the flag's two bars is variously called sky blue
Sky blue is a shade of light blue comparable to that of a clear daytime sky. The term (as "sky blew") is attested from 1681. A 1585 translation of Nicolas de Nicolay's 1576 ''Les navigations, peregrinations et voyages faicts en la Turquie'' in ...
or pale blue; in a 1917 article of a speech by designer, Wallace Rice, it was called "the color of water".
Stars
 There are four red
There are four red six-pointed star
Star polygons and polygonal compounds are the basis for numerous figures of significance in arts and culture. The figure may be the border or interior of the polygon, or one or more closed polygonal paths that include all of the border and als ...
s on the center white bar. Six-pointed stars are used because five-pointed star
A five-pointed star (☆), geometrically an equilateral concave decagon, is a common ideogram in modern culture.
Comparatively rare in classical heraldry, it was notably introduced for the flag of the United States in the Flag Act of 1777 and ...
s represent sovereign states and because the star as designed was found on no other known flags as of 1917. From the hoist outwards, the stars represent:
* Added in 1939: Commemorates Fort Dearborn
Fort Dearborn was a United States fort built in 1803 beside the Chicago River, in what is now Chicago, Illinois. It was constructed by troops under Captain John Whistler and named in honor of Henry Dearborn, then United States Secretary of War. ...
, and its six points stand for political entities the Chicago region has belonged to and the flags that have flown over the area: France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, 1693; Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, 1763; Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, 1778; the Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1 ...
, 1789; Indiana Territory
The Indiana Territory, officially the Territory of Indiana, was created by a United States Congress, congressional act that President of the United States, President John Adams signed into law on May 7, 1800, to form an Historic regions of the U ...
, 1802; and Illinois (territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
, 1809, and state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
, since 1818).
* Original to the 1917 flag: This star stands for the Great Chicago Fire
The Great Chicago Fire was a conflagration that burned in the American city of Chicago during October 8–10, 1871. The fire killed approximately 300 people, destroyed roughly of the city including over 17,000 structures, and left more than 10 ...
of 1871. Its six points represent the virtues of religion, education, aesthetics, justice, beneficence, and civic pride.
* Original to the 1917 flag: This star symbolizes the World's Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition (also known as the Chicago World's Fair) was a world's fair held in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordi ...
of 1893. Its six points symbolize transportation, labor, commerce, finance, populousness, and salubrity (health).
* Added in 1933: This star represents the Century of Progress
A Century of Progress International Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, from 1933 to 1934. The fair, registered under the Bureau International des Expositi ...
Exposition (1933–34). Its points refer to: Chicago's status as the United States' second largest city at the time of the star's addition (Chicago became third largest in a 1990 census when passed by Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
); Chicago's Latin motto, ' ("City in a garden"); Chicago's "I Will" motto; the Great Central Marketplace; Wonder City; and Convention City.
Additional stars have been proposed, with varying degrees of seriousness. The following reasons have been suggested for possible additions of a fifth star:


 * A fifth star could represent Chicago's contribution to the nuclear age (see
* A fifth star could represent Chicago's contribution to the nuclear age (see Metallurgical Laboratory
The Metallurgical Laboratory (or Met Lab) was a scientific laboratory at the University of Chicago that was established in February 1942 to study and use the newly discovered chemical element plutonium. It researched plutonium's chemistry and m ...
), an idea first suggested in a 1940s letter published by the ''Chicago Tribune
The ''Chicago Tribune'' is a daily newspaper based in Chicago, Illinois, United States, owned by Tribune Publishing. Founded in 1847, and formerly self-styled as the "World's Greatest Newspaper" (a slogan for which WGN radio and television ar ...
'' and later championed by Mayor Daley in the 1960s.
* In the 1980s, a star was proposed in honor of Harold Washington
Harold Lee Washington (April 15, 1922 – November 25, 1987) was an American lawyer and politician who was the 51st Mayor of Chicago. Washington became the first African American to be elected as the city's mayor in April 1983. He served as ma ...
, the first African-American mayor of Chicago.
* The 1992 Chicago Flood was suggested as an additional natural disaster deserving of a star, in line with the existing star for the 1871 Great Chicago Fire. Another fifth star was in the works from a group of Chicago real estate professionals to represent Chicago's entrepreneurial spirit in the early 1990s.
* When Chicago was bidding to host the 2016 Summer Olympics
The 2016 Summer Olympics ( pt, Jogos Olímpicos de Verão de 2016), officially the Games of the XXXI Olympiad ( pt, Jogos da XXXI Olimpíada) and also known as Rio 2016, was an international multi-sport event held from 5 to 21 August 20 ...
, the Bid Committee proposed that a fifth star be added to the flag in commemoration, but the bid was won instead by Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
.
* Anne Burke, Tim Shriver, and others have proposed adding a fifth star to commemorate the Special Olympics
Special Olympics is the world's largest sports organization for children and adults with intellectual disabilities and physical disabilities, providing year-round training and activities to 5 million participants and Unified Sports partners in 1 ...
, which were founded in Chicago.
* Other sports-related suggestions include recognizing the Chicago Bulls
The Chicago Bulls are an American professional basketball team based in Chicago. The Bulls compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the league's Eastern Conference Central Division. The team was founded on January 1 ...
