Fuzzy Cognitive Map on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A fuzzy cognitive map (FCM) is a
A fuzzy cognitive map (FCM) is a
Lethal American Confusion
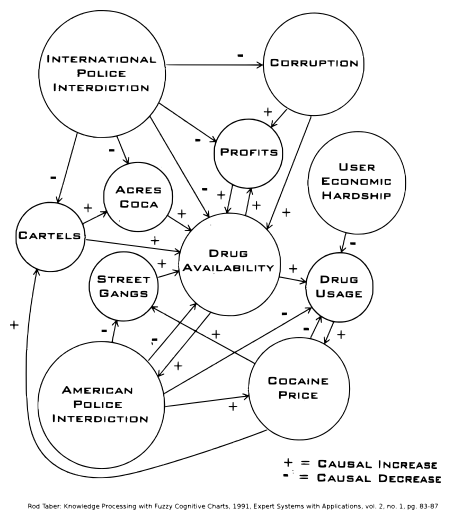
(How Bush and the Pacifists Each Failed in the War on Terrorism)'', 2006, (FCM application in chapter 14) of William R. Taylor, where the war in Afghanistan and Iraq is analyzed. In Bart Kosko's book ''Fuzzy Thinking'',Bart Kosko: ''Fuzzy Thinking'', 1993/1995, (Chapter 12: Adaptive Fuzzy Systems)'' several Hasse diagrams illustrate the use of FCMs. As an example, one FCM quoted from Rod TaberRod Taber: ''Knowledge Processing with Fuzzy Cognitive Maps'', Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 2, no. 1, 83-87, 1991 ( Hasse diagram in German Wikipedia) describes 11 factors of the American cocaine market and the relations between these factors. For computations, Taylor uses pentavalent logic (scalar values out of ). That particular map of Taber uses
 A fuzzy cognitive map (FCM) is a
A fuzzy cognitive map (FCM) is a cognitive map
A cognitive map is a type of mental representation which serves an individual to acquire, code, store, recall, and decode information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in their everyday or metaphorical spatial environment. ...
within which the relations between the elements (e.g. concepts, events, project resources) of a "mental landscape" can be used to compute the "strength of impact" of these elements. Fuzzy cognitive maps were introduced by Bart Kosko. Robert Axelrod introduced cognitive maps as a formal way of representing social scientific knowledge and modeling decision making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either ra ...
in social and political systems, then brought in the computation.
Details
Fuzzy cognitive maps are signed fuzzy digraphs. They are visually similar to, but distinct from, Hasse diagrams.Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in ce ...
s or tables are used to map FCMs into matrices for further computation.
FCM is a technique used for causal knowledge acquisition and representation, it supports causal knowledge reasoning process and belong to the neuro-fuzzy
In the field of artificial intelligence, neuro-fuzzy refers to combinations of artificial neural networks and fuzzy logic.
Overview
Neuro-fuzzy hybridization results in a hybrid intelligent system that these two techniques by combining the human ...
system that aim at solving decision making problems, modeling and simulate complex system
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communicatio ...
s.
Learning algorithms have been proposed for training and updating FCMs weights mostly based on ideas coming from the field of Artificial Neural Network
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains.
An ANN is based on a collection of connected units ...
s. Adaptation and learning methodologies used to adapt the FCM model and adjust its weights. Kosko and Dickerson (Dickerson & Kosko, 1994) suggested the Differential Hebbian Learning
Hebbian theory is a neuroscientific theory claiming that an increase in synaptic efficacy arises from a presynaptic cell's repeated and persistent stimulation of a postsynaptic cell. It is an attempt to explain synaptic plasticity, the adaptatio ...
(DHL) to train FCM. There have been proposed algorithms based on the initial Hebbian algorithm; others algorithms come from the field of genetic algorithms
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to gene ...
, swarm intelligence
Swarm intelligence (SI) is the collective behavior of decentralized, self-organized systems, natural or artificial. The concept is employed in work on artificial intelligence. The expression was introduced by Gerardo Beni and Jing Wang in 1989, ...
and evolutionary computation
In computer science, evolutionary computation is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the subfield of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms. In technical terms, ...
. Learning algorithms are used to overcome the shortcomings that the traditional FCM present i.e. decreasing the human intervention by suggested automated FCM candidates; or by activating only the most relevant concepts every execution time; or by making models more transparent and dynamic.
