Environmental communication on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
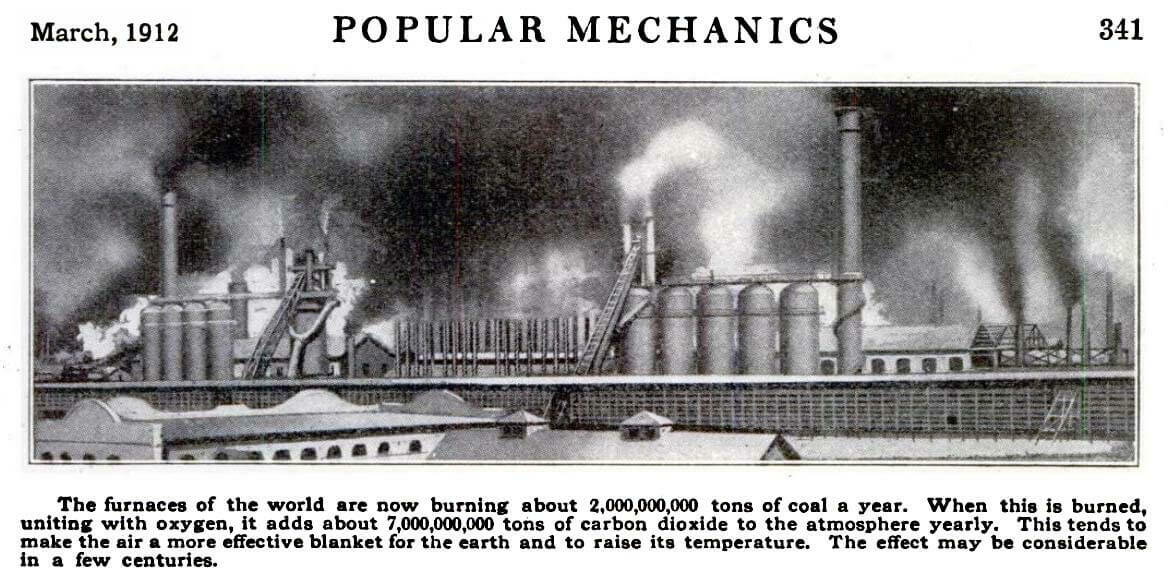 Environmental communication is "the dissemination of information and the implementation of communication practices that are related to the environment. In the beginning, environmental communication was a narrow area of communication; however, nowadays, it is a broad field that includes research and practices regarding how different actors (e.g., institutions, states, people) interact with regard to topics related to the environment and how cultural products influence society toward environmental issues".
Environmental communication also includes human interactions with the environment. This includes a wide range of possible interactions, from
Environmental communication is "the dissemination of information and the implementation of communication practices that are related to the environment. In the beginning, environmental communication was a narrow area of communication; however, nowadays, it is a broad field that includes research and practices regarding how different actors (e.g., institutions, states, people) interact with regard to topics related to the environment and how cultural products influence society toward environmental issues".
Environmental communication also includes human interactions with the environment. This includes a wide range of possible interactions, from
International Environmental Communication Association (IECA)
– a professional association for environmental communication practitioners, teachers, and scholars
ClimateClock: clock counting down to 1,5°C temperature rise
*Lexington book series o
Environmental Communication and Nature: Conflict and Ecoculture in the Anthropocene
Talk.Eco: Resources for Environmental Communicators
– a website featuring curated resources for environmental communication professionals
Environmental Communication: What it is and Why it Matters
by Mark Meisner
Environmental Communication: Research Into Practice
– an online course
Bibliography of books in environmental communication
by Mark Meisner
ECOresearch Network
– Research Network on Environmental Online Communication
Indications: Environmental Communication
blog (inactive), 2010–2012
About the Environmental Communication Division
– The International Communication Association Environmental Communication Division
Communication et environnement, le pacte impossible
by Thierry Libaert {{Environmental humanities Interdisciplinary subfields of sociology Communication studies
 Environmental communication is "the dissemination of information and the implementation of communication practices that are related to the environment. In the beginning, environmental communication was a narrow area of communication; however, nowadays, it is a broad field that includes research and practices regarding how different actors (e.g., institutions, states, people) interact with regard to topics related to the environment and how cultural products influence society toward environmental issues".
