Ed Schieffelin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
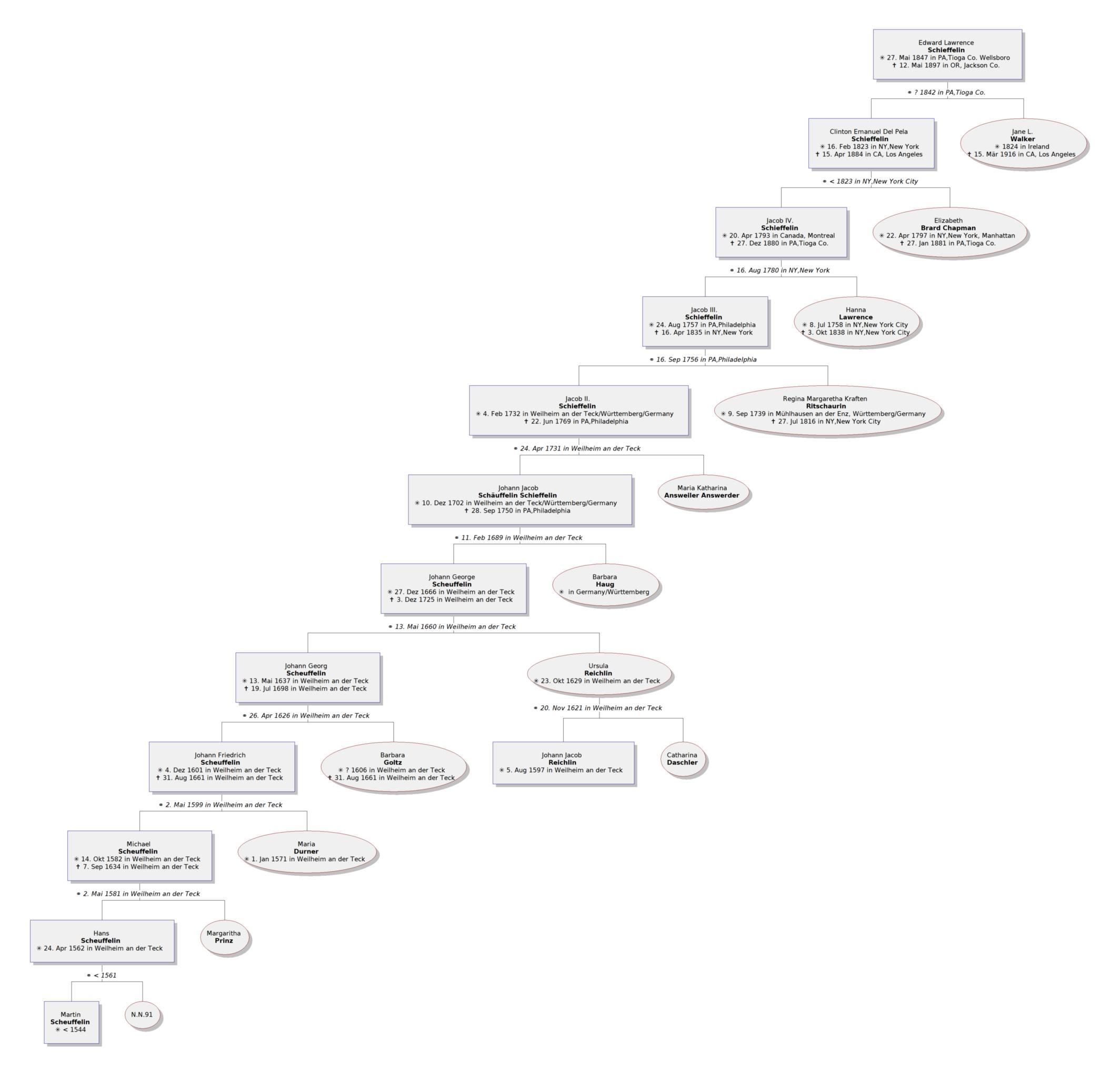
Edward Lawrence Schieffelin (1847–1897) was an Indian scout and
 Ed Schieffelin was born in a coal-mining region of
Ed Schieffelin was born in a coal-mining region of

 Frederick Brunckow, a Prussian-born mining engineer, discovered silver in the hills of Cochise County in 1858. He built a cabin near the San Pedro River after finding a small silver deposit nearby. He hired three other white men and about a dozen Mexican miners. In September 1860, two of the white men were robbed and murdered at the cabin and Brunckow was found dead in the mine with a rock drill through him. The German cook blamed the Mexican workers for the murders. After Brunckow's death, ongoing conflict with native Indians prevented further development of the mines for several years. Brunckow's San Pedro mine influenced Ed Schieffelin to prospect the rocky outcropping northeast of the cabin. In 1876, Schieffelin and his party were attacked by
Frederick Brunckow, a Prussian-born mining engineer, discovered silver in the hills of Cochise County in 1858. He built a cabin near the San Pedro River after finding a small silver deposit nearby. He hired three other white men and about a dozen Mexican miners. In September 1860, two of the white men were robbed and murdered at the cabin and Brunckow was found dead in the mine with a rock drill through him. The German cook blamed the Mexican workers for the murders. After Brunckow's death, ongoing conflict with native Indians prevented further development of the mines for several years. Brunckow's San Pedro mine influenced Ed Schieffelin to prospect the rocky outcropping northeast of the cabin. In 1876, Schieffelin and his party were attacked by

 When Ed finally located his brother in February 1878, Al asked the foreman at the McCracken mine to look at brother Ed's ore specimens. The foreman thought the samples were mostly lead. Unconvinced, Schieffelin showed the samples to 20 or 30 others who had some expertise, and they all thought the ore worthless. Frustrated, Schieffelin threw his ore specimens out his brother's cabin door, as far as he could throw, but at the last minute held on to three of them. For the next four weeks he worked in the McCracken Mine, wielding a pick and shovel.
