fructoside on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
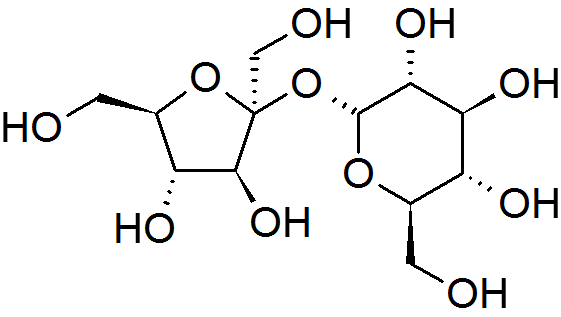 Fructosides are
Fructosides are
 The formation of fructosides via fructosyltransferases can lead to drastic changes in the qualities of the target compound. Phlorizin, a naturally occurring
The formation of fructosides via fructosyltransferases can lead to drastic changes in the qualities of the target compound. Phlorizin, a naturally occurring
 Fructosides are
Fructosides are glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. ...
s that contain fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
. They are abundant in living organisms, food, and the environment. This makes them a particular interest in pharmacology and food science. C1 of fructose may be bonded to any organic moiety, forming a fructoside. The configuration of the fructoside can be denoted as an α-fructosidase or β-fructosidase depending on whether the organic moiety is bonded below or above the plane of fructose, respectively. The naming of fructoside-related enzymes also follows this nomenclature.
Formation and cleavage
The formation of fructosides is catalyzed through enzymes called fructosyltransferases. These operate by transferring fructose to other organic moieties. This can be done repeatedly to make polymers or configure addition to diversify the molecule. Fructosyltransferases are most active in forming sucrose-derived fructosides and fructans. The breakdown of fructosides is catalyzed through enzymes called fructosidases. A notable example is the breakdown ofsucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
into glucose and fructose, which is catalyzed through a fructosidase called invertase
β-Fructofuranosidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis (breakdown) of the table sugar sucrose into fructose and glucose. Sucrose is a fructoside. Alternative names for β-fructofuranosidase include invertase, saccharase, glucosucrase ...
. This is metabolically relevant since glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and fructose are used as energy sources via glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
. Some fructosides are resistant to breakdown, such as fructan
A fructan is a polymer of fructose molecules. Fructans with a short chain length are known as fructooligosaccharides. Fructans can be found in over 12% of the angiosperms including both monocots and dicotyledon, dicots such as agave, artichokes, a ...
s - a polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
of fructose with glucose at the end which serves as a dietary fiber and promotes probiotic growth.
Research applications
glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. ...
that lowers blood sugar and thus has peaked medicinal interest, is a target of interest. Phlorizin fructoside derivatives have a higher solubility than their phlorizin counterparts, increasing bioavailability. The role of fructosides in promoting microbiome health possibly can be used in tandem with phlorizin's blood-sugar reducing properties as well.
References
{{biochem-stub