Environmental communication also includes human interactions with the environment. This includes a wide range of possible interactions, from
Environmental communication is "the dissemination of information and the implementation of communication practices that are related to the environment. In the beginning, environmental communication was a narrow area of communication; however, nowadays, it is a broad field that includes research and practices regarding how different actors (e.g., institutions, states, people) interact with regard to topics related to the environment and how cultural products influence society toward environmental issues".
Environmental communication also includes human interactions with the environment. This includes a wide range of possible interactions, from interpersonal communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish several personal and relational goals. Communica ...
and virtual communities
A virtual community is a social network of individuals who connect through specific social media, potentially crossing geographical and political boundaries in order to pursue mutual interests or goals. Some of the most pervasive virtual commu ...
to participatory decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
and environmental media coverage. From the perspective of practice, Alexander Flor defines environmental communication as the application of communication approaches, principles, strategies, and techniques to environmental management and protection.
History
Environmental Communication, breaking off from traditional rhetorical theory, emerged in the United States around the 1980s. Researchers began studying environmental communication as a stand-alone theory because of the way environmental activists used images and wording to persuade their public's. Since then, environmental communication theory has reached multiple milestones including the creation of the journal of environmental communication in 2007.In academia
As an academic field, environmental communication emerged from interdisciplinary work involvingcommunication
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether Intention, unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not onl ...
, environmental studies
Environmental studies (EVS or EVST) is a multidisciplinary academic field which systematically studies human behavior, human interaction with the Natural environment, environment. Environmental studies connects principles from the physical sci ...
, environmental science, risk analysis
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environ ...
and management, sociology
Sociology is the scientific study of human society that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of Interpersonal ties, social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. The term sociol ...
, and political ecology
Political ecology is the study of the relationships between political, economic and social factors with environmental issues and changes. Political ecology differs from apolitical ecological studies by politicizing environmental issues and pheno ...
.
In his 2004 textbook, Alexander Flor considers environmental communication to be a significant element in the environmental sciences, which he believes to be transdisciplinary
Transdisciplinarity is an approach that iteratively interweaves knowledge systems, skills, methodologies, values and fields of expertise within inclusive and innovative collaborations that bridge academic disciplines and community perspectives, ...
. He begins his textbook on environmental communication with a declarative statement: "Environmentalism as we know it today began with environmental communication. The environmental movement
The environmental movement (sometimes referred to as the ecology movement) is a social movement that aims to protect the natural world from harmful environmental practices in order to create sustainable living. In its recognition of humanity a ...
was ignited by a spark from a writer’s pen, or more specifically and accurately, Rachel Carson
Rachel Louise Carson (May 27, 1907 – April 14, 1964) was an American marine biologist, writer, and conservation movement, conservationist whose sea trilogy (1941–1955) and book ''Silent Spring'' (1962) are credited with advancing mari ...
’s typewriter." According to Flor, environmental communication has six essentials: knowledge of ecological laws; sensitivity to the cultural dimension; ability to network effectively; efficiency in using media for social agenda setting; appreciation and practice of environmental ethics
In environmental philosophy, environmental ethics is an established field of practical philosophy "which reconstructs the essential types of argumentation that can be made for protecting natural entities and the sustainable use of natural resourc ...
; and conflict resolution, mediation and arbitration. In an earlier book published in 1993, Flor and colleague Ely Gomez explore the development of an environmental communication curriculum from the perspectives of practitioners from the government, the private sector, and the academe.
The role of Environmental Communication in education and academia is centered around goals through pedagogy
Pedagogy (), most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political, and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken ...
. These are aimed at trying to increase ecological wakefulness, support a variety of practice-based ways of learning and building a relationship of being environmental change advocates.
In general, Environmental skepticism is an increasing challenge for environmental rhetoric.
