Flat-four engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine or boxer engine, is a four-cylinder
A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine or boxer engine, is a four-cylinder
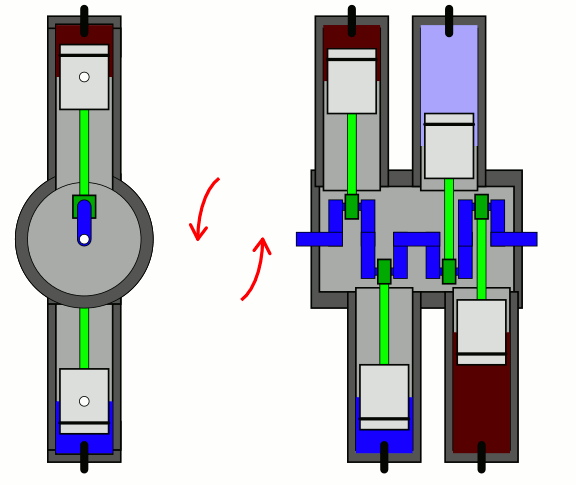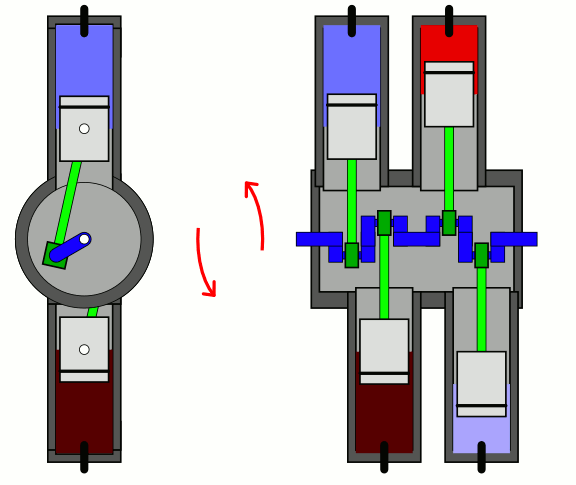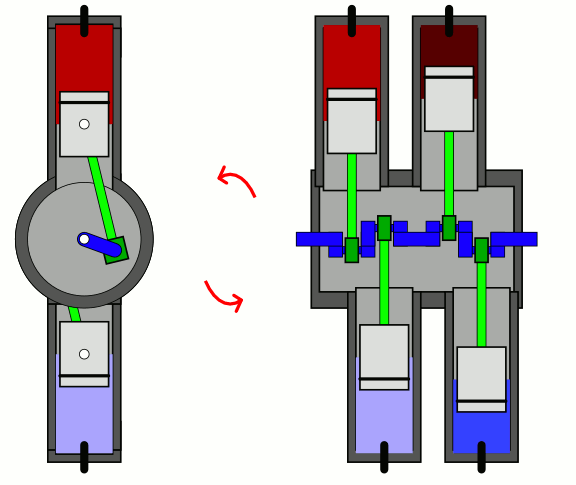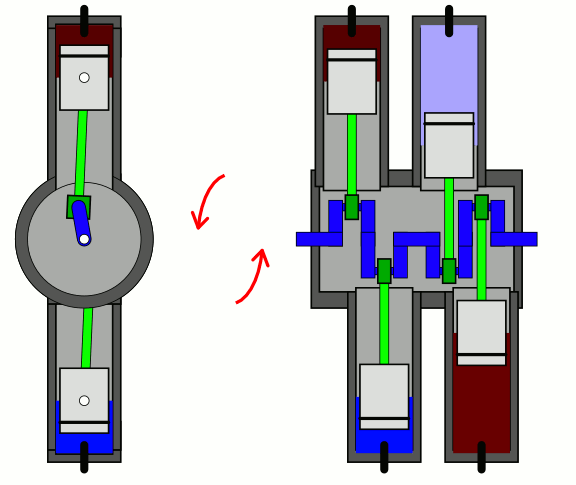 In a flat-four engine, each pair of opposing
In a flat-four engine, each pair of opposing
 In 1900, the first flat-four engine was produced by
In 1900, the first flat-four engine was produced by
 Most motorcycles with four-cylinder engines use a
Most motorcycles with four-cylinder engines use a

 A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine or boxer engine, is a four-cylinder
A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine or boxer engine, is a four-cylinder piston engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more Reciprocating motion, reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a Circular motion, rotating motion. This article ...
with two banks of cylinders lying on opposite sides of a common crankshaft. The most common type of flat-four engine is the boxer-four engine, each pair of opposed pistons moves inwards and outwards at the same time.
A boxer-four engine has perfect primary and secondary balance, however, the two cylinder heads means the design is more expensive to produce than a straight-four engine
A straight-four engine (also referred to as an inline-four engine) is a four-cylinder Reciprocating engine, piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a ...
