Electron Gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Electron gun from a cathode-ray tube
The electron gun from an RCA Vidicon video camera tube">Vidicon.html" ;"title="RCA Vidicon">RCA Vidicon video camera tube
An electron gun (also called electron emitter) is an electrical component in some
 Photoinjectors play a leading role in X-ray
Photoinjectors play a leading role in X-ray
Simulation of an Electron Gun
Interactive tutorial from LMU Munich
''Introduction to Electron Guns for Accelerators'' Dunham 2008
{{Electron microscopy Electron beam Accelerator physics Microscope components Vacuum tubes
vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
s that produces a narrow, collimation, collimated electron beam that has a precise kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.
In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Rober ...
.
The largest use is in cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a ...
s (CRTs), used in older television set
A television set or television receiver (more commonly called TV, TV set, television, telly, or tele) is an electronic device for viewing and hearing television broadcasts, or as a computer monitor. It combines a tuner, display, and loudspeake ...
s, computer display
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
T ...
s and oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing i ...
s, before the advent of flat-panel displays. Electron guns are also used in field-emission displays (FEDs), which are essentially flat-panel displays made out of rows of extremely small cathode-ray tubes. They are also used in microwave linear beam vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
s such as klystron
A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian,Pond, Norman H. "The Tube Guys". Russ Cochran, 2008 p.31-40 which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequenci ...
s, inductive output tube
The inductive output tube (IOT) or klystrode is a variety of linear-beam vacuum tube, similar to a klystron, used as a power amplifier for high frequency radio waves. It evolved in the 1980s to meet increasing efficiency requirements for high-po ...
s, travelling-wave tubes, and gyrotron
High-power 140 GHz gyrotron for plasma heating in the Wendelstein 7-X fusion experiment, Germany.
A gyrotron is a class of high-power linear-beam vacuum tubes that generates millimeter-wave electromagnetic waves by the cyclotron resonance of e ...
s, as well as in scientific instruments such as electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing it ...
s and particle accelerators
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental ...
.
Electron guns may be classified by the type of electric field generation (DC or RF), by emission mechanism (thermionic
Thermionic emission is the liberation of charged particles from a hot electrode whose thermal energy gives some particles enough kinetic energy to escape the material's surface. The particles, sometimes called ''thermions'' in early literature, a ...
, photocathode
A photocathode is a surface engineered to convert light (photons) into electrons using the photoelectric effect. Photocathodes are important in accelerator physics where they are utilised in a photoinjector to generate high brightness electron ...
, cold emission, plasmas source), by focusing (pure electrostatic or with magnetic fields), or by the number of electrodes.
Design
file:Kathodestraalbuis2.jpg, left, Electron gun from anoscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing i ...
CRT
file:Electron Gun with Wehnelt Cylinder.svg, Setup of an electron gun. 1. Hot cathode. 2. Wehnelt cylinder. 3. Anode
A direct current, electrostatic thermionic electron gun is formed from several parts: a hot cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element ...
, which is heated to create a stream of electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
via thermionic emission
Thermionic emission is the liberation of charged particles from a hot electrode whose thermal energy gives some particles enough kinetic energy to escape the material's surface. The particles, sometimes called ''thermions'' in early literature, a ...
; electrodes generating an electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
to focus the electron beam (such as a Wehnelt cylinder); and one or more anode
An anode usually is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, which is usually an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the devic ...
electrodes which accelerate and further focus the beam. A large voltage difference between the cathode and anode accelerates the electrons away from the cathode. A repulsive ring placed between the electrodes focuses the electrons onto a small spot on the anode, at the expense of a lower extraction field strength on the cathode surface. There is often a hole through the anode at this small spot, through which the electrons pass to form a collimated beam before reaching a second anode, called the collector. This arrangement is similar to an Einzel lens.