Climate change communication
Information Technology and Environmental Communication
The technological breakthroughs empowered by the appearance of the Internet are also contributing to environmental problems. Air pollution, acid rain, global warming, and the reduction of natural sources are also an outcome of online technologies. Netcraft argued that in the world, there are 7,290,968 web-facing computers, 214,036,874 unique domain names, and 1,838,596,056 websites leading to significant power consumption. Therefore, notions such as “Green Websites” have emerged for helping to tackle this issue. “Green Websites” is “associated with the climate-friendly policies and aims to improve the natural habitat of Earth. Renewable sources, the use of black color, and the highlight of the environmental news are some of the easiest and cheapest ways to contribute positively to climate issues”. The aforementioned term is under the umbrella of “Green Computing,” which is aiming to limit the carbon footprints, energy consumption and benefit the computing performance. Information and Communications technology aka ICT, has an obsessive amount of environment impacts through different types of disposal of devices and equipment that have been portrayed to give off harmful gasses and Bluetooth waves into the atmosphere that increase the carbon emissions. This has also shown that the technology has been used to minimize energy use, society always wants new technology no matter if it affects the environment good or not, but ICT has been cutting back and putting out better technology for our environment while still being able to communicate through society.Symbolic action
Environmental communication is also a type of symbolic action that serves two functions: Environmental human communication is pragmatic because it helps individuals and organizations to accomplish goals and do things through communication. Examples include educating, alerting, persuading, and collaborating. Environmental human communication is constitutive because it helps shape human understanding ofenvironmental issue
Environmental issues are disruptions in the usual function of ecosystems. Further, these issues can be caused by humans (human impact on the environment) or they can be natural. These issues are considered serious when the ecosystem cannot recov ...
s, themselves, and nature. Examples include values, attitudes, and ideologies regarding nature and environmental issues.
In the book ''Pragmatic Environmentalism: Towards a Rhetoric of Eco-Justice'', environmental philosopher Shane Ralston criticizes Cox's pragmatic function of environmental communication for being too shallow and instrumental, recommending instead a deeper account borrowed from Pragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition that views language and thought as tools for prediction, problem solving, and action, rather than describing, representing, or mirroring reality. Pragmatists contend that most philosophical topics� ...
: " even better way to move beyond a conception of pragmatic rhetoric as shallow instrumentalism and deepen the meaning of pragmatic ..is to look instead to philosophical pragmatism’s other rich resources, for instance, to its fallibilism, experimentalism, and meliorism."
Environmental nature communication occurs when plants actually communicate within ecosystems: "A plant injured on one leaf by a nibbling insect can alert its other leaves to begin anticipatory defense responses." Furthermore, "plant biologists have discovered that when a leaf gets eaten, it warns other leaves by using some of the same signals as animals". The biologists are "starting to unravel a long-standing mystery about how different parts of a plant communicate with one another."
All beings are connected by the Systems Theory
Systems theory is the Transdisciplinarity, transdisciplinary study of systems, i.e. cohesive groups of interrelated, interdependent components that can be natural or artificial. Every system has causal boundaries, is influenced by its context, de ...
, which submits that one of the three critical functions of living systems is the exchange of information with its environment and with other living systems (the other two being the exchange of materials and the exchange of energy). Flor extends this argument, saying: "All living systems, from the simplest to the most complex, are equipped to perform these critical functions. They are called ''critical'' because they are necessary for the survival of the living system. Communication is nothing more than the exchange of information. Hence, at its broadest sense, environmental communication is necessary for the survival of every living system, be it an organism, an ecosystem, or (even) a social system."
Environmental Communication plays an integral role in sustainability science
Sustainability science first emerged in the 1980s and has become a new academic discipline.
Similar to agricultural science or health science, it is an applied science defined by the practical problems it addresses. Sustainability science focuses ...
. By taking knowledge and putting it into action. Since Environmental Communication is focused on everyday practices of speaking and collaborating, it has a deep understanding in the public discussion of environmental policy. Something that sustainability science has a shortcoming of. Sustainability science requires cooperation between stakeholders and thus requires constructive communication between those stakeholders to create sustainable change.