. There is a minor, secondary unbalanced rotational torque pulse in the plane of the pistons, when a piston pair at one end of the engine is at TDC and the other pair at BDC. The TDC pair creates a torque greater than the BDC pair, so the net unbalanced torque pulse is the difference. The difference in TDC vs BDC inertial forces is explained in the Engine balance section. Boxer-four engines have been used in cars since 1897, especially by Volkswagen and Subaru. They have also occasionally been used in motorcycles and frequently in aircraft. Cessna
Cessna () is an American brand of general aviation aircraft owned by Textron Aviation since 2014, headquartered in Wichita, Kansas. Originally, it was a brand of the Cessna Aircraft Company, an American general aviation aircraft manufactu ...
and Piper use flat four engines from Lycoming and Continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' (album), an album by Saint Etienne
* Continen ...
in the most common civil aircraft in the world - the Cessna 172, and Piper Cherokee, while many ultralight
Ultralight aviation (called microlight aviation in some countries) is the flying of lightweight, 1- or 2-seat fixed-wing aircraft. Some countries differentiate between weight-shift control and conventional three-axis control aircraft with aile ...
and LSA planes use versions of the Rotax 912.
Design
 In a flat-four engine, each pair of opposing
In a flat-four engine, each pair of opposing piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder a ...
s successively moves inwards together and outwards together. The advantages of the boxer-four layout are perfect secondary vibration (resulting in minimal vibration), a low centre of gravity, and a short engine length. Flat-four engine have successfully used air cooling
Air cooling is a method of dissipating heat. It works by expanding the surface area or increasing the flow of air over the object to be cooled, or both. An example of the former is to add cooling fins to the surface of the object, either by maki ...
, although air-cooled engines are noisier and have a lower power output than an equivalent engine with liquid cooling
Liquid cooling refers to cooling by means of the convection or circulation (fluid dynamics), circulation of a liquid.
Examples of liquid cooling technologies include:
* Cooling by convection or circulation of coolant, including water cooling
* L ...
. In light aircraft, where lightness is of primary importance, air-cooling has traditionally been common.
The downsides of boxer-four engines (compared with inline-four engines) are their extra width, the increased costs associated with having two cylinder heads instead of one, and the long exhaust manifold required to achieve evenly spaced exhaust pulses. Due to these factors, straight-four engine
A straight-four engine (also referred to as an inline-four engine) is a four-cylinder Reciprocating engine, piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a ...
s are more common in cars than are flat-four engines, and V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six- cylinder piston engine where the cylinders and cylinder blocks share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, ...
s are often used where larger displacements are required.
Engine balance
The equal and opposing forces generated in a boxer-four engine result in perfect secondary balance (unlike the unbalanced vertical forces produced by inline-four engines). Boxer-four engines are therefore better suited to displacements above , since they do not requirebalance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in the opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force ...
s to reduce the secondary vibration.
In a boxer engine, each cylinder is slightly offset from its opposing pair due to the distance between the crankpin journals. This offset gives rise to a slight rocking couple, but any resulting vibration is normally insufficient to require balance shafts.
As with all four-stroke engines of four cylinders or fewer, the lack of overlap in the power strokes results in a pulsating delivery of torque to the flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device that uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy, a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, a ...
, causing a torsional vibration along the crankshaft axis. Such vibration, if excessive, may be minimised using a harmonic damper.
Exhaust manifold
The typical firing order for a boxer-four engine is for the left bank of cylinders to ignite one after another, followed by the right bank of cylinders (or vice versa), with the firing interval evenly spaced at 180 degrees. Traditionally, the exhausts from the two cylinders on each bank were merged, with the resulting uneven exhaust pulses causing a characteristic "flat-four burble" exhaust sound. The other common exhaust configuration (such as used by Subaru since the mid-2000s) is to pair the cylinders with a firing interval offset of 360 degrees, in order to optimise the exhaust pulses. This configuration requires long exhaust manifolds, in order to pair the cylinders on opposite banks, and results in a less distinctive exhaust sound.Use in automobiles
1900–1935
 In 1900, the first flat-four engine was produced by
In 1900, the first flat-four engine was produced by Benz & Cie
Carl (or Karl) Friedrich Benz (; born Karl Friedrich Michael Vaillant; 25 November 1844 – 4 April 1929) was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent-Motorwagen from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automob ...
, based on Benz's 1897 "contra" flat-twin engine. This engine was used in Benz racing cars, produced , had a displacement of and was designed by Georg Diehl.
London company Wilson-Pilcher released its first car in 1901, which was powered by a flat-four engine. This engine was mounted longitudinally in the chassis, water-cooled, produced and had a displacement of . Unusually for its day, the bore and stroke were equal, with each being .
