Flexural modulus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 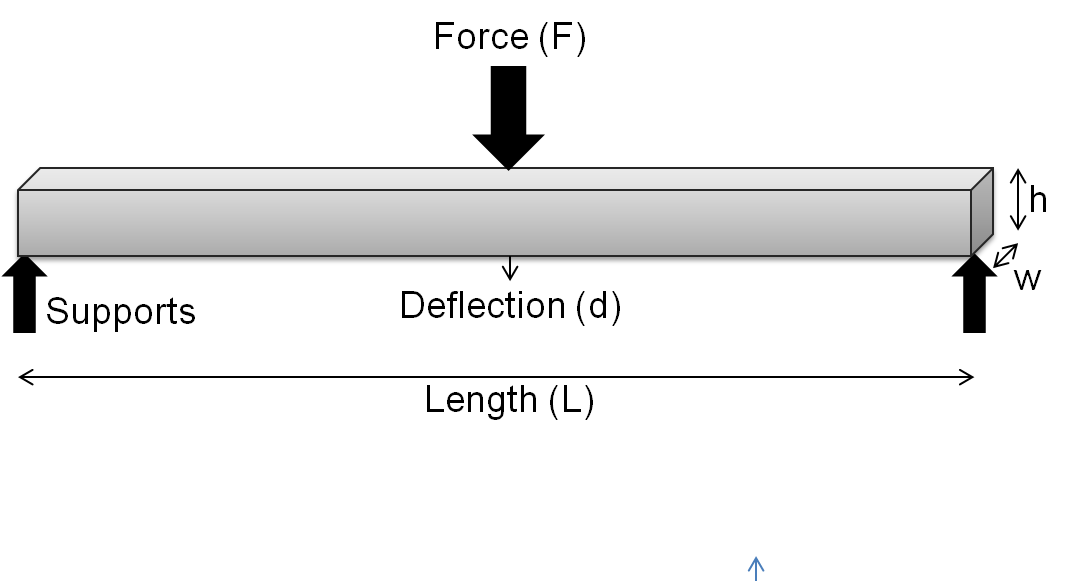 For a 3-point test of a rectangular beam behaving as an isotropic linear material, where ''w'' and ''h'' are the width and height of the beam, ''I'' is the
For a 3-point test of a rectangular beam behaving as an isotropic linear material, where ''w'' and ''h'' are the width and height of the beam, ''I'' is the
mechanics
Mechanics () is the area of physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among Physical object, physical objects. Forces applied to objects may result in Displacement (vector), displacements, which are changes of ...
, the flexural modulus, bending modulus, or modulus of rigidity is an intensive property
Physical or chemical properties of materials and systems can often be categorized as being either intensive or extensive, according to how the property changes when the size (or extent) of the system changes.
The terms "intensive and extensive ...
that is computed as the ratio of stress to strain in flexural deformation, or the tendency for a material to resist bending. It is determined from the slope of a stress-strain curve produced by a flexural test (such as the ASTM
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is a standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical international standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems and s ...
D790), and uses units of force per area. The flexural modulus defined using the 2-point (cantilever) and 3-point bend tests assumes a linear stress strain response.
 For a 3-point test of a rectangular beam behaving as an isotropic linear material, where ''w'' and ''h'' are the width and height of the beam, ''I'' is the
For a 3-point test of a rectangular beam behaving as an isotropic linear material, where ''w'' and ''h'' are the width and height of the beam, ''I'' is the second moment of area
The second moment of area, or second area moment, or quadratic moment of area and also known as the area moment of inertia, is a geometrical property of an area which reflects how its points are distributed with regard to an arbitrary axis. Th ...
of the beam's cross-section, ''L'' is the distance between the two outer supports, and ''d'' is the deflection due to the load ''F'' applied at the middle of the beam, the flexural modulus:
:
From elastic beam theory
:
and for rectangular beam
:
thus (Elastic modulus
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity (MOE)) is a quantity that describes an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it.
Definition
The elastic modu ...
)
For very small strains in isotropic materials – like glass, metal or polymer – flexural or bending modulus of elasticity is equivalent to the tensile modulus (Young's modulus
Young's modulus (or the Young modulus) is a mechanical property of solid materials that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness when the force is applied lengthwise. It is the modulus of elasticity for tension or axial compression. Youn ...
) or compressive modulus of elasticity. However, in anisotropic materials, for example wood, these values may not be equivalent. Moreover, composite materials
A composite or composite material (also composition material) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a ...
like fiber-reinforced polymers or biological tissues are inhomogeneous combinations of two or more materials, each with different material properties, therefore their tensile, compressive, and flexural moduli usually are not equivalent.
Related pages
*Stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a ...
References
Materials science Elasticity (physics) {{materials-sci-stub