Ed learned about the McCracken Mine's recently arrived assayer, Richard Gird, who had a reputation as an expert. Taking his last three ore samples, Ed Schieffelin asked Gird if he thought they were worth assaying. Gird took a look and said he'd get back to Ed. Three days later, Al shook Ed out of his bunk and said Gird wanted to see him now. When they met, Gird told Ed that he valued the best of the ore samples at $2,000 a ton. Ed, Al Schieffelin and Richard Gird formed a partnership on the spot. Gird offered his expertise, connections, and a grubstake. They shook hands on their three-way deal, a
When Ed finally located his brother in February 1878, Al asked the foreman at the McCracken mine to look at brother Ed's ore specimens. The foreman thought the samples were mostly lead. Unconvinced, Schieffelin showed the samples to 20 or 30 others who had some expertise, and they all thought the ore worthless. Frustrated, Schieffelin threw his ore specimens out his brother's cabin door, as far as he could throw, but at the last minute held on to three of them. For the next four weeks he worked in the McCracken Mine, wielding a pick and shovel.
Ed learned about the McCracken Mine's recently arrived assayer, Richard Gird, who had a reputation as an expert. Taking his last three ore samples, Ed Schieffelin asked Gird if he thought they were worth assaying. Gird took a look and said he'd get back to Ed. Three days later, Al shook Ed out of his bunk and said Gird wanted to see him now. When they met, Gird told Ed that he valued the best of the ore samples at $2,000 a ton. Ed, Al Schieffelin and Richard Gird formed a partnership on the spot. Gird offered his expertise, connections, and a grubstake. They shook hands on their three-way deal, a  The three partners formed the Tombstone Gold and Silver Mining Company to hold title to their claims. Gird built a crude assay furnace in the cabin's fireplace. He found that Schieffelin's initial find of silver ore was valuable, but within a few weeks of mining the vein, Ed discovered it ended in a pinch about three feet deep. His brother Al and Gird were despondent but Ed was optimistic he could find more ore deposits. He continued his search for many more weeks until one day Al found Ed joyously exclaiming over another sample of float ore he had found. Indifferently, Al told Ed he was a "lucky cuss," and that became the name of one of the richest mining claims in the Tombstone District. The ore samples assayed at $15,000 a ton. Ed shortly afterward identified another claim, the " Tough Nut" lode, rich in
The three partners formed the Tombstone Gold and Silver Mining Company to hold title to their claims. Gird built a crude assay furnace in the cabin's fireplace. He found that Schieffelin's initial find of silver ore was valuable, but within a few weeks of mining the vein, Ed discovered it ended in a pinch about three feet deep. His brother Al and Gird were despondent but Ed was optimistic he could find more ore deposits. He continued his search for many more weeks until one day Al found Ed joyously exclaiming over another sample of float ore he had found. Indifferently, Al told Ed he was a "lucky cuss," and that became the name of one of the richest mining claims in the Tombstone District. The ore samples assayed at $15,000 a ton. Ed shortly afterward identified another claim, the " Tough Nut" lode, rich in
 When the first claims were filed, the initial settlement of tents and cabins was located at Watervale near the Lucky Cuss mine. By March 1879, about 100 residents occupied tents and shacks at Watervale. Former Territorial Governor Anson P.K. Safford offered financial backing for a cut of the men's mining claims, and Ed Schieffelin, his brother Al, and their partner Richard Gird formed the Tombstone Mining and Milling Company and built a stamping mill. On March 5, 1879, U.S. Deputy Mineral Surveyor Solon M. Allis finished laying out a new town site on a
When the first claims were filed, the initial settlement of tents and cabins was located at Watervale near the Lucky Cuss mine. By March 1879, about 100 residents occupied tents and shacks at Watervale. Former Territorial Governor Anson P.K. Safford offered financial backing for a cut of the men's mining claims, and Ed Schieffelin, his brother Al, and their partner Richard Gird formed the Tombstone Mining and Milling Company and built a stamping mill. On March 5, 1879, U.S. Deputy Mineral Surveyor Solon M. Allis finished laying out a new town site on a  Ed Schieffelin preferred prospecting to running a mine and he left Tombstone to find more ore. When he returned four months later, Gird had lined up buyers for their interest in the Contention, which they sold for $10,000 to J.H. White and S. Denson, who represented W.D. Dean of San Francisco. The sellers thought the $10,000 price was exorbitant. The Grand Central and Contention claims turned out to be the richest claims in the district, producing millions of dollars in bullion. The Schieffelin company also soon sold a half-interest in the Lucky Cuss, and the other half turned into a steady stream of money.
Ed Schieffelin preferred prospecting to running a mine and he left Tombstone to find more ore. When he returned four months later, Gird had lined up buyers for their interest in the Contention, which they sold for $10,000 to J.H. White and S. Denson, who represented W.D. Dean of San Francisco. The sellers thought the $10,000 price was exorbitant. The Grand Central and Contention claims turned out to be the richest claims in the district, producing millions of dollars in bullion. The Schieffelin company also soon sold a half-interest in the Lucky Cuss, and the other half turned into a steady stream of money.