In 1902 the Buffum automobile was equipped with opposed four cylinder engines that were rated at 16 horsepower. Herbert H. Buffum produced an American Automobile called the Buffum in Abington, Massachusetts from 1903 to 1907.
Having previously produced flat-twin engines, the 1926 Tatra 30 was the Czech company's first model powered by a flat-four engine. Tatra produced various flat-four engined model through the 1920s and 1930s.
1936–1999
The 1936 Tatra T97 pioneered the rear-engined, air-cooled flat-four, backbone chassis layout (later used by theVolkswagen Beetle
The Volkswagen Beetle, officially the Volkswagen Type 1, is a small family car produced by the German company Volkswagen from 1938 to 2003. One of the most iconic cars in automotive history, the Beetle is noted for its distinctive shape. Its pr ...
), and at the same time, though unrelated, came the Steyr 50
The Steyr 50 is a supermini, small car released in 1936 by the Austrian automobile manufacturer Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG.
Design
The streamliner, streamlined body was approved by Director Karl Jenschke to be constructed in 1935, however, in November ...
from Austria, sporting a front boxer 4 engine with rear wheel drive. Also in 1936, English company Jowett expanded its model range from flat-twin engines to also include flat-four engines. Production of Jowett flat-four engines continued until 1954, when the Jowett Javelin saloon and Jowett Jupiter
The Jowett Jupiter is a British sports car which was produced by Jowett, Jowett Cars Ltd of Idle, West Yorkshire, Idle, near Bradford.
Following the launch of the all new Jowett Javelin and its successes in competition, Jowett decided to use it ...
sports models ended production.
The longest production flat-four engine is the Volkswagen air-cooled engine, which was produced from 1938 until 2006 and was most famously used in the rear-engined 1938–2003 Volkswagen Beetle
The Volkswagen Beetle, officially the Volkswagen Type 1, is a small family car produced by the German company Volkswagen from 1938 to 2003. One of the most iconic cars in automotive history, the Beetle is noted for its distinctive shape. Its pr ...
and 1950–1983 Volkswagen Transporter
The Volkswagen Transporter, based on the Volkswagen Group's T platform, now in its seventh generation, refers to a series of vans produced for over 70 years and marketed worldwide.
The T series is now considered an official list of Volkswagen G ...
. This air-cooled engine was designed by Porsche and was also used in the 1948–1965 Porsche 356
The Porsche 356 is a rear-engine sports car, and the first ever production Porsche model.
The 356 is a lightweight and nimble-handling, rear-engine, rear-wheel drive, two-door available both in hardtop coupé and open configurations. Engineer ...
, 1953–1956 Porsche 550, 1965–1969 Porsche 912
The Porsche 912 is a sports car produced by Porsche AG of Stuttgart, Germany, for the 1965 through 1969 model years. An entry-level variant of the Porsche 911 (classic), 911, it was also offered in compact 2+2 (car body style), 2+2 Coupé and Targ ...
and 1969–1976 Porsche 914. In 1984, to comply with exhaust emissions regulations a water-cooled version called the Volkswagen Wasserboxer engine was introduced in the Volkswagen Transporter (T3)
During the 1960s and 1970s, several manufacturers produced flat-four engines including the air-cooled Citroën flat-four engine, the water-cooled Alfa Romeo flat-four engine, the water-cooled Lancia flat-four engine and the water-cooled Subaru EA engine.
Two important engines designed during this period, but never saw the light of day in series production, were the Morris 800cc side valve engine by Alec Issigonis in 1947 originally destined for the Morris Minor, and the Ferguson 2.2 litre SOHC engine by Claude Hill in 1966 as part of the R5 vehicle research project.
2000–present
By 2000, most manufacturers had replaced flat-four engines with inline-four engines. A notable exception is Subaru, with the water-cooled Subaru EJ engine being available in turbocharged form in theSubaru WRX
The Subaru WRX is an all-wheel drive sport compact, sport compact car manufactured by the Japanese automaker Subaru, originally based on the Subaru Impreza, Impreza created for the World Rally Championship in 1992. Subaru claimed the name WRX ...
sports sedan and its World Rally Car counterpart. Subaru's adoption of all-wheel drive
An all-wheel drive vehicle (AWD vehicle) is one with a powertrain capable of providing power to all its wheels, whether full-time or on-demand.
Types
The most common forms of all-wheel drive are:
;1x1 : All unicycles Reflects one axle with ...
was a factor in retaining the flat-four engine, since the shorter length of this engine assists in fitting the all-wheel drive components into the chassis. Although it is more expensive than an inline-four engine, the flat-four engine allows Subaru to build an all-wheel drive vehicle at little extra cost from two-wheel drive.
