Electron Capture Detector on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
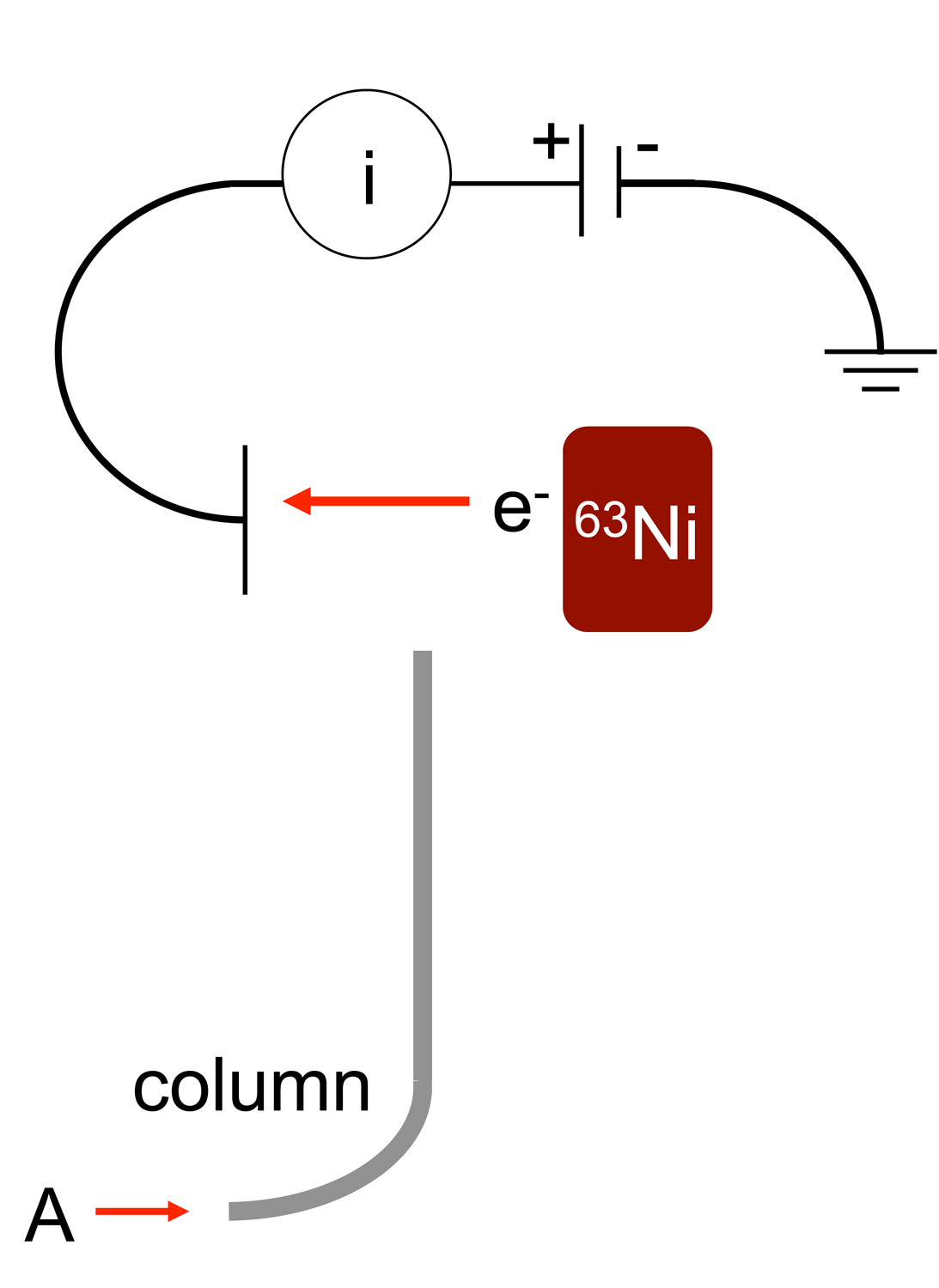 An electron capture detector (ECD) is a device for detecting
An electron capture detector (ECD) is a device for detecting
 An electron capture detector (ECD) is a device for detecting
An electron capture detector (ECD) is a device for detecting atoms
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas ...
and molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioc ...
in a gas through the attachment of electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary partic ...
via electron capture ionization Electron capture ionization is the ionization of a gas phase atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common ...