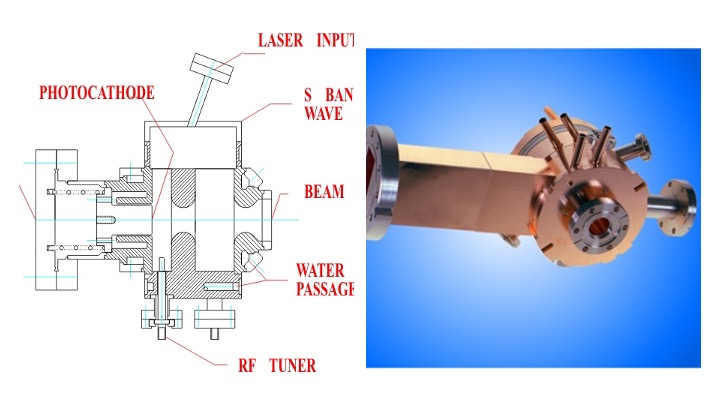
An RF electron gunH.G. Kirk, R. Miller, D. Yeremian, ''Electron guns and pre-injectors'', pp. 99-103, in A. W. Chao and M. Tigner, Editors, "Accelerator Physics and Engineering" World Scientific, Singapore, 1998 consists of a Microwave cavity
A microwave cavity or radio frequency cavity (RF cavity) is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed (or largely closed) metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave or radio frequency, RF region of the spect ...
, either single cell or multi-cell, and a cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional curren ...
. In order to obtain a smaller beam emittance at a given beam current, a photocathode
A photocathode is a surface engineered to convert light (photons) into electrons using the photoelectric effect. Photocathodes are important in accelerator physics where they are utilised in a photoinjector to generate high brightness electron ...
is used.I. Ben-Zvi, ''photoinjectors'', pp. 158-175, in A. W. Chao, H.O. Moser and Z. Zhao, Editors, "Accelerator Physics and Technology Applications" World Scientific, Singapore, 2004 An RF electron gun with a photocathode is called a photoinjector
A photoinjector is a type of source for intense electron beams which relies on the photoelectric effect. A laser pulse incident onto the cathode of a photoinjector drives electrons out of it, and into the accelerating field of the electron gun. In ...
.
 Photoinjectors play a leading role in X-ray
Photoinjectors play a leading role in X-ray Free-electron laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a fourth generation light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions much as a laser but employs relativistic electrons as a active laser medium, gain medium instead of using ...
s and small beam emittance accelerator physics
Accelerator physics is a branch of applied physics, concerned with designing, building and operating particle accelerators. As such, it can be described as the study of motion, manipulation and observation of relativistic charged particle beams ...
facilities.
Applications
file:Schottky-Emitter 01.jpg, left, Schottky-emitter electron source of anelectron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing it ...
The most common use of electron guns is in cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a ...
s, which were widely used in computer and television monitors before the advent of flat screen displays. Most color cathode-ray tubes incorporate three electron guns, each one producing a different stream of electrons. Each stream travels through a shadow mask
A shadow is a dark area on a surface where light from a light source is blocked by an object. In contrast, shade occupies the three-dimensional volume behind an object with light in front of it. The cross-section of a shadow is a two-dimensional ...
where the electrons will impinge upon either a red, green or blue phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
to light up a color pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
on the screen. The resultant color that is seen by the viewer will be a combination of these three primary color
Primary colors are colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color prin ...
s.
An electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
gun can also be used to ionize
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule i ...
particles by adding electrons to, or removing electrons from an atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
. This technology is sometimes used in mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used ...
in a process called electron ionization
Electron ionization (EI, formerly known as electron impact ionization and electron bombardment ionization) is an ionization method in which energetic electrons interact with solid or gas phase atoms or molecules to produce ions. EI was one of th ...
to ionize vaporized or gaseous particles. More powerful electron guns are used for welding, metal coating, 3D metal printers, metal powder production and vacuum furnaces.
Electron guns are also used in medical applications to produce X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
using a linac (linear accelerator); a high energy electron beam hits a target, stimulating emission of X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
.
Electron guns are also used in travelling-wave tube amplifiers for microwave frequencies.
Measurement and detection
Electron gun from a travelling-wave tube, cutaway through axis to show construction A nanocoulombmeter in combination with a Faraday cup can be used to detect and measure the beams emitted from electron gun and ion guns. Another way to detect electron beams from an electron gun is by using aphosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
screen which will glow when struck by an electron.
See also
*Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
* Electron-beam technology
References
External links
Simulation of an Electron Gun
Interactive tutorial from LMU Munich
''Introduction to Electron Guns for Accelerators'' Dunham 2008
{{Electron microscopy Electron beam Accelerator physics Microscope components Vacuum tubes