Fuzzy cognitive maps (FCMs) have gained considerable research interest due to their ability in representing structured knowledge and model complex systems in various fields. This growing interest led to the need for enhancement and making more reliable models that can better represent real situations.
A first simple application of FCMs is described in a bookWilliam R. Taylor: Lethal American Confusion
(How Bush and the Pacifists Each Failed in the War on Terrorism)'', 2006, (FCM application in chapter 14) of William R. Taylor, where the war in Afghanistan and Iraq is analyzed. In Bart Kosko's book ''Fuzzy Thinking'',Bart Kosko: ''Fuzzy Thinking'', 1993/1995, (Chapter 12: Adaptive Fuzzy Systems)'' several Hasse diagrams illustrate the use of FCMs. As an example, one FCM quoted from Rod TaberRod Taber: ''Knowledge Processing with Fuzzy Cognitive Maps'', Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 2, no. 1, 83-87, 1991 ( Hasse diagram in German Wikipedia) describes 11 factors of the American cocaine market and the relations between these factors. For computations, Taylor uses pentavalent logic (scalar values out of ). That particular map of Taber uses
trivalent logic
In logic, a three-valued logic (also trinary logic, trivalent, ternary, or trilean, sometimes abbreviated 3VL) is any of several many-valued logic systems in which there are three truth values indicating ''true'', ''false'' and some indeterminate ...
(scalar values out of ). Taber et al. also illustrate the dynamics of map fusion and give a theorem on the convergence of combination in a related article.
While applications in social sciences introduced FCMs to the public, they are used in a much wider range of applications, which all have to deal with creating and using models of uncertainty and complex processes and systems. Examples:
*In business FCMs can be used for product planning and decision support.
*In economics, FCMs support the use of game theory in more complex settings.
* In education for modeling Critical Success Factors
Critical or Critically may refer to:
*Critical, or critical but stable, medical states
**Critical, or intensive care medicine
*Critical juncture, a discontinuous change studied in the social sciences.
*Critical Software, a company specializing in ...
of Learning Management Systems
A learning management system (LMS) is a software application for the administration, documentation, tracking, reporting, automation, and delivery of educational courses, training programs, materials or learning and development programs. The learni ...
.
* In medical applications to model systems, provide diagnosis, develop decision support systems
A decision support system (DSS) is an information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSSs serve the management, operations and planning levels of an organization (usually mid and higher management) and h ...
and medical assessment
A health assessment is a plan of care that identifies the specific needs of a person and how those needs will be addressed by the healthcare system or skilled nursing facility. Health assessment is the evaluation of the health status by performing ...
.
* In engineering for modeling and control mainly of complex systems and reliability engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specifi ...
*In project planning FCMs help to analyze the mutual dependencies between project resources.
*In robotics FCMs support machines to develop fuzzy models of their environments and to use these models to make crisp decisions.
*In computer assisted learning FCMs enable computers to check whether students understand their lessons.
*In expert system
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert.
Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as if� ...
s a few or many FCMs can be aggregated into one FCM in order to process estimates of knowledgeable persons.
*In IT project management, a FCM-based methodology helps to success modelling, risk analysis and assessment, IT scenarios
FCMappers is an international online community for the analysis and the visualization of fuzzy cognitive maps. FCMappers offer support for starting with FCM and also provide a Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for ...
-based tool that is able to check and analyse FCMs. The output is saved as Pajek file and can be visualized within third party software like Pajek, Visone, etc. They also offer to adapt the software to specific research needs.
Additional FCM software tools, such as Mental Modeler, have recently been developed as a decision-support tool for use in social science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of soc ...
research, collaborative decision-making, and natural resource planning.
See also
*Causal diagram
In the philosophy of science, a causal model (or structural causal model) is a conceptual model that describes the causal mechanisms of a system. Causal models can improve study designs by providing clear rules for deciding which independent ...
*Causal loop diagram
A causal loop diagram (CLD) is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. The diagram consists of a set of words and arrows. Causal loop diagrams are accompanied by a narrative which de ...
*System dynamics
System dynamics (SD) is an approach to understanding the nonlinear behaviour of complex systems over time using stocks, flows, internal feedback loops, table functions and time delays.
Overview
System dynamics is a methodology and mathematic ...
*Cognitive map
A cognitive map is a type of mental representation which serves an individual to acquire, code, store, recall, and decode information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in their everyday or metaphorical spatial environment. ...
References
{{Reflist, 30em Knowledge representation Fuzzy logic