. The device was invented in 1957 by James Lovelock
James Ephraim Lovelock (26 July 1919 – 26 July 2022) was an English independent scientist, environmentalist and futurist. He is best known for proposing the Gaia hypothesis, which postulates that the Earth functions as a self-regulating sy ...
and is used in gas chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, ...
to detect trace amounts of chemical compounds in a sample.
Gas chromatograph detector
The electron capture detector is used for detecting electron-absorbing components (highelectronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the ...
) such as halogenated compounds in the output stream of a gas chromatograph
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or qua ...
. The ECD uses a radioactive beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β� ...
(electron) emitter in conjunction with a so-called makeup gas flowing through the detector chamber. The electron emitter typically consists of a metal foil holding 10 millicuries (370 M Bq) of the radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transfer ...
. Usually, nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seve ...
is used as makeup gas, because it exhibits a low excitation energy, so it is easy to remove an electron from a nitrogen molecule. The electrons emitted from the electron emitter collide with the molecules of the makeup gas, resulting in many more free electrons. The electrons are accelerated towards a positively charged anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemoni ...
, generating a current. There is therefore always a background signal present in the chromatogram
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it ...
. As the sample is carried into the detector by the carrier gas, electron-absorbing analyte molecules capture electrons and thereby reduce the current between the collector anode and a cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction i ...
. Over a wide range of concentrations the rate of electron capture is proportional to the analyte concentration. ECD detectors are particularly sensitive to halogens, organometallic compounds
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and so ...
, nitrile
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The prefix '' cyano-'' is used interchangeably with the term ''nitrile'' in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including me ...
s, or nitro compound
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nit ...
s.
Response mechanism
It is not immediately obvious why the capture of electrons by electronegative analytes reduces the current that flows between the anode and cathode: the molecular negative ions of the analyte carry the same charge as the electrons that were captured. The key to understanding why the current decreases is to ask where charged entities can go ''besides'' being collected at the anode and cathode. The answer is recombination of negative ions or electrons with the positive ions of the makeup gas before these charged entities can be collected at anode and cathode respectively. Negative and positive ions recombine much more rapidly than electrons and positive ions; it is this more rapid neutralization that is the origin of the observed decrease in current. Examination of the rate balance equation with all charge production and loss mechanisms considered reveals that the current collected when the electron capture detector is saturated with analyte is not zero: it is half the current collected when no analyte is present. To laboratory chromatographers this theoretical result is a well known experimental observation.Sensitivity
Depending on the analyte, an ECD can be 10-1000 times more sensitive than aflame ionization detector
A flame ionization detector (FID) is a scientific instrument that measures analytes in a gas stream. It is frequently used as a detector in gas chromatography. The measurement of ion per unit time make this a mass sensitive instrument. Standa ...
(FID), and one million times more sensitive than a thermal conductivity detector (TCD). An ECD has a limited dynamic range
Dynamic range (abbreviated DR, DNR, or DYR) is the ratio between the largest and smallest values that a certain quantity can assume. It is often used in the context of signals, like sound and light. It is measured either as a ratio or as a base- ...
and finds its greatest application in analysis of halogenated compounds. The detection limit for electron capture detectors is 5 femtograms per second (fg/s) and the detector commonly exhibits a 10,000-fold linear range. This made it possible to detect halogenated compounds such as pesticides and CFCs, even at levels of only one part per trillion ( ppt), thus revolutionizing our understanding of the atmosphere and pollutants.
References
{{Reflist Electron Capture Detector (ECD) Gas chromatography