Limitations
Robert Cox is a leader in the discipline of environmental communication and its role in thepublic sphere
The public sphere () is an area in social relation, social life where individuals can come together to freely discuss and identify societal problems, and through that discussion, Social influence, influence political action. A "Public" is "of or c ...
. Cox covers the importance of Environmental Communication and the role it plays in policy-making processes, advocacy campaigns, journalism, and environmental movements. Something that Cox overlooks in the importance of ''Environmental communication in the Public Sphere'' is the role visual and aural communication, electronic and digital media, and perhaps most glaringly, popular culture. Along with the aforementioned limitations the media plays a major role in the conversation around the environment because of the framing effect and the impact that it has on the overall perception of the environment and the discussion surrounding it. Framing is something that has been important to many movements in the past but it is more than just creating slogans and the like. George Lakoff argues in favor of a social movement approach similar to the feminist movement or the civil rights movement.
The field of Environmental Communication also faces challenges of being silenced and invalidated by governments. Environmental communication like many disciplines had challenges with people with opposing views points that make it difficult to spread a certain message. Environmental Communication like many highly polarized topics is prone to confirmation bias
Confirmation bias (also confirmatory bias, myside bias, or congeniality bias) is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or Value (ethics and social sciences), val ...
which makes it difficult to have compromises in the world of policy making for the environmental crisis. Along with confirmation bias, Echo chambers do much the same thing and are discussed by Christel van Eck who says with respect to environmental communication that echo chambers can reinforce preexisting climate change perceptions. which serve to make it more difficult to engage in real conversations about the topic. Another reason that it can be difficult to communicate about these things is that many people try to use directional motivated reasoning in which they try to find evidence to push a specific narrative on the topic. The effect that this has had on communicating this idea is examined by Robin Bayes and others who say that it can be very detrimental and divisive. One of the things that makes environmental narratives so dangerous is that it changes so often that it is very difficult to keep the information the same as it travels. This according to Miyase Christensen makes it so that the spreading of these narratives can be dangerous.
Environmental Communication faces a variety of challenges in the political environment due to increased polarization. People often feel threatened by arguments that do not align with their beliefs ( boomerang effect). These can lead to psychological reactance
In psychology, reactance is an unpleasant motivational reaction to offers, persons, rules, regulations, advice, recommendations, information, and messages that are perceived to threaten or eliminate specific behavioral freedoms. Reactance occurs ...
, counter-arguing, and anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
. This can cause difficulty in making progress in political change regarding environmental issues. When it comes to the increased polarization of movements regarding the environment some people point to the impact of identity campaigns because of the argument that fear is counterproductive. Robert Brulle argues this point and calls for a shift away from these identity campaigns and moving towards challenge campaigns.
Another limitation of the conversation regarding the environment is the fact that there are multiple agendas being set by different groups in China and the fact that they are different from one another. Along with this the idea that these two different groups are in some sort of a discussion is presented by Xiaohui Wang et. al.
A culture centered approach has been suggested by some like Debashish Munshi. These people argue for enacting change based on the knowledge of older cultures however it has to exist in a way that does not abuse the relationship between the older cultures and our current one which according to Munshi makes it very difficult to enact.
Environmental Communication Theory
To understand the ways in which environmental communication has an effect on individuals, researchers believe that one's view on the environment shapes their views in a variety of ways. The overall study of environmental communication consists of the idea that nature "speaks." In this field, theories exist in an effort to understand the basis of environmental communication.Material-Symbolic Discourse
Researchers view environmental communication as symbolic and material. They argue that the material world helps shape communication as communication helps shape the world. The word environment, a primary symbol in western culture, is used to shape cultural understandings of the material world. This understanding gives researchers the ability to study how cultures react to the environment around them.Mediating-Human Nature Relations
Humans react and form opinions based on the environment around them. Nature plays a role in human relations. This theory strives to make a connection between human and nature relations. This belief is at the core of environmental communication because it seeks to understand how nature affects human behavior and identity. Researchers point out that there can be a connection made with this theory andphenomenology
Phenomenology may refer to:
Art
* Phenomenology (architecture), based on the experience of building materials and their sensory properties
Philosophy
* Phenomenology (Peirce), a branch of philosophy according to Charles Sanders Peirce (1839� ...