 On March 13, 1879, Al and Ed Schieffelin sold their two-thirds interest in the Tombstone Mining and Milling Company, which owned the Tough Nut mine, for US$1 million each to the Corbin brothers, Hamilton Distin of Philadelphia, and Simmons Squire of Boston. Safford became president of the new Tombstone Gold and Silver Milling and Mining Company with Richard Gird as superintendent. Ed moved on, but Al remained in Tombstone for some time longer. Gird later sold off his one-third interest for US$1 million, doubling what the Schieffelins had been paid. Gird remained in the territory but Ed Schieffelin left to pursue other interests.
When
On March 13, 1879, Al and Ed Schieffelin sold their two-thirds interest in the Tombstone Mining and Milling Company, which owned the Tough Nut mine, for US$1 million each to the Corbin brothers, Hamilton Distin of Philadelphia, and Simmons Squire of Boston. Safford became president of the new Tombstone Gold and Silver Milling and Mining Company with Richard Gird as superintendent. Ed moved on, but Al remained in Tombstone for some time longer. Gird later sold off his one-third interest for US$1 million, doubling what the Schieffelins had been paid. Gird remained in the territory but Ed Schieffelin left to pursue other interests.
When
 Ed had accumulated more than $1 million in wealth as a result of the silver boom. While he had maintained a casual appearance, including long hair and beard, he cleaned himself up. He traveled to New York City, Chicago, Washington, D.C., and other cities. He met many distinguished people. Ever restless, over the next 20 years Ed showed up at nearly every boom town in the West.
Schieffelin had made a practice of studying maps and believed there was a great "continental belt" of mineral wealth that extended from South America through Mexico, the United States, and British Columbia.Berton, P., (1958). ''The Klo(=)dike Fever''. Alfred A Knopf: New York, pp. 11–12. During 1882, Ed prepared for what he planned to be a three-year survey of mineral wealth. He began the expedition with his brother Al and three others on a trip up the
Ed had accumulated more than $1 million in wealth as a result of the silver boom. While he had maintained a casual appearance, including long hair and beard, he cleaned himself up. He traveled to New York City, Chicago, Washington, D.C., and other cities. He met many distinguished people. Ever restless, over the next 20 years Ed showed up at nearly every boom town in the West.
Schieffelin had made a practice of studying maps and believed there was a great "continental belt" of mineral wealth that extended from South America through Mexico, the United States, and British Columbia.Berton, P., (1958). ''The Klo(=)dike Fever''. Alfred A Knopf: New York, pp. 11–12. During 1882, Ed prepared for what he planned to be a three-year survey of mineral wealth. He began the expedition with his brother Al and three others on a trip up the

 In 1897 Schieffelin bought a ranch near his brothers Effingham (Eff) and Jacob (Jay) outside Woodville, now
In 1897 Schieffelin bought a ranch near his brothers Effingham (Eff) and Jacob (Jay) outside Woodville, now
prospector
Prospector may refer to:
Space exploration
* Prospector (spacecraft), a planned lunar probe, canceled in 1962
* '' Lunar Prospector'', a NASA spacecraft
Trains
* Prospector (train), a passenger train operated by the Denver & Rio Grande Western ...
who discovered silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
in the Arizona Territory
The Territory of Arizona (also known as Arizona Territory) was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863, until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of ...
, which led to the founding of Tombstone, Arizona
Tombstone is a historic city in Cochise County, Arizona, United States, founded in 1877 by prospector Ed Schieffelin in what was then Pima County, Arizona Territory. It became one of the last boomtowns in the American frontier. The town grew si ...
. He partnered with his brother Al and mining engineer Richard Gird in a handshake deal that produced millions of dollars in wealth for all three men. During the course of Tombstone's mining history, about US $85,000,000 in silver was produced from its mines.
Early life
 Ed Schieffelin was born in a coal-mining region of
Ed Schieffelin was born in a coal-mining region of Wellsboro, Pennsylvania
Wellsboro is a borough in Tioga County, Pennsylvania. The borough was founded by Benjamin Wistar Morris. It is located northwest of Williamsport. The population was 3,472 at the 2020 census.
Early in the 20th century, Wellsboro was the shipp ...
, the son of a prominent New York and Pennsylvania family, in 1847. His great-grandfather Jacob Schieffelin, Sr., born in 1757, joined the Loyalist army and served as Henry Hamilton's secretary during the Revolutionary War. Schieffelin was captured in 1779 and held prisoner in Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an Independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it had a population of 15,425. Located on the Virginia Peninsula ...
. He escaped to Canada, where in 1780 he was appointed a lieutenant in the Queen's Rangers
The Queen's Rangers, also known as the Queen's American Rangers, and later Simcoe's Rangers, were a Loyalist military unit of the American Revolutionary War. Formed in 1776, they were named for Queen Charlotte, consort of George III. The Queen' ...
by Henry Clinton. He spent time in Montreal and Detroit, before returning to New York, where in 1794 he founded a drug company with his brother Lawrence. This firm still exists as a liquor import house, Schieffelin & Somerset. Jacob's wife, Hannah Lawrence, was a descendant of Quaker colonial religious pioneer John Bowne
John Bowne (1627–1695), the progenitor of the Bowne family in America, was a Quaker and an English immigrant residing in the Dutch colony of New Netherland. He is historically significant for his struggle for religious liberty.
Background
Born i ...