' dominance of the NBA
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is a professional basketball league in North America. The league is composed of 30 teams (29 in the United States and 1 in Canada) and is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United St ...
in the 1990s and a proposal for a fifth star if the Chicago Cubs
The Chicago Cubs are an American professional baseball team based in Chicago. The Cubs compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as part of the National League (NL) Central division. The club plays its home games at Wrigley Field, which is located ...
should ever win the World Series
The World Series is the annual championship series of Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, contested since 1903 between the champion teams of the American League (AL) and the National League (NL). The winner of the World ...
, which did not happen between their long drought of series wins in 1908, up to 2016
File:2016 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Bombed-out buildings in Ankara following the 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt; the impeachment trial of Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff; Damaged houses during the 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh ...
.
* The Chicago History Museum
Chicago History Museum is the museum of the Chicago Historical Society (CHS). The CHS was founded in 1856 to study and interpret Chicago's history. The museum has been located in Lincoln Park since the 1930s at 1601 North Clark Street at the in ...
has an ongoing exhibition where the public is encouraged to vote for a potential fifth star.
* Chicago Mayor Lori Lightfoot
Lori Elaine Lightfoot (born August 4, 1962) is an American attorney and politician serving since 2019 as the 56th mayor of Chicago. She is a member of the Democratic Party. Before becoming mayor, Lightfoot worked in private legal practice as ...
suggested that Chicago's response to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
could warrant adding a fifth star to Chicago's flag.
Unlawful private use
Per theMunicipal Code of Chicago The ''Municipal Code of Chicago'' is the codification of local ordinances of a general and permanent nature of the City of Chicago. The Code contains original and new ordinances, adopted by the Chicago City Council, organized into eighteen titles ...
, it is unlawful to use the flag, or any imitation or design thereof, except for the usual and customary purposes of decoration or display. Causing to be displayed on the flag, any letter, word, legend, or device not provided for in the Code is also prohibited. Violators are subject to fines between $5.00 and $25.00 for each offense. However, the First Amendment to the United States Constitution
The First Amendment (Amendment I) to the United States Constitution prevents the government from making laws that regulate an establishment of religion, or that prohibit the free exercise of religion, or abridge the freedom of speech, the ...
prohibits this section from being enforced ( U.S. v. Eichman).
History
In 1915, MayorWilliam Hale Thompson
William Hale Thompson (May 14, 1869 – March 19, 1944) was an American politician who served as mayor of Chicago from 1915 to 1923 and again from 1927 to 1931. Known as "Big Bill", Reynolds, Paul (November 29, 2009)"US-UK 'Special Relationshi ...
appointed a municipal flag commission chaired by Alderman James A. Kearnes. Among the commission members were wealthy industrialist Charles Deering
Charles Deering (July 31, 1852 – February 5, 1927) was an American businessman, art collector, and philanthropist. He was an executive of the agricultural machinery company founded by his father that became International Harvester. Charles's s ...
and impressionist painter Lawton S. Parker
Lawton S. Parker (7 April 1868 – 1954) was an American impressionist Painting, painter.
Biography
Born in Fairfield, Michigan, raised in Kearney, Nebraska, Parker studied at the Art Institute of Chicago beginning in 1886. He traveled to Fran ...
. Parker asked lecturer and poet Wallace Rice
Wallace deGroot Cecil Rice (10 November 1859 – 15 December 1939) was an American author and vexillographer from Hamilton, Ontario.
Biography
Wallace Rice was born 10 November 1859, to John Asaph Rice (1829–1888) and Margaret Van Slyke ...
to develop the rules for an open public competition for the best flag design. Over a thousand entries were received. The 318th Cavalry Regiment (United States) incorporated the flag into their insignia.
References
Further reading
* "Art and Architecture: How the Chicago Municipal Flag Came to be Chosen", ''Chicago Daily Tribune
The ''Chicago Tribune'' is a daily newspaper based in Chicago, Illinois, United States, owned by Tribune Publishing. Founded in 1847, and formerly self-styled as the "World's Greatest Newspaper" (a slogan for which WGN radio and television are ...
'', July 17, 1921, p. 21.
* "City Gets New Flag Today with Third Star for 1933 Fair", ''Chicago Daily Tribune
The ''Chicago Tribune'' is a daily newspaper based in Chicago, Illinois, United States, owned by Tribune Publishing. Founded in 1847, and formerly self-styled as the "World's Greatest Newspaper" (a slogan for which WGN radio and television are ...
'', October 9, 1933, p. 7.
* "Fort Dearborn Gets a Star on Chicago's Flag", ''Chicago Daily Tribune
The ''Chicago Tribune'' is a daily newspaper based in Chicago, Illinois, United States, owned by Tribune Publishing. Founded in 1847, and formerly self-styled as the "World's Greatest Newspaper" (a slogan for which WGN radio and television are ...
'', December 22, 1939. p. 18.
External links
NAVA city flag survey
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chicago, Illinois, Flag of
Flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design empl ...
Flags of cities in Illinois
Flags introduced in 1917
1917 establishments in Illinois