.
= Applied Activist Theory
= It is difficult to avoid the "call to action" when talking about environmental communication because it is directly linked with issues such as climate change, endangered animals, and pollution. Scholars find it difficult to publish objective studies in this field. However, others argue that it is their ethical duty to inform the public on environmental change while providing solutions to these issues. This idea that it can be damaging to a scientist's reputation to offer up opinions or solutions to the problem of Climate Change has been furthered by research done by Doug Cloud who had findings affirming this idea. As the following section suggests, there are many divisions of studies and practices in the field of environmental communication, one of which being social marketing and advocacy campaigns. Though this is a broad topic, a key aspect of successful environmental campaigns is the language used in campaign material. Researchers have found that when individuals are concerned & interested about environmental actions, they take well to messages with assertive language; However, individuals who are less concerned & interested about environmental stances, are more receptive to less assertive messages. Although communications on environmental issues often aim to push into action consumers who already perceive the issue being promoted as important, it is important for such message producers to analyze their target audience and tailor messages accordingly. While there are some findings that there is a problem with scientists advocating for certain positions in a study conducted by John Kotcher and others it was found that there was no real difference between the credibility of scientists regardless of their advocacy unless they directly tried to argue in favor a specific solution to the problem.Areas of study and practice
According to J. Robert Cox, the field of environmental communication is composed of seven major areas of study and practice: # Environmental rhetoric and discourse # Media andenvironmental journalism
Environmental journalism is the collection, verification, production, distribution and exhibition of information regarding current events, trends, and issues associated with the non-human world. To be an environmental journalist, one must have an ...
# Public participation in environmental decision making
# Social marketing
Social marketing is a marketing approach which focuses on influencing behavior with the primary goal of achieving the "common good". It utilizes the elements of commercial marketing and applies them to social concepts. However, to see social ...
and advocacy campaigns
# Environmental collaboration and conflict resolution
# Risk communication
# Representations of nature in popular culture
Popular culture (also called pop culture or mass culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of cultural practice, practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as popular art
and f. pop art
F is the sixth letter of the Latin alphabet.
F may also refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* F or f, the number 15 (number), 15 in hexadecimal and higher positional systems
* ''p'F'q'', the hypergeometric function
* F-distributi ...
or mass art, sometimes contraste ...green marketing
Green marketing refers to the marketing of products that are considered environmentally safe. It encompasses a broad range of activities, including product modification, changes to the production process, sustainable packaging, and modifications to ...
Publications
Journals
Peer-reviewed journals related to environmental communication include: * '' Applied Environmental Education and Communication'' * ''Environmental Communication
Environmental communication is "the dissemination of information and the implementation of communication practices that are related to the Natural environment, environment. In the beginning, environmental communication was a narrow area of commun ...
''
Books
* Anderson, Alison (1997). ''Media, Culture and the Environment''. London:Routledge
Routledge ( ) is a British multinational corporation, multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, academic journals, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanit ...
* Anderson, Alison (2014). ''Media, Environment and the Network Society''. Basingstoke: Palgrave
* Boykoff, Maxwell T (2019). ''Creative (Climate) Communications: Productive Pathways for Science, Policy and Society''. London: Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
* Corbett, Julia B (2006). ''Communicating Nature: How We Create and Understand Environmental Messages''. Washington, D.C.: Island Press
Island Press is a nonprofit, environmental publisher based in Washington, D.C., United States, that specializes in natural history, ecology, conservation, and the built environment. Established in 1978, Island Press generates about half of its ...
