Estimation statistics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Estimation statistics, or simply estimation, is a data analysis framework that uses a combination of
meta-analysis
Starting in the 1980s, the
citations
to "meta-analysis" in
Kenneth Rothman
banned the use of p-values from the journal ''Epidemiology''; compliance was high among authors but this did not substantially change their analytical thinking. In the 2010s, Geoff Cumming published
textbook
dedicated to estimation statistics, along with software in Excel designed to teach effect-size thinking, primarily to psychologists. Also in the 2010s, estimation methods were increasingly adopted in neuroscience. In 2013, the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association recommended to use estimation in addition to hypothesis testing. Also in 2013, the Uniform Requirements for Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical Journals document made a similar recommendation: "Avoid relying solely on statistical hypothesis testing, such as P values, which fail to convey important information about effect size." In 2019, over 800 scientists signed an open comment calling for the entire concept of statistical significance to be abandoned. In 2019, the
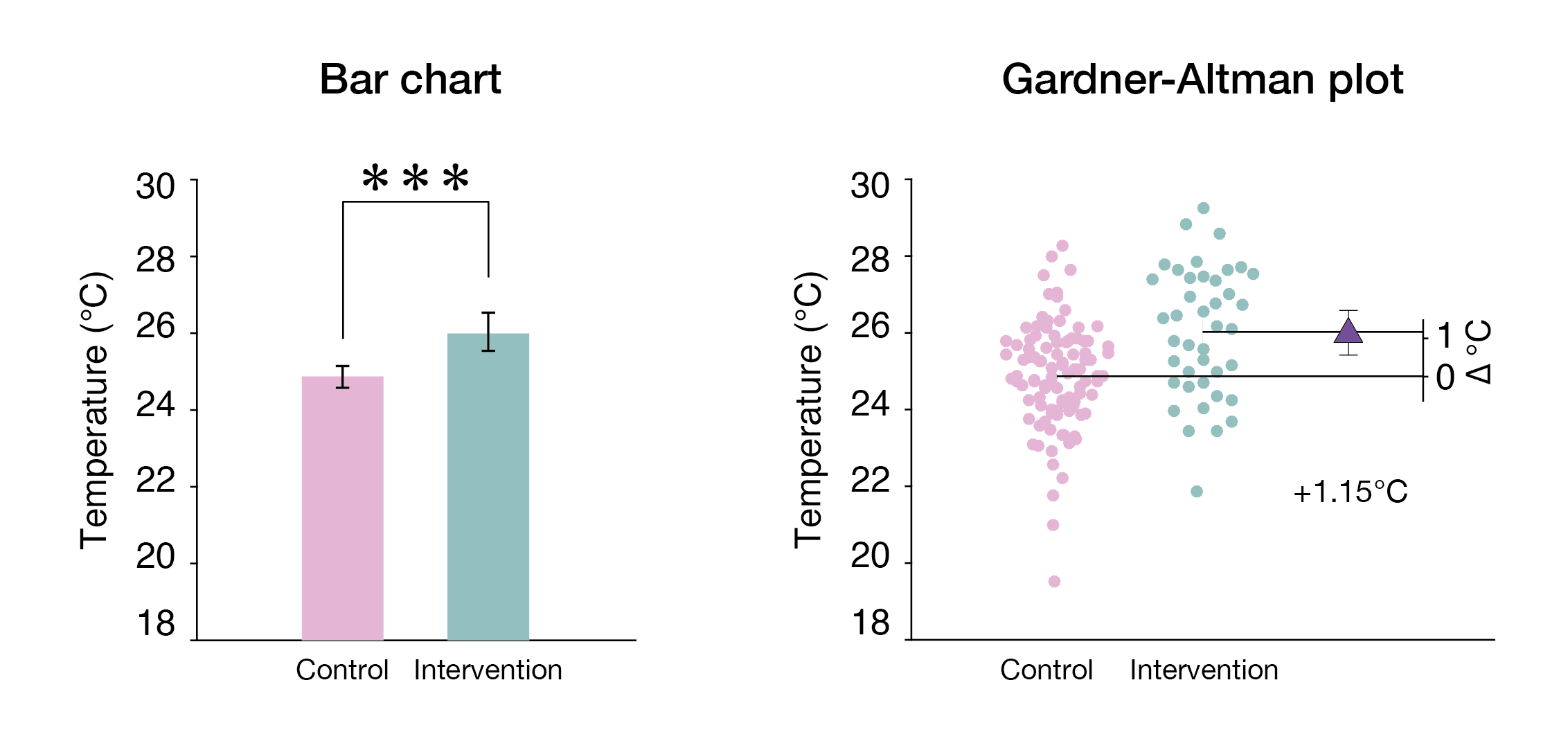
paired data
The key instructions to make this chart are as follows: (1) display all observed values for both groups side-by-side; (2) place a second axis on the right, shifted to show the mean difference scale; and (3) plot the mean difference with its confidence interval as a marker with error bars. Gardner-Altman plots can be generated wit
DABEST-Python
o
dabestr
alternatively, the analyst can use GUI software like th
Estimation Stats
app.
