Ferdinand Carré on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ferdinand Philippe Edouard Carré (11 March 1824 – 11 January 1900) was a French engineer, born at Moislains (
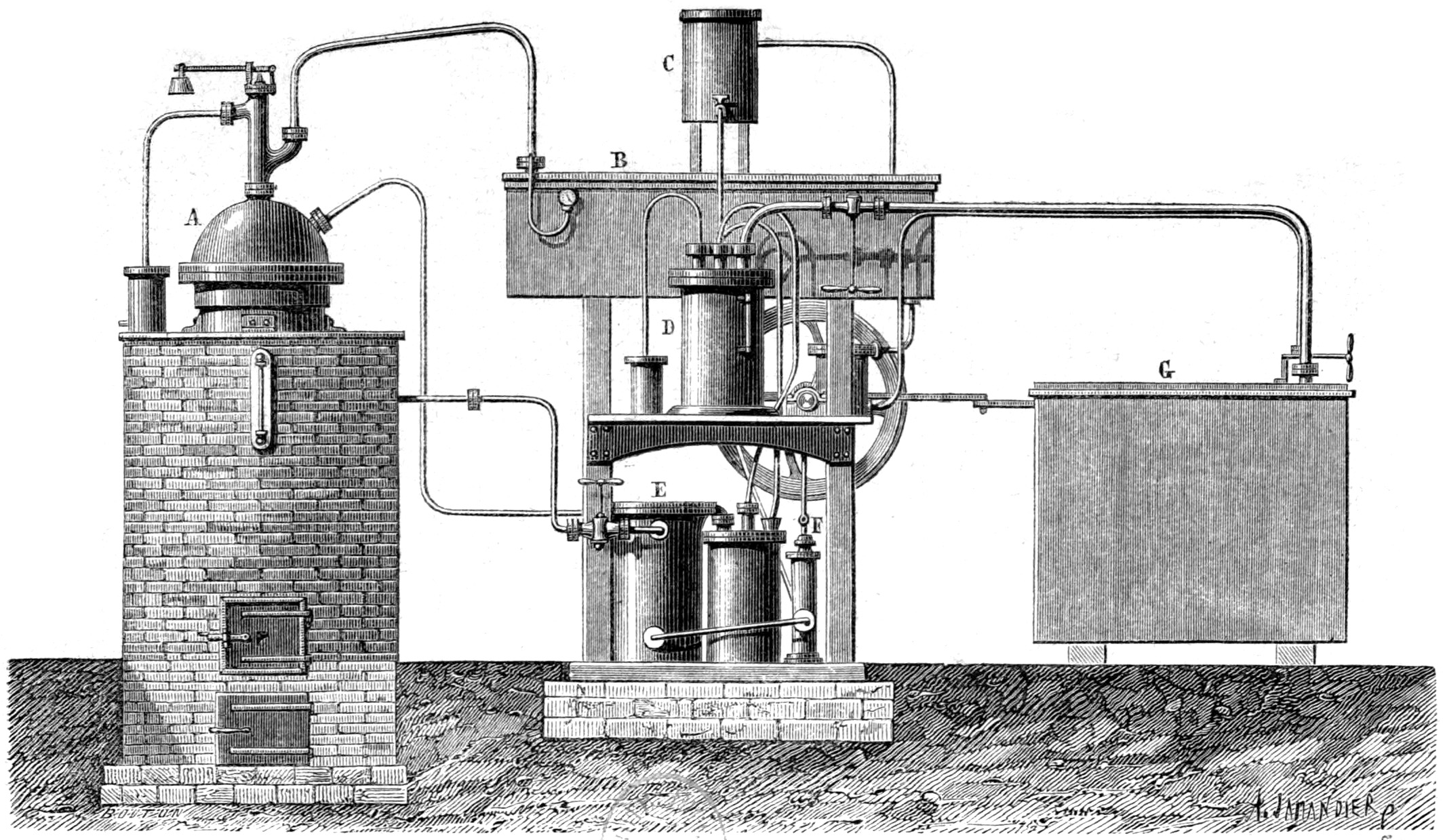 In 1850, Ferdinand's brother Edmond Carré (22 January 1833 – 7 May 1894) developed the first
In 1850, Ferdinand's brother Edmond Carré (22 January 1833 – 7 May 1894) developed the first Modified Carré electrical machine
Institute and Museum of the History of Science.
Somme __NOTOC__
Somme or The Somme may refer to: Places
*Somme (department), a department of France
*Somme, Queensland, Australia
*Canal de la Somme, a canal in France
*Somme (river), a river in France
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Somme'' (book), a ...
) on 11 March 1824. Carré is best known as the inventor of refrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, ht ...
equipment used to produce ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaq ...
. He died on 11 January 1900 at Pommeuse (Seine-et-Marne
Seine-et-Marne () is a department in the Île-de-France region in Northern France. Named after the rivers Seine and Marne, it is the region's largest department with an area of 5,915 square kilometres (2,284 square miles); it roughly covers its ...
).
Work
 In 1850, Ferdinand's brother Edmond Carré (22 January 1833 – 7 May 1894) developed the first
In 1850, Ferdinand's brother Edmond Carré (22 January 1833 – 7 May 1894) developed the first absorption refrigerator
An absorption refrigerator is a refrigerator that uses a heat source (e.g., solar energy, a fossil-fueled flame, waste heat from factories, or district heating systems) to provide the energy needed to drive the cooling process. The system uses t ...
, using water and sulphuric acid
Sulfuric acid ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
. Ferdinand continued Edmond's work on the process and in 1858 developed a machine which used water as the absorbent and ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogeno ...
as refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulate ...
. His absorption machine was patented in France in 1859 and in the United States in 1860. In 1862 he exhibited his ice-making machine
An icemaker, ice generator, or ice machine may refer to either a consumer device for making ice, found inside a home freezer; a stand-alone appliance for making ice, or an industrial machine for making ice on a large scale. The term "ice machine ...
at the Universal London Exhibition, producing an output of per hour. His design was based on the gas–vapour system of Australian inventor James Harrison.
In 1876 he equipped the ship ''Paraguay'' with an absorption refrigeration system, allowing the ship to carry frozen meat on an intercontinental trip. Carré's method remained popular through the early 1900s. It was replaced by systems using the liquid vapor compression cycle.
Carré also conducted research in the field of electricity. In 1877, he invented an electric light regulator. He also invented the Carré machine, an electrostatic generator
An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is an electrical generator that produces ''static electricity'', or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current. The knowledge of static electricity dates back to the earliest ci ...
used to produce high voltages.Institute and Museum of the History of Science.
See also
*Timeline of low-temperature technology
The following is a timeline of low-temperature technology and cryogenic technology (refrigeration down to –273.15 °C, –459.67 °F or 0 K). It also lists important milestones in thermometry, thermodynamics, statistical physics and ca ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Carre, Ferdinand 1824 births 1900 deaths French engineers