*
*Fletcher, C Vail & Jeanette Lovejoy (2018) ''Natural Disasters and Risk Communication: Implications of the Cascadia Subduction Zone Megaquake. Maryland: Lexington Books
Bloomsbury Publishing plc is a British worldwide publishing house of fiction and non-fiction. Bloomsbury's head office is located on Bedford Square in Bloomsbury, an area of the London Borough of Camden. It has a US publishing office located in ...
''
* Flor, Alexander G (2004). ''Environmental Communication: Principles, Approaches and Strategies of Communication Applied to Environmental Management''. Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines: University of the Philippines Open University
The University of the Philippines Open University (UPOU) is a public research university and is the fifth constituent university of the University of the Philippines System. The majority of UPOU students are based in the Philippines but all of ...
*Mathur, Piyush (2017). ''Technological Forms and Ecological Communication: A Theoretical Heuristic''. Lanham, Maryland: Lexington Books
Bloomsbury Publishing plc is a British worldwide publishing house of fiction and non-fiction. Bloomsbury's head office is located on Bedford Square in Bloomsbury, an area of the London Borough of Camden. It has a US publishing office located in ...
*Ralston, Shane (2013). ''Pragmatic Environmentalism: Towards a Rhetoric of Eco-Justice.'' Leicester: Troubador.
*Stephens, Murdoch (2018). ''Critical Environmental Communication: How Does Critique Respond to the Urgency of Climate Change.'' Maryland: Lexington Books
Bloomsbury Publishing plc is a British worldwide publishing house of fiction and non-fiction. Bloomsbury's head office is located on Bedford Square in Bloomsbury, an area of the London Borough of Camden. It has a US publishing office located in ...
See also
* Climate emergency declaration (includes usage of the term "climate emergency") *Climate crisis
''Climate crisis'' is a term that is used to describe global warming and climate change and their effects. This term and the term ''climate emergency'' have been used to emphasize the threat of global warming to Earth's natural environment an ...
(about usage of the term)
* Communication studies
Communication studies (or communication science) is an academic discipline that deals with processes of human communication and behavior, patterns of communication in interpersonal relationships, social interactions and communication in differ ...
* List of environmental issues
Environmental issues are harmful aspects of human activity on the biophysical environment. This alphabetical list is loosely divided into causes, effects and mitigation, noting that effects are interconnected and can cause new effects.
Issues
* ...
* List of environmental studies topics
* Lists of environmental publications
This is a list of all environmental publication lists.
*List of environmental books
**List of Australian environmental books
**List of books about energy issues
**List of climate change books
*List of environmental journals
**List of botany journ ...
* Media coverage of climate change
* Science Communication Observatory
References
Further reading
* * Tema Milstein, "Environmental Communication Theories," in Stephen W. Littlejohn and Karen A. Foss (Eds.), ''Encyclopedia of Communication Theory'', Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2009, pp. 344–349. http://sk.sagepub.com/reference/communicationtheory/n130.xml * Tema Milstein and Gabi Mocatta, "Environmental Communication Theory and Practice for Global Transformation: An Ecocultural Approach," in Yoshitaka Miike and Jing Yin (Eds.), ''The Handbook of Global Interventions in Communication Theory'', New York: Routledge, 2022, pp. 474–490. http://dx.doi.org/10.4324/9781003043348-35 * *External links
International Environmental Communication Association (IECA)
– a professional association for environmental communication practitioners, teachers, and scholars
ClimateClock: clock counting down to 1,5°C temperature rise
*Lexington book series o
Environmental Communication and Nature: Conflict and Ecoculture in the Anthropocene
Talk.Eco: Resources for Environmental Communicators
– a website featuring curated resources for environmental communication professionals
Environmental Communication: What it is and Why it Matters
by Mark Meisner
Environmental Communication: Research Into Practice
– an online course
Bibliography of books in environmental communication
by Mark Meisner
ECOresearch Network
– Research Network on Environmental Online Communication
Indications: Environmental Communication
blog (inactive), 2010–2012
About the Environmental Communication Division
– The International Communication Association Environmental Communication Division
Communication et environnement, le pacte impossible
by Thierry Libaert {{Environmental humanities Interdisciplinary subfields of sociology Communication studies