Geoff Cumming
introduced the use of a secondary panel to plot two or more mean differences and their confidence intervals, placed below the observed values panel; this arrangement enable
easy comparison
of mean differences ('deltas') over several data groupings. Cumming plots can be generated with th
ESCI packageDABEST
or th
Estimation Stats app
robust effect sizes
including Cliff's delta and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic.
ESCI web app
effect size
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the ...
s, confidence intervals, precision planning, and meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
to plan experiments, analyze data and interpret results. It complements hypothesis testing approaches such as null hypothesis significance testing (NHST), by going beyond the question is an effect present or not, and provides information about how large an effect is. Estimation statistics is sometimes referred to as ''the new statistics''.
The primary aim of estimation methods is to report an effect size
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the ...
(a point estimate
In statistics, point estimation involves the use of sample data to calculate a single value (known as a point estimate since it identifies a point in some parameter space) which is to serve as a "best guess" or "best estimate" of an unknown popu ...
) along with its confidence interval, the latter of which is related to the precision of the estimate. The confidence interval summarizes a range of likely values of the underlying population effect. Proponents of estimation see reporting a ''P'' value as an unhelpful distraction from the important business of reporting an effect size with its confidence intervals, and believe that estimation should replace significance testing for data analysis.
History
Starting in 1929, physicist Raymond Thayer Birge published review papers in which he used weighted-averages methods to calculate estimates of physical constants, a procedure that can be seen as the precursor to modernmeta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
.
In the 1930s Jerzy Neyman
Jerzy Spława-Neyman (April 16, 1894 – August 5, 1981; ) was a Polish mathematician and statistician who first introduced the modern concept of a confidence interval into statistical hypothesis testing and, with Egon Pearson, revised Ronald Fis ...
published a series of papers on statistical estimation where he defined the mathematics and terminology of confidence intervals.
Neyman, J. (1934). On the Two Different Aspects of the Representative Method: The Method of Stratified Sampling and the Method of Purposive Selection. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 97(4), 558–625. https://doi.org/10.2307/2342192 (see Note I in the appendix)
In the 1960s, estimation statistics was adopted by the non-physical sciences with the development of the standardized effect size by Jacob Cohen.
In the 1970s, modern research synthesis was pioneered by Gene V. Glass with the first systematic review and meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
for psychotherapy. This pioneering work subsequently influenced the adoption of meta-analyses for medical treatments more generally.
In the 1980s and 1990s, estimation methods were extended and refined for practical application by biostatisticians including Larry Hedges, Michael Borenstein, Doug Altman, Martin Gardner, and many others, with the development of the modern (medicalmeta-analysis
Starting in the 1980s, the
systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
, used in conjunction with meta-analysis, became a technique widely used in medical research. There are over 200,00citations
to "meta-analysis" in
PubMed
PubMed is an openly accessible, free database which includes primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institute ...
.
In the 1990s, editoKenneth Rothman
banned the use of p-values from the journal ''Epidemiology''; compliance was high among authors but this did not substantially change their analytical thinking. In the 2010s, Geoff Cumming published
textbook
dedicated to estimation statistics, along with software in Excel designed to teach effect-size thinking, primarily to psychologists. Also in the 2010s, estimation methods were increasingly adopted in neuroscience. In 2013, the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association recommended to use estimation in addition to hypothesis testing. Also in 2013, the Uniform Requirements for Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical Journals document made a similar recommendation: "Avoid relying solely on statistical hypothesis testing, such as P values, which fail to convey important information about effect size." In 2019, over 800 scientists signed an open comment calling for the entire concept of statistical significance to be abandoned. In 2019, the
Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience (SfN) is a professional society, headquartered in Washington, D.C., for basic scientists and physicians around the world whose research is focused on the study of the brain and nervous system. It is especially well k ...
journal eNeuro instituted a policy recommending the use of estimation graphics as the preferred method for data presentation. And in 2022, the International Society of Physiotherapy Journal Editors recommended the use of estimation methods instead of null hypothesis statistical tests.
Despite the widespread adoption of meta-analysis for clinical research, and recommendations by several major publishing institutions, the estimation framework is not routinely used in primary biomedical research.
Methodology
Many significance tests have an estimation counterpart; in almost every case, the test result (or itsp-value
In null-hypothesis significance testing, the ''p''-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the result actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct. A very small ''p''-value means ...
) can be simply substituted with the effect size and a precision estimate. For example, instead of using Student's t-test
Student's ''t''-test is a statistical test used to test whether the difference between the response of two groups is statistically significant or not. It is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's ''t''- ...
, the analyst can compare two independent groups by calculating the mean difference and its 95% confidence interval. Corresponding methods can be used for a paired t-test and multiple comparisons. Similarly, for a regression analysis, an analyst would report the coefficient of determination
In statistics, the coefficient of determination, denoted ''R''2 or ''r''2 and pronounced "R squared", is the proportion of the variation in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variable(s).
It is a statistic used in t ...
(R2) and the model equation instead of the model's p-value.