, Elizabeth Fones
Elizabeth Fones Winthrop Feake Hallett (21 January 1610 – c. 1673) was an early settler in the Massachusetts Bay Colony. In 1640 Fones, with her then-husband Robert Feake, were founders of Greenwich, Connecticut. Wolfe (2012)
She married her t ...
, and the Winthrop family of New England.
In January 1849, Jacob, Jr. traveled to California with his sons Alfred and Edward Girard on the ship ''Morrison''. They arrived in September, but almost immediately booked passage home via Panama in November. Jacob Schieffelin, Jr. traveled overland and joined his brother and Ed. Schieffelin's father Clinton Emanuel Del Pela Schieffelin settled in the Rogue Valley
The Rogue Valley is a valley region in southwestern Oregon in the United States. Located along the middle Rogue River and its tributaries in Josephine and Jackson counties, the valley forms the cultural and economic heart of Southern Oregon nea ...
, Oregon Territory
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. Ori ...
, in the mid-1850s to raise cattle, grain and children. The family maintained an interest in the mining activities in the area.
Hunt for gold and silver
At age 17, Schieffelin set out on his own as a prospector and miner. He began looking for gold and silver in about 1865. From Oregon, he went east to Coeur d'Alene, then searched across Nevada intoDeath Valley
Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. During summer, it is the Highest temperature recorded on Earth, hottest place on Earth.
Death Valley's Badwater Basin is the ...
, back into Colorado and then New Mexico.
In 1876, David P. Lansing of Phoenix, Arizona, described Schieffelin as "about the strangest specimen of human flesh I ever saw. He was tall and had black hair that hung several inches below his shoulder and a beard that had not been trimmed or combed for so long a time that it was a mass of unkempt knots and mats. He wore clothing pieced and patched from deerskins, corduroy and flannel, and his hat was originally a slouch hat that had been pieced with rabbit skin until very little of the original felt remained."
A year later as a 30-year-old, Schieffelin moved to California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
to find gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
. He surveyed the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon (, yuf-x-yav, Wi:kaʼi:la, , Southern Paiute language: Paxa’uipi, ) is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a m ...
area as well. Unsuccessful, he heard that a group of Hualapai
The Hualapai (, , yuf-x-wal, Hwalbáy) is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Arizona with about 2300 enrolled members. Approximately 1353 enrolled members reside on the Hualapai Reservation, which spans over three counties in Nort ...
Indians had enlisted as scouts
Scouting, also known as the Scout Movement, is a worldwide youth movement employing the Scout method, a program of informal education with an emphasis on practical outdoor activities, including camping, woodcraft, aquatics, hiking, backpacking ...
for the U.S. Army, which was establishing a camp to counter the Chiricahua Apache
Chiricahua ( ) is a band of Apache Native Americans.
Based in the Southern Plains and Southwestern United States, the Chiricahua (Tsokanende ) are related to other Apache groups: Ndendahe (Mogollon, Carrizaleño), Tchihende (Mimbreño), Sehende ...
threat and to secure the nearby border with Mexico. The Army established Camp Huachuca at the foot of the Huachuca Mountains
The Huachuca Mountains are part of the Sierra Vista Ranger District of the Coronado National Forest in Cochise County in southeastern Arizona, approximately south-southeast of Tucson and southwest of the city of Sierra Vista. Included in this ar ...
in Pima County
Pima County ( ) is a county in the south central region of the U.S. state of Arizona. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,043,433, making it Arizona's second-most populous county. The county seat is Tucson, where most of the population ...
, Arizona Territory
The Territory of Arizona (also known as Arizona Territory) was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863, until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of ...
on March 3, 1877. Silver had already been discovered in some northern areas of Arizona Territory, but the southern portion had been under continued Apache attack.
Schieffelin accompanied the scouts on a few trips into the back country while prospecting part-time. He finally decided to stay put and explore the hills east full-time. The hills east of the San Pedro River where he prospected could be dangerous. They were only about from the hostile Chiricahua Apache Indians led by Cochise
Cochise (; Apache: ''Shi-ka-She'' or ''A-da-tli-chi'', lit.: ''having the quality or strength of an oak''; later ''K'uu-ch'ish'' or ''Cheis'', lit. ''oak''; June 8, 1874) was leader of the Chihuicahui local group of the Chokonen and principa ...
, Geronimo
Geronimo ( apm, Goyaałé, , ; June 16, 1829 – February 17, 1909) was a prominent leader and medicine man from the Bedonkohe band of the Ndendahe Apache people. From 1850 to 1886, Geronimo joined with members of three other Central Apache ba ...
and Victorio
Victorio (Bidu-ya, Beduiat; ca. 1825–October 14, 1880) was a warrior and chief of the Warm Springs band of the Tchihendeh (or Chihenne, often called Mimbreño) division of the central Apaches in what is now the American states of Texas, New ...
that had established a stronghold in the Dragoon Mountains
The Dragoon Mountains are a range of mountains located in Cochise County, Arizona. The range is about 25 mi (40 km) long, running on an axis extending south-south east through Willcox. The name originates from the 3rd U.S. Cavalry Drag ...
.
Ore discovery

 Frederick Brunckow, a Prussian-born mining engineer, discovered silver in the hills of Cochise County in 1858. He built a cabin near the San Pedro River after finding a small silver deposit nearby. He hired three other white men and about a dozen Mexican miners. In September 1860, two of the white men were robbed and murdered at the cabin and Brunckow was found dead in the mine with a rock drill through him. The German cook blamed the Mexican workers for the murders. After Brunckow's death, ongoing conflict with native Indians prevented further development of the mines for several years. Brunckow's San Pedro mine influenced Ed Schieffelin to prospect the rocky outcropping northeast of the cabin. In 1876, Schieffelin and his party were attacked by
Frederick Brunckow, a Prussian-born mining engineer, discovered silver in the hills of Cochise County in 1858. He built a cabin near the San Pedro River after finding a small silver deposit nearby. He hired three other white men and about a dozen Mexican miners. In September 1860, two of the white men were robbed and murdered at the cabin and Brunckow was found dead in the mine with a rock drill through him. The German cook blamed the Mexican workers for the murders. After Brunckow's death, ongoing conflict with native Indians prevented further development of the mines for several years. Brunckow's San Pedro mine influenced Ed Schieffelin to prospect the rocky outcropping northeast of the cabin. In 1876, Schieffelin and his party were attacked by Apaches
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño and ...
, and a man named Lenox was killed. The cabin was the site of 22 murders during the frontier days.
When friend and fellow army scout Al Sieber
Al Sieber (February 27, 1843 1844 was a leap year, leading to some confusion about Sieber's birth date. His tombstone in Globe gives his birth date as 1844, as does the book ''Chief of Scouts''. Both are incorrect. – February 19, 1907) was a Ge ...
learned what Schieffelin was up to, he is quoted as telling him, "The only rock you will find out there will be your own tombstone". Another account reported Schieffelin's friends told him, "Better take your coffin with you; you will find your tombstone there, and nothing else."
In 1877, Schieffelin used Brunckow's cabin as a base of operations to survey the country. After many months, Ed was working the hills east of the San Pedro River when he found pieces of silver ore
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical cond ...
in a dry wash on a high plateau called Goose Flats. It took him several more months to find the source. When he located the vein, he estimated the vein to be long and wide. Schieffelin's claim was sited near Lenox's grave site, and when he filed his first mining claim on September 21, 1877, he fittingly named his stake "Tombstone".
Flat broke, Schieffelin persuaded William Griffith to pay for the legal paperwork required to file a mining claim on September 3, 1877. Tucson did not have an assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a ...
office, and when they showed the sample ore to some local men, they thought it was worthless.
With only 30 cents in his pocket, Schieffelin set out to find his brother Al, whom he had not seen in four years. He believed Al was working the Silver King mine, about to the north in central Arizona Territory
The Territory of Arizona (also known as Arizona Territory) was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863, until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of ...
near present-day Globe
A globe is a spherical model of Earth, of some other celestial body, or of the celestial sphere. Globes serve purposes similar to maps, but unlike maps, they do not distort the surface that they portray except to scale it down. A model globe ...
. But Schieffelin learned that Al had moved on to the McCracken Mine in Signal City, Arizona, another north. Schieffelin spent his 30 cents on tobacco and had to pause in his search for his brother to earn enough money to go on. He found a job as a hoist operator at the Champion silver mine, and for fourteen days hauled up a dozen tons of ore every night by cranking a hand windlass.
Partnership formed


 When Ed finally located his brother in February 1878, Al asked the foreman at the McCracken mine to look at brother Ed's ore specimens. The foreman thought the samples were mostly lead. Unconvinced, Schieffelin showed the samples to 20 or 30 others who had some expertise, and they all thought the ore worthless. Frustrated, Schieffelin threw his ore specimens out his brother's cabin door, as far as he could throw, but at the last minute held on to three of them. For the next four weeks he worked in the McCracken Mine, wielding a pick and shovel.
Ed learned about the McCracken Mine's recently arrived assayer, Richard Gird, who had a reputation as an expert. Taking his last three ore samples, Ed Schieffelin asked Gird if he thought they were worth assaying. Gird took a look and said he'd get back to Ed. Three days later, Al shook Ed out of his bunk and said Gird wanted to see him now. When they met, Gird told Ed that he valued the best of the ore samples at $2,000 a ton. Ed, Al Schieffelin and Richard Gird formed a partnership on the spot. Gird offered his expertise, connections, and a grubstake. They shook hands on their three-way deal, a
When Ed finally located his brother in February 1878, Al asked the foreman at the McCracken mine to look at brother Ed's ore specimens. The foreman thought the samples were mostly lead. Unconvinced, Schieffelin showed the samples to 20 or 30 others who had some expertise, and they all thought the ore worthless. Frustrated, Schieffelin threw his ore specimens out his brother's cabin door, as far as he could throw, but at the last minute held on to three of them. For the next four weeks he worked in the McCracken Mine, wielding a pick and shovel.
Ed learned about the McCracken Mine's recently arrived assayer, Richard Gird, who had a reputation as an expert. Taking his last three ore samples, Ed Schieffelin asked Gird if he thought they were worth assaying. Gird took a look and said he'd get back to Ed. Three days later, Al shook Ed out of his bunk and said Gird wanted to see him now. When they met, Gird told Ed that he valued the best of the ore samples at $2,000 a ton. Ed, Al Schieffelin and Richard Gird formed a partnership on the spot. Gird offered his expertise, connections, and a grubstake. They shook hands on their three-way deal, a gentlemen's agreement
A gentlemen's agreement, or gentleman's agreement, is an informal and legally non-binding agreement between two or more parties. It is typically oral, but it may be written or simply understood as part of an unspoken agreement by convention or th ...
that was never put down on paper but that resulted in millions of dollars of wealth for all three men. When Richard resigned, his employer offered to make him general superintendent of the mine, but he refused.
Gird bought a second-hand blue spring wagon and loaded it with supplies, his assay equipment, and also bought a second mule that with Ed's mule could haul the wagon. Gird wanted time to wind up his affairs and to wait for spring and better weather, but Ed insisted they depart immediately. Al hesitated to leave his well-paid, $4.00 a day job as a miner. Ed and Gird didn't wait for him, but left that day. Al reconsidered and joined them that night. Reaching Arizona Territory, and despite reports of continued Apache raids and the murder of miners and ranchers in the area, the three men returned to Cochise County and set up camp at the Brunckow cabin. The deaths of several locals at the hands of the Apache Indians were testified to by the fresh graves near the cabin.
 The three partners formed the Tombstone Gold and Silver Mining Company to hold title to their claims. Gird built a crude assay furnace in the cabin's fireplace. He found that Schieffelin's initial find of silver ore was valuable, but within a few weeks of mining the vein, Ed discovered it ended in a pinch about three feet deep. His brother Al and Gird were despondent but Ed was optimistic he could find more ore deposits. He continued his search for many more weeks until one day Al found Ed joyously exclaiming over another sample of float ore he had found. Indifferently, Al told Ed he was a "lucky cuss," and that became the name of one of the richest mining claims in the Tombstone District. The ore samples assayed at $15,000 a ton. Ed shortly afterward identified another claim, the " Tough Nut" lode, rich in
The three partners formed the Tombstone Gold and Silver Mining Company to hold title to their claims. Gird built a crude assay furnace in the cabin's fireplace. He found that Schieffelin's initial find of silver ore was valuable, but within a few weeks of mining the vein, Ed discovered it ended in a pinch about three feet deep. His brother Al and Gird were despondent but Ed was optimistic he could find more ore deposits. He continued his search for many more weeks until one day Al found Ed joyously exclaiming over another sample of float ore he had found. Indifferently, Al told Ed he was a "lucky cuss," and that became the name of one of the richest mining claims in the Tombstone District. The ore samples assayed at $15,000 a ton. Ed shortly afterward identified another claim, the " Tough Nut" lode, rich in horn silver
Chlorargyrite is the mineral form of silver chloride (AgCl). Chlorargyrite occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation of silver mineral deposits. It crystallizes in the isometric - hexoctahedral crystal class. Typically massive to colum ...
.
On June 17, 1879, Schieffelin showed up in Tucson driving the blue spring wagon carrying the first load of silver bullion valued at $18,744 (about $ today)
Tombstone founded
 When the first claims were filed, the initial settlement of tents and cabins was located at Watervale near the Lucky Cuss mine. By March 1879, about 100 residents occupied tents and shacks at Watervale. Former Territorial Governor Anson P.K. Safford offered financial backing for a cut of the men's mining claims, and Ed Schieffelin, his brother Al, and their partner Richard Gird formed the Tombstone Mining and Milling Company and built a stamping mill. On March 5, 1879, U.S. Deputy Mineral Surveyor Solon M. Allis finished laying out a new town site on a
When the first claims were filed, the initial settlement of tents and cabins was located at Watervale near the Lucky Cuss mine. By March 1879, about 100 residents occupied tents and shacks at Watervale. Former Territorial Governor Anson P.K. Safford offered financial backing for a cut of the men's mining claims, and Ed Schieffelin, his brother Al, and their partner Richard Gird formed the Tombstone Mining and Milling Company and built a stamping mill. On March 5, 1879, U.S. Deputy Mineral Surveyor Solon M. Allis finished laying out a new town site on a mesa
A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by ...
named Goose Flats at , to top of the Tough Nut mine, and large enough to hold a growing town. The town was named " Tombstone" after Schieffelin's initial mining claim. The shelters at Watervale were relocated to the new town site and a scattering of cabins and tents were quickly built for about 100 residents.
During the first few months of mining, the upper portion of the Tombstone mining district was accidentally discovered by Ed Williams and Jack Friday. Late one night, their mules broke loose and dragging their chain, left the miners' dry camp for water along an Indian trail. The men tracked the mules' chain trail all the way to the Schieffelin camp. Williams and Friday noticed a bright gleam where the iron had dragged across bare rock. They filed a claim for their find, but Al and Ed Schieffelin and Richard Gird contested their claim, asserting it violated their earlier claims. When the two parties finally resolved their arguments and counterclaims, they agreed to divide the ground. Williams and Friday took the higher end, which they called the Grand Central, and the Schieffelin company took the lower end, which they named the Contention in remembrance of the quarrel that led to its founding. Those two mines were eventually the most profitable mines in Tombstone. Some of the ore from the "Lucky Cuss", "Tough Nut", and the "Contention" mines assayed at around $15,000 to the ton.
 Ed Schieffelin preferred prospecting to running a mine and he left Tombstone to find more ore. When he returned four months later, Gird had lined up buyers for their interest in the Contention, which they sold for $10,000 to J.H. White and S. Denson, who represented W.D. Dean of San Francisco. The sellers thought the $10,000 price was exorbitant. The Grand Central and Contention claims turned out to be the richest claims in the district, producing millions of dollars in bullion. The Schieffelin company also soon sold a half-interest in the Lucky Cuss, and the other half turned into a steady stream of money.
Ed Schieffelin preferred prospecting to running a mine and he left Tombstone to find more ore. When he returned four months later, Gird had lined up buyers for their interest in the Contention, which they sold for $10,000 to J.H. White and S. Denson, who represented W.D. Dean of San Francisco. The sellers thought the $10,000 price was exorbitant. The Grand Central and Contention claims turned out to be the richest claims in the district, producing millions of dollars in bullion. The Schieffelin company also soon sold a half-interest in the Lucky Cuss, and the other half turned into a steady stream of money.
 On March 13, 1879, Al and Ed Schieffelin sold their two-thirds interest in the Tombstone Mining and Milling Company, which owned the Tough Nut mine, for US$1 million each to the Corbin brothers, Hamilton Distin of Philadelphia, and Simmons Squire of Boston. Safford became president of the new Tombstone Gold and Silver Milling and Mining Company with Richard Gird as superintendent. Ed moved on, but Al remained in Tombstone for some time longer. Gird later sold off his one-third interest for US$1 million, doubling what the Schieffelins had been paid. Gird remained in the territory but Ed Schieffelin left to pursue other interests.
When
On March 13, 1879, Al and Ed Schieffelin sold their two-thirds interest in the Tombstone Mining and Milling Company, which owned the Tough Nut mine, for US$1 million each to the Corbin brothers, Hamilton Distin of Philadelphia, and Simmons Squire of Boston. Safford became president of the new Tombstone Gold and Silver Milling and Mining Company with Richard Gird as superintendent. Ed moved on, but Al remained in Tombstone for some time longer. Gird later sold off his one-third interest for US$1 million, doubling what the Schieffelins had been paid. Gird remained in the territory but Ed Schieffelin left to pursue other interests.
When Cochise County
Cochise County () is a county in the southeastern corner of the U.S. state of Arizona. It is named after the Native American chief Cochise.
The population was 125,447 at the 2020 census. The county seat is Bisbee and the most populous city is ...
was formed in February 1881, Tombstone became the county seat. In 1881, early in Tombstone's rapid growth, Ed's brother Al built Schieffelin Hall
Schieffelin Hall is a building from the American Old West in Tombstone, Arizona Territory, the largest standing adobe structure still existent in the United States southwest. It was built in 1881 by Albert Schieffelin, brother of Tombstone founde ...
as a theater, recital hall, and a meeting place for Tombstone citizens. His great-niece Mary Schieffelin Brady reopened it in 1964 and it remains an attraction in Tombstone. It is the largest standing adobe structure in the southwest United States.
At its height in the mid-1880s, Tombstone's population was officially about 7,000 miners, but some estimates figure in an additional 5–7,000 women and children, Chinese, Mexicans, and prostitutes. In the late 1880s, the silver mines reached the water table and the mines eventually filled with water. Tombstone's population faded, until tourism became its main attraction.
Later life
 Ed had accumulated more than $1 million in wealth as a result of the silver boom. While he had maintained a casual appearance, including long hair and beard, he cleaned himself up. He traveled to New York City, Chicago, Washington, D.C., and other cities. He met many distinguished people. Ever restless, over the next 20 years Ed showed up at nearly every boom town in the West.
Schieffelin had made a practice of studying maps and believed there was a great "continental belt" of mineral wealth that extended from South America through Mexico, the United States, and British Columbia.Berton, P., (1958). ''The Klo(=)dike Fever''. Alfred A Knopf: New York, pp. 11–12. During 1882, Ed prepared for what he planned to be a three-year survey of mineral wealth. He began the expedition with his brother Al and three others on a trip up the
Ed had accumulated more than $1 million in wealth as a result of the silver boom. While he had maintained a casual appearance, including long hair and beard, he cleaned himself up. He traveled to New York City, Chicago, Washington, D.C., and other cities. He met many distinguished people. Ever restless, over the next 20 years Ed showed up at nearly every boom town in the West.
Schieffelin had made a practice of studying maps and believed there was a great "continental belt" of mineral wealth that extended from South America through Mexico, the United States, and British Columbia.Berton, P., (1958). ''The Klo(=)dike Fever''. Alfred A Knopf: New York, pp. 11–12. During 1882, Ed prepared for what he planned to be a three-year survey of mineral wealth. He began the expedition with his brother Al and three others on a trip up the Yukon River
The Yukon River (Gwichʼin language, Gwich'in: ''Ųųg Han'' or ''Yuk Han'', Central Alaskan Yup'ik language, Yup'ik: ''Kuigpak'', Inupiaq language, Inupiaq: ''Kuukpak'', Deg Xinag language, Deg Xinag: ''Yeqin'', Hän language, Hän: ''Tth'echù' ...
. They commissioned construction of and fitted out a small, shallow-draft sternwheel steamer which they named the ''New Packet''. Schieffelin prospected during the trip in Alaska and found some specks of gold. He was for a while convinced he had found the continental belt he had been searching for. But he was extremely discouraged by the Arctic cold he experienced, up to 50 F below zero (-46 C). He decided that mining in Alaska was a lost cause and he returned to the lower 48 states.
In 1883, he returned to San Francisco, where he met Mrs. Mary E. Brown. They married the same year in La Junta, Colorado
La Junta is a home rule municipality in , the county seat of, and the most populous municipality of Otero County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 7,322 at the 2020 United States Census. La Junta is located on the Arkansas Ri ...
, and they spent part of the winter in Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Utah, most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the county seat, seat of Salt Lake County, Utah, Sal ...
, Utah. In the spring of 1884, they returned to California, where Ed built a mansion for his wife across the bay from San Francisco in Alameda
An alameda is a Avenue (landscape), street or path lined with trees () and may refer to:
Places Canada
*Alameda, Saskatchewan, town in Saskatchewan
**Grant Devine Dam, formerly ''Alameda Dam'', a dam and reservoir in southern Saskatchewan
Chile
...
. They bought a home in Los Angeles that they shared with Ed's brother Al until Al died of consumption
Consumption may refer to:
*Resource consumption
*Tuberculosis, an infectious disease, historically
* Consumption (ecology), receipt of energy by consuming other organisms
* Consumption (economics), the purchasing of newly produced goods for curren ...
in 1885.
Early death

 In 1897 Schieffelin bought a ranch near his brothers Effingham (Eff) and Jacob (Jay) outside Woodville, now
In 1897 Schieffelin bought a ranch near his brothers Effingham (Eff) and Jacob (Jay) outside Woodville, now Rogue River, Oregon
Rogue River is a city in Jackson County, Oregon, United States. As of the 2020 census the population was 2,407.
History
The settlement was known as "Woodville" for many years, but was changed to "Rogue River" about 1912. The Woodville post offi ...
. He continued prospecting in the Canyonville area, where he searched for gold and silver. On May 12, 1897, after he had not shown up in town for supplies for several days, his neighbor checked on him and found him face down on the floor of his miner's cabin. The coroner ruled that he had died of a heart attack. The ore samples found in his cabin were later reported to have assayed at more than $2,000 to the ton. Other reports from his family said it was only valued at $7 per ton. Schieffelin did not leave a map or directions behind pointing to the origins of his discovery. He was initially buried near his cabin about east of Canyonville.
It was shortly afterward learned that he had requested to be buried in Tombstone. "It is my wish, if convenient, to be buried in the dress of a prospector, my old pick and canteen with me, on top of the granite hills, about three miles westerly from the City of Tombstone, Arizona, and that a monument, such as prospectors build when locating a mining claim, be built over my grave." Schieffelin was interred about northwest of Tombstone, Arizona
Tombstone is a historic city in Cochise County, Arizona, United States, founded in 1877 by prospector Ed Schieffelin in what was then Pima County, Arizona Territory. It became one of the last boomtowns in the American frontier. The town grew si ...
, near the dry wash in which he originally found silver ore and the later location of the Grand Central Mine. He was buried as his will specified: in mining clothes, with pick, shovel, and his old canteen. He divided his estate between his wife and his brother Jay. "I give my wife, Mary E. Schieffelin, all interests, both real and personal properties—in Alameda and Santa Clara Counties, California—also fifteen $1,000 University of Arizona Bonds. All other properties, both real and personal, I give to my brother, Jay L. Schieffelin." Mary Schieffelin moved to New York City after her husband's death.
Legacy
A tall monument representing the type of marker a miner makes in claiming a strike was erected near the spot of his original claim. The plaque on it reads, "Ed Shieffelin, died May 12, 1897, aged 49 years, 8 months. A dutiful son, a faithful husband, a kind brother, and a true friend." Years before, Schieffelin had written, "I never wanted to be rich, I just wanted to get close to the earth and see mother nature's gold." Schieffelin Gulch Road in the Rogue Valley, Oregon is named after the family who homesteaded there. There are widely varying estimates of the value of gold and silver mined during the course of Tombstone's history. In 1883, writer Patrick Hamilton estimated that during the first four years of activity the mines produced about $25,000,000 (approximately $ today). Other estimates include $40 million to $85 million (about $ to $ today). Renewed mining is planned for the area. Thecharacter actor
A character actor is a supporting actor who plays unusual, interesting, or eccentric characters.28 April 2013, The New York Acting SchoolTen Best Character Actors of All Time Retrieved 7 August 2014, "..a breed of actor who has the ability to b ...
Strother Martin
Strother Douglas Martin Jr. (March 26, 1919 – August 1, 1980) was an American character actor who often appeared in support of John Wayne and Paul Newman and in Western films directed by John Ford and Sam Peckinpah. Among Martin's memorable pe ...
played Schieffelin in the 1967 episode "Silver Tombstone" of the syndicated television series
A television show – or simply TV show – is any content produced for viewing on a television set which can be broadcast via over-the-air, satellite television, satellite, or cable television, cable, excluding breaking news, television adverti ...
''Death Valley Days
''Death Valley Days'' is an American old-time radio and television anthology series featuring true accounts of the American Old West, particularly the Death Valley country of southeastern California. Created in 1930 by Ruth Woodman, the program ...
''. In the story line, after years of failure, Schieffelin is convinced that he is on the verge of a bonanza. He invites his brother to join him in the pending strike. Jamie Farr
Jamie Farr (born Jameel Joseph Farah; July 1, 1934) is an American comedian and actor. He is best known for playing the cross-dressing Corporal turned Sergeant Maxwell Q. Klinger in the CBS television sitcom ''M*A*S*H''.
He was inducted to ...
appears as Dick Gird.
References
Further reading
* Craig, R. Bruce, editor. ''Portrait of a Prospector: Edward Schieffelin's Own Story''. (2017) Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press. {{DEFAULTSORT:Schieffelin, Edward 1847 births 1897 deaths American frontier American prospectors Explorers of Alaska People from Douglas County, Oregon People of the American Old West People of the Klondike Gold Rush People of pre-statehood Alaska Southwestern United States People from Wellsboro, Pennsylvania People from Rogue River, Oregon Winthrop family