In 2012, a naturally aspirated version of the Subaru FA engine was used in the Toyota 86
The Toyota 86 and the Subaru BRZ are 2+2 sports cars jointly developed by Toyota and Subaru, manufactured at Subaru's Gunma assembly plant.
The 2+2 fastback coupé has a naturally aspirated boxer engine, front-engined, rear-wheel-drive ...
(also called the "Subaru BRZ" and "Scion FR-S") rear-wheel drive sports coupe. This engine is water-cooled, has gasoline direct injection
Gasoline direct injection (GDI), also known as petrol direct injection (PDI), is a fuel injection system for internal combustion engines that run on gasoline (petrol) which injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber. This is distinct f ...
, produces and has a displacement of .
The 2016 Porsche Boxster/Cayman (982) mid-engined sports cars downsized from a naturally aspirated flat-six engine to a turbocharged flat-four engine, Porsche's first flat-four since the mid-1970s. This engine is produced in displacements of and produces up to . Several reviewers criticised the Boxster/Cayman for an uninspiring engine sound.
In 2025, Chinese automaker BYD introduced its first flat-four engine in the BYD U7 luxury sedan, marking a modern revival of the boxer engine layout. This water-cooled, turbocharged powerplant combined direct injection and hybrid technology, delivering 268 hp (200 kW) while maintaining a compact design ideal for the sedan’s all-wheel-drive system. The engine drew inspiration from Porsche’s turbocharged flat-four units and showcased BYD’s push into high-performance powertrains alongside its electric vehicle lineup.
Use in motorcycles
 Most motorcycles with four-cylinder engines use a
Most motorcycles with four-cylinder engines use a straight-four engine
A straight-four engine (also referred to as an inline-four engine) is a four-cylinder Reciprocating engine, piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a ...
layout, however, several flat-four engine engines have been used in shaft drive motorcycles:
* 1938–1939 Zündapp K800 (air-cooled)
* 1974–1987 Honda Gold Wing (liquid-cooled)
* 1955–1956 Wooler 500cc (air-cooled)
* 1981–1982 , using the air-cooled Citroën flat-four car engine. Approximately 450 were built, with one quarter of these purchased by the French police.
Use in aircraft

Light aircraft
A light aircraft is an aircraft that has a Maximum Takeoff Weight, maximum gross takeoff weight of or less.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 308. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997.
Light aircraft are use ...
commonly use flat-four engines with displacements up to from manufacturers such as Rotax
Rotax is the brand name for a range of internal combustion engines developed and manufactured by the Austrian company BRP-Rotax GmbH & Co KG (until 2016 BRP-Powertrain GmbH & Co. KG), in turn owned by the Canadian Bombardier Recreational Prod ...
, Lycoming Engines
Lycoming Engines is a major American manufacturer of aircraft engines. With a factory in Williamsport, Pennsylvania, Lycoming produces a line of horizontally opposed, air-cooled, four, six and eight-cylinder engines.
The company has built more ...
, Continental Motors and Franklin Engine Company.
For radio-controlled aircraft
A radio-controlled aircraft (often called RC aircraft or RC plane) is a small flying machine that is radio controlled by an operator on the ground using a hand-held radio transmitter. The transmitter continuously communicates with a receiver (rad ...
, flat-four engines with displacements of are produced by companies such as O.S. Engines.
A notable recent flat-four aero-engine is the side-valve
A flathead engine, also known as a sidevalve engine''American Rodder'', 6/94, pp.45 & 93. or valve-in-block engine, is an internal combustion engine with its poppet valves contained within the Cam-in-block, engine block, instead of in the cyl ...
Belgian D-Motor LF26. Although the side-valve format has long been abandoned for most automotive applications because its combustion chamber is a bar to high engine rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or r⋅min−1) is a unit of rotational speed (or rotational frequency) for rotating machines.
One revolution per minute is equivalent to hertz.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 def ...
, the massively over-square (1.295:1) D-Motor is a very simple, low-revving, compact, reliable lightweight aero-engine (without the heavy complication of ohv valve-gear)Note: A low-revving engine is eminently suitable to drive a propeller, which is typically most effective at about 2,000 rpm. If a valve in a side-valve engine should stick open, it cannot hit the piston and cause engine failure; the engine will continue with just that cylinder inoperative. This is an important safety feature for aero-engines.
See also
*Straight-four engine
A straight-four engine (also referred to as an inline-four engine) is a four-cylinder Reciprocating engine, piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a ...
* V4 engine
A V4 engine is a four-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V engine, V configuration.
The V4 engine is less common compared to straight-four engines. However, V4 engines have been used in au ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Flat-Four Engine 04 Flat-04