However, proponents of estimation statistics warn against reporting only a few numbers. Rather, it is advised to analyze and present data using data visualization. Examples of appropriate visualizations include the scatter plot
A scatter plot, also called a scatterplot, scatter graph, scatter chart, scattergram, or scatter diagram, is a type of plot or mathematical diagram using Cartesian coordinates to display values for typically two variables for a set of dat ...
for regression, and Gardner–Altman plots for two independent groups. While historical data-group plots (bar charts, box plots, and violin plots) do not display the comparison, estimation plots add a second axis to explicitly visualize the effect size.

Gardner–Altman plot
The Gardner–Altman mean difference plot was first described byMartin Gardner
Martin Gardner (October 21, 1914May 22, 2010) was an American popular mathematics and popular science writer with interests also encompassing magic, scientific skepticism, micromagic, philosophy, religion, and literatureespecially the writin ...
and Doug Altman in 1986; it is a statistical graph designed to display data from two independent groups. There is also a version suitable fopaired data
The key instructions to make this chart are as follows: (1) display all observed values for both groups side-by-side; (2) place a second axis on the right, shifted to show the mean difference scale; and (3) plot the mean difference with its confidence interval as a marker with error bars. Gardner-Altman plots can be generated wit
DABEST-Python
o
dabestr
alternatively, the analyst can use GUI software like th
Estimation Stats
app.
Cumming plot
For multiple groupsGeoff Cumming
introduced the use of a secondary panel to plot two or more mean differences and their confidence intervals, placed below the observed values panel; this arrangement enable
easy comparison
of mean differences ('deltas') over several data groupings. Cumming plots can be generated with th
ESCI package
or th
Estimation Stats app
Other methodologies
In addition to the mean difference, there are numerous othereffect size
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the ...
types, all with relative benefits. Major types include effect sizes in the Cohen's ''d'' class of standardized metrics, and the coefficient of determination
In statistics, the coefficient of determination, denoted ''R''2 or ''r''2 and pronounced "R squared", is the proportion of the variation in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variable(s).
It is a statistic used in t ...
(R2) for regression analysis. For non-normal distributions, there are a number of morrobust effect sizes
including Cliff's delta and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic.
Flaws in hypothesis testing
Inhypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data provide sufficient evidence to reject a particular hypothesis. A statistical hypothesis test typically involves a calculation of a test statistic. T ...
, the primary objective of statistical calculations is to obtain a p-value
In null-hypothesis significance testing, the ''p''-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the result actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct. A very small ''p''-value means ...
, the probability of seeing an obtained result, or a more extreme result, when assuming the null hypothesis
The null hypothesis (often denoted ''H''0) is the claim in scientific research that the effect being studied does not exist. The null hypothesis can also be described as the hypothesis in which no relationship exists between two sets of data o ...
is true. If the p-value is low (usually < 0.05), the statistical practitioner is then encouraged to reject the null hypothesis. Proponents of estimation reject the validity of hypothesis testing for the following reasons, among others:
* P-values are easily and commonly misinterpreted. For example, the p-value is often mistakenly thought of as 'the probability that the null hypothesis is true.'
* The null hypothesis is always wrong for every set of observations: there is always some effect, even if it is minuscule.
* Hypothesis testing produces dichotomous yes-no answers, while discarding important information about magnitude.
* Any particular p-value arises through the interaction of the effect size
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the ...
, the sample size
Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences abo ...
(all things being equal a larger sample size produces a smaller p-value) and sampling error.
*At low power, simulation reveals that sampling error makes p-values extremely volatile.
Benefits of estimation statistics
Quantification
While p-values focus on yes/no answers, estimation directs the analyst's attention to quantification.Advantages of confidence intervals
Confidence intervals behave in a predictable way. By definition, 95% confidence intervals have a 95% chance of covering the underlying population mean (μ). This feature remains constant with increasing sample size; what changes is that the interval becomes smaller. In addition, 95% confidence intervals are also 83% prediction intervals: one (pre experimental) confidence interval has an 83% chance of covering any future experiment's mean. As such, knowing a single experiment's 95% confidence intervals gives the analyst a reasonable range for the population mean. Nevertheless, confidence distributions and posterior distributions provide a whole lot more information than a single point estimate or intervals, that can exacerbate dichotomous thinking according to the interval covering or not covering a "null" value of interest (i.e. the Inductive behavior of Neyman as opposed to that of Fisher).Evidence-based statistics
Psychological studies of the perception of statistics reveal that reporting interval estimates leaves a more accurate perception of the data than reporting p-values.Precision planning
The precision of an estimate is formally defined as 1/variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion ...
, and like power, increases (improves) with increasing sample size. Like power, a high level of precision is expensive; research grant applications would ideally include precision/cost analyses. Proponents of estimation believe precision planning should replace power since statistical power itself is conceptually linked to significance testing. Precision planning can be done with thESCI web app
See also
*Effect size
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the ...
* Cohen's h
* Interval estimation
In statistics, interval estimation is the use of sample data to estimate an '' interval'' of possible values of a parameter of interest. This is in contrast to point estimation, which gives a single value.
The most prevalent forms of interval es ...
* Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
* Statistical significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when a result at least as "extreme" would be very infrequent if the null hypothesis were true. More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the ...
References
{{Statistics